Dracoraptor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Dracoraptor'' (meaning "dragon thief") is a
 The first ''Dracoraptor''
The first ''Dracoraptor''  The
The  The holotype consists of a partial skeleton with skull. It contains both praemaxilla (frontmost upper jaw bones), both
The holotype consists of a partial skeleton with skull. It contains both praemaxilla (frontmost upper jaw bones), both

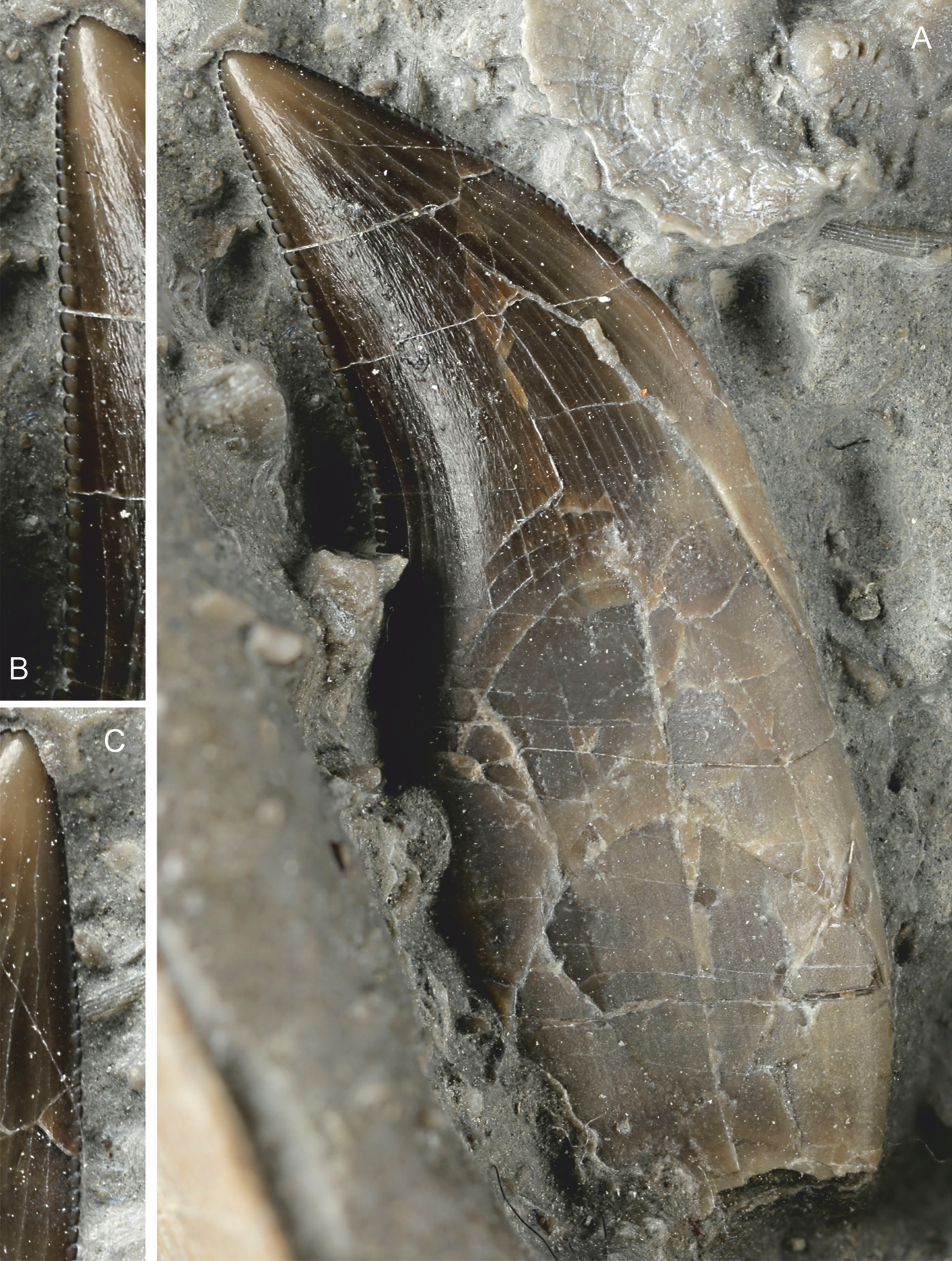
 In the front of the snout each praemaxilla embraces the front of a very large nostril. The skull bears three praemaxillary teeth per side and at least seven maxillary teeth. The teeth are recurved or dagger-shaped. The edges of the tooth crown are serrated with six to eight denticles per millimetre (0.03 in). On the trailing edge these serrations run all the way to the root, on the leading edge they end at a higher position. Towards the tip of the tooth, these denticles become gradually somewhat smaller. The maxilla borders an
In the front of the snout each praemaxilla embraces the front of a very large nostril. The skull bears three praemaxillary teeth per side and at least seven maxillary teeth. The teeth are recurved or dagger-shaped. The edges of the tooth crown are serrated with six to eight denticles per millimetre (0.03 in). On the trailing edge these serrations run all the way to the root, on the leading edge they end at a higher position. Towards the tip of the tooth, these denticles become gradually somewhat smaller. The maxilla borders an  The neck vertebrae are elongated, opisthocoelous, i.e. with a vertebral body that is convex in front and concave at the rear, and crowned by low
