E961 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Neotame, also known by the
 Industrially neotame is made from 3,3-dimethylbutanal and aspartame via
Industrially neotame is made from 3,3-dimethylbutanal and aspartame via
 In humans and many other animals like dogs, rats and rabbits, neotame is rapidly but incompletely absorbed. Its
In humans and many other animals like dogs, rats and rabbits, neotame is rapidly but incompletely absorbed. Its
Official neotame website
Sugar substitutes Dipeptides E-number additives Carboxylic acids Methyl esters
brand name
A brand is a name, term, design, symbol or any other feature that distinguishes one seller's goods or service from those of other sellers. Brands are used in business, marketing, and advertising for recognition and, importantly, to create and ...
Newtame, is a non-caloric artificial sweetener
A sugar substitute or artificial sweetener, is a food additive that provides a sweetness like that of sugar while containing significantly less food energy than sugar-based sweeteners, making it a zero-calorie () or low-calorie sweetener. Arti ...
and aspartame
Aspartame is an artificial non-saccharide sweetener commonly used as a sugar substitute in foods and beverages. 200 times sweeter than sucrose, it is a methyl ester of the aspartic acid/phenylalanine dipeptide with brand names NutraSwe ...
analog
Analog or analogue may refer to:
Computing and electronics
* Analog signal, in which information is encoded in a continuous variable
** Analog device, an apparatus that operates on analog signals
*** Analog electronics, circuits which use analog ...
by NutraSweet
The NutraSweet Company is an American nutrient company that produces and markets NutraSweet Neotame, their trademarked brand name for the high-intensity sweetener neotame.
In 2021, NutraSweet was placed 43rd by FoodTalks' list of Top 50 Global ...
. By mass
Mass is an Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsic property of a physical body, body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the physical quantity, quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physi ...
, it is 7,000 to 13,000 times sweeter than sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
. It has no notable off-flavors when compared to sucrose. It enhances original food flavors. It can be used alone, but is often mixed with other sweeteners to increase their individual sweetness (i.e. synergistic
Synergy is an interaction or cooperation giving rise to a whole that is greater than the simple sum of its parts (i.e., a non-linear addition of force, energy, or effect). The term ''synergy'' comes from the Attic Greek word συνεργία ' f ...
effect) and decrease their off-flavors (''e.g.'' saccharin
Saccharin, also called saccharine, benzosulfimide, or E954, or used in saccharin sodium or saccharin calcium forms, is a non-nutritive artificial sweetener. Saccharin is a sultam that is about 500 times sweeter than sucrose, but has a bitter or ...
). It is chemically somewhat more stable than aspartame. Its use can be cost effective in comparison to other sweeteners as smaller amounts of neotame are needed.
It is suitable for use in carbonated
Carbonation is the chemical reaction of carbon dioxide to give carbonates, bicarbonates, and carbonic acid. In chemistry, the term is sometimes used in place of carboxylation, which refers to the formation of carboxylic acids.
In inorganic che ...
soft drink
A soft drink (see #Terminology, § Terminology for other names) is a class of non-alcoholic drink, usually (but not necessarily) Carbonated water, carbonated, and typically including added Sweetness, sweetener. Flavors used to be Natural flav ...
s, yogurt
Yogurt (; , from , ; also spelled yoghurt, yogourt or yoghourt) is a food produced by bacterial Fermentation (food), fermentation of milk. Fermentation of sugars in the milk by these bacteria produces lactic acid, which acts on milk protein to ...
s, cake
Cake is a flour confection usually made from flour, sugar, and other ingredients and is usually baked. In their oldest forms, cakes were modifications of bread, but cakes now cover a wide range of preparations that can be simple or elabor ...
s, drink powders, and bubble gum
Bubble gum (or bubblegum) is a type of chewing gum, designed to be inflated out of the mouth as a bubble.
Composition
In modern chewing gum, if natural rubber such as chicle is used, it must pass several purity and cleanliness tests. However, ...
s among other foods. It can be used as a table top sweetener for hot drinks like coffee
Coffee is a beverage brewed from roasted, ground coffee beans. Darkly colored, bitter, and slightly acidic, coffee has a stimulating effect on humans, primarily due to its caffeine content, but decaffeinated coffee is also commercially a ...
. It covers bitter tastes (e.g. caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine chemical classification, class and is the most commonly consumed Psychoactive drug, psychoactive substance globally. It is mainly used for its eugeroic (wakefulness pr ...
).
In 2002, FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
approved it as a non-nutritive sweetener and flavor enhancer within the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
in foods generally, except meat and poultry. In 2010, it was approved for use in foods within the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
with the E number
E numbers, short for Europe numbers, are codes for substances used as food additives, including those found naturally in many foods, such as vitamin C, for use within the European Union (EU) and European Free Trade Association (EFTA). Commonly ...
