Elk Circovirus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The elk (''Cervus canadensis''), also known as the wapiti, is one of the largest species within the


 Members of the
Members of the
File:Audubon-eastern-elk.jpg, Illustration of eastern elk
File:The deer of all lands (1898) Altai wapiti.png, Illustration of Altai wapiti
File:The deer of all lands (1898) Bedford's deer.png, Illustration of Manchurian wapiti
File:The deer of all lands (1898) Hangul.png, Illustration of Kashmir stag
 Elk have thick bodies with slender legs and short tails. They have a shoulder height of with a nose-to-tail length of . Males are larger and weigh while females weigh . The largest of the subspecies is the Roosevelt elk (''C. c. roosevelti''), found west of the Cascade Range in the
Elk have thick bodies with slender legs and short tails. They have a shoulder height of with a nose-to-tail length of . Males are larger and weigh while females weigh . The largest of the subspecies is the Roosevelt elk (''C. c. roosevelti''), found west of the Cascade Range in the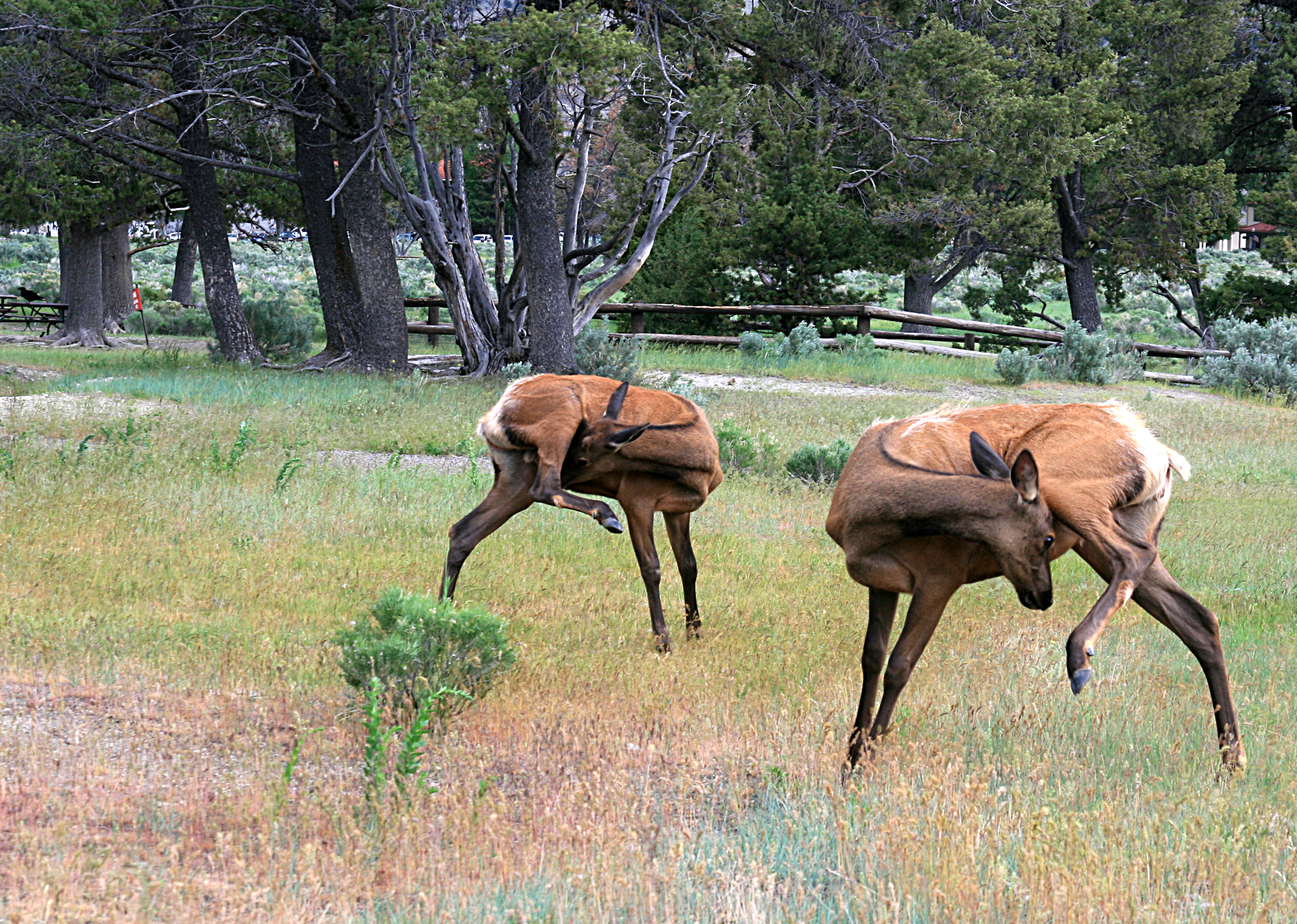  During the fall, elk grow a thicker coat of hair, which helps to insulate them during the winter. Both male and female North American elk grow thin neck manes; females of other subspecies may not. By early summer, the heavy winter coat has been shed. Elk are known to rub against trees and other objects to help remove hair from their bodies. All elk have small and clearly defined rump patches with short tails. They have different coloration based on the seasons and types of habitats, with gray or lighter coloration prevalent in the winter and a more reddish, darker coat in the summer. Subspecies living in arid climates tend to have lighter colored coats than do those living in forests. Most have lighter yellow-brown to orange-brown coats in contrast to dark brown hair on the head, neck, and legs during the summer. Forest-adapted Manchurian and Alashan wapitis have red or reddish-brown coats with less contrast between the body coat and the rest of the body during the summer months. Calves are born spotted, as is common with many deer species, and lose them by the end of summer. Adult Manchurian wapiti may retain a few orange spots on the back of their summer coats until they are older. This characteristic has also been observed in the forest-adapted European red deer.
During the fall, elk grow a thicker coat of hair, which helps to insulate them during the winter. Both male and female North American elk grow thin neck manes; females of other subspecies may not. By early summer, the heavy winter coat has been shed. Elk are known to rub against trees and other objects to help remove hair from their bodies. All elk have small and clearly defined rump patches with short tails. They have different coloration based on the seasons and types of habitats, with gray or lighter coloration prevalent in the winter and a more reddish, darker coat in the summer. Subspecies living in arid climates tend to have lighter colored coats than do those living in forests. Most have lighter yellow-brown to orange-brown coats in contrast to dark brown hair on the head, neck, and legs during the summer. Forest-adapted Manchurian and Alashan wapitis have red or reddish-brown coats with less contrast between the body coat and the rest of the body during the summer months. Calves are born spotted, as is common with many deer species, and lose them by the end of summer. Adult Manchurian wapiti may retain a few orange spots on the back of their summer coats until they are older. This characteristic has also been observed in the forest-adapted European red deer.
 Elk are among the most
Elk are among the most
 A bull interacts with cows in his harem in two ways: herding and courtship. When a female wanders too far away from the harem's range, the male will rush ahead of her, block her path and aggressively rush her back to the harem. Herding behavior is accompanied by a stretched out and lowered neck and the antlers laid back. A bull may get violent and hit the cow with his antlers. During courtship, the bull is more peaceful and approaches her with his head and antlers raised. The male signals his intention to test the female for sexual receptivity by flicking his tongue. If not ready, a cow will lower her head and weave from side to side while opening and closing her mouth. The bull will stop in response in order not to scare her. Otherwise, the bull will copiously lick the female and then mount her.
