ear wax on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
/ref> The
 The middle ear lies between the outer ear and the inner ear. It consists of an air-filled cavity called the
The middle ear lies between the outer ear and the inner ear. It consists of an air-filled cavity called the
 The inner ear sits within the temporal bone in a complex cavity called the
The inner ear sits within the temporal bone in a complex cavity called the
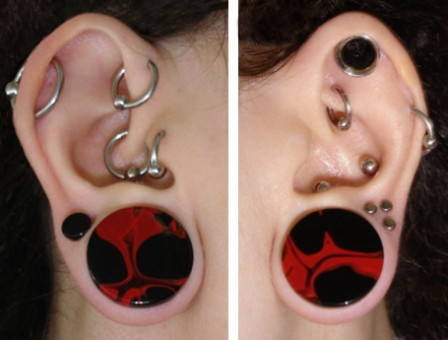 The ears have been ornamented with jewelry for thousands of years, traditionally by piercing of the
The ears have been ornamented with jewelry for thousands of years, traditionally by piercing of the

 The ears of
The ears of  This serves as evidence of homology between related species. In humans, there is variability in these muscles, such that some people are able to move their ears in various directions, and it has been said that it may be possible for others to gain such movement by repeated trials. In such primates, the inability to move the ear is compensated for mainly by the ability to easily turn the
This serves as evidence of homology between related species. In humans, there is variability in these muscles, such that some people are able to move their ears in various directions, and it has been said that it may be possible for others to gain such movement by repeated trials. In such primates, the inability to move the ear is compensated for mainly by the ability to easily turn the
File:Elephant near ndutu.jpg,
File:2009-03-07Vulpes zerda016.jpg,
Image:Iceland-1979445.jpg,
File:Rabbit - French Lop breed.jpg,
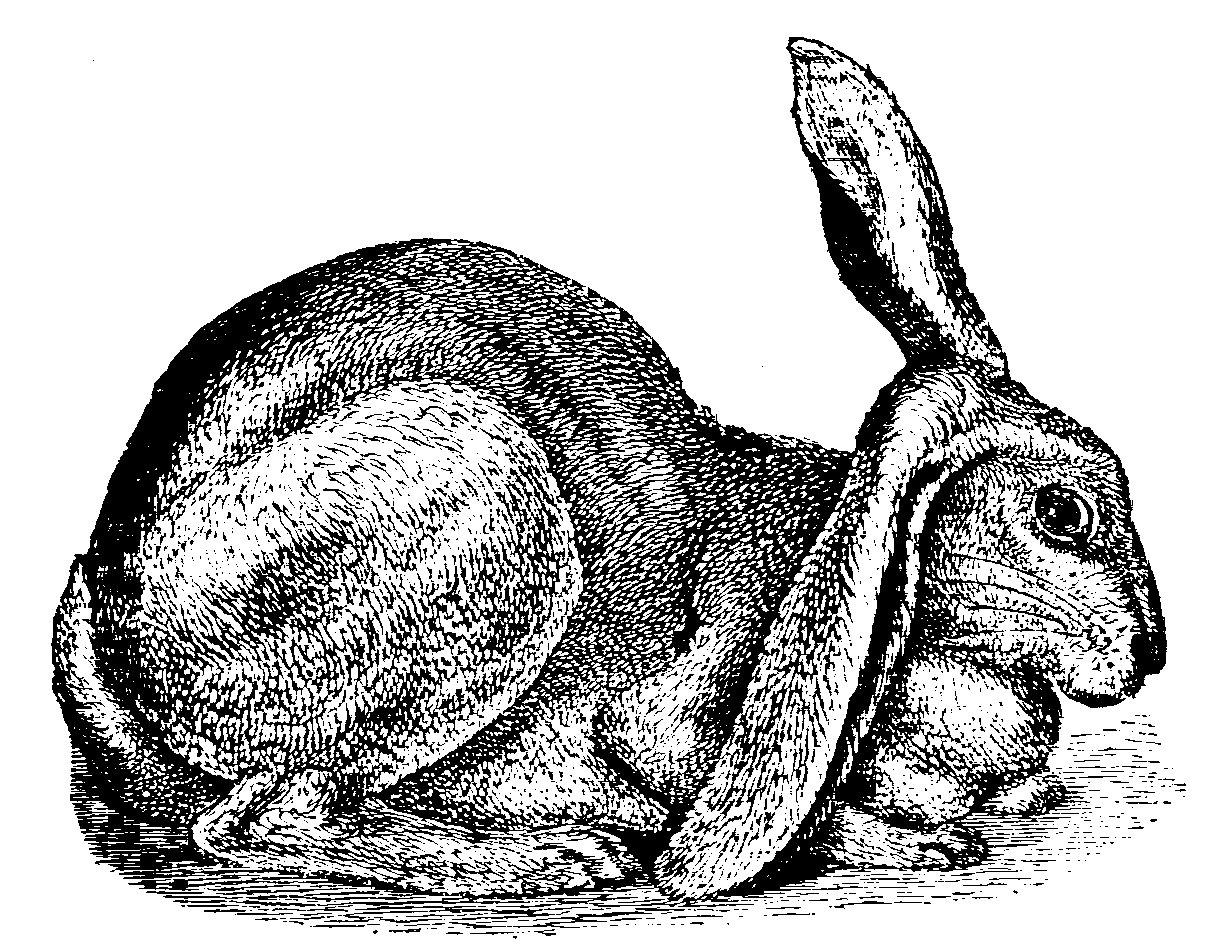 The ear, with its blood vessels close to the surface, is an essential thermoregulator in some land mammals, including the elephant, the fox, and the rabbit. There are five types of ear carriage in domestic rabbits, some of which have been bred for exaggerated ear length—a potential health risk that is controlled in some countries. Abnormalities in the skull of a half-lop rabbit were studied by Charles Darwin in 1868. In marine mammals,
The ear, with its blood vessels close to the surface, is an essential thermoregulator in some land mammals, including the elephant, the fox, and the rabbit. There are five types of ear carriage in domestic rabbits, some of which have been bred for exaggerated ear length—a potential health risk that is controlled in some countries. Abnormalities in the skull of a half-lop rabbit were studied by Charles Darwin in 1868. In marine mammals,
vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s, an ear is the organ
Organ and organs may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a group of tissues organized to serve a common function
* Organ system, a collection of organs that function together to carry out specific functions within the body.
Musical instruments
...
that enables hearing
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory sci ...
and (in mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s) body balance using the vestibular system
The vestibular system, in vertebrates, is a sensory system that creates the sense of balance and spatial orientation for the purpose of coordinating motor coordination, movement with balance. Together with the cochlea, a part of the auditory sys ...
. In humans, the ear is described as having three parts: the outer ear
The outer ear, external ear, or auris externa is the external part of the ear, which consists of the auricle (also pinna) and the ear canal. It gathers sound energy and focuses it on the eardrum ( tympanic membrane).
Structure
Auricle
The ...
, the middle ear
The middle ear is the portion of the ear medial to the eardrum, and distal to the oval window of the cochlea (of the inner ear).
The mammalian middle ear contains three ossicles (malleus, incus, and stapes), which transfer the vibrations ...
and the inner ear
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the ...
. The outer ear consists of the auricle and the ear canal
The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal extends from the auricle to the eardrum and is about in length and in diameter.
S ...
. Since the outer ear is the only visible portion of the ear, the word "ear" often refers to the external part (auricle) alone. The middle ear includes the tympanic cavity
The tympanic cavity is a small cavity surrounding the bones of the middle ear. Within it sit the ossicles, three small bones that transmit vibrations used in the detection of sound.
Structure
On its lateral surface, it abuts the external audit ...
and the three ossicle
The ossicles (also called auditory ossicles) are three irregular bones in the middle ear of humans and other mammals, and are among the smallest bones in the human body. Although the term "ossicle" literally means "tiny bone" (from Latin ''ossicu ...
s. The inner ear sits in the bony labyrinth
The bony labyrinth (also osseous labyrinth or otic capsule) is the rigid, bony outer wall of the inner ear in the temporal bone. It consists of three parts: the vestibule, semicircular canals, and cochlea. These are cavities hollowed out of the ...
, and contains structures which are key to several senses: the semicircular canal
The semicircular canals are three semicircular interconnected tubes located in the innermost part of each ear, the inner ear. The three canals are the lateral, anterior and posterior semicircular canals. They are the part of the bony labyrinth, ...
s, which enable balance and eye tracking when moving; the utricle and saccule
The saccule (Latin: sacculus) is a bed of sensory cells in the inner ear that detects linear acceleration and head tilting in the vertical plane, and converts these vibrations into electrical impulses to be interpreted by the brain. When the he ...
, which enable balance when stationary; and the cochlea
The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, in humans making 2.75 turns around its axis, the modiolus (cochlea), modiolus. A core component of the cochlea is the organ of Cort ...
