Drug trafficker on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The illegal drug trade, drug trafficking, or narcotrafficking is a global

World Drug Report 2010 Statistical Annex: Drug seizures
to sixth in the world in 2012. On 18 November 2016, following what was known as the Narcosobrinos incident, Venezuelan President
How the feds took down the Dread Pirate Roberts
, 3 October 2013 This prompted the creation of new platforms such as Silk Road 2.0, which were also shut down.

 Statistics about profits from the drug trade are largely unknown due to its illicit nature. An online report published by the UK Home Office in 2007 estimated the illicit drug market in the UK at £4–6.6 billion a year.
In December 2009,
Statistics about profits from the drug trade are largely unknown due to its illicit nature. An online report published by the UK Home Office in 2007 estimated the illicit drug market in the UK at £4–6.6 billion a year.
In December 2009,  Costa declined to identify countries or banks that may have received any drug money, saying that would be inappropriate because his office is supposed to address the problem, not apportion blame.
Though street-level drug sales are widely viewed as lucrative, a study by Sudhir Venkatesh suggested that many low-level employees receive low wages. In a study he made in the 1990s working closely with members of the Black Gangster Disciple Nation in
Costa declined to identify countries or banks that may have received any drug money, saying that would be inappropriate because his office is supposed to address the problem, not apportion blame.
Though street-level drug sales are widely viewed as lucrative, a study by Sudhir Venkatesh suggested that many low-level employees receive low wages. In a study he made in the 1990s working closely with members of the Black Gangster Disciple Nation in


 Although narcotics are illegal in the US, they have become integrated into the nation's culture and are seen as a recreational activity by sections of the population. Illicit drugs are considered to be a commodity with strong demand, as they are typically sold at a high value. This high price is caused by a combination of factors that include the potential legal ramifications that exist for suppliers of illicit drugs and their high demand. Despite the constant effort by politicians to win the war on drugs, the US is still the world's largest importer of illegal drugs.
Throughout the 20th century, narcotics other than cocaine also crossed the Mexican border, meeting the US demand for alcohol during the 1920s
Although narcotics are illegal in the US, they have become integrated into the nation's culture and are seen as a recreational activity by sections of the population. Illicit drugs are considered to be a commodity with strong demand, as they are typically sold at a high value. This high price is caused by a combination of factors that include the potential legal ramifications that exist for suppliers of illicit drugs and their high demand. Despite the constant effort by politicians to win the war on drugs, the US is still the world's largest importer of illegal drugs.
Throughout the 20th century, narcotics other than cocaine also crossed the Mexican border, meeting the US demand for alcohol during the 1920s
 In 1929, the
In 1929, the
 Throughout the 1980s, estimates of illegal drug value in Colombia ranged from $2bn to $4bn. This made up about 7–10% of the $36bn estimated Gross National Product (GNP) of Colombia during this decade. In the 1990s, the estimates of the illegal drug value remained roughly within the same range (~$2.5bn). As the Colombian GNP rose throughout the 1990s ($68.5bn in 1994 and $96.3bn in 1997), illegal drug values began to comprise a decreasing fraction of the national economy.
By the early 1990s, although Colombia led in the exportation of cocaine, it found increasing confrontations within its state. These confrontations were primarily between cartels and government institutions. This led to a decrease in the drug trade's contribution to the GDP of Colombia; dropping from 5.5% to 2.6%. Though a contributor of wealth, the distribution of cocaine has had negative effects on the socio-political situation of Colombia and has weakened its economy as well.
Throughout the 1980s, estimates of illegal drug value in Colombia ranged from $2bn to $4bn. This made up about 7–10% of the $36bn estimated Gross National Product (GNP) of Colombia during this decade. In the 1990s, the estimates of the illegal drug value remained roughly within the same range (~$2.5bn). As the Colombian GNP rose throughout the 1990s ($68.5bn in 1994 and $96.3bn in 1997), illegal drug values began to comprise a decreasing fraction of the national economy.
By the early 1990s, although Colombia led in the exportation of cocaine, it found increasing confrontations within its state. These confrontations were primarily between cartels and government institutions. This led to a decrease in the drug trade's contribution to the GDP of Colombia; dropping from 5.5% to 2.6%. Though a contributor of wealth, the distribution of cocaine has had negative effects on the socio-political situation of Colombia and has weakened its economy as well.
 While the recreational use of (and consequently the distribution of)
While the recreational use of (and consequently the distribution of)
Rolling Meth Labs In Vogue – Methamphetamine Makers Turn Vehicles Into Rolling Drug Labs
." ''
Illicit drug issues by country, by the CIA
. {{Authority control Smuggling
black market
A black market is a Secrecy, clandestine Market (economics), market or series of transactions that has some aspect of illegality, or is not compliant with an institutional set of rules. If the rule defines the set of goods and services who ...
dedicated to the cultivation, manufacture, distribution and sale of prohibited drugs. Most jurisdictions prohibit trade, except under license
A license (American English) or licence (Commonwealth English) is an official permission or permit to do, use, or own something (as well as the document of that permission or permit).
A license is granted by a party (licensor) to another part ...
, of many types of drugs through the use of drug prohibition laws. The think tank Global Financial Integrity's ''Transnational Crime and the Developing World'' report estimates the size of the global illicit drug market between US$426 and US$652billion in 2014, which is equal to the UK's national debt alone. With a world GDP of US$78 trillion in the same year, the illegal drug trade may be estimated as nearly 1% of total global trade. Consumption of illegal drugs is widespread globally, and it remains very difficult for local authorities to reduce the rates of drug consumption.
History
Prior to the 20th century, governments rarely made a major effort to proscriberecreational drug use
Recreational drug use is the use of one or more psychoactive drugs to induce an altered state of consciousness, either for pleasure or for some other casual purpose or pastime. When a psychoactive drug enters the user's body, it induces an Sub ...
, though several smoking ban
Smoking bans, or smoke-free laws, are public policies, including criminal laws and occupational safety and health regulations, that prohibit tobacco smoking in certain spaces. The spaces most commonly affected by smoking bans are indoor employ ...
s were passed by authorities in Europe and Asia during the early modern era
The early modern period is a historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There is no exact date ...
. Tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
and opium
Opium (also known as poppy tears, or Lachryma papaveris) is the dried latex obtained from the seed Capsule (fruit), capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid mor ...
were the two first drugs to be subject to prohibitory government legislation, with officials in New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( ; Nahuatl: ''Yankwik Kaxtillan Birreiyotl''), originally the Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain. It was one of several ...
, the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
, Germany, Austria and the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
passing laws against smoking tobacco; the government of the Qing dynasty issued edicts banning opium smoking in 1730, 1796 and 1800. Beginning in the 18th century, the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
(EIC) began to smuggle Indian opium to Chinese merchants, resulting in the creation of an illegal drug trade in China
The Illegal drug trade in China is largely focused on the golden-triangle area near the China-Myanmar border.
Opium
Opium has played an important role in China's history since the First and Second Opium Wars in the mid-19th century. The fall o ...
. By 1838, there were between four and 12 million opium addicts in China, and Qing officials responded by strengthening their suppression of the illegal opium trade. Incidents such as the destruction of opium at Humen
The destruction of opium at Humen began on 3June 1839, lasted for 23 days, and involved the destruction of 1,000 long tons (1,016 t) of illegal opium seized from British traders under the aegis of Lin Zexu, an Imperial Commissioner of Qin ...
led to the outbreak of the First Opium War
The First Opium War ( zh, t=第一次鴉片戰爭, p=Dìyīcì yāpiàn zhànzhēng), also known as the Anglo-Chinese War, was a series of military engagements fought between the British Empire and the Chinese Qing dynasty between 1839 and 1 ...
between China and Britain in 1839; the 1842 Treaty of Nanking
The Treaty of Nanking was the peace treaty which ended the First Opium War (1839–1842) between United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, Great Britain and the Qing dynasty of China on 29 August 1842. It was the first of what the Chinese ...
ending the war did not legalize the importation of opium into China, but Western merchants continued to smuggle the drug to Chinese merchants in ever-increasing amounts. The 1858 Treaty of Tianjin
The Treaty of Tientsin, also known as the Treaty of Tianjin, is a collective name for several unequal treaties signed at Tianjin (then romanized as Tientsin) in June 1858. The Qing dynasty, Russian Empire, Second French Empire, United Kingdom, ...
, which ended the Second Opium War
The Second Opium War (), also known as the Second Anglo-Chinese War or ''Arrow'' War, was fought between the United Kingdom, France, Russia, and the United States against the Qing dynasty of China between 1856 and 1860. It was the second major ...
, stipulated that the Qing government would open several ports to foreign trade, including opium.
Western governments began prohibiting addictive drugs during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. In 1868, as a result of the increased use of opium in Britain, the British government restricted the sale of opium by implementing the 1868 Pharmacy Act. In the United States, control of opium remained under the control of individual US state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its so ...
s until the introduction of the Harrison Act
The Harrison Narcotics Tax Act (Ch. 1, ) was a United States federal law that regulated and taxed the production, importation, and distribution of opiates and coca products. The act was proposed by Representative Francis Burton Harrison of N ...
in 1914, after 12 international powers signed the International Opium Convention
The expression International Opium Convention refers either to the first International Opium Convention signed at The Hague in 1912, or to the second International Opium Convention signed at Geneva in 1925.
First International Opium Convention ...
in 1912. Between 1920 and , the Eighteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
The Eighteenth Amendment (Amendment XVIII) to the United States Constitution established the prohibition of alcohol in the United States. The amendment was proposed by Congress on December 18, 1917, and ratified by the requisite number of sta ...
banned alcohol in the United States. Prohibition proved almost impossible to enforce and resulted in the rise of organized crime, including the modern American Mafia
The American Mafia, commonly referred to in North America as the Italian-American Mafia, the Mafia, or the Mob, is a highly organized Italian-American criminal society and organized crime group. The terms Italian Mafia and Italian Mob apply to ...
