Electronic symbol on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An electronic symbol is a
IEEE Std 315-1975
or CSA Z99-1975). *
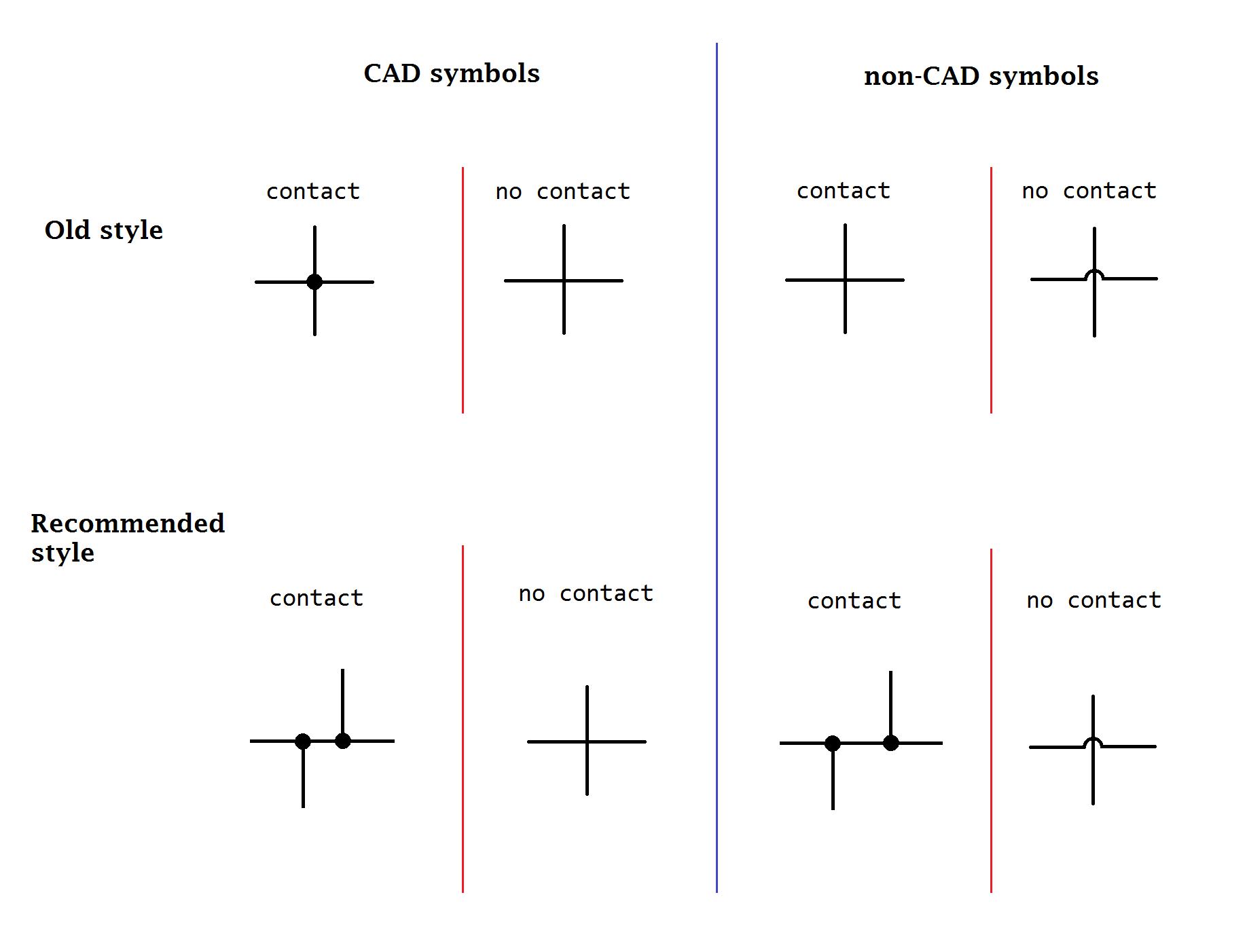
File:IEEE 315 Transmission Path Symbols (13).svg , Trace connection
( IEC-style) File:IEEE 315 Transmission Path Symbols (15).svg , Trace junction
(IEC-style) File:IEEE 315 Transmission Path Symbols (11).svg , Trace crossing (unconnected) File:Trace crossing.svg , Trace crossing
(hand drawn schematics)
File:IEEE 315 Transmission Path Symbols (75).svg , General
( IEC-style) File:IEEE 315 Transmission Path Symbols (80).svg , Signal/low-noise ground (the asterisk is not part of the symbol) File:IEEE 315 Transmission Path Symbols (78).svg , Chassis ground
(IEC-style)
File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (90).svg , Battery, single-cell
File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (92).svg , Battery, multi-cell
File:IEEE 315-1975 (1993) 8.7.3.svg ,
pictogram
A pictogram, also called a pictogramme, pictograph, or simply picto, and in computer usage an icon, is a graphic symbol that conveys its meaning through its pictorial resemblance to a physical object. Pictographs are often used in writing and g ...
used to represent various electrical
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described ...
and electronic
Electronic may refer to:
*Electronics, the science of how to control electric energy in semiconductor
* ''Electronics'' (magazine), a defunct American trade journal
*Electronic storage, the storage of data using an electronic device
*Electronic co ...
devices or functions, such as wire
Overhead power cabling. The conductor consists of seven strands of steel (centre, high tensile strength), surrounded by four outer layers of aluminium (high conductivity). Sample diameter 40 mm
A wire is a flexible strand of metal.
Wire is co ...
s, batteries
Battery most often refers to:
* Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power
* Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact
Battery may also refer to:
Energy source
*Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ...
, resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias activ ...
s, and transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
s, in a schematic diagram
A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a designed representation of the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the key information the s ...
of an electrical or electronic circuit
An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow. It is a type of electri ...
. These symbols are largely standardized internationally today, but may vary from country to country, or engineering discipline, based on traditional conventions.
Standards for symbols
The graphic symbols used for electrical components incircuit diagram
A circuit diagram (wiring diagram, electrical diagram, elementary diagram, electronic schematic) is a graphical representation of an electrical circuit. A pictorial circuit diagram uses simple images of components, while a schematic diagram ...
s are covered by national and international standards, in particular:
* IEC 60617 (also known as BS 3939).
* There is also IEC 61131-3 – for ladder-logic symbols.
* JIC JIC (Joint Industrial Council) symbols as approved and adopted by the NMTBA (National Machine Tool Builders Association). They have been extracted from the Appendix of the NMTBA Specification EGPl-1967.
* ANSI
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organ ...
Y32.2-1975 (also known aIEEE Std 315-1975
or CSA Z99-1975). *
IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operati ...
Std 91/91a: graphic symbols for logic functions (used in digital electronics). It is referenced in ANSI Y32.2/IEEE Std 315.
* Australian Standard AS 1102 (based on a slightly modified version of IEC 60617; withdrawn without replacement with a recommendation to use IEC 60617).
The number of standards leads to confusion and errors.
Symbols usage is sometimes unique to engineering disciplines, and national or local variations to international standards exist. For example, lighting and power symbols used as part of architectural drawings may be different from symbols for devices used in electronics.
Common electronic symbols
Symbols shown are typical examples, not a complete list.Traces

( IEC-style) File:IEEE 315 Transmission Path Symbols (15).svg , Trace junction
(IEC-style) File:IEEE 315 Transmission Path Symbols (11).svg , Trace crossing (unconnected) File:Trace crossing.svg , Trace crossing
(hand drawn schematics)
Grounds
The shorthand for ground is GND. Optionally, the triangle in the middle symbol may be filled in.ground
Ground may refer to:
Geology
* Land, the surface of the Earth not covered by water
* Soil, a mixture of clay, sand and organic matter present on the surface of the Earth
Electricity
* Ground (electricity), the reference point in an electrical c ...
