Dropped Out on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dropping out refers to leaving
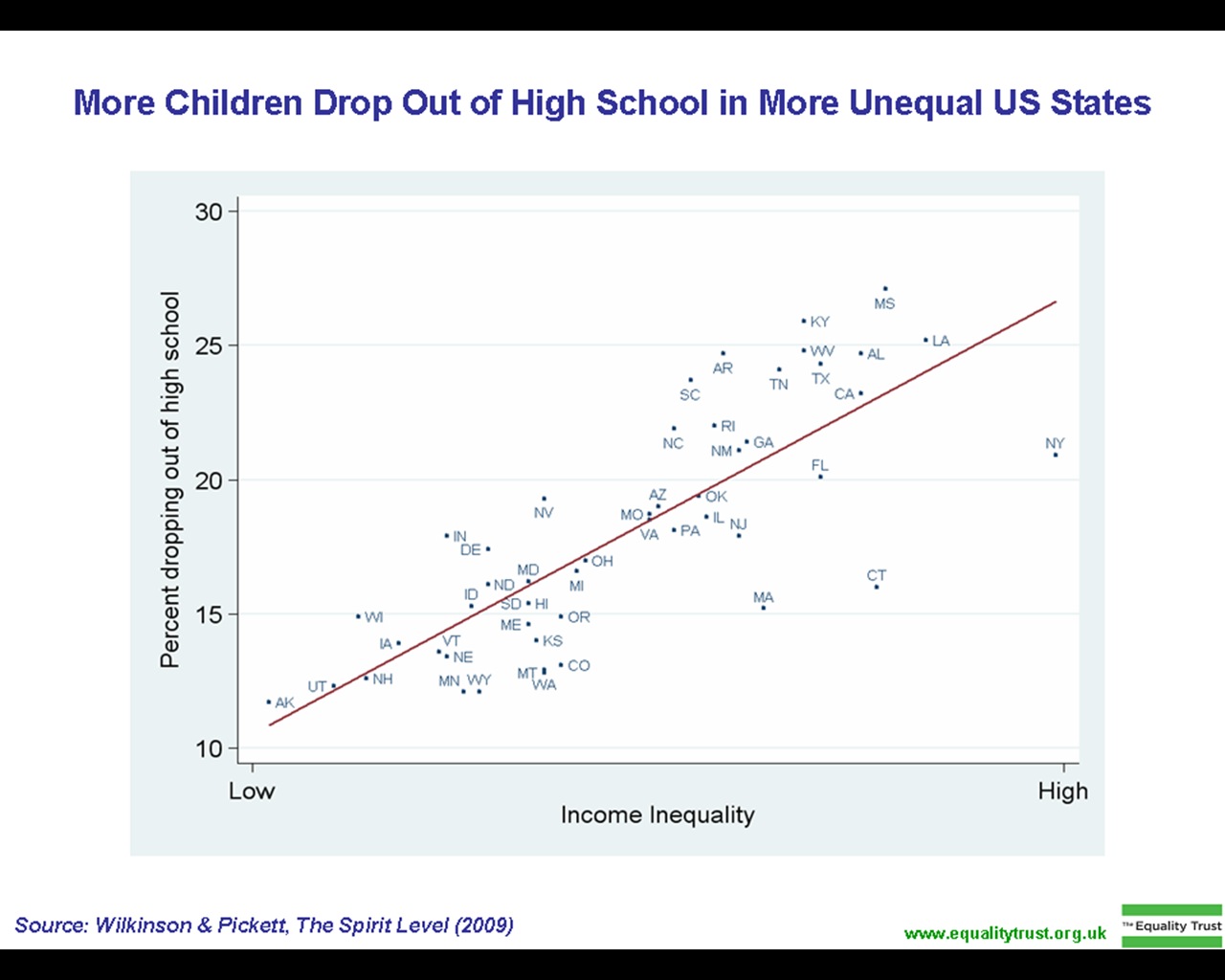 In the
In the
high school
A secondary school, high school, or senior school, is an institution that provides secondary education. Some secondary schools provide both ''lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) and ''upper secondary education'' (ages 14 to 18), i.e., ...
, college
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') may be a tertiary educational institution (sometimes awarding degrees), part of a collegiate university, an institution offering vocational education, a further education institution, or a secondary sc ...