, which identified enormous business opportunities in the manufacturing, smuggling and sale of illicit liquor.
The beginning of the 21st century saw drug use increase in North America and Europe, with a particularly increased demand for marijuana
Cannabis (), commonly known as marijuana (), weed, pot, and ganja, List of slang names for cannabis, among other names, is a non-chemically uniform psychoactive drug from the ''Cannabis'' plant. Native to Central or South Asia, cannabis has ...
and cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
. As a result, international organized crime
Organized crime is a category of transnational organized crime, transnational, national, or local group of centralized enterprises run to engage in illegal activity, most commonly for profit. While organized crime is generally thought of as a f ...
syndicates such as the Sinaloa Cartel
The Sinaloa Cartel (, , after the native Sinaloa region), also known as the ''CDS'', the ''Guzmán-Loera Organization'', the ''Federation'', the ''Sinaloa Cartel'', or the Pacific Cartel, is a large, drug trafficking transnational organized cri ...
and 'Ndrangheta
The 'Ndrangheta (, , ) is a mafia-type organized crime, criminal syndicate originating from the Calabria region of Italy. Gratteri & Nicaso, ''Fratelli di Sangue'', pp. 65–68 This body, also referred to as the Commission in reference to the ...
have increased cooperation among each other in order to facilitate trans-Atlantic drug-trafficking. Use of another illicit drug, hashish
Hashish (; ), usually abbreviated as hash, is a Compression (physics), compressed form of resin (trichomes) derived from the cannabis flowers. European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction, Lisbon, As a Psychoactive drug, psychoactive ...
, has also increased in Europe. Drug trafficking is widely regarded by lawmakers as a serious offense around the world. Penalties often depend on the type of drug (and its classification in the country into which it is being trafficked), the quantity trafficked, where the drugs are sold and how they are distributed. If the drugs are sold to underage people, then the penalties for trafficking may be harsher than in other circumstances.
Drug smuggling carries severe penalties in many countries. Sentencing may include lengthy periods of incarceration, flogging
Flagellation (Latin , 'whip'), flogging or whipping is the act of beating the human body with special implements such as whips, rods, switches, the cat o' nine tails, the sjambok, the knout, etc. Typically, flogging has been imposed ...
and even the death penalty
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence ordering that an offender be punished in s ...
(in Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia and elsewhere). In December 2005, Van Tuong Nguyen
Van Tuong Nguyen (Vietnamese: ''Nguyễn Tường Vân'', ; 17 August 1980 – 2 December 2005), baptised Caleb, was an Australian from Melbourne, Victoria convicted of drug trafficking in Singapore. A Vietnamese Australian, he was also add ...
, a 25-year-old Australian drug smuggler, was hanged in Singapore after being convicted in March 2004. In 2010, two people were sentenced to death in Malaysia for trafficking of cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae that is widely accepted as being indigenous to and originating from the continent of Asia. However, the number of species is disputed, with as many as three species be ...
into the country. Execution is mostly used as a deterrent, and many have called upon much more effective measures to be taken by countries to tackle drug trafficking; for example, targeting specific criminal organisations that are often also active in the smuggling of other goods (i.e. wildlife) and even people. In many cases, links between politicians and the criminal organisations have been proven to exist. In June 2021, Interpol
The International Criminal Police Organization – INTERPOL (abbreviated as ICPO–INTERPOL), commonly known as Interpol ( , ; stylized in allcaps), is an international organization that facilitates worldwide police cooperation and crime cont ...
revealed an operation in 92 countries that shut down 113,000 websites and online marketplaces selling counterfeit or illicit medicines and medical products a month earlier, led to the arrests of 227 people worldwide, recovered pharmaceutical products worth $23 million, and led to the seizure of approximately nine million devices and drugs, including large quantities of fake COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever ...
tests and face masks.
Societal effects
The countries of drug production and transit are some of the most affected by the trade, though countries receiving the illegallyimported substances are also adversely affected. For example, Ecuador has absorbed up to 300,000 refugees from Colombia who are running from guerrillas, paramilitaries and drug lords. While some applied for asylum, others are still illegal immigrants. The drugs that pass from Colombia through Ecuador to other parts of South America create economic and social problems.Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Ocean at the Gulf of Fonseca, ...
, through which an estimated 79% of cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
passes on its way to the United States, had, as of 2011, the highest murder rate in the world. According to the International Crisis Group
The International Crisis Group (ICG; also known as the Crisis Group) is a global non-profit, non-governmental organisation founded in 1995. It is a think tank, used by policymakers and academics, conducting research and analysis on global crises. ...
, the most violent regions in Central America, particularly along the Guatemala–Honduras border, are highly correlated with an abundance of drug trafficking activity.
Violent crime
In several countries, the illegal drug trade is thought to be directly linked toviolent crime
A violent crime, violent felony, crime of violence or crime of a violent nature is a crime in which an offender or perpetrator uses or threatens to use harmful Force (law), force upon a victim. This entails both crimes in which the violence, vio ...
s such as murder and gun violence. This is especially true in all developing
countries, such as Honduras
Honduras, officially the Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Ocean at the Gulf of Fonseca, ...
, but is also an issue for many developed countries worldwide. In the late 1990s in the United States, the Federal Bureau of Investigation
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic Intelligence agency, intelligence and Security agency, security service of the United States and Federal law enforcement in the United States, its principal federal law enforcement ag ...
estimated that 5% of murders were drug-related. In Colombia, drug violence can be caused by factors such as the economy, poor governments, and no authority within law enforcement.
After a crackdown by US and Mexican authorities in the first decade of the 21st century as part of tightened border security in the wake of the September 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, also known as 9/11, were four coordinated Islamist terrorist suicide attacks by al-Qaeda against the United States in 2001. Nineteen terrorists hijacked four commercial airliners, crashing the first two into ...
, border violence inside Mexico surged. The Mexican government estimated that 90% of the killings were drug-related.
A report by the UK government's Drug Strategy Unit that was leaked to the press, stated that due to the expensive price of highly addictive drugs heroin
Heroin, also known as diacetylmorphine and diamorphine among other names, is a morphinan opioid substance synthesized from the Opium, dried latex of the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy; it is mainly used as a recreational drug for its eupho ...
and cocaine, drug use was responsible for the great majority of crime, including 85% of shoplifting, 70–80% of burglaries and 54% of robberies. It concluded " e cost of crime committed to support illegal cocaine and heroin habits amounts to £16 billion a year in the UK"
Drug trafficking routes
Africa
East and South
Heroin is increasingly trafficked from Afghanistan to Europe and America through eastern and southern African countries. This path is known as the "southern route" or "smack track". Repercussions of this trade include burgeoning heroin use and political corruption among intermediary African nations.West
Cocaine produced in Colombia and Bolivia has increasingly been shipped viaWest Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
(especially in Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
, Cape Verde
Cape Verde or Cabo Verde, officially the Republic of Cabo Verde, is an island country and archipelagic state of West Africa in the central Atlantic Ocean, consisting of ten volcanic islands with a combined land area of about . These islands ...
, Guinea-Bissau
Guinea-Bissau, officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau, is a country in West Africa that covers with an estimated population of 2,026,778. It borders Senegal to Guinea-Bissau–Senegal border, its north and Guinea to Guinea–Guinea-Bissau b ...
, Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the R ...
, Mali
Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is the List of African countries by area, eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The country is bordered to the north by Algeria, to the east b ...
, Benin
Benin, officially the Republic of Benin, is a country in West Africa. It was formerly known as Dahomey. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north-west, and Niger to the north-east. The majority of its po ...
, Togo
Togo, officially the Togolese Republic, is a country in West Africa. It is bordered by Ghana to Ghana–Togo border, the west, Benin to Benin–Togo border, the east and Burkina Faso to Burkina Faso–Togo border, the north. It is one of the le ...
, and Ghana
Ghana, officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It is situated along the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, and shares borders with Côte d’Ivoire to the west, Burkina Faso to the north, and Togo to t ...
). The money is often laundered in countries such as Nigeria, Ghana, and Senegal
Senegal, officially the Republic of Senegal, is the westernmost country in West Africa, situated on the Atlantic Ocean coastline. It borders Mauritania to Mauritania–Senegal border, the north, Mali to Mali–Senegal border, the east, Guinea t ...
.
According to the Africa Economic Institute, the value of illicit drug smuggling in Guinea-Bissau is almost twice the value of the country's GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performance o ...
. Police officers are often bribed. A police officer's normal monthly wage of $ is less than 2% of the value of of cocaine (€7000 or $). The money can also be laundered using real estate. A house is built using illegal funds, and when the house is sold, legal money is earned. When drugs are sent over land, through the Sahara, the drug traders have been forced to cooperate with terrorist organizations, such as Al-Qaeda
, image = Flag of Jihad.svg
, caption = Jihadist flag, Flag used by various al-Qaeda factions
, founder = Osama bin Laden{{Assassinated, Killing of Osama bin Laden
, leaders = {{Plainlist,
* Osama bin Lad ...
in Islamic Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ), also known as the Arab Maghreb () and Northwest Africa, is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb al ...
.
Asia
Drugs in Asia traditionally traveled the southern routesthe main caravan axes of Southeast Asia and Southern Chinaand include the former opium-producing countries ofThailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, and Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
. After the 1990s, particularly after the end of the Cold War
End, END, Ending, or ENDS may refer to:
End Mathematics
*End (category theory)
* End (topology)
* End (graph theory)
* End (group theory) (a subcase of the previous)
* End (endomorphism) Sports and games
*End (gridiron football)
*End, a division ...
(1991), borders were opened and trading and customs agreements were signed so that the routes expanded to include China, Central Asia, and Russia. There are, therefore, diversified drug trafficking routes available today, particularly in the heroin trade and these thrive due to the continuous development of new markets. A large amount of drugs are smuggled into Europe from Asia. The main sources of these drugs are Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
, along with countries that constituted the so-called Golden Crescent. From these producers, drugs are smuggled into the West and Central Asia to its destinations in Europe and the United States. Iran is now a common route for smugglers, having been previously a primary trading route, due to its large-scale and costly war against drug trafficking. The Border Police Chief of Iran said that his country "is a strong barrier against the trafficking of illegal drugs to Caucasus, especially the Republic of Azerbaijan." The drugs produced by the Golden Triangle of Myanmar, Laos, and Thailand, on the other hand, pass through the southern routes to feed the Australian, US, and Asian markets.
South America

Venezuela
Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It com ...
has been a path to the United States and Europe for illegal drugs originating in Colombia, through Central America, Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
and Caribbean countries such as Haiti
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, is a country on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of the Bahamas. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island, which it shares with the Dominican ...
, the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles of the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean. It shares a Maritime boundary, maritime border with Puerto Rico to the east and ...
, and Puerto Rico
; abbreviated PR), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Government of Puerto Rico, self-governing Caribbean Geography of Puerto Rico, archipelago and island organized as an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territo ...
.
According to the United Nations, cocaine trafficking through Venezuela increased from 2002 to 2008. In 2005, the government of Hugo Chávez
Hugo Rafael Chávez Frías (; ; 28 July 1954 – 5 March 2013) was a Venezuelan politician, Bolivarian Revolution, revolutionary, and Officer (armed forces), military officer who served as the 52nd president of Venezuela from 1999 until De ...
severed ties with the United States Drug Enforcement Administration
The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) is a Federal law enforcement in the United States, United States federal law enforcement agency under the U.S. Department of Justice tasked with combating illicit Illegal drug trade, drug trafficking a ...
(DEA), accusing its representatives of spying. Following the departure of the DEA from Venezuela and the expansion of DEA's partnership with Colombia in 2005, Venezuela became more attractive to drug traffickers. Between 2008 and 2012, Venezuela's cocaine seizure ranking among other countries declined, going from being ranked fourth in the world for cocaine seizures in 2008United NationsWorld Drug Report 2010 Statistical Annex: Drug seizures
to sixth in the world in 2012. On 18 November 2016, following what was known as the Narcosobrinos incident, Venezuelan President
Nicolás Maduro
Nicolás Maduro Moros (; born 23 November 1962) is a Venezuelan politician and former union leader serving as the 53rd president of Venezuela since 2013. Previously, he was the 24th Vice President of Venezuela, vice president from 2012 to 20 ...
's two nephews were found guilty of trying to ship drugs into the United States so they could "obtain a large amount of cash to help their family stay in power".
According to a research conducted by the Israel-based Abba Eban Institute as part of an initiative called Janus Initiative, the main routes that Hezbollah uses for smuggling drugs are from Colombia, Venezuela and Brazil into West Africa and then transported through northern Africa into Europe. This route serves Hezbollah in making a profit in the cocaine smuggling market in order to leverage it for their activities.
Online trafficking
Drugs are increasingly traded online on thedark web
The dark web is the World Wide Web content that exists on darknets ( overlay networks) that use the Internet but require specific software, configurations, or authorization to access. Through the dark web, private computer networks can communica ...
on darknet markets
A darknet market is a commercial website on the Dark Web, dark web that operates via darknets such as Tor (anonymity network), Tor and I2P. They function primarily as black markets, selling or brokering transactions involving Illegal drug trade, d ...
. Internet-based drug trafficking is the global distribution of narcotics, making extensive use of technology. Similarly, the use of the Internet for the illegal trafficking of two controlled categories of drugs can also be identified as Internet-related drug trafficking. The platform Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over , it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the ...
provided goods and services to 100,000 buyers before being shut down in October 2013.Ars Technica
''Ars Technica'' is a website covering news and opinions in technology, science, politics, and society, created by Ken Fisher and Jon Stokes in 1998. It publishes news, reviews, and guides on issues such as computer hardware and software, sci ...
How the feds took down the Dread Pirate Roberts
, 3 October 2013 This prompted the creation of new platforms such as Silk Road 2.0, which were also shut down.
Profits

 Statistics about profits from the drug trade are largely unknown due to its illicit nature. An online report published by the UK Home Office in 2007 estimated the illicit drug market in the UK at £4–6.6 billion a year.
In December 2009,
Statistics about profits from the drug trade are largely unknown due to its illicit nature. An online report published by the UK Home Office in 2007 estimated the illicit drug market in the UK at £4–6.6 billion a year.
In December 2009, United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime
The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC; French language, French: ''Office des Nations unies contre la drogue et le crime'') is a United Nations office that was established in 1997 as the Office for Drug Control and Crime Prevention ...
Executive Director Antonio Maria Costa claimed illegal drug money saved the banking industry from collapse. He claimed he had seen evidence that the proceeds of organized crime were "the only liquid investment capital" available to some banks on the brink of collapse during 2008. He said that a majority of the $352 billion (£216bn) of drug profits was absorbed into the economic system as a result: "In many instances, the money from drugs was the only liquid investment capital. In the second half of 2008, liquidity was the banking system's main problem and hence liquid capital became an important factor ... Inter-bank loans were funded by money that originated from the trade and other illegal activities...there were signs that some banks were rescued that way".
 Costa declined to identify countries or banks that may have received any drug money, saying that would be inappropriate because his office is supposed to address the problem, not apportion blame.
Though street-level drug sales are widely viewed as lucrative, a study by Sudhir Venkatesh suggested that many low-level employees receive low wages. In a study he made in the 1990s working closely with members of the Black Gangster Disciple Nation in
Costa declined to identify countries or banks that may have received any drug money, saying that would be inappropriate because his office is supposed to address the problem, not apportion blame.
Though street-level drug sales are widely viewed as lucrative, a study by Sudhir Venkatesh suggested that many low-level employees receive low wages. In a study he made in the 1990s working closely with members of the Black Gangster Disciple Nation in Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
, he found that one gang (essentially a franchise) consisted of a leader (a college graduate named J.T.), three senior officers, and 25 to 75 street level salesmen ('foot soldiers') depending on season. Selling crack cocaine
Crack cocaine, commonly known simply as crack, and also known as rock, is a free base form of the stimulant cocaine that can be Smoking, smoked. Crack offers a short, intense Euphoria (emotion), high to smokers. The ''Manual of Adolescent Sub ...
, they took in approximately $32,000 per month over a six-year period. This was spent as follows: $5,000 to the board of twenty directors of the Black Gangster Disciple Nation, who oversaw 100 such gangs for approximately $500,000 in monthly income. Another $5,000 monthly was paid for cocaine, and $4,000 for other non-wage expenses. J.T. took $8,500 monthly for his own salary. The remaining $9,500 monthly went to pay the employees a $7 per hour wage for officers and a $3.30 per hour wage for foot soldiers. Contrary to a popular image of drug sales as a lucrative profession, many of the employees were living with their mothers by necessity. Despite this, the gang had four times as many unpaid members who dreamed of becoming foot soldiers.
Impact of free trade
There are several arguments on whether or not free trade has a correlation to an increased activity in the illicit drug trade. Currently, the structure and operation of the illicit drug industry is described mainly in terms of an international division of labor. Free trade can open new markets to domestic producers who would otherwise resort to exporting illicit drugs. Additionally, extensive free trade among states increases cross-border drug enforcement and coordination between law enforcement agencies in different countries. However, free trade also increases the sheer volume of legal cross-border trade and provides cover for drug smuggling—by providing ample opportunity to conceal illicit cargo in legal trade. While international free trade continues to expand the volume of legal trade, the ability to detect and interdict drug trafficking is severely diminished. Towards the late 1990s, the top ten seaports in the world processed 33.6 million containers. Free trade has fostered integration of financial markets and has provided drug traffickers with more opportunities to launder money and invest in other activities. This strengthens the drug industry while weakening the efforts of law enforcement to monitor the flow of drug money into the legitimate economy. Cooperation among cartels expands their scope to distant markets and strengthens their abilities to evade detection by local law enforcement. Additionally, criminal organizations work together to coordinate money-laundering activities by having separate organizations handle specific stages of laundering process. One organization structures the process of how financial transactions will be laundered, while another criminal group provides the "dirty" money to be cleaned. By fostering expansion of trade and global transportation networks, free trade encourages cooperation and formation of alliances among criminal organizations across different countries. The drug trade in Latin America emerged in the early 1930s. It saw significant growth in the Andean countries, including Peru, Bolivia, Chile, Ecuador, Colombia and Venezuela. The underground market in the early half of the 20th century mainly had ties to Europe. After World War II, the Andean countries saw an expansion of trade, specifically with cocaine.Drug trafficking by country

Syria
The Ba'athist government of Syria ruled by the Al-Assad family is known for its extensive involvement in drug trade since the 1970s. As of 2022, the Syrian government financed the biggest multi-billion dollar drug trade in the world, mostly focused on an illegal drug known as Captagon, making it the world's largest narco-state. Its revenues from Captagon smuggling alone is estimated to worth 57 billion dollars annually in 2022, which is approximately thrice the total trade of all Mexican cartels. General Maher al-Assad, younger brother of Syrian dictatorBashar al-Assad
Bashar al-Assad (born 11September 1965) is a Syrian politician, military officer and former dictator
Sources characterising Assad as a dictator:
who served as the president of Syria from 2000 until fall of the Assad regime, his government ...
and commander of the Fourth Armoured Division, directly supervised the production, smuggling and profiteering of the drug business. Already suffering from severe financial problems as a result of corruption and civil war, profits from Captagon are said to be the "lifeline" of the Assad regime, through which it earned more than 90% of its total revenue. The smugglers receive direct training from Syrian military
The Syrian Armed Forces () are the military forces of Syria.
Up until the fall of Bashar al-Assad's Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party – Syria Region, Ba'ath Party Ba'athist Syria, regime in December 2024, the Syrian Arab Armed Forces were the sta ...
to successfully conduct trafficking operations.
Republican Guard
A republican guard, sometimes called a national guard, is a state organization of a country (often a republic, hence the name ''Republican'') which typically serves to protect the head of state and the government, and thus is often synonymous wit ...
, commanded by Maher al-Assad was one of the main Ba'athist military divisions that was engaged in perpetrating brutal crackdowns and mass violence against protestors across the country. In 2018, Bashar al-Assad assigned Maher as the commander of the 4th Armoured Division, a military unit that supervised the Assad regime's criminal enterprises like smuggling, drug trafficking, narcotics production and plunder
Looting is the act of stealing, or the taking of goods by force, typically in the midst of a military, political, or other social crisis, such as war, natural disasters (where law and civil enforcement are temporarily ineffective), or rioting. ...
of goods and resources. Under Maher's supervision, the 4th Armoured Division expanded captagon production and trafficking from Syria into a "business model controlled by the regime".
In 2022, 90% of all captagon pills manufactured in Syria exported by drug cartels affiliated with Assad regime arrived at its customer destinations across the world. Although hundreds of millions of pills were intercepted and seized by police forces, these accounted only for 10% of the total captagon exports of the drug cartels linked to the Assad regime. In 2020, Italian police seized 84 million captagon pills originating from Syrian ports while intercepting a single shipment. In June 2023, US State Department
The United States Department of State (DOS), or simply the State Department, is an executive department of the U.S. federal government responsible for the country's foreign policy and relations. Equivalent to the ministry of foreign affairs o ...
's Bureau of Near Eastern Affairs published a detailed report to the US Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature, legislative branch of the federal government of the United States. It is a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, including a Lower house, lower body, the United States House of Representatives, ...
, elucidating a strategy to eliminate the narcotics production, drug trafficking and drug cartel networks affiliated with the Assad regime
Ba'athist Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic (SAR), was the Syrian state between 1963 and 2024 under the one-party rule of the Syrian regional branch of the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party. From 1971 until its collapse in 2024, it was rule ...
and Hezbollah
Hezbollah ( ; , , ) is a Lebanese Shia Islamist political party and paramilitary group. Hezbollah's paramilitary wing is the Jihad Council, and its political wing is the Loyalty to the Resistance Bloc party in the Lebanese Parliament. I ...
.
A joint investigation conducted by Organized Crime and Corruption Reporting Project (OCCRP) and BBC News Arabic
BBC News Arabic (), formerly BBC Arabic Television, is a television news channel broadcast to the Arab world by the BBC. It was launched on 11 March 2008. It is run by the BBC World Service and funded from the British television licence fee.
H ...
published a documentary in June 2023, revealing further details about the activities of regime officials, Ba'athist military commanders and Assad family members in their involvement in Syria's drug cartel. The investigation found that Lebanese criminal and drug kingpin Hassan Daqou collaborated with Syria's Fourth Armoured Division on trafficiking billions of dollars of drugs, under the command of General Ghassan Bilal, the right-hand man of Maher al-Assad. The report also unearthed Hezbollah
Hezbollah ( ; , , ) is a Lebanese Shia Islamist political party and paramilitary group. Hezbollah's paramilitary wing is the Jihad Council, and its political wing is the Loyalty to the Resistance Bloc party in the Lebanese Parliament. I ...
's close participation in the drug production and smuggling networks. The Fourth Armoured Division, being an elite military unit permitted to move freely across Assad regime's checkpoints, oversees the smuggling operations from Syria, including the trafficking of cash, weapons, illegal drugs, etc. Days after the publication of the joint BBC-OCCRP documentary; Assad government banned all activities of BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is a British public service broadcaster headquartered at Broadcasting House in London, England. Originally established in 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company, it evolved into its current sta ...
media outlets and entry of affiliated media personnel in Syria.
The extensive involvement of Syrian Armed Forces
The Syrian Armed Forces () are the military forces of Syria.
Up until the fall of Bashar al-Assad's Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party – Syria Region, Ba'ath Party Ba'athist Syria, regime in December 2024, the Syrian Arab Armed Forces were the sta ...
in sponsorship of drug production and trade has led to pervasive drug addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to use a drug or engage in a behavior that produces natural reward, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use can ...
problems amongst pro-Assad soldiers. In many instances, military officials encourage the soldiers to consume Captagon and other illegal drugs, leading to overdose or drug abuse. Pro-Assad fighters in the National Defence Forces
The National Defense Forces (NDF; ''Quwāt ad-Difāʿ al-Watanī'') was a Syrian paramilitary volunteer militia, that was formed on 1 November 2012 and organized by Ba'athist Syria during the Syrian civil war as a part-time volunteer reserve co ...
and Hezbollah
Hezbollah ( ; , , ) is a Lebanese Shia Islamist political party and paramilitary group. Hezbollah's paramilitary wing is the Jihad Council, and its political wing is the Loyalty to the Resistance Bloc party in the Lebanese Parliament. I ...
also consume illegal drugs in large quantities. In July 2023, German police busted a major captagon network run by two Syrian-born men in southern German state of Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
. Assad regime sponsors the largest Captagon production network in Syria; which is the source of about 80% of total captagon supply in the world.
In an investigative report published by '' The Insider'' news-outlet in 2024, journalist Yuriy Matsarsky stated:"...Captagon produced in underground labs—and in actual Syrian pharmaceutical facilities—is distributed to the fighters of Bashar Assad's army. Interestingly, however, the quantities the country produces far exceed its own military’s demand. ... By some estimates, this business gives Syria more money than its entire legal export, and the regime constantly works to increase its profits, primarily by expanding its market reach. To this end, criminal gangs associated with Damascus or Hezbollah have built distribution networks for Captagon in countries where the drug was not previously popular."
United States

Background
The effects of the illegal drug trade in the United States can be seen in a range of political, economic and social aspects. Increasing drug related violence can be tied to the racial tension that arose during the late 20th century along with the political upheaval prevalent throughout the 1960s and 70s. The second half of the 20th century was a period when increased wealth, and increased discretionary spending, increased the demand for illicit drugs in certain areas of the United States. Large-scale drug trafficking is one of the capital crimes, and may result in adeath sentence
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence ordering that an offender be punished in s ...
prescribed at the federal level when it involves murder.
Political impact
A large generation, thebaby boomers
Baby boomers, often shortened to boomers, are the demographic cohort preceded by the Silent Generation and followed by Generation X. The generation is often defined as people born from 1946 to 1964 during the mid-20th century baby boom that ...
, came of age in the 1960s. Their social tendency to confront the law on specific issues, including illegal drugs, overwhelmed the understaffed judicial system. The federal government attempted to enforce the law, but with meager effect.
Marijuana was a popular drug seen through the Latin American trade route in the 1960s. Cocaine became a major drug product in the later decades. Much of the cocaine is smuggled from Colombia and Mexico via Jamaica. This led to several administrations combating the popularity of these drugs. Due to the influence of this development on the US economy, the Reagan administration began "certifying" countries for their attempts at controlling drug trafficking. This allowed the United States to intervene in activities related to illegal drug transport in Latin America. Continuing into the 1980s, the United States instated stricter policy pertaining to drug transit through sea. As a result, there was an influx in drug-trafficking across the Mexico–US border, which increased the drug cartel activity in Mexico.
By the early 1990s, so much as 50% of the cocaine available in the United States market originated from Mexico, and by the 2000s, over 90% of the cocaine in the United States was imported from Mexico. In Colombia, however, there was a fall of the major drug cartels in the mid-1990s. Visible shifts occurred in the drug market in the United States. Between 1996 and 2000, US cocaine consumption dropped by 11%.
In 2008, the US government initiated another program, known as the Merida Initiative, to help combat drug trafficking in Mexico. This program increased US security assistance to $1.4 billion over several years, which helped supply Mexican forces with "high-end equipment from helicopters to surveillance technology". Despite US aid, Mexican "narcogangs" continue to outnumber and outgun the Mexican Army
The Mexican Army () is the combined Army, land and Air Force, air branch and is the largest part of the Mexican Armed Forces; it is also known as the National Defense Army.
The Army is under the authority of the Secretariat of National Defense o ...
, allowing for continued activities of drug cartels across the US–Mexico border.
Social impacts
 Although narcotics are illegal in the US, they have become integrated into the nation's culture and are seen as a recreational activity by sections of the population. Illicit drugs are considered to be a commodity with strong demand, as they are typically sold at a high value. This high price is caused by a combination of factors that include the potential legal ramifications that exist for suppliers of illicit drugs and their high demand. Despite the constant effort by politicians to win the war on drugs, the US is still the world's largest importer of illegal drugs.
Throughout the 20th century, narcotics other than cocaine also crossed the Mexican border, meeting the US demand for alcohol during the 1920s
Although narcotics are illegal in the US, they have become integrated into the nation's culture and are seen as a recreational activity by sections of the population. Illicit drugs are considered to be a commodity with strong demand, as they are typically sold at a high value. This high price is caused by a combination of factors that include the potential legal ramifications that exist for suppliers of illicit drugs and their high demand. Despite the constant effort by politicians to win the war on drugs, the US is still the world's largest importer of illegal drugs.
Throughout the 20th century, narcotics other than cocaine also crossed the Mexican border, meeting the US demand for alcohol during the 1920s Prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic b ...
, opiates in the 1940s, marijuana in the 1960s, and heroin in the 1970s. Most of the US imports of drugs come from Mexican drug cartels. In the United States, around 195 cities have been infiltrated by drug trafficking that originated in Mexico. An estimated $10bn of the Mexican drug cartel's profits come from the United States, not only supplying the Mexican drug cartels with the profit necessary for survival, but also furthering America's economic dependence on drugs.
