E-M35 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
E-M35, also known as E1b1b1-M35, is a
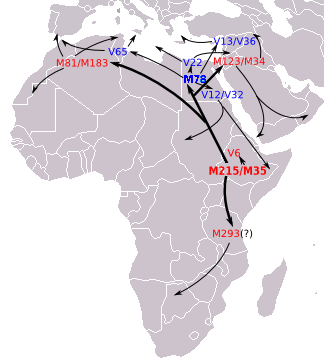 In June 2015, Trombetta et al. reported a previously unappreciated large difference in the age between haplogroup E-M215 (38.6 kya; 95% CI 31.4–45.9 kya) and its sub-haplogroup E-M35 (25.0 kya; 95% CI 20.0–30.0 kya) and estimated its origin to be in
In June 2015, Trombetta et al. reported a previously unappreciated large difference in the age between haplogroup E-M215 (38.6 kya; 95% CI 31.4–45.9 kya) and its sub-haplogroup E-M35 (25.0 kya; 95% CI 20.0–30.0 kya) and estimated its origin to be in
Chiara Batini et al, ''nature.com'', 2015 All major sub-branches of E-M35 are thought to have originated in the same general area as the parent clade: in
Coia et al. (2013)
E-M35 Phylogeny Project
the E-M35 phylogeny project
had records of four E-M123* tests, compared to 93 test results with E-M34.
* * * * * * * * Also se
Supplementary Data
* * * * * * * * * * * * * *. Se
comment on the Spitoon blog
an
public release
* * *. Published online April 2, 2008. See als
Supplementary Material.
* * * * * * * *. (Also se
Errata
* * * * * * * * *. * Pontikos D. "Phylogeographic refinement of haplogroup E" http://dienekes.blogspot.ru/2015/07/phylogeographic-refinement-of.html * * * * * *. Published online 9 March 2005 * *. * * * * * * * * * * * Trombetta B. "Phylogeographic Refinement and Large Scale Genotyping of Human Y Chromosome Haplogroup E Provide New Insights into the Dispersal of Early Pastoralists in the African Continent" http://gbe.oxfordjournals.org/content/7/7/1940.long * * * * *. * * * * * * *
E-M35 Phylogeny Project WikiE-M35 Phylogeny Project (all labs site)E-M35 Phylogeny Project Public ForumJewish E3b Project at FTDNAMap of E-M35 distribution in EuropeHaplogroup E3B1 (E1b1b1) Facebook Group (M35 community)E1b1b1b*-A Project
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Haplogroup E1b1b (Y-Dna) Human Y-DNA haplogroups
human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup
In human genetics, a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by specific mutations in the non-Genetic recombination, recombining portions of DNA on the male-specific Y chromosome (Y-DNA). Individuals within a haplogroup share ...
. E-M35 has two basal branches, E-V68 and E-Z827. E-V68 and E-Z827 are primarily distributed in North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
and the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
, and occur at lower frequencies in the Middle East
The Middle East (term originally coined in English language) is a geopolitical region encompassing the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, Turkey, Egypt, Iran, and Iraq.
The term came into widespread usage by the United Kingdom and western Eur ...
, Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, and Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost region of Africa. No definition is agreed upon, but some groupings include the United Nations geoscheme for Africa, United Nations geoscheme, the intergovernmental Southern African Development Community, and ...
.
Origins
 In June 2015, Trombetta et al. reported a previously unappreciated large difference in the age between haplogroup E-M215 (38.6 kya; 95% CI 31.4–45.9 kya) and its sub-haplogroup E-M35 (25.0 kya; 95% CI 20.0–30.0 kya) and estimated its origin to be in
In June 2015, Trombetta et al. reported a previously unappreciated large difference in the age between haplogroup E-M215 (38.6 kya; 95% CI 31.4–45.9 kya) and its sub-haplogroup E-M35 (25.0 kya; 95% CI 20.0–30.0 kya) and estimated its origin to be in Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
, where the node separating the E-V38 and E-M215 branches occurs about 47,500 years ago (95% CI: 41.3–56.8 ka). E-M35 was dated by Batini in 2015 to between 15,400 and 20,500 years ago.Large-scale recent expansion of European patrilineages shown by population resequencingChiara Batini et al, ''nature.com'', 2015 All major sub-branches of E-M35 are thought to have originated in the same general area as the parent clade: in
North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
, the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
, or nearby areas of the Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
. Some branches of E-M35 are assumed to have left Africa thousands of years ago, whereas others may have arrived from the Near East. For example, associates the spread of the haplogroup with the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, also known as the First Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period in Afro-Eurasia from a lifestyle of hunter-gatherer, hunting and gathering to one of a ...
, believing that the structure and regional pattern of E-M35 subclades potentially give "reagents with which to infer specific episodes of population histories associated with the Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
agricultural expansion". also estimate that E-M78 (called E1b1b1a1 in that paper) has been in Europe longer than 10,000 years. Accordingly, human remains excavated in a Spanish funeral cave dating from approximately 7,000 years ago were shown to be in this haplogroup. Two more E-M78 have been found in the Neolithic Sopot
Sopot (; or ) is a seaside resort city in Pomerelia on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea in northern Poland, with a population of approximately 40,000. It is located in Pomeranian Voivodeship, Pomerania Province and has the City with powiat ri ...
and Lengyel culture
__NOTOC__
The Lengyel culture is an archaeological culture of the European Neolithic, centered on the Middle Danube in Central Europe. It flourished from 5000 to 4000 BC, ending with phase IV, e.g., in Bohemia represented by the ' Jordanow/Jord ...
s too.