, which enables hearing. The ear canal is cleaned via earwax
Earwax, also known by the medical term cerumen, is a waxy substance secreted in the ear canal of humans and other mammals. Earwax can be many colors, including brown, orange, red, yellowish, and gray. Earwax protects the skin of the human ear ...
, which naturally migrates to the auricle.
The ear develops from the first pharyngeal pouch and six small swellings that develop in the early embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
called otic placode
In embryology, the otic placode is a thickening of the ectoderm on the outer surface of a developing embryo from which the ear develops. The ear, including both the vestibular system and the auditory system, develops from the otic placode beginni ...
s, which are derived from the ectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from the o ...
.
The ear may be affected by disease, including infection and traumatic damage. Diseases of the ear may lead to hearing loss
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to acquire spo ...
, tinnitus
Tinnitus is a condition when a person hears a ringing sound or a different variety of sound when no corresponding external sound is present and other people cannot hear it. Nearly everyone experiences faint "normal tinnitus" in a completely ...
and balance disorders such as vertigo
Vertigo is a condition in which a person has the sensation that they are moving, or that objects around them are moving, when they are not. Often it feels like a spinning or swaying movement. It may be associated with nausea, vomiting, perspira ...
, although many of these conditions may also be affected by damage to the brain or neural pathways leading from the ear.
The ear has been adorned by earring
Earrings are jewelry that can be worn on one's ears. Earrings are commonly worn in a piercing in the earlobe or another external part of the ear, or by #Clip-on and other non-pierced earrings, some other means, such as stickers or clip-ons. Earr ...
s and other jewelry in numerous cultures for thousands of years, and has been subjected to surgical and cosmetic alterations.
Structure
The human ear consists of three parts—theouter ear
The outer ear, external ear, or auris externa is the external part of the ear, which consists of the auricle (also pinna) and the ear canal. It gathers sound energy and focuses it on the eardrum ( tympanic membrane).
Structure
Auricle
The ...
, middle ear
The middle ear is the portion of the ear medial to the eardrum, and distal to the oval window of the cochlea (of the inner ear).
The mammalian middle ear contains three ossicles (malleus, incus, and stapes), which transfer the vibrations ...
and inner ear
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the ...
.Alt URL/ref> The
ear canal
The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal extends from the auricle to the eardrum and is about in length and in diameter.
S ...
of the outer ear is separated from the air-filled tympanic cavity
The tympanic cavity is a small cavity surrounding the bones of the middle ear. Within it sit the ossicles, three small bones that transmit vibrations used in the detection of sound.
Structure
On its lateral surface, it abuts the external audit ...
of the middle ear by the eardrum
In the anatomy of humans and various other tetrapods, the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane or myringa, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. Its function is to transmit changes in pres ...
. The middle ear contains the three small bones—the ossicles
The ossicles (also called auditory ossicles) are three irregular bones in the middle ear of humans and other mammals, and are among the smallest bones in the human body. Although the term "ossicle" literally means "tiny bone" (from Latin ''ossi ...
—involved in the transmission of sound, and is connected to the throat
In vertebrate anatomy, the throat is the front part of the neck, internally positioned in front of the vertebrae. It contains the Human pharynx, pharynx and larynx. An important section of it is the epiglottis, separating the esophagus from the t ...
at the nasopharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its ...
, via the pharyngeal opening of the Eustachian tube
The Eustachian tube (), also called the auditory tube or pharyngotympanic tube, is a tube that links the nasopharynx to the middle ear, of which it is also a part. In adult humans, the Eustachian tube is approximately long and in diameter. It ...
. The inner ear contains the otolith
An otolith (, ' ear + , ', a stone), also called otoconium, statolith, or statoconium, is a calcium carbonate structure in the saccule or utricle (ear), utricle of the inner ear, specifically in the vestibular system of vertebrates. The saccule ...
organs—the utricle and saccule
The saccule (Latin: sacculus) is a bed of sensory cells in the inner ear that detects linear acceleration and head tilting in the vertical plane, and converts these vibrations into electrical impulses to be interpreted by the brain. When the he ...
—and the semicircular canal
The semicircular canals are three semicircular interconnected tubes located in the innermost part of each ear, the inner ear. The three canals are the lateral, anterior and posterior semicircular canals. They are the part of the bony labyrinth, ...
s belonging to the vestibular system
The vestibular system, in vertebrates, is a sensory system that creates the sense of balance and spatial orientation for the purpose of coordinating motor coordination, movement with balance. Together with the cochlea, a part of the auditory sys ...
, as well as the cochlea
The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, in humans making 2.75 turns around its axis, the modiolus (cochlea), modiolus. A core component of the cochlea is the organ of Cort ...
of the auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the ear, sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system.
System overview
The outer ear funnels sound vibrations to the eardrum, incre ...
.
Outer ear
The outer ear is the external portion of the ear and includes the fleshy visible auricle, the ear canal, and the outer layer of the eardrum (also called the tympanic membrane). The auricle consists of the curving outer rim called thehelix
A helix (; ) is a shape like a cylindrical coil spring or the thread of a machine screw. It is a type of smooth space curve with tangent lines at a constant angle to a fixed axis. Helices are important in biology, as the DNA molecule is for ...
, the inner curved rim called the antihelix
The antihelix (anthelix) is a part of the visible ear; the pinna.
The antihelix is a curved prominence of cartilage parallel with and in front of the helix on the pinna.
The antihelix divides above into two ''legs'' or crura; the ''crura anti ...
, and opens into the ear canal. The tragus protrudes and partially obscures the ear canal, as does the facing antitragus
The antitragus is a feature of mammalian ear anatomy.
In humans, it is a small Tubercle (anatomy)#Ears, tubercle on the visible part of the ear, the Auricle (anatomy), auricle. The antitragus is located just above the earlobe and points anatomical ...
. The hollow region in front of the ear canal is called the concha. The ear canal stretches for about 1inch (2.5cm). The first part of the canal is surrounded by cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. Semi-transparent and non-porous, it is usually covered by a tough and fibrous membrane called perichondrium. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints ...
, while the second part near the eardrum is surrounded by bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
. This bony part is known as the auditory bulla
The tympanic part of the temporal bone is a curved plate of bone lying below the squamous part of the temporal bone, in front of the mastoid process, and surrounding the external part of the ear canal.
It originates as a separate bone (tympanic b ...
and is formed by the tympanic part of the temporal bone
The tympanic part of the temporal bone is a curved plate of bone lying below the squamous part of the temporal bone, in front of the mastoid process, and surrounding the external part of the ear canal.
It originates as a separate bone (tympan ...
. The ear canal ends at the external surface of the eardrum, while the surrounding skin contains ceruminous and sebaceous gland
A sebaceous gland or oil gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in ...
s that produce protective earwax
Earwax, also known by the medical term cerumen, is a waxy substance secreted in the ear canal of humans and other mammals. Earwax can be many colors, including brown, orange, red, yellowish, and gray. Earwax protects the skin of the human ear ...
. Earwax naturally migrates outward through ear canal, constituting a self-cleaning system.
Two sets of muscles are associated with the outer ear: the intrinsic
In science and engineering, an intrinsic property is a property of a specified subject that exists itself or within the subject. An extrinsic property is not essential or inherent to the subject that is being characterized. For example, mass i ...
and extrinsic
In science and engineering, an intrinsic property is a property of a specified subject that exists itself or within the subject. An extrinsic property is not essential or inherent to the subject that is being characterized. For example, mass i ...
muscles. In some mammals, these muscles can adjust the direction of the pinna. In humans, these muscles have little or no effect. The ear muscles are supplied by the facial nerve
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of ta ...
, which also supplies sensation to the skin of the ear itself, as well as to the external ear cavity. The great auricular nerve
The great auricular nerve is a Cutaneous nerve, cutaneous (sensory) nerve of the head. It originates from the second and third spinal nerve, cervical (spinal) nerves (C2-C3) of the cervical plexus. It provides sensory innervation to the skin over ...
, auricular nerve, auriculotemporal nerve
The auriculotemporal nerve is a sensory branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) that runs with the superficial temporal artery and vein, and provides sensory innervation to parts of the external ear, scalp, and temporomandibular joint. The nerve a ...
, and lesser and greater occipital nerves of the cervical plexus
The cervical plexus is a nerve plexus of the anterior rami of the first (i.e. upper-most) four cervical spinal nerves C1-C4. The cervical plexus provides motor innervation to some muscles of the neck, and the diaphragm; it provides sensory inne ...
all supply sensation to parts of the outer ear and the surrounding skin.
The auricle consists of a single piece of elastic cartilage with a complicated relief on its inner surface and a fairly smooth configuration on its posterior surface. A tubercle
In anatomy, a tubercle (literally 'small tuber', Latin for 'lump') is any round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on external or internal organs of a plant or an animal.
In plants
A tubercle is generally a wart-like projectio ...