The neck vertebrae are elongated, opisthocoelous, i.e. with a vertebral body that is convex in front and concave at the rear, and crowned by low
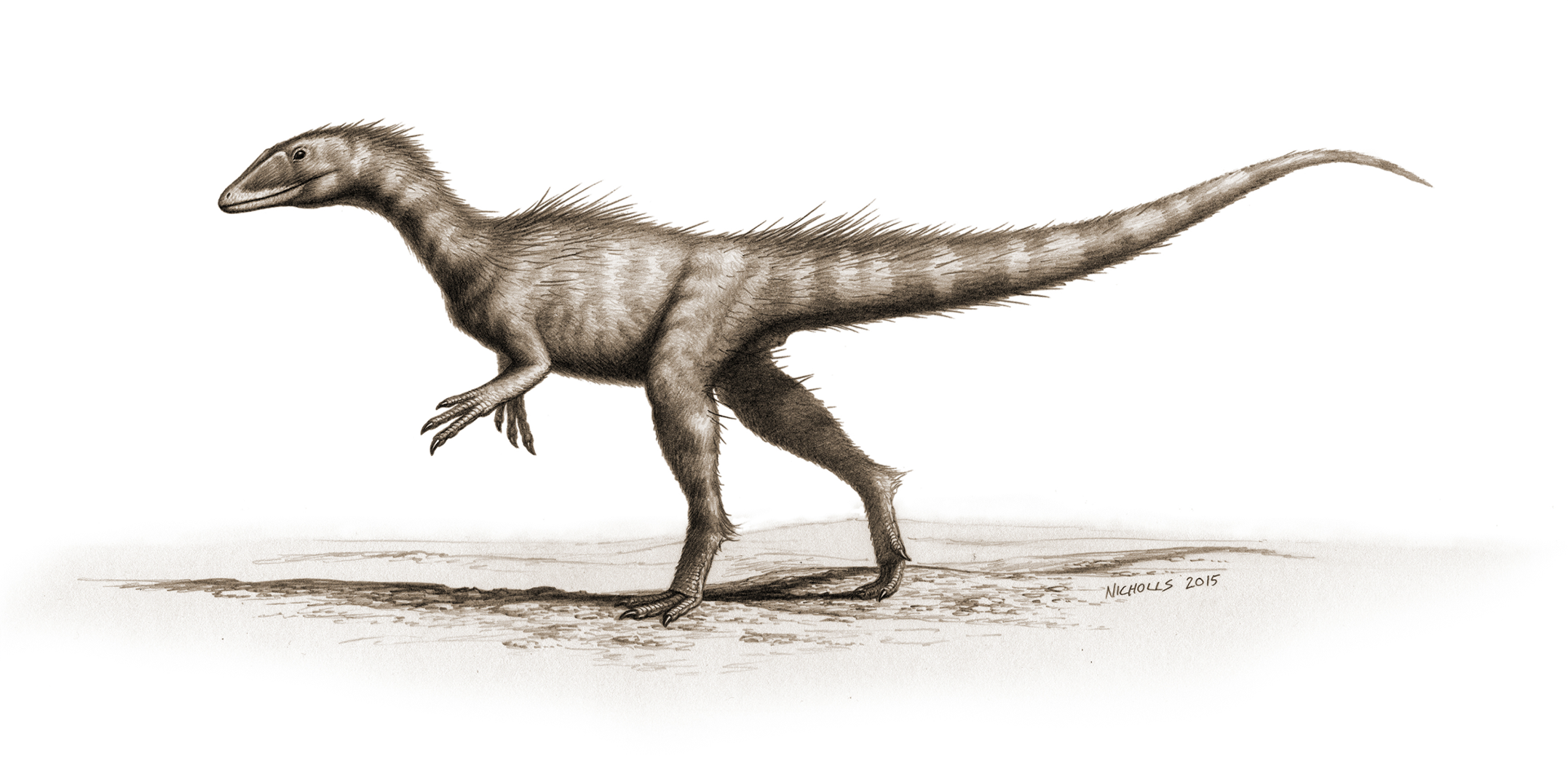 A
A
 At the end of the Triassic Period roughly half of Earth's species became extinct in the Triassic-Jurassic extinction event. This
At the end of the Triassic Period roughly half of Earth's species became extinct in the Triassic-Jurassic extinction event. This
genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
of coelophysoid dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutio ...
that lived during the Hettangian
The Hettangian is the earliest age and lowest stage of the Jurassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between 201.3 ± 0.2 Ma and 199.3 ± 0.3 Ma (million years ago). The Hettangian follows the Rhaetian (part of the Triass ...
stage
Stage, stages, or staging may refer to:
Arts and media Acting
* Stage (theatre), a space for the performance of theatrical productions
* Theatre, a branch of the performing arts, often referred to as "the stage"
* ''The Stage'', a weekly Brit ...
of the Early Jurassic
The Early Jurassic Epoch (geology), Epoch (in chronostratigraphy corresponding to the Lower Jurassic series (stratigraphy), Series) is the earliest of three epochs of the Jurassic Period. The Early Jurassic starts immediately after the Triassic� ...
Period of what is now Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic ...
