drop foot on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Foot drop is a
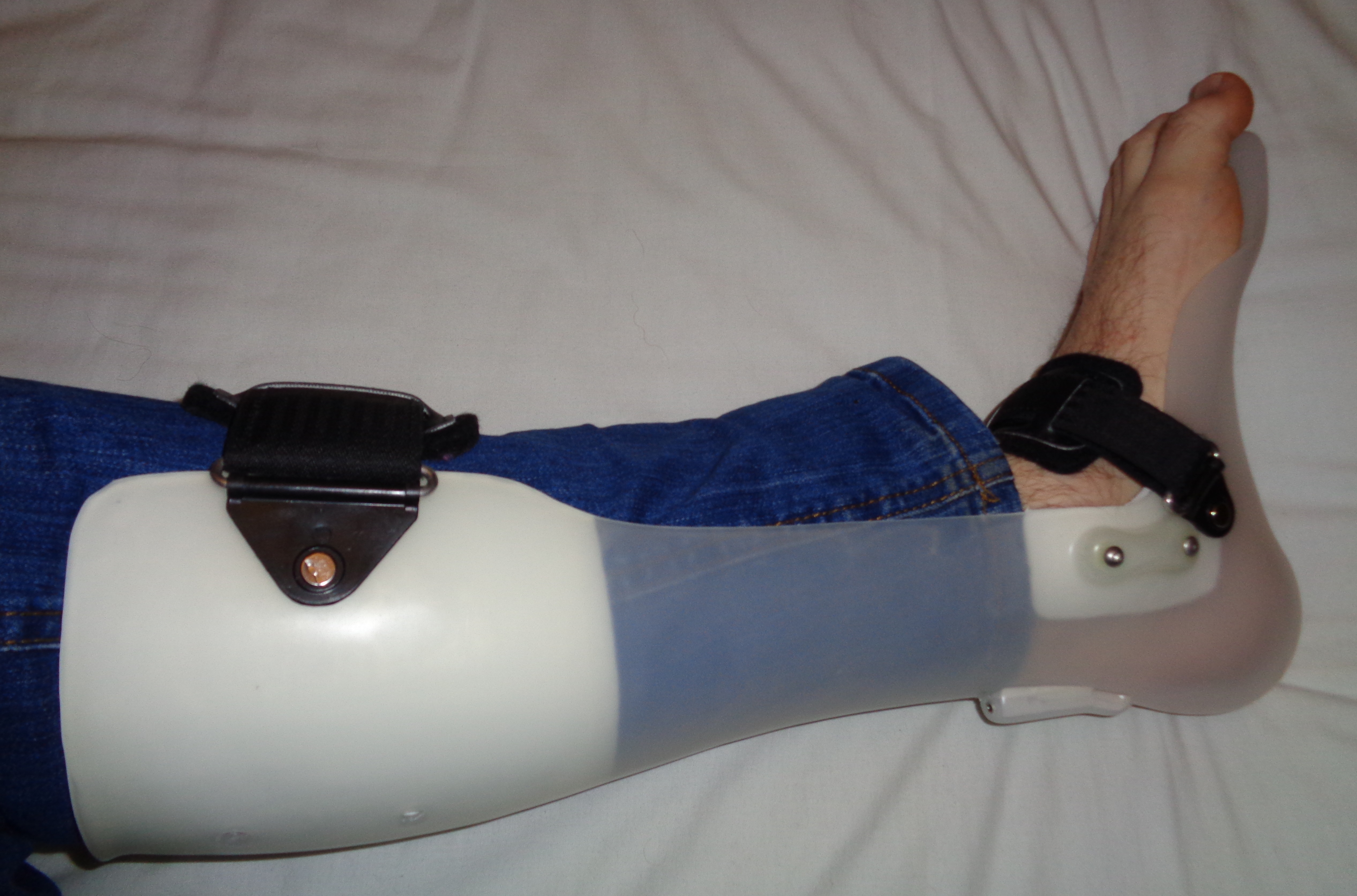 The underlying disorder must be treated. For example, if a
The underlying disorder must be treated. For example, if a  Ankles can be stabilized by lightweight
Ankles can be stabilized by lightweight
Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project
* Balali-Mood, Mahdi (January 2008)
"Neurotoxic disorders of organophosphorus compounds and their managements"
''Arch Iran Med.'' 11(1):65–89. . * Jokanovic, Milan, Melita Kosanovic, Dejan Brkic, and Predrag Vukomanovic (2011)
"Organophosphate Induced Delayed Polyneuropathy in Man: An Overview"
''Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery'' 113.1: 7–10. . . * Mayo Clinic
"Foot Drop"
* Pritchett, James W., MD (June 21, 2018)
"Foot Drop"
Vinod K Panchbhavi, MD, FACS (ed.). * Saladin, Kenneth (2015). ''Anatomy & Physiology: A Unity of Form & Function''. 7th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education. Print. {{authority control Gait abnormalities Musculoskeletal disorders Neurological disorders
gait abnormality
Gait abnormality is a deviation from normal walking (gait). Watching a patient walk is an important part of the neurological examination. Normal gait requires that many systems, including strength, sensation and coordination, function in an integ ...