, known as Darwin's tubercle
Darwin's tubercle (or auricular tubercle) is a congenital ear condition which often presents as a thickening on the helix at the junction of the upper and middle thirds.
History
This atavistic feature is so called because its description wa ...
, is sometimes present, lying in the descending part of the helix and corresponding to the ear-tip of mammals. The earlobe
The human earlobe (''lobulus auriculae''), the lower portion of the outer ear, is composed of tough areolar and adipose connective tissues, lacking the firmness and elasticity of the rest of the auricle (the external structure of the ear). In ...
consists of areola
The human areola (''areola mammae'', or ) is the pigmented area on the breast around the nipple. More generally, an areola is a small circular area on the Human body, body with a different histology from the surrounding Tissue (biology), tissue ...
and adipose tissue
Adipose tissue (also known as body fat or simply fat) is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. It also contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, Blood vessel, vascular endothel ...
. The symmetrical arrangement of the two ears allows for the localisation of sound. The brain accomplishes this by comparing arrival-times and intensities from each ear, in circuits located in the superior olivary complex
The superior olivary complex (SOC) or superior olive is a collection of brainstem nuclei that is located in pons, functions in multiple aspects of hearing and is an important component of the ascending and descending auditory pathways of the aud ...
and the trapezoid bodies, which are connected via pathways to both ears.
Middle ear
 The middle ear lies between the outer ear and the inner ear. It consists of an air-filled cavity called the
The middle ear lies between the outer ear and the inner ear. It consists of an air-filled cavity called the tympanic cavity
The tympanic cavity is a small cavity surrounding the bones of the middle ear. Within it sit the ossicles, three small bones that transmit vibrations used in the detection of sound.
Structure
On its lateral surface, it abuts the external audit ...
and includes the three ossicles
The ossicles (also called auditory ossicles) are three irregular bones in the middle ear of humans and other mammals, and are among the smallest bones in the human body. Although the term "ossicle" literally means "tiny bone" (from Latin ''ossi ...
and their attaching ligaments; the auditory tube
The Eustachian tube (), also called the auditory tube or pharyngotympanic tube, is a tube that links the nasopharynx to the middle ear, of which it is also a part. In adult humans, the Eustachian tube is approximately long and in diameter. It ...
; and the round
Round or rounds may refer to:
Mathematics and science
* Having no sharp corners, as an ellipse, circle, or sphere
* Rounding, reducing the number of significant figures in a number
* Round number, ending with one or more zeroes
* Round (crypt ...
and oval window
The oval window (or ''fenestra vestibuli'' or ''fenestra ovalis'') is a connective tissue membrane-covered opening from the middle ear to the cochlea of the inner ear.
Vibrations that contact the tympanic membrane travel through the three ossicl ...
s. The ossicles are three small bones that function together to receive, amplify, and transmit the sound from the eardrum to the inner ear. The ossicles are the malleus
The ''malleus'', or hammer, is a hammer-shaped small bone or ossicle of the middle ear. It connects with the incus, and is attached to the inner surface of the eardrum. The word is Latin for 'hammer' or 'mallet'. It transmits the sound vibra ...
(hammer), incus
The ''incus'' (: incudes) or anvil in the ear is one of three small bones (ossicles) in the middle ear. The incus receives vibrations from the malleus, to which it is connected laterally, and transmits these to the stapes medially. The incus i ...
(anvil), and the stapes
The ''stapes'' or stirrup is a bone in the middle ear of humans and other tetrapods which is involved in the conduction of sound vibrations to the inner ear. This bone is connected to the oval window by its annular ligament, which allows the f ...
(stirrup). The stapes is the smallest named bone in the body
Body may refer to:
In science
* Physical body, an object in physics that represents a large amount, has mass or takes up space
* Body (biology), the physical material of an organism
* Body plan, the physical features shared by a group of anim ...
. The middle ear also connects to the upper throat
In vertebrate anatomy, the throat is the front part of the neck, internally positioned in front of the vertebrae. It contains the Human pharynx, pharynx and larynx. An important section of it is the epiglottis, separating the esophagus from the t ...
at the nasopharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its ...
via the pharyngeal opening of the Eustachian tube.
The three ossicles transmit sound from the outer ear to the inner ear. The malleus receives vibrations from sound pressure on the eardrum, where it is connected at its longest part (the manubrium or handle) by a ligament. It transmits vibrations to the incus, which in turn transmits the vibrations to the small stapes bone. The wide base of the stapes rests on the oval window. As the stapes vibrates, vibrations are transmitted through the oval window, causing movement of fluid within the cochlea
The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, in humans making 2.75 turns around its axis, the modiolus (cochlea), modiolus. A core component of the cochlea is the organ of Cort ...
.
The round window allows for the fluid within the inner ear to move. As the stapes pushes the secondary tympanic membrane, fluid in the inner ear moves and pushes the membrane of the round window out by a corresponding amount into the middle ear. The ossicles help amplify sound waves by nearly 15–20 times.
Inner ear
 The inner ear sits within the temporal bone in a complex cavity called the
The inner ear sits within the temporal bone in a complex cavity called the bony labyrinth
The bony labyrinth (also osseous labyrinth or otic capsule) is the rigid, bony outer wall of the inner ear in the temporal bone. It consists of three parts: the vestibule, semicircular canals, and cochlea. These are cavities hollowed out of the ...
. A central area known as the vestibule contains two small fluid-filled recesses, called the utricle and saccule
The saccule (Latin: sacculus) is a bed of sensory cells in the inner ear that detects linear acceleration and head tilting in the vertical plane, and converts these vibrations into electrical impulses to be interpreted by the brain. When the he ...
. These connect to the semicircular canal
The semicircular canals are three semicircular interconnected tubes located in the innermost part of each ear, the inner ear. The three canals are the lateral, anterior and posterior semicircular canals. They are the part of the bony labyrinth, ...
s and the cochlea
The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, in humans making 2.75 turns around its axis, the modiolus (cochlea), modiolus. A core component of the cochlea is the organ of Cort ...
. There are three semicircular canals angled at right angles to each other which are responsible for dynamic balance. The cochlea is a spiral shell-shaped organ responsible for the sense of hearing. These structures together create the membranous labyrinth
The membranous labyrinth is a collection of fluid filled tubes and chambers in the inner ear
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for soun ...
.
The bony labyrinth refers to the bony compartment which contains the membranous labyrinth, contained within the temporal bone. The inner ear structurally begins at the oval window, which receives vibrations from the incus of the middle ear. Vibrations are transmitted into the inner ear into a fluid called endolymph
Endolymph is the fluid contained in the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear. The major cation in endolymph is potassium, with the values of sodium and potassium concentration in the endolymph being 0.91 mM and 154 mM, respectively. ...
, which fills the membranous labyrinth. The endolymph is situated in two vestibules, the utricle and saccule, and eventually transmits to the cochlea, a spiral-shaped structure. The cochlea consists of three fluid-filled spaces: the vestibular duct
The vestibular duct or scala vestibuli is a perilymph-filled cavity inside the cochlea of the inner ear that conducts sound vibrations to the cochlear duct.
It is separated from the cochlear duct by Reissner's membrane and extends from the ve ...
, the cochlear duct Cochlear, the adjective form of cochlea, may refer to:
* Cochlear implant, a sensory aid for the deaf
* Cochlear nuclei, the ventral cochlear nucleus and the dorsal (or lateral) cochlear nucleus
* Vestibular-cochlear or Vestibulocochlear nerve, ...
, and the tympanic duct
The tympanic duct or scala tympani is one of the perilymph-filled cavities in the inner ear of humans. It is separated from the cochlear duct by the basilar membrane, and it extends from the round window to the helicotrema, where it continues ...
. Hair cell
Hair cells are the sensory receptors of both the auditory system and the vestibular system in the ears of all vertebrates, and in the lateral line organ of fishes. Through mechanotransduction, hair cells detect movement in their environment. ...
s responsible for transduction—changing mechanical changes into electrical stimuli are present in the organ of Corti
The organ of Corti, or spiral organ, is the receptor organ for hearing and is located in the mammalian cochlea. This highly varied strip of epithelial cells allows for transduction of auditory signals into nerve impulses' action potential. Trans ...
in the cochlea.
Blood supply
The blood supply of the ear differs according to each part of the ear. The outer ear is supplied by a number of arteries. Theposterior auricular artery
The posterior auricular artery is a small artery that arises from the external carotid artery. It ascends along the side of the head. It supplies several muscles of the neck and several structures of the head.
Structure
Origin
The artery ar ...
provides the majority of the blood supply. The anterior auricular arteries provide some supply to the outer rim of the ear and scalp behind it. The posterior auricular artery is a direct branch of the external carotid artery, and the anterior auricular arteries are branches from the superficial temporal artery
In human anatomy, the superficial temporal artery is a major artery of the head. It arises from the external carotid artery when it splits into the superficial temporal artery and maxillary artery.
