The European Space Agency (ESA) is a 23-member
international organization
An international organization, also known as an intergovernmental organization or an international institution, is an organization that is established by a treaty or other type of instrument governed by international law and possesses its own le ...
devoted to
space exploration
Space exploration is the process of utilizing astronomy and space technology to investigate outer space. While the exploration of space is currently carried out mainly by astronomers with telescopes, its physical exploration is conducted bo ...
.
With its headquarters in Paris and a staff of around 2,547 people globally as of 2023, ESA was founded in 1975 in the context of
European integration
European integration is the process of political, legal, social, regional and economic integration of states wholly or partially in Europe, or nearby. European integration has primarily but not exclusively come about through the European Union ...
. Its 2025 annual budget was €7.7 billion.
The ESA Human and Robotic Exploration programme includes
human spaceflight
Human spaceflight (also referred to as manned spaceflight or crewed spaceflight) is spaceflight with a crew or passengers aboard a spacecraft, often with the spacecraft being operated directly by the onboard human crew. Spacecraft can also be ...
(mainly through participation in the
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
programme); as well as the launch and operation of missions to Mars and Moon. Further activities include science missions to Jupiter, Mercury, the Sun, Earth observation,
Asteroid impact avoidance
Asteroid impact avoidance encompasses the methods by which near-Earth objects (NEO) on a potential collision course with Earth could be diverted, preventing destructive impact events. An impact by a sufficiently large asteroid or other NEOs w ...
and
Telecommunications
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of ...
missions, designing launch vehicles; and maintaining Europe's Spaceport, the
Guiana Space Centre
The Guiana Space Centre (; CSG), also called Europe's Spaceport, is a spaceport to the northwest of Kourou in French Guiana, an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas region of France in South America. Kourou is located approxim ...
at
Kourou
Kourou (; ) is a commune in French Guiana, an overseas region and department of France in South America. Kourou is famous for being the location of the Guiana Space Centre, the main spaceport of France and the European Space Agency (ESA). It ...
(
French Guiana
French Guiana, or Guyane in French, is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France located on the northern coast of South America in the Guianas and the West Indies. Bordered by Suriname to the west ...
). Further programmes include space safety, satellite navigation, applications and commercialisation.
The main European launch vehicle
Ariane 6
Ariane 6 is a European expendable launch system developed for the European Space Agency (ESA) and manufactured by a consortium of European companies, led by the prime contractor ArianeGroup. As part of the Ariane rocket family, it is operate ...
is operated through
Arianespace
Arianespace SA is a French company founded in March 1980 as the world's first commercial launch service provider. It operates two launch vehicles: Vega C, a Small-lift launch vehicle, small-lift rocket, and Ariane 6, a Medium-lift launch vehicl ...
with ESA sharing in the costs of launching and further developing the launch vehicle. The agency also collaborates with
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
to manufacture the
Orion spacecraft
Orion (Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle or Orion MPCV) is a partially reusable crewed spacecraft used in NASA's Artemis program. The spacecraft consists of a Crew Module (CM) space capsule designed by Lockheed Martin that is paired with a Eu ...
service module
A service module (also known as an equipment module or instrument compartment) is a component of a crewed space capsule containing a variety of support systems used for spacecraft operations. Usually located in the uninhabited area of the spacec ...
ESM which flies on the
Space Launch System
The Space Launch System (SLS) is an American Super heavy-lift launch vehicle, super heavy-lift Expendable launch system, expendable launch vehicle used by NASA. As the primary launch vehicle of the Artemis program, Artemis Moon landing progra ...
.
History
Foundation
After
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, many European scientists left
Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's extent varies depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the Western half of the ancient Mediterranean ...
in order to work with the United States. Although the 1950s boom made it possible for Western European countries to invest in research and specifically in space-related activities, Western European scientists realised solely national projects would not be able to compete with the two main superpowers. In 1958, only months after the
Sputnik shock,
Edoardo Amaldi
Edoardo Amaldi (5 September 1908 – 5 December 1989) was an Italian physicist. He coined the term "neutrino" in conversations with Enrico Fermi distinguishing it from the heavier "neutron". He has been described as "one of the leading nuclear p ...
(Italy) and
Pierre Auger (France), two prominent members of the Western European scientific community, met to discuss the foundation of a common Western European space agency. The meeting was attended by scientific representatives from eight countries.
The Western European nations decided to have two agencies: one concerned with developing a launch system,
ELDO
250px, Europa II
200px, Rolls-Royce ''RZ-12''
200px, ''Coralie''
200px, ''Astris''
The European Launcher Development Organisation (ELDO) is a former European space research organisation. It was first developed in order to establish a sate ...
(European Launcher Development Organisation), and the other the precursor of the European Space Agency,
ESRO
The European Space Research Organisation (ESRO) was an international organisation founded by 10 European nations with the intention of jointly pursuing scientific research in space. It was founded in 1964. As an organisation ESRO was based on a ...
(European Space Research Organisation). The latter was established on 20 March 1964 by an agreement signed on 14 June 1962. From 1968 to 1972, ESRO launched seven research satellites, but ELDO was not able to deliver a launch vehicle. Both agencies struggled with the underfunding and diverging interests of their participants.
The ESA in its current form was founded with the ESA Convention in 1975, when ESRO was merged with ELDO. The ESA had ten founding member states:
Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
,
Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
,
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
,
West Germany
West Germany was the common English name for the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) from its formation on 23 May 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with East Germany on 3 October 1990. It is sometimes known as the Bonn Republi ...
,
Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
,
the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
,
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
,
Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
,
Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
, and the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
. These signed the ESA Convention in 1975 and deposited the instruments of ratification by 1980, when the convention came into force. During this interval the agency functioned in a de facto fashion. ESA launched its first major scientific mission in 1975,
Cos-B, a space probe monitoring
gamma-ray emissions in the universe, which was first worked on by ESRO.
Later activities

ESA collaborated with
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
on the
International Ultraviolet Explorer
International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE or Explorer 57, formerly SAS-D) was the first Space telescope, space observatory primarily designed to take ultraviolet (UV) electromagnetic spectrum. The satellite was a collaborative project between NA ...
(IUE), the world's first high-orbit telescope, which was launched in 1978 and operated successfully for 18 years. A number of successful Earth-orbit projects followed, and in 1986 ESA began
Giotto
Giotto di Bondone (; – January 8, 1337), known mononymously as Giotto, was an List of Italian painters, Italian painter and architect from Florence during the Late Middle Ages. He worked during the International Gothic, Gothic and Italian Ren ...
, its first deep-space mission, to study the comets
Halley Halley may refer to:
Science
* Halley's Comet, officially designated 1P/Halley, a comet that becomes visible from Earth every 75-76 years
* Halley (lunar crater), a lunar crater named after Edmond Halley
* Halley (Martian crater), a Martian cra ...
and
Grigg–Skjellerup.
Hipparcos
''Hipparcos'' was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions and distances of ...
, a star-mapping mission, was launched in 1989 and in the 1990s
SOHO
SoHo, short for "South of Houston Street, Houston Street", is a neighborhood in Lower Manhattan, New York City. Since the 1970s, the neighborhood has been the location of many artists' lofts and art galleries, art installations such as The Wall ...
, ''
Ulysses
Ulysses is the Latin name for Odysseus, a legendary Greek hero recognized for his intelligence and cunning. He is famous for his long, adventurous journey home to Ithaca after the Trojan War, as narrated in Homer's Odyssey.
Ulysses may also refer ...
'' and the
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the Orbiting Solar Observatory, first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most ...
were all jointly carried out with NASA. Later scientific missions in cooperation with NASA include the ''
Cassini–Huygens
''Cassini–Huygens'' ( ), commonly called ''Cassini'', was a space research, space-research mission by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI) to send a space probe to study the planet Saturn and its system, i ...
'' space probe, to which the ESA contributed by building the
Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
landing module ''
Huygens''.
As the successor of
ELDO
250px, Europa II
200px, Rolls-Royce ''RZ-12''
200px, ''Coralie''
200px, ''Astris''
The European Launcher Development Organisation (ELDO) is a former European space research organisation. It was first developed in order to establish a sate ...
, the ESA has also constructed rockets for scientific and commercial payloads.