E961. It has also been approved as an additive in many other countries outside US and EU.
Its metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
is fast and is not retained in the body. Methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical compound and the simplest aliphatic Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with the chemical formula (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often ab ...
forms in its metabolism. Only trace amounts of neotame are added to foods, so the amount of methanol is insignificant for health. It is safe for type 2 diabetics
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent uri ...
and those with phenylketonuria
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an inborn error of metabolism that results in decreased metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. Untreated PKU can lead to intellectual disability, seizures, behavioral problems, and mental disorders. It may also r ...
.
French scientists Claude Nofre and Jean-Marie Tinti invented neotame. In 1992, they filed a United States patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling discl ...
, which was granted in 1996.
Safety
In US and EU, theacceptable daily intake
Acceptable daily intake or ADI is a measure of the amount of a specific substance (originally applied for a food additive, later also for a residue of a veterinary drug or pesticide) in food or drinking water that can be ingested (orally) daily ove ...
(ADI) of neotame for humans is 0.3 and 2 mg per kg of bodyweight (mg/kg bw), respectively. NOAEL
The no-observed-adverse-effect level (NOAEL) denotes the level of exposure of an organism, found by experiment or observation, at which there is no biologically or statistically significant increase in the frequency or severity of any adverse effe ...
for humans is 200 mg/kg bw per day within EU. Estimated possible daily intakes from foods are well below ADI levels. Ingested neotame can form phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituent, substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of ...
, but in normal use of neotame, this is not significant to those with phenylketonuria
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an inborn error of metabolism that results in decreased metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. Untreated PKU can lead to intellectual disability, seizures, behavioral problems, and mental disorders. It may also r ...
. It also has no adverse effects in type 2 diabetics
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent uri ...
. It is not considered to be carcinogenic
A carcinogen () is any agent that promotes the development of cancer. Carcinogens can include synthetic chemicals, naturally occurring substances, physical agents such as ionizing and non-ionizing radiation, and Biological agent, biologic agent ...
or mutagenic
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that permanently changes genetic material, usually DNA, in an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer in ...
. The Center for Science in the Public Interest
The Center for Science in the Public Interest (CSPI) is a Washington, D.C.–based non-profit watchdog and consumer advocacy group.
History and funding
CSPI is a consumer advocacy organization. Its focus is nutrition and health, food safety ...
has ranked neotame as safe.
Sweetness
Water solutions of neotame that are equivalent insweetness
Sweetness is a basic taste most commonly perceived when eating foods rich in sugars. Sweet tastes are generally regarded as pleasurable. In addition to sugars like sucrose, many other chemical compounds are sweet, including aldehydes, ketones ...
to sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
water solutions increase logarithmically
In mathematics, the logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, must be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of to base is , because is to the rd power: . More generally, if , then ...
in relative sweetness as the sucrose concentration of a comparably sweet sucrose solution increases until a plateau is reached. Maximum sweetness is reached at neotame solution concentrations that are relatively as sweet as a water solution that is 15.1 percentage sucrose by weight, i.e., at 15.1 sucrose equivalence % (SE%). For comparison, acesulfame K
Acesulfame potassium (, or ), also known as acesulfame K or Ace K, is a synthetic calorie-free sugar substitute (artificial sweetener) often marketed under the trade names Sunett and Sweet One. In the European Union, it is known under the E n ...
, cyclamate
Cyclamate is an artificial sweetener. It is 30–50 times sweeter than sucrose (table sugar), making it the least potent of the commercially used artificial sweeteners. It is often used with other artificial sweeteners, especially saccharin; the ...
and saccharin
Saccharin, also called saccharine, benzosulfimide, or E954, or used in saccharin sodium or saccharin calcium forms, is a non-nutritive artificial sweetener. Saccharin is a sultam that is about 500 times sweeter than sucrose, but has a bitter or ...
reach their maximum sweetness at 11.6 SE%, 11.3 SE% and 9 SE%, respectively.
Neotame is a high-potency sweetener, and it is 7,000 to 13,000 times sweeter than table sugar. Neotame contains flavor-enhancing properties, and compared to sucrose or aspartame, it has a relatively lower cost per sweetness factor.
Chemistry
Structure
Neotame is formally asecondary amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
of 3,3-dimethylbutanal and aspartame. The latter is a dipeptide
A dipeptide is an organic compound derived from two amino acids. The constituent amino acids can be the same or different. When different, two isomers of the dipeptide are possible, depending on the sequence. Several dipeptides are physiological ...
of phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the chemical formula, formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituent, substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of ...
and aspartic acid
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. The L-isomer of aspartic acid is one of the 22 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the building blocks of protei ...