in which the dropping of the forefoot happens out of weakness, irritation or damage to the deep fibular nerve
The deep fibular nerve (also known as deep peroneal nerve) begins at the bifurcation of the common fibular nerve between the fibula and upper part of the fibularis longus, passes infero-medially, deep to the extensor digitorum longus, to the a ...
(deep peroneal), including the sciatic nerve
The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals. It is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the right lower limb. It is the longest and widest ...
, or paralysis of the muscles in the anterior portion of the lower leg. It is usually a symptom of a greater problem, not a disease in itself. Foot drop is characterized by inability or impaired ability to raise the toes or raise the foot from the ankle (dorsiflexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relativ ...
). Foot drop may be temporary or permanent, depending on the extent of muscle weakness or paralysis, and it can occur in one or both feet. In walking, the raised leg is slightly bent at the knee to prevent the foot from dragging along the ground.
Foot drop can be caused by nerve damage alone or by muscle or spinal cord trauma, abnormal anatomy, toxins, or disease. Toxins include organophosphate
In organic chemistry, organophosphates (also known as phosphate esters, or OPEs) are a class of organophosphorus compounds with the general structure , a central phosphate molecule with alkyl or aromatic substituents. They can be considered ...
compounds which have been used as pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s and as chemical agents in warfare. The poison can lead to further damage to the body such as a neurodegenerative disorder called organophosphorus induced delayed polyneuropathy. This disorder causes loss of function of the motor and sensory neural pathways. In this case, foot drop could be the result of paralysis due to neurological dysfunction. Diseases that can cause foot drop include trauma to the posterolateral neck of fibula, stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or—in the United States—Lou Gehrig's disease (LGD), is a rare, Terminal illness, terminal neurodegenerative disease, neurodegenerative disorder that results i ...
, muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophies (MD) are a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare neuromuscular diseases that cause progressive weakness and breakdown of skeletal muscles over time. The disorders differ as to which muscles are primarily affe ...
, poliomyelitis
Poliomyelitis ( ), commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 75% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe ...
, Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT) is an inherited neurological disorder that affects the peripheral nerves responsible for transmitting signals between the brain, spinal cord, and the rest of the body.
This is the most common inherited neuropath ...
, multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit ...
, cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, spasticity, stiff muscles, Paresis, weak muscles, and tremors. There may b ...
, hereditary spastic paraplegia
Hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP) is a group of inherited diseases whose main feature is a progressive Gait abnormality, gait disorder. The disease presents with progressive stiffness (spasticity) and contraction in the lower limbs. HSP is als ...
, Guillain–Barré syndrome
Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rapid-onset Paralysis, muscle weakness caused by the immune system damaging the peripheral nervous system. Typically, both sides of the body are involved, and the initial symptoms are changes in sensation ...
, Welander distal myopathy, Friedreich's ataxia
Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA) is a rare, inherited, autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects the nervous system, causing progressive damage to the spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and cerebellum, leading to impaired ...
, chronic compartment syndrome
Compartment syndrome is a serious medical condition in which increased pressure within a Fascial compartment, body compartment compromises blood flow and tissue function, potentially leading to permanent damage if not promptly treated. There are ...
, and severe nerve entrapment
Nerve compression syndrome, or compression neuropathy, or nerve entrapment syndrome, is a medical condition caused by chronic, direct pressure on a peripheral nerve. It is known colloquially as a ''trapped nerve'', though this may also refer to n ...
. It may also occur as a result of hip replacement surgery or knee ligament reconstruction surgery.
