Several articles in several parts of the
Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany
The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany () is the constitution of the Germany, Federal Republic of Germany.
The West German Constitution was approved in Bonn on 8 May 1949 and came into effect on 23 May after having been approved b ...
govern elections and establish constitutional requirements such as the
secret ballot
The secret ballot, also known as the Australian ballot, is a voting method in which a voter's identity in an election or a referendum is anonymous. This forestalls attempts to influence the voter by intimidation, blackmailing, and potential vote ...
, and the requirement that all elections be conducted in a free and fair manner. The Basic Law also requires that the federal legislature enact detailed federal laws to govern elections; electoral law(s). One such article is Article 38, regarding the election of deputies in the federal Bundestag. Article 38.2 of the Basic Law establishes universal suffrage: "Any person who has attained the age of eighteen shall be entitled to vote; any person who has attained the age of majority may be elected."
German federal elections are for all members of the Bundestag, which in turn determines who is the
chancellor of Germany
The chancellor of Germany, officially the federal chancellor of the Federal Republic of Germany, is the head of the federal Cabinet of Germany, government of Germany. The chancellor is the chief executive of the Federal Government of Germany, ...
. The most recent federal election was held
on 23 February 2025.
Latest election
Result in history
1919 German federal election
November 1933 German parliamentary election
1949 West German federal election
1949 East German Constitutional Assembly election
German elections from 1871 to 1945

After the
unification of Germany
The unification of Germany (, ) was a process of building the first nation-state for Germans with federalism, federal features based on the concept of Lesser Germany (one without Habsburgs' multi-ethnic Austria or its German-speaking part). I ...
under
Emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
Wilhelm I
Wilhelm I (Wilhelm Friedrich Ludwig; 22 March 1797 – 9 March 1888) was King of Prussia from 1861 and German Emperor from 1871 until his death in 1888. A member of the House of Hohenzollern, he was the first head of state of a united Germany. ...
in 1871, elections were held to the German
Reichstag or Imperial Assembly, which supplanted its namesake, the
Reichstag of the
North German Confederation
The North German Confederation () was initially a German military alliance established in August 1866 under the leadership of the Kingdom of Prussia, which was transformed in the subsequent year into a confederated state (a ''de facto'' feder ...
. The Reichstag could be dissolved by the emperor or, after the
abdication
Abdication is the act of formally relinquishing monarchical authority. Abdications have played various roles in the Order of succession, succession procedures of monarchies. While some cultures have viewed abdication as an extreme abandonment of ...
of
Wilhelm II
Wilhelm II (Friedrich Wilhelm Viktor Albert; 27 January 18594 June 1941) was the last German Emperor and King of Prussia from 1888 until Abdication of Wilhelm II, his abdication in 1918, which marked the end of the German Empire as well as th ...
in 1918, the
president of Germany
The president of Germany, officially titled the Federal President of the Federal Republic of Germany (),The official title within Germany is ', with ' being added in international correspondence; the official English title is President of the F ...
. With the
Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic, officially known as the German Reich, was the German Reich, German state from 1918 to 1933, during which it was a constitutional republic for the first time in history; hence it is also referred to, and unofficially proclai ...
's
Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these pri ...
of 1919, the voting system changed from single-member constituencies to proportional representation. The election age was reduced from 25 to 20 years of age.
Women's suffrage
Women's suffrage is the women's rights, right of women to Suffrage, vote in elections. Several instances occurred in recent centuries where women were selectively given, then stripped of, the right to vote. In Sweden, conditional women's suffra ...
had already been established by a new electoral law in 1918 following the
November Revolution of that year.
Following the
Nazi seizure of power
The rise to power of Adolf Hitler, dictator of Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945, began in the newly established Weimar Republic in September 1919, when Hitler joined the '' Deutsche Arbeiterpartei'' (DAP; German Workers' Party). He quickly rose t ...
in January 1933, another
national election was held on 5 March. This was the last competitive election before World War II, although it was neither free nor fair. Violence and intimidation by the , and had been underway for months against
trade-unionists,
communists
Communism () is a sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology within the socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a socioeconomic order centered on common ownership of the means of production, d ...
,
social democrats
Social democracy is a social, economic, and political philosophy within socialism that supports political and economic democracy and a gradualist, reformist, and democratic approach toward achieving social equality. In modern practice, s ...