Its pulse can be felt above the zygomatic ar ...
. The occipital artery
The occipital artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that provides arterial supply to the back of the scalp, sternocleidomastoid muscles, and deep muscles of the back and neck.
Structure
Origin
The occipital artery arises from (the ...
also plays a role.
The middle ear is supplied by the mastoid branch of either the occipital or posterior auricular arteries and the deep auricular artery, a branch of the maxillary artery
The maxillary artery (eg, internal maxillary artery) supplies deep structures of the face. It branches from the external carotid artery just deep to the neck of the mandible.
Structure
The maxillary artery, the larger of the two terminal branches ...
. Other arteries which are present but play a smaller role include branches of the middle meningeal artery
The middle meningeal artery (') is typically the third branch of the maxillary artery#First portion, first portion of the maxillary artery. After branching off the maxillary artery in the infratemporal fossa, it runs through the foramen spinosum t ...
, ascending pharyngeal artery, internal carotid artery
The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior cerebral artery, anterior and middle cerebral artery, middle cerebral circulation.
In human anatomy, the internal and external carotid artery, external carotid ari ...
, and the artery of the pterygoid canal.
The inner ear is supplied by the anterior tympanic branch of the maxillary artery; the stylomastoid branch of the posterior auricular artery; the petrosal branch of middle meningeal artery; and the labyrinthine artery
The labyrinthine artery (auditory artery, internal auditory artery) is a branch of either the anterior inferior cerebellar artery or the basilar artery. It accompanies the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) through the internal acoustic meatus. It ...
, arising from either the anterior inferior cerebellar artery
The anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) is one of three pairs of artery, arteries that supplies blood to the cerebellum.
It arises from the basilar artery on each side at the level of the junction between the medulla oblongata and the pons ...
or the basilar artery
The basilar artery (U.K.: ; U.S.: ) is one of the arteries that supplies the brain with oxygen-rich blood.
The two vertebral arteries and the basilar artery are known as the vertebral basilar system, which supplies blood to the posterior part o ...
.
Functions
Hearing
Sound wave
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the ...
s travel through the outer ear, are modulated by the middle ear, and are transmitted to the vestibulocochlear nerve
The vestibulocochlear nerve or auditory vestibular nerve, also known as the eighth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VIII, or simply CN VIII, is a cranial nerve that transmits sound and equilibrium (balance) information from the inner ear to the br ...
in the inner ear. This nerve transmits information to the temporal lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.
The temporal lobe is involved in pr ...
of the brain, where it is registered as sound.
Sound that travels through the outer ear impacts on the eardrum, and causes it to vibrate. The three ossicles bones transmit this sound to a second window (the oval window
The oval window (or ''fenestra vestibuli'' or ''fenestra ovalis'') is a connective tissue membrane-covered opening from the middle ear to the cochlea of the inner ear.
Vibrations that contact the tympanic membrane travel through the three ossicl ...
), which protects the fluid-filled inner ear. In detail, the pinna of the outer ear helps to focus a sound, which impacts on the eardrum. The malleus rests on the membrane, and receives the vibration. This vibration is transmitted along the incus and stapes to the oval window. Two small muscles, the tensor tympani
The tensor tympani is a muscle within the middle ear, located in the bony canal above the bony part of the auditory tube, and connects to the malleus bone. Its role is to dampen loud sounds, such as those produced from chewing, shouting, or thun ...
and stapedius
The stapedius is the smallest skeletal muscle in the human body. At just over one millimeter in length, its purpose is to stabilize the smallest bone in the body, the stapes or stirrup bone of the middle ear.
Structure
The stapedius emerges from ...
, also help modulate noise. The two muscles reflexively contract to dampen excessive vibrations. Vibration of the oval window causes vibration of the endolymph within the vestibule and the cochlea.
The inner ear houses the apparatus necessary to change the vibrations transmitted from the outside world via the middle ear into signals passed along the vestibulocochlear nerve to the brain. The hollow channels of the inner ear are filled with liquid, and contain a sensory epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
that is studded with hair cells
Hair cells are the sensory receptors of both the auditory system and the vestibular system in the ears of all vertebrates, and in the lateral line organ of fishes. Through mechanotransduction, hair cells detect movement in their environment. ...
. The microscopic "hairs" of these cells are structural protein filaments that project out into the fluid. The hair cells are mechanoreceptor
A mechanoreceptor, also called mechanoceptor, is a sensory receptor that responds to mechanical pressure or distortion. Mechanoreceptors are located on sensory neurons that convert mechanical pressure into action potential, electrical signals tha ...
s that release a chemical neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a Chemical synapse, synapse. The cell receiving the signal, or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neurotra ...
when stimulated. Sound waves moving through fluid flows against the receptor
Receptor may refer to:
* Sensory receptor, in physiology, any neurite structure that, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and respond ...
cells of the organ of Corti. The fluid pushes the filaments of individual cells; movement of the filaments causes receptor cells to become open to receive the potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
-rich endolymph. This causes the cell to depolarise, and creates an action potential
An action potential (also known as a nerve impulse or "spike" when in a neuron) is a series of quick changes in voltage across a cell membrane. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific Cell (biology), cell rapidly ri ...
that is transmitted along the spiral ganglion
The spiral (cochlear) ganglion is a group of neuron cell bodies in the modiolus, the conical central axis of the cochlea. These bipolar neurons innervate the hair cells of the organ of Corti. They project their axons to the ventral and dorsa ...
, which sends information through the auditory portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve to the temporal lobe
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.
The temporal lobe is involved in pr ...
of the brain.
The human ear can generally hear sounds with frequencies between 20 Hz and 20 kHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in terms of SI base uni ...
( the audio range). Sounds outside this range are considered infrasound
Infrasound, sometimes referred to as low frequency sound or incorrectly subsonic (subsonic being a descriptor for "less than the speed of sound"), describes sound waves with a Audio frequency, frequency below the lower limit of human audibility ...
(below 20 Hz) or ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound with frequency, frequencies greater than 20 Hertz, kilohertz. This frequency is the approximate upper audible hearing range, limit of human hearing in healthy young adults. The physical principles of acoustic waves apply ...
(above 20 kHz) Although hearing requires an intact and functioning auditory portion of the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
as well as a working ear, human deafness (extreme insensitivity to sound) most commonly occurs because of abnormalities of the inner ear, rather than in the nerves or tracts of the central auditory system.
Balance
Providing balance, when moving or stationary, is also a central function of the ear. The ear facilitates two types of balance: static balance, which allows a person to feel the effects ofgravity
In physics, gravity (), also known as gravitation or a gravitational interaction, is a fundamental interaction, a mutual attraction between all massive particles. On Earth, gravity takes a slightly different meaning: the observed force b ...
, and dynamic balance, which allows a person to sense acceleration.
Static balance is provided by two ventricles, the utricle and the saccule. Cells lining the walls of these ventricles contain fine filaments, and the cells are covered with a fine gelatinous layer. Each cell has 50–70 small filaments, and one large filament, the kinocilium
A kinocilium is a special type of cilium on the apex of hair cells located in the sensory epithelium of the vertebrate inner ear. Contrasting with stereocilia, which are numerous, there is only one kinocilium on each hair cell. The kinocilium can ...
. Within the gelatinous layer lie otolith
An otolith (, ' ear + , ', a stone), also called otoconium, statolith, or statoconium, is a calcium carbonate structure in the saccule or utricle (ear), utricle of the inner ear, specifically in the vestibular system of vertebrates. The saccule ...
s, tiny formations of calcium carbonate
Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a common substance found in Rock (geology), rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite, most notably in chalk and limestone, eggshells, gastropod shells, shellfish skel ...
. When a person moves, these otoliths shift position. This shift alters the positions of the filaments, which opens ion channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by Gating (electrophysiol ...
s within the cell membranes, creating depolarisation
In biology, depolarization or hypopolarization is a change within a cell, during which the cell undergoes a shift in electric charge distribution, resulting in less negative charge inside the cell compared to the outside. Depolarization is esse ...
and an action potential
An action potential (also known as a nerve impulse or "spike" when in a neuron) is a series of quick changes in voltage across a cell membrane. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific Cell (biology), cell rapidly ri ...
that is transmitted to the brain along the vestibulocochlear nerve.
Dynamic balance is provided through the three semicircular canals. These three canals are orthogonal (at right angles) to each other. At the end of each canal is a slight enlargement, known as the ampulla, which contains numerous cells with filaments in a central area called the cupula. The fluid in these canals rotates according to the momentum of the head. When a person changes acceleration, the inertia of the fluid changes. This affects the pressure on the cupula, and results in the opening of ion channels. This causes depolarisation, which is passed as a signal to the brain along the vestibulocochlear nerve. Dynamic balance also helps maintain eye tracking when moving, via the vestibulo-ocular reflex
The vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) is a reflex that acts to stabilize Gaze (physiology), gaze during head movement, with eye movement due to activation of the vestibular system, it is also known as the cervico-ocular reflex. The reflex acts to im ...