Younger, less dominant bulls, known as "spike bulls" because their antlers have not yet forked, will harass unguarded cows. These bulls are impatient and will not perform any courtship rituals and will continue to pursue a female even when she signals him to stop. As such, they are less reproductively successful, and a cow may stay close to the big bull to avoid harassment. Dominant bulls are intolerant of spike bulls and will chase them away from their harems.
A bull interacts with cows in his harem in two ways: herding and courtship. When a female wanders too far away from the harem's range, the male will rush ahead of her, block her path and aggressively rush her back to the harem. Herding behavior is accompanied by a stretched out and lowered neck and the antlers laid back. A bull may get violent and hit the cow with his antlers. During courtship, the bull is more peaceful and approaches her with his head and antlers raised. The male signals his intention to test the female for sexual receptivity by flicking his tongue. If not ready, a cow will lower her head and weave from side to side while opening and closing her mouth. The bull will stop in response in order not to scare her. Otherwise, the bull will copiously lick the female and then mount her.
Younger, less dominant bulls, known as "spike bulls" because their antlers have not yet forked, will harass unguarded cows. These bulls are impatient and will not perform any courtship rituals and will continue to pursue a female even when she signals him to stop. As such, they are less reproductively successful, and a cow may stay close to the big bull to avoid harassment. Dominant bulls are intolerant of spike bulls and will chase them away from their harems.
 The
The
 As is true for many species of deer, especially those in mountainous regions, elk
As is true for many species of deer, especially those in mountainous regions, elk
 Elk are ruminants and therefore have four-chambered stomachs. Unlike white-tailed deer and moose, which are chiefly browsers, elk are similar to
Elk are ruminants and therefore have four-chambered stomachs. Unlike white-tailed deer and moose, which are chiefly browsers, elk are similar to
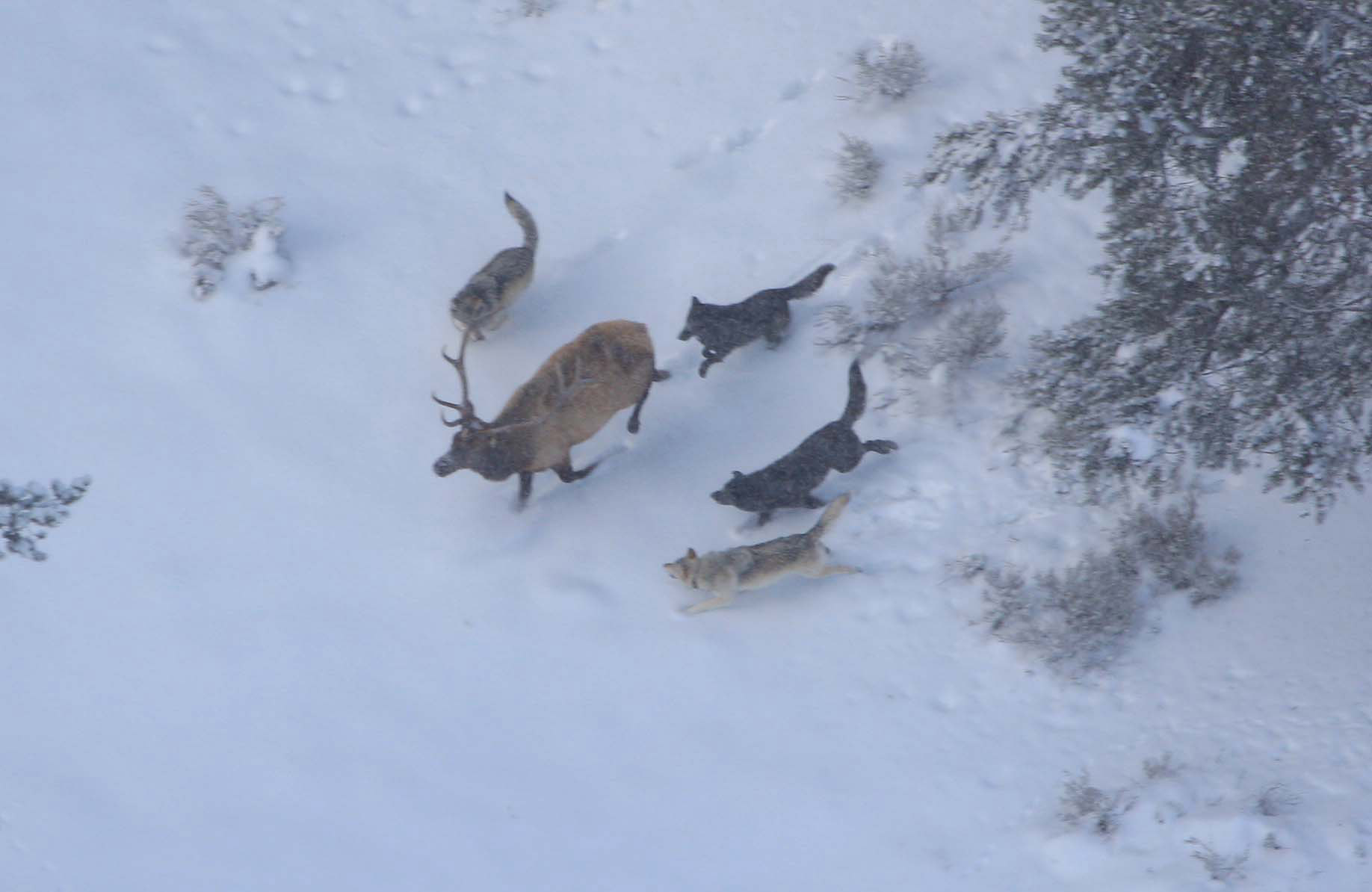 Predators of elk include
Predators of elk include

 The elk ranges from central Asia though to Siberia and east Asia and in North America. They can be found in open deciduous woodlands, boreal forests, upland moors, mountainous areas and grasslands. The International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) list the species as least-concern species. The habitat of Siberian elk in Asia is similar to that of the Rocky Mountain subspecies in North America. During the Late Pleistocene their range was much more extensive, being distributed across Eurasia, with remains being found as far west as France. These populations are most closely related to modern Asian populations of the elk. Their range collapsed at the start of the Holocene, possibly because they were specialized to cold periglacial tundra-steppe habitat. When this environment was replaced largely by closed forest the red deer might have outcompeted the elk. Relict (biology), Relictual populations survived into the early Holocene (until around 3000 years ago) in southern Sweden and the Alps, where the environment remained favorable.
The elk ranges from central Asia though to Siberia and east Asia and in North America. They can be found in open deciduous woodlands, boreal forests, upland moors, mountainous areas and grasslands. The International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) list the species as least-concern species. The habitat of Siberian elk in Asia is similar to that of the Rocky Mountain subspecies in North America. During the Late Pleistocene their range was much more extensive, being distributed across Eurasia, with remains being found as far west as France. These populations are most closely related to modern Asian populations of the elk. Their range collapsed at the start of the Holocene, possibly because they were specialized to cold periglacial tundra-steppe habitat. When this environment was replaced largely by closed forest the red deer might have outcompeted the elk. Relict (biology), Relictual populations survived into the early Holocene (until around 3000 years ago) in southern Sweden and the Alps, where the environment remained favorable.
 As of 2014, population figures for all North American elk subspecies were around one million. Prior to the European colonization of North America, there were an estimated 10 million on the continent.