( IEC-style) File:IEEE 315 Transmission Path Symbols (80).svg , Signal/low-noise ground (the asterisk is not part of the symbol) File:IEEE 315 Transmission Path Symbols (78).svg , Chassis ground
(IEC-style)
Sources
Solar cell
A solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect, which is a physical and chemical phenomenon.
File:Resistor, Rheostat (variable resistor), and Potentiometer symbols.svg ,
(c)
(c) Potentiometer / Trimmer
File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (31).svg , Photoresistor (ANSI)
File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (26).svg ,
Use -t for NTC symbol.
Use +t for PTC symbol. File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (13).svg , Varistor (ANSI)
File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (32).svg , General capacitor
(IEC-style) File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (36).svg , Polarized capacitor
(American-style) File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (38).svg , Variable capacitor File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (41).svg , ''Ganged'' (co-moving) variable capacitors
( IEC-style) File:Trimmer capacitor symbol GOST.svg , Trimmer variable capacitor
File:Diode symbol.svg , Diode (rectifier)
File:Schottky diode symbol.svg ,
File:Bridge Rectifier.svg , Bridge rectifier
File:УГО диодного моста.svg , Bridge rectifier
File:4 diodes bridge rectifier.jpg , Bridge rectifier
File:Bridge Rectifier for single-phase alternating current (symbolic diagram).png , Bridge rectifier
File:3 fase bridge rectifier.jpg , Three-phase bridge rectifier
File:IEC Inductor.svg , Air-core
( IEC-style) File:IEC Inductor with magnetic core.svg , Magnetic-core
(IEEE-style) File:IEC Tapped inductor.svg , Tapped
(IEC-style) File:Ferrite bead ring.svg ,
(IEEE-style)
File:Transformer Iron Core.svg ,
IEEE 315-1975 (1993) 8.6.2.svg , NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT)
IEEE 315-1975 (1993) 8.6.1.svg , PNP bipolar junction transistor (BJT)
IEEE 315-1975 (1993) 8.6.17.svg , NPN Darlington transistor
File:PNP darlington.svg , PNP Darlington transistor
File:IEEE 315-1975 (1993) 8.6.10.1.b.svg , N-channel junction gate field-effect transistor (JFET)
File:IEEE 315-1975 (1993) 8.6.11.1.b.svg , P-channel junction gate field-effect transistor (JFET)
File:IGFET N-Ch Enh Labelled simplified.svg , Metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET)
File:Enh N channel Mosfet.svg , Enhancement mode, N-channel
File:Dioda symbol.svg , Vacuum tube diode
File:Trioda symbol.svg , Vacuum tube
(pin letters are not part of the symbol) File:Pentoda symbol.svg , Vacuum tube
File:Poussoir-NO-symbol.png ,
File:SPST-Switch.svg , Switch, 1P1T, SPST (single-pole single-throw)
File:SPDT-Switch.svg , Switch, 1P2T, SPDT (single-pole double-throw)
File:DPST-symbol.svg , Switch, 2P1T, DPST (double-pole single-throw)
File:DPDT-symbol.svg , Switch, 2P2T, DPDT (double-pole double-throw)
IEEE 315 Contacts, Switches, Contactors, and Relays Symbols (85).svg , Slide switch, 1P3T,
break-before-make, nonshorting style IEEE 315 Contacts, Switches, Contactors, and Relays Symbols (87).svg , Slide switch, 1P4T,
break-before-make, nonshorting style IEEE 315 Contacts, Switches, Contactors, and Relays Symbols (89).svg , Slide switch, 1P4T,
make-before-break, shorting style
IEEE 315 Contacts, Switches, Contactors, and Relays Symbols (84).svg ,
break-before-make, nonshorting style IEEE 315 Contacts, Switches, Contactors, and Relays Symbols (86).svg , Rotary switch, 1P4T,