.
Development
Duringembryogenesis
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male ...
, the ear develops as three distinct structures: the inner ear, the middle ear and the outer ear. Each structure originates from a different germ layer
A germ layer is a primary layer of cell (biology), cells that forms during embryonic development. The three germ layers in vertebrates are particularly pronounced; however, all eumetazoans (animals that are sister taxa to the sponges) produce tw ...
: the ectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from the o ...
, endoderm
Endoderm is the innermost of the three primary germ layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm (outside layer) and mesoderm (middle layer). Cells migrating inward along the archenteron form the inner layer of the gastr ...
and mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood, or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly ever ...
.
Inner ear
Around its second to third week, the developing embryo consists of three layers: ectoderm,mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical ...
, and endoderm. The first part of the ear to develop is the inner ear, which begins to form from the ectoderm around the embryo's 22nd day, derived from two thickenings called otic placode
In embryology, the otic placode is a thickening of the ectoderm on the outer surface of a developing embryo from which the ear develops. The ear, including both the vestibular system and the auditory system, develops from the otic placode beginni ...
s on either side of the head. Each otic placode recedes below the ectoderm, forms an otic pit
The auditory pit, also known as the otic pit, is the first rudiment of the internal ear. It appears shortly after that of the eye, in the form of a patch of thickened ectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in ear ...
and then an otic vesicle
Otic vesicle, or auditory vesicle, consists of either of the two sac-like invaginations formed and subsequently closed off during embryonic development. It is part of the neural ectoderm, which will develop into the membranous labyrinth of the in ...
. This entire mass is eventually surrounded by mesenchyme to form the bony labyrinth.
Around the 28th day, parts of the otic vesicle begin to form the vestibulocochlear nerve. These form bipolar neuron
A bipolar neuron, or bipolar cell, is a type of neuron characterized by having both an axon and a dendrite extending from the soma (cell body) in opposite directions. These neurons are predominantly found in the retina and olfactory system. The em ...
s, which supply sensation to parts of the inner ear (namely the sensory parts of the semicircular canals, macular of the utricle and saccule, and organ of Corti).
Around the 33rd day, the vesicles begin to differentiate. Posteriorly, they form what will become the utricle and semicircular canals. Anteriorly, the vesicles differentiate into a rudimentary saccule, which eventually becomes the saccule and cochlea. Part of the saccule eventually gives rise and connects to the cochlear duct, which appears approximately during the sixth week and connects to the saccule through the ductus reuniens.
As the cochlear duct's mesenchyme begins to differentiate, three cavities are formed: the scala vestibuli, the scala tympani and the scala media
Scala or SCALA may refer to:
Automobiles
* Renault Scala, multiple automobile models
* Škoda Scala, a Czech compact hatchback
Music
* Scala (band), an English electronic music group
* Escala (group), an electronic string quartet formerly know ...
. Both the scala vestibuli and the scala tympani contain an extracellular fluid called perilymph
Perilymph is an extracellular fluid located within the inner ear. It is found within the scala tympani and scala vestibuli of the cochlea. The ionic composition of perilymph is comparable to that of plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. The major ca ...
, while the scala media contains endolymph. The vestibular membrane and the basilar membrane
The basilar membrane is a stiff structural element within the cochlea of the inner ear which separates two liquid-filled tubes that run along the coil of the cochlea, the scala media and the scala tympani. The basilar membrane moves up and down ...
develop to separate the cochlear duct from the vestibular duct and the tympanic duct, respectively.
;Molecular regulation
Most of the genes responsible for the regulation
Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biology and society, but the term has slightly different meanings according to context. Fo ...
of inner ear formation and its morphogenesis
Morphogenesis (from the Greek ''morphê'' shape and ''genesis'' creation, literally "the generation of form") is the biological process that causes a cell, tissue or organism to develop its shape. It is one of three fundamental aspects of deve ...
are members of the homeobox gene
A homeobox is a DNA sequence, around 180 base pairs long, that regulates large-scale anatomical features in the early stages of embryonic development. Mutations in a homeobox may change large-scale anatomical features of the full-grown organism ...
family such as Pax, Msx and Otx homeobox genes. The development of inner ear structures such as the cochlea
The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, in humans making 2.75 turns around its axis, the modiolus (cochlea), modiolus. A core component of the cochlea is the organ of Cort ...
is regulated by Dlx5/ Dlx6, Otx1/ Otx2 and Pax2, which in turn are controlled by the master gene Shh. Shh is secreted by the notochord
The notochord is an elastic, rod-like structure found in chordates. In vertebrates the notochord is an embryonic structure that disintegrates, as the vertebrae develop, to become the nucleus pulposus in the intervertebral discs of the verteb ...
.
Middle ear
The middle ear and its components develop from the first and secondpharyngeal arch
The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches'','' are transient structures seen in the Animal embryonic development, embryonic development of humans and other vertebrates, that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, t ...
es. The tympanic cavity and auditory tube develop from the first part of the pharyngeal pouch between the first two arches in an area which will also go on to develop the pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates ...
. This develops as a structure called the tubotympanic recess
Human embryonic development or human embryogenesis is the development and formation of the human embryo. It is characterised by the processes of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of deve ...
. The ossicles (malleus, incus and stapes) normally appear during the first half of fetal development. The first two (malleus and incus) derive from the first pharyngeal arch and the stapes derives from the second. All three ossicles develop from the neural crest
The neural crest is a ridge-like structure that is formed transiently between the epidermal ectoderm and neural plate during vertebrate development. Neural crest cells originate from this structure through the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, ...
. Eventually, cells from the tissue surrounding the ossicles will experience apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biol ...
and a new layer of endodermal epithelial will constitute the formation of the tympanic cavity wall.
Outer ear
Unlike structures of the inner and middle ear, which develop from pharyngeal pouches, the ear canal originates from the dorsal portion of the firstpharyngeal cleft
A pharyngeal groove (or branchial groove, or pharyngeal cleft) is made up of ectoderm unlike its counterpart the pharyngeal pouch (embryology), pharyngeal pouch on the endodermal side.
The first pharyngeal groove produces the external auditory mea ...
. It is fully expanded by the end of the 18th week of development. The eardrum is made up of three layers (ectoderm, endoderm and connective tissue). The auricle originates as a fusion of six hillocks. The first three hillocks are derived from the lower part of the first pharyngeal arch and form the tragus, crus of the helix, and helix, respectively. The final three hillocks are derived from the upper part of the second pharyngeal arch and form the antihelix, antitragus, and earlobe. The outer ears develop in the lower neck
The neck is the part of the body in many vertebrates that connects the head to the torso. It supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that transmit sensory and motor information between the brain and the rest of the body. Addition ...
. As the mandible
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbone i ...
forms, they move towards their final position level with the eyes.
Growth
The ears of newborn humans are proportionally very large, even more so than the head's largeness as compared to the body. Ears grow quickly until about the age of nine, then continue to grow steadily in circumference (about 0.5 millimeters a year) throughout life, with the increase in length more extreme in males.Uniqueness
Ears are individually very unique, with the odds of two people having matching ears very low. Additionally, the ear's proportions are normally retained for life, and have thus been employed forforensic identification
Forensic identification is the application of forensic science, or "forensics", and technology to identify specific objects from the trace evidence they leave, often at a crime scene or the scene of an accident. Forensic means "for the courts".
Hu ...
since the 1950s.
Clinical significance
Hearing loss
Hearing loss may be either partial or total. This may be a result of injury or damage, congenital disease, orphysiological
Physiology (; ) is the science, scientific study of function (biology), functions and mechanism (biology), mechanisms in a life, living system. As a branches of science, subdiscipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ syst ...
causes. When hearing loss is a result of injury or damage to the outer ear or middle ear, it is known as conductive hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss (CHL) is a type of hearing impairment that occurs when sound waves are unable to efficiently travel through the outer ear, tympanic membrane (eardrum), or middle ear structures such as the ossicles. This blockage or dysfun ...
. When deafness is a result of injury or damage to the inner ear, vestibulochoclear nerve, or brain, it is known as sensorineural hearing loss
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is a type of hearing loss in which the root cause lies in the inner ear, sensory organ (cochlea and associated structures), or the vestibulocochlear nerve (Cranial nerves, cranial nerve VIII). SNHL accounts for a ...
.
Causes of conductive hearing loss include an ear canal blocked by earwax, ossicles that are fixed together or absent, or holes in the eardrum. Conductive hearing loss may also result from middle ear inflammation causing fluid build-up in the normally air-filled space, such as by otitis media
Otitis media is a group of Inflammation, inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. One of the two main types is acute otitis media (AOM), an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pullin ...