Concerning E-M35 in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
within this scheme, have remarked that E-M215 seems to represent a late-Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
migration from North Africa to Europe over the Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai ( ; ; ; ), is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a land bridge between Asia and Afri ...
in Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
."Y chromosome data show a signal for a separate late-Pleistocene migration from Africa to Europe via Sinai as evidenced through the distribution of haplogroup E3b lineages, which is not manifested in mtDNA haplogroup distributions." While this proposal remains uncontested, it has more recently been proposed by that there is also evidence for additional migration of E-M215 carrying men directly from North Africa to southwestern Europe, via a maritime route (see below.)
Ancient DNA
According to Lazaridis et al. (2016),Natufian
The Natufian culture ( ) is an archaeological culture of the late Epipalaeolithic Near East in West Asia from 15–11,500 Before Present. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentism, sedentary or semi-sedentary population even befor ...
skeletal remains from the ancient Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
predominantly carried the Y-DNA haplogroup E1b1b. Of the five Natufian specimens analysed for paternal lineages, three belonged to the E1b1b1b2(xE1b1b1b2a,E1b1b1b2b), E1b1(xE1b1a1,E1b1b1b1) and E1b1b1b2(xE1b1b1b2a,E1b1b1b2b) subclades (60%). Haplogroup E1b1b was also found at moderate frequencies among fossils from the ensuing Pre-Pottery Neolithic B
Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (PPNB) is part of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, a Neolithic culture centered in upper Mesopotamia and the Levant, dating to years ago, that is, 8800–6500 BC. It was Type site, typed by British archaeologist Kathleen Kenyon ...
culture, with the E1b1b1 and E1b1b1b2(xE1b1b1b2a,E1b1b1b2b) subclades observed in two of seven PPNB specimens (~29%). The scientists suggest that the Levantine early farmers may have spread southward into East Africa, bringing along Western Eurasian and Basal Eurasian
Basal Eurasian is a proposed lineage of anatomically modern humans with reduced, or zero, Neanderthal admixture (ancestry) compared to other ancient non-Africans. Basal Eurasians represent a sister lineage to other Eurasians and may have originat ...
ancestral components separate from that which would arrive later in North Africa.
Additionally, haplogroup E1b1b1 has been found in an ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
ian mummy excavated at the Abusir el-Meleq
Abusir el-Meleq (Arabic, Ar. ''أبو صير الملق''), also Abusir el-Melek - a town and archaeological site in Egypt, located in Beni Suef ( is the capital city of the Beni Suef Governorate in Egypt, an important agricultural trade centre o ...
archaeological site in Middle Egypt, which dates from a period between the late New Kingdom
New or NEW may refer to:
Music
* New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz
* ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013
** "New" (Paul McCartney song), 2013
* ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, 1995
* "New" (Daya song), 2017
* "New" (No Doubt song), 1 ...
and the Roman era
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Em ...
. Fossils at the Iberomaurusian
The Iberomaurusian is a backed bladelet lithic industry found near the coasts of Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia. It is also known from a single major site in Libya, the Haua Fteah, where the industry is known as the Eastern Oranian.The "Weste ...
site of Ifri n'Amr or Moussa
Ifri n'Amr Ou Moussa is an archaeological site discovered in 2005, located in the rural commune of Aït Siberne, Khémisset Province, in Western Morocco. This site has revealed burials associated with both Moroccan Early Neolithic and Bell Beaker ...
in Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
, which have been dated to around 5,000 BCE, also carried haplotype E-L19 related to the E1b1b1b1a (E-M81) subclade. These ancient individuals bore an autochthonous Maghrebi genomic component that peaks among modern North Africans
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
, indicating that they were ancestral to populations in the area. The E1b1b haplogroup has likewise been observed in ancient Guanche Guanche may refer to:
*Guanches, the indigenous people of the Canary Islands
*Guanche language, an extinct language, spoken by the Guanches until the 16th or 17th century
*''Conus guanche
''Conus guanche'' is a species of sea snail, a marine ga ...
fossils excavated in Gran Canaria
Gran Canaria (, ; ), also Grand Canary Island, is the third-largest and second-most-populous island of the Canary Islands, a Spain, Spanish archipelago off the Atlantic coast of Northwest Africa. the island had a population of that constitut ...
and Tenerife
Tenerife ( ; ; formerly spelled ''Teneriffe'') is the largest and most populous island of the Canary Islands, an Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain. With a land area of and a population of 965,575 inhabitants as of A ...
on the Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; ) or Canaries are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean and the southernmost Autonomous communities of Spain, Autonomous Community of Spain. They are located in the northwest of Africa, with the closest point to the cont ...
, which have been radiocarbon-dated to between the 7th and 11th centuries CE. The clade-bearing individuals that were analysed for paternal DNA were inhumed at the Tenerife site, with all of these specimens found to belong to the E1b1b1b1a1 or E-M183 subclade (3/3; 100%).
Loosdrecht et al. (2018) analysed genome-wide data from seven ancient Iberomaurusian
The Iberomaurusian is a backed bladelet lithic industry found near the coasts of Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia. It is also known from a single major site in Libya, the Haua Fteah, where the industry is known as the Eastern Oranian.The "Weste ...
individuals from the Grotte des Pigeons near Taforalt
Taforalt, or Grotte des Pigeons, is a cave in the province of Berkane, Aït Iznasen region, Morocco, possibly the oldest cemetery in North Africa. It contained at least 34 Iberomaurusian adolescent and adult human skeletons, as well as young ...
in eastern Morocco. The fossils were directly dated to between 15,100 and 13,900 calibrated years before present. The scientists found that five male specimens with sufficient nuclear DNA preservation belonged to the E1b1b1a1 (M78) subclade, with one skeleton bearing the E1b1b1a1b1 parent lineage to E-V13, another male specimen belonged to E1b1b (M215*).