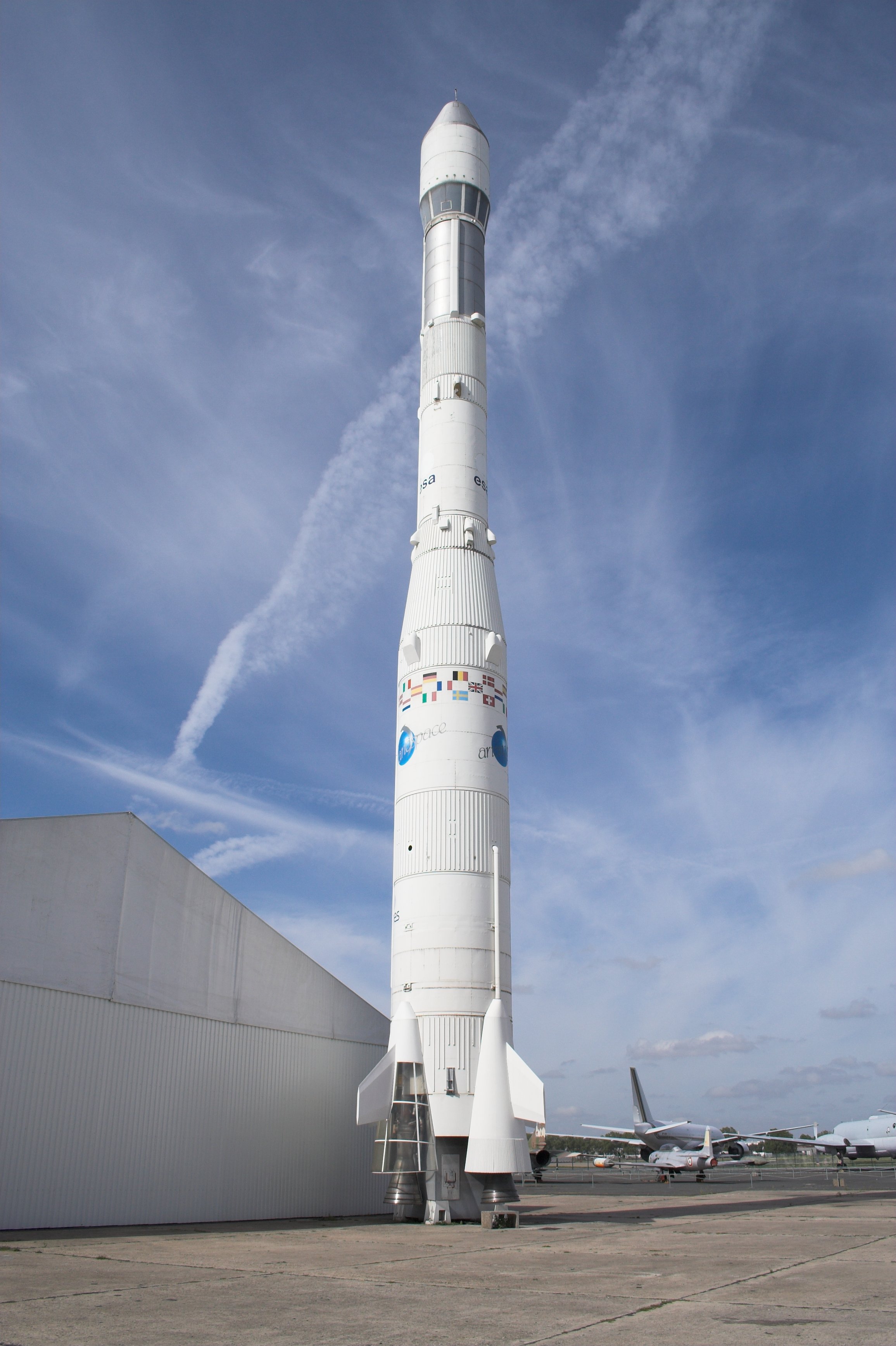
Ariane 1
Ariane 1 () was the first rocket in the Ariane family of expendable launch systems. It was developed for and operated by the European Space Agency (ESA), which had been formed in 1973, the same year that development of the launcher had commenc ...
, launched in 1979, carried mostly commercial payloads into orbit from 1984 onward. The next two versions of the Ariane rocket were intermediate stages in the development of a more advanced launch system, the
Ariane 4
The Ariane 4 was a European expendable rocket, expendable launch vehicle in the Ariane (rocket family), Ariane family, developed by the (CNES), the Government of France, French space agency, for the European Space Agency (ESA). The manufacturi ...
, which operated between 1988 and 2003 and established the ESA as the world leader in commercial space launches in the 1990s. Although the succeeding
Ariane 5
Ariane 5 is a retired European heavy-lift space launch vehicle operated by Arianespace for the European Space Agency (ESA). It was launched from the Guiana Space Centre (CSG) in French Guiana. It was used to deliver payloads into geostationar ...
experienced a failure on its first flight, it has since firmly established itself within the heavily competitive commercial space launch market with 112 successful launches until 2023. The successor launch vehicle,
Ariane 6
Ariane 6 is a European expendable launch system developed for the European Space Agency (ESA) and manufactured by a consortium of European companies, led by the prime contractor ArianeGroup. As part of the Ariane rocket family, it is operate ...
, had its maiden flight on 9 July 2024. It was followed by flight VA263, the first commercial launch, on 6 March 2025 at 13:24 local time (16:24 BST, 17:24 CET), delivering the
Composante Spatiale Optique
Composante Spatiale Optique (CSO; English: Optical Space Component) is a French military Reconnaissance satellite program of third generation. It replaces the Helios 2 satellites. It is sometimes referred to as the MUltinational Space-based Im ...
CSO-3 satellite.
The beginning of the new millennium saw the ESA become, along with agencies like NASA,
JAXA
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into o ...
,
ISRO
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO ) is India's national space agency, headquartered in Bengaluru, Karnataka. It serves as the principal research and development arm of the Department of Space (DoS), overseen by the Prime Minister o ...
, the
CSA and
Roscosmos
The State Corporation for Space Activities "Roscosmos", commonly known simply as Roscosmos (), is a State corporation (Russia), state corporation of the Russian Federation responsible for space science, space flights, List of space agencies, c ...
, one of the major participants in scientific
space research
Space research is scientific study carried out in outer space, and by studying outer space. From the use of space technology to the observable universe, space research is a wide research field. Earth science, materials science, biology, medicine ...
. Although ESA had relied on co-operation with NASA in previous decades, especially the 1990s, changed circumstances (such as tough legal restrictions on information sharing by the
United States military
The United States Armed Forces are the Military, military forces of the United States. U.S. United States Code, federal law names six armed forces: the United States Army, Army, United States Marine Corps, Marine Corps, United States Navy, Na ...
) led to decisions to rely more on itself and on co-operation with Russia. A 2011 press issue thus stated:
Notable ESA programmes include
SMART-1
SMART-1 was a European Space Agency satellite that orbited the Moon. It was launched on 27 September 2003 at 23:14 Coordinated Universal Time, UTC from the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana. "SMART-1" stands for Small Missions for Ad ...
, a probe testing cutting-edge space propulsion technology, the ''
Mars Express
''Mars Express'' is a space exploration mission by the European Space Agency, European Space Agency (ESA) exploring the planet Mars and its moons since 2003, and the first planetary mission attempted by ESA.
''Mars Express'' consisted of two ...
'' and ''
Venus Express
''Venus Express'' (VEX) was the first Venus exploration mission of the European Space Agency (ESA). Launched in November 2005, it arrived at Venus in April 2006 and began continuously sending back science data from its polar orbit around Venus. ...
'' missions, as well as the development of the Ariane 5 rocket and its role in the
ISS
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), ESA (Europe), ...
partnership. The ESA maintains its scientific and research projects mainly for astronomy-space missions such as
Corot
CoRoT (French: ; English: Convection, Rotation and planetary Transits) was a space telescope mission which operated from 2006 to 2013. The mission's two objectives were to search for extrasolar planets with short orbital periods, particularly t ...
, launched on 27 December 2006, a milestone in the search for
exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first confirmed detection of an exoplanet was in 1992 around a pulsar, and the first detection around a main-sequence star was in 1995. A different planet, first det ...
s.
On 21 January 2019,
ArianeGroup
ArianeGroup (formerly Airbus Safran Launchers) is an aerospace company based in France. A joint venture between Airbus and Safran, the company was founded in 2015 and is headquartered in Issy-les-Moulineaux near Paris. It consists of three core ...
and
Arianespace
Arianespace SA is a French company founded in March 1980 as the world's first commercial launch service provider. It operates two launch vehicles: Vega C, a Small-lift launch vehicle, small-lift rocket, and Ariane 6, a Medium-lift launch vehicl ...
announced a one-year contract with the ESA to study and prepare for a mission to mine the Moon for lunar
regolith
Regolith () is a blanket of unconsolidated, loose, heterogeneous superficial deposits covering solid rock. It includes dust, broken rocks, and other related materials and is present on Earth, the Moon, Mars, some asteroids, and other terrestria ...
.
In 2021 the ESA ministerial council agreed to the "
Matosinhos
Matosinhos () is a City#Portugal, city and a Concelho, municipality in the district of Porto District, Porto in Portugal. The municipality covers an area of approximately and had 172,557 inhabitants in 2021. It is bordered by the municipalities o ...
manifesto" which set three priority areas (referred to as ''accelerators'') "space for a green future, a rapid and resilient crisis response, and the protection of space assets", and two further high visibility projects (referred to as ''inspirators'') an icy moon sample return mission; and human space exploration. In the same year the recruitment process began for the
2022 European Space Agency Astronaut Group
The 2022 European Space Agency Astronaut Group is the latest class of the European Astronaut Corps. The selection recruited five "career" astronauts as well as 12 "reserve/project" astronauts (including one "astronaut with a physical disability" ...
.