. Tympanoplasty is the general name of the operation to repair the middle ear's eardrum and ossicles. Grafts from muscle fascia are ordinarily used to rebuild an intact eardrum. Sometimes artificial ear bones are placed to substitute for damaged ones, or a disrupted ossicular chain is rebuilt in order to conduct sound effectively.
Hearing aid
A hearing aid is a device designed to improve hearing by making sound audible to a person with hearing loss. Hearing aids are classified as medical devices in most countries, and regulated by the respective regulations. Small audio amplifiers ...
s or cochlear implant
A cochlear implant (CI) is a surgically implanted Neuroprosthetics, neuroprosthesis that provides a person who has moderate-to-profound sensorineural hearing loss with sound perception. With the help of therapy, cochlear implants may allow for imp ...
s may be used if the hearing loss is severe or prolonged. Hearing aids work by amplifying the sound of the local environment and are best suited to conductive hearing loss. Cochlear implants transmit the sound that is heard as if it were a nervous signal, bypassing the cochlea. Active middle ear implants send sound vibrations to the ossicles in the middle ear, bypassing any non-functioning parts of the outer and middle ear.
Congenital abnormalities
Anomalies and malformations of the auricle are common. These anomalies include chromosome syndromes such asring 18
Ring chromosome 18 is a genetic condition caused by a deletion of the two ends of chromosome 18 followed by the formation of a ring-shaped chromosome. It was first reported in 1964.
Signs and symptoms
Ring 18 causes a wide range of medical and ...
. Children may also present cases of abnormal ear canals and low ear implantation. In rare cases, no auricle is formed (atresia
Atresia is a condition in which an orifice or passage in the body is (usually abnormally) closed or absent.
Types Anotia
Anotia is characterized by the complete absence of the ear and is extremely rare. This condition may affect one or both ...
), or is extremely small (microtia
Microtia is a congenital deformity where the auricle (external ear) is underdeveloped. A completely undeveloped auricle is referred to as anotia. Because microtia and anotia have the same origin, it can be referred to as microtia-anotia. Micro ...
). Small auricles can develop when the auricular hillocks do not develop properly. The ear canal can fail to develop if it does not channelise properly or if there is an obstruction. Reconstructive surgery to treat hearing loss is considered as an option for children older than five, with a cosmetic surgical procedure to reduce the size or change the shape of the ear is called an otoplasty
Otoplasty (, , "ear" + , , "to shape") is a procedure for correcting the deformities and defects of the Pinna (anatomy), auricle (Ear, external ear), whether these defects are congenital defect, congenital conditions (e.g. microtia, anotia, etc.) o ...
. The initial medical intervention is aimed at assessing the baby's hearing and the condition of the ear canal, as well as the middle and inner ear. Depending on the results of tests, reconstruction of the outer ear is done in stages, with planning for any possible repairs of the rest of the ear.
Approximately one out of one thousand children suffer some type of congenital deafness related to the development of the inner ear. Inner ear congenital anomalies are related to sensorineural hearing loss and are generally diagnosed with a computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
(CT) scan or a magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
(MRI) scan. Hearing loss problems also derive from inner ear anomalies because its development is separate from that of the middle and external ear. Middle ear anomalies can occur because of errors during head and neck development. The first pharyngeal pouch syndrome associates middle ear anomalies to the malleus and incus structures as well as to the non-differentiation of the annular stapedial ligament
The annular stapedial ligament (also called the stapediovestibular joint) is a ring of fibrous soft tissue that connects the base of the stapes to the oval window of the inner ear.
Calcification and hardening of the annular ligament of the stap ...
. Temporal bone and ear canal anomalies are also related to this structure of the ear and are known to be associated with sensorineural hearing loss and conductive hearing loss.
Vertigo
Vertigo refers to the inappropriate perception of motion. This is due to dysfunction of thevestibular system
The vestibular system, in vertebrates, is a sensory system that creates the sense of balance and spatial orientation for the purpose of coordinating motor coordination, movement with balance. Together with the cochlea, a part of the auditory sys ...
. One common type of vertigo is benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is a disorder arising from a problem in the inner ear. Symptoms are repeated, brief periods of vertigo with movement, characterized by a spinning sensation upon changes in the position of the head.
* ...
, when an otolith
An otolith (, ' ear + , ', a stone), also called otoconium, statolith, or statoconium, is a calcium carbonate structure in the saccule or utricle (ear), utricle of the inner ear, specifically in the vestibular system of vertebrates. The saccule ...
is displaced from the ventricles to the semicircular canal. The displaced otolith rests on the cupola, causing a sensation of movement when there is none. Ménière's disease
Ménière's disease (MD) is a disease of the inner ear that is characterized by potentially severe and incapacitating episodes of vertigo, tinnitus, hearing loss, and a feeling of fullness in the ear. Typically, only one ear is affected in ...
, labyrinthitis
Labyrinthitis is inflammation of the labyrinth, a maze of fluid-filled channels in the inner ear. Vestibular neuritis is inflammation of the vestibular nerve (the nerve in the ear that sends messages related to motion and position to the brain) ...
, stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
s, and other infective and congenital diseases may also result in the perception of vertigo.
Injury
;Outer ear Injuries to the external ear occur fairly frequently, and can leave minor to major deformity. Injuries include:laceration
A wound is any disruption of or damage to living tissue, such as skin, mucous membranes, or organs. Wounds can either be the sudden result of direct trauma (mechanical, thermal, chemical), or can develop slowly over time due to underlying diseas ...
, avulsion injuries, burn
A burn is an injury to skin, or other tissues, caused by heat, electricity, chemicals, friction, or ionizing radiation (such as sunburn, caused by ultraviolet radiation). Most burns are due to heat from hot fluids (called scalding), soli ...
and repeated twisting or pulling of an ear, for discipline or torture. Chronic damage to the ears can cause cauliflower ear
Cauliflower ear is an irreversible condition that occurs when the Auricle (anatomy), external portion of the ear is hit and develops a Thrombus, blood clot or other collection of fluid under the perichondrium. This separates the cartilage from the ...
, a common condition in boxers and wrestlers
Wrestling is a Martial arts, martial art, combat sport, and form of entertainment that involves grappling with an opponent and striving to obtain a position of advantage through different throws or techniques, within a given ruleset. Wrestling ...
in which the cartilage around the ears becomes lumpy and distorted owing to persistence of a haematoma
A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillaries. A hematoma is ...
around the perichondrium
The perichondrium (from Greek and ) is a layer of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the cartilage of developing bone. It consists of two separate layers: an outer fibrous layer and inner chondrogenic layer. The fibrous layer conta ...
, which can impair blood supply and healing. Owing to its exposed position, the external ear is susceptible to frostbite
Frostbite is a skin injury that occurs when someone is exposed to extremely low temperatures, causing the freezing of the skin or other tissues, commonly affecting the fingers, toes, nose, ears, cheeks and chin areas. Most often, frostbite occ ...
as well as skin cancer
Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the Human skin, skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells (biology), cells that have the ability to invade or metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. It occurs when skin cells grow ...
s, including squamous-cell carcinoma
Squamous-cell carcinoma (SCC), also known as epidermoid carcinoma, comprises a number of different types of cancer that begin in squamous cells. These cells form on the surface of the skin, on the lining of hollow organs in the body, and on the ...
and basal-cell carcinoma
Basal-cell carcinoma (BCC), also known as basal-cell cancer, basalioma, or rodent ulcer, is the most common type of skin cancer. It often appears as a painless, raised area of skin, which may be shiny with small blood vessels running over it. ...
s.
;Middle ear
The ear drum may become perforated in the event of a large sound or explosion, when diving or flying (called barotrauma
Barotrauma is physical damage to body tissues caused by a difference in pressure between a gas space inside, or in contact with, the body and the surrounding gas or liquid. The initial damage is usually due to over-stretching the tissues in ...
), or by objects inserted into the ear. Another common cause of injury is due to an infection such as otitis media. These may cause a discharge from the ear called otorrhea, and are often investigated by otoscopy and audiometry
Audiometry () is a branch of audiology and the science of measuring hearing acuity for variations in sound intensity and pitch and for tonal purity, involving thresholds and differing frequencies. Typically, audiometric tests determine a subje ...
. Treatment may include watchful waiting
Watchful waiting (also watch and wait or WAW) is an approach to a medical problem in which time is allowed to pass before medical intervention or therapy is used. During this time, repeated testing may be performed.
Related terms include ''expe ...
, antibiotics and possibly surgery, if the injury is prolonged or the position of the ossicles is affected. Skull fractures that go through the part of the skull containing the ear structures (the temporal bone) can also cause damage to the middle ear. A cholesteatoma
Cholesteatoma is a destructive and expanding growth consisting of keratinizing squamous epithelium in the middle ear and/or mastoid process. Cholesteatomas are not cancerous as the name may suggest, but can cause significant problems because of the ...
is a cyst of squamous skin cells that may develop from birth or secondary to other causes such as chronic ear infections. It may impair hearing or cause dizziness or vertigo, and is usually investigated by otoscopy and may require a CT scan. The treatment for cholesteatoma is surgery.