Signs and symptoms
Foot drop is characterized bysteppage gait
Steppage gait (high stepping, neuropathic gait) is a form of gait abnormality characterised by foot drop or ankle equinus due to loss of dorsiflexion. The foot hangs with the toes pointing down, causing the toes to scrape the ground while walking, ...
. While walking, people suffering the condition drag their toes along the ground or bend their knees to lift their foot higher than usual to avoid the dragging. This serves to raise the foot high enough to prevent the toe from dragging and prevents the slapping. To accommodate the toe drop, the patient may use a characteristic tiptoe walk on the opposite leg, raising the thigh
In anatomy, the thigh is the area between the hip (pelvis) and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.
The single bone in the thigh is called the femur. This bone is very thick and strong (due to the high proportion of bone tissu ...
excessively, as if walking upstairs, while letting the toe drop. Other gaits such as a wide outward leg swing (to avoid lifting the thigh excessively or to turn corners in the opposite direction of the affected limb) may also indicate foot drop.
Patients with painful disorders of sensation (dysesthesia
Dysesthesia is an unpleasant, abnormal sense of touch. Its etymology comes from the Greek word "dys," meaning "bad," and "aesthesis," which means "sensation" (abnormal sensation). It often presents as pain but may also present as an inappropriate, ...
) of the soles of the feet may have a similar gait but do not have foot drop. Because of the extreme pain evoked by even the slightest pressure on the feet, the patient walks as if walking barefoot on hot sand.
Pathophysiology
The causes of foot drop, as for all causes of neurological lesions, should be approached using a localization-focused approach before etiologies are considered. Most of the time, foot drop is the result of neurological disorder; only rarely is the muscle diseased or nonfunctional. The source for the neurological impairment can be central (spinal cord or brain) or peripheral (nerves located connecting from the spinal cord to an end-site muscle or sensory receptor). Foot drop is rarely the result of a pathology involving the muscles or bones that make up the lower leg. Theanterior tibialis
The tibialis anterior muscle is a muscle of the anterior compartment of the lower leg. It originates from the upper portion of the tibia; it inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. It acts to dorsiflex and invert ...
is the muscle that picks up the foot. Although the anterior tibialis plays a major role in dorsiflexion, it is assisted by the fibularis tertius
In human anatomy, the fibularis tertius (also known as the peroneus tertius) is a muscle in the anterior compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body ( eversion) and to pull the foot upward towar ...
, extensor digitorum longus
The extensor digitorum longus is a pennate muscle, situated at the lateral part of the front of the leg.
Structure
It arises from the lateral condyle of the tibia; from the upper three-quarters of the anterior surface of the body of the fibula; ...
and the extensor hallucis longus
The extensor hallucis longus muscle is a thin skeletal muscle, situated between the tibialis anterior and the extensor digitorum longus. It extends the big toe and dorsiflects the foot. It also assists with foot eversion and inversion.
Struc ...
. If the drop foot is caused by neurological disorder all of these muscles could be affected because they are all innervated by the deep fibular (peroneal) nerve, which branches from the sciatic nerve
The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals. It is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the right lower limb. It is the longest and widest ...
. The sciatic nerve exits the lumbar plexus
The lumbar plexus is a web of nerves (a nerve plexus) in the lumbar region of the body which forms part of the larger lumbosacral plexus. It is formed by the divisions of the first four lumbar nerves (L1–L4) and from contributions of the su ...
with its root arising from the fifth lumbar nerve space.
Occasionally, spasticity in the muscles opposite the anterior tibialis
The tibialis anterior muscle is a muscle of the anterior compartment of the lower leg. It originates from the upper portion of the tibia; it inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. It acts to dorsiflex and invert ...
, the gastrocnemius and soleus, exists in the presence of foot drop, making the pathology much more complex than foot drop. Isolated foot drop is usually a flaccid condition. There are gradations of weakness that can be seen with foot drop, as follows according to MRC:
* 0 = complete paralysis,
* 1 = flicker of contraction,
* 2 = contraction with gravity eliminated alone,
* 3 = contraction against gravity alone,
* 4 = contraction against gravity and some resistance, and
* 5 = contraction against powerful resistance (normal power).
''foot slap'' is a heel strike abnormality, which is the audible slapping of the foot to the floor with each step that occurs when the foot first hits the floor on each step. Sometimes it is not visible and the diagnosis is done by actually hearing the slap.
Treated systematically, possible lesion sites causing foot drop include (going from peripheral to central):
# Neuromuscular disease
A neuromuscular disease is any disease affecting the peripheral nervous system (PNS), the neuromuscular junctions, or skeletal muscles, all of which are components of the motor unit. Damage to any of these structures can cause muscle atrophy and we ...
;
# Peroneal nerve
The common fibular nerve (also known as the common peroneal nerve, external popliteal nerve, or lateral popliteal nerve) is a nerve in the lower leg that provides sensation over the posterolateral part of the leg and the knee joint. It divides a ...
(common, i.e., frequent) —chemical, mechanical, disease;
# Sciatic nerve
The sciatic nerve, also called the ischiadic nerve, is a large nerve in humans and other vertebrate animals. It is the largest branch of the sacral plexus and runs alongside the hip joint and down the right lower limb. It is the longest and widest ...
—direct trauma, iatrogenic;
# Lumbosacral plexus
The anterior divisions of the lumbar nerves, sacral nerves, and coccygeal nerve form the lumbosacral plexus, the first lumbar nerve being frequently joined by a branch from the twelfth thoracic. For descriptive purposes this plexus is usually d ...
;
# L5 nerve root A nerve root () is the initial segment of a nerve leaving the central nervous system. Nerve roots can be classified as:
* Cranial nerve roots: the initial or proximal segment of one of the twelve pairs of cranial nerves leaving the central nervous s ...
(common, especially in association with pain in back radiating down leg);
# Cauda equina syndrome
Cauda equina syndrome (CES) is a condition that occurs when the bundle of nerves below the end of the spinal cord known as the cauda equina is damaged. Signs and symptoms include low back pain, sciatica, pain that radiates down the leg, numbness ...
, which is caused by impingement of the nerve roots within the spinal canal distal to the end of the spinal cord;
# Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
(rarely causes isolated foot drop) —poliomyelitis, tumor;
# Brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
(uncommon, but often overlooked) —stroke, TIA, tumor;
# Genetic (as in Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease and hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies);
# Nonorganic causes, e.g. as part of a functional neurological symptom disorder
Functional neurological symptom disorder (FNSD), also referred to as dissociative neurological symptom disorder (DNSD), is a condition in which patients experience neurological symptoms such as weakness, movement problems, sensory symptoms, and ...
.
If the L5 nerve root is involved, the most common cause is a herniated disc
A disc herniation or spinal disc herniation is an injury to the intervertebral disc between two vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, ...
. Other causes of foot drop are diabetes (due to generalized peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropa ...
), trauma, motor neuron disease (MND), adverse reaction to a drug or alcohol, and multiple sclerosis.
Gait cycle
Drop foot and foot drop are interchangeable terms that describe an abnormal neuromuscular disorder that affects the patient's ability to raise their foot at the ankle. Drop foot is further characterized by an inability to point the toes toward the body (dorsiflexion) or move the foot at the ankle inward or outward. Therefore, the normal gait cycle is affected by the drop foot syndrome. The normal gait cycle is as follows: * Swing phase (SW): The period of time when the foot is not in contact with the ground. In those cases where the foot never leaves the ground (foot drag), it can be defined as the phase when all portions of the foot are in forward motion. * Initial contact (IC): The point in the gait cycle when the foot initially makes contact with the ground; this represents the beginning of the stance phase. It is suggested that heel strike not be a term used in clinical gait analysis as in many circumstances initial contact is not made with the heel. Suggestion: Should use foot strike. * Terminal contact (TC): The point in the gait cycle when the foot leaves the ground: this represents the end of the stance phase or beginning of the swing phase. Also referred to as foot off. Toe-off should not be used in situations where the toe is not the last part of the foot to leave the ground. The drop foot gait cycle requires more exaggerated phases. * Drop foot SW: If the foot in motion happens to be the affected foot, there will be greater flexion at the knee to accommodate the inability to dorsiflex. This increase in knee flexion will cause a stair-climbing movement. * Drop foot IC: Initial contact of the foot that is in motion will not have normal heel-toe foot strike. Instead, the foot may either slap the ground or the entire foot may be planted on the ground all at once. * Drop foot TC: Terminal contact that is observed in patients that have drop foot is quite different. Since patients tend to have weakness in the affected foot, they may not have the ability to support their body weight. Often, a walker or cane will be used to assist in this aspect. Drop Foot is the inability to dorsiflex, evert, or invert the foot. So when looking at the Gait cycle, the part of the gait cycle that involves most dorsiflexion action would be Heel Contact of the foot at 10% of Gait Cycle, and the entire swing phase, or 60-100% of the Gait Cycle. This is also known as Gait Abnormalities.Diagnosis
Initial diagnosis often is made during routine physical examination. Such diagnosis can be confirmed by a medical professional such as aphysiatrist
Physical medicine and rehabilitation (PM&R), also known as physiatry, and outside the United States as physical and rehabilitation medicine (PRM), is a branch of medicine that aims to enhance and restore functional ability and quality of life ...