There are many past and ongoing examples of reintroduction into areas of the US. Elk were reintroduced in Michigan in 1918 after going extinct in 1875. The Rocky Mountain elk subspecies was reintroduced by hunter-conservation organizations into the Appalachian region of the U.S. where the now extinct eastern elk once lived. Since the late 1990s, they were reintroduced and recolonized in the U.S. states, states of Wisconsin, Kentucky, North Carolina, Tennessee, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia, Virginia and West Virginia. In the state of Kentucky, the elk population in 2022 had increased to over 15,000 animals. In 2016, a male elk, likely from the Great Smoky Mountains, Smoky Mountains population, was sighted in South Carolina for the first time in nearly 300 years. Since 2015, elk have also been reintroduced in a number of other states, including Pennsylvania, Missouri, and introduced to the islands of Etolin Island, Etolin and Afognak in Alaska. Reintroduction of the elk into Ontario began in the early 20th century and is ongoing with limited success.
Elk and red deer were introduced to
As of 2014, population figures for all North American elk subspecies were around one million. Prior to the European colonization of North America, there were an estimated 10 million on the continent.
There are many past and ongoing examples of reintroduction into areas of the US. Elk were reintroduced in Michigan in 1918 after going extinct in 1875. The Rocky Mountain elk subspecies was reintroduced by hunter-conservation organizations into the Appalachian region of the U.S. where the now extinct eastern elk once lived. Since the late 1990s, they were reintroduced and recolonized in the U.S. states, states of Wisconsin, Kentucky, North Carolina, Tennessee, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia, Virginia and West Virginia. In the state of Kentucky, the elk population in 2022 had increased to over 15,000 animals. In 2016, a male elk, likely from the Great Smoky Mountains, Smoky Mountains population, was sighted in South Carolina for the first time in nearly 300 years. Since 2015, elk have also been reintroduced in a number of other states, including Pennsylvania, Missouri, and introduced to the islands of Etolin Island, Etolin and Afognak in Alaska. Reintroduction of the elk into Ontario began in the early 20th century and is ongoing with limited success.
Elk and red deer were introduced to
 Elk have played an important role in the cultural history of a number of peoples. Neolithic petroglyphs from Asia depict antler-less female elk, which have been interpreted as symbolizing life and sustenance. They were also frequently overlaid with boats and associated with rivers, suggesting they also represented paths to the underworld. Petroglyphs of elk were carved into cliffs by the Ancestral Puebloans of the southwestern U.S. hundreds of years ago. The elk was of particular importance to the Lakota people, Lakota and played a spiritual role in their society. The male elk was admired for its ability to attract mates, and Lakota men will play a courting flute imitating a bugling elk to attract women. Men used elks' antlers as love charms and wore clothes decorated with elk images.
The Rocky Mountain elk is the List of U.S. state mammals, official state animal for Utah. An image of an elk and a moose appear on the state Seal of Michigan, seal and Flag of Michigan, flag of Michigan. The Benevolent and Protective Order of Elks (B.P.O.E.) chose the elk as its namesake because a number of its attributes seemed appropriate for cultivation by members of the fraternity. Jewel encrusted, gold mounted elk teeth are prized possession of many members of the B.P.O.E..
Elk have played an important role in the cultural history of a number of peoples. Neolithic petroglyphs from Asia depict antler-less female elk, which have been interpreted as symbolizing life and sustenance. They were also frequently overlaid with boats and associated with rivers, suggesting they also represented paths to the underworld. Petroglyphs of elk were carved into cliffs by the Ancestral Puebloans of the southwestern U.S. hundreds of years ago. The elk was of particular importance to the Lakota people, Lakota and played a spiritual role in their society. The male elk was admired for its ability to attract mates, and Lakota men will play a courting flute imitating a bugling elk to attract women. Men used elks' antlers as love charms and wore clothes decorated with elk images.
The Rocky Mountain elk is the List of U.S. state mammals, official state animal for Utah. An image of an elk and a moose appear on the state Seal of Michigan, seal and Flag of Michigan, flag of Michigan. The Benevolent and Protective Order of Elks (B.P.O.E.) chose the elk as its namesake because a number of its attributes seemed appropriate for cultivation by members of the fraternity. Jewel encrusted, gold mounted elk teeth are prized possession of many members of the B.P.O.E..
 Although breakdown figures for each game species are not available in the 2006 National Survey from the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, hunting of wild elk is most likely the primary economic impact.
While elk are not generally harvested for meat production on a large scale, some restaurants offer the meat as a specialty item and it is also available in some grocery stores. The meat has a taste somewhere between beef and venison and is higher in
Although breakdown figures for each game species are not available in the 2006 National Survey from the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, hunting of wild elk is most likely the primary economic impact.
While elk are not generally harvested for meat production on a large scale, some restaurants offer the meat as a specialty item and it is also available in some grocery stores. The meat has a taste somewhere between beef and venison and is higher in
Arizona Elk
Arizona Game and Fish Department
Rocky Mountain Elk FoundationSmithsonian Institution - North American Mammals: ''Cervus'' (''elaphus'') ''canadensis''
{{Taxonbar, from=Q180404 Cervus Elk and red deer Fauna of Siberia Holarctic fauna Mammals of the United States Fauna of Central Asia Mammals of Canada Fauna of East Asia Extant Pleistocene first appearances Herbivorous mammals Mammals described in 1777 Taxa named by Johann Christian Polycarp Erxleben
deer
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the ...
family, Cervidae
Deer or true deer are hoofed ruminant mammals forming the family Cervidae. The two main groups of deer are the Cervinae, including the muntjac, the elk (wapiti), the red deer, and the fallow deer; and the Capreolinae, including the rei ...
, and one of the largest terrestrial mammals in its native range of North America and Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known a ...
and East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea ...
. The common name of "elk" is open to confusion, as "elk" is the name used in British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in ...
for the larger ''Alces alces
The moose (in North America) or elk (in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is a member of the New World deer subfamily and is the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is the largest and heaviest extant species in the deer family. Most adult ma ...
'', with similar names used by other European languages (German ''Elch'', Swedish ''älg'', and French ''élan''). In North America, the common name for ''Alces alces'' is "moose". The name "wapiti" is sometimes used for ''Cervus canadensis'', which derives from the Shawnee
The Shawnee are an Algonquian-speaking indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands. In the 17th century they lived in Pennsylvania, and in the 18th century they were in Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana and Illinois, with some bands in Kentucky a ...
and Cree word ''waapiti'', meaning 'white rump'.
Elk range in forest and forest-edge habitat, feeding on grasses, plants, leaves, and bark. Male elk have large antler
Antlers are extensions of an animal's skull found in members of the Cervidae (deer) family. Antlers are a single structure composed of bone, cartilage, fibrous tissue, skin, nerves, and blood vessels. They are generally found only on ...
s which they shed each year. Males also engage in ritualized mating behaviors during the rut, including posturing, antler wrestling (sparring), and ''bugling'', a loud series of vocalizations that establishes dominance over other males and attracts females. Although it is currently native to North America and central/eastern Asia, it had a much wider distribution in the past. Populations were present across Eurasia into Western Europe during the Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as Upper Pleistocene from a stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division of the Pleistocene Epoch within ...
and survived into the early Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
in southern Sweden and the Alps; the extinct Merriam's elk subspecies ranged into Mexico. The elk has adapted well to countries where it has been introduced, including Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, t ...
and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 List of islands of New Zealand, smaller islands. It is the ...
. Its adaptability may in fact threaten endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found els ...
species and the ecosystems into which it has been introduced.
Elk are susceptible to a number of infectious disease
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable d ...
s, some of which can be transmitted to livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to anima ...