dated at 201.3 ± 0.2 million years old.
The fossil was first discovered in 2014 by Rob and Nick Hanigan and Sam Davies at the Blue Lias Formation on the South Wales coast. The genus name ''Dracoraptor'' is from Draco referring to the Welsh dragon
The Welsh Dragon (, meaning 'the red dragon'; ) is a heraldic symbol that represents Wales and appears on the national flag of Wales.
Ancient leaders of the Celtic Britons that are personified as dragons include Maelgwn Gwynedd, Mynyddog Mwynf ...
and raptor, meaning robber, a commonly employed suffix for theropod dinosaurs with the type species
In International_Code_of_Zoological_Nomenclature, zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the spe ...
being ''Dracoraptor hanigani''. It is the oldest known Jurassic dinosaur and is the first dinosaur skeleton from the Jurassic of Wales.
Discovery and naming
 The first ''Dracoraptor''
The first ''Dracoraptor'' fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
s were discovered in 2014 near the Welsh town of Penarth
Penarth ( , ) is a town and Community (Wales), community in the Vale of Glamorgan, Wales, approximately south of Cardiff city centre on the west shore of the Severn Estuary at the southern end of Cardiff Bay.
Penarth is a Seaside resort#Brit ...
. In March 2014, brothers and amateur palaeontologists Nick and Rob Hanigan, while searching for ichthyosaur
Ichthyosauria is an order of large extinct marine reptiles sometimes referred to as "ichthyosaurs", although the term is also used for wider clades in which the order resides.