The first half of 2023 saw the launches of the
Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer
The Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (Juice, formerly JUICE) is an interplanetary spacecraft on its way to orbit and study three icy moons of Jupiter (planet), Jupiter: Ganymede (moon), Ganymede, Callisto (moon), Callisto, and Europa (moon), Europa ...
and the
Euclid spacecraft, the latter developed jointly with the Euclid Consortium. After 10 years of planning and building, it is designed to better understand
dark energy
In physical cosmology and astronomy, dark energy is a proposed form of energy that affects the universe on the largest scales. Its primary effect is to drive the accelerating expansion of the universe. It also slows the rate of structure format ...
and
dark matter
In astronomy, dark matter is an invisible and hypothetical form of matter that does not interact with light or other electromagnetic radiation. Dark matter is implied by gravity, gravitational effects that cannot be explained by general relat ...
by accurately measuring the
accelerating expansion of the universe.
The most notable ESA mission of 2024 was
Hera (space mission)
''Hera'' is a spacecraft developed by the European Space Agency for its space safety program. Its primary mission objective is to study the Didymos binary asteroid system that was impacted four years earlier by the NASA Double Asteroid Redirec ...
, which launched on 7 October that year to perform a post-impact survey of the asteroid
Dimorphos
Dimorphos (formal designation (65803) Didymos I; provisional designation S/2003 (65803) 1) is a natural satellite or minor-planet moon, moon of the near-Earth object, near-Earth asteroid 65803 Didymos, with which it forms a Binary asteroid, bina ...
which was deflected by NASA's
Double Asteroid Redirection Test
The Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) was a NASA space mission aimed at testing a method of planetary defense against near-Earth objects (NEOs). It was designed to assess how much a spacecraft impact deflects an asteroid through its trans ...
mission.
In early 2025, the European Space Agency released its Strategy 2040, a long-term roadmap adopted by the ESA council to define the agency's priorities. The strategy is centered on 5 key goals:
* Protecting the planet and climate
* Advancing space exploration
* Strengthening European autonomy and resilience
* Boosting economic growth and competitiveness
* Inspiring future generations
In March 2025, ESA officially launched its European Launcher Challenge (ELC) by publishing the Invitation to Tender (ITT). Initially introduced in November 2023, the program aims to foster new European sovereign launch capabilities, beginning with small launch vehicles and ultimately paving the way for an Ariane 6 successor.
Facilities
The agency's facilities date back to ESRO and are deliberately distributed among various countries and areas. The most important are the following centres:
*ESA headquarters in Paris, France;
*ESA science missions are based at
ESTEC
The European Space Research and Technology Centre (ESTEC) is the European Space Agency's main technology development and test centre for spacecraft and space technology. It is situated in Noordwijk, South Holland, in the western Netherlands, alth ...
in
Noordwijk
Noordwijk () is a town and municipality in the west of the Netherlands, in the provinces of the Netherlands, province of South Holland. The municipality covers an area of of which is water and had a population of in .
On 1 January 2019, the f ...
, Netherlands;
*Earth Observation missions at the
ESA Centre for Earth Observation
The ESA Centre for Earth Observation (also known as the European Space Research Institute or ESRIN) is a research centre belonging to the European Space Agency (ESA), located in Frascati (Rome) Italy. It is dedicated to research involving ear ...
in
Frascati
Frascati () is a city and in the Metropolitan City of Rome Capital in the Lazio region of central Italy. It is located south-east of Rome, on the Alban Hills close to the ancient city of Tusculum. Frascati is closely associated with science, ...
, Italy;
*ESA Mission Control (
ESOC
The European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) serves as the main mission control centre for the European Space Agency (ESA) and is located in Darmstadt, Germany. ESOC's primary function is the operation of uncrewed spacecraft on behalf of ESA and ...
) is in
Darmstadt
Darmstadt () is a city in the States of Germany, state of Hesse in Germany, located in the southern part of the Frankfurt Rhine Main Area, Rhine-Main-Area (Frankfurt Metropolitan Region). Darmstadt has around 160,000 inhabitants, making it the ...
, Germany;
*The
European Astronaut Centre
The European Astronaut Centre (EAC) (German: Europäisches Astronautenzentrum, French: Centre des astronautes européens), is an establishment of the European Space Agency and home of the European Astronaut Corps. It is near to Cologne, Germany, ...
(EAC) that trains astronauts for future missions is situated in
Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
, Germany;
*The
European Centre for Space Applications and Telecommunications
The European Centre for Space Applications and Telecommunications or ECSAT is a research centre belonging to the European Space Agency (ESA) and located on the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus in Oxfordshire, United Kingdom.
It was creat ...
(ECSAT), a research institute created in 2009, is located in
Harwell, England, United Kingdom;
*The
European Space Astronomy Centre
The European Space Astronomy Centre (ESAC) near Madrid in Spain is a research centre of the European Space Agency (ESA). ESAC is the lead institution for space science (astronomy, Solar System exploration and fundamental physics) using ESA miss ...
(ESAC) is located in
Villanueva de la Cañada,
Madrid
Madrid ( ; ) is the capital and List of largest cities in Spain, most populous municipality of Spain. It has almost 3.5 million inhabitants and a Madrid metropolitan area, metropolitan area population of approximately 7 million. It i ...
, Spain.
*The
European Space Security and Education Centre
The European Space Security and Education Centre (ESEC) is a centre of excellence for space cybersecurity services of the European Space Agency (ESA), home to its Proba mission control centres, the Space Weather Data Centre, the Education Training ...
(ESEC), located in Redu, Belgium;
*The
ESTRACK
The European Space Tracking (ESTRACK) network consists of a number of ground-based space-tracking stations belonging to the European Space Agency (ESA), and operated by the European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) in Darmstadt, Germany. The st ...
tracking and deep space communication network.
*Many other facilities are operated by national space agencies in close collaboration with ESA.
**
Esrange
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
Esrange Space Center is a rocket range and research centre located about 40 kilometers east of the town of Kiruna in northern Sweden. It is a base for scientific research with high-altitude balloons, investigation of the a ...
near
Kiruna
(; ; ; ) is the northernmost Stad (Sweden), city in Sweden, situated in the province of Lapland, Sweden, Lapland. It had 17,002 inhabitants in 2016 and is the seat of Kiruna Municipality (population: 23,167 in 2016) in Norrbotten County. The c ...
in Sweden;
**
Guiana Space Centre
The Guiana Space Centre (; CSG), also called Europe's Spaceport, is a spaceport to the northwest of Kourou in French Guiana, an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas region of France in South America. Kourou is located approxim ...
in Kourou, France;
**
Toulouse Space Centre
The Toulouse Space Centre (; CST) is a research and development centre of CNES. Founded in September 1968, it is located in the Rangueil-Lespinet district of Toulouse in the Haute-Garonne department in the Occitanie region in France. The larg ...
, France;
**
Institute of Space Propulsion
An institute is an organizational body created for a certain purpose. They are often research organisations (research institutes) created to do research on specific topics, or can also be a professional body.
In some countries, institutes ca ...
in
Lampoldshausen
Lampoldshausen is a small village on the southern edge of the Harthausen Forest near Möckmühl in Baden-Württemberg, Germany.
Aerospace Village
Within the global Aerospace community Lampoldshausen is known as Aerospace Village by the Institute ...
, Germany;
**
Columbus Control Centre
The Columbus Control Centre also known by its radio callsign, Mission Control Munich, is the mission control centre which is used to control the ''Columbus'' research laboratory, which is part of the International Space Station (ISS). The co ...
in
Oberpfaffenhofen
Oberpfaffenhofen is a village that is part of the municipality of Weßling in the district of Starnberg, Bavaria, Germany. It is located about from the city center of Munich.
Village
The village is home to the Oberpfaffenhofen Airport and a ...
, Germany.
Mission
The treaty establishing the European Space Agency reads:
The ESA is responsible for setting a unified space and related industrial policy, recommending space objectives to the member states, and integrating national programs like satellite development, into the European program as much as possible.
Jean-Jacques Dordain
Jean-Jacques Dordain (born 14 April 1946) was Director General of the European Space Agency between 2003 and 2015.
Graduating at École Centrale Paris in 1968, Dordain began his scientific career in the French Aerospace Research Agency (ONERA) and ...
– ESA's Director General (2003–2015) – outlined the European Space Agency's mission in a 2003 interview:
Activities and programmes
The ESA describes its work in two overlapping ways:
* For the general public, the various fields of work are described as "Activities".
* Budgets are organised as "Programmes".
These are either mandatory or optional.
Activities
According to the ESA website, the activities are:
*Observing the Earth
*Human and Robotic Exploration
*Launchers
*Navigation
*Space Science
*Space Engineering & Technology
*Operations
*Telecommunications & Integrated Applications
*Preparing for the Future
*Space for Climate
Programmes
Mandatory
Every member country (known as 'Member States') must contribute to these programmes: The
European Space Agency Science Programme
The Science Programme of the European Space Agency is a long-term programme of Outline of space science, space science and space exploration missions. Managed by the agency's Directorate of Science, The programme funds the development, launch, ...
is a long-term programme of space science missions.