, university or another group for practical reasons, necessities, inability, apathy, or disillusionment with the system from which the individual in question leaves.
Canada
In Canada, most individuals graduate from grade 12 by the age of 18, according to Jason Gilmore who collects data on employment and education using the Labour Force Survey (LFS), the official survey used to collectunemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is the proportion of people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work du ...
data in Canada (2010). Using this tool, assessing educational attainment and school attendance can calculate a dropout rate (Gilmore, 2010). It was found by the LFS that by 2009, one in twelve 20- to 24-year-old adults did not have a high school diploma
A high school diploma (sometimes referred to as a high school degree) is a diploma awarded upon graduation of high school
A secondary school, high school, or senior school, is an institution that provides secondary education. Some secondary s ...
(Gilmore, 2010). The study also found that men still have higher dropout rates than women, and that students outside of major cities and in the northern territories also have a higher risk of dropping out. Although since 1990 dropout rates have gone down from 20% to a low of 9% in 2010, the rate does not seem to be dropping since this time (2010).
The average Canadian
Canadians () are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being ''C ...
dropout earns $70 less per week than their peers with a high school diploma
A high school diploma (sometimes referred to as a high school degree) is a diploma awarded upon graduation of high school
A secondary school, high school, or senior school, is an institution that provides secondary education. Some secondary s ...
. Graduates (without post-secondary) earned an average of $621 per week, whereas dropout students earned an average of $551 (Gilmore, 2010).
Even though dropout rates have gone down in the last 20 to 25 years, the concerns of the impact dropping out has on the labour market are very real (Gilmore, 2010). One in four students without a high school diploma
A high school diploma (sometimes referred to as a high school degree) is a diploma awarded upon graduation of high school
A secondary school, high school, or senior school, is an institution that provides secondary education. Some secondary s ...
who was in the labour market in 2009-2010 had less likelihood of finding a job due to economic downturn (Gilmore, 2010).
In 2018, graduation rates at universities
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
within Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
were as low as 44% (Macleans, 2018). This is almost half of the student population (Macleans, 2018) There tends to be an increase in students dropping-out as a result of feeling disconnected from their school community (Binfet et al., 2016). This is most common with students within their first two years of post-secondary where students will withdraw from their program, or their entire education completely (Binfet et al., 2018). One preventable measure that post-secondary institutions have used within Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
to combat students dropping out is to incorporate animal support programs (Binfet et al., 2016., & Binfet et al., 2018). Allowing students to interact with support dogs and their owners allowed students to feel connected to their peers, school and school community (Binfet et al., 2016., & Binfet et al., 2018).
United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, a dropout is anyone who leavesschool
A school is the educational institution (and, in the case of in-person learning, the Educational architecture, building) designed to provide learning environments for the teaching of students, usually under the direction of teachers. Most co ...
, college
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') may be a tertiary educational institution (sometimes awarding degrees), part of a collegiate university, an institution offering vocational education, a further education institution, or a secondary sc ...
or university without either completing their course of study or transferring to another educational institution. Attendance at a school is compulsory until age 16.
Dropout rate benchmarks are set for each higher education institution and monitored by the Higher Education Funding Council for England
The Higher Education Funding Council for England (HEFCE) was a non-departmental public body in the United Kingdom, which was responsible for the distribution of funding for higher education to universities and further education colleges in Engl ...
(HEFCE), the Higher Education Funding Council for Wales (HEFCW) and the Scottish Funding Council (SFC). Dropout rates are often one of the factors assessed when ranking UK universities in league tables.
In November 2014, a report from the Institute for Fiscal Studies found that students from poorer home backgrounds were 8.4 percentage points more likely to drop out of university in the first two years of an undergraduate
Undergraduate education is education conducted after secondary education and before postgraduate education, usually in a college or university. It typically includes all postsecondary programs up to the level of a bachelor's degree. For example, ...
course than those from the richest homes; they were also 22.9 percentage points less likely to obtain a 2:1 or first degree. For students studying on the same course and who arrived at university with similar grades, the differences fell but remained significant. The report concluded that more should be done both to raise the attainment levels of poorer students prior to their arrival at university and to provide additional support to them at university.