=Demographics
= With a large wave of immigrants in the 1960s and onwards, the United States saw an increased heterogeneity in its public. In the 1980s and 1990s, drug-related homicide was at a record high. This increase in drug violence became increasingly tied to these ethnic minorities. Though the rate of violence varied tremendously among cities in America, it was a common anxiety in communities across urban America. An example of this could be seen in Miami, a city with a host of ethnic enclaves. Between 1985 and 1995, the homicide rate in Miami was one of the highest in the nation—four times the national homicide average. This crime rate was correlated with regions with low employment and was not entirely dependent on ethnicity. The baby boomer generation also felt the effects of the drug trade in their increased drug use from the 1960s to 1980s. Along with substance use, criminal involvement, suicide and murder were also on the rise. Due to the large amount of baby boomers, commercial marijuana use was on the rise. This increased the supply and demand for marijuana during this time period.Mexico
Political influences
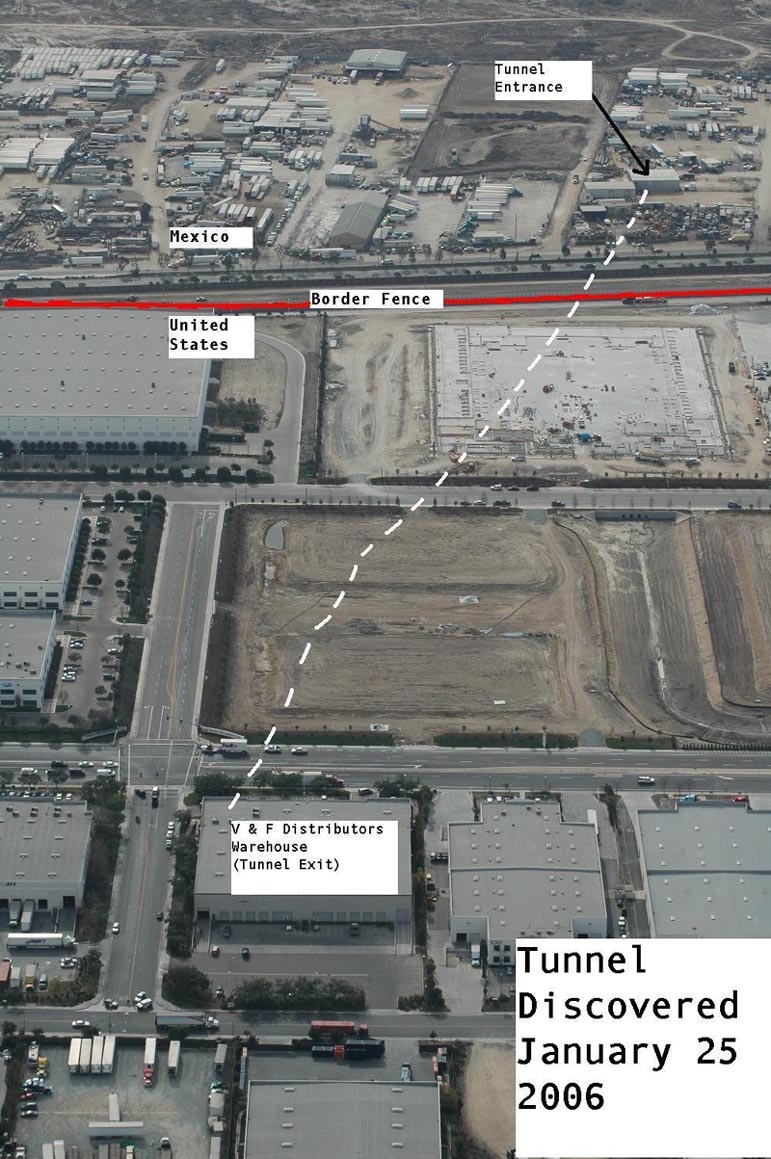
Corruption in Mexico has contributed to the domination of Mexican cartels in the illicit drug trade. Since the beginning of the 20th century, Mexico's political environment allowed the growth of drug-related activity. The loose regulation over the transportation of illegal drugs and the failure to prosecute known drug traffickers and gangs increased the growth of the drug industry. Toleration of drug trafficking has undermined the authority of the Mexican government and has decreased the power of law enforcement officers in regulation over such activities. These policies of tolerance fostered the growing power of drug cartels in the Mexican economy and have made drug traders wealthier. Many states in Mexico lack policies that establish stability in governance. There also is a lack of local stability, as mayors cannot be re-elected. This requires electing a new mayor each term. Drug gangs have manipulated this, using vacuums in local leadership to their own advantage. In 1929, the
In 1929, the Institutional Revolutionary Party
The Institutional Revolutionary Party (, , PRI) is a List of political parties in Mexico, political party in Mexico that was founded in 1929 as the National Revolutionary Party (, PNR), then as the Party of the Mexican Revolution (, PRM) and fin ...
(PRI) was formed to resolve the chaos resulting from the Mexican Revolution
The Mexican Revolution () was an extended sequence of armed regional conflicts in Mexico from 20 November 1910 to 1 December 1920. It has been called "the defining event of modern Mexican history". It saw the destruction of the Federal Army, its ...
. Over time, this party gained political influence and had a major impact on Mexico's social and economic policies. The party created ties with various groups as a power play in order to gain influence, and as a result created more corruption in the government. One such power play was an alliance with drug traffickers. This political corruption
Political corruption is the use of powers by government officials or their network contacts for illegitimate private gain. Forms of corruption vary but can include bribery, lobbying, extortion, cronyism, nepotism, parochialism, patronage, influen ...
obscured justice, making it difficult to identify violence when it related to drugs. By the 1940s, the tie between the drug cartels and the PRI had solidified. This arrangement created immunity for the leaders of the drug cartels and allowed drug trafficking to grow under the protection of the government officials.
During the 1990s, the PRI lost some elections to the new National Action Party (PAN). Chaos again emerged as elected government in Mexico changed drastically. As the PAN party took control, drug cartel leaders took advantage of the ensuing confusion and used their existing influence to further gain power. Instead of negotiating with the central government as was done with the PRI party, drug cartels utilized new ways to distribute their supply and continued operating through force and intimidation. As Mexico became more democratized, the corruption fell from a centralized power to the local authorities. Cartels began to bribe local authorities, thus eliminating the structure and rules placed by the government—giving cartels more freedom. As a response, Mexico saw an increase in violence caused by drug trafficking.
The corruption cartels created resulted in distrust of government by the Mexican public. This distrust became more prominent after the collapse of the PRI party. In response, the presidents of Mexico
The Head of State of Mexico is the person who controls the executive power in the country. Under the current constitution, this responsibility lies with the President of the United Mexican States, who is head of the supreme executive power of th ...
, in the late twentieth century and early twenty-first century, implemented several different programs relating to law enforcement and regulation. In 1993, President Salinas created the National Institute for the Combat of Drugs in Mexico. From 1995 to 1998, President Zedillo established policies regarding increased punishment of organized crime, allowing " ire taps protected witnesses, covert agents and seizures of goods", and increasing the quality of law enforcement at the federal level. From 2001 to 2005, President Vicente Fox
Vicente Fox Quesada (; born 2 July 1942) is a Mexican businessman and politician who served as the 62nd president of Mexico from 2000 to 2006. After campaigning as a Right-wing populism, right-wing populist, Fox was elected president on the Nat ...
created the Federal Agency of Investigation.
These policies resulted in the arrests of major drug-trafficking bosses:
Mexico's economy
Over the past few decades, drug cartels have become integrated into Mexico's economy. Approximately 500 cities are directly engaged in drug trafficking and nearly 450,000 people are employed by drug cartels. Additionally, the livelihood of 3.2 million people is dependent on the drug cartels. Between local and international sales, such as to Europe and the United States, drug cartels in Mexico see a $25–30 bn yearly profit, a great deal of which circulates through international banks such asHSBC
HSBC Holdings plc ( zh, t_hk=滙豐; initialism from its founding member The Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation) is a British universal bank and financial services group headquartered in London, England, with historical and business li ...
. Drug cartels are fundamental in local economics. A percentage of the profits seen from the trade are invested in the local community. Such profits contribute to the education and healthcare of the community. While these cartels bring violence and hazards into communities, they create jobs and provide income for its many members.
Culture of drug cartels
Major cartels saw growth due to a prominent set culture of Mexican society that created the means for drug capital. One of the sites of origin for drug trafficking within Mexico, was the state ofMichoacán
Michoacán, formally Michoacán de Ocampo, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Michoacán de Ocampo, is one of the 31 states which, together with Mexico City, compose the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. The stat ...
. In the past, Michoacán was mainly an agricultural society. This provided an initial growth of trade. Industrialization of rural areas of Mexico facilitated a greater distribution of drugs, expanding the drug market into different provinces. Once towns became industrialized, cartels such as the Sinaloa Cartel
The Sinaloa Cartel (, , after the native Sinaloa region), also known as the ''CDS'', the ''Guzmán-Loera Organization'', the ''Federation'', the ''Sinaloa Cartel'', or the Pacific Cartel, is a large, drug trafficking transnational organized cri ...
started to form and expand. The proliferation of drug cartel culture largely stemmed from the ranchero culture seen in Michoacán. Ranchero culture values the individual as opposed to the society as a whole. This culture fostered the drug culture of valuing the family that is formed within the cartel. This ideal allowed for greater organization within the cartels.
Gangs play a major role in the activity of drug cartels. MS-13
Mara Salvatrucha, commonly known as MS-13, is an international criminal gang that originated in Los Angeles, California, in the 1980s. Originally, the gang was set up to protect Salvadoran immigrants from other gangs in the Los Angeles area ...
and the 18th Street gang
The 18th Street Gang, also known as , , , or simply in North America, is a multi-ethnic (largely Central American and Culture of Mexico, Mexican) street gang in Los Angeles. It is one of the largest street gangs in Los Angeles, with around 30 ...
are notorious for their contributions and influence over drug trafficking throughout Latin America. MS-13 has controlled much of the activity in the drug trade spanning from Mexico to Panama. Female involvement is present in the Mexican drug culture. Although females are not treated as equals to males, they typically hold more power than their culture allows and acquire some independence. The increase in power has attracted females from higher social classes. Financial gain has also prompted women to become involved in the illegal drug market. Many women in the lower levels of major drug cartels belong to a low economic class. Drug trafficking offers women an accessible way to earn income. Females from all social classes have become involved in the trade due to outside pressure from their social and economic environments.