Ichthyosaurians thrived during much of the Mesozoic era; based on fo ...
remains at Lavernock Point, a large cape south of Cardiff
Cardiff (; ) is the capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of Wales. Cardiff had a population of in and forms a Principal areas of Wales, principal area officially known as the City and County of Ca ...
, found stone plates containing dinosaur fossils which had fallen off the high cliff face. Judith Adams and Philip Manning of the University of Manchester
The University of Manchester is a public university, public research university in Manchester, England. The main campus is south of Manchester city centre, Manchester City Centre on Wilmslow Road, Oxford Road. The University of Manchester is c ...
took X-ray pictures and CAT-scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
s of the fossils. The remains were donated to Amgueddfa Cymru – Museum Wales
Amgueddfa Cymru – Museum Wales, branded as simply Amgueddfa Cymru (formerly the National Museums and Galleries of Wales and legally National Museum of Wales), is a Welsh Government sponsored body that comprises seven museums in Wales:
* N ...
, and prepared by Craig Chivers and Gary Blackwell. In 2015, student Sam Davies found additional rock plates at the dig site which contained foot bones assigned to ''Dracoraptor''.
 The
The type species
In International_Code_of_Zoological_Nomenclature, zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the spe ...
, ''Dracoraptor hanigani'', was named and described in 2016 by British palaeontologists David Martill, Steven Vidovic, Cindy Howells, and John Nudds. The generic name combines the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
''draco'', "dragon", a reference to the Welsh Dragon
The Welsh Dragon (, meaning 'the red dragon'; ) is a heraldic symbol that represents Wales and appears on the national flag of Wales.
Ancient leaders of the Celtic Britons that are personified as dragons include Maelgwn Gwynedd, Mynyddog Mwynf ...
, with ''raptor'', "robber". The specific name Specific name may refer to:
* in Database management systems, a system-assigned name that is unique within a particular database
In taxonomy, either of these two meanings, each with its own set of rules:
* Specific name (botany), the two-part (bino ...
honours Nick and Rob Hanigan as discoverers.
The holotype
A holotype (Latin: ''holotypus'') is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of s ...
, NMW 2015.5G.1–2015.5G.11, was discovered in the lower Bull Cliff Member of the Blue Lias
The Blue Lias is a formation (stratigraphy), geological formation in southern, eastern and western England and parts of South Wales, part of the Lias Group. The Blue Lias consists of a sequence of limestone and shale layers, laid down in latest ...
Formation in the United Kingdom. More precisely, it came from a layer just metres below the first occurrence of Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
ammonite
Ammonoids are extinct, (typically) coiled-shelled cephalopods comprising the subclass Ammonoidea. They are more closely related to living octopuses, squid, and cuttlefish (which comprise the clade Coleoidea) than they are to nautiluses (family N ...
''Psiloceras
''Psiloceras'' is an extinct genus of ammonite. ''Psiloceras'' is among the earliest known Jurassic ammonites, and the appearance of the earliest ''Psiloceras'' species form the definition for the base of the Jurassic. Unlike most earlier ammonit ...
'' and above the Paper Shales that represent the lithological Triassic
The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is t ...
-Jurassic boundary, precisely dating the dinosaur to the earliest Hettangian
The Hettangian is the earliest age and lowest stage of the Jurassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between 201.3 ± 0.2 Ma and 199.3 ± 0.3 Ma (million years ago). The Hettangian follows the Rhaetian (part of the Triass ...
stage
Stage, stages, or staging may refer to:
Arts and media Acting
* Stage (theatre), a space for the performance of theatrical productions
* Theatre, a branch of the performing arts, often referred to as "the stage"
* ''The Stage'', a weekly Brit ...
, 201.3 million years ago ± 0.2 million years. The holotype consists of a partial skeleton with skull. It contains both praemaxilla (frontmost upper jaw bones), both
The holotype consists of a partial skeleton with skull. It contains both praemaxilla (frontmost upper jaw bones), both maxillae
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillar ...