Distribution
E-M215 and E-M35 are quite common among Afroasiatic speakers. The linguistic group and carriers of E-M35 lineage have a high probability to have arisen and dispersed together from theAfroasiatic Urheimat
The Proto-Afroasiatic homeland is the hypothetical place where speakers of the Proto-Afroasiatic language lived in a single linguistic community, or complex of communities, before this original language dispersed geographically and divided into s ...
. Amongst populations with an Afro-Asiatic speaking history, a significant proportion of Palestinians and Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
male lineages are E-M35. Haplogroup E-M35, which accounts for approximately 18% to 20% of 18% of Palestinians and Ashkenazi
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; also known as Ashkenazic Jews or Ashkenazim) form a distinct subgroup of the Jewish diaspora, that Ethnogenesis, emerged in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium Common era, CE. They traditionally spe ...
and 8.6% to 30% of Sephardi
Sephardic Jews, also known as Sephardi Jews or Sephardim, and rarely as Iberian Peninsular Jews, are a Jewish diaspora population associated with the historic Jewish communities of the Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal) and their descendant ...
Y-chromosomes, appears to be one of the major founding lineages of the Palestinian and the Jewish population."Paragroup E-M35 * and haplogroup J-12f2a* fit the criteria for major AJ founding lineages because they are widespread both in AJ populations and in Near Eastern populations, and occur at much lower frequencies in European non-Jewish populations."
The following table only includes sample populations with more than 1% E-M215 men with all known subclades as of June 2015. It contains the E-V1515 clade defined by Trombetta et al. 2015, and all the E1b1b subclades distributed below the Sahara (E-V42, E-M293, E-V92, E-V6), which were identified as E-M35 basal clades in a former phylogeny.
Exceptional cases of men who are M215 positive but M35 negative ("E-M215*") have been discovered so far in two Amharas
Amharas (; ) are a Semitic-speaking ethnic group indigenous to Ethiopia in the Horn of Africa, traditionally inhabiting parts of the northwest Highlands of Ethiopia, particularly the Amhara Region.
According to the 2007 national census, Amh ...
of Ethiopia and one Yemen
Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in South Arabia, southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the north, Oman to Oman–Yemen border, the northeast, the south-eastern part ...
i. At least some of these men, perhaps all, are known since early 2011 to be in a rare sibling clade to E-M35, known as E-V16 or E-M281. The discovery of M281 was announced by , who found it in two Ethiopian Oromo Oromo may refer to:
* Oromo people, an ethnic group of Ethiopia and Kenya
* Oromo language, an Afroasiatic language
See also
*
*Orma (clan), Oromo tribe
*Oromia
Oromia (, ) is a Regions of Ethiopia, regional state in Ethiopia and the homelan ...
. found 5 more Ethiopian individuals and an equivalent SNP to M281, V16. It was in the 2011 paper that the family tree position (M215+/M35-) was discovered as described above.
The E-M215 derivative, E-M35 is defined by the M35 SNP. 1 Turkmen
Turkmen, Türkmen, Turkoman, or Turkman may refer to:
Peoples Historical ethnonym
* Turkoman (ethnonym), ethnonym used for the Oghuz Turks during the Middle Ages
Ethnic groups
* Turkmen in Anatolia and the Levant (Seljuk and Ottoman-Turkish desc ...
individual from Jawzjan with a subclade defining mutation is referred to as E-M35*.(Figure S.7) J D Cristofaro et al., 2013, "Afghan Hindu Kush: Where Eurasian Sub-Continent Gene Flows Converge", http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0076748 As of June 2015, there is an increasingly complex tree structure which divides most men in E-M35 into two branches: E-V68 and E-Z827.
The most frequently described subclades are E-M78, a part of E-V68, and E-M81, which is a branch of E-Z827. These two subclades represent the largest proportion of the modern E-M215 population. E-M78 is found over most of the range where E-M215 is found excluding Southern Africa. E-M81 is found mainly in North Africa. E-M123 is less common but widely scattered, with significant populations in specific parts of the Horn of Africa, the Levant, Arabia, Iberia, and Anatolia. A new clade (E-V1515) was defined by Trombetta et al. 2015, which originated about 12 kya (95% CI 8.6–16.4) in eastern Africa where it is currently mainly distributed. This clade includes the E-V42, E-M293, E-V92 and E-V6 subclades, which were identified as E-M35 basal clades in a previous phylogeny.
TMRCA of the major nodes in E-M35
Subclades
E-V68 (E1b1b1a)
E-V68, is dominated by its longer-known subclade E-M78. Three "E-V68*" individuals who are in E-V68 but not E-M78 have been reported inSardinia
Sardinia ( ; ; ) is the Mediterranean islands#By area, second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, and one of the Regions of Italy, twenty regions of Italy. It is located west of the Italian Peninsula, north of Tunisia an ...
, by , when announcing the discovery of V68. The authors noted that because E-V68* was not found in the Middle Eastern samples, this appears to be evidence of maritime migration from Africa to southwestern Europe.
E-M78 is a commonly occurring subclade, widely distributed in North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
, the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
, West Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian ...
, (the Middle East and Near East) "up to Southern Asia", and all of Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
. The European distribution has a frequency peak centered in parts of the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
(up to almost 50% in some areas) and Sicily, and declining frequencies evident toward western, central, and northeastern Europe.
Based on genetic STR variance data, suggests that E-M78 originated in the region of Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
and Libya
Libya, officially the State of Libya, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–L ...