Colombia
Political ties
It was common for smugglers in Colombia to import liquor, alcohol, cigarettes and textiles, while exporting cocaine. Personnel with knowledge of the terrain were able to supply the local market while also exporting a large amount of product. The established trade initially involved Peru, Bolivia, Colombia, Venezuela and Cuba. Peasant farmers produced coca paste in Peru and Bolivia, while Colombian smugglers would process the coca paste into cocaine in Colombia, and trafficked product throughBatista
Batista is a Spanish language, Spanish or Portuguese language, Portuguese surname. Notable persons with the name include:
* Batista (footballer, born 1955), Brazilian football player João Batista da Silva
* Dave Bautista, Batista (wrestler) (Dave ...
's Cuba. This trade route established ties between Cuban and Colombian organized crime.
From Cuba, cocaine would be transported to Miami
Miami is a East Coast of the United States, coastal city in the U.S. state of Florida and the county seat of Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade County in South Florida. It is the core of the Miami metropolitan area, which, with a populat ...
, Florida; and Union City, New Jersey
Union City is a City (New Jersey), city in the North Hudson, New Jersey, northern part of Hudson County, New Jersey, Hudson County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. As of the 2020 United States census, the city was List of municipalities in Ne ...
. Quantities of the drug were then smuggled throughout the US. The international drug trade created political ties between the involved countries, encouraging the governments of the countries involved to collaborate and instate common policies to eradicate drug cartels. Cuba stopped being a center for transport of cocaine following the Cuban Revolution
The Cuban Revolution () was the military and political movement that overthrew the dictatorship of Fulgencio Batista, who had ruled Cuba from 1952 to 1959. The revolution began after the 1952 Cuban coup d'état, in which Batista overthrew ...
and the establishment of Fidel Castro
Fidel Alejandro Castro Ruz (13 August 1926 – 25 November 2016) was a Cuban politician and revolutionary who was the leader of Cuba from 1959 to 2008, serving as the prime minister of Cuba from 1959 to 1976 and President of Cuba, president ...
's communist government in 1959.
As a result, Miami and Union City became the sole locations for trafficking. The relations between Cuban and Colombian organized crime remained strong until the 1970s, when Colombian cartels began to vie for power. In the 1980s and 90s, Colombia emerged as a key contributor of the drug trade industry in the Western Hemisphere. While the smuggling of drugs such as marijuana, poppy, opium and heroin became more ubiquitous during this time period, the activity of cocaine cartels drove the development of the Latin American drug trade. The trade emerged as a multinational effort as supplies (i.e. coca plant substances) were imported from countries such as Bolivia and Peru, were refined in Colombian cocaine labs and smuggled through Colombia, and exported to countries such as the US.
Colombia's economy
Colombia has had a significant role in the illegal drug trade in Latin America. While active in the drug trade since the 1930s, Colombia's role in the drug trade did not truly become dominant until the 1970s. When Mexico eradicated marijuana plantations, demand stayed the same. Colombia met much of the demand by growing more marijuana. Grown in the strategic northeast region of Colombia, marijuana soon became the leading cash crop in Colombia. This success was short-lived due to anti-marijuana campaigns that were enforced by the US military throughout the Caribbean. Instead, drug traffickers in Colombia continued their focus on exporting cocaine. Having been an export of Colombia since the early 1950s, cocaine remained popular for a host of reasons. Colombia's location facilitated its transportation from South America into Central America, and then to its destination of North America. This continued into the 1990s, when Colombia remained the chief exporter of cocaine. The business of drug trafficking can be seen in several stages in Colombia towards the latter half of the 20th century. Colombia served as the dominant force in the distribution and sale of cocaine by the 1980s. As drug producers gained more power, they became more centralized and organized into what became drug cartels. Cartels controlled the major aspects of each stage in the traffic of their product. Their organization allowed cocaine to be distributed in great amounts throughout the United States. By the late 1980s, intra-industry strife arose within the cartels. This stage was marked by increased violence as different cartels fought for control of export markets. Despite this strife, this power struggle led to then having multiple producers of coca leaf farms. This in turn caused an improvement in quality control and reduction of police interdiction in the distribution of cocaine. This also led to cartels attempting to repatriate their earnings which would eventually make up 5.5% of Colombia's GDP. This drive to repatriate earnings led to the pressure of legitimizing their wealth, causing an increase in violence throughout Colombia. Throughout the 1980s, estimates of illegal drug value in Colombia ranged from $2bn to $4bn. This made up about 7–10% of the $36bn estimated Gross National Product (GNP) of Colombia during this decade. In the 1990s, the estimates of the illegal drug value remained roughly within the same range (~$2.5bn). As the Colombian GNP rose throughout the 1990s ($68.5bn in 1994 and $96.3bn in 1997), illegal drug values began to comprise a decreasing fraction of the national economy.
By the early 1990s, although Colombia led in the exportation of cocaine, it found increasing confrontations within its state. These confrontations were primarily between cartels and government institutions. This led to a decrease in the drug trade's contribution to the GDP of Colombia; dropping from 5.5% to 2.6%. Though a contributor of wealth, the distribution of cocaine has had negative effects on the socio-political situation of Colombia and has weakened its economy as well.
Throughout the 1980s, estimates of illegal drug value in Colombia ranged from $2bn to $4bn. This made up about 7–10% of the $36bn estimated Gross National Product (GNP) of Colombia during this decade. In the 1990s, the estimates of the illegal drug value remained roughly within the same range (~$2.5bn). As the Colombian GNP rose throughout the 1990s ($68.5bn in 1994 and $96.3bn in 1997), illegal drug values began to comprise a decreasing fraction of the national economy.
By the early 1990s, although Colombia led in the exportation of cocaine, it found increasing confrontations within its state. These confrontations were primarily between cartels and government institutions. This led to a decrease in the drug trade's contribution to the GDP of Colombia; dropping from 5.5% to 2.6%. Though a contributor of wealth, the distribution of cocaine has had negative effects on the socio-political situation of Colombia and has weakened its economy as well.
Social impacts
By the 1980s, Colombian cartels became the dominant cocaine distributors in the US. This led to the spread of increased violence throughout both Latin America and Miami. In the 1980s, two major drug cartels emerged in Colombia: theMedellín
Medellín ( ; or ), officially the Special District of Science, Technology and Innovation of Medellín (), is the List of cities in Colombia, second-largest city in Colombia after Bogotá, and the capital of the department of Antioquia Departme ...
and Cali
Santiago de Cali (), or Cali, is the capital of the Valle del Cauca department, and the most populous city in southwest Colombia, with 2,280,522 residents estimate by National Administrative Department of Statistics, DANE in 2023. The city span ...
groups.
Throughout the 1990s however, several factors led to the decline of these major cartels and to the rise of smaller Colombian cartels. The US demand for cocaine dropped while Colombian production rose, pressuring traffickers to find new drugs and markets. In this time period, there was an increase in activity of Caribbean cartels that led to the rise of an alternate route of smuggling through Mexico. This led to the increased collaboration between major Colombian and Mexican drug traffickers. Such drastic changes in the execution of drug trade in Colombia paired with the political instabilities and rise of drug wars in Medellin and Cali, gave way for the rise of the smaller Colombian drug trafficking organizations (and the rise of heroin trade). As the drug trade's influence over the economy increased, drug lords and their networks grew in their power and influence in society. The occurrences in drug-related violence increased during this time period as drug lords fought to maintain their control in the economy.
Typically, a drug cartel had support networks that consisted of a number of individuals. These people individuals ranged from those directly involved in the trade (such as suppliers, chemists, transporters, smugglers, etc.) as well as those involved indirectly in the trade (such as politicians, bankers, police, etc.). As these smaller Colombian drug cartels grew in prevalence, several notable aspects of the Colombian society gave way for further development of the Colombian drug industry. For example, until the late 1980s, the long-term effects of the drug industry were not realized by much of society. Additionally, there was a lack of regulation in prisons where captured traffickers were sent. These prisons were under-regulated, under-funded, and under-staffed, which allowed for the formation of prison gangs, for the smuggling of arms/weapons/etc., for feasible escapes, and even for captured drug lords to continue running their businesses from prison.
Western Balkans
Since the beginning of the 21st century, the global drug trade network witnessed the emergence of criminal groups from the WesternBalkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
as crucial players. These groups have moved up from being small-time crooks to major drug distributors. Most of these organized crime groups belonged to Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to th ...
, Kosovo
Kosovo, officially the Republic of Kosovo, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe with International recognition of Kosovo, partial diplomatic recognition. It is bordered by Albania to the southwest, Montenegro to the west, Serbia to the ...
, Montenegro
, image_flag = Flag of Montenegro.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Montenegro.svg
, coa_size = 80
, national_motto =
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map = Europe-Mont ...
, North Macedonia
North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Greece to the south, Albania to the west, Bulgaria to the east, Kosovo to the northwest and Serbia to the n ...
and Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
. The illicit trade activities of the Balkans primarily involved Latin America
Latin America is the cultural region of the Americas where Romance languages are predominantly spoken, primarily Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese. Latin America is defined according to cultural identity, not geogr ...
, Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's extent varies depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the Western half of the ancient Mediterranean ...
, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic O ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
and Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
. These groups keep their operations outside the Western Balkans, while staying connected to their homeland. Within the network of these groups, the dealmakers operate in a proximity of supply sources and the distribution networks are managed by foot soldiers. However, the bosses of the organized criminal groups stay and keep their wealth in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). The UAE is amongst the enablers of global corruption and illicit financial flows. Analysts have claimed that criminal actors across the world either operate from or through the Emirates. It was a haven for criminals, where the risk for illicit activities remains low.