, and even
centre-right
Centre-right politics is the set of right-wing politics, right-wing political ideologies that lean closer to the political centre. It is commonly associated with conservatism, Christian democracy, liberal conservatism, and conservative liberalis ...
Catholics.
[Evans, Richard J., ''The Coming of the Third Reich'', Penguin Press, New York, 2004.] On 27 February, just prior to the election, the
Reichstag Fire Decree
The Reichstag Fire Decree () is the common name of the Decree of the Reich President for the Protection of People and State () issued by German President Paul von Hindenburg on the advice of Chancellor Adolf Hitler on 28 February 1933 in immed ...
suspended
freedom of the press
Freedom of the press or freedom of the media is the fundamental principle that communication and expression through various media, including printed and electronic Media (communication), media, especially publication, published materials, shoul ...
and most
civil liberties
Civil liberties are guarantees and freedoms that governments commit not to abridge, either by constitution, legislation, or judicial interpretation, without due process. Though the scope of the term differs between countries, civil liberties of ...
. Mass arrests followed, including all
Communist
Communism () is a sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology within the socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a socioeconomic order centered on common ownership of the means of production, di ...
and several
Social Democrat
Social democracy is a Social philosophy, social, Economic ideology, economic, and political philosophy within socialism that supports Democracy, political and economic democracy and a gradualist, reformist, and democratic approach toward achi ...
delegates to the Reichstag. 50000 members of the (auxiliary Nazi police) "monitored" polling places on election day to further intimidate voters.
While the Nazi Party performed better than it had in the
elections of November 1932, it still won only 33% of the vote. By placing their rivals in jail and intimidating others not to take their seats, the Nazis went from a plurality to the majority. Just two weeks after the election, the
Enabling Act of 1933
The Enabling Act of 1933 ( German: ', officially titled ' ), was a law that gave the German Cabinet—most importantly, the chancellor, Adolf Hitler—the power to make and enforce laws without the involvement of the Reichstag or President Pa ...
effectively gave Hitler dictatorial power. Three more elections were held in Nazi Germany before the war. They all took the form of a one-question referendum, asking voters to approve a predetermined list of candidates composed exclusively of Nazis and nominally independent "guests" of the party.
Imperial elections
*
1848
1848 is historically famous for the wave of revolutions, a series of widespread struggles for more liberal governments, which broke out from Brazil to Hungary; although most failed in their immediate aims, they significantly altered the polit ...
*
1871
Events January–March
* January 3 – Franco-Prussian War: Battle of Bapaume – Prussians win a strategic victory.
* January 18 – Proclamation of the German Empire: The member states of the North German Confederation and the sout ...
*
1874
*
1877
Events January
* January 1 – Queen Victoria is proclaimed Empress of India by the Royal Titles Act 1876, introduced by Benjamin Disraeli, the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom .
* January 8 – Great Sioux War of 1876: Batt ...
*
1878
Events January
* January 5 – Russo-Turkish War: Battle of Shipka Pass IV – Russian and Bulgarian forces defeat the Ottoman Empire.
* January 9 – Umberto I becomes King of Italy.
* January 17 – Russo-Turkish War: ...
*
1881
*
1884
Events January
* January 4 – The Fabian Society is founded in London to promote gradualist social progress.
* January 5 – Gilbert and Sullivan's comic opera '' Princess Ida'', a satire on feminism, premières at the Savoy The ...
*
1887
Events January
* January 11 – Louis Pasteur's anti-rabies treatment is defended in the Académie Nationale de Médecine, by Dr. Joseph Grancher.
* January 20
** The United States Senate allows the United States Navy to lease Pearl Har ...
*
1890
Events
January
* January 1 – The Kingdom of Italy establishes Eritrea as its colony in the Horn of Africa.
* January 2 – Alice Sanger becomes the first female staffer in the White House.
* January 11 – 1890 British Ultimatum: The Uni ...
*
1893
*
1898
Events
January
* January 1 – New York City annexes land from surrounding counties, creating the City of Greater New York as the world's second largest. The city is geographically divided into five boroughs: Manhattan, Brooklyn, Queen ...
*
1903
*
1907
Events
January
* January 14 – 1907 Kingston earthquake: A 6.5 Moment magnitude scale, Mw earthquake in Kingston, Jamaica, kills between 800 and 1,000.
February
* February 9 – The "Mud March (suffragists), Mud March", the ...