break-before-make, nonshorting style IEEE 315 Contacts, Switches, Contactors, and Relays Symbols (88).svg , Rotary switch, 1P4T,
make-before-break, shorting style
File:Reed switch symbol.svg ,
File:Relay symbols.svg , SPST, SPDT, DPST, DPDT relays
(American-style) File:Relay-IEC.svg , SPDT relay
(IEC-style)
File:Neon lamp schematics.svg ,
(IEEE-style) File:Lamp symbol, old.svg ,
File:Fuces.svg , IEC
File:IEEE Loudspeaker.svg ,
(IEEE-style) File:Buzzer-IEC-Symbol.svg , Buzzer
(IEC-style) File:IEEE MIC.svg ,
(IEEE-style) File:IEC MIC.svg , Microphone
( IEC-style)
File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (55).svg , General antenna
( IEC-style) File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (58).svg , Dipole antenna
(IEC-style) File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (61).svg, Loop antenna
(IEC-style) File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (60).svg, Loop antenna
(IEEE-style)
IEEE 315 Transmission Path Symbols (26).svg , Cable, Shielded 1 conductor
IEEE 315 Transmission Path Symbols (30).svg , Cable, 2 conductor
IEEE 315 Transmission Path Symbols (29).svg , Cable, Shielded 2 conductor with shield connected to ground
IEEE 315 Transmission Path Symbols (31).svg , Cable, 5 conductor
IEEE 315 Transmission Path Symbols (27).svg , Cable, Shielded 5 conductor
File:Phone Jack Symbols.svg , TRS phone jacks
File:Buffer ANSI Labelled.svg , Buffer
File:NOT ANSI Labelled.svg ,
The above logic symbols may have additional I/O variations too: 1)
File:Schmitt trigger symbol.svg , Buffer gate with
(B is the tri-state control)
File:Inverted SR Flip-flop.svg , Simple SR flip-flop (inverted S & R inputs)
File:Gated SR flip-flop Symbol.svg , Gated SR flip-flop
File:Transparent Latch Symbol.svg , Gated D flip-flop (Transparent Latch)
File:D-Type Flip-flop.svg , Clocked D flip-flop
(Set & Reset inputs) File:JK Flip-flop (Simple) Symbol.svg , Clocked JK flip-flop File:T-Type Flip-flop.svg , Clocked T flip-flop
File:Op-amp symbol.svg ,
File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (113).svg ,
(IEEE-style) File:Schaltsymbol-Keramikresonator.svg ,
(3 pins)
File:Common Hall Sensor Symbol.png , Hall-effect sensor
File:Symbol Surge Arrester.svg , Gas-discharge tubes (GDT) for ESD discharge
File:Symbol Spark gap.svg ,
for ESD discharge
File:Polarized capacitor symbol 5.png , Obsolete capacitor
(very old style) File:Capacitor old.svg , Obsolete capacitor File:Capacitor old with polarity.svg , Obsolete capacitor File:Polarized capacitor symbol 3.svg , Obsolete capacitor File:Elco's.jpg , Obsolete capacitor
''How to Read Electronic Circuit Diagrams''
2nd Ed; Brown, Lawrence, Whitson; Tab Books; 214 pages; 1988; .
''How to Read Schematic Diagrams''
4th Ed; Donald Herrington; Sams Publishing; 160 pages; 1986; .
(2nd Ed in 1967)
'
''Engineer's Mini-Notebook : Schematic Symbols, Device Packages, Design and Testing''
1st Ed; Forrest M. Mims III; Radio Shack; 48 pages; 1988.
IEEE Standard American National Standard Canadian Standard Graphic Symbols for Electrical and Electronics Diagrams (Including Reference Designation Letters)IEC 60617 : Graphical Symbols for Diagrams (2012)
- International standard
MIL-STD-806B : Graphical Symbols for Logic Diagrams (1962)
- U.S. DoD standard {{DEFAULTSORT:Electronic Symbol Electronic engineering Pictograms
ANSI
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organ ...