(main upper jaw bone), teeth, a lacrimal, a jugal
The jugal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians and birds. In mammals, the jugal is often called the malar or zygomatic. It is connected to the quadratojugal and maxilla, as well as other bones, which may vary by species.
Anatomy ...
, a postorbital
The ''postorbital'' is one of the bones in vertebrate skulls which forms a portion of the dermal skull roof and, sometimes, a ring about the orbit. Generally, it is located behind the postfrontal and posteriorly to the orbital fenestra. In some ve ...
, a squamosal
The squamosal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians, and birds. In fishes, it is also called the pterotic bone.
In most tetrapods, the squamosal and quadratojugal bones form the cheek series of the skull. The bone forms an ancestra ...
, a supraoccipital, parts of the lower jaws, a possible hyoid
The hyoid-bone (lingual-bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid-cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical verte ...
, two cervical (neck) vertebrae
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal ...
(backbones), cervical ribs, rear dorsal
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
The fus ...
(back) vertebrae, at least five front caudal (tail) vertebrae, chevrons, ribs
The rib cage or thoracic cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrates that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protect the vital organs of the thoracic cavity, such as the heart, lungs and great vessels ...
, gastralia
Gastralia (: gastralium) are dermal bones found in the ventral body wall of modern crocodilians and tuatara, and many prehistoric tetrapods. They are found between the sternum and pelvis, and do not articulate with the vertebrae. In these reptil ...
(or "belly ribs"), the lower parts of a left forelimb, a furcula
The (Latin for "little fork"; : furculae) or wishbone is a forked bone found in most birds and some species of non-avian dinosaurs, and is either an interclavicle or formed by the fusion of the two clavicles. In birds, its primary function is ...
(wishbone), both pubic bones
In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone () forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing (ventral and anterior) of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones ar ...
, a left ischium
The ischium (; : is ...
(lower and rearmost hip bone), a right femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg.
The Femo ...
, a tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outsi ...
(shin bone), the upper part of a fibula
The fibula (: fibulae or fibulas) or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. ...
(calf bone), a left astragalus
Astragalus may refer to:
* ''Astragalus'' (plant), a large genus of herbs and small shrubs
*Astragalus (bone)
The talus (; Latin for ankle or ankle bone; : tali), talus bone, astragalus (), or ankle bone is one of the group of foot bones known ...
(ankle bone), three tarsals, and three metatarsals
The metatarsal bones or metatarsus (: metatarsi) are a group of five long bones in the midfoot, located between the tarsal bones (which form the heel and the ankle) and the phalanges (toes). Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are nu ...
. About 40% of the skeleton is presented. ''Dracoraptor'' is thus the most complete Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian r ...
non-bird theropod
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek , (''therion'') "wild beast"; , (''pous, podos'') "foot"">wiktionary:ποδός"> (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (clades) of dinosaurs, alongside Ornithischia and Sauropodom ...
dinosaur known from Wales.
Description
Size and distinguishing traits
''Dracoraptor'' was a biped, much like its relatives. The fossil discovered in Wales is a juvenile with a hip height of ; adults may have been long. In 2016, some autapomorphies (distinguishing traits) were established for ''Dracoraptor''. The praemaxillae carried only three teeth, a basal trait. The jugal had a thin front branch running to the maxilla. The bony externalnostril
A nostril (or naris , : nares ) is either of the two orifices of the nose. They enable the entry and exit of air and other gasses through the nasal cavities. In birds and mammals, they contain branched bones or cartilages called turbinates ...
is large and had a thin branch beneath it. The pubic bone
In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone () forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing (ventral and anterior) of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones ar ...
is obliquely directed to the front and is considerably longer than the ischium
The ischium (; : is ...
. The fourth tarsal had a process at the upper side.
Skeleton
 In the front of the snout each praemaxilla embraces the front of a very large nostril. The skull bears three praemaxillary teeth per side and at least seven maxillary teeth. The teeth are recurved or dagger-shaped. The edges of the tooth crown are serrated with six to eight denticles per millimetre (0.03 in). On the trailing edge these serrations run all the way to the root, on the leading edge they end at a higher position. Towards the tip of the tooth, these denticles become gradually somewhat smaller. The maxilla borders an
In the front of the snout each praemaxilla embraces the front of a very large nostril. The skull bears three praemaxillary teeth per side and at least seven maxillary teeth. The teeth are recurved or dagger-shaped. The edges of the tooth crown are serrated with six to eight denticles per millimetre (0.03 in). On the trailing edge these serrations run all the way to the root, on the leading edge they end at a higher position. Towards the tip of the tooth, these denticles become gradually somewhat smaller. The maxilla borders an antorbital fenestra
An antorbital fenestra (plural: fenestrae) is an opening in the skull that is in front of the eye sockets. This skull character is largely associated with Archosauriformes, archosauriforms, first appearing during the Triassic Period. Among Extant ...
with a shallow depression. The jugal is a slender element with a straight lower edge, a thin front branch overlapped by the rear branch of the maxilla and an ascending process towards the lacrimal that is thin but not pointed. The lacrimal is rectangular and pinched in the middle.
neural spines
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal ...
. Their undersides are slightly convex and their cross-sections are rectangular. At the front side the vertebral body is pierced by a pleurocoel, a depression with a pneumatic opening for the air sac to enter the inside of the vertebra. The tail vertebrae had two parallel keels at their undersides, which peter out towards the front. Their side processes are flat and broad.
The presence of a furcula
The (Latin for "little fork"; : furculae) or wishbone is a forked bone found in most birds and some species of non-avian dinosaurs, and is either an interclavicle or formed by the fusion of the two clavicles. In birds, its primary function is ...
was reported. Furculae have only rarely been recovered from early theropod fossils; other examples include those of ''Segisaurus
''Segisaurus'' (meaning "Tsegi Canyon lizard") is a genus of small coelophysid theropod dinosaur, that measured approximately 1 metre (3.3 feet) in length. The only known specimen was discovered in early Jurassic strata in Tsegi Canyon, Arizona, ...
'' and ''Coelophysis
''Coelophysis'' ( Traditional English pronunciation of Latin, traditionally; or , as heard more commonly in recent decades) is a genus of coelophysid Theropoda, theropod dinosaur that lived Approximation, approximately 215 to 201.4 million y ...
''. The lower arm bones, the ulna
The ulna or ulnar bone (: ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone in the forearm stretching from the elbow to the wrist. It is on the same side of the forearm as the little finger, running parallel to the Radius (bone), radius, the forearm's other long ...
and the radius, had a length of about seven centimetres. Hand elements are present but a formula of the phalanges could not determined.
In the pelvis, the pubic bone
In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone () forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing (ventral and anterior) of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones ar ...
had a length of 212 millimetres. It points obliquely to the front. The pubic foot is moderately broadened in side view, bot at the front and at the rear. The shaft of the ischium
The ischium (; : is ...
is with a length of 129 millimetres markedly shorter than the pubic shaft. On the upper front edge a rectangular obturator process is present, forming a clear obturator notch with the ischial shaft. The shaft fan out to below, into an ischial foot.
On the thighbone, the lesser trochanter had about two thirds of the height of the greater trochanter
The greater trochanter of the femur is a large, irregular, quadrilateral eminence and a part of the skeletal system.
It is directed lateral and medially and slightly posterior. In the adult it is about 2–4 cm lower than the femoral head.Sta ...
and is separated from it by a V-shaped cleft. A clear fourth trochanter is present. In the foot, the third metatarsal had a length of 116 millimetres.
Classification
cladistic
Cladistics ( ; from Ancient Greek 'branch') is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups ("clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is ...
analysis in 2016 determined that ''Dracoraptor'' was a basal member, positioned low in the evolutionary tree, of the Neotheropoda
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek , (''therion'') "wild beast"; , (''pous, podos'') "foot"">wiktionary:ποδός"> (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (clades) of dinosaurs, alongside Ornithischia and Sauropodomo ...