*Technology Development Element Programme
*Science Core Technology Programme
*General Study Programme
*European Component Initiative
Optional
Depending on their individual choices the countries can contribute to the following programmes, becoming 'Participating States', listed according to:
Employment
As of 2023, Many other facilities are operated by national space agencies in close collaboration with the ESA. The ESA employs around 2,547 people, and thousands of contractors. Initially, new employees are contracted for an expandable four-year term, which is until the organization's retirement age of 63. According to the ESA's documents, the staff can receive myriad of perks, such as financial childcare support, retirement plans, and financial help when migrating. The ESA also prevents employees from disclosing any private documents or correspondences to outside parties. ''
Ars Technica
''Ars Technica'' is a website covering news and opinions in technology, science, politics, and society, created by Ken Fisher and Jon Stokes in 1998. It publishes news, reviews, and guides on issues such as computer hardware and software, sci ...
s 2023 report, which contained testimonies of 18 people, suggested that there is a widespread harassment between management and its employees, especially with its contractors. Since the ESA is an international organization, unaffiliated with any single nation, any form of legal action is difficult to raise against the organization.
Member states, funding and budget
Membership and contribution to the ESA
Member states participate to varying degrees with both mandatory space programs and those that are optional. , the mandatory programmes made up 25% of total expenditures while optional space programmes were the other 75%.
The ESA has traditionally implemented a policy of "georeturn", where funds that ESA member states provide to the ESA "are returned in the form of contracts to companies in those countries."
By 2015, the ESA was an intergovernmental organisation of 22 member states.
The 2008 ESA budget amounted to €3.0 billion whilst the 2009 budget amounted to €3.6 billion. The total budget amounted to about €3.7 billion in 2010, €3.99 billion in 2011, €4.02 billion in 2012, €4.28 billion in 2013, €4.10 billion in 2014, €4.43 billion in 2015, €5.25 billion in 2016, €5.75 billion in 2017, €5.60 billion in 2018, €5.72 billion in 2019, €6,68 billion in 2020, €6.49 billion in 2021, €7.15 billion in 2022, €7.46 billion in 2023 and €7.79 billion in 2024.
[*
*
*
*
]
/ref>
English and French are the two official languages of the ESA. Additionally, official documents are also provided in German and documents regarding the Spacelab
Spacelab was a reusable laboratory developed by European Space Agency (ESA) and used on certain spaceflights flown by the Space Shuttle. The laboratory comprised multiple components, including a pressurized module, an unpressurized carrier, ...
have been also provided in Italian. If found appropriate, the agency may conduct its correspondence in any language of a member state.
The following table lists all the member states and adjunct members, their ESA convention ratification dates, and their contributions as of 2024:
Non-full member states
Previously associated members were Austria, Norway and Finland and Slovenia, all of which later joined the ESA as full members. Since January 2025 there have been four associate members: Latvia, Lithuania, Slovakia and Canada. The three European members have shown interest in full membership and may eventually apply within the next years.
Latvia
Latvia became the second current associated member on 30 June 2020, when the Association Agreement was signed by ESA Director Jan Wörner and the Minister of Education and Science of Latvia
Minister may refer to:
* Minister (Christianity), a Christian cleric
** Minister (Catholic Church)
* Minister (government), a member of government who heads a ministry (government department)
** Minister without portfolio, a member of government w ...
, Ilga Šuplinska
Ilga Šuplinska (born in Dagda, Latvia, Dagda) is a Latvia, Latvian politician. From 23 January 2019 to 3 June 2021, she served as Minister for Education and Science in the First Kariņš cabinet, Kariņš cabinet.
References
Living ...
in Riga
Riga ( ) is the capital, Primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Latvia, largest city of Latvia. Home to 591,882 inhabitants (as of 2025), the city accounts for a third of Latvia's total population. The population of Riga Planni ...
. The Saeima
The Saeima () is the parliament of the Latvia, Republic of Latvia. It is a unicameral parliament consisting of 100 members who are elected by proportional representation, with seats allocated to political parties which gain at least 5% of the p ...
ratified it on 27 July.
Lithuania
In May 2021, Lithuania became the third current associated member. As a consequence its citizens became eligible to apply to the 2022 ESA Astronaut group
The 2022 European Space Agency Astronaut Group is the latest class of the European Astronaut Corps. The selection recruited five "career" astronauts as well as 12 "reserve/project" astronauts (including one "astronaut with a physical disability") ...
, applications for which were scheduled to close one week later. The deadline was therefore extended by three weeks to allow Lithuanians a fair chance to apply.
Slovakia
Slovakia's Associate membership came into effect on 13 October 2022, for an initial duration of seven years. The Association Agreement supersedes the European Cooperating State (ECS) Agreement, which entered into force upon Slovakia's subscription to the Plan for European Cooperating States Charter on 4 February 2016, a scheme introduced at ESA in 2001. The ECS Agreement was subsequently extended until 3 August 2022.
Canada
Since 1 January 1979, Canada has had the special status of a Cooperating State within the ESA. By virtue of this accord, the Canadian Space Agency
The Canadian Space Agency (CSA; ) is the national space agency of Canada, established in 1990 by the ''Canadian Space Agency Act''.
The President of the Canadian Space Agency, president is Lisa Campbell (civil servant), Lisa Campbell, who took ...
takes part in the ESA's deliberative bodies and decision-making and also in the ESA's programmes and activities. Canadian firms can bid for and receive contracts to work on programmes. The accord has a provision ensuring a fair industrial return to Canada. The most recent Cooperation Agreement was signed on 15 December 2010 with a term extending to 2020. For 2014, Canada's annual assessed contribution to the ESA general budget was €6,059,449 ( CAD$8,559,050). For 2017, Canada has increased its annual contribution to €21,600,000 ( CAD$30,000,000).
Budget appropriation and allocation
 The ESA is funded from annual contributions by
The ESA is funded from annual contributions by national
National may refer to:
Common uses
* Nation or country
** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen
Places in the United States
* National, Maryland, c ...
governments of members as well as from an annual contribution by the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
(EU).COROT
CoRoT (French: ; English: Convection, Rotation and planetary Transits) was a space telescope mission which operated from 2006 to 2013. The mission's two objectives were to search for extrasolar planets with short orbital periods, particularly t ...
). Also, the ESA is not the only European governmental space organisation (for example European Union Satellite Centre
The European Union Satellite Centre (EU SatCen; previously EUSC) is the agency of the European Union (EU) that supports the EU's decision-making in the field of the Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP), including crisis management missi ...
and the European Union Space Programme Agency).
Enlargement
After the decision of the ESA Council of 21/22 March 2001, the procedure for accession of the European states was detailed as described the document titled "The Plan for European Co-operating States (PECS)". Nations that want to become a full member of the ESA do so in 3 stages. First a Cooperation Agreement is signed between the country and ESA. In this stage, the country has very limited financial responsibilities. If a country wants to co-operate more fully with ESA, it signs a European Cooperating State (ECS) Agreement, albeit to be a candidate for said agreement, a country must be European. The ECS Agreement makes companies based in the country eligible for participation in ESA procurements. The country can also participate in all ESA programmes, except for the Basic Technology Research Programme. While the financial contribution of the country concerned increases, it is still much lower than that of a full member state. The agreement is normally followed by a Plan For European Cooperating State (or PECS Charter). This is a 5-year programme of basic research and development
Research and development (R&D or R+D), known in some countries as OKB, experiment and design, is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products. R&D constitutes the first stage ...
activities aimed at improving the nation's space industry
Space industry refers to economic activities related to manufacturing components that go into outer space (Earth's orbit or beyond), delivering them to those regions, and related services. Owing to the prominence of satellite-related activiti ...
capacity. At the end of the 5-year period, the country can either begin negotiations to become a full member state or an associated state or sign a new PECS Charter. Many countries, most of which joined the EU in both 2004 and 2007, have started to co-operate with the ESA on various levels:
During the Ministerial Meeting in December 2014, ESA ministers approved a resolution calling for discussions to begin with Israel, Australia and South Africa on future association agreements. The ministers noted that "concrete cooperation is at an advanced stage" with these nations and that "prospects for mutual benefits are existing".LEO
Leo is the Latin word for lion. It most often refers to:
* Leo (constellation), a constellation of stars in the night sky
* Leo (astrology), an astrological sign of the zodiac
* Leo (given name), a given name in several languages, usually mas ...
exploration, including a continuation of ISS
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), ESA (Europe), ...
cooperation and the development of a robust plan for the coordinated use of space transportation vehicles and systems for exploration purposes, participation in robotic missions for the exploration of the Moon, the robotic exploration of Mars, leading to a broad Mars Sample Return mission in which Europe should be involved as a full partner, and human missions beyond LEO in the longer term."Australian Space Agency
The Australian Space Agency is an agency of the Australian Government responsible for the development of Australia's commercial aerospace industry, coordinating domestic space activities, identifying opportunities and facilitating internatio ...
signed a joint statement of intent "to explore deeper cooperation and identify projects in a range of areas including deep space, communications, navigation, remote asset management, data analytics
Analytics is the systematic computational analysis of data or statistics. It is used for the discovery, interpretation, and communication of meaningful patterns in data, which also falls under and directly relates to the umbrella term, data sci ...
and mission support."framework agreement
In the context of negotiations, a framework agreement is an agreement between two parties that recognizes that the parties have not come to a final agreement on all matters relevant to the relationship between them, but have come to agreement on en ...
signed by the two entities.