United States
 In the
In the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, dropping out most commonly refers to a student quitting school without fulfilling the requirements for graduation. It cannot always be ascertained that a student has dropped out, as they may stop attending without terminating enrollment. It is estimated 1.2 million students annually drop out of high school
A secondary school, high school, or senior school, is an institution that provides secondary education. Some secondary schools provide both ''lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) and ''upper secondary education'' (ages 14 to 18), i.e., ...
in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, where high school
A secondary school, high school, or senior school, is an institution that provides secondary education. Some secondary schools provide both ''lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) and ''upper secondary education'' (ages 14 to 18), i.e., ...
graduation rates rank 19th in the world. Reasons are varied and may include: to find employment, avoid bullying, family emergency, poor grades, depression and other mental illnesses, unexpected pregnancy, bad environment, lack of freedom, and even boredom. ''The Silent Epidemic: Perspectives of High School Dropouts'' by Civic Enterprises explores reasons students leave school without
graduating. The consequences of dropping out of school can have long-term economic and social repercussions. Students who drop out of school in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
are more likely to be unemployed, homeless, receiving welfare and incarcerated. A four-year study in San Francisco found that 94 percent of young murder victims were high school
A secondary school, high school, or senior school, is an institution that provides secondary education. Some secondary schools provide both ''lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) and ''upper secondary education'' (ages 14 to 18), i.e., ...
dropouts.
The United States Department of Education
The United States Department of Education is a cabinet-level department of the United States government, originating in 1980. The department began operating on May 4, 1980, having been created after the Department of Health, Education, and ...
's measurement of the ''status'' dropout rate is the percentage of 16-24-year-olds who are not enrolled in school and have not earned a high school
A secondary school, high school, or senior school, is an institution that provides secondary education. Some secondary schools provide both ''lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) and ''upper secondary education'' (ages 14 to 18), i.e., ...
credential.NCES 2011 This rate is different from the event dropout rate and related measures of the status completion and average freshman
A freshman, fresher, first year, or colloquially frosh, is a person in the first year at an educational institution, usually a secondary school or at the college and university level, but also in other forms of post-secondary educational in ...
completion rates.NCES 2009 The status high school dropout rate in 2009 was 8.1%. There are many risk factors for high school dropout. These can be categorized into social and academic risk factors. Members of racial and ethnic minority groups drop out at higher rates than white students, as do those from low-income families, from single-parent households, and from families in which one or both parents also did not complete high school.Lee 2003 Students at risk for dropout based on academic risk factors are those who often have a history of absenteeism and grade retention, academic trouble, and more general disengagement from school life.
Australia
InAustralia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
, dropping out most commonly refers to a student quitting school before they graduate. Reasons for students dropping out vary but usually include: Avoiding bullies, finding employment, family problems, depression and other mental illnesses, teenage pregnancy, substance abuse
Substance misuse, also known as drug misuse or, in older vernacular, substance abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods that are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder, differing definition ...
and in some cases even boredom. Researchers at Melbourne's Mitchell Institute have found that a quarter of Australian high school
A secondary school, high school, or senior school, is an institution that provides secondary education. Some secondary schools provide both ''lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) and ''upper secondary education'' (ages 14 to 18), i.e., ...
students are not graduating year 12, and that completion rates are much worse in remote or economically disadvantaged communities. Professor Teese believes the segregation of students in schools through geography as well as in the private and public systems means student disadvantage is stronger in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
than other western nations such as New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
. Drop out rates vary throughout different locations in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
. Students that attend school in remote communities have a higher chance of not completing year 12 (56.6%), whereas students that come from a wealthy background share an average completion rate of 90%. These remote schooling programs serve primarily indigenous students. Indigenous students to have lower rates of completion: the gap between indigenous and non-indigenous year 12 graduates is over 40 percentage points. As a result of this substantial difference, lower socioeconomic students who drop out are considered at-risk-students and are ultimately prone to unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is the proportion of people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work du ...
, incarceration, low-paying employment and having children at early ages.
Latin America
When analysing the household surveys of some countries in theLatin America
Latin America is the cultural region of the Americas where Romance languages are predominantly spoken, primarily Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese. Latin America is defined according to cultural identity, not geogr ...
n region – notably, those of Bolivia
Bolivia, officially the Plurinational State of Bolivia, is a landlocked country located in central South America. The country features diverse geography, including vast Amazonian plains, tropical lowlands, mountains, the Gran Chaco Province, w ...
, Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
, Panama
Panama, officially the Republic of Panama, is a country in Latin America at the southern end of Central America, bordering South America. It is bordered by Costa Rica to the west, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the north, and ...