. Neotame has 2 stereocenter
In stereochemistry, a stereocenter of a molecule is an atom (center), axis or plane that is the focus of stereoisomerism; that is, when having at least three different groups bound to the stereocenter, interchanging any two different groups cr ...
s and 4 stereoisomers
In stereochemistry, stereoisomerism, or spatial isomerism, is a form of isomerism in which molecules have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution), but differ in the three-dimensional orientations of their atoms i ...
. Sweetness is due to the (2''S''),(3''S'')-stereoisomer.
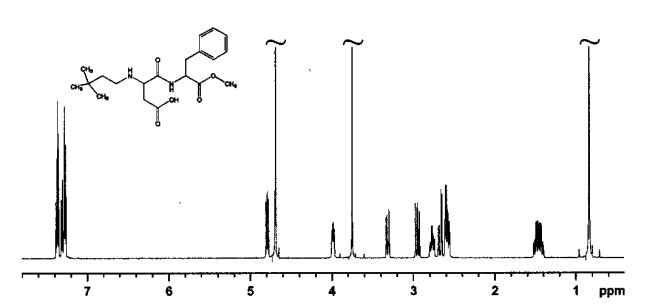
Spectroscopy
NeotameNMR spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy or magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), is a spectroscopic technique based on re-orientation of atomic nuclei with non-zero nuclear spins in an external magnetic f ...
identifies its structure with a peak at 0.84 ppm indicating the three methyl groups on the carbon chain bonded to the nitrogen.

Synthesis
Neotame is synthesized from aspartame through a reductivealkylation Alkylation is a chemical reaction that entails transfer of an alkyl group. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene (or their equivalents). Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting al ...
with 3,3-dimethylbutyraldehyde in a palladium
Palladium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1802 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas (formally 2 Pallas), ...
catalyst with methanol. The stereochemistry of aspartame is conserved during the synthesis and therefore, neotame and aspartame have the same stereochemistry. (2''S''),(3''S'')-stereoisomer of aspartame is needed to synthesize the (2''S''),(3''S'')-stereoisomer of neotame.
Properties and reactivity
Neotame has similar stability as aspartame, but has greater stability especially in heated and dairy foods. Increased temperature, moisture or pH increase losses, and are the main relevant properties of a food when considering the stability of neotame. For example, about 90% of original neotame remains after 8 weeks of storage in pH 3.2 beverages. Neotame is especially stable as a dry powder at room temperature andhumidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, dew, or fog t ...
even if mixed with glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
or maltodextrin
Maltodextrin is a name shared by two different families of chemicals. Both families are glucose polymers (also called ''dextrose polymers'' or ''Dextrin, dextrins''), but have little chemical or nutritional similarity.
The digestible maltodextr ...
, and is relatively inert in foods with reducing sugar
A reducing sugar is any sugar that is capable of acting as a reducing agent. In an alkaline solution, a reducing sugar forms some aldehyde or ketone, which allows it to act as a reducing agent, for example in Benedict's reagent. In such a react ...
s like fructose
Fructose (), or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and gal ...
.
Unlike aspartame, neotame doesn't form diketopiperazine
A diketopiperazine (DKP), also known as a ''dioxopiperazine'' or ''piperazinedione'', is a class of organic compounds related to piperazine but containing two amide linkages. DKP's are the smallest known class of cyclic peptide. Despite their name ...
s via intra-molecular cyclization due to its N-alkyl substitution with 3,3-dimethylbutyl. This increases its heat stability.
Over 1000 g of neotame dissolves in 1 kg of ethanol at 15 °C. At 15 °C the solubility of neotame is 10.6 g/kg in water and 43.6 g/kg in ethyl acetate
Ethyl acetate commonly abbreviated EtOAc, ETAC or EA) is the organic compound with the formula , simplified to . This flammable, colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell (similar to pear drops) and is used in glues, nail polish removers, ...
. At 25 °C the solubilities are 12.6 g/kg and 77.0 g/kg, respectively. At 40 °C the solubilities are 18.0 g/kg and 238 g/kg, respectively. At 50 °C the solubilities are 25.2 g/kg and 872 g/kg, respectively. Neotame is acidic
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid.
The first category of acids are the ...
and its 0.5 wt%
In chemistry, the mass fraction of a substance within a mixture is the ratio w_i (alternatively denoted Y_i) of the mass m_i of that substance to the total mass m_\text of the mixture. Expressed as a formula, the mass fraction is:
: w_i = \frac ...
solution has a pH of 5.80.
Manufacture
reductive amination
Reductive amination (also known as reductive alkylation) is a form of amination that converts a carbonyl group to an amine via an intermediate imine. The carbonyl group is most commonly a ketone or an aldehyde. It is a common method to make amine ...