;Inner ear
There are two principal damage mechanisms to the inner ear in industrialised society, and both injure hair cells. The first is exposure to elevated sound levels (noise trauma), and the second is exposure to drugs and other substances (ototoxicity
Ototoxicity is the property of being toxic to the ear (''oto-''), specifically the cochlea or auditory nerve and sometimes the vestibular system, for example, as a side effect of a drug. The effects of ototoxicity can be reversible and tempora ...
). A large number of people are exposed to sound levels on a daily basis that are likely to lead to significant hearing loss
Hearing loss is a partial or total inability to hear. Hearing loss may be present at birth or acquired at any time afterwards. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to acquire spo ...
. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH, ) is the List of United States federal agencies, United States federal agency responsible for conducting research and making recommendations for the prevention of work-related occ ...
has recently published research on the estimated numbers of persons with hearing difficulty (11%) and the percentage of those that can be attributed to occupational noise exposure (24%). Furthermore, according to the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) is a survey research program conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) to assess the health and nutritional status of adults and children in the United States, and ...
(NHANES), approximately twenty-two million (17%) US workers reported exposure to hazardous workplace noise. Workers exposed to hazardous noise further exacerbate the potential for developing noise-induced hearing loss
Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is a Hearing loss, hearing impairment resulting from exposure to loud sound. People may have a loss of perception of a narrow range of Frequency, frequencies or impaired perception of sound including hyperacusi ...
when they do not wear hearing protection
A hearing protection device, also known as a HPD, is an ear protection device worn in or over the ears while exposed to hazardous noise and provide hearing protection to help prevent noise-induced hearing loss. HPDs reduce the level of the no ...
.
Tinnitus
Tinnitus
Tinnitus is a condition when a person hears a ringing sound or a different variety of sound when no corresponding external sound is present and other people cannot hear it. Nearly everyone experiences faint "normal tinnitus" in a completely ...
is the hearing of sound
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the br ...
when no external sound is present. While often described as a ringing, it may also sound like a clicking, hiss or roaring. Rarely, unclear voices or music are heard. The sound may be soft or loud, low pitched or high pitched and appear to be coming from one ear or both. Most of the time, it comes on gradually. In some people, the sound causes depression, anxiety, or concentration difficulties.
Tinnitus is not a disease but a symptom that can result from a number of underlying causes. One of the most common causes is noise-induced hearing loss
Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is a Hearing loss, hearing impairment resulting from exposure to loud sound. People may have a loss of perception of a narrow range of Frequency, frequencies or impaired perception of sound including hyperacusi ...
. Other causes include: ear infections, disease of the heart or blood vessels, Ménière's disease
Ménière's disease (MD) is a disease of the inner ear that is characterized by potentially severe and incapacitating episodes of vertigo, tinnitus, hearing loss, and a feeling of fullness in the ear. Typically, only one ear is affected in ...
, brain tumor
A brain tumor (sometimes referred to as brain cancer) occurs when a group of cells within the Human brain, brain turn cancerous and grow out of control, creating a mass. There are two main types of tumors: malignant (cancerous) tumors and benign ...
s, emotional stress
In psychology, stress is a feeling of emotional strain and pressure. Stress is a form of psychological and mental discomfort. Small amounts of stress may be beneficial, as it can improve athletic performance, motivation and reaction to the env ...
, exposure to certain medications, a previous head injury
A head injury is any injury that results in trauma to the skull or brain. The terms ''traumatic brain injury'' and ''head injury'' are often used interchangeably in the medical literature. Because head injuries cover such a broad scope of inju ...
, and earwax. It is more common in those with depression and anxiety.
Society and culture
 The ears have been ornamented with jewelry for thousands of years, traditionally by piercing of the
The ears have been ornamented with jewelry for thousands of years, traditionally by piercing of the earlobe
The human earlobe (''lobulus auriculae''), the lower portion of the outer ear, is composed of tough areolar and adipose connective tissues, lacking the firmness and elasticity of the rest of the auricle (the external structure of the ear). In ...
. In ancient and modern cultures, ornaments have been placed to stretch and enlarge the earlobes, allowing for larger plugs to be slid into a large fleshy gap in the lobe. Tearing of the earlobe from the weight of heavy earring
Earrings are jewelry that can be worn on one's ears. Earrings are commonly worn in a piercing in the earlobe or another external part of the ear, or by #Clip-on and other non-pierced earrings, some other means, such as stickers or clip-ons. Earr ...
s, or from traumatic pull of an earring (for example, by snagging on a sweater), is fairly common.
Injury to the ears has been present since Roman times as a method of reprimand or punishment – "In Roman times, when a dispute arose that could not be settled amicably, the injured party cited the name of the person thought to be responsible before the Praetor; if the offender did not appear within the specified time limit, the complainant summoned witnesses to make statements. If they refused, as often happened, the injured party was allowed to drag them by the ear and to pinch them hard if they resisted. Hence the French expression "", of which the literal meaning is "to have one's ear pulled" and the figurative meaning "to take a lot of persuading". We use the expression "to tweak (or pull) someone's ears" to mean "inflict a punishment"."
The auricles have an effect on facial appearance. In Western societies, protruding ears (present in about 5% of ethnic Europeans
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common ancestry, language, faith, historical continuity, etc. There are ...
) have been considered unattractive, particularly if asymmetric. The first surgery to reduce the projection of prominent ears was published in the medical literature by Ernst Dieffenbach
Johann Karl Ernst Dieffenbach (27 January 1811 – 1 October 1855), also known as Ernest Dieffenbach, was a German physician, geologist and naturalist, the first trained scientist to live and work in New Zealand, where he travelled widely under th ...
in 1845, and the first case report
In medicine, a case report is a detailed report of the symptoms, signs, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of an individual patient. Case reports may contain a demographic profile of the patient, but usually describe an unusual or novel occurrenc ...
in 1881.
Pointy ears
Pointy ears or pointed ears are a characteristic of many animals, a genetic condition in humans, as well as a cliché in popular culture, particularly in the fantasy genre. They are commonly known as elf ears for their depiction in Peter Jackso ...
are a characteristic of some creatures in folklore
Folklore is the body of expressive culture shared by a particular group of people, culture or subculture. This includes oral traditions such as Narrative, tales, myths, legends, proverbs, Poetry, poems, jokes, and other oral traditions. This also ...
such as the French croquemitaine, Brazilian curupira or Japanese earth spider. It has been a feature of characters on art as old as that of Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically r ...
and medieval Europe
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
. Pointy ears are a common characteristic of many creatures in the fantasy
Fantasy is a genre of speculative fiction that involves supernatural or Magic (supernatural), magical elements, often including Fictional universe, imaginary places and Legendary creature, creatures.
The genre's roots lie in oral traditions, ...
genre, including elves
An elf (: elves) is a type of humanoid supernatural being in Germanic folklore. Elves appear especially in North Germanic mythology, being mentioned in the Icelandic ''Poetic Edda'' and the ''Prose Edda''.
In medieval Germanic-speakin ...
, faeries
A fairy (also called fay, fae, fae folk, fey, fair folk, or faerie) is a type of mythical being or legendary creature, generally described as anthropomorphism, anthropomorphic, found in the folklore of multiple European cultures (including Cel ...
, pixie
A pixie (also called pisky, pixy, pixi, pizkie, piskie, or pigsie in parts of Cornwall and Devon) is a mythical creature of British folklore. Pixies are speculated to be particularly concentrated in the high moorland areas around Devon and Cor ...
s, hobbit
Hobbits are a fictional race of people in the novels of J. R. R. Tolkien. About half average human height, Tolkien presented hobbits as a variety of humanity, or close relatives thereof. Occasionally known as halflings in Tolkien's writings, ...
s, or orcs. They are a characteristic of creatures in the horror genre, such as vampire
A vampire is a mythical creature that subsists by feeding on the Vitalism, vital essence (generally in the form of blood) of the living. In European folklore, vampires are undead, undead humanoid creatures that often visited loved ones and c ...
s. Pointy ears are also found in the science fiction
Science fiction (often shortened to sci-fi or abbreviated SF) is a genre of speculative fiction that deals with imaginative and futuristic concepts. These concepts may include information technology and robotics, biological manipulations, space ...
genre; for example among the Vulcan and Romulan races of the ''Star Trek
''Star Trek'' is an American science fiction media franchise created by Gene Roddenberry, which began with the Star Trek: The Original Series, series of the same name and became a worldwide Popular culture, pop-culture Cultural influence of ...
'' universe and the Nightcrawler character from the X-Men
The X-Men are a superhero team in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. Created by writer/editor Stan Lee and artist/co-plotter Jack Kirby, the team first appeared in Uncanny X-Men, ''The X-Men'' #1 (September 1963). Although initial ...
universe.