, Costa Rica
Costa Rica, officially the Republic of Costa Rica, is a country in Central America. It borders Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the northeast, Panama to the southeast, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, as well as Maritime bo ...
, Nicaragua
Nicaragua, officially the Republic of Nicaragua, is the geographically largest Sovereign state, country in Central America, comprising . With a population of 7,142,529 as of 2024, it is the third-most populous country in Central America aft ...
and Paraguay
Paraguay, officially the Republic of Paraguay, is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the Argentina–Paraguay border, south and southwest, Brazil to the Brazil–Paraguay border, east and northeast, and Boli ...
– researching the opinions of boys, girls, adolescents, young people as well as their families on the reasons they drop out of school, some recurring features surface that enable us to group the analyses into two main categories. The first is directly related to 'the material dimension' of education. In this case, financial difficulties are the main reason why families do not manage to keep their children and adolescents in school. The other major group of factors for school drop out falls into the 'subjective dimension' of the educational experience. Surveys revealed that 22% of out-of-school boys and girls aged 10 or 11 years state that they are in this situation because they have no interest in studying. This percentage jumps to 38% in adolescents aged 15 to 17 years who also provided this reason for their disengagement with the education system.
Dropout recovery
A "dropout recovery" initiative is anycommunity
A community is a social unit (a group of people) with a shared socially-significant characteristic, such as place, set of norms, culture, religion, values, customs, or identity. Communities may share a sense of place situated in a given g ...
, government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a State (polity), state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive (government), execu ...
, non-profit or business program in which students who have previously left school are sought out for the purpose of re-enrollment. In the U.S
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
., such initiatives are often focused on former high school students who are still young enough to have their educations publicly subsidized, generally those 22 years of age and younger. In Rwanda
Rwanda, officially the Republic of Rwanda, is a landlocked country in the Great Rift Valley of East Africa, where the African Great Lakes region and Southeast Africa converge. Located a few degrees south of the Equator, Rwanda is bordered by ...
, dropout recovery is often focused on primary- and ordinary-level students who are still young and able to continue their education.
Dropout recovery programs can be initiated in traditional "brick-and-mortar" institutions of learning, in community centers or online.
Dropping out of high school can have drastic long-term economic and social repercussions, especially in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
which has a less equitable education system than many other western countries. Therefore, different pathways and courses of study are being implemented by the government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a State (polity), state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive (government), execu ...
, non-profit organizations
A nonprofit organization (NPO), also known as a nonbusiness entity, nonprofit institution, not-for-profit organization, or simply a nonprofit, is a non-governmental (private) legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public, or so ...
, and private companies to offer a selection of education recovery plans for young adults around the age of 22 and below.
Attrition
Students that drop out of high-school are generally those that struggle to engage behaviorally and/or academically. However, it is not entirely clear whether different types of contextual or self-system variables affect students' engagement or contribute to their decision to drop out. According to data collected by the national education longitudinal study of 1988, Rumberger found that students with moderate to high absenteeism, behavior problems and having no school or outside activities were highly predictive of dropping out.Prevention
Family dynamics
Under the pact of educational inclusion at the secondary level, how families organize themselves internally to produce well-being is an unavoidable topic for countries to address when seeking to broaden the effective opportunities of access to, retention in and graduation from the secondary education. Therefore, the construction of a new policy, the adolescent and the young person at school, is an acknowledgement of what is happening in reality and shapes a mutually beneficial alliance between the state and families to generate dynamics where young people can become exclusive recipients of care – at least until completion of their secondary schooling.See also
* All but dissertation * Alternative Learning System of basic education for either grade school or high school dropouts in the Philippines * At-risk students * Disengagement from education * Expulsion (education) * Rustication (academia) * School-leaving age * Suspension (punishment) * TAFE * List of Harvard University non-graduate alumniSources
References
Binfet, J., Passmore, H., Cebry, A., Struik, K., & McKay, C. (2018). Reducing university students' stress through a drop-in canine-therapy program. Journal of Mental Health, 27(3), 197–204. Binfet, J., & Passmore, H. (2016). Hounds and homesickness: The effects of an animal-assisted therapeutic intervention for first-year university students. Anthrozoös, 29(3), 441–454. {{Authority control Education issues Counterculture Human behavior Youth culture Types of students Education