-style: (a) Resistor, (b) Rheostat
A potentiometer is a three- terminal resistor with a sliding or rotating contact that forms an adjustable voltage divider. If only two terminals are used, one end and the wiper, it acts as a variable resistor or rheostat.
The measuring instrum ...
,(c)
Potentiometer
A potentiometer is a three- terminal resistor with a sliding or rotating contact that forms an adjustable voltage divider. If only two terminals are used, one end and the wiper, it acts as a variable resistor or rheostat.
The measuring instrum ...
/ Trimmer
File:IEC resistors.svg , IEC-style: (a) Resistor, (b) Rheostat,(c) Potentiometer / Trimmer
Thermistor
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance is strongly dependent on temperature, more so than in standard resistors. The word thermistor is a portmanteau of ''thermal'' and ''resistor''.
Thermistors are divided based on their conduction ...
(ANSI).Use -t for NTC symbol.
Use +t for PTC symbol. File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (13).svg , Varistor (ANSI)
Capacitors
(IEC-style) File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (36).svg , Polarized capacitor
(American-style) File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (38).svg , Variable capacitor File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (41).svg , ''Ganged'' (co-moving) variable capacitors
( IEC-style) File:Trimmer capacitor symbol GOST.svg , Trimmer variable capacitor
Diodes
Optionally, the triangle in these symbols may be filled in. Note: The words anode and cathode typically aren't part of the diode symbols.Schottky diode
The Schottky diode (named after the German physicist Walter H. Schottky), also known as Schottky barrier diode or hot-carrier diode, is a semiconductor diode formed by the junction of a semiconductor with a metal. It has a low forward voltag ...
File:Zener_diode_symbol-2.svg , Zener diode
A Zener diode is a special type of diode designed to reliably allow current to flow "backwards" (inverted polarity) when a certain set reverse voltage, known as the ''Zener voltage'', is reached.
Zener diodes are manufactured with a great var ...
File:TVS diode symbols.svg , Transient-voltage-suppression diode (TVS)
File:LED symbol.svg , Light-emitting diode
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light ( ...
(LED)
File:Photodiode symbol.svg , Photodiode
File:Tunnel diode symbol.svg , Tunnel diode
A tunnel diode or Esaki diode is a type of semiconductor diode that has effectively " negative resistance" due to the quantum mechanical effect called tunneling. It was invented in August 1957 by Leo Esaki, Yuriko Kurose, and Takashi Su ...
File:Varicap symbol.svg , Varicap
In electronics, a varicap diode, varactor diode, variable capacitance diode, variable reactance diode or tuning diode is a type of diode designed to exploit the voltage-dependent capacitance of a reverse-biased p–n junction.
Applications
Var ...
File:Shockley diode.svg , Shockley diode
File:SCR symbol.svg , Silicon-controlled rectifier
A silicon controlled rectifier or semiconductor controlled rectifier is a four-layer solid-state current-controlling device. The name "silicon controlled rectifier" is General Electric's trade name for a type of thyristor. The principle of fou ...
(SCR)
File:Diac-schematic-symbol.png , Diac (may be a varistor in older schematics)
File:Constant Regulating Diode.png , Constant-current diode
A constant-current diode is an electronic device that limits current to a maximal specified value for the device. It is known as a current-limiting diode (CLD) or current-regulating diode (CRD).
It consists of an n-channel JFET with the gate sho ...
File:Symbol Opto-Isulator.svg , Opto-isolator: LED (left), photo transistor (right)
Bridge rectifiers
There are many ways to draw a single-phase bridge rectifier symbol. Some show the internal diode circuit, some don't.Inductors
inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. An inductor typically consists of an insulated wire wound into a ...
( IEC-style) File:IEC Inductor with magnetic core.svg , Magnetic-core
inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. An inductor typically consists of an insulated wire wound into a ...
(IEEE-style) File:IEC Tapped inductor.svg , Tapped
inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. An inductor typically consists of an insulated wire wound into a ...