For the Balkan criminals, a growing trend was to relocate to the UAE, which became an attraction to dirty money and kingpins from several European nations and the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
. Besides, Dubai was also dubbed as the "new Costa del Crime", replacing the crime hideaway of Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, the Costa del Sol
The Costa del Sol (; literally "Coast of the Sun") is a region in the south of Spain in the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia, comprising the coastal towns and communities along the coastline of the Province of ...
. The UAE had poor regulations for money laundering
Money laundering is the process of illegally concealing the origin of money obtained from illicit activities (often known as dirty money) such as drug trafficking, sex work, terrorism, corruption, and embezzlement, and converting the funds i ...
and for screening of suspicious transactions. The lack of regulations against illicit financial activities prompted the Financial Action Task Force
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF), also known by its French name, Groupe d'action financière (GAFI), is an intergovernmental organisation founded in 1989 on the initiative of the G7 to develop policies to combat money laundering and to ma ...
(FATF) to place the Gulf country on its grey list in March 2022. Consequently, the Emirates' remained a safe option for the criminals. Nearly two-thirds of the Albanian criminal groups, who were active in trade of drugs like cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
, were believed to be hiding in the UAE. One of such individuals, Eldi Dizdari was accused of international drug trafficking and was living in Dubai. Research revealed that these criminals invested huge amounts in the Emirates' real estate and other economical sectors to live there. Another trafficker of cocaine from Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to th ...
, Edin Gačanin was living in the UAE using his extensive profits to buy property and protection in the country. Dubbed as the "European Escobar", he connected the supply network between production markets of Latin America and consumer markets of Western European. He was able to evade the arrest and investigations, including by the US Drug Enforcement Administration, by seeking shelter in the Emirates.
Trade in specific drugs
Cannabis
cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae that is widely accepted as being indigenous to and originating from the continent of Asia. However, the number of species is disputed, with as many as three species be ...
is illegal in most countries throughout the world, recreational distribution is legal in some countries, such as Canada, and medical distribution is permitted in some places, such as 38 of the 50 US states (although importation and distribution is still federally prohibited). Beginning in 2014, Uruguay
Uruguay, officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay, is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast, while bordering the Río de la Plata to the south and the A ...
became the first country to legalize cultivation, sale, and consumption of cannabis for recreational use for adult residents. In 2018, Canada became the second country to legalize use, sale and cultivation of cannabis. The first few weeks were met with extremely high demand, most shops being out of stock after operating for only four days.
Cannabis use is tolerated in some areas, most notably the Netherlands, which has legalized the possession and licensed sale (but not cultivation) of the drug. Many nations have decriminalized the possession of small amounts of marijuana. Due to the hardy nature of the cannabis plant, marijuana is grown all across the world; today, it is the world's most popular illegal drug with the highest level of availability. Cannabis is grown legally in many countries for industrial, non-drug use (known as hemp
Hemp, or industrial hemp, is a plant in the botanical class of ''Cannabis sativa'' cultivars grown specifically for industrial and consumable use. It can be used to make a wide range of products. Along with bamboo, hemp is among the fastest ...
) as well. Cannabis-hemp may also be planted for other non-drug domestic purposes, such as seasoning that occurs in Aceh
Aceh ( , ; , Jawi script, Jawoë: ; Van Ophuijsen Spelling System, Old Spelling: ''Atjeh'') is the westernmost Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia. It is located on the northern end of Sumatra island, with Banda Aceh being its capit ...
.
The demand for cannabis around the world, coupled with the drug's relative ease of cultivation, makes the illicit cannabis trade one of the primary ways in which organized criminal groups finance many of their activities. In Mexico, for example, the illicit trafficking of cannabis is thought to constitute the majority of many of the cartels' earnings, and the main way in which the cartels finance many other illegal activities; including the purchase of other illegal drugs for trafficking, and for acquiring weapons that are ultimately used to commit murders (causing a burgeoning in the homicide rates of many areas of the world, but particularly Latin America).
Some studies show that the increased legalization of cannabis in the United States (beginning in 2012 with Washington Initiative 502
Washington Initiative 502 (I-502) "on marijuana reform" was an Initiatives and referendums in the United States, initiative to the Washington State Legislature, which appeared on the November 2012 general ballot, passing by a margin of approxim ...
and Colorado Amendment 64
Colorado Amendment 64 was a successful popular initiative ballot measure to amend the Constitution of the State of Colorado, outlining a statewide drug policy for cannabis. The measure passed on November 6, 2012, and along with a similar mea ...
) has led Mexican cartels to smuggle less cannabis in exchange for more heroin.
Alcohol
Alcohol, in the context ofalcoholic beverage
Drinks containing alcohol (drug), alcohol are typically divided into three classes—beers, wines, and Distilled beverage, spirits—with alcohol content typically between 3% and 50%. Drinks with less than 0.5% are sometimes considered Non-al ...
s rather than denatured alcohol
Denatured alcohol, also known as methylated spirits, metho, or meths in Australia, Ireland, New Zealand, South Africa, and the United Kingdom, and as Rectified spirit, denatured rectified spirit, is ethanol that has additives to make it poisonou ...
, is illegal in a number of Muslim countries, such as Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
; this has resulted in a thriving illegal trade in alcohol. The manufacture, sale, transportation, import, and export of alcoholic beverages were illegal in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
during the time known as the Prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic b ...
in the 1920s and early 1930s.
Heroin
In the 1950s and 1960s, most heroin was produced inTurkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
and transshipped in France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
via the ''French Connection
The French Connection was a scheme through which heroin was smuggled from Indochina through Turkey to France and then to the United States and Canada. The operation started in the 1930s, reached its peak in the 1960s, and was dismantled in the 1 ...
'' crime ring, with much of it arriving in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
. This resulted in the record setting April 26, 1968 seizure of of heroin smuggled in a vehicle on the ''SS France (1960)
SS ''France'' was a Compagnie Générale Transatlantique (CGT, or French Line) ocean liner, constructed by the Chantiers de l'Atlantique shipyard at Saint-Nazaire, France, and put into service in February 1962. From the time of her construc ...
ocean liner.'' By the time of The French Connection (1971 film), this route was being supplanted.
Then, until , the majority of the world's heroin was produced in an area known as the Golden Triangle. However, by 2007, 93% of the opiates on the world market originated in Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
. This amounted to an export value of about US$4 billion, with a quarter being earned by opium farmers and the rest going to district officials, insurgents, warlords and drug traffickers. Another significant area where poppy fields are grown for the manufacture of heroin is Mexico. In November 2023, a U.N report showed that in the entirety of Afghanistan, poppy cultivation dropped by over 95%, removing it from its place as being the world's largest opium producer.
According to the United States Drug Enforcement Administration
The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) is a Federal law enforcement in the United States, United States federal law enforcement agency under the U.S. Department of Justice tasked with combating illicit Illegal drug trade, drug trafficking a ...
, the price of heroin is typically valued 8 to 10 times that of cocaine on American streets, making it a high-profit substance for smugglers and dealers. In Europe (except the transit countries Portugal and the Netherlands), for example, a purported gram of street heroin, usually consisting of 700–800 mg of a light to dark brown powder containing 5–10% heroin base, costs €30–70, making the effective value per gram of pure heroin €300–700. Heroin is generally a preferred product for smuggling and distribution—over unrefined opium due to the cost-effectiveness and increased efficacy
Efficacy is the ability to perform a task to a satisfactory or expected degree. The word comes from the same roots as '' effectiveness'', and it has often been used synonymously, although in pharmacology a distinction is now often made betwee ...
of heroin.
Because of the high cost per volume, heroin is easily smuggled. A US quarter-sized (2.5 cm) cylindrical vial can contain hundreds of doses. From the 1930s to the early 1970s, the so-called French Connection
The French Connection was a scheme through which heroin was smuggled from Indochina through Turkey to France and then to the United States and Canada. The operation started in the 1930s, reached its peak in the 1960s, and was dismantled in the 1 ...
supplied the majority of US demand. Allegedly, during the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (1 November 1955 – 30 April 1975) was an armed conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia fought between North Vietnam (Democratic Republic of Vietnam) and South Vietnam (Republic of Vietnam) and their allies. North Vietnam w ...
, drug lords such as Ike Atkinson used to smuggle hundreds of kilograms of heroin to the US in coffins of dead American soldiers (see Cadaver Connection). Since that time it has become more difficult for drugs to be imported into the US than it had been in previous decades, but that does not stop the heroin smugglers from getting their product across US borders. Purity levels vary greatly by region with Northeastern cities having the most pure heroin in the United States. On 17 October 2018 police in Genoa
Genoa ( ; ; ) is a city in and the capital of the Italian region of Liguria, and the sixth-largest city in Italy. As of 2025, 563,947 people live within the city's administrative limits. While its metropolitan city has 818,651 inhabitan ...
, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
discovered of heroin hidden in a ship coming from the Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
ian southern port of Bandar Abbas
Bandar Abbas (, ) is a city in the Central District of Bandar Abbas County, Hormozgan province, Iran, serving as capital of the province, the county, and the district. Bandar Abbas is a port on the southern coast of the country, on the Persian ...
. The ship had already passed and stopped at Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg,. is the List of cities in Germany by population, second-largest city in Germany after Berlin and List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, 7th-lar ...
in Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
and Valencia
Valencia ( , ), formally València (), is the capital of the Province of Valencia, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Valencian Community, the same name in Spain. It is located on the banks of the Turia (r ...
in Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
.
Penalties for smuggling heroin or morphine are often harsh in most countries. Some countries will readily hand down a death sentence (e.g. Singapore) or life in prison for the illegal smuggling of heroin or morphine, which are both internationally Schedule I drugs under the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs
The Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, 1961 (Single Convention, 1961 Convention, or C61) is an international treaty that controls activities (cultivation, production, supply, trade, transport) involving specific narcotic drugs and lays down a ...
.