. use the term Northeastern Africa to refer to Egypt and Libya, as shown in Table 1 of the study. Prior to , East Africa as a possible place of origin of E-M78, based upon Ethiopian testing. This was because of the high frequency and diversity of E-M78 lineages in the region of Ethiopia. However, were able to study more data, including populations from North Africa who were not represented in the study, and found evidence that the E-M78 lineages which make up a significant proportion of some populations in that region, were relatively young branches (see E-V32 below). They therefore concluded that "Northeast Africa" was the likely place of origin of E-M78 based on "the peripheral geographic distribution of the most derived subhaplogroups with respect to northeastern Africa, as well as the results of quantitative analysis of UEP and microsatellite diversity". So according to E-M35, the parent clade of E-M78, originated in East Africa, subsequently spread to Northeast Africa, and then there was a "back migration" of E-M215 chromosomes that had acquired the E-M78 mutation. therefore note this as evidence for "a corridor for bidirectional migrations" between Northeast Africa (Egypt and Libya in their data) on the one hand and East Africa on the other. The authors believe there were "at least 2 episodes between 23.9–17.3 ky and 18.0–5.9 ky ago". about 18,600 years ago (17,300 – 20,000 years ago). use two calculation methods for estimating the age of E-M78 which give very different results. For the main 18,600 years ago, the ASD method is used, while for a second " ρ method", used as a check, gives 13.7kya with a standard deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation of the values of a variable about its Expected value, mean. A low standard Deviation (statistics), deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean ( ...
of 2.3kya, but the difference between the two methods is only large for the age estimation of E-M78, not its subclades. The authors state that the big difference is "attributable to the relevant departure from a star-like structure because of repeated founder effects
In population genetics, the founder effect is the loss of genetic variation that occurs when a new population is established by a very small number of individuals from a larger population. It was first fully outlined by Ernst Mayr in 1942, using ...
" describe Egypt as "a hub for the distribution of the various geographically localized M78-related subclades" and, based on archaeological data, they propose that the point of origin of E-M78 (as opposed to later dispersal from Egypt) may have been in a refugium which "existed on the border of present-day Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi ...
and Egypt, near Lake Nubia
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from t ...
, until the onset of a humid phase around 8500 BC. The northward-moving rainfall belts during this period could have also spurred a rapid migration of Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
foragers northwards in Africa, the Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use toda ...
and ultimately onward to Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
and Europe, where they each eventually differentiated into their regionally distinctive branches". Towards the south, also explain evidence that some subclades of E-M78, specifically E-V12 and E-V22, "might have been brought to Sudan from North Africa after the progressive desertification
Desertification is a type of gradual land degradation of Soil fertility, fertile land into arid desert due to a combination of natural processes and human activities.
The immediate cause of desertification is the loss of most vegetation. This i ...
of the Sahara around 6,000–8,000 years ago". And similarly, propose that E-M78 in Ethiopia, Somalia and surrounding areas, back-migrated to this region from the direction of Egypt after acquiring the E-M78 mutation.
Recently, E-M78 was dated by Trombetta et al. 2015. between 20,300 and 14,800 years ago.
Subclades of E-M78
Listed here are the main subclades of M78 as of June 2015. Within the E-M78 subclade, Trombetta et al. 2015 allocated most of the former E-M78* chromosomes to three new distinct branches: E-V1083*, E-V1477 and E-V259. The first is a paragroup sister to clades E-V22 and E-V13. The mutation V1477 defines a new basal branch that has been observed only in one northern African sample. Finally, a sister clade of E-V12 defined by V264 includes E-V65 and V259, a new lineage distributed in central Africa. *E-M78 (E1b1b1a1) North Africa, Horn of Africa, West Asia, Europe (formerly "E1b1b1a"). **E-M78* Found in Morocco, southern Portugal, southern Spain and Iran (Tehran and Semnan provinces). **E-V1477 Found in Tunisian Jews. **E-V1083 ***E-V1083* Found only in Eritrea (1.1%) and Sardinia (0.3%). ***E-V13 This is the most common subclade of E-M215 found in Europe. It is especially common in the Balkans. ***E-V22. Concentrated in Northeast Africa and the Near East. Peaks among the Saho. **E-V1129 ***E-V12. Found in Egypt, Sudan, and Chad other places. Has an important subclade ****E-V12* Most common lineage among Southern Egyptians (74.5%). ****E-V32. Very common among Somalis, Tigre and Oromos. ***E-V264 ****E-V259 Found in North Cameroon. ****E-V65 Associated with North Africa, but also found in Sicily and also found in continental Italy. **E-M521 Not mentioned by Trombetta et al.2015. Found in two individuals in Greece by and in one individual from the Eastern Alpine region of Italy bCoia et al. (2013)
E-Z827 (E1b1b1b)
In human genetics, E-Z827, is the name of a majorhuman Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup
In human genetics, a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by specific mutations in the non-Genetic recombination, recombining portions of DNA on the male-specific Y chromosome (Y-DNA). Individuals within a haplogroup share ...
abundantly found in North Africa, particularly the Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb al ...
, and to a lesser extent in Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
, the Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
and Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
.
E-V257/E-L19 (E1b1b1b1)
E-V257* individuals in their samples who were E-V257, but not E-M81. A Borana from Kenya, a Marrakesh Berber, a Corsican, a Sardinian, a southern Spaniard and a Cantabrian. As mentioned above, propose that the absence of E-V257* in the Middle East (Yfull found a young one inIranian Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan or Azarbaijan (, , ), also known as Iranian Azerbaijan, is a historical region in northwestern Iran that borders Iraq and Turkey to the west and Armenia, Azerbaijan, and the Azerbaijani exclave of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republ ...
and a different young one in Armenia) makes a maritime movement from northern Africa to southern Europe the most plausible hypothesis so far to explain its distribution. Yfull lists 24 individuals, all of whom belong to a single branch that is 30% younger than their common ancestor with M81.
=E-M81
= E-M81 is the most common subclade of haplogroup E-L19/V257. It is concentrated in theMaghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb al ...
, and is dominated by its E-M183 subclade. E-M183 is believed to have originated in the Northwest Africa and has an estimated age of 4700 ybp.