(IEC-style) File:Ferrite bead ring.svg ,
Ferrite bead
A ferrite bead at the end of a Mini USB cable
A ferrite bead (also known as a ferrite block, ferrite core, ferrite ring, EMI filter, or ferrite choke) is a type of choke that suppresses high-frequency electronic noise in electronic circuits.
...
(IEEE-style)
Transformers
Transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer' ...
File:Transformer center tap.svg , Transformer with center tap on secondary winding (right side)
File:Transformer two secondary windings.svg , Transformer with two secondary windings (right side)
File:Basic Current Transformer Symbol.svg , Current transformer
File:Zero Sequence Current Transformer Symbol.svg , Zero-sequence current transformer (ZSCT) (also known as a window-type current transformer)
File:Bushing Type Current Transformer Symbol.svg , Bushing-type current transformer
File:Voltage Transformer.svg , Voltage transformer
Transistors
Optionally, transistor symbols may include a circle. Note: The pin letters B/C/E and G/D/S aren't part of the transistor symbols.Bipolar
Unipolar
MOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which d ...
File:Enh P channel Mosfet 2.svg , Enhancement mode, P-channel MOSFET
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET) is a type of field-effect transistor (FET), most commonly fabricated by the controlled oxidation of silicon. It has an insulated gate, the voltage of which d ...
Vacuum tubes
triode
A triode is an electronic amplifying vacuum tube (or ''valve'' in British English) consisting of three electrodes inside an evacuated glass envelope: a heated filament or cathode, a grid, and a plate (anode). Developed from Lee De Forest's 1 ...
File:Vacuum Tube Tetrode.svg , Vacuum tube tetrode
A tetrode is a vacuum tube (called ''valve'' in British English) having four active electrodes. The four electrodes in order from the centre are: a thermionic cathode, first and second grids and a plate (called ''anode'' in British English). ...
(pin letters are not part of the symbol) File:Pentoda symbol.svg , Vacuum tube
pentode
A pentode is an electronic device having five electrodes. The term most commonly applies to a three-grid amplifying vacuum tube or thermionic valve that was invented by Gilles Holst and Bernhard D.H. Tellegen in 1926. The pentode (called a ''tripl ...
Switches
Pushbutton
''Pushbutton'' was a UK-based digital agency specialising in designing, developing, and delivering interactive television. Pushbutton was acquired by Amazon.com on 28 July 2011 and many of its staff are now members of Amazon Development Centre ( ...
, normally open, push-to-make (horizontal line on top)
File:IEEE 315 Contacts, Switches, Contactors, and Relays Symbols (57).svg , Pushbutton, normally open, push-to-make (IEEE-style)
File:IEEE 315 Contacts, Switches, Contactors, and Relays Symbols (58).svg , Pushbutton, normally closed, push-to-break (IEEE-style)
File:IEEE 315 Contacts, Switches, Contactors, and Relays Symbols (59).svg , Pushbutton, normally closed, two circuits (IEEE-style)
break-before-make, nonshorting style IEEE 315 Contacts, Switches, Contactors, and Relays Symbols (87).svg , Slide switch, 1P4T,
break-before-make, nonshorting style IEEE 315 Contacts, Switches, Contactors, and Relays Symbols (89).svg , Slide switch, 1P4T,
make-before-break, shorting style
Rotary switch
A rotary switch is a switch operated by rotation. These are often chosen when more than 2 positions are needed, such as a three-speed fan or a CB radio with multiple frequencies of reception or "channels".
A rotary switch consists of a spin ...
, 1P3T,break-before-make, nonshorting style IEEE 315 Contacts, Switches, Contactors, and Relays Symbols (86).svg , Rotary switch, 1P4T,
break-before-make, nonshorting style IEEE 315 Contacts, Switches, Contactors, and Relays Symbols (88).svg , Rotary switch, 1P4T,
make-before-break, shorting style
Reed switch
Reed or Reeds may refer to:
Science, technology, biology, and medicine
* Reed bird (disambiguation)
* Reed pen, writing implement in use since ancient times
* Reed (plant), one of several tall, grass-like wetland plants of the order Poales
* ...