On 17 November 2020, ESA signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with the South African National Space Agency
The South African National Space Agency (SANSA) is South Africa's government agency responsible for the promotion and development of aeronautics and aerospace space research. It fosters cooperation in space-related activities and research in sp ...
(SANSA). SANSA CEO Dr. Valanathan Munsami tweeted: "Today saw another landmark event for SANSA with the signing of an MoU with the ESA. This builds on initiatives that we have been discussing for a while already and which gives effect to these. Thanks Jan for your hand of friendship and making this possible."
Launch vehicles
The ESA currently has two operational launch vehicles Vega-C
VegaC, or Vega Consolidation, is a European expendable, small-lift launch vehicle developed and produced by Avio. It is an evolution of the original Vega launcher, designed to offer greater launch performance and flexibility.
Approved for devel ...
and Ariane 6
Ariane 6 is a European expendable launch system developed for the European Space Agency (ESA) and manufactured by a consortium of European companies, led by the prime contractor ArianeGroup. As part of the Ariane rocket family, it is operate ...
. Rocket launches are carried out by Arianespace
Arianespace SA is a French company founded in March 1980 as the world's first commercial launch service provider. It operates two launch vehicles: Vega C, a Small-lift launch vehicle, small-lift rocket, and Ariane 6, a Medium-lift launch vehicl ...
, which has 23 shareholders representing the industry that manufactures the Ariane 5 as well as CNES
CNES () is the French national space agency. Headquartered in central Paris, the agency is overseen by the ministries of the Armed Forces, Economy and Finance and Higher Education, Research and Innovation.
It operates from the Toulouse Spac ...
, at the ESA's Guiana Space Centre
The Guiana Space Centre (; CSG), also called Europe's Spaceport, is a spaceport to the northwest of Kourou in French Guiana, an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas region of France in South America. Kourou is located approxim ...
. Because many communication satellites have equatorial orbits, launches from French Guiana
French Guiana, or Guyane in French, is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France located on the northern coast of South America in the Guianas and the West Indies. Bordered by Suriname to the west ...
are able to take larger payloads into space than from spaceports at higher latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
s. In addition, equatorial launches give spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle that is designed spaceflight, to fly and operate in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth observation, Weather s ...
an extra 'push' of nearly 500 m/s due to the higher rotational velocity
Rotational frequency, also known as rotational speed or rate of rotation (symbols ''ν'', lowercase Greek nu, and also ''n''), is the frequency of rotation of an object around an axis.
Its SI unit is the reciprocal seconds (s−1); other com ...
of the Earth at the equator compared to near the Earth's poles where rotational velocity approaches zero.
Ariane 6
Ariane 6 is a heavy lift
In transportation, heavy lift refers to the handling and installation of heavy items which are indivisible, and of weights generally accepted to be over 100 tons and of widths/heights of more than 100 meters. These oversized items are transported ...
expendable launch vehicle
An expendable launch system (or expendable launch vehicle/ELV) is a launch vehicle that can be launched only once, after which its components are destroyed during reentry or impact with Earth, or discarded in space. ELVs typically consist of s ...
developed by Arianespace
Arianespace SA is a French company founded in March 1980 as the world's first commercial launch service provider. It operates two launch vehicles: Vega C, a Small-lift launch vehicle, small-lift rocket, and Ariane 6, a Medium-lift launch vehicl ...
. The Ariane 6 entered into its inaugural flight campaign on 26 April 2024 with the flight conducted on 9 July 2024.
Vega-C
 Vega is the ESA's carrier for small satellites. Developed by seven ESA members led by
Vega is the ESA's carrier for small satellites. Developed by seven ESA members led by Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
. It is capable of carrying a payload with a mass of between 300 and 1500 kg to an altitude of 700 km, for low polar orbit
A polar orbit is one in which a satellite passes above or nearly above both poles of the body being orbited (usually a planet such as the Earth, but possibly another body such as the Moon or Sun) on each revolution. It has an inclination of abo ...
. Its maiden launch from Kourou
Kourou (; ) is a commune in French Guiana, an overseas region and department of France in South America. Kourou is famous for being the location of the Guiana Space Centre, the main spaceport of France and the European Space Agency (ESA). It ...
was on 13 February 2012. Vega began full commercial exploitation in December 2015.
The rocket has three solid propulsion stages and a liquid propulsion upper stage
A multistage rocket or step rocket is a launch vehicle that uses two or more rocket ''stages'', each of which contains its own Rocket engine, engines and Rocket propellant, propellant. A ''tandem'' or ''serial'' stage is mounted on top of anoth ...
(the AVUM
Vega (, , ) was a European expendable small-lift launch vehicle developed by Avio and operated by Arianespace for the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Italian Space Agency (ASI). Designed to carry payloads between into low Earth and pol ...
) for accurate orbital insertion and the ability to place multiple payloads
Payload is the object or the entity that is being carried by an aircraft or launch vehicle. Sometimes payload also refers to the carrying capacity of an aircraft or launch vehicle, usually measured in terms of weight. Depending on the nature of t ...
into different orbits.
A larger version of the Vega launcher, Vega-C
VegaC, or Vega Consolidation, is a European expendable, small-lift launch vehicle developed and produced by Avio. It is an evolution of the original Vega launcher, designed to offer greater launch performance and flexibility.
Approved for devel ...
had its first flight in July 2022. The new evolution of the rocket incorporates a larger first stage booster, the P120C
The P120C is a solid-fuel rocket motor developed for use as the first stage of the Vega-C launch vehicle and as strap-on boosters for the Ariane 6. It was developed by Europropulsion, a joint venture between Avio and ArianeGroup, for the Europ ...
replacing the P80, an upgraded Zefiro (rocket stage)
Zefiro is a family of solid-fuel rocket motors developed by Avio and used on the European Space Agency Vega rocket. The name Zefiro derives from the acronym ZEro FIrst stage ROcket, conceived when this motor was intended to be used as first ...
second stage, and the AVUM+ upper stage. This new variant enables larger single payloads, dual payloads, return missions, and orbital transfer capabilities.
Ariane launch vehicle development funding
Historically, the Ariane family rockets have been funded primarily "with money contributed by ESA governments seeking to participate in the program rather than through competitive industry bids. This as meant thatgovernments commit multiyear funding to the development with the expectation of a roughly 90% return on investment in the form of industrial workshare." ESA is proposing changes to this scheme by moving to competitive
Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, indi ...
bids for the development of the Ariane 6
Ariane 6 is a European expendable launch system developed for the European Space Agency (ESA) and manufactured by a consortium of European companies, led by the prime contractor ArianeGroup. As part of the Ariane rocket family, it is operate ...
.
Future rocket development
Future projects include the Prometheus
In Greek mythology, Prometheus (; , , possibly meaning "forethought")Smith"Prometheus". is a Titans, Titan. He is best known for defying the Olympian gods by taking theft of fire, fire from them and giving it to humanity in the form of technol ...
reusable engine technology demonstrator, Phoebus (an upgraded second stage for Ariane 6), and Themis
In Greek mythology and religion, Themis (; ) is the goddess and personification of justice, divine order, law, and custom. She is one of the twelve Titan children of Gaia and Uranus, and the second wife of Zeus. She is associated with oracles a ...
(a reusable first stage).
Human space flight
Formation and development
 At the time the ESA was formed, its main goals did not encompass human space flight; rather it considered itself to be primarily a scientific research organisation for uncrewed space exploration in contrast to its American and Soviet counterparts. It is therefore not surprising that the first non-Soviet European in space was not an ESA astronaut on a European space craft; it was
At the time the ESA was formed, its main goals did not encompass human space flight; rather it considered itself to be primarily a scientific research organisation for uncrewed space exploration in contrast to its American and Soviet counterparts. It is therefore not surprising that the first non-Soviet European in space was not an ESA astronaut on a European space craft; it was Czechoslovak
Czechoslovak may refer to:
*A demonym or adjective pertaining to Czechoslovakia (1918–93)
**First Czechoslovak Republic (1918–38)
**Second Czechoslovak Republic (1938–39)
**Third Czechoslovak Republic (1948–60)
** Fourth Czechoslovak Repu ...
Vladimír Remek
Vladimír Remek (born 26 September 1948) is a Czech politician and diplomat, as well as a former cosmonaut and military pilot. He flew aboard Soyuz 28 from 2 to 10 March 1978, becoming the first and only Czechoslovak in space. As the first c ...
who in 1978 became the first non-Soviet or American in space (the first man in space being Yuri Gagarin
Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin; Gagarin's first name is sometimes transliterated as ''Yuriy'', ''Youri'', or ''Yury''. (9 March 1934 – 27 March 1968) was a Soviet pilot and cosmonaut who, aboard the first successful Human spaceflight, crewed sp ...
of the Soviet Union) – on a Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
Soyuz spacecraft
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraf ...