. They are dissolved in methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical compound and the simplest aliphatic Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with the chemical formula (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often ab ...
, palladium on carbon
Palladium on carbon, often referred to as Pd/C, is a form of palladium used as a catalyst. The metal is supported on activated carbon to maximize its surface area and activity.
Uses Hydrogenation
Palladium on carbon is used for catalytic hydrog ...
catalyst
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quick ...
is added, air is replaced with hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
and the reaction is carried out in room temperature under pressure for a few hours. Catalyst is filtered out. This can be aided with diatomaceous earth
Diatomaceous earth ( ), also known as diatomite ( ), celite, or kieselguhr, is a naturally occurring, soft, siliceous rock, siliceous sedimentary rock that can be crumbled into a fine white to off-white powder. It has a particle size ranging fr ...
. Methanol is distilled
Distillation, also classical distillation, is the process of separating the component substances of a liquid mixture of two or more chemically discrete substances; the separation process is realized by way of the selective boiling of the mixt ...
followed by addition of water. The mixture is cooled for a few hours, neotame is isolated via centrifugation
Centrifugation is a mechanical process which involves the use of the centrifugal force to separate particles from a solution according to their size, shape, density, medium viscosity and rotor speed. The denser components of the mixture migrate ...
, washed with water and vacuum dried. Neotame is milled to suitable size.
Metabolism
metabolites
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, c ...
are not retained or concentrated in specific tissues.
In humans at oral doses of about 0.25 mg per kg of bodyweight (mg/kg bw), about 34% is absorbed into blood. Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics (from Ancient Greek ''pharmakon'' "drug" and ''kinetikos'' "moving, putting in motion"; see chemical kinetics), sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to describing how the body affects a specific su ...
of oral doses of 0.1–0.5 mg/kg bw are somewhat linear, and at such doses, maximum neotame concentration in blood plasma
Blood plasma is a light Amber (color), amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but which contains Blood protein, proteins and other constituents of whole blood in Suspension (chemistry), suspension. It makes up ...
is reached after about 0.5 hours with a half-life Half-life is a mathematical and scientific description of exponential or gradual decay.
Half-life, half life or halflife may also refer to:
Film
* Half-Life (film), ''Half-Life'' (film), a 2008 independent film by Jennifer Phang
* ''Half Life: ...
of about 0.75 hours. In blood and in body in general, non-specific esterase
In biochemistry, an esterase is a class of enzyme that splits esters into an acid and an alcohol in a chemical reaction with water called hydrolysis (and as such, it is a type of hydrolase).
A wide range of different esterases exist that differ ...
s degrade neotame to de-esterified neotame and methanol
Methanol (also called methyl alcohol and wood spirit, amongst other names) is an organic chemical compound and the simplest aliphatic Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with the chemical formula (a methyl group linked to a hydroxyl group, often ab ...
, which is the main metabolic pathway in humans. De-esterified neotame has a plasma half-life of about 2 hours, and is the main metabolite in plasma.
In humans, over 80% of the original oral dose is excreted in feces and urine within 48 hours and the rest later. About 64% of the original dose is excreted in feces mostly as metabolites. Major metabolite in feces is the de-esterified neotame. Over 1% of the original dose is excreted in feces as ''N''-(3,3-dimethylbutyl)-L-aspartyl - L - phenylalanine. Over 1% is excreted in urine as carnitine
Carnitine is a quaternary ammonium compound involved in metabolism in most mammals, plants, and some bacteria. In support of energy metabolism, carnitine transports long-chain fatty acids from the cytosol into mitochondria to be oxidized for f ...
conjugate of 3,3-dimethylbutyric acid. Other minor metabolites form.
The major metabolic pathway leads to ''N''-(3,3-dimethylbutyl)-L-aspartyl - L - phenylalanine with a side product of methanol, and the minor pathway happens when the ''N''-(3,3-dimethylbutyl)-L-aspartyl - L - phenylalanine is oxidized into 3,3-dimethylbutyric acid. The side products for the minor pathway is methanol, aspartic acid and phenylalanine.
Methanol from neotame metabolism is insignificant at regulated levels used in foods and in comparison to methanol naturally found in foods.
Patent
Thepatent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling discl ...
covering the neotame molecule in the US, 5,480,668, was originally set to expire 7 November 2012, but was extended for 973 days by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office
The United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) is an agency in the U.S. Department of Commerce that serves as the national patent office and trademark registration authority for the United States. The USPTO's headquarters are in Alex ...
. The patent expired on 8 July 2015.
References
External links
*{{Commons category-inlineOfficial neotame website
Sugar substitutes Dipeptides E-number additives Carboxylic acids Methyl esters