, neurologist
Neurology (from , "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the nervous system, which comprises the brain, the ...
, orthopedic surgeon
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics (American and British English spelling differences, alternative spelling orthopaedics) is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgic ...
or neurosurgeon
Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the medical specialty that focuses on the surgical treatment or rehabilitation of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, ...
. A person with foot drop will have difficulty walking on his or her heels because
they will be unable to lift the front of the foot (balls and toes) off the ground. Therefore, a simple test of asking the patient to dorsiflex may determine diagnosis of the problem. This is measured on a 0-5 scale that observes mobility. The lowest point, 0, will determine complete paralysis and the highest point, 5, will determine complete mobility.
There are other tests that may help determine the underlying etiology for this diagnosis. Such tests may include MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and rad ...
, MRN, or EMG to assess the surrounding areas of damaged nerves and the damaged nerves themselves, respectively. The nerve that communicates to the muscles that lift the foot is the peroneal nerve
The common fibular nerve (also known as the common peroneal nerve, external popliteal nerve, or lateral popliteal nerve) is a nerve in the lower leg that provides sensation over the posterolateral part of the leg and the knee joint. It divides a ...
. This nerve innervates the anterior muscles of the leg that are used during dorsiflexion of the ankle. The muscles that are used in plantar flexion are innervated by the tibial nerve
The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.
Structure Popliteal fossa
The tibial nerve is the larger terminal branch of the sciatic nerve with root val ...
and often develop tightness in the presence of foot drop. The muscles that keep the ankle from supination (as from an ankle sprain) are also innervated by the peroneal nerve, and it is not uncommon to find weakness in this area as well. Paraesthesia in the lower leg, particularly on the top of the foot and ankle, also can accompany foot drop, although it is not in all instances.
A common yoga
Yoga (UK: , US: ; 'yoga' ; ) is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines that originated with its own philosophy in ancient India, aimed at controlling body and mind to attain various salvation goals, as pra ...
kneeling exercise, the Varjrasana has, under the name "yoga foot drop", been linked to foot drop.
Treatment
spinal disc herniation
A disc herniation or spinal disc herniation is an injury to the intervertebral disc between two vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, ...
in the low back is impinging on the nerve that goes to the leg and causing symptoms of foot drop, then the herniated disc should be treated. If the foot drop is the result of a peripheral nerve injury, a window for recovery of 18 months to 2 years is often advised. If it is apparent that no recovery of nerve function takes place, surgical intervention to repair or graft the nerve can be considered, although results from this type of intervention are mixed.
Non-surgical treatments for spinal stenosis
Spinal stenosis is an abnormal narrowing of the spinal canal or neural foramen that results in pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. Symptoms may include pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs. Symptoms are typically gradual in ...
include a suitable exercise program developed by a physical therapist, activity modification (avoiding activities that cause advanced symptoms of spinal stenosis), epidural injections, and anti-inflammatory medications like ibuprofen or aspirin. If necessary, a decompression surgery that is minimally destructive of normal structures may be used to treat spinal stenosis.
Non-surgical treatments for this condition are very similar to the non-surgical methods described above for spinal stenosis. Spinal fusion
Spinal fusion, also called spondylodesis or spondylosyndesis, is a surgery performed by Orthopedic surgery#Practice, orthopaedic surgeons or neurosurgeons that joins two or more vertebrae. This procedure can be performed at any level in the spine ...
surgery may be required to treat this condition, with many patients improving their function and experiencing less pain.
