Einasleigh Uplands on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
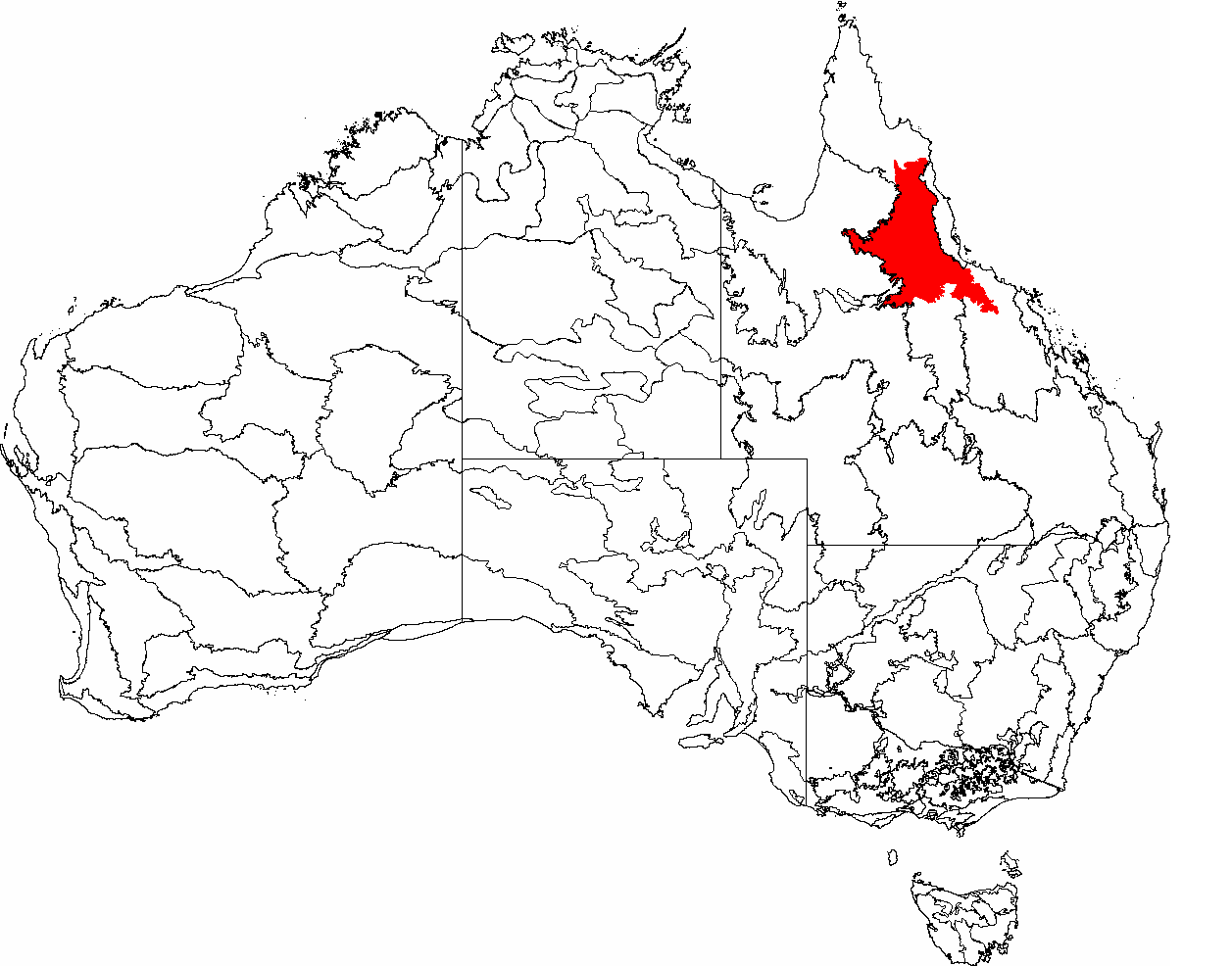
The Einasleigh Uplands is an interim Australian bioregion, with vegetation consisting of
savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) biome and ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach th ...
and woodland located on a large plateau in inland Queensland
Queensland ( , commonly abbreviated as Qld) is a States and territories of Australia, state in northeastern Australia, and is the second-largest and third-most populous state in Australia. It is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Austr ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
. It corresponds to the Einasleigh Uplands savanna ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) is an ecological and geographic area that exists on multiple different levels, defined by type, quality, and quantity of environmental resources. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and c ...
, as identified by the World Wildlife Fund
The World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) is a Swiss-based international non-governmental organization founded in 1961 that works in the field of wilderness preservation and the reduction of human impact on the environment. It was formerly named the ...
.
Location and description
This area is inland from the moist Queensland coast but is not as dry as theBrigalow Belt
The Brigalow Belt is a wide band of acacia-wooded grassland that runs between tropical rainforest of the coast and the semi-arid interior of Queensland and northern New South Wales, Australia. The
Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Aus ...
and the Mitchell Grass Downs savannas to the south, while the Cape York Peninsula
The Cape York Peninsula is a peninsula located in Far North Queensland, Australia. It is the largest wilderness in northern Australia.Mittermeier, R.E. et al. (2002). Wilderness: Earth's last wild places. Mexico City: Agrupación Sierra Madre, ...
to the north is lower-lying and wetter. The region contains a number of specialised habitats that add to the variety of wildlife found here. These include lava tube
A lava tube, more rarely called a pyroduct, is a 'roofed conduit through which molten lava travels away from its vent'. If lava in the tube drains out, it will leave an empty cave. Lava tubes are common in low-viscosity volcanic systems. La ...
s and caves such as those of Chillagoe.