, followed by the Pole Mirosław Hermaszewski
Mirosław Hermaszewski (; 15 September 1941 – 12 December 2022) was a Polish cosmonaut, fighter plane pilot, and Polish Air Force officer. He became the first and, at the time of his death in December 2022, only Polish national to ever go t ...
and East German Sigmund Jähn
Sigmund Werner Paul Jähn (; 13 February 1937 – 21 September 2019) was a German Aircraft pilot, pilot, cosmonaut, and ''Generalmajor#Generalmajor in East Germany, Generalmajor'' (equivalent to a Brigadier General in Western armies) in the Nat ...
in the same year. This Soviet co-operation programme, known as Intercosmos
Interkosmos () was a Soviet space program, designed to help the Soviet Union's allies with crewed and uncrewed space missions.
The program was formed in April 1967 in Moscow. All members of the program from USSR were given the Hero of the Sov ...
, primarily involved the participation of Eastern bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
countries. In 1982, however, Jean-Loup Chrétien
Jean-Loup Jacques Marie Chrétien (born 20 August 1938) is a French retired ''Général de Brigade'' (brigadier general) in the ''Armée de l'Air'' (French air force), and a former CNES spationaut. He flew on two Franco-Soviet space missions ...
became the first non-Communist Bloc astronaut on a flight to the Soviet Salyut 7
Salyut 7 (), also known as DOS-6 (Durable Orbital Station 6) was a space station in low Earth orbit from April 1982 to February 1991. It was first crewed in May 1982 with two crew via Soyuz T-5, and last visited in June 1986, by Soyuz T-15. Va ...
space station.
Because Chrétien did not officially fly into space as an ESA astronaut, but rather as a member of the French CNES
CNES () is the French national space agency. Headquartered in central Paris, the agency is overseen by the ministries of the Armed Forces, Economy and Finance and Higher Education, Research and Innovation.
It operates from the Toulouse Spac ...
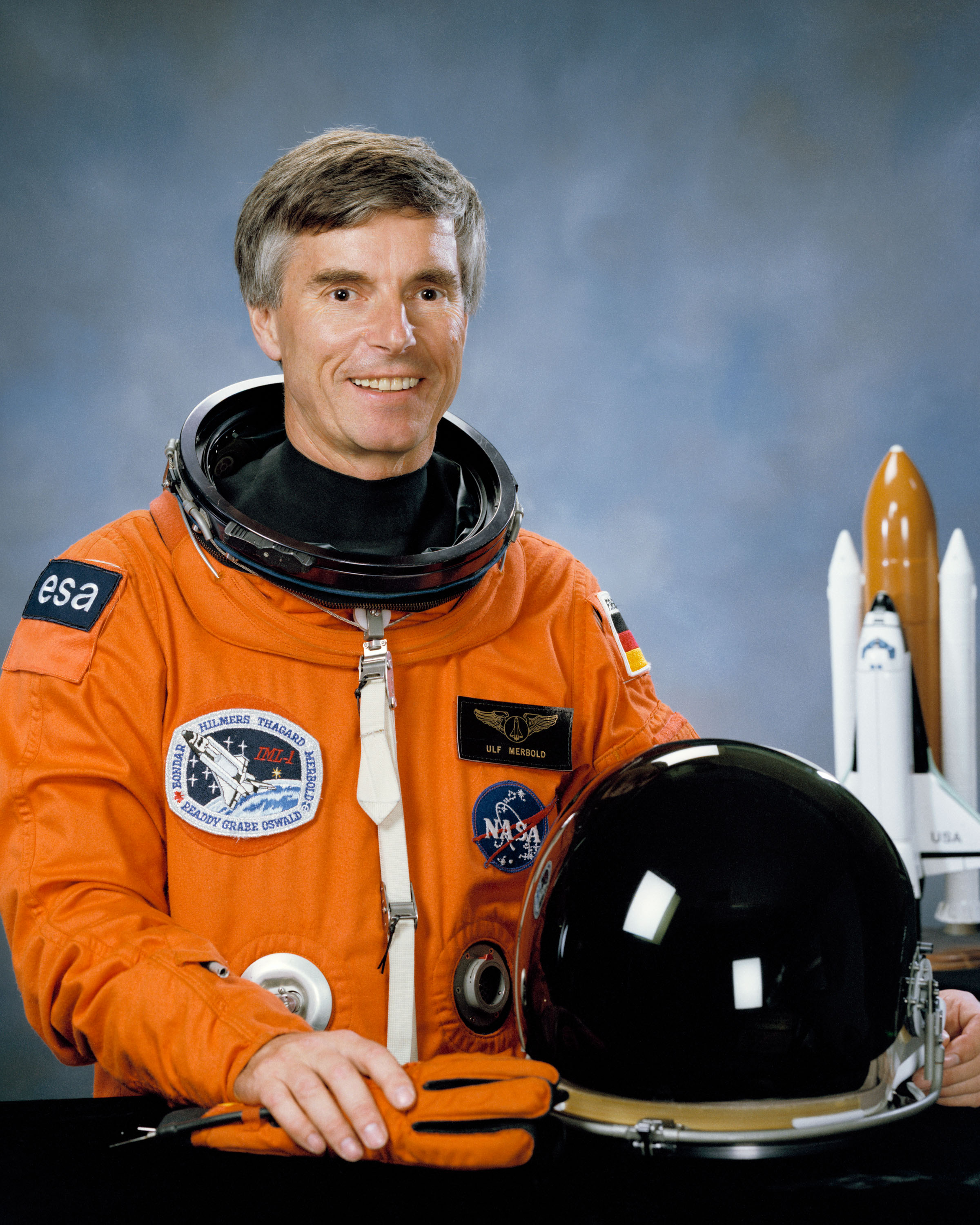
astronaut corps, the German Ulf Merbold
Ulf Dietrich Merbold (; born 20 June 1941) is a German physicist and astronaut who flew to space three times, becoming the first West German citizen in space and the first non-American to fly on a NASA spacecraft. Merbold flew on two Space Shu ...
is considered the first ESA astronaut to fly into space. He participated in the STS-9
STS-9 (also referred to Spacelab 1) was the ninth NASA Space Shuttle mission and the sixth mission of the Space Shuttle ''Columbia''. Launched on November 28, 1983, the ten-day mission carried the first Spacelab laboratory module into orbit.
...
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable launch system, reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. ...
mission that included the first use of the European-built Spacelab
Spacelab was a reusable laboratory developed by European Space Agency (ESA) and used on certain spaceflights flown by the Space Shuttle. The laboratory comprised multiple components, including a pressurized module, an unpressurized carrier, ...
in 1983. STS-9 marked the beginning of an extensive ESA/NASA joint partnership that included dozens of space flights of ESA astronauts in the following years. Some of these missions with Spacelab were fully funded and organisationally and scientifically controlled by the ESA (such as two missions by Germany and one by Japan) with European astronauts as full crew members rather than guests on board. Beside paying for Spacelab flights and seats on the shuttles, the ESA continued its human space flight co-operation with the Soviet Union and later Russia, including numerous visits to Mir.
During the latter half of the 1980s, European human space flights changed from being the exception to routine and therefore, in 1990, the European Astronaut Centre
The European Astronaut Centre (EAC) (German: Europäisches Astronautenzentrum, French: Centre des astronautes européens), is an establishment of the European Space Agency and home of the European Astronaut Corps. It is near to Cologne, Germany, ...
in Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
, Germany was established. It selects and trains prospective astronauts and is responsible for the co-ordination with international partners, especially with regard to the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
. As of 2006, the ESA astronaut corps officially included twelve members, including nationals from most large European countries except the United Kingdom.
In 2008, the ESA started to recruit new astronauts so that final selection would be due in spring 2009. Almost 10,000 people registered as astronaut candidates before registration ended in June 2008. 8,413 fulfilled the initial application criteria. Of the applicants, 918 were chosen to take part in the first stage of psychological testing, which narrowed down the field to 192. After two-stage psychological tests and medical evaluation in early 2009, as well as formal interviews, six new members of the European Astronaut Corps were selected – five men and one woman.
Crew vehicles
In the 1980s, France pressed for an independent European crew launch vehicle. Around 1978, it was decided to pursue a reusable spacecraft model and starting in November 1987 a project to create a mini-shuttle by the name of Hermes (shuttle), Hermes was introduced. The craft was comparable to early proposals for the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable launch system, reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. ...
and consisted of a small reusable spaceship that would carry 3 to 5 astronauts and 3 to 4 metric tons of payload for scientific experiments. With a total maximum weight of 21 metric tons it would have been launched on the Ariane 5
Ariane 5 is a retired European heavy-lift space launch vehicle operated by Arianespace for the European Space Agency (ESA). It was launched from the Guiana Space Centre (CSG) in French Guiana. It was used to deliver payloads into geostationar ...
rocket, which was being developed at that time. It was planned solely for use in low Earth orbit space flights. The planning and pre-development phase concluded in 1991; the production phase was never fully implemented because at that time the political landscape had changed significantly. With the fall of the Soviet Union, the ESA looked forward to co-operation with Russia to build a next-generation space vehicle. Thus the Hermes programme was cancelled in 1995 after about 3 billion dollars had been spent. The Columbus Man-Tended Free Flyer, Columbus space station programme had a similar fate.