. It was the basalmost coelophysoid.
The precise affinities of ''Dracoraptor'' are indicated by its various traits. The build of the pelvis shows it was a saurischia
Saurischia ( , meaning "reptile-hipped" from the Greek ' () meaning 'lizard' and ' () meaning 'hip joint') is one of the two basic divisions of dinosaurs (the other being Ornithischia), classified by their hip structure. Saurischia and Ornithi ...
n dinosaur. Among dinosaurs, the dagger-shaped transversely flattened teeth are only found with Theropoda. A membership of the clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
Neotheropoda is proven by the shallow depression around the antorbital fenestra, the forward position of a pleurocoel on the neck vertebrae and the presence of an obturator notch in the ischium. The position in the Coelophysoidea
Coelophysoidea is an extinct clade of theropod dinosaurs common during the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic periods. They were widespread geographically, probably living on all continents. Coelophysoids were all slender, carnivorous forms with a ...
is more uncertain. ''Dracoraptor'' does not clearly share many of the synapomorphies
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to ...
of the group, such as a rounded jugal branch towards the lacrimal. This accounts for its basal position in the analysis. Further preparation of the fossils might provide additional information about its phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree or phylogeny is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or Taxon, taxa during a specific time.Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, M ...
.
Paleobiology
extinction event
An extinction event (also known as a mass extinction or biotic crisis) is a widespread and rapid decrease in the biodiversity on Earth. Such an event is identified by a sharp fall in the diversity and abundance of multicellular organisms. It occ ...
allowed dinosaurs to become the dominant land animals. The largest land predators at the end of the Triassic were Rauisuchia
"Rauisuchia" is a paraphyletic group of mostly large and carnivorous Triassic archosaurs. Rauisuchians are a category of archosaurs within a larger group called Pseudosuchia, which encompasses all archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians ...
, large quadrupedal
Quadrupedalism is a form of Animal locomotion, locomotion in which animals have four legs that are used to weight-bearing, bear weight and move around. An animal or machine that usually maintains a four-legged posture and moves using all four l ...
reptiles which disappeared in the extinction, paving the way for carnivorous dinosaurs to become the dominant land predators.
''Dracoraptor'' had pointed and serrated teeth, indicating it was a meat-eater. But the teeth were small, about one centimetre long, showing it ate small vertebrate animals. In the early Jurassic, South Wales was a coastal area with several small islands in a warm shallow sea. The area which is now Lavernock Point was offshore, so the cadaver of ''Dracoraptor'' had probably been washed into the sea from the land to the north. Despite the lack of data regarding its ecology
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their Natural environment, environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community (ecology), community, ecosystem, and biosphere lev ...
, the authors in 2016 had it tentatively illustrated as a "shore-dwelling predator and scavenger".
''Dracoraptor'' is the oldest known Jurassic dinosaur. Vidovic stated: "So this dinosaur starts to fill in some gaps in our knowledge about the dinosaurs that survived the Triassic extinction and gave rise to all the dinosaurs that we know from Jurassic Park
''Jurassic Park'', later referred to as ''Jurassic World'', is an American science fiction media franchise created by Michael Crichton, centered on a disastrous attempt to create a theme park of De-extinction#Cloning, cloned dinosaurs. It bega ...
, books and TV" and "Dinosaurs diversified and populated the ecological niches in the Early Jurassic."
See also
*2016 in paleontology
Flora Plants
Fungi
Cnidarians
Research
* ''Yunnanoascus haikouensis'', previously thought to be a member of Ctenophora, is reinterpreted as a Crown group, crown-group medusozoan by Han ''et al.'' (2016).
* A study on the fossil corals fro ...
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q22135509 Coelophysoidea Dinosaur genera Hettangian dinosaurs Fossil taxa described in 2016 Dinosaurs of the United Kingdom