In May 2021, Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
seized 1.4 tonnes of heroin at Constanța
Constanța (, , ) is a city in the Dobruja Historical regions of Romania, historical region of Romania. A port city, it is the capital of Constanța County and the country's Cities in Romania, fourth largest city and principal port on the Black ...
port of a shipment from Iran that was headed for Western Europe.
Methamphetamine
Methamphetamine is another popular drug among distributors. Three common street names are "meth", "crank", and "ice". According to the Community Epidemiology Work Group, the number of clandestine methamphetamine laboratory incidents reported to the National Clandestine Laboratory Database decreased from 1999 to 2009. During this period, methamphetamine lab incidents increased in mid-western States (Illinois, Michigan, Missouri, and Ohio), and in Pennsylvania. In 2004, more lab incidents were reported in Missouri (2,788) and Illinois (1,058) than in California (764). In 2003, methamphetamine lab incidents reached new highs in Georgia (250), Minnesota (309), and Texas (677). There were only seven methamphetamine lab incidents reported in Hawaii in 2004, though nearly 59 percent of substance use treatment admissions (excluding alcohol) were for primary methamphetamine use during the first six months of 2004. As of 2007, Missouri leads the United States in drug-lab seizures, with 1,268 incidents reported. Often canine units are used for detectingrolling meth lab
A rolling meth lab is a transportable laboratory that is used to illegally produce methamphetamine.Staff writerMethamphetamine, meth-lab assessment and clean-up." ''Forensic Applications Consulting Technologies Inc.'' Retrieved on 2009-02-14. R ...
s which can be concealed on large vehicles, or transported on something as small as a motorcycle. These labs are more difficult to detect than stationary ones, and can often be obscured among legal cargo in big trucks.Bootie Cosgrove-MatherRolling Meth Labs In Vogue – Methamphetamine Makers Turn Vehicles Into Rolling Drug Labs
." ''
CBS News
CBS News is the news division of the American television and radio broadcaster CBS. It is headquartered in New York City. CBS News television programs include ''CBS Evening News'', ''CBS Mornings'', news magazine programs ''CBS News Sunday Morn ...
.'' Published July 17, 2002. Retrieved on 2009-02-14.
Methamphetamine is sometimes used intravenously, placing users and their partners at risk for transmission of HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of '' Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the im ...
and hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection period, people often have mild or no symptoms. Early symptoms can include ...
. "Meth" can also be inhaled, most commonly vaporized on aluminum foil or in a glass pipe. This method is reported to give "an unnatural high" and a "brief intense rush".
In South Africa, methamphetamine is called "tik" or "tik-tik". Known locally as "tik", the substance was virtually unknown as late as 2003. Now, it is the country's main addictive substance, even when alcohol is included. Children as young as eight are abusing the substance, smoking it in crude glass vials made from light bulbs. Since methamphetamine is easy to produce, the substance is manufactured locally in staggering quantities.
The government of North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders China and Russia to the north at the Yalu River, Yalu (Amnok) an ...
currently operates methamphetamine production facilities. There, the drug is used as medicine because no alternatives are available; it also is smuggled across the Chinese border.
The Australian Crime Commission's illicit drug data report for 2011–2012 stated that the average strength of crystal methamphetamine doubled in most Australian jurisdictions within a 12-month period, and the majority of domestic laboratory closures involved small "addict-based" operations.
Temazepam
Temazepam, a strong hypnoticbenzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), colloquially known as "benzos", are a class of central nervous system (CNS) depressant, depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed t ...
, is illicitly manufactured in clandestine laboratories (called ''jellie labs'') to supply the increasingly high demand for the drug internationally. Many clandestine temazepam labs are in Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
. The labs manufacture temazepam by chemically altering diazepam, oxazepam or lorazepam. "Jellie labs" have been identified and shut down in Russia, Ukraine, Latvia and Belarus.
Cocaine
Cocaine is a highly trafficked drug. In 2017 the value of the global market for illicit cocaine was estimated at between $94 and $143 billion. In 2022, illicit sales in Europe were estimated at $11.1 billion. In 2020, almost 2,000 tons of cocaine were produced for distribution through illicit markets.Fentanyl
Fentanyl, a syntheticopioid
Opioids are a class of Drug, drugs that derive from, or mimic, natural substances found in the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy plant. Opioids work on opioid receptors in the brain and other organs to produce a variety of morphine-like effects, ...
, is 20 to 40 times more potent than heroin
Heroin, also known as diacetylmorphine and diamorphine among other names, is a morphinan opioid substance synthesized from the Opium, dried latex of the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy; it is mainly used as a recreational drug for its eupho ...
and 100 times more potent than morphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
; its primary clinical utility is in pain management
Pain management is an aspect of medicine and health care involving relief of pain (pain relief, analgesia, pain control) in various dimensions, from acute (medicine), acute and simple to chronic condition, chronic and challenging. Most physici ...
for cancer patients and those recovering from painful surgeries. Illicit use of fentanyl continues to fuel an epidemic of synthetic opioid drug overdose deaths in the US. From 2011 to 2021, synthetic opioid deaths per year increased from 2,600 overdoses to 70,601. Since 2018, fentanyl and its analogues have been responsible for most drug overdose deaths in the US, causing over 71,238 deaths in 2021. Fentanyl is often mixed, cut, or ingested alongside other drugs, including cocaine and heroin. The fentanyl epidemic has erupted in a highly acrimonious dispute between the US and Mexican governments. While US officials blame the flood of fentanyl crossing the border primarily on Mexican crime groups, President Andrés Manuel López Obrador
Andrés Manuel López Obrador (; born 13 November 1953), also known by his initials AMLO, is a Mexican former politician, political scientist, public administrator and writer who served as the 65th president of Mexico from 2018 to 2024. He se ...
insists that the main source of this synthetic drug is Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
. He believes that the crisis of a lack of family values in the US drives people to use the drug.
See also
* Allegations of CIA drug trafficking *Arguments for and against drug prohibition
Commonly-cited arguments for and against the prohibition of drugs include the following:
Efficiency
Arguments that drug laws are effective
Supporters of prohibition claim that drug laws have a successful track record suppressing illicit drug us ...
* Corruption
Corruption is a form of dishonesty or a criminal offense that is undertaken by a person or an organization that is entrusted in a position of authority to acquire illicit benefits or abuse power for one's gain. Corruption may involve activities ...
* Counterfeit medications
A counterfeit medication or a counterfeit drug is a medication or pharmaceutical item which is produced and sold with the intent to deceptively represent its origin, authenticity, or effectiveness. A counterfeit drug may contain inappropriate qua ...
* Counterfeit money
Counterfeit money is currency produced outside of the legal sanction of a state or government, usually in a deliberate attempt to imitate that currency and so as to deceive its recipient. Producing or using counterfeit money is a form of fraud ...
* Environmental impact of illicit drug production
* Rum running
* Illicit cigarette trade
The illicit cigarette trade is defined as "the production, import, export, purchase, sale, or possession of tobacco goods which fail to comply with legislation" by the intergovernmental Financial Action Task Force (FATF). Illicit cigarette tra ...
* Human trafficking
Human trafficking is the act of recruiting, transporting, transferring, harboring, or receiving individuals through force, fraud, or coercion for the purpose of exploitation. This exploitation may include forced labor, sexual slavery, or oth ...
* Arms trafficking
Arms trafficking or gunrunning is the illicit trade of contraband small arms, explosives, and ammunition, which constitutes part of a broad range of illegal activities often associated with transnational criminal organizations. The illegal tra ...
* Wildlife trafficking
* Illegal organ trade
* Drug liberalization
Drug liberalization is a drug policy process of decriminalizing, legalizing, or repealing laws that prohibit the production, possession, sale, or use of prohibited drugs. Variations of drug liberalization include drug legalization, drug releg ...
* Drug trafficking organizations
Drug trafficking organizations are defined by the United States Department of Justice as, "complex organizations with highly defined command-and-control structures that produce, transport, and/or distribute large quantity "Law enforcement reportin ...
* Golden Crescent
* Golden Triangle (Southeast Asia)
The Golden Triangle is a large, mountainous region of approximately in northeastern Myanmar, northwestern Thailand and northern Laos, centered on the confluence of the Ruak River, Ruak and Mekong rivers. The name "Golden Triangle" was coined by ...
* Illegal drug trade in the Indian Ocean region
* Maritime drug smuggling into Australia
* Narco-capitalism
Narco-state (also narco-capitalism or narco-economy) is a political and economic term applied to countries where all legitimate institutions State capture, become penetrated by the power and wealth of the illegal drug trade. The term was first ...
* Narco-state
Narco-state (also narco-capitalism or narco-economy) is a political and economic term applied to countries where all legitimate institutions become penetrated by the power and wealth of the illegal drug trade. The term was first used to descr ...
* Narcoterrorism
* Organized crime
Organized crime is a category of transnational organized crime, transnational, national, or local group of centralized enterprises run to engage in illegal activity, most commonly for profit. While organized crime is generally thought of as a f ...
* Operation Show Me How
* Proxy criminal networks Proxy criminal networks refers to the use of organized crime syndicates based in a foreign country by a state to conduct covert, illicit, or deniable operations, including espionage, sabotage, assassination, cyberattacks, arms trafficking, or money ...
International coordination
* International Day Against Drug Abuse and Illicit Trafficking *Interpol
The International Criminal Police Organization – INTERPOL (abbreviated as ICPO–INTERPOL), commonly known as Interpol ( , ; stylized in allcaps), is an international organization that facilitates worldwide police cooperation and crime cont ...
* United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances
The United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances of 1988 is one of three major drug control treaties currently in force. It provides additional legal mechanisms for enforcing the 1961 Single C ...
References
External links
* of theUnited Nations Office on Drugs and Crime
The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC; French language, French: ''Office des Nations unies contre la drogue et le crime'') is a United Nations office that was established in 1997 as the Office for Drug Control and Crime Prevention ...
(UNODC)
Illicit drug issues by country, by the CIA
. {{Authority control Smuggling