*
1912
This year is notable for Sinking of the Titanic, the sinking of the ''Titanic'', which occurred on April 15.
In Albania, this leap year runs with only 353 days as the country achieved switching from the Julian to Gregorian Calendar by skippin ...
Weimar Republic federal elections
*
1919
Events
January
* January 1
** The Czechoslovak Legions occupy much of the self-proclaimed "free city" of Pressburg (later Bratislava), enforcing its incorporation into the new republic of Czechoslovakia.
** HMY ''Iolaire'' sinks off th ...
*
1920
Events January
* January 1
** Polish–Soviet War: The Russian Red Army increases its troops along the Polish border from 4 divisions to 20.
** Kauniainen in Finland, completely surrounded by the city of Espoo, secedes from Espoo as its ow ...
*
May 1924
*
December 1924
*
1928
Events January
* January – British bacteriologist Frederick Griffith reports the results of Griffith's experiment, indirectly demonstrating that DNA is the genetic material.
* January 1 – Eastern Bloc emigration and defection: Boris B ...
*
1930
Events
January
* January 15 – The Moon moves into its nearest point to Earth, called perigee, at the same time as its fullest phase of the Lunar Cycle. This is the closest moon distance at in recent history, and the next one will be on J ...
*
July 1932
*
November 1932
Elections in Nazi Germany
*
March 1933, federal
*
November 1933, federal
*
1936, parliamentary
*
1938, parliamentary
German elections since 1949
Federal Republic of Germany
Election system

Federal elections () are conducted approximately every four years, resulting from the
constitutional
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organization or other type of entity, and commonly determines how that entity is to be governed.
When these princ ...
requirement for elections to be held 46 to 48 months after the assembly of the Bundestag. Elections can be held earlier in exceptional constitutional circumstances: for example, were the Chancellor to lose a vote of confidence in the Bundestag, then, during a grace period before the Bundestag can vote in a replacement Chancellor, the Chancellor could request the Federal President to dissolve the Bundestag and hold elections. Should the Bundestag be dismissed before the four-year period has ended, elections must be held within 100 days. The exact date of the election is chosen by the
President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
and must be a Sunday or public holiday.
German nationals over the age of 18 who have resided in Germany for at least three months are eligible to vote. Eligibility for candidacy is essentially the same.
The federal
legislature
A legislature (, ) is a deliberative assembly with the legal authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country, nation or city on behalf of the people therein. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial power ...
in Germany has a one chamber parliament—the
Bundestag
The Bundestag (, "Federal Diet (assembly), Diet") is the lower house of the Germany, German Federalism in Germany, federal parliament. It is the only constitutional body of the federation directly elected by the German people. The Bundestag wa ...
(Federal Diet); the
Bundesrat (Federal Council) represents the
States
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
(in particular the state Governments) and is not considered a chamber as its members are not elected. The Bundestag is elected using a
mixed member proportional
Mixed-member proportional representation (MMP or MMPR) is a type of representation provided by some mixed electoral systems which combine local winner-take-all elections with a compensatory tier with party lists, in a way that produces p ...
system. The Bundestag has 598 nominal members, elected for a four-year term. Half, 299 members, are elected in
single-member constituencies
A single-member district or constituency is an electoral district represented by a single officeholder. It contrasts with a Multiwinner voting, multi-member district, which is represented by multiple officeholders.
In some countries, such as ...
by
first-past-the-post voting
First-past-the-post (FPTP)—also called choose-one, first-preference plurality (FPP), or simply plurality—is a single-winner voting rule. Voters mark one candidate as their favorite, or first-preference, and the candidate with more first- ...
, while a further 299 members are allocated from party lists to achieve a proportional distribution in the legislature, conducted according to a form of
proportional representation
Proportional representation (PR) refers to any electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to political divisions (Political party, political parties) amon ...
called the
Mixed member proportional representation
Mixed-member proportional representation (MMP or MMPR) is a type of representation provided by some mixed electoral system, mixed electoral systems which combine local Winner-take-all system, winner-take-all elections with a Compensation (el ...
system (MMP). Voters vote once for a constituency representative, and a second time for a party, and the lists are used to make the party balances match the distribution of second votes.
Overhang seats may add to the nominal number of 598 members: for example, in the
2009 federal election there were 24
overhang seats, giving a total of 622 seats. This is caused by larger parties winning additional single-member constituencies above the totals determined by their proportional party vote.