This haplogroup reaches a mean frequency of 61% in the Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb al ...
and 51% in North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
, decreasing in frequency from approximately 80% to 100% in Berber populations, including Saharawis, to approximately 29% to the east of this range in Egypt. Because of its young age and prevalence among these groups and also others such as Mozabite, Middle Atlas
The Middle Atlas (Amazigh: ⴰⵟⵍⴰⵚ ⴰⵏⴰⵎⵎⴰⵙ, ''Atlas Anammas'', Arabic: الأطلس المتوسط, ''al-Aṭlas al-Mutawassiṭ'') is a mountain range in Morocco. It is part of the Atlas mountain range, a mountainous regio ...
, Kabyle and other Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–196 ...
groups, it is sometimes referred to as a genetic "Berber marker". report high levels amongst Tuareg
The Tuareg people (; also spelled Twareg or Touareg; endonym, depending on variety: ''Imuhaɣ'', ''Imušaɣ'', ''Imašeɣăn'' or ''Imajeɣăn'') are a large Berber ethnic group, traditionally nomadic pastoralists, who principally inhabit th ...
in two Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
n populations – 77.8% near Gorom-Gorom
Gorom-Gorom is a town in northern Burkina Faso. Its name translates as "''you sit down, (and) we'll sit down''", reminiscent of its role as an important crossroads in the Sahel. It is the capital of Oudalan Province.
Known for its market and many ...
, in Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso is a landlocked country in West Africa, bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and Ivory Coast to the southwest. It covers an area of 274,223 km2 (105,87 ...
, and 81.8% from Gosi in Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
. There was a much lower frequency of 11.1% in the vicinity of Tanut in Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east ...
. E-M81 is also quite common among Maghrebi Arabic
Maghrebi Arabic, often known as ''ad-Dārija'' to differentiate it from Literary Arabic, is a vernacular Arabic dialect continuum spoken in the Maghreb. It includes the Moroccan, Algerian, Tunisian, Libyan, Hassaniya and Saharan Arabic di ...
-speaking groups. It is generally found at frequencies around 45% in coastal cities of Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
and Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
(Jijel
Jijel (), the classical Igilgili, is the capital of Jijel Province in north-eastern Algeria. It is flanked by the Mediterranean Sea in the region of Corniche Jijelienne and had a population of 131,513 in 2008.
Jijel is the administrative and trad ...
, Oran
Oran () is a major coastal city located in the northwest of Algeria. It is considered the second most important city of Algeria, after the capital, Algiers, because of its population and commercial, industrial and cultural importance. It is w ...
, Tizi Ouzou
Tizi Ouzou or Thizi Wezzu (, Kabyle: Tizi Wezzu) is a city in north central Algeria, and capital of Tizi Ouzou Province and Tizi Ouzou District. It is among the largest cities in Algeria. It is the second most populous city in the Kabylia reg ...
, Algiers
Algiers is the capital city of Algeria as well as the capital of the Algiers Province; it extends over many Communes of Algeria, communes without having its own separate governing body. With 2,988,145 residents in 2008Census 14 April 2008: Offi ...
, Tunis
Tunis (, ') is the capital city, capital and largest city of Tunisia. The greater metropolitan area of Tunis, often referred to as "Grand Tunis", has about 2,700,000 inhabitants. , it is the third-largest city in the Maghreb region (after Casabl ...
, Sousse
Sousse, Sūsah , or Soussa (, ), is a city in Tunisia, capital of the Sousse Governorate. Located south of the capital Tunis, the city has 271,428 inhabitants (2014). Sousse is in the central-east of the country, on the Gulf of Hammamet, which ...
).
In this key area from Egypt to the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
, report a M183-SM001 pattern of decreasing microsatellite
A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain Sequence motif, DNA motifs (ranging in length from one to six or more base pairs) are repeated, typically 5–50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations within an organ ...
haplotype variation (implying greater lineage age in the former areas) from the Reguibat tribe
The Reguibat (; variously transliterated ''Reguibate'', ''Rguibat'', ''R'gaybat'', ''R'gibat'', ''Erguibat'', ''Ergaybat'') is a Sahrawi tribal confederation of mixed Arab and Sanhaja Berber origins. The Reguibat speak Hassaniya Arabic, and are ...
in Oran
Oran () is a major coastal city located in the northwest of Algeria. It is considered the second most important city of Algeria, after the capital, Algiers, because of its population and commercial, industrial and cultural importance. It is w ...
and they found M183* (not SM001) in Iberia, Libya and Morocco. however showed microsatellite variation decrease from East to West, accompanied by a substantial increasing frequency. At the eastern extreme of this core range, found M81 in 28.6% (10 out of 35 men) in el-Hayez in the Libyan Desert
The Libyan Desert (not to be confused with the Libyan Sahara) is a geographical region filling the northeastern Sahara Desert, from eastern Libya to the Western Desert (Egypt), Western Desert of Egypt and far northwestern Sudan. On medieval m ...
in Egypt.
believe the pattern of distribution and variance to be consistent with the hypothesis of a "demic diffusion
Demic diffusion, as opposed to trans-cultural diffusion, is a demographic term referring to a migratory model, developed by Luigi Luca Cavalli-Sforza, of population diffusion into and across an area that had been previously uninhabited by that g ...
" from the East. There is no autochthonous presence of E-M81 in the Near East (there is one in Lebanon), indicating that M81 most likely emerged from its parent clade M35 either in North Africa, or possibly as far south as the Horn of Africa.