The uplands are an area of eroded volcanic rock on and to the west of the Atherton Tableland
The Atherton Tableland is a fertile plateau, which is part of the Great Dividing Range in Queensland, Australia. It has very deep, rich basaltic soils and the main industry is agriculture. The principal river flowing across the plateau is the B ...
in the northern section of Australia's Great Dividing Range
The Great Dividing Range, also known as the East Australian Cordillera or the Eastern Highlands, is a cordillera system in eastern Australia consisting of an expansive collection of mountain ranges, plateaus and rolling hills. It runs roughl ...
running inland as far as the town of Croydon
Croydon is a large town in South London, England, south of Charing Cross. Part of the London Borough of Croydon, a Districts of England, local government district of Greater London; it is one of the largest commercial districts in Greater Lond ...
in the southwest. The plateau is covered in grassland dotted with eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of more than 700 species of flowering plants in the family Myrtaceae. Most species of ''Eucalyptus'' are trees, often Mallee (habit), mallees, and a few are shrubs. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalyp ...
trees and cut through with ridges, gorges and lava tubes. The area has rich fertile soil. Natural features include the Great Basalt Wall of dried volcanic lava and the lava tubes of Undara Volcanic National Park.
Rivers that have their source in the uplands include the Flinders River
The Flinders River is the longest river in Queensland, Australia, at approximately . It was named in honour of the explorer Matthew Flinders. The catchment is sparsely populated and mostly undeveloped. The Flinders rises on the western slopes o ...
which runs northwest to the Gulf of Carpentaria
The Gulf of Carpentaria is a sea off the northern coast of Australia. It is enclosed on three sides by northern Australia and bounded on the north by the eastern Arafura Sea, which separates Australia and New Guinea. The northern boundary ...
along with the Palmer
Palmer may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Palmer (pilgrim), a medieval European pilgrim to the Holy Land
* Palmer (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters
* Palmer (surname), including a list of people and f ...
, Mitchell and Gilbert-Einasleigh while the Burdekin and Herbert Rivers run south-east from the tablelands to the Coral Sea
The Coral Sea () is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific off the northeast coast of Australia, and classified as an Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia, interim Australian bioregion. The Coral Sea extends down t ...
coast.
Urban areas include Herberton and Croydon.

Climate
The climate is cooler than the coast with summer nights being as cool as 9 °C compared with 20 °C on the coast. The summer high temperatures are around 35 °C. There is a wet season between December and March.Flora
This stony upland habitat is dominated by ironbark eucalyptus woodland but there are wetlands and patches of rainforest too. Lava flows are home to stands of thicker forest.Fauna
These woodlands are home to many animals including a number ofmarsupial
Marsupials are a diverse group of mammals belonging to the infraclass Marsupialia. They are natively found in Australasia, Wallacea, and the Americas. One of marsupials' unique features is their reproductive strategy: the young are born in a r ...
s such as the antilopine kangaroo
The antilopine kangaroo (''Osphranter antilopinus''), also known as the antilopine wallaroo or the antilopine wallaby, is a species of Macropodidae, macropod found in northern Australia: in Cape York Peninsula in Queensland, the Top End of the N ...
, the large eastern grey kangaroo
The eastern grey kangaroo (''Macropus giganteus'': gigantic large-foot; also great grey kangaroo or forester kangaroo) is a marsupial found in the eastern third of Australia, with a population of several million. Although a large ''M. giganteus ...
and the near-endemic Godman's rock-wallaby and Mareeba rock-wallaby. There are a number of endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
mammals, reptiles and insects in the region especially in the more thickly forested areas where a large number of endemic reptiles occur. The caves and lava flows harbour specific wildlife of their own as do the wetter east-facing slopes of the uplands. Rivers such as the Burdekin have important populations of waterbirds as do the unique (to Australia) wetlands of Innot Hot Springs
Innot Hot Springs is a rural town and locality in the Tablelands Region, Queensland, Australia. In the , the locality of Innot Hot Springs had a population of 189 people.
Geography
Innot Hot Springs is south-west of Cairns via the Bruce ...
.
Threats and preservation
The area has long been used for cattleranching
A ranch (from /Mexican Spanish) is an area of land, including various structures, given primarily to ranching, the practice of raising grazing livestock such as cattle and sheep. It is a subtype of farm. These terms are most often applied to li ...
but apart from the heavily farmed Atherton Tableland is thinly populated so the landscape is well preserved although it has been changed by overgrazing
Overgrazing occurs when plants are exposed to intensive grazing for extended periods of time, or without sufficient recovery periods. It can be caused by either livestock in poorly managed agricultural applications, game reserves, or nature ...
, clearance for agriculture and the introduction of weeds. Some areas of the acacia
''Acacia'', commonly known as wattles or acacias, is a genus of about of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa, South America, and Austral ...
gidgee ''( Acacia cambagei)'' in the southeast of the uplands have suffered in particular. There are a number of protected areas containing a good variety of the different types of habitat found in the region, including Undara and the Great Basalt Wall as well as Blackbraes National Park, Kinrara National Park, Littleton National Park, part of Bulleringa National Park and the caves of Chillagoe.
See also
*Geography of Australia
The geography of Australia describes the systematic study of Australian sovereign territory, which, in a geographical sense, refers to the mainland Australia (also called continental Australia), the insular state of Tasmania and thousands of L ...
*Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia
The Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) is a biogeography, biogeographic regionalisation of Australia developed by the Australian government's Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population and Communities ( ...
References
{{Australasia grasslands navbox Ecoregions of Queensland IBRA regions North Queensland Plateaus of Australia Tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands