Dracovenator Scale on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Dracovenator'' () is a
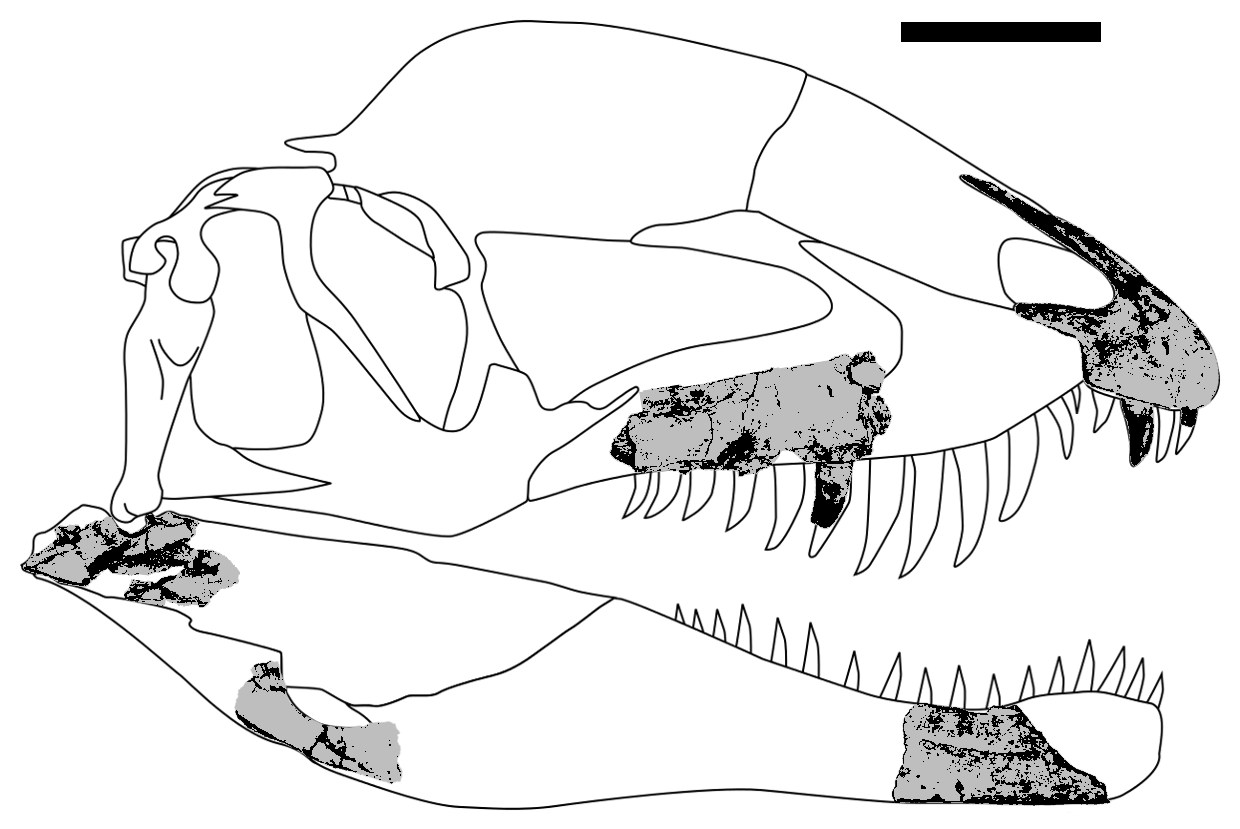 The type material BP/1/5243 for ''Dracovenator'' was discovered at the "Upper Drumbo Farm" locality in the upper
The type material BP/1/5243 for ''Dracovenator'' was discovered at the "Upper Drumbo Farm" locality in the upper
 ''Dracovenator'' is estimated to have measured between in length and in body mass.Smith, N.D., Makovicky, P.J., Pol, D., Hammer, W.R., and Currie, P.J. (2007).
''Dracovenator'' is estimated to have measured between in length and in body mass.Smith, N.D., Makovicky, P.J., Pol, D., Hammer, W.R., and Currie, P.J. (2007).
The Dinosaurs of the Early Jurassic Hanson Formation of the Central Transantarctic Mountains: Phylogenetic Review and Synthesis
. ''U.S. Geological Survey and The National Academies'' The holotype specimen, BP/1/5243, consists of both
 Yates (2005) assigned ''Dracovenator'' to the clade
Yates (2005) assigned ''Dracovenator'' to the clade 
Dinosaur Mailing List announcing discovery (includes full abstract)
{{Taxonbar, from=Q60778 Prehistoric neotheropods Hettangian life Early Jurassic dinosaurs of Africa Jurassic South Africa Fossils of South Africa Fossil taxa described in 2005
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial n ...
of neotheropod
Neotheropoda (meaning "new theropods") is a clade that includes coelophysoids and more advanced theropod dinosaurs, and is the only group of theropods that survived the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event. All neotheropods became extinct by the ...
dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
that lived approximately 201 to 199 million years ago
The abbreviation Myr, "million years", is a unit of a quantity of (i.e. ) years, or 31.556926 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr (million years) is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used with Mya (million years ago). ...
during the early part of the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ...
Period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Era, a length or span of time
* Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept ...
in what is now South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring count ...
. ''Dracovenator'' was a medium-sized, moderately-built, ground-dwelling, bipedal
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' 'double' ...
carnivore
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other ...
, that could grow up to an estimated in length and in body mass. Its type specimen was based on only a partial skull that was recovered.
Discovery
 The type material BP/1/5243 for ''Dracovenator'' was discovered at the "Upper Drumbo Farm" locality in the upper
The type material BP/1/5243 for ''Dracovenator'' was discovered at the "Upper Drumbo Farm" locality in the upper Elliot Formation
The Elliot Formation is a geological formation and forms part of the Stormberg Group, the uppermost geological group that comprises the greater Karoo Supergroup. Outcrops of the Elliot Formation have been found in the northern Eastern Cape, south ...
which is part of the Stormberg Group
The Stormberg Group is one of the four geological groups that comprises the Karoo Supergroup in South Africa. It is the uppermost geological group representing the final phase of preserved sedimentation of the Karoo Basin. The Stormberg Group ro ...
in Eastern Cape Province, South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring count ...
. It was collected by James Kitching and Regent "Lucas" Huma in sandstone that was deposited during the Hettangian
The Hettangian is the earliest age and lowest stage of the Jurassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between 201.3 ± 0.2 Ma and 199.3 ± 0.3 Ma (million years ago). The Hettangian follows the Rhaetian (part of the Triassi ...
stage of the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ...
period, approximately 201 to 199 million years ago. The paratype material BP/1/5278 (originally assigned to ''Syntarsus rhodesiensis'') was discovered in 1981, also at the Elliot Formation
The Elliot Formation is a geological formation and forms part of the Stormberg Group, the uppermost geological group that comprises the greater Karoo Supergroup. Outcrops of the Elliot Formation have been found in the northern Eastern Cape, south ...
in pinkish-maroon silty mudstone that was deposited in Hettangian
The Hettangian is the earliest age and lowest stage of the Jurassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between 201.3 ± 0.2 Ma and 199.3 ± 0.3 Ma (million years ago). The Hettangian follows the Rhaetian (part of the Triassi ...
sediments. Both the holotype and paratype specimen were housed in the fossil collection of the Evolutionary Studies Institute
The Evolutionary Studies Institute (ESI) is a paleontological, paleoanthropological and archeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeo ...
, part of the School of Geosciences of the University of the Witwatersrand
The University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg (), is a multi-campus South African public research university situated in the northern areas of central Johannesburg. It is more commonly known as Wits University or Wits ( or ). The university ...
, in Johannesburg
Johannesburg ( , , ; Zulu language, Zulu and xh, eGoli ), colloquially known as Jozi, Joburg, or "The City of Gold", is the largest city in South Africa, classified as a Megacity#List of megacities, megacity, and is List of urban areas by p ...
, South Africa. Unfortunately the cranial material house at the Evolutionary Studies Institute
The Evolutionary Studies Institute (ESI) is a paleontological, paleoanthropological and archeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeo ...
was lost and no new fossils of ''Dracovenator'' have currently been found.
The genus name is a contraction of the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
words ''draco'' meaning "dragon", and ''venator'' meaning "hunter"; thus, "dragon hunter". "Draco" refers to its discovery in the foothills of Drakensberg, which is "Dragon’s Mountain" in the Dutch language. The specific name, ''regenti'', was named in the honor of the late Regent ‘Lucas’ Huma, who was Professor Kitching’s field assistant. ''Dracovenator'' was described and named by Adam M. Yates in 2005 and the type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen( ...
is ''Dracovenator regenti''.
Description
The Dinosaurs of the Early Jurassic Hanson Formation of the Central Transantarctic Mountains: Phylogenetic Review and Synthesis
. ''U.S. Geological Survey and The National Academies'' The holotype specimen, BP/1/5243, consists of both
premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has ...
e, a fragment of the maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The ...
, two dentary
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone ...
fragments, a partial surangular
The suprangular or surangular is a jaw bone found in most land vertebrates, except mammals. Usually in the back of the jaw, on the upper edge, it is connected to all other jaw bones: dentary, angular, splenial and articular
The articular bone ...
bone, a partial angular
Angular may refer to:
Anatomy
* Angular artery, the terminal part of the facial artery
* Angular bone, a large bone in the lower jaw of amphibians and reptiles
* Angular incisure, a small anatomical notch on the stomach
* Angular gyrus, a region o ...
bone, a partial prearticular bone, an articular
The articular bone is part of the lower jaw of most vertebrates, including most jawed fish, amphibians, birds and various kinds of reptiles, as well as ancestral mammals.
Anatomy
In most vertebrates, the articular bone is connected to two oth ...
bone, and several teeth. ''Dracovenator'' has a kink in its upper jaws, between the maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The ...
and the premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has ...
. The back end of the lower jaw features an array of lumps and bumps, a condition seen in ''Dilophosaurus
''Dilophosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of theropod dinosaurs that lived in what is now North America during the Early Jurassic, about 193 million years ago. Three skeletons were discovered in northern Arizona in 1940, and the two best preserv ...
'', but to a much smaller extent. Munyikwa and Raath (1999) reassigned paratype BP/1/5278, which was originally assigned to ''Syntarsus rhodesiensis
''Megapnosaurus'' (meaning "big dead lizard", from Greek μεγα = "big", 'απνοος = "not breathing", "dead", σαυρος = "lizard") is an extinct genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 188 million years ago duri ...
'', to ''Dracovenator'', a juvenile specimen which consists of bones from the front of the skull, teeth, and jaw bones.Munyikwa and Raath, 1999. Further material of the ceratosaurian dinosaur ''Syntarsus'' from the Elliot Formation
The Elliot Formation is a geological formation and forms part of the Stormberg Group, the uppermost geological group that comprises the greater Karoo Supergroup. Outcrops of the Elliot Formation have been found in the northern Eastern Cape, south ...
(Early Jurassic) of South Africa. ''Palaeontologia Africana''. 35:55-59.
A diagnosis is a statement of the anatomical features of an organism (or group) that collectively distinguish it from all other organisms. Some, but not all, of the features in a diagnosis are also autapomorphies. An autapomorphy is a distinctive anatomical feature that is unique to a given organism. According to Yates (2005) ''Dracovenator'' can be distinguished based on the following characteristics: the presence of a large bilobed fossa surrounding a large lateral premaxillary foramen that is connected to the alveolar margin by a deep narrow channel; a deep, oblique notch on the lateral surface of the articular
The articular bone is part of the lower jaw of most vertebrates, including most jawed fish, amphibians, birds and various kinds of reptiles, as well as ancestral mammals.
Anatomy
In most vertebrates, the articular bone is connected to two oth ...
bone, separating the retroarticular process from the posterior margin of the glenoid
The glenoid fossa of the scapula or the glenoid cavity is a bone part of the shoulder. The word ''glenoid'' is pronounced or (both are common) and is from el, gléne, "socket", reflecting the shoulder joint's ball-and-socket form. It is a sha ...
, a particularly well-developed dorsal, tab-like processes on the articular
The articular bone is part of the lower jaw of most vertebrates, including most jawed fish, amphibians, birds and various kinds of reptiles, as well as ancestral mammals.
Anatomy
In most vertebrates, the articular bone is connected to two oth ...
bone-the first on the medial side, just posterior to the opening of the chorda tympanic foramen and the second on the lateral side on the anterolateral margin of the fossa for the m. depressor mandibulae.
Classification
Neotheropoda
Neotheropoda (meaning "new theropods") is a clade that includes coelophysoids and more advanced theropod dinosaurs, and is the only group of theropods that survived the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event. All neotheropods became extinct by the ...
.A. M. Yates. 2005. A new theropod dinosaur from the Early Jurassic of South Africa and its implications for the early evolution of theropods. Palaeontologia Africana 41:105-122 The first cladistic
Cladistics (; ) is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups (" clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is typically shared derived ch ...
analysis found that this genus formed a clade with the basal theropods ''Dilophosaurus
''Dilophosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of theropod dinosaurs that lived in what is now North America during the Early Jurassic, about 193 million years ago. Three skeletons were discovered in northern Arizona in 1940, and the two best preserv ...
'' and ''Zupaysaurus
''Zupaysaurus'' (; "ZOO-pay-SAWR-us") is an extinct genus of early theropod dinosaur living during the Norian stage of the Late Triassic in what is now Argentina. Fossils of the dinosaur were found in the Los Colorados Formation of the Ischigua ...
''. The skull of the type specimen, exhibits a mosaic of both ancestral and derived theropod characteristics. The following cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ...
, based on the phylogenetic analysis conducted by Smith, Makovicky, Pol, Hammer, and Currie in 2007, outlines the relationships of ''Dracovenator'' and its close relatives:Smith, N.D., Makovicky, P.J., Pol, D., Hammer, W.R., and Currie, P.J. (2007). "The dinosaurs of the Early Jurassic Hanson Formation of the Central Transantarctic Mountains: Phylogenetic review and synthesis." In Cooper, A.K. and Raymond, C.R. et al. (eds.), Antarctica: A Keystone in a Changing World––Online Proceedings of the 10th ISAES, USGS Open-File Report 2007-1047, Short Research Paper 003, 5 p.

Paleoecology
TheUpper Elliot Formation
The Elliot Formation is a geological formation and forms part of the Stormberg Group, the uppermost geological group that comprises the greater Karoo Supergroup. Outcrops of the Elliot Formation have been found in the northern Eastern Cape, sout ...
is thought to have been an ancient floodplain. Fossils of the prosauropod dinosaur ''Massospondylus
''Massospondylus'' ( ; from Greek, (massōn, "longer") and (spondylos, "vertebra")) is a genus of sauropodomorph dinosaur from the Early Jurassic. (Hettangian to Pliensbachian ages, ca. 200–183 million years ago). It was described by S ...
'' and ''Plateosaurus
''Plateosaurus'' (probably meaning "broad lizard", often mistranslated as "flat lizard") is a genus of plateosaurid dinosaur that lived during the Late Triassic period, around 214 to 204 million years ago, in what is now Central and Northern Eu ...
'' have been recovered from the Upper Elliot Formation
The Elliot Formation is a geological formation and forms part of the Stormberg Group, the uppermost geological group that comprises the greater Karoo Supergroup. Outcrops of the Elliot Formation have been found in the northern Eastern Cape, sout ...
, which boasts the world's most diverse fauna of early Jurassic ornithischian dinosaurs, including ''Abrictosaurus
''Abrictosaurus'' (; "wakeful lizard") is a genus of heterodontosaurid dinosaur that lived during the Early Jurassic in what is now in parts of southern Africa such as Lesotho and South Africa. It was a bipedal herbivore or omnivore and was one ...
'', ''Fabrosaurus
''Fabrosaurus'' ( ) is an extinct genus of ornithischian dinosaur that lived during the Early Jurassic during the Hettangian to Sinemurian stages 199 - 189 mya.Ginsburg, L., (1964), "Decouverte d’un Scelidosaurien (Dinosaure ornithischien) d ...
'', ''Heterodontosaurus
''Heterodontosaurus'' is a genus of heterodontosaurid dinosaur that lived during the Early Jurassic, 200–190 million years ago. Its only known member species, ''Heterodontosaurus tucki'', was named in 1962 based on a skull discovered in South ...
'', and ''Lesothosaurus
''Lesothosaurus'' is a monospecific genus of ornithischian dinosaur that lived during the Early Jurassic in what is now South Africa and Lesotho. It was named by paleontologist Peter Galton in 1978, the name meaning "lizard from Lesotho". The genu ...
'', among others. The Forest Sandstone Formation
The Forest Sandstone is a geological formation in southern Africa, dating to roughly between 200 and 190 million years ago and covering the Hettangian to Sinemurian stages of the Jurassic Period in the Mesozoic Era. As its name suggests, it ...
was the paleoenvironment of protosuchid crocodiles, sphenodonts, the dinosaur ''Massospondylus'' and indeterminate remains of a prosauropod
Sauropodomorpha ( ; from Greek, meaning "lizard-footed forms") is an extinct clade of long-necked, herbivorous, saurischian dinosaurs that includes the sauropods and their ancestral relatives. Sauropods generally grew to very large sizes, had ...
. ''Dracovenator'' is thought to have preyed on the prosauropod
Sauropodomorpha ( ; from Greek, meaning "lizard-footed forms") is an extinct clade of long-necked, herbivorous, saurischian dinosaurs that includes the sauropods and their ancestral relatives. Sauropods generally grew to very large sizes, had ...
dinosaurs in its paleoenvironment
Paleoecology (also spelled palaeoecology) is the study of interactions between organisms and/or interactions between organisms and their environments across geologic timescales. As a discipline, paleoecology interacts with, depends on and informs ...
.
References
External links
Dinosaur Mailing List announcing discovery (includes full abstract)
{{Taxonbar, from=Q60778 Prehistoric neotheropods Hettangian life Early Jurassic dinosaurs of Africa Jurassic South Africa Fossils of South Africa Fossil taxa described in 2005