In Europe, E-M81 is widespread but rare, in the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula ( ), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees, it includes the territories of peninsular Spain and Continental Portugal, comprisin ...
shows an average frequency of 4% (45/1140) in the Iberian Peninsula with frequencies reaching 3.5% in Galicia, 4% in Western Andalusia
Andalusia ( , ; , ) is the southernmost autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in Peninsular Spain, located in the south of the Iberian Peninsula, in southwestern Europe. It is the most populous and the second-largest autonomou ...
and Northwest Castile. However this study includes 153 individuals from Majorca, Minorca and Ibiza islands as well as 24 individuals from Gascony which are not in the Iberian Peninsula. Without these 177 individuals, average for Iberian Peninsula is 4.1% (40/963), it is found at comparable levels to E-M78, with an average frequency of around 5%. Its frequencies are higher in the western half of the peninsula with frequencies reaching 8% in Extremadura
Extremadura ( ; ; ; ; Fala language, Fala: ''Extremaúra'') is a landlocked autonomous communities in Spain, autonomous community of Spain. Its capital city is Mérida, Spain, Mérida, and its largest city is Badajoz. Located in the central- ...
and southern Portugal, 4% to 5% in Galicia, 5% in western Andalusia
Andalusia ( , ; , ) is the southernmost autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community in Peninsular Spain, located in the south of the Iberian Peninsula, in southwestern Europe. It is the most populous and the second-largest autonomou ...
and 4% in northwest Castile and 9% to 17% in Cantabria
Cantabria (, ; ) is an autonomous community and Provinces of Spain, province in northern Spain with Santander, Cantabria, Santander as its capital city. It is called a , a Nationalities and regions of Spain, historic community, in its current ...
. The highest frequencies of this clade found so far in Europe were observed in the Valles Pasiegos
Valles Pasiegos is an administrative ''comarca'' in Cantabria, Spain. It is formed by the valleys of the Pas and Miera rivers, each one being a natural ''comarca'' of its own.
History
In the whole valley, the repopulation allowed by the found ...
from Cantabria
Cantabria (, ; ) is an autonomous community and Provinces of Spain, province in northern Spain with Santander, Cantabria, Santander as its capital city. It is called a , a Nationalities and regions of Spain, historic community, in its current ...
, ranging from 5.5% (8/45) to 41% (23/56). An average frequency of 8.28% (54/652) has also been reported in the Spanish Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; ) or Canaries are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean and the southernmost Autonomous communities of Spain, Autonomous Community of Spain. They are located in the northwest of Africa, with the closest point to the cont ...
with frequencies over 10% in the three largest islands of Tenerife
Tenerife ( ; ; formerly spelled ''Teneriffe'') is the largest and most populous island of the Canary Islands, an Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain. With a land area of and a population of 965,575 inhabitants as of A ...
(10.68%), Gran Canaria
Gran Canaria (, ; ), also Grand Canary Island, is the third-largest and second-most-populous island of the Canary Islands, a Spain, Spanish archipelago off the Atlantic coast of Northwest Africa. the island had a population of that constitut ...
(11.54%) and Fuerteventura
Fuerteventura () is one of the Canary Islands, in the Atlantic Ocean, geographically part of Macaronesia, and politically part of Spain. It is located away from the coast of North Africa. The island was declared a biosphere reserve by UNESCO i ...
(13.33%).
E-M81 is also found in France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, 2.70% (15/555) overall with frequencies surpassing 5% in Auvergne
Auvergne (; ; or ) is a cultural region in central France.
As of 2016 Auvergne is no longer an administrative division of France. It is generally regarded as conterminous with the land area of the historical Province of Auvergne, which was dis ...
(5/89) and Île-de-France
The Île-de-France (; ; ) is the most populous of the eighteen regions of France, with an official estimated population of 12,271,794 residents on 1 January 2023. Centered on the capital Paris, it is located in the north-central part of the cou ...
(5/91), 0,7% to 5,8% in Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; ; ) is the Mediterranean islands#By area, second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, and one of the Regions of Italy, twenty regions of Italy. It is located west of the Italian Peninsula, north of Tunisia an ...
, approximately 2.12% overall in Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
(but up to 7.14% in Piazza Armerina
Piazza Armerina (Gallo-Italic of Sicily: ''Ciazza''; Sicilian: ''Chiazza'') is a ''comune'' in the province of Enna of the autonomous island region of Sicily, southern Italy.
History
The city of Piazza (as it was called before 1862) developed ...
), and in very much lower frequency near Lucera
Lucera (Neapolitan language, Lucerino: ) is an Italian city of 34,243 inhabitants in the province of Foggia in the region of Apulia, and the seat of the Diocese of Lucera-Troia.
Located upon a flat knoll in the Tavoliere delle Puglie, Tavoliere ...
(1.7%), in continental Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, possibly due to ancient migrations during the Islamic
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
, Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
, and Carthaginian The term Carthaginian ( ) usually refers to the civilisation of ancient Carthage.
It may also refer to:
* Punic people, the Semitic-speaking people of Carthage
* Punic language
The Punic language, also called Phoenicio-Punic or Carthaginian, i ...
empires. In a 2014 study by Stefania Sarno et al. with 326 samples from Cosenza
Cosenza (; Languages of Calabria#Northern Calabrian (Cosentian), Cosentian: ''Cusenza'', ) is a city located in Calabria, Italy. The city centre has a population of approximately 70,000, while the urban area counts more than 200,000 inhabitants. ...
, Reggio Calabria
Reggio di Calabria (; ), commonly and officially referred to as Reggio Calabria, or simply Reggio by its inhabitants, is the List of cities in Italy, largest city in Calabria as well as the seat of the Metropolitan City of Reggio Calabria. As ...
, Lecce
Lecce (; ) is a city in southern Italy and capital of the province of Lecce. It is on the Salentine Peninsula, at the heel of the Italian Peninsula, and is over two thousand years old.
Because of its rich Baroque architecture, Lecce is n ...
and five Sicilian provinces, E-M81 shows an average frequency of 1.53%, but the typical Maghrebin core haplotype 13-14-30-24-9-11-13 has been found in only two out of the five E-M81 individuals. These results, along with the negligible contribution from North-African populations revealed by the admixture-like plot analysis, suggest only a marginal impact of trans-Mediterranean gene flows on the current SSI genetic pool.