Germany has a
multi-party system
In political science, a multi-party system is a political system where more than two meaningfully-distinct political parties regularly run for office and win elections. Multi-party systems tend to be more common in countries using proportional ...
with two historically strong
political parties
A political party is an organization that coordinates candidates to compete in a particular area's elections. It is common for the members of a party to hold similar ideas about politics, and parties may promote specific ideological or p ...
and some other third parties also represented in the Bundestag. Since 1990, and including the results of the most recent federal election in 2021, just six main political parties have managed to secure representation in the Bundestag (counting the CDU and CSU as one, and excluding recognised minority group parties such as the SSW which are exempted in federal law from the 5% threshold that is normally required to be breached in order to win party-list seats).
In 2008, some modifications to the electoral system were required under an order of the
Federal Constitutional Court
The Federal Constitutional Court ( ; abbreviated: ) is the supreme constitutional court for the Federal Republic of Germany, established by the constitution or Basic Law () of Germany. Since its inception with the beginning of the post-W ...
. The court had found that a provision in the Federal Election Law made it possible for a party to experience a
negative vote weight Negative vote weight (also known as ''inverse success value'') refers to an effect that occurs in certain elections where votes can have the opposite effect of what the voter intended. A vote for a party might result in the loss of seats in parliam ...
, thus ''losing'' seats due to ''more'' votes, and found that this violated the constitutional guarantee of the electoral system being equal and direct.
The court allowed three years to amend the law. Accordingly, the
2009 federal election was allowed to proceed under the previous system. The changes were due by 30 June 2011, but appropriate legislation was not completed by that deadline. A new electoral law was enacted in late 2011, but declared unconstitutional once again by the Federal Constitutional Court upon lawsuits from the opposition parties and a group of some 4,000 private citizens.
Finally, four of the five factions in the Bundestag agreed on an electoral reform whereby the number of seats in the Bundestag will be increased as much as necessary to ensure that any overhang seats are
compensated through apportioned
leveling seat
Leveling seats (, , , , ), commonly known also as adjustment seats, are an election mechanism employed for many years by all Nordic countries (except Finland) in elections for their national legislatures. Germany also used national leveling seats ...
s, to ensure full proportionality according to the political party's share of party votes at the national level. The Bundestag approved and enacted the new electoral reform in February 2013.
List of federal election results

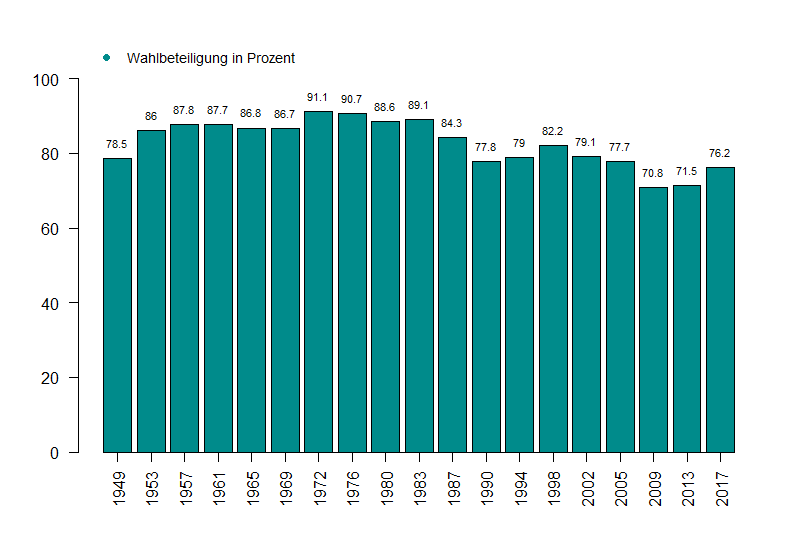
* 1st:
1949 West German federal election
Federal elections were held in West Germany on 14 August 1949 to elect the members of the first Bundestag, with a further eight seats elected in West Berlin between 1949 and January 1952 and another eleven between February 1952 and 1953. They w ...
* 2nd:
1953 West German federal election
Federal elections were held in West Germany on 6 September 1953 to elect the members of the second Bundestag. The Christian Democratic Union (CDU) emerged as the largest party.
This was the last election before Saarland joined West Germany in ...