. Efforts to eliminate infectious diseases from elk populations, largely by vaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating ...
, have had mixed success. Some cultures revere the elk as having spiritual significance. In parts of Asia, antlers and their velvet
Weave details visible on a purple-colored velvet fabric
Velvet is a type of woven tufted fabric in which the cut threads are evenly distributed, with a short pile, giving it a distinctive soft feel. By extension, the word ''velvety'' means ...
are used in traditional medicine
Traditional medicine (also known as indigenous medicine or folk medicine) comprises medical aspects of traditional knowledge that developed over generations within the folk beliefs of various societies, including indigenous peoples, before th ...
s. Elk are hunted as a game species. Their meat is leaner and higher in protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
than beef
Beef is the culinary name for meat from cattle (''Bos taurus'').
In prehistoric times, humankind hunted aurochs and later domesticated them. Since that time, numerous breeds of cattle have been bred specifically for the quality or quant ...
or chicken
The chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus'') is a domestication, domesticated junglefowl species, with attributes of wild species such as the grey junglefowl, grey and the Ceylon junglefowl that are originally from Southeastern Asia. Rooster ...
. Elk were long believed to belong to a subspecies of the European red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or hart, and a female is called a hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Iran, and parts of wes ...
(''Cervus elaphus''), but evidence from many mitochondrial DNA genetic studies beginning in 1998 shows that the two are distinct species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of ...
. Key morphological differences that distinguish ''C. canadensis'' from ''C. elaphus'' are the former's wider rump patch and paler-hued antlers.
Naming and etymology
By the 17th century, ''Alces alces'' (called "elk" in Europe) had long beenextirpated
Local extinction, also known as extirpation, refers to a species (or other taxon) of plant or animal that ceases to exist in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with global extinct ...
from the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles (O ...
, and the meaning of the word "elk" to English-speakers became rather vague, acquiring a meaning similar to "large deer". The name ''wapiti'' is from the Shawnee
The Shawnee are an Algonquian-speaking indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands. In the 17th century they lived in Pennsylvania, and in the 18th century they were in Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana and Illinois, with some bands in Kentucky a ...
and Cree word ''waapiti'' (in Cree syllabics
Cree syllabics are the versions of Canadian Aboriginal syllabics used to write Cree dialects, including the original syllabics system created for Cree and Ojibwe. There are two main varieties of syllabics for Cree: Western Cree syllabics and ...
: or ), meaning "white rump". There is a subspecies of wapiti in Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 millio ...
called the Altai wapiti (''Cervus canadensis sibiricus''), also known as the Altai maral.
According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the first and foundational historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP). It traces the historical development of the English language, providing a com ...
'', the etymology of the word "elk" is "of obscure history". In Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations ...
, the European ''Alces alces'' was known as and , words probably borrowed from a Germanic language
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken ...
or another language of northern Europe. By the 8th century, during the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the M ...
, the moose was known as derived from the Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic bran ...
: ''*elho-'', ''*elhon-'' and possibly connected with the . Later, the species became known in Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English ...
as ''elk'', ''elcke'', or ''elke'', appearing in the Latinized form ''alke'', with the spelling ''alce'' borrowed directly from . Noting that ''elk'' "is not the normal phonetic representative" of the Old English ''elch'', the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' derives ''elk'' from , itself from .
The American ''Cervus canadensis'' was recognized as a relative of the red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') of Europe, and so ''Cervus canadensis'' was referred to as "red deer" Richard Hakluyt
Richard Hakluyt (; 1553 – 23 November 1616) was an English writer. He is known for promoting the English colonization of North America through his works, notably ''Divers Voyages Touching the Discoverie of America'' (1582) and ''The Pri ...
, in his 1584 '' Discourse Concerning Western Planting'', mentioned the continent's plentiful red deer (). Similarly, John Smith
John Smith is a common personal name. It is also commonly used as a placeholder name and pseudonym, and is sometimes used in the United States and the United Kingdom as a term for an average person. It may refer to:
People
:''In chronological ...
's 1616 ''A Description of New England
''A Description of New England'' (in full: ''A description of New England, or, Observations and discoveries in the north of America in the year of Our Lord 1614, with the success of six ships that went the next year, 1615'') is a work written by ...
'' referred to red deer. Sir William Talbot's 1672 English translation of John Lederer
John Lederer was a 17th-century German physician and an explorer of the Appalachian Mountains. He and the members of his party became the first Europeans to crest the Blue Ridge Mountains (1669) and the first to see the Shenandoah Valley and the ...
's Latin ''Discoveries'' likewise called the species "Red Deer", but noted in parentheses
A bracket is either of two tall fore- or back-facing punctuation marks commonly used to isolate a segment of text or data from its surroundings. Typically deployed in symmetric pairs, an individual bracket may be identified as a 'left' or 'r ...
that they were "for their unusual largeness improperly termed Elks by ignorant people". Both Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was previously the nati ...
's 1785 ''Notes on the State of Virginia
''Notes on the State of Virginia'' (1785) is a book written by the American statesman, philosopher, and planter Thomas Jefferson. He completed the first version in 1781 and updated and enlarged the book in 1782 and 1783. It originated in Jeffers ...
'' and David Bailie Warden's 1816 ''Statistical, Political, and Historical Account of the United States'' used "red deer" to refer to ''Cervus canadensis''..
Taxonomy


 Members of the
Members of the genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial n ...
''Cervus
''Cervus'' is a genus of deer that primarily are native to Eurasia, although one species occurs in northern Africa and another in North America. In addition to the species presently placed in this genus, it has included a whole range of other s ...
'' (and hence early relatives or possible ancestors of the elk) first appear in the fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
record 25 million years ago, during the Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but ...
in Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelag ...
, but do not appear in the North American fossil record until the early Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" ...
. The extinct Irish elk
The Irish elk (''Megaloceros giganteus''), also called the giant deer or Irish deer, is an extinct species of deer in the genus '' Megaloceros'' and is one of the largest deer that ever lived. Its range extended across Eurasia during the Pleist ...
(''Megaloceros'') was not a member of the genus ''Cervus'' but rather the largest member of the wider deer family (Cervidae) known from the fossil record.
Until recently, red deer and elk were considered to be one species, ''Cervus elaphus'', with over a dozen subspecies. But mitochondrial DNA studies conducted in 2004 on hundreds of samples from red deer and elk subspecies and other species of the ''Cervus'' deer family, strongly indicate that elk, or wapiti, should be a distinct species, namely ''Cervus canadensis''. DNA evidence validates that elk are more closely related to Thorold's deer and even sika deer
The sika deer (''Cervus nippon''), also known as the Northern spotted deer or the Japanese deer, is a species of deer native to much of East Asia and introduced to other parts of the world. Previously found from northern Vietnam in the south to ...
than they are to the red deer.
Elk and red deer produce fertile offspring in captivity, and the two species have freely inter-bred in New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 List of islands of New Zealand, smaller islands. It is the ...
's Fiordland National Park
Fiordland National Park occupies the southwest corner of the South Island of New Zealand. It is by far the largest of the 13 national parks in New Zealand, with an area of , and a major part of the Te Wahipounamu World Heritage Site. The park ...
. The cross-bred animals have resulted in the disappearance of virtually all pure elk blood from the area. Key morphological differences that distinguish ''C. canadensis'' from ''C. elaphus'' are the former's wider rump patch and paler-hued antlers.