As a result of its old world distribution, this subclade is found throughout Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
5.4% in Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
(Rio de Janeiro),(6 out of 112), "The presence of chromosomes of North African origin (E3b1b-M81; Cruciani et al., 2004) can also be explained by a Portuguese but especially Italian-mediated influx, since this haplogroup reaches a frequency of 4.6% in Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
and of 4.8% Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, quite similar to the frequency found in Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro, or simply Rio, is the capital of the Rio de Janeiro (state), state of Rio de Janeiro. It is the List of cities in Brazil by population, second-most-populous city in Brazil (after São Paulo) and the Largest cities in the America ...
(4.4%) among European contributors." and among Hispanic
The term Hispanic () are people, Spanish culture, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or broadly. In some contexts, Hispanic and Latino Americans, especially within the United States, "Hispanic" is used as an Ethnici ...
men from California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
and Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
2.4%.
In smaller numbers, E-M81 men can be found in areas in contact with North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
, both around the Sahara
The Sahara (, ) is a desert spanning across North Africa. With an area of , it is the largest hot desert in the world and the list of deserts by area, third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Ar ...
, in places like Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi ...
, and around the Mediterranean in places like Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
, Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, and amongst Sephardi Jews
Sephardic Jews, also known as Sephardi Jews or Sephardim, and rarely as Iberian Peninsular Jews, are a Jewish diaspora population associated with the historic Jewish communities of the Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal) and their descendant ...
.
There are two recognized subclades of E-M81, although one is much more important than the other.
The E-M81 subclade has been found in ancient Guanche Guanche may refer to:
*Guanches, the indigenous people of the Canary Islands
*Guanche language, an extinct language, spoken by the Guanches until the 16th or 17th century
*''Conus guanche
''Conus guanche'' is a species of sea snail, a marine ga ...
(Bimbapes) fossils excavated in Punta Azul, El Hierro
El Hierro (), nicknamed ''Isla del Meridiano'' (the "Meridian Island"), is the farthest south and west of the Canary Islands (an autonomous community of Spain), in the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Africa, with a population of 11,659 (2023). ...
, Canary Islands
The Canary Islands (; ) or Canaries are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean and the southernmost Autonomous communities of Spain, Autonomous Community of Spain. They are located in the northwest of Africa, with the closest point to the cont ...
, which are dated to the 10th century (~44%).E-M107 found one example of E-M107 in
Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
.
E-M183 E-M183 is extremely dominant (more than 99%) within E-M81. first described it as a subclade of E-M81. The known subclades of E-M183 include: *E-M165 found one example in Middle East. *E-L351 Found in two related participants in Th
E-M35 Phylogeny Project
E-Z830 (E1b1b1b2)
This is a recently discovered subclade which has not yet been included in most haplogroup trees, E-Z830 includes the confirmed subclades of E-M123, E-V1515 (E-M293, E-V42, E-V6, E-V92), and E-Z830*, and is a sibling clade to E-L19. Currently, the E-M35 phylogeny project] recognizes four distinct clusters of Z830* carriers, two of which are exclusively Jewish in origin. The remaining two are significantly smaller, and include scattered individuals in Germany, Spain, Latin America, Egypt, and Ethiopia.=E-M123
= E-M123 is mostly known for its major subclade E-M34, which dominates this clade.As of 11 November 2008 for examplethe E-M35 phylogeny project
had records of four E-M123* tests, compared to 93 test results with E-M34.
=E-V1515
= A new clade (E-V1515) was defined by Trombetta et al. 2015, which originated about 12 kya (95% CI 8.6–16.4) in eastern Africa where it is currently mainly distributed. This clade includes all the sub-Saharan haplogroups (E-V42, E-M293, E-V92, E-V6) reported as E-M35 basal clades in a previous phylogeny.E-M293 E-M293 is a subclade of E-V1515. It was first identified by ISOGG as the second clade within E-Z830. It was discovered before E-Z830, being announced in , which associated it with the spread of
pastoralism
Pastoralism is a form of animal husbandry where domesticated animals (known as "livestock") are released onto large vegetated outdoor lands (pastures) for grazing, historically by nomadic people who moved around with their herds. The anim ...
from East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
into Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost region of Africa. No definition is agreed upon, but some groupings include the United Nations geoscheme for Africa, United Nations geoscheme, the intergovernmental Southern African Development Community, and ...
. So far high levels have been found in specific ethnic groups in Tanzania and Southern Africa. Highest were the Datooga (43%), Khwe (Kxoe) (31%), Burunge (28%), and Sandawe people
The Sandawe are an indigenous ethnic group of Southeast Africa, based in the Chemba District kwamtoro ward of Dodoma Region in central Tanzania. In 2000, the Sandawe population was estimated to be 40,000.
The Sandawe language is a tonal lan ...
s (24%). Henn (2008) in their study also found two Bantu-speaking Kenyan males with the M293 mutation.
Other E-M215 subclades are rare in Southern Africa. The authors state "Without information about M293 in the Maasai, Hema, and other populations in Kenya, Sudan, and Ethiopia, we cannot pinpoint the precise geographic source of M293 with greater confidence. However, the available evidence points to present-day Tanzania as an early and important geographic locus of M293 evolution.". They also say that "M293 is only found in sub-Saharan Africa, indicating a separate phylogenetic history for M35.1 * (former) samples further north".
E-P72 appears in Karafet (2008). announced that this is a subclade of E-M293.
E-V42 announced the discovery of E-V42 in two
Beta Israel
Beta Israel, or Ethiopian Jews, is a Jewish group originating from the territory of the Amhara Region, Amhara and Tigray Region, Tigray regions in northern Ethiopia, where they are spread out across more than 500 small villages over a wide ter ...
persons. It was suggested that it may be restricted to the region around Ethiopia. However, further testing by commercial DNA testing companies confirmed many positive results for this subclade in Saudi Arabia, Kuwait and one person in Portugal who has a root from Arabia.
E-V6 The E-V6 subclade of E-V1515 is defined by V6. identified a significant presence of these lineages in Ethiopia and also some in the neighboring
Somalis
The Somali people (, Wadaad's writing, Wadaad: , Arabic: ) are a Cushitic peoples, Cushitic ethnic group and nation native to the Somali Peninsula. who share a common ancestry, culture and history.
The Lowland East Cushitic languages, East ...
. Among the Ethiopian and Somali samples, the highest were 14.7% among the Amhara and 16.7% among the Wolayta.
To the south, identified one V6+ man in a sample of 35 Datooga of Tanzania. And further to the north, identified another 6 men in a sample of 93 from the Siwa Oasis
The Siwa Oasis ( ) is an urban oasis in Egypt. It is situated between the Qattara Depression and the Great Sand Sea in the Western Desert (Egypt), Western Desert, east of the Egypt–Libya border and from the Egyptian capital city of Cairo. I ...
, which is a Berber population
E-V92 announced the discovery of E-V92 in two Amharas. Like E-V6 and E-V42 it possibly only exists in the area of Ethiopia.
Phylogenetics
Phylogenetic history
Prior to 2002, there were in academic literature at least seven naming systems for the Y-Chromosome phylogenetic tree. This led to considerable confusion. In 2002, the major research groups came together and formed the Y-Chromosome Consortium (YCC). They published a joint paper that created a single new tree that all agreed to use. Later, a group of citizen scientists with an interest in population genetics and genetic genealogy formed a working group to create an amateur tree aiming at being above all timely. The table below brings together all of these works at the point of the landmark 2002 YCC Tree. This allows a researcher reviewing older published literature to quickly move between nomenclatures.Research publications
The following research teams per their publications were represented in the creation of the YCC Tree.Phylogenetic trees
Cladogram with the main subclades: The followingphylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree or phylogeny is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or taxa during a specific time.Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA. In ...
is based on the YCC 2008 tree and subsequent published research as summarized by ISOGG. It includes all known subclades as of June 2015 (Trombetta et al. 2015)
*E-M215 (E1b1b)
**E-M215*. Rare or non-existent.
**E-M35 (E1b1b1)
*** E-V68 (E1b1b1a)
****E-V2009. Found in individuals in Sardinia and Morocco.
****E-M78 (E1b1b1a1). North Africa, Horn of Africa, West Asia, Sicily. (Formerly "E1b1b1a".)
*****E-M78*
*****E-V1477. Found in Tunisian Jews.
*****E-V1083.
******E-V1083*. Found only in Eritrea (1.1%) and Sardinia (0.3%).
******E-V13
******E-V22
*****E-V1129
******E-V12
*******E-V12*
*******E-V32
******E-V264
*******E-V259. Found in North Cameroon.
*******E-V65
********E-CTS194
*** E-Z827 (E1b1b1b)ISOGG 2015
****E-V257/L19 (L19, V257) – E1b1b1b1
*****E-PF2431
*****E-M81 (M81)
******E-PF2546
*******E-PF2546*
*******E-CTS12227
********E-MZ11
*********E-MZ12
*******E-A929
********E-Z5009
*********E-Z5009*
*********E-Z5010
*********E-Z5013
**********E-Z5013*
**********E-A1152
********E-A2227
*********E-A428
*********E-MZ16
********E-PF6794
*********E-PF6794*
*********E-PF6789
**********E-MZ21
**********E-MZ23
**********E-MZ80
********E-A930
********E-Z2198/E-MZ46
*********E-A601
*********E-L351
****E-Z830 (Z830) – E1b1b1b2
***** E-M123 (M123)
******E-M34 (M34)
*******E-M84 (M84)
********E-M136 (M136)
*******E-M290 (M290)
*******E-V23 (V23)
*******E-L791 (L791,L792)
*****E-V1515. E-V1515 and its subclades are mainly restricted to eastern Africa.
******E-V1515*
******E-V1486
*******E-V1486*
*******E-V2881
********E-V2881*
********E-V1792
********E-V92
*******E-M293 (M293)
********E-M293*
********E-P72 (P72)
********E-V3065*
******E-V1700
*******E-V42 (V42)
*******E-V1785
********E-V1785*
********E-V6 (V6)
***E-V16/E-M281 (E1b1b2). Rare. Found in individuals in Ethiopia, Yemen and Saudi Arabia.
See also
Genetics
Y-DNA E subclades
Y-DNA backbone tree
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * *. Also at http://www.ucl.ac.uk/tcga/tcgapdf/Behar-AJHG-03.pdf and https://web.archive.org/web/20090304100321/http://www.familytreedna.com/pdf/400971.pdf * * * * * * * * also a* * * * * * * * Also se
Supplementary Data
* * * * * * * * * * * * * *. Se
an
public release
* * *. Published online April 2, 2008. See als
Supplementary Material.
* * * * * * * *. (Also se
Errata
* * * * * * * * *. * Pontikos D. "Phylogeographic refinement of haplogroup E" http://dienekes.blogspot.ru/2015/07/phylogeographic-refinement-of.html * * * * * *. Published online 9 March 2005 * *. * * * * * * * * * * * Trombetta B. "Phylogeographic Refinement and Large Scale Genotyping of Human Y Chromosome Haplogroup E Provide New Insights into the Dispersal of Early Pastoralists in the African Continent" http://gbe.oxfordjournals.org/content/7/7/1940.long * * * * *. * * * * * * *
Sources for conversion tables
* * * * * * *External links
E-M35 Phylogeny Project Wiki
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Haplogroup E1b1b (Y-Dna) Human Y-DNA haplogroups