In the 21st century, the ESA started new programmes in order to create its own crew vehicles, most notable among its various projects and proposals is Hopper (spacecraft), Hopper, whose prototype by Airbus, EADS, called EADS Phoenix, Phoenix, has already been tested. While projects such as Hopper (spacecraft), Hopper are neither concrete nor to be realised within the next decade, other possibilities for human spaceflight in co-operation with the Russian Space Agency have emerged. Following talks with the Russian Space Agency in 2004 and June 2005, a co-operation between the ESA and the Russian Space Agency was announced to jointly work on the Russian-designed Kliper, a reusable spacecraft that would be available for space travel beyond LEO (e.g. the moon or even Mars). It was speculated that Europe would finance part of it. A €50 million participation study for Kliper, which was expected to be approved in December 2005, was finally not approved by ESA member states. The Russian state tender for the project was subsequently cancelled in 2006.
In June 2006, ESA member states granted 15 million to the CSTS, Crew Space Transportation System (CSTS) study, a two-year study to design a spacecraft capable of going beyond Low-Earth orbit based on the current Soyuz spacecraft, Soyuz design. This project was pursued with Roskosmos instead of the cancelled Kliper proposal. A decision on the actual implementation and construction of the CSTS spacecraft was contemplated for 2008.
In mid-2009 EADS Astrium was awarded a €21 million study into designing a crew vehicle based on the European ATV which is believed to now be the basis of the Advanced Crew Transportation System design.
In November 2012, the ESA decided to join NASA's Orion (spacecraft), Orion programme. The ATV would form the basis of a propulsion unit for NASA's new crewed spacecraft. The ESA may also seek to work with NASA on Orion's launch system as well in order to secure a seat on the spacecraft for its own astronauts.
In September 2014, the ESA signed an agreement with Sierra Nevada Corporation for co-operation in Dream Chaser project. Further studies on the Dream Chaser for European Utilization or DC4EU project were funded, including the feasibility of launching a Europeanised Dream Chaser onboard Ariane 5.[
]
Cooperation with other countries and organisations
The ESA has signed co-operation agreements with the following states that currently neither plan to integrate as tightly with ESA institutions as Canada, nor envision future membership of the ESA: Argentina, Brazil, China, India (for the Chandrayan mission), RussiaNASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
of the United States and is participating in the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
together with the United States (NASA), Russia and Japan (JAXA).
National space organisations of member states
*The ''CNES, Centre National d'Études Spatiales'' (CNES) (National Centre for Space Study) is the French government space agency (administratively, a "public establishment of industrial and commercial character"). Its headquarters are in central Paris. CNES is the main participant on the Ariane project. Indeed, CNES designed and tested all Ariane family rockets (mainly from its centre in Évry, Essonne, Évry near Paris)
*The UK Space Agency is a partnership of the UK government departments which are active in space. Through the UK Space Agency, the partners provide delegates to represent the UK on the various ESA governing bodies. Each partner funds its own programme.
*The Italian Space Agency (''Agenzia Spaziale Italiana'' or ASI) was founded in 1988 to promote, co-ordinate and conduct space activities in Italy. Operating under the Ministry of the Universities and of Scientific and Technological Research, the agency cooperates with numerous entities active in space technology and with the president of the Council of Ministers. Internationally, the ASI provides Italy's delegation to the Council of the European Space Agency and to its subordinate bodies.
*The German Aerospace Center (DLR) (German: ''Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt e. V.'') is the national research centre for aviation and space flight of the Federal Republic of Germany and of other member states in the Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres, Helmholtz Association. Its extensive research and development projects are included in national and international cooperative programmes. In addition to its research projects, the centre is the assigned space agency of Germany bestowing headquarters of German space flight activities and its associates.
*The Instituto Nacional de Técnica Aeroespacial (INTA) (National Institute for Aerospace Technique) is a Public Research Organisation specialised in aerospace research and technology development in Spain. Among other functions, it serves as a platform for space research and acts as a significant testing facility for the aeronautic and space sector in the country.
NASA
The ESA has a long history of collaboration with NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
. Since ESA's astronaut corps was formed, the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable launch system, reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. ...
has been the primary launch vehicle used by the ESA's astronauts to get into space through partnership programmes with NASA. In the 1980s and 1990s, the Spacelab
Spacelab was a reusable laboratory developed by European Space Agency (ESA) and used on certain spaceflights flown by the Space Shuttle. The laboratory comprised multiple components, including a pressurized module, an unpressurized carrier, ...
programme was an ESA-NASA joint research programme that had the ESA develop and manufacture orbital labs for the Space Shuttle for several flights in which the ESA participates with astronauts in experiments.
In robotic science mission and exploration missions, NASA has been the ESA's main partner. ''Cassini–Huygens
''Cassini–Huygens'' ( ), commonly called ''Cassini'', was a space research, space-research mission by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI) to send a space probe to study the planet Saturn and its system, i ...
'' was a joint NASA-ESA mission, along with the Infrared Space Observatory, INTEGRAL, SOHO
SoHo, short for "South of Houston Street, Houston Street", is a neighborhood in Lower Manhattan, New York City. Since the 1970s, the neighborhood has been the location of many artists' lofts and art galleries, art installations such as The Wall ...
, and others. Also, the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the Orbiting Solar Observatory, first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most ...
is a joint project of NASA and the ESA. Future ESA-NASA joint projects include the James Webb Space Telescope and the proposed Laser Interferometer Space Antenna. NASA has supported the ESA's MarcoPolo-R mission which landed on asteroid Bennu in October 2020 and is scheduled to return a sample to Earth for further analysis in 2023. NASA and the ESA will also likely join for a Mars sample-return mission. In October 2020, the ESA entered into a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with NASA to work together on the Artemis program, which will provide an orbiting Lunar Gateway and also accomplish the first crewed lunar landing in 50 years, whose team will include the first woman on the Moon. Astronaut selection announcements are expected within two years of the 2024 scheduled launch date. The ESA also purchases seats on the NASA operated Commercial Crew Program. The first ESA astronaut to be on a Commercial Crew Program mission is Thomas Pesquet. Pesquet launched into space aboard Dragon 2, Crew Dragon Crew Dragon Endeavour, Endeavour on the SpaceX Crew-2, Crew-2 mission. The ESA also has seats on SpaceX Crew-3, Crew-3 with Matthias Maurer and SpaceX Crew-4, Crew-4 with Samantha Cristoforetti.
SpaceX
In 2023, following the successful launch of the Euclid (spacecraft), Euclid telescope in July on a Falcon 9 rocket, the ESA approached SpaceX to launch four Galileo communication satellites on two Falcon 9 rockets in 2024, however it would require approval from the European Commission and all member states of the European Union to proceed.
Cooperation with other space agencies
Since China has invested more money into space activities, the Chinese Space Agency has sought international partnerships. Besides the Russian Space Agency, ESA is one of its most important partners. Both space agencies cooperated in the development of the Double Star Mission. In 2017, the ESA sent two astronauts to China for two weeks sea survival training with Chinese astronauts in Yantai, Shandong.
The ESA entered into a major joint venture with Russia in the form of the CSTS, the preparation of French Guiana
French Guiana, or Guyane in French, is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France located on the northern coast of South America in the Guianas and the West Indies. Bordered by Suriname to the west ...
spaceport for launches of Soyuz-2 (rocket), Soyuz-2 rockets and other projects. With India, the ESA agreed to send instruments into space aboard the ISRO
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO ) is India's national space agency, headquartered in Bengaluru, Karnataka. It serves as the principal research and development arm of the Department of Space (DoS), overseen by the Prime Minister o ...
's Chandrayaan-1 in 2008. The ESA is also co-operating with Japan, the most notable current project in collaboration with JAXA
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into o ...
is the ''BepiColombo'' mission to Mercury (planet), Mercury.