Subspecies
There are numerous subspecies of elk described, with six from North America and four from Asia, although some taxonomists consider them differentecotype
In evolutionary ecology, an ecotype,Greek: ''οίκος'' = home and ''τύπος'' = type, coined by Göte Turesson in 1922 sometimes called ecospecies, describes a genetically distinct geographic variety, population, or race within a specie ...
s or races of the same species (adapted to local environments through minor changes in appearance and behavior). Populations vary in antler shape and size, body size, coloration and mating behavior. DNA investigations of the Eurasian subspecies revealed that phenotypic
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological proper ...
variation in antlers, mane and rump patch development are based on "climatic-related lifestyle factors".
Of the six subspecies of elk known to have inhabited North America in historical times, four remain, including the Roosevelt's (''C. canadensis roosevelti''), tule
''Schoenoplectus acutus'' (syn. ''Scirpus acutus, Schoenoplectus lacustris, Scirpus lacustris'' subsp. ''acutus''), called tule , common tule, hardstem tule, tule rush, hardstem bulrush, or viscid bulrush, is a giant species of sedge in the pla ...
(''C. canadensis nannodes''), Manitoban (''C. canadensis manitobensis'') and Rocky Mountain elk
The Rocky Mountain elk (''Cervus canadensis nelsoni'') is a subspecies of elk found in the Rocky Mountains and adjacent ranges of Western North America.
Habitat
The winter ranges are most common in open forests and floodplain marshes in the ...
(''C. canadensis nelsoni''). The eastern elk (''C. canadensis canadensis'') and Merriam's elk (''C. canadensis merriami'') subspecies have been extinct for at least a century.
Four subspecies described in Asia include the Altai wapiti (''C. canadensis sibiricus'') and the Tianshan wapiti
The Tian Shan wapiti or Tian Shan maral (''Cervus canadensis songaricus''), is a subspecies of ''C. canadensis''. It is also called the Tian Shan elk in North American English.
Description
It is native to the Tian Shan Mountains in eastern Ky ...
(''C. canadensis songaricus''). Two distinct subspecies found in China, Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 millio ...
, the Korean Peninsula
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic ...
and Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
are the Manchurian wapiti (''C. canadensis xanthopygus'') and the Alashan wapitis (''C. canadensis alashanicus''). The Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym "Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East ( Outer ...
n wapiti is darker and more reddish in coloration than the other populations. The Alashan wapiti of north central China is the smallest of all subspecies, has the lightest coloration and is the least studied.
Recent DNA studies suggest that there are no more than three or four subspecies of elk. All American forms, aside from possibly the tule and Roosevelt's elk, seem to belong to one subspecies (''Cervus canadensis canadensis''). Even the Siberian elk (''Cervus canadensis sibiricus'') are more or less identical to the American forms and therefore may belong to this subspecies, too. However, the Manchurian wapiti (''Cervus canadensis xanthopygus'') is clearly distinct from the Siberian forms, but not distinguishable from the Alashan wapiti. The Chinese forms (the Sichuan deer
The Sichuan deer (''Cervus canadensis macneilli''), also known as MacNeill's deer, is a subspecies of the Elk native to Western China.
Description
This large, highland deer is of very pale, finely spotted color with gray or brownish black. The ...
, Kansu red deer
The Kansu red deer (''Cervus canadensis kansuensis'') is a subspecies of wapiti found in the Gansu province of China. This subspecies forms, along with the closely related Sichuan deer, and Tibetan red deer, the southernmost wapiti group.
R ...
, and Tibetan red deer
The Tibetan red deer (''Cervus canadensis wallichi'') also known as ''shou'', is a subspecies of elk/wapiti native to the southern Tibetan highlands and Bhutan. Once believed to be near-extinct, its population has increased to over 8,300, the ma ...
) also belong to the wapiti, and were not distinguishable from each other by mitochondrial DNA studies. These Chinese subspecies are sometimes treated as a distinct species, namely the Central Asian red deer
The Central Asian red deer (''Cervus hanglu''), also known as the Tarim red deer is a deer species native to Central Asia, where it used to be widely distributed, but is scattered today with small population units in several countries. It has bee ...
(''Cervus hanglu''), which also includes the Kashmir stag.Mattioli (2011). ''Family Cervidae (Deer).'' (350-443). In: Wilson, D. E., Mittermeier, R. A., (Hrsg.). ''Handbook of the Mammals of the World. Volume 2: Hooved Mammals.'' Lynx Edicions, 2009.
* North American group
** Roosevelt's elk (''C. c. roosevelti'')
** Tule elk
The tule elk (''Cervus canadensis nannodes'') is a subspecies of elk found only in California, ranging from the grasslands and marshlands of the Central Valley to the grassy hills on the coast. The subspecies name derives from the tule (), a ...
(''C. c. nannodes'')
** Manitoban elk
The Manitoban elk (''Cervus canadensis manitobensis'') is a subspecies of elk found in the Midwestern United States (specifically North Dakota) and southern regions of the Canadian Prairies (specifically Manitoba, Saskatchewan, and north-c ...
(''C. c. manitobensis'')
** Rocky Mountain elk
The Rocky Mountain elk (''Cervus canadensis nelsoni'') is a subspecies of elk found in the Rocky Mountains and adjacent ranges of Western North America.
Habitat
The winter ranges are most common in open forests and floodplain marshes in the ...
(''C. c. nelsoni'')
** Eastern elk (''C. c. canadensis''; extinct)
** Merriam's elk (''C. c. merriami''; extinct)
* Eastern group
** Altai wapiti (''C. c. sibiricus'')
** Tian Shan wapiti (''C. c. songaricus'')
** Manchurian wapiti (''C. c. xanthopygus'')
** Alashan wapiti (''C. c. alashanicus'')
** Tibetan red deer
The Tibetan red deer (''Cervus canadensis wallichi'') also known as ''shou'', is a subspecies of elk/wapiti native to the southern Tibetan highlands and Bhutan. Once believed to be near-extinct, its population has increased to over 8,300, the ma ...
(''C. c. wallichii'')
Characteristics
U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sove ...
s of California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the ...
, Oregon
Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idah ...
and Washington, and in the Canadian
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
province of British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include ...
. Roosevelt elk have been introduced into Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S ...
, where the largest males are estimated to weigh up to . More typically, male Roosevelt elk weigh around , while females weigh .. Male tule elk weigh while females weigh . The whole weights of adult male Manitoban elk range from . Females have a mean weight of . The elk is the second largest extant species of deer, after the moose
The moose (in North America) or elk (in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is a member of the New World deer subfamily and is the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is the largest and heaviest extant species in the deer family. Most adult ma ...
.
Antlers are made of bone, which can grow at a rate of per day. While actively growing, a soft layer of highly vascularized skin known as velvet
Weave details visible on a purple-colored velvet fabric
Velvet is a type of woven tufted fabric in which the cut threads are evenly distributed, with a short pile, giving it a distinctive soft feel. By extension, the word ''velvety'' means ...
covers and protects them. This is shed in the summer when the antlers have fully developed. Bull elk typically have around six tines on each antler. The Siberian and North American elk carry the largest antlers while the Altai wapiti has the smallest. Roosevelt bull antlers can weigh . The formation and retention of antlers are testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteris ...
-driven. In late winter and early spring, the testosterone level drops, which causes the antlers to shed.