Georg von Békésy was a Hungarian biophysicist
Biophysics is an interdisciplinary science that applies approaches and methods traditionally used in physics to study biological phenomena. Biophysics covers all scales of biological organization, from molecular to organismic and populations ...
born in Budapest
Budapest is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns of Hungary, most populous city of Hungary. It is the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, tenth-largest city in the European Union by popul ...
, Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
. In 1961, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine () is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or medicine. The Nobel Prize is not a single prize, but five separate prizes that, acco ...
for his research on the function of the cochlea
The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, in humans making 2.75 turns around its axis, the modiolus (cochlea), modiolus. A core component of the cochlea is the organ of Cort ...
in the mammalian hearing organ.
The Vacanti mouse was a laboratory mouse
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus'' ...
that had what looked like a human ear grown on its back. The "ear" was actually an ear-shaped cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. Semi-transparent and non-porous, it is usually covered by a tough and fibrous membrane called perichondrium. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints ...
structure grown by seeding cow cartilage cells into a biodegradable ear-shaped mold and then implanted under the skin of the mouse; then the cartilage naturally grew by itself. It was developed as an alternative to ear repair or grafting procedures and the results met with much publicity and controversy in 1997.
Other animals

 The ears of
The ears of vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s are placed somewhat symmetrically on either side of the head, an arrangement that aids sound localization
Sound localization is a listener's ability to identify the location or origin of a detected sound in direction and distance.
The sound localization mechanisms of the mammalian auditory system have been extensively studied. The auditory system u ...
.
All mammals have three auditory ossicles. The external pinna in theria
Theria ( or ; ) is a scientific classification, subclass of mammals amongst the Theriiformes. Theria includes the eutherians (including the Placentalia, placental mammals) and the metatherians (including the marsupials) but excludes the egg-lay ...
n mammals helps direct sound through the ear canal to the eardrum. The complex geometry of ridges on the inner surface of some mammalian ears helps to sharply focus sounds produced by prey, using echolocation signals. These ridges can be regarded as the acoustic equivalent of a Fresnel lens
A Fresnel lens ( ; ; or ) is a type of composite compact lens (optics), lens which reduces the amount of material required compared to a conventional lens by dividing the lens into a set of concentric annular sections.
The simpler Dioptrics, d ...
, and may be seen in a wide range of animals, including the bat
Bats are flying mammals of the order Chiroptera (). With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most birds, flying with their very long spread-out ...
, aye-aye
The aye-aye (''Daubentonia madagascariensis'') is a long-fingered lemur, a Strepsirrhini, strepsirrhine primate native to Madagascar with rodent-like teeth that perpetually grow and a special thin middle finger that they can use to catch grubs ...
, lesser galago
Lesser bushbabies, or lesser galagos, are strepsirrhine primates of the genus ''Galago''. They are classified, along with the other bushbaby and galago genera in the family Galagidae. They are probably the most numerous primate in Africa, and can ...
, bat-eared fox
The bat-eared fox (''Otocyon megalotis'') is a species of fox found on the African savanna. It is the only extant species of the genus ''Otocyon'' and a Basal (phylogenetics), basal species of Canidae, canid. Fossil records indicate this canid ...
, mouse lemur
The mouse lemurs are nocturnal lemurs of the genus ''Microcebus''. Like all lemurs, mouse lemurs are native to Madagascar.
Mouse lemurs have a combined head, body and tail length of and weigh , making them the smallest primates (the smallest sp ...
and others.
Some large primate
Primates is an order (biology), order of mammals, which is further divided into the Strepsirrhini, strepsirrhines, which include lemurs, galagos, and Lorisidae, lorisids; and the Haplorhini, haplorhines, which include Tarsiiformes, tarsiers a ...
s such as gorilla
Gorillas are primarily herbivorous, terrestrial great apes that inhabit the tropical forests of equatorial Africa. The genus ''Gorilla'' is divided into two species: the eastern gorilla and the western gorilla, and either four or five su ...
s and orangutan
Orangutans are great apes native to the rainforests of Indonesia and Malaysia. They are now found only in parts of Borneo and Sumatra, but during the Pleistocene they ranged throughout Southeast Asia and South China. Classified in the genus ...
s (and also human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s) have undeveloped ear muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
s that are non-functional vestigial structure
Vestigiality is the retention, during the process of evolution, of genetically determined structures or attributes that have lost some or all of the ancestral function in a given species. Assessment of the vestigiality must generally rely on co ...
s, yet are still large enough to be easily identified. Darwin, Charles (1871). ''The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex
''The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex'' is a book by English naturalist Charles Darwin, first published in 1871, which applies evolutionary theory to human evolution, and details his theory of sexual selection, a form of biolog ...
''. John Murray: London. An ear muscle that cannot move the ear, for whatever reason, has lost that biological function.  This serves as evidence of homology between related species. In humans, there is variability in these muscles, such that some people are able to move their ears in various directions, and it has been said that it may be possible for others to gain such movement by repeated trials. In such primates, the inability to move the ear is compensated for mainly by the ability to easily turn the
This serves as evidence of homology between related species. In humans, there is variability in these muscles, such that some people are able to move their ears in various directions, and it has been said that it may be possible for others to gain such movement by repeated trials. In such primates, the inability to move the ear is compensated for mainly by the ability to easily turn the head
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple ani ...
on a horizontal plane, an ability which is not common to most monkeys—a function once provided by one structure is now replaced by another.
In some animals with mobile pinnae (like the horse), each pinna can be aimed independently to better receive the sound. For these animals, the pinnae help localise the direction of the sound source.
 The ear, with its blood vessels close to the surface, is an essential thermoregulator in some land mammals, including the elephant, the fox, and the rabbit. There are five types of ear carriage in domestic rabbits, some of which have been bred for exaggerated ear length—a potential health risk that is controlled in some countries. Abnormalities in the skull of a half-lop rabbit were studied by Charles Darwin in 1868. In marine mammals,
The ear, with its blood vessels close to the surface, is an essential thermoregulator in some land mammals, including the elephant, the fox, and the rabbit. There are five types of ear carriage in domestic rabbits, some of which have been bred for exaggerated ear length—a potential health risk that is controlled in some countries. Abnormalities in the skull of a half-lop rabbit were studied by Charles Darwin in 1868. In marine mammals, earless seal
The earless seals, phocids, or true seals are one of the three main groups of mammals within the seal lineage, Pinnipedia. All true seals are members of the family Phocidae (). They are sometimes called crawling seals to distinguish them from th ...
s are one of three groups of Pinniped
Pinnipeds (pronounced ), commonly known as seals, are a widely range (biology), distributed and diverse clade of carnivorous, fin-footed, semiaquatic, mostly marine mammals. They comprise the extant taxon, extant families Odobenidae (whose onl ...
ia.
Invertebrates
Only vertebrate animals have ears, though many invertebrates detect sound using other kinds of sense organs. In insects,tympanal organ
A tympanal organ (or tympanic organ) is a hearing organ in insects, consisting of a tympanal membrane ( tympanum) stretched across a frame backed by an air sac and associated sensory neurons. Sounds vibrate the membrane, and the vibrations are s ...
s are used to hear distant sounds. They are located either on the head or elsewhere, depending on the insect family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
. The tympanal organs of some insects are extremely sensitive, offering acute hearing beyond that of most other animals. The female cricket fly '' Ormia ochracea'' has tympanal organs on each side of her abdomen. They are connected by a thin bridge of exoskeleton and they function like a tiny pair of eardrums, but, because they are linked, they provide acute directional information. The fly uses her "ears" to detect the call of her host, a male cricket. Depending on where the song of the cricket is coming from, the fly's hearing organs will reverberate at slightly different frequencies. This difference may be as little as 50 billionths of a second, but it is enough to allow the fly to home in directly on a singing male cricket and parasitise it.
Simpler structures allow other arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s to detect near-field sounds. Spiders and cockroaches, for example, have hairs on their legs, which are used for detecting sound. Caterpillars may also have hairs on their body that perceive vibrationsScoble, M.J. 1992. The Lepidoptera: Form, function, and diversity. Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books ...
and allow them to respond to sound.
See also
* Hear, hear * Hearing test *Righting reflex
The righting reflex, also known as the labyrinthine righting reflex, or the Cervico-collic reflex; is a reflex that corrects the orientation of the body when it is taken out of its normal upright position. It is initiated by the vestibular system, ...
* Eustachian tube
The Eustachian tube (), also called the auditory tube or pharyngotympanic tube, is a tube that links the nasopharynx to the middle ear, of which it is also a part. In adult humans, the Eustachian tube is approximately long and in diameter. It ...
– The tube which connects the middle ear to the throat
References
External links
* * {{Authority control Articles containing video clips Auditory system Human head and neckEar
In vertebrates, an ear is the organ that enables hearing and (in mammals) body balance using the vestibular system. In humans, the ear is described as having three parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear co ...