* 3rd:
1957 West German federal election
Federal elections were held in West Germany on 15 September 1957 to elect the members of the third Bundestag. The Christian Democratic Union and its longtime ally, the Christian Social Union in Bavaria, won a sweeping victory, taking 270 seat ...
* 4th:
1961 West German federal election
Federal elections were held in West Germany on 17 September 1961 to elect the members of the fourth Bundestag. The CDU/CSU remained the largest faction, winning 242 of the 499 seats. However, the loss of its majority and the All-German Party ...
* 5th:
1965 West German federal election
* 6th:
1969 West German federal election
Federal elections in Germany, Federal elections were held in West Germany on 28 September 1969 to elect the members of the 6th Bundestag. The CDU/CSU remained the largest faction and the Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democratic Part ...
* 7th:
1972 West German federal election
Federal elections were held in West Germany on 19 November 1972 to elect the members of the 7th Bundestag. In the first snap elections since the resumption of democratic elections in 1949, the Social Democratic Party became the largest party ...
* 8th:
1976 West German federal election
Federal elections were held in West Germany on 3 October 1976 to elect the members of the 8th Bundestag. Although the CDU/CSU alliance became the largest faction in parliament, Helmut Schmidt of the Social Democratic Party remained Chancello ...
* 9th:
1980 West German federal election
Federal elections were held in West Germany on 5 October 1980 to elect the members of the 9th Bundestag. Although the CDU/CSU remained the largest faction in parliament, Helmut Schmidt of the Social Democratic Party remained Chancellor.
Iss ...
* 10th:
1983 West German federal election
Federal elections were held in West Germany on 6 March 1983 to elect the members of the 10th Bundestag. The CDU/CSU alliance led by Helmut Kohl remained the largest faction in parliament, with Kohl remaining Chancellor.
Issues and campaign
The ...
* 11th:
1987 West German federal election
Federal elections in Germany, Federal elections were held in West Germany on 25 January 1987 to elect the members of the 11th Bundestag. This was the last federal election held in West Germany before German reunification.
Issues and campaign
T ...
* 12th:
1990 German federal election (1st of the re-united Germany)
* 13th:
1994 German federal election
* 14th:
1998 German federal election
The 1998 German federal election was held in Germany on 27 September 1998 to elect the members of the 14th Bundestag. The Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democratic Party (SPD) emerged as the largest faction in parliament for the first ...
* 15th:
2002 German federal election
* 16th:
2005 German federal election
The 2005 German federal election was held in Germany on 18 September 2005 to elect the members of the 16th Bundestag. The snap election was called after the government's defeat in the North Rhine-Westphalia state election, which caused them to i ...
* 17th:
2009 German federal election
The 2009 German federal election was held in Germany on 27 September 2009 to elect the members of the 17th Bundestag.
The Christian Democratic Union (Germany), Christian Democratic Union (CDU), its Bavarian sister party, the Christian Social Uni ...
* 18th:
2013 German federal election
* 19th:
2017 German federal election
The 2017 German federal election was held in Germany on 24 September 2017 to elect the List of members of the 19th Bundestag, members of the 19th Bundestag. At stake were at least 598 seats in the Bundestag, as well as 111 Overhang seat, overhan ...
* 20th:
2021 German federal election
* ''21st:
2025 German federal election
The 2025 German federal election was held in Germany on 23 February 2025 to elect the 630 members of the List of members of the 21st Bundestag, 21st Bundestag, down from 736 in 2021 due to reforms in seat distribution. The 2025 election took plac ...
''
File:1949 West German federal election.svg, 1949
File:1953 West German federal election.svg, 1953
File:1957 West German federal election.svg, 1957
File:1961 West German federal election.svg, 1961
File:1965 West German federal election.svg, 1965
File:1969 West German federal election.svg, 1969
File:1972 West German federal election.svg, 1972
File:1976 West German federal election.svg, 1976
File:1980 West German federal election.svg, 1980
File:1983 West German federal election.svg, 1983
File:1987 West German federal election.svg, 1987
File:1990 German federal election - Results by constituency.svg, 1990
File:1994 German federal election - Results by constituency.svg, 1994
File:1998 German federal election - Results by constituency.svg, 1998
File:2002 German federal election - Results by constituency.svg, 2002
File:2005 German federal election - Results by constituency.svg, 2005
File:2009 German federal election - Results by constituency.svg, 2009
File:German Federal Election 2013 - Results By Constituency.svg, 2013
File:German Federal Election 2017 - Results by Constituency & Regional Seats.svg, 2017
File:German Federal Election 2021 - Results by Constituency & Regional Seats.svg, 2021
European elections
Every 5 years, Germany, as a founding member of the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
, votes to select their delegates to the
European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the two legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it ...
