Eccentric Jupiter on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 An eccentric Jupiter is a
An eccentric Jupiter is a
 Various theories about the origin of orbits with high eccentricity compared to the planets of the Solar System have been proposed, and can be modeled and analyzed via
Various theories about the origin of orbits with high eccentricity compared to the planets of the Solar System have been proposed, and can be modeled and analyzed via
 An eccentric Jupiter is a
An eccentric Jupiter is a Jovian planet
Jovian is the adjectival form of Jupiter and may refer to:
* Jovian (emperor) (Flavius Iovianus Augustus), Roman emperor (363–364 AD)
* Jovians and Herculians, Roman imperial guard corps
* Jovian (lemur), a Coquerel's sifaka known for ''Zoboom ...
or Jupiter analogue that orbits its star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
in an eccentric orbit. Note: this study treats eccentric Jupiters as giant planets having an orbital eccentricity of 0.1 or greater. Eccentric Jupiters may disqualify a planetary system
A planetary system is a set of gravity, gravitationally bound non-stellar Astronomical object, bodies in or out of orbit around a star or star system. Generally speaking, systems with one or more planets constitute a planetary system, although ...
from having Earth-like planets (though not always from having habitable exomoons) in it, because a massive gas giant
A gas giant is a giant planet composed mainly of hydrogen and helium. Jupiter and Saturn are the gas giants of the Solar System. The term "gas giant" was originally synonymous with "giant planet". However, in the 1990s, it became known that Uranu ...
with an eccentric orbit may eject all Earth mass
An Earth mass (denoted as ''M''🜨, ''M''♁ or ''M''E, where 🜨 and ♁ are the astronomical symbols for Earth), is a unit of mass equal to the mass of the planet Earth. The current best estimate for the mass of Earth is , with a relative ...
exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first confirmed detection of an exoplanet was in 1992 around a pulsar, and the first detection around a main-sequence star was in 1995. A different planet, first det ...
s from the habitable zone
In astronomy and astrobiology, the habitable zone (HZ), or more precisely the circumstellar habitable zone (CHZ), is the range of orbits around a star within which a planetary surface can support liquid water given sufficient atmospheric pressu ...
, if not from the system entirely.
The planets of the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
, except for Mercury, have orbits with an eccentricity of less than 0.1. However, two-thirds of the exoplanets discovered in 2006 have elliptical orbits with an eccentricity of 0.2 or more. The typical exoplanet with an orbital period greater than five days has a median eccentricity of 0.23. The discovery of this type of exoplanet, together with hot Jupiter
Hot Jupiters (sometimes called hot Saturns) are a class of gas giant exoplanets that are inferred to be physically similar to Jupiter (i.e. Jupiter analogue, Jupiter analogues) but that have very short orbital periods (). The close proximity to t ...
s, has challenged some widely-held theories about Solar System formation.
History of discovery
The first exoplanet categorized as an eccentric Jupiter was confirmed in 1996, orbiting 16 Cygni. The first exoplanet around a main sequence star was discovered in51 Pegasi
51 Pegasi (abbreviated 51 Peg), formally named Helvetios , is a Sun-like star located from Earth in the constellation of Pegasus. It was the first main-sequence star found to have an exoplanet (designated 51 Pegasi b, officially named ...
the previous year. The celestial bodies that revolve around 16 Cygni and 70 Virginis with orbital eccentricities greater than 0.5 were initially regarded as brown dwarfs, prior to more accurate measurements of their masses.
Formation of eccentric orbits
 Various theories about the origin of orbits with high eccentricity compared to the planets of the Solar System have been proposed, and can be modeled and analyzed via
Various theories about the origin of orbits with high eccentricity compared to the planets of the Solar System have been proposed, and can be modeled and analyzed via computer simulation
Computer simulation is the running of a mathematical model on a computer, the model being designed to represent the behaviour of, or the outcome of, a real-world or physical system. The reliability of some mathematical models can be determin ...
. One model, termed the "slingshot model", describes such orbits in the case with a hot Jupiter in a multi-planetary system.
In any planetary system, the orbit of a planet is initially close to a perfect circle, but if there are three or more gas giant
A gas giant is a giant planet composed mainly of hydrogen and helium. Jupiter and Saturn are the gas giants of the Solar System. The term "gas giant" was originally synonymous with "giant planet". However, in the 1990s, it became known that Uranu ...
planets, its orbit will probably become distorted after a certain period of time. In some cases, one planet may be ejected from the system, and the remaining planets will fall into orbits with a very high eccentricity.
This is because the energy exchanged between the three planets during their revolution is concentrated on a specific planet. This phenomenon almost always occurs after a certain period of time, but when there are only one or two giant gas planets (that is, only Jupiter and Saturn in the solar system), the system is more stable over the lifespan of a main sequence star, and such a planet is virtually stable in a circular orbit. Therefore, there is a calculation result that each planet remains in a circular orbit semi-permanently in the solar system. Conversely, if there are three or more giant gas planets, the "fixed period" will be greatly affected by the mass and orbital spacing of the planets. If a massive planet has a narrow orbital spacing, this period will be shorter than the life of the star, and orbital crossing will occur shortly after the formation of the planetary system.