 During the fall, elk grow a thicker coat of hair, which helps to insulate them during the winter. Both male and female North American elk grow thin neck manes; females of other subspecies may not. By early summer, the heavy winter coat has been shed. Elk are known to rub against trees and other objects to help remove hair from their bodies. All elk have small and clearly defined rump patches with short tails. They have different coloration based on the seasons and types of habitats, with gray or lighter coloration prevalent in the winter and a more reddish, darker coat in the summer. Subspecies living in arid climates tend to have lighter colored coats than do those living in forests. Most have lighter yellow-brown to orange-brown coats in contrast to dark brown hair on the head, neck, and legs during the summer. Forest-adapted Manchurian and Alashan wapitis have red or reddish-brown coats with less contrast between the body coat and the rest of the body during the summer months. Calves are born spotted, as is common with many deer species, and lose them by the end of summer. Adult Manchurian wapiti may retain a few orange spots on the back of their summer coats until they are older. This characteristic has also been observed in the forest-adapted European red deer.
During the fall, elk grow a thicker coat of hair, which helps to insulate them during the winter. Both male and female North American elk grow thin neck manes; females of other subspecies may not. By early summer, the heavy winter coat has been shed. Elk are known to rub against trees and other objects to help remove hair from their bodies. All elk have small and clearly defined rump patches with short tails. They have different coloration based on the seasons and types of habitats, with gray or lighter coloration prevalent in the winter and a more reddish, darker coat in the summer. Subspecies living in arid climates tend to have lighter colored coats than do those living in forests. Most have lighter yellow-brown to orange-brown coats in contrast to dark brown hair on the head, neck, and legs during the summer. Forest-adapted Manchurian and Alashan wapitis have red or reddish-brown coats with less contrast between the body coat and the rest of the body during the summer months. Calves are born spotted, as is common with many deer species, and lose them by the end of summer. Adult Manchurian wapiti may retain a few orange spots on the back of their summer coats until they are older. This characteristic has also been observed in the forest-adapted European red deer.
Behavior and ecology
 Elk are among the most
Elk are among the most gregarious
Sociality is the degree to which individuals in an animal population tend to associate in social groups (gregariousness) and form cooperative societies.
Sociality is a survival response to evolutionary pressures. For example, when a mother w ...
deer species. During the summer group size can reach 400 individuals. For most of the year, adult males and females are segregated into different herds. Female herds are larger while bulls form small groups and may even travel alone. Young bulls may associate with older bulls or female groups. Male and female herds come together during the mating season, which may begin in late August. Males try to intimidate rivals by vocalizing and displaying with their antlers. If neither bull backs down, they engage in antler wrestling, sometimes sustaining serious injuries.
Bulls have a loud, high-pitched, whistle-like vocalization known as ''bugling'', which advertise the male's fitness over great distances. Unusual for a vocalization produced by a large animal, buglings can reach a frequency of 4000 Hz. This is achieved by blowing air from the glottis
The glottis is the opening between the vocal folds (the rima glottidis). The glottis is crucial in producing vowels and voiced consonants.
Etymology
From Ancient Greek ''γλωττίς'' (glōttís), derived from ''γλῶττα'' (glôtta), ...
through the nasal cavities. Elk can produce deeper pitched (150 Hz) sounds using the larynx. Cows produce an alarm bark to alert other members of the herd to danger, while calves will produce a high-pitched scream when attacked.
Reproduction and life cycle
Female elk have a shortestrus
The estrous cycle (, originally ) is the set of recurring physiological changes that are induced by reproductive hormones in most mammalian therian females. Estrous cycles start after sexual maturity in females and are interrupted by anestrous p ...
cycle of only a day or two, and matings usually involve a dozen or more attempts. By the autumn of their second year, females can produce one and, very rarely, two offspring. Reproduction is most common when cows weigh at least . Dominant bulls follow groups of cows during the rut from August into early winter. A bull will defend his harem of 20 cows or more from competing bulls and predators. Bulls also dig holes in the ground called wallows, in which they urinate and roll their bodies. A male elk's urethra points upward so that urine is sprayed almost at a right angle to the penis. The urine soaks into their hair and gives them a distinct smell which attracts cows.
 A bull interacts with cows in his harem in two ways: herding and courtship. When a female wanders too far away from the harem's range, the male will rush ahead of her, block her path and aggressively rush her back to the harem. Herding behavior is accompanied by a stretched out and lowered neck and the antlers laid back. A bull may get violent and hit the cow with his antlers. During courtship, the bull is more peaceful and approaches her with his head and antlers raised. The male signals his intention to test the female for sexual receptivity by flicking his tongue. If not ready, a cow will lower her head and weave from side to side while opening and closing her mouth. The bull will stop in response in order not to scare her. Otherwise, the bull will copiously lick the female and then mount her.
Younger, less dominant bulls, known as "spike bulls" because their antlers have not yet forked, will harass unguarded cows. These bulls are impatient and will not perform any courtship rituals and will continue to pursue a female even when she signals him to stop. As such, they are less reproductively successful, and a cow may stay close to the big bull to avoid harassment. Dominant bulls are intolerant of spike bulls and will chase them away from their harems.
A bull interacts with cows in his harem in two ways: herding and courtship. When a female wanders too far away from the harem's range, the male will rush ahead of her, block her path and aggressively rush her back to the harem. Herding behavior is accompanied by a stretched out and lowered neck and the antlers laid back. A bull may get violent and hit the cow with his antlers. During courtship, the bull is more peaceful and approaches her with his head and antlers raised. The male signals his intention to test the female for sexual receptivity by flicking his tongue. If not ready, a cow will lower her head and weave from side to side while opening and closing her mouth. The bull will stop in response in order not to scare her. Otherwise, the bull will copiously lick the female and then mount her.
Younger, less dominant bulls, known as "spike bulls" because their antlers have not yet forked, will harass unguarded cows. These bulls are impatient and will not perform any courtship rituals and will continue to pursue a female even when she signals him to stop. As such, they are less reproductively successful, and a cow may stay close to the big bull to avoid harassment. Dominant bulls are intolerant of spike bulls and will chase them away from their harems.
gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during preg ...
period is eight to nine months and the offspring weigh around . When the females are near to giving birth, they tend to isolate themselves from the main herd, and will remain isolated until the calf is large enough to escape predators. Calves are born spotted, as is common with many deer species, and they lose their spots by the end of summer. After two weeks, calves are able to join the herd, and are fully weaned at two months of age. Elk calves are as large as an adult white-tailed deer
The white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), also known as the whitetail or Virginia deer, is a medium-sized deer native to North America, Central America, and South America as far south as Peru and Bolivia. It has also been introduced t ...
by the time they are six months old. Elk will leave their natal (birth) ranges before they are three years old. Males disperse more often than females, as adult cows are more tolerant of female offspring from previous years. Elk live 20 years or more in captivity but average 10 to 13 years in the wild. In some subspecies that suffer less predation, they may live an average of 15 years in the wild.
Migration
 As is true for many species of deer, especially those in mountainous regions, elk
As is true for many species of deer, especially those in mountainous regions, elk migrate
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
into areas of higher altitude in the spring, following the retreating snows, and the opposite direction in the fall. Hunting pressure impacts migration and movement. During the winter, they favor wooded areas for the greater availability of food to eat. Elk do not appear to benefit from thermal cover. The Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem elk herds comprise as many as 40,000 individuals. During the spring and fall, they take part in the longest elk migration in the continental U.S., traveling as much as between summer and winter ranges. The Teton herd consists of between 9,000 and 13,000 elk and they spend winters on the National Elk Refuge
The National Elk Refuge is a Wildlife Refuge located in Jackson Hole in the U.S. state of Wyoming. It was created in 1912 to protect habitat and provide sanctuary for one of the largest elk (also known as wapiti) herds. With a total of , the ref ...
, having migrated south from the southern portions of Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming
Wyoming () is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is border ...
and west from the Shoshone
The Shoshone or Shoshoni ( or ) are a Native American tribe with four large cultural/linguistic divisions:
* Eastern Shoshone: Wyoming
* Northern Shoshone: southern Idaho
* Western Shoshone: Nevada, northern Utah
* Goshute: western Utah, e ...
and Bridger–Teton National Forest
Bridger–Teton National Forest is located in western Wyoming, United States. The forest consists of , making it the third largest National Forest outside Alaska. The forest stretches from Yellowstone National Park, along the eastern bounda ...
s.
Diet
 Elk are ruminants and therefore have four-chambered stomachs. Unlike white-tailed deer and moose, which are chiefly browsers, elk are similar to
Elk are ruminants and therefore have four-chambered stomachs. Unlike white-tailed deer and moose, which are chiefly browsers, elk are similar to cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult ...
in that they are primarily grazers. But like other deer, they also browse. Elk have a tendency to do most of their feeding in the mornings and evenings, seeking sheltered areas in between feedings to digest. Their diets vary somewhat depending on the season, with native grasses being a year-round supplement, tree bark being consumed in winter, and forbs
A forb or phorb is an herbaceous flowering plant that is not a graminoid (grass, sedge, or rush). The term is used in biology and in vegetation ecology, especially in relation to grasslands and understory. Typically these are dicots without wo ...
and tree sprouts during the summer. Elk consume an average of of vegetation daily. Particularly fond of aspen
Aspen is a common name for certain tree species; some, but not all, are classified by botanists in the section ''Populus'', of the ''Populus'' genus.
Species
These species are called aspens:
*'' Populus adenopoda'' – Chinese aspen (Chin ...
sprouts which rise in the spring, elk have had some impact on aspen groves which have been declining in some regions where elk exist. Range and wildlife managers conduct surveys of elk pellet groups to monitor populations and resource use.
Predators and defensive tactics
 Predators of elk include
Predators of elk include wolves
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly u ...
, coyotes
The coyote (''Canis latrans'') is a species of canine native to North America. It is smaller than its close relative, the wolf, and slightly smaller than the closely related eastern wolf and red wolf. It fills much of the same ecological nich ...
, brown
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing or painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors orange and black. In the RGB color model use ...
and black
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white ha ...
bears
Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family Ursidae. They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats throughout the Nor ...
, cougars
The cougar (''Puma concolor'') is a large cat native to the Americas. Its range spans from the Canadian Yukon to the southern Andes in South America and is the most widespread of any large wild terrestrial mammal in the Western Hemisphere. ...
, and Siberian tigers. Coyote
The coyote (''Canis latrans'') is a species of canine native to North America. It is smaller than its close relative, the wolf, and slightly smaller than the closely related eastern wolf and red wolf. It fills much of the same ecological ni ...
packs mostly prey on elk calves, though they can sometimes take a winter- or disease-weakened adult. In the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem
The Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem (GYE) is one of the last remaining large, nearly intact ecosystems in the northern temperate zone of the Earth. It is located within the northern Rocky Mountains, in areas of northwestern Wyoming, southwestern M ...
, which includes Yellowstone National Park, bears are the most significant predators of calves while healthy bulls have never been recorded to be killed by bears and such encounters can be fatal for bears. The killing of cows in their prime is more likely to affect population growth than the killing of bulls or calves.
Elk may avoid predation by switching from grazing to browsing. Grazing puts an elk in the compromising situation of being in an open area with its head down, leaving it unable to see what is going on in the surrounding area. Living in groups also lessens the risk of an individual falling to predation. Large bull elk are less vulnerable and can afford to wander alone, while cows stay in larger groups for protection for their calves. Bulls are more vulnerable to predation by wolves in late winter, after they have been weakened by months of chasing females and fighting. Males that have recently lost their antlers are more likely to be preyed upon.
Parasites and disease
At least 53 species ofprotist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the e ...
and animal parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted structurally to this way of lif ...
s have been identified in elk. Most of these parasites seldom lead to significant mortality among wild or captive elk. ''Parelaphostrongylus tenuis
''Parelaphostrongylus tenuis'' (also known as meningeal worm or brainworm) is a neurotropic nematode parasite common to white-tailed deer, ''Odocoileus virginianus'', which causes damage to the central nervous system.
Moose (''Alces alces'' ...
'' (brainworm or meningeal worm) is a parasitic nematode known to affect the spinal cord and brain tissue of elk and other species, leading to death. The definitive host is the white-tailed deer, in which it normally has no ill effects. Snails and slugs, the intermediate hosts, can be inadvertently consumed by elk during grazing. The liver fluke
Liver fluke is a collective name of a polyphyletic group of parasitic trematodes under the phylum Platyhelminthes.
They are principally parasites of the liver of various mammals, including humans. Capable of moving along the blood circulation, ...
''Fascioloides magna
''Fascioloides magna'', also known as giant liver fluke, large American liver fluke or deer fluke, is trematode parasite that occurs in wild and domestic ruminants in North America and Europe. Adult flukes occur in the liver of the definitive hos ...
'' and the nematode '' Dictyocaulus viviparus'' are also commonly found parasites that can be fatal to elk. Since infection by either of these parasites can be lethal to some commercial livestock species, their presence in elk herds is of some concern.

Chronic wasting disease
Chronic wasting disease (CWD), sometimes called zombie deer disease, is a transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) affecting deer. TSEs are a family of diseases thought to be caused by misfolded proteins called prions and include similar dis ...
, transmitted by a misfolded protein known as a prion
Prions are misfolded proteins that have the ability to transmit their misfolded shape onto normal variants of the same protein. They characterize several fatal and transmissible neurodegenerative diseases in humans and many other animals. It ...
, affects the brain tissue in elk, and has been detected throughout their range in North America. First documented in the late 1960s in mule deer, the disease has affected elk on game farms and in the wild in a number of regions. Elk that have contracted the disease begin to show weight loss, changes in behavior, increased watering needs, excessive salivation and urinating and difficulty swallowing, and at an advanced stage, the disease leads to death. No risks to humans have been documented, nor has the disease been demonstrated to pose a threat to domesticated cattle. In 2002, South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and sharing a Korean Demilitarized Zone, land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed ...
banned the importation of elk antler velvet due to concerns about chronic wasting disease.
The Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative bacterial disease brucellosis occasionally affects elk in the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem, the only place in the U.S. where the disease is still known to exist, though this can extend out to the Bighorn Mountains. In domesticated cattle, brucellosis causes infertility, abortions, and reduced milk production. It is transmitted to humans as undulant fever, producing influenza-like symptoms that may last for years. Though bison are more likely to transmit the disease to other animals, elk inadvertently transmitted brucellosis to horses in Wyoming and cattle in Idaho. Researchers are attempting to eradicate the disease through vaccinations and herd-management measures, which are expected to be successful. Nevertheless, research has been ongoing since 2002, and a successful vaccine has yet to be developed .
A recent Autopsy, necropsy study of captive elk in Pennsylvania attributed the cause of death in 33 of 65 cases to either gastrointestinal parasites (21 cases, primarily ''Eimeria'' sp. and ''Strongylida, Ostertagia'' sp.) or bacterial infections (12 cases, mostly pneumonia).
Elk hoof disease was first noticed in the state of Washington in the late 1990s in the Cowlitz River basin, with sporadic reports of deformed hooves. Since then, the disease has spread rapidly with increased sightings throughout southwest Washington and into Oregon. The disease is characterised by deformed, broken, or missing hooves and leads to severe lameness in elk. The primary cause is not known, but it is associated with Treponema, treponeme bacteria, which are known to cause digital dermatitis in commercial livestock. The mode of transmission is also not known, but it appears to be highly contagious among elk. Studies are being undertaken by government departments to determine how to halt or eliminate the disease.
Distribution and status
 The elk ranges from central Asia though to Siberia and east Asia and in North America. They can be found in open deciduous woodlands, boreal forests, upland moors, mountainous areas and grasslands. The International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) list the species as least-concern species. The habitat of Siberian elk in Asia is similar to that of the Rocky Mountain subspecies in North America. During the Late Pleistocene their range was much more extensive, being distributed across Eurasia, with remains being found as far west as France. These populations are most closely related to modern Asian populations of the elk. Their range collapsed at the start of the Holocene, possibly because they were specialized to cold periglacial tundra-steppe habitat. When this environment was replaced largely by closed forest the red deer might have outcompeted the elk. Relict (biology), Relictual populations survived into the early Holocene (until around 3000 years ago) in southern Sweden and the Alps, where the environment remained favorable.
The elk ranges from central Asia though to Siberia and east Asia and in North America. They can be found in open deciduous woodlands, boreal forests, upland moors, mountainous areas and grasslands. The International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) list the species as least-concern species. The habitat of Siberian elk in Asia is similar to that of the Rocky Mountain subspecies in North America. During the Late Pleistocene their range was much more extensive, being distributed across Eurasia, with remains being found as far west as France. These populations are most closely related to modern Asian populations of the elk. Their range collapsed at the start of the Holocene, possibly because they were specialized to cold periglacial tundra-steppe habitat. When this environment was replaced largely by closed forest the red deer might have outcompeted the elk. Relict (biology), Relictual populations survived into the early Holocene (until around 3000 years ago) in southern Sweden and the Alps, where the environment remained favorable.
Introductions and reintroductions
Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, t ...
in the early 20th century. There they are now considered an invasive species, encroaching on Argentinian ecosystems where they compete for food with the indigenous South Andean deer, Chilean huemul and other herbivores. This negative impact on native animal species has led the IUCN to identify the elk as one of the world's 100 worst invaders.
The introduction of deer to New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 List of islands of New Zealand, smaller islands. It is the ...
began in the middle of the 19th century, and current populations are primarily European red deer, with only 15 percent being elk. There is significant hybridization of elk with red deer. These deer have had an adverse impact on forest regeneration of some plant species, as they consume more palatable species, which are replaced with those that are less favored by the elk. The long-term impact will be an alteration of the types of plants and trees found, and in other animal and plant species dependent upon them. As in Chile and Argentina, the IUCN has declared that red deer and elk populations in New Zealand are an invasive species.
Estimated number of elk per U.S. state
Cultural references
 Elk have played an important role in the cultural history of a number of peoples. Neolithic petroglyphs from Asia depict antler-less female elk, which have been interpreted as symbolizing life and sustenance. They were also frequently overlaid with boats and associated with rivers, suggesting they also represented paths to the underworld. Petroglyphs of elk were carved into cliffs by the Ancestral Puebloans of the southwestern U.S. hundreds of years ago. The elk was of particular importance to the Lakota people, Lakota and played a spiritual role in their society. The male elk was admired for its ability to attract mates, and Lakota men will play a courting flute imitating a bugling elk to attract women. Men used elks' antlers as love charms and wore clothes decorated with elk images.
The Rocky Mountain elk is the List of U.S. state mammals, official state animal for Utah. An image of an elk and a moose appear on the state Seal of Michigan, seal and Flag of Michigan, flag of Michigan. The Benevolent and Protective Order of Elks (B.P.O.E.) chose the elk as its namesake because a number of its attributes seemed appropriate for cultivation by members of the fraternity. Jewel encrusted, gold mounted elk teeth are prized possession of many members of the B.P.O.E..
Elk have played an important role in the cultural history of a number of peoples. Neolithic petroglyphs from Asia depict antler-less female elk, which have been interpreted as symbolizing life and sustenance. They were also frequently overlaid with boats and associated with rivers, suggesting they also represented paths to the underworld. Petroglyphs of elk were carved into cliffs by the Ancestral Puebloans of the southwestern U.S. hundreds of years ago. The elk was of particular importance to the Lakota people, Lakota and played a spiritual role in their society. The male elk was admired for its ability to attract mates, and Lakota men will play a courting flute imitating a bugling elk to attract women. Men used elks' antlers as love charms and wore clothes decorated with elk images.
The Rocky Mountain elk is the List of U.S. state mammals, official state animal for Utah. An image of an elk and a moose appear on the state Seal of Michigan, seal and Flag of Michigan, flag of Michigan. The Benevolent and Protective Order of Elks (B.P.O.E.) chose the elk as its namesake because a number of its attributes seemed appropriate for cultivation by members of the fraternity. Jewel encrusted, gold mounted elk teeth are prized possession of many members of the B.P.O.E..
Commercial uses
 Although breakdown figures for each game species are not available in the 2006 National Survey from the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, hunting of wild elk is most likely the primary economic impact.
While elk are not generally harvested for meat production on a large scale, some restaurants offer the meat as a specialty item and it is also available in some grocery stores. The meat has a taste somewhere between beef and venison and is higher in
Although breakdown figures for each game species are not available in the 2006 National Survey from the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, hunting of wild elk is most likely the primary economic impact.
While elk are not generally harvested for meat production on a large scale, some restaurants offer the meat as a specialty item and it is also available in some grocery stores. The meat has a taste somewhere between beef and venison and is higher in protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
and lower in fat and cholesterol than beef, pork, and chicken. Elk meat is a good source of iron, phosphorus and zinc.
A male elk can produce of Velvet antler, antler velvet annually and on ranches in the United States, Canada and New Zealand, it is collected and sold to markets in East Asia, where it is used in medicine. Some cultures consider velvet to be an aphrodisiac. However, consuming velvet from elk in North America may be risky since velvet from animals infected with chronic wasting disease may contain prions that could result in a human getting variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease.
Antlers are also used in artwork, furniture and other novelty items. All Asian subspecies, along with other deer, have been raised for their antlers in central and eastern Asia by Han Chinese, Turkic peoples, Tungusic peoples, Mongols, Mongolians, and Koreans. Elk farming, Elk farms are relatively common in North America and New Zealand. Native Americans have used elk hides for tepee covering, clothing and footwear.
Since 1967, the Boy Scouts of America have assisted employees at the National Elk Refuge
The National Elk Refuge is a Wildlife Refuge located in Jackson Hole in the U.S. state of Wyoming. It was created in 1912 to protect habitat and provide sanctuary for one of the largest elk (also known as wapiti) herds. With a total of , the ref ...
in Wyoming by collecting the antlers which are shed each winter. They are then auctioned, with 80% of the proceeds returned to the refuge. In 2010, of antlers were auctioned, bringing in over United States dollar, $46,000.
References
External links
Arizona Elk
Arizona Game and Fish Department
Rocky Mountain Elk Foundation
{{Taxonbar, from=Q180404 Cervus Elk and red deer Fauna of Siberia Holarctic fauna Mammals of the United States Fauna of Central Asia Mammals of Canada Fauna of East Asia Extant Pleistocene first appearances Herbivorous mammals Mammals described in 1777 Taxa named by Johann Christian Polycarp Erxleben