Nearly half of all vertebral fractures occur without any significant back pain. If pain medication, progressive activity, or a brace or support does not help with the fracture, two minimally invasive procedures - vertebroplasty
Vertebral augmentation, including vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty, refers to similar percutaneous spinal procedures in which bone cement is injected through a small hole in the skin into a fractured vertebra in order to relieve back pain caused b ...
or kyphoplasty
Vertebral augmentation, including vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty, refers to similar percutaneous spinal procedures in which bone cement is injected through a small hole in the skin into a fractured vertebra in order to relieve back pain caused ...
- may be options.
 Ankles can be stabilized by lightweight
Ankles can be stabilized by lightweight orthoses
Orthotics () is a medical specialty that focuses on the design and application of orthoses, sometimes known as braces, calipers, or splints. An is "an externally applied device used to influence the structural and functional characteristics of ...
, available in molded plastics as well as softer materials that use elastic properties to prevent foot drop. Additionally, shoes can be fitted with traditional spring-loaded braces to prevent foot drop while walking. Regular exercise is usually prescribed.
Functional electrical stimulation
Functional electrical stimulation (FES) is a technique that uses low-energy electrical pulses to artificially generate body movements in individuals who have been paralyzed due to injury to the central nervous system. More specifically, FES ca ...
(FES) is a technique that uses electrical currents to activate nerves innervating extremities affected by paralysis resulting from spinal cord injury (SCI), head injury, stroke and other neurological disorders. FES is primarily used to restore function in people with disabilities. It is sometimes referred to as neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES)
The latest treatments include stimulation of the peroneal nerve, which lifts the foot when you step. Many stroke and multiple sclerosis patients with foot drop have had success with it. Often, individuals with foot drop prefer to use a compensatory technique like steppage gait or hip hiking as opposed to a brace or splint.
FES is applied to lower extremities for improving functional walking in stroke patients; for the correction of foot drop. They have benefited patients by improving gait speed, muscle strength and other functions.
Treatment for some can be as easy as an underside L-shaped foot-up ankle support ( ankle-foot orthoses). Another method uses a cuff placed around the patient's ankle, and a topside spring and hook installed under the shoelaces. The hook connects to the ankle cuff and lifts the shoe up when the patient walks.
Both these techniques show significant improvement on usage.
Identification of a suspect in a murder case
In December 2021, police in Toronto, Canada said they were looking for a person with a distinctive gait as a suspect in the murder ofBarry Sherman
Bernard Charles "Barry" Sherman, (February 25, 1942 – December 13, 2017) was a Canadian businessman and philanthropy, philanthropist who was chairman and CEO of Apotex, Apotex Inc. With an estimated net worth of US$3.2 billion at the ti ...
and Honey Sherman. Medical professionals quoted by the ''Toronto Star'' said that the distinctive gait could be caused by foot drop.
See also
*Yoga foot drop
Vajrasana (), Thunderbolt Pose, or Diamond Pose, is a kneeling asana in hatha yoga and modern yoga as exercise. Ancient texts describe a variety of poses under this name.
Etymology and origins
The name comes from the Sanskrit words ''vajra' ...
* Toe walking
* Polymyositis
Polymyositis (PM) is a type of chronic inflammation of the muscles ( inflammatory myopathy) related to dermatomyositis and inclusion body myositis. Its name is derived . The inflammation of polymyositis is mainly found in the endomysial layer ...
* Inclusion body myositis
Inclusion body myositis (IBM) () (sometimes called sporadic inclusion body myositis, sIBM) is the most common inflammatory muscle disease in older adults. The disease is characterized by slowly progressive weakness and wasting of both proximal m ...
References
Further reading
* Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (2011)Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project
* Balali-Mood, Mahdi (January 2008)
"Neurotoxic disorders of organophosphorus compounds and their managements"
''Arch Iran Med.'' 11(1):65–89. . * Jokanovic, Milan, Melita Kosanovic, Dejan Brkic, and Predrag Vukomanovic (2011)
"Organophosphate Induced Delayed Polyneuropathy in Man: An Overview"
''Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery'' 113.1: 7–10. . . * Mayo Clinic
"Foot Drop"
* Pritchett, James W., MD (June 21, 2018)
"Foot Drop"
Vinod K Panchbhavi, MD, FACS (ed.). * Saladin, Kenneth (2015). ''Anatomy & Physiology: A Unity of Form & Function''. 7th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education. Print. {{authority control Gait abnormalities Musculoskeletal disorders Neurological disorders