Another theory proposes that the interaction between giant planets and protoplanetary disk
A protoplanetary disk is a rotating circumstellar disc of dense gas and dust surrounding a young newly formed star, a T Tauri star, or Herbig Ae/Be star. The protoplanetary disk may not be considered an accretion disk; while the two are sim ...
s may increase eccentricity. However, it is difficult to explain an eccentric planet with an eccentricity exceeding 0.4 with this mechanism. Also, if the planet is orbiting a star belonging to a star system
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravity, gravitational attraction. It may sometimes be used to refer to a single star. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally calle ...
, the gravity
In physics, gravity (), also known as gravitation or a gravitational interaction, is a fundamental interaction, a mutual attraction between all massive particles. On Earth, gravity takes a slightly different meaning: the observed force b ...
of the companion star
A binary star or binary star system is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved as separate stars us ...
may increase the orbital eccentricity.
Relation to hot Jupiters
It has been proposed that hot Jupiters, whose orbits have much smaller semi-major axes, evolve from gas giants in high-eccentricity orbits. For instance, an eccentric Jupiter may have an elongated elliptical orbit withperiapsis
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. The line of apsides (also called apse line, or major axis of the orbit) is the line connecting the two extreme values.
Apsides perta ...
around 0.05 au, and experience tidal braking upon its closest approach to its star. As a result, the planet settles into a roughly circular orbit with a semi-major axis comparable to its original periapsis, and thus receives a greater radiant flux
In radiometry, radiant flux or radiant power is the radiant energy emitted, reflected, transmitted, or received per unit time, and spectral flux or spectral power is the radiant flux per unit frequency or wavelength, depending on whether the ...
throughout its entire orbit. For example, the eccentric planet HD 80606 b has an extremely elliptical orbit with a periapsis distance of 0.03 au and apoapsis distance of 0.87 au, and may be a celestial body that is transitioning to a hot Jupiter with an orbital radius of 0.03 au.
A limitation of this model is that tidal forces weaken rapidly at greater orbital distances (inversely proportional to the cube of the distance), requiring a planet to orbit closer to the main star for a longer time period to experience sufficient braking. As an example, if another giant planet has a more distant orbit than the celestial body that is evolving into a hot Jupiter, its gravity will change the periapsis distance of the inner planet, and if the potentially evolving body has a stable orbit with a too-distant periapsis, the tidal force will be almost ineffective. In addition, hot Jupiters have been found at slightly more distant orbits – with semi-major axes of at least 0.1 au – but another model is needed to explain these.
Confusion with multiplanetary systems
Some of the detected "eccentric planets" may actually be multiple planets with near-circular orbits. The majority of eccentric planets have been reported based on radial velocity measurements usingDoppler spectroscopy
Doppler spectroscopy (also known as the radial-velocity method, or colloquially, the wobble method) is an indirect method for finding extrasolar planets and brown dwarfs from radial-velocity measurements via observation of Doppler shifts in ...
by which eccentricity is directly measurable. In the case where the planet is in a circular orbit, the fluctuation pattern of the radial velocity is a simple sine curve
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or sinusoid (symbol: ∿) is a periodic wave whose waveform (shape) is the trigonometric sine function. In mechanics, as a linear motion over time, this is '' simple harmonic motion''; as rotation, it correspon ...
, but in the case of an elliptical orbit, it deviates from the sine curve and is recognized as an eccentric planet. However, such a distorted waveform can also occur due to the synthesis of radial velocity fluctuations (wave interference
In physics, interference is a phenomenon in which two coherent waves are combined by adding their intensities or displacements with due consideration for their phase difference. The resultant wave may have greater amplitude (constructive in ...
) caused by multiple planets. The two cannot be distinguished if the radial velocity sampling is insufficient (the number of times is small, only a part of the orbital period can be covered, etc.). In this situation, the simplest model that can reproduce the observations is preferred to be a single eccentric planet rather than a multiplanetary system.
Due to these circumstances, there are cases where observations initially attributed to an eccentric planet were instead due to a multiplanetary system with planets in low-eccentricity orbits, due to the accumulation of observations and improvements in analytical techniques. As an example, a study that re-examined 82 planetary systems that were alleged to have a single eccentric planet in 2013 found that multiplanetary models were more accurate than single-planet models; nine multiplanetary systems were reported.
The situation where multiple planetary systems and eccentric planets are confused is likely to occur in cases where the waveform distortion is relatively small, such as when the eccentricity is 0.5 or less when interpreted as a single planet. On the other hand, a planet with an orbital eccentricity of 0.5 or more is considered unlikely to be mistaken for a multiplanetary system.
List
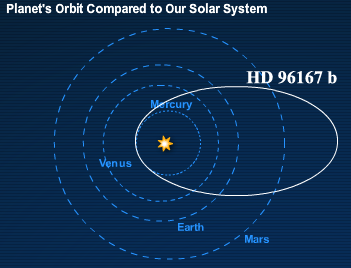
This is a list of eccentric Jupiters:See also
* * *References
{{exoplanet Types of planet *