. Members of the European Parliament (MEPs) are elected through a proportional party list system, which, unlike federal elections, do not require a minimum threshold to win seats or constituency seats. The
voting age
A legal voting age is the minimum age that a person is allowed to Voting, vote in a democracy, democratic process. For General election, general elections around the world, the right to vote is restricted to adults, and most nations use 18 year ...
is set at 16.
* 1st:
1979 European Parliament election in West Germany
* 2nd:
1984 European Parliament election in West Germany
* 3rd:
1989 European Parliament election in West Germany
* 4th:
1994 European Parliament election in Germany
* 5th:
1999 European Parliament election in Germany
* 6th:
2004 European Parliament election in Germany
The election of Members of the European Parliament, MEPs representing Germany (European Parliament constituency), Germany constituency for the 2004–2009 term of the European Parliament was held on 13 June 2004.
The elections saw a heavy defeat ...
* 7th:
2009 European Parliament election in Germany
* 8th:
2014 European Parliament election in Germany
* 9th:
2019 European Parliament election in Germany
The 2019 European Parliament election in Germany was held on 26 May 2019, electing the List of members of the European Parliament for Germany, 2019–2024, 96 members of the national Germany (European Parliament constituency), Germany constitue ...
* 10th
2024 European Parliament election in Germany
The 2024 European Parliament election in Germany (European Parliament constituency), Germany was held on 9 June 2024. It was the tenth parliamentary election since the 1979 European Parliament election, first direct elections in 1979, and the fi ...
File:2009 European Parliament election in Germany.svg, 2009
File:2014 European election in Germany - Results.svg, 2014
File:2019 European election in Germany - Results.svg, 2019
File:2024 European Parliament election in Germany - Results.svg, 2024
Presidential elections
Germans do not directly vote for their
President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
. Instead the President is elected every 5 years by the
Federal Convention. All members of the Bundestag and an equal number of state delegates elected by the
state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
parliaments specifically for this purpose, proportional to their population, comprise the voters of the convention.
State elections in the Federal Republic of Germany
State elections are conducted under various rules set by the
states
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
. In general they are conducted according to some form of party-list proportional representation, either the same as the federal system or some simplified version. The election period is generally four to five years, and the dates of elections vary from state to state.
Baden-Württemberg state election results
*
2001 Baden-Württemberg state election
*
2006 Baden-Württemberg state election
*
2011 Baden-Württemberg state election
*
2016 Baden-Württemberg state election
The 2016 Baden-Württemberg state election was held on 13 March 2016 to elect the members of the 15th Landtag of Baden-Württemberg. The incumbent government of Alliance 90/The Greens, The Greens and the Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social ...
*
2021 Baden-Württemberg state election
* ''
2026 Baden-Württemberg state election''
Bavaria state election results
*
1986 Bavarian state election
*
1990 Bavarian state election
*
1994 Bavarian state election
*
1998 Bavarian state election
*
2003 Bavarian state election
The 2003 Bavarian state election was held on 21 September 2003 to elect the members to the 15th Landtag of Bavaria. The Christian Social Union in Bavaria, Christian Social Union (CSU) led by List of Ministers-President of Bavaria, Minister-Presid ...
*
2008 Bavarian state election
*
2013 Bavarian state election
*
2018 Bavarian state election
*
2023 Bavarian state election
* ''
2028 Bavarian state election
Berlin state election results
*
2001 Berlin state election
*
2006 Berlin state election
*
2011 Berlin state election
*
2016 Berlin state election
The 2016 Berlin state election was held on 18 September 2016 to elect the members to the 18th Abgeordnetenhaus of Berlin. The incumbent grand coalition of the Social Democratic Party (SPD) and Christian Democratic Union (CDU) was defeated, with ...
*
2021 Berlin state election
*
2023 Berlin repeat state election
* ''
2026 Berlin state election''
Brandenburg state election results
*
1999 Brandenburg state election
*
2004 Brandenburg state election
*
2009 Brandenburg state election
*
2014 Brandenburg state election
*
2019 Brandenburg state election
*
2024 Brandenburg state election
Bremen state election results
*
2003 Bremen state election
*
2007 Bremen state election
*
2011 Bremen state election
*
2015 Bremen state election
*
2019 Bremen state election
*
2023 Bremen state election
Hamburg state election results
*
2004 Hamburg state election
*
2008 Hamburg state election
*
2011 Hamburg state election
*
2015 Hamburg state election
*
2020 Hamburg state election
*''
2025 Hamburg state election''
Hessian state election results
*
1999 Hessian state election
*
2003 Hessian state election
*
2008 Hessian state election
*
2009 Hessian state election
*
2013 Hessian state election
*
2018 Hessian state election
*
2023 Hessian state election
Lower Saxony state election results
*
1998 Lower Saxony state election
*
2003 Lower Saxony state election
The 2003 Lower Saxony state election was held on 2 February 2003 to elect the members of the 15th Landtag of Lower Saxony. The incumbent Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democratic Party (SPD) majority government led by Minister Presiden ...
*
2008 Lower Saxony state election
*
2013 Lower Saxony state election
*
2017 Lower Saxony state election
*
2022 Lower Saxony state election
* ''
2027 Lower Saxony state election''
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern state election results
*
2002 Mecklenburg-Vorpommern state election
*
2006 Mecklenburg-Vorpommern state election
*
2011 Mecklenburg-Vorpommern state election
*
2016 Mecklenburg-Vorpommern state election
*
2021 Mecklenburg-Vorpommern state election
* ''
2026 Mecklenburg-Vorpommern state election''
North Rhine-Westphalia state election results
*
2000 North Rhine-Westphalia state election
*
2005 North Rhine-Westphalia state election
*
2010 North Rhine-Westphalia state election
*
2012 North Rhine-Westphalia state election
The 2012 North Rhine-Westphalia state election was held on 13 May 2012 to elect the members of the Landtag of North Rhine-Westphalia. The incumbent minority government of the Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democratic Party (SPD) and A ...
*
2017 North Rhine-Westphalia state election
*
2022 North Rhine-Westphalia state election
* ''
2027 North Rhine-Westphalia state election''
Rhineland-Palatinate state election results
*
2001 Rhineland-Palatinate state election
*
2006 Rhineland-Palatinate state election
*
2011 Rhineland-Palatinate state election
*
2016 Rhineland-Palatinate state election
*
2021 Rhineland-Palatinate state election
* ''
2026 Rhineland-Palatinate state election''
Saarland state election results
*
1999 Saarland state election
*
2004 Saarland state election
*
2009 Saarland state election
*
2012 Saarland state election
*
2017 Saarland state election
*
2022 Saarland state election
* ''
2027 Saarland state election''
Saxony state election results
*
1999 Saxony state election
*
2004 Saxony state election
*
2009 Saxony state election
*
2014 Saxony state election
*
2019 Saxony state election
*
2024 Saxony state election
Saxony-Anhalt state election results
*
2002 Saxony-Anhalt state election
*
2006 Saxony-Anhalt state election
*
2011 Saxony-Anhalt state election
*
2016 Saxony-Anhalt state election
*
2021 Saxony-Anhalt state election
* ''
2026 Saxony-Anhalt state election''
Schleswig-Holstein state election results
*
2000 Schleswig-Holstein state election
*
2005 Schleswig-Holstein state election
*
2009 Schleswig-Holstein state election
*
2012 Schleswig-Holstein state election
*
2017 Schleswig-Holstein state election
*
2022 Schleswig-Holstein state election
* ''
2027 Schleswig-Holstein state election''
Thuringia state election results
*
2004 Thuringian state election
*
2009 Thuringian state election
*
2014 Thuringian state election
*
2019 Thuringian state election
*
2024 Thuringian state election
German Democratic Republic
In the
German Democratic Republic
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from Foundation of East Germany, its formation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on ...
, elections to the were effectively controlled by the
Socialist Unity Party of Germany
The Socialist Unity Party of Germany (, ; SED, ) was the founding and ruling party of the German Democratic Republic (East Germany) from the country's foundation in 1949 until its dissolution after the Peaceful Revolution in 1989. It was a Mar ...