International Space Station
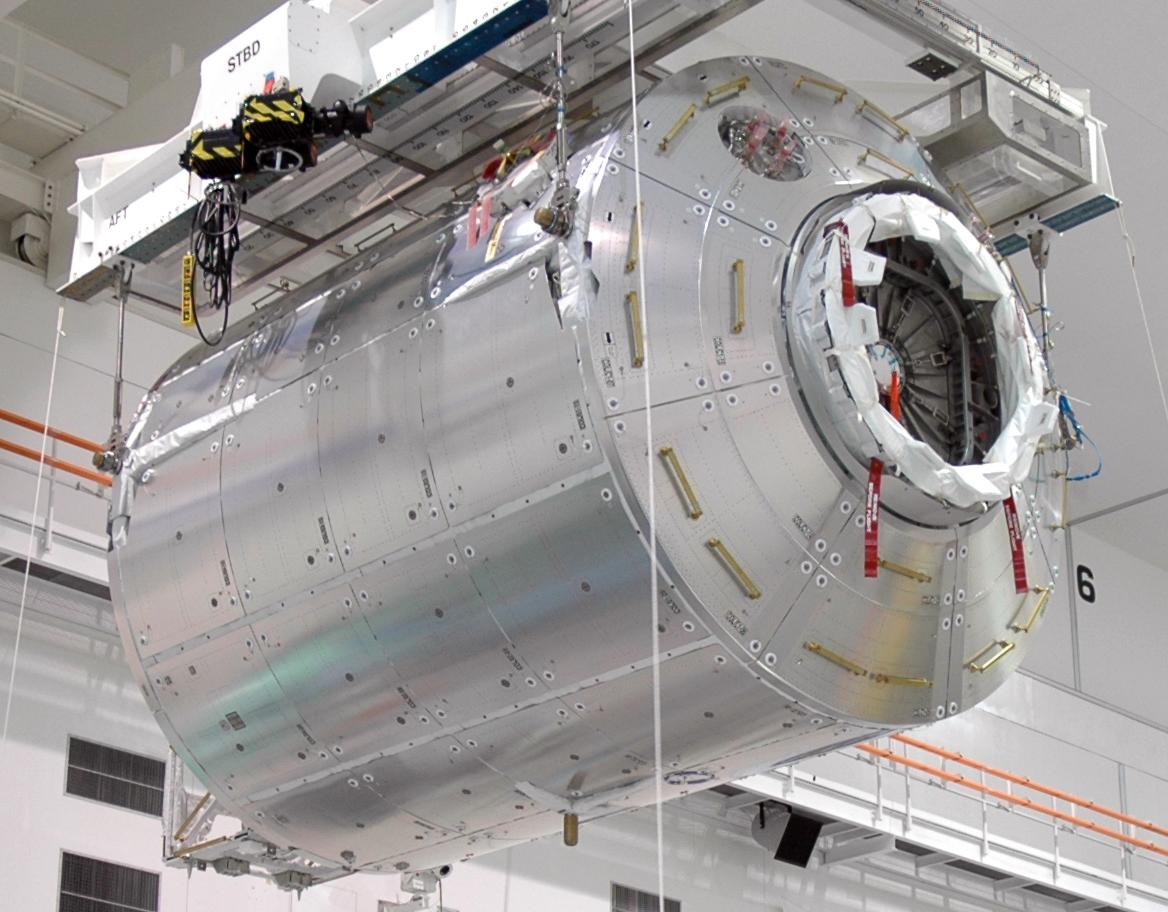 With regard to the
With regard to the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
(ISS), the ESA is not represented by all of its member states: 11 of the 22 ESA member states currently participate in the project: Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Netherlands, Norway, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and United Kingdom. Austria, Finland and Ireland chose not to participate, because of lack of interest or concerns about the expense of the project. Portugal, Luxembourg, Greece, the Czech Republic, Romania, Poland, Estonia and Hungary joined ESA after the agreement had been signed.
The ESA takes part in the construction and operation of the ISS
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), ESA (Europe), ...
, with contributions such as Columbus (ISS module), Columbus, a science laboratory module that was brought into orbit by NASA's STS-122 Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable launch system, reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. ...
mission, and the Cupola (ISS module), Cupola observatory module that was completed in July 2005 by Alenia Aeronautica, Alenia Spazio for the ESA. The current estimates for the ISS are approaching €100 billion in total (development, construction and 10 years of maintaining the station) of which the ESA has committed to paying €8 billion. About 90% of the costs of the ESA's ISS share will be contributed by Germany (41%), France (28%) and Italy (20%). German ESA astronaut Thomas Reiter was the first long-term ISS crew member.
The ESA has developed the Automated Transfer Vehicle for ISS resupply. Each ATV has a cargo capacity of .
Facilities
*ESA Headquarters, Paris, France
*European Space Operations Centre (ESOC), Darmstadt
Darmstadt () is a city in the States of Germany, state of Hesse in Germany, located in the southern part of the Frankfurt Rhine Main Area, Rhine-Main-Area (Frankfurt Metropolitan Region). Darmstadt has around 160,000 inhabitants, making it the ...
, Germany
*European Space Research and Technology Centre (ESTEC), Noordwijk
Noordwijk () is a town and municipality in the west of the Netherlands, in the provinces of the Netherlands, province of South Holland. The municipality covers an area of of which is water and had a population of in .
On 1 January 2019, the f ...
, Netherlands
*European Space Astronomy Centre
The European Space Astronomy Centre (ESAC) near Madrid in Spain is a research centre of the European Space Agency (ESA). ESAC is the lead institution for space science (astronomy, Solar System exploration and fundamental physics) using ESA miss ...
(ESAC), Madrid, Spain
*European Centre for Space Applications and Telecommunications
The European Centre for Space Applications and Telecommunications or ECSAT is a research centre belonging to the European Space Agency (ESA) and located on the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus in Oxfordshire, United Kingdom.
It was creat ...
(ECSAT), Oxfordshire, United Kingdom
*European Astronaut Centre
The European Astronaut Centre (EAC) (German: Europäisches Astronautenzentrum, French: Centre des astronautes européens), is an establishment of the European Space Agency and home of the European Astronaut Corps. It is near to Cologne, Germany, ...
(EAC), Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
, Germany
*ESA Centre for Earth Observation
The ESA Centre for Earth Observation (also known as the European Space Research Institute or ESRIN) is a research centre belonging to the European Space Agency (ESA), located in Frascati (Rome) Italy. It is dedicated to research involving ear ...
(ESRIN), Frascati
Frascati () is a city and in the Metropolitan City of Rome Capital in the Lazio region of central Italy. It is located south-east of Rome, on the Alban Hills close to the ancient city of Tusculum. Frascati is closely associated with science, ...
, Italy
*Centre Spatial Guyanais, Guiana Space Centre (CSG), Kourou
Kourou (; ) is a commune in French Guiana, an overseas region and department of France in South America. Kourou is famous for being the location of the Guiana Space Centre, the main spaceport of France and the European Space Agency (ESA). It ...
, French Guiana
*ESTRACK, European Space Tracking Network (ESTRACK)
*European Data Relay System
Link between ESA and EU
The ESA is an independent space agency and not under the jurisdiction of the European Union, although they have common goals, share funding, and work together often.European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
(EU) was to make the European Space Agency an Agency of the European Union, agency of the EU by 2014. While the EU and its member states fund together 86% of the budget of the ESA, it is not an EU agency. Furthermore, the ESA has several non-EU members, most notably the United Kingdom which Brexit, left the EU while remaining a full member of the ESA. The ESA is partnered with the EU on its two current flagship space programmes, the Copernicus Programme, Copernicus series of Earth observation satellites and the Galileo (satellite navigation), Galileo satellite navigation system, with the ESA providing technical oversight and, in the case of Copernicus, some of the funding.
Security incidents
On 3 August 1984, the ESA's Paris headquarters were severely damaged and six people were hurt when a bomb exploded. It was planted by the far-left armed Action directe (armed group), Action Directe group.
On 14 December 2015, hackers from Anonymous (group), Anonymous breached the ESA's subdomains and leaked thousands of login credentials.
See also
*
*European Space Security and Education Centre
The European Space Security and Education Centre (ESEC) is a centre of excellence for space cybersecurity services of the European Space Agency (ESA), home to its Proba mission control centres, the Space Weather Data Centre, the Education Training ...
*Eurospace
*List of European Space Agency programmes and missions
*List of government space agencies
*SEDS
*Space Night
European Union matters
*Agencies of the European Union
*Directorate-General for Defence Industry and Space
*Enhanced co-operation
*European Union Agency for the Space Programme
Notes
References
Further reading
ESA Bulletin
ESA Bulletin
) is a quarterly magazine about the work of ESA that can be subscribed t
European Space Agency
free of charge.
*Bonnet, Roger; Manno, Vittorio (1994). ''International Cooperation in Space: The Example of the European Space Agency'' (Frontiers of Space). Harvard University Press. .
*Johnson, Nicholas (1993). ''Space technologies and space science activities of member states of the European Space Agency''. .
*Peeters, Walter (2000). ''Space Marketing: A European Perspective'' (Space Technology Library). .
*
*Harvey, Brian (2003). ''Europe's Space Programme: To Ariane and Beyond''. .
External links
*
A European strategy for space
– Europa (web portal), Europa
Convention for the establishment of a European Space Agency
September 2005
Convention for the Establishment of a European Space Agency, Annex I: Privileges and ImmunitiesEuropean Space Agency fonds
an
'Oral History of Europe in Space'
project run by the European Space Agency at th
Historical Archives of the EU
in Florence
Open access at the European Space Agency
{{Authority control
European Space Agency,
Organizations established in 1975
International scientific organizations based in Europe
Organizations based in Paris
1975 establishments in Europe
European astronauts
European space programmes, *
Space agencies
Space policy of the European Union
 ESA collaborated with
ESA collaborated with  The ESA is funded from annual contributions by
The ESA is funded from annual contributions by  Vega is the ESA's carrier for small satellites. Developed by seven ESA members led by
Vega is the ESA's carrier for small satellites. Developed by seven ESA members led by  At the time the ESA was formed, its main goals did not encompass human space flight; rather it considered itself to be primarily a scientific research organisation for uncrewed space exploration in contrast to its American and Soviet counterparts. It is therefore not surprising that the first non-Soviet European in space was not an ESA astronaut on a European space craft; it was
At the time the ESA was formed, its main goals did not encompass human space flight; rather it considered itself to be primarily a scientific research organisation for uncrewed space exploration in contrast to its American and Soviet counterparts. It is therefore not surprising that the first non-Soviet European in space was not an ESA astronaut on a European space craft; it was  With regard to the
With regard to the