, normally open
Relays
Note: The pin letters aren't part of the symbols.(American-style) File:Relay-IEC.svg , SPDT relay
(IEC-style)
Lamps
LED is located in diode section.Neon lamp
A neon lamp (also neon glow lamp) is a miniature gas discharge lamp. The lamp typically consists of a small glass capsule that contains a mixture of neon and other gases at a low pressure and two electrodes (an anode and a cathode). When suffi ...
File:Indicating lamp.svg , Indicating lamp(IEEE-style) File:Lamp symbol, old.svg ,
Incandescent lamp
An incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is an electric light with a wire filament heated until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb with a vacuum or inert gas to protect the filament from oxida ...
File:Lamp symbol.svg , Incandescent light bulb
An incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is an electric light with a wire filament heated until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb with a vacuum or inert gas to protect the filament from oxida ...
(as an indicator)
File:Light bulb 3.svg , Light bulb
Current limiters
fuse
Fuse or FUSE may refer to:
Devices
* Fuse (electrical), a device used in electrical systems to protect against excessive current
** Fuse (automotive), a class of fuses for vehicles
* Fuse (hydraulic), a device used in hydraulic systems to prote ...
(b), equivalent symbols (a, c) (IEEE Std 315-1975)
File:Moulded Case Circuit Breaker.svg , Moulded-case circuit breaker
A circuit breaker is an electrical safety device designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by an overcurrent or short circuit. Its basic function is to interrupt current flow to protect equipment and to prevent the risk ...
(MCCB)
File:Fuse-basic-symbols.svg , Fuse
Fuse or FUSE may refer to:
Devices
* Fuse (electrical), a device used in electrical systems to protect against excessive current
** Fuse (automotive), a class of fuses for vehicles
* Fuse (hydraulic), a device used in hydraulic systems to prote ...
: IEC (top) and American (lower two)
Electro-acoustic devices
Loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or speaker driver) is an electroacoustic transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into a corresponding sound. A ''speaker system'', also often simply referred to as a "speaker" or ...
(IEEE-style) File:Buzzer-IEC-Symbol.svg , Buzzer
(IEC-style) File:IEEE MIC.svg ,
Microphone
A microphone, colloquially called a mic or mike (), is a transducer that converts sound into an electrical signal. Microphones are used in many applications such as telephones, hearing aids, public address systems for concert halls and pub ...
(IEEE-style) File:IEC MIC.svg , Microphone
( IEC-style)
Antennas
( IEC-style) File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (58).svg , Dipole antenna
(IEC-style) File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (61).svg, Loop antenna
(IEC-style) File:IEEE 315 Fundamental Items Symbols (60).svg, Loop antenna
(IEEE-style)
Cables
Connectors
ICs
Logic gates
For the symbols below: A and B are inputs, Q is output. Note: These letters are not part of the symbols. There are variations of these logic gate symbols. Depending on the IC, the two-input gates below may have: 1) two or more inputs; 2) infrequently some have a second inverted output too.Inverter
A power inverter, inverter or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the oppo ...
(NOT)
File:AND ANSI Labelled.svg , AND
File:NAND ANSI Labelled.svg , NAND
File:OR ANSI Labelled.svg , OR
File:NOR ANSI Labelled.svg , NOR
File:XOR ANSI Labelled.svg , XOR
File:XNOR ANSI Labelled.svg , XNOR
schmitt trigger
In electronics, a Schmitt trigger is a comparator circuit with hysteresis implemented by applying positive feedback to the noninverting input of a comparator or differential amplifier. It is an active circuit which converts an analog input ...
inputs, 2) tri-state outputs, 3) open-collector
An open collector is a common type of output found on many integrated circuits (IC), which behaves like a switch that is either connected to ground or disconnected. Instead of outputting a signal of a specific voltage or current, the output sig ...
or open-drain outputs (not shown).
schmitt trigger
In electronics, a Schmitt trigger is a comparator circuit with hysteresis implemented by applying positive feedback to the noninverting input of a comparator or differential amplifier. It is an active circuit which converts an analog input ...
input
File:Tristate buffer.svg , Buffer gate with tri-state output control.(B is the tri-state control)
Flip-flops
For the symbols below: Q is output, is inverted output, E is enable input, internal triangle shape is clock input, S is Set, R is Reset (some datasheets use clear (CLR) instead of reset along the bottom). There are variations of these flip-flop symbols. Depending on the IC, a flip-flop may have: 1) one or both outputs (Q only, only, both Q & ); 2) one or both forced inputs along top & bottom (R only, S only, both R & S); 3) some inputs may be inverted.(Set & Reset inputs) File:JK Flip-flop (Simple) Symbol.svg , Clocked JK flip-flop File:T-Type Flip-flop.svg , Clocked T flip-flop
OpAmps
Note: The outside text isn't part of these symbols.Operational amplifier
An operational amplifier (often op amp or opamp) is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op amp produces an output potential (relative to ...
(opamp)
File:Comparator symbol.svg , Comparator
Oscillators
Crystal oscillator
A crystal oscillator is an electronic oscillator circuit that uses a piezoelectric crystal as a frequency-selective element. The oscillator frequency is often used to keep track of time, as in quartz wristwatches, to provide a stable clock ...
(IEEE-style) File:Schaltsymbol-Keramikresonator.svg ,
Ceramic resonator
A Ceramic Resonator is an electronic component consisting of a piece of a piezoelectric ceramic material with two or more metal electrodes attached. When connected in an electronic oscillator circuit, resonant mechanical vibrations in the device ge ...
(3 pins)
Miscellaneous devices
Spark gap
A spark gap consists of an arrangement of two conducting electrodes separated by a gap usually filled with a gas such as air, designed to allow an electric spark to pass between the conductors. When the potential difference between the condu ...
for ESD discharge
Historical electronic symbols
The shape of some electronic symbols have changed over time. The following historical electronic symbols can be found in old electronic books / magazines / schematics, and now considered obsolete.Capacitors (historical)
All of the following are obsolete capacitor symbols.(very old style) File:Capacitor old.svg , Obsolete capacitor File:Capacitor old with polarity.svg , Obsolete capacitor File:Polarized capacitor symbol 3.svg , Obsolete capacitor File:Elco's.jpg , Obsolete capacitor
See also
*Circuit diagram
A circuit diagram (wiring diagram, electrical diagram, elementary diagram, electronic schematic) is a graphical representation of an electrical circuit. A pictorial circuit diagram uses simple images of components, while a schematic diagram ...
* Reference designator
* Symbols for appliance classes
References
Further reading
* ''Beginner's Guide to Reading Schematics''; 4th Ed; Stan Gibilisco; McGraw-Hill, 224 pages; 2018; .''How to Read Electronic Circuit Diagrams''
2nd Ed; Brown, Lawrence, Whitson; Tab Books; 214 pages; 1988; .
''How to Read Schematic Diagrams''
4th Ed; Donald Herrington; Sams Publishing; 160 pages; 1986; .
(2nd Ed in 1967)
'
''Engineer's Mini-Notebook : Schematic Symbols, Device Packages, Design and Testing''
1st Ed; Forrest M. Mims III; Radio Shack; 48 pages; 1988.
External links
IEEE Standard American National Standard Canadian Standard Graphic Symbols for Electrical and Electronics Diagrams (Including Reference Designation Letters)
- International standard
MIL-STD-806B : Graphical Symbols for Logic Diagrams (1962)
- U.S. DoD standard {{DEFAULTSORT:Electronic Symbol Electronic engineering Pictograms