(SED) and state hierarchy, even though multiple ''pro forma'' parties existed. The
18 March 1990 election were the first free ones held in the GDR, producing a government whose major mandate was to negotiate an end to itself and its state.
Prior to the
Fall of the Berlin Wall
The fall of the Berlin Wall (, ) on 9 November in German history, 9 November 1989, during the Peaceful Revolution, marked the beginning of the destruction of the Berlin Wall and the figurative Iron Curtain, as East Berlin transit restrictions we ...
, East Germany did not have
free elections. Polling places were under surveillance by the state security apparatuses and the ruling party, the SED, presented voters with a slate of proposed candidates. Voters could optionally enter a booth to strike any candidates the voter did not want; a voter who agreed with the SED's full list simply folded the unmarked ballot in half and placed it into the ballot box. Entering a voting booth was considered suspicious and was noted by the state security apparatuses, which could lead to consequences later for the voter. East German voters commonly referred to the act of voting as "folding" (). Election outcomes prior to 1990 commonly saw 99% of voters in favor of the suggested slate of candidates. On top of this, the government engaged in
electoral fraud
Electoral fraud, sometimes referred to as election manipulation, voter fraud, or vote rigging, involves illegal interference with the process of an election, either by increasing the vote share of a favored candidate, depressing the vote share o ...
and commonly falsified both results and voter turnout percentages, even as late as the May 1989 municipal elections.
*
1949 East German Constitutional Assembly election
*
1950 East German general election
*
1954 East German general election
*
1958 East German general election
*
1963 East German general election
*
1967 East German general election
*
1971 East German general election
*
1976 East German general election
*
1981 East German general election
*
1986 East German general election
The year 1986 was designated as the International Year of Peace by the United Nations.
Events January
* January 1
** Aruba gains increased autonomy from the Netherlands by separating from the Netherlands Antilles.
** Spain and Portugal ent ...
*
1990 East German general election
Elections in Germany#German Democratic Republic, General elections were held in East Germany on 18 March 1990. They were the first free elections in the region since November 1932 German federal election, 1932, and were the first and only free el ...
Local elections
Local elections in Germany () include elections for most regional and local subdivisions, unless their representatives are appointed or elected by another assembly or office. Such local elections are conducted for representatives in
districts
A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions ...
, cities, towns, villages and various other administrative regional organizations. In cities and towns local elections usually include voting for a
lord mayor
Lord mayor is a title of a mayor of what is usually a major city in a Commonwealth realm, with special recognition bestowed by the sovereign. However, the title or an equivalent is present in other countries, including forms such as "high mayor". A ...
or
mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a Municipal corporation, municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilitie ...
. Smaller villages and settlements may elect a representative () with limited administrative power. Local elections are also often combined with polls about important local matters and questions of general public interest (i.e. the construction of local roads or other infrastructure facilities). While such polls are not legally binding in most cases, their results have considerable influence on local political decisions.
After the
Maastricht Treaty
The Treaty on European Union, commonly known as the Maastricht Treaty, is the foundation treaty of the European Union (EU). Concluded in 1992 between the then-twelve Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Communities, ...
of 1992 to strengthen the European integration, Germany and other
EU member states implemented legislative changes to grant foreigners of other EU countries the
right to vote in local elections in their host country. Foreign EU citizens can vote in elections on district and municipal level in Germany, after the
German states adapted their regulations between 1995 and 1998.
See also
*
Electoral calendar
This national electoral calendar for 2025 lists the national/ federal elections scheduled to be held in 2025 in all sovereign states and their dependent territories. By-elections are excluded, though national referenda are included. Specific d ...
*
Electoral system
An electoral or voting system is a set of rules used to determine the results of an election. Electoral systems are used in politics to elect governments, while non-political elections may take place in business, nonprofit organizations and inf ...
*
Electoral system of Germany
*
Referendums in Germany
Referendums in Germany are an element of direct democracy. On the federal level only two types of a mandatory binding referendum exist – adopting a new constitution and regional referendums in case of restructuring the states. On the state l ...
References
Further reading
*
*
External links
Adam Carr's Election ArchiveOpinion poll tracker with data, graph and daily average
Official Site of the
Federal Returning Officer.
Collection of German Election Posters of Weimar Republic and Federal RepublicNSD: European Election Database – Germany publishes regional level election data; allows for comparisons of election results, 1990–2009
{{Germany topics
 After the
After the  * 1st:
* 1st: