Double-jointed on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hypermobility, also known as double-jointedness, describes
 Hypermobility generally results from one or more of the following:
* Abnormally shaped ends of one or more bones at a joint or increased angle of the bone such as in
Hypermobility generally results from one or more of the following:
* Abnormally shaped ends of one or more bones at a joint or increased angle of the bone such as in
 Hypermobility syndrome is generally considered to comprise hypermobility together with other symptoms, such as
Hypermobility syndrome is generally considered to comprise hypermobility together with other symptoms, such as
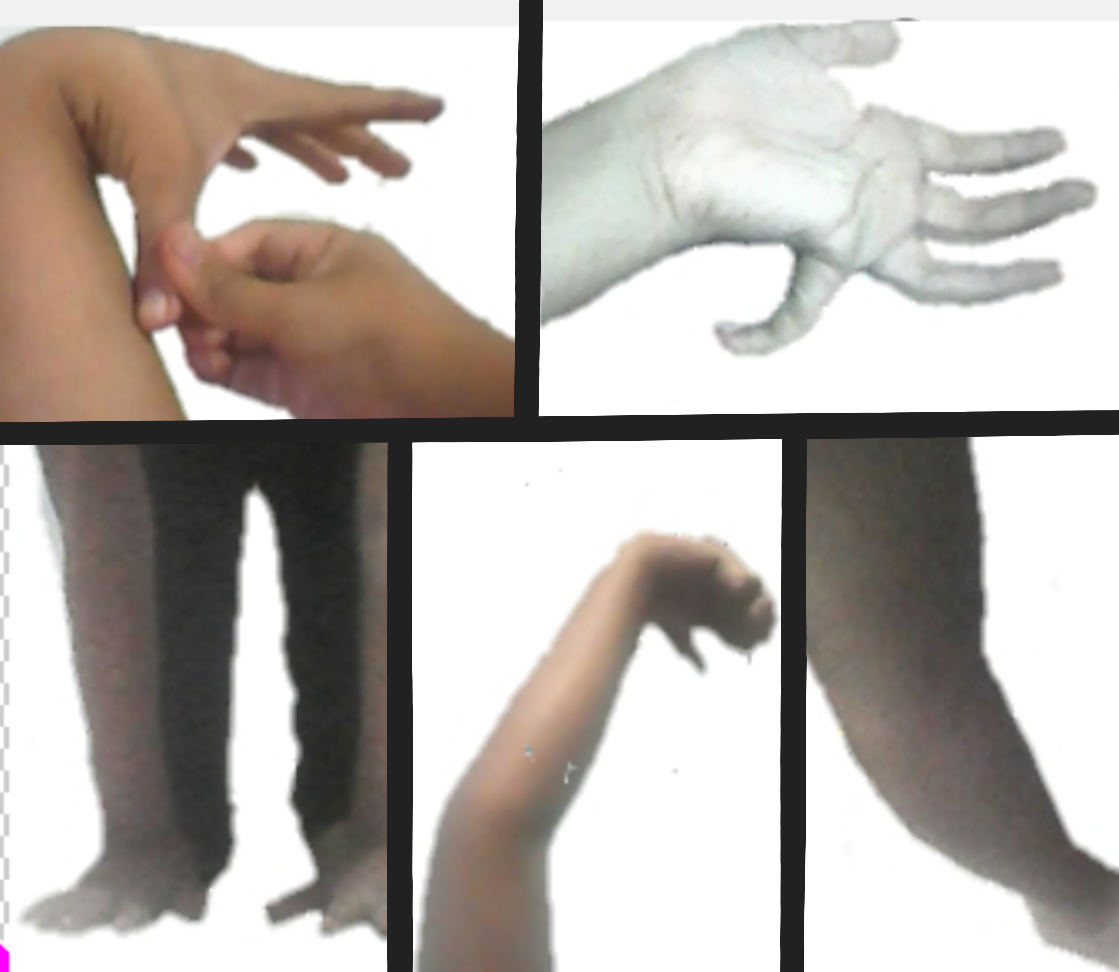 The Beighton score has been widely used among athletes for screening purposes. It does not appear to be a valid scale when used for this purpose: there exists a statistically significant correlation between the score and the athlete's passive shoulder and hip ranges of motion, but the difference is small enough to be buried by measurement error.
The Beighton score has been widely used among athletes for screening purposes. It does not appear to be a valid scale when used for this purpose: there exists a statistically significant correlation between the score and the athlete's passive shoulder and hip ranges of motion, but the difference is small enough to be buried by measurement error.
joint
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
s that stretch farther than normal. For example, some hypermobile people can bend their thumbs backwards to their wrists
In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; "The wrist contains eight bones, roughly aligned in two rows, known as the carpal ...
, bend their knee
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the hu ...
joints backwards, put their leg behind the head, or perform other contortionist
Contortion (sometimes contortionism) is a performance art in which performers called contortionists showcase their skills of extreme physical flexibility. Contortion acts often accompany acrobatics, circus acts, street performers and other liv ...
"tricks". It can affect one or more joints throughout the body.
Hypermobile joints are common and occur in about 10 to 25% of the population. In a minority of people, pain and other symptoms are present. This may be a sign of hypermobility spectrum disorder
Hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD), related to earlier diagnoses such as hypermobility syndrome (HMS), and joint hypermobility syndrome (JHS) is a heritable connective tissue disorder that affects joints and ligaments. Different forms and s ...
(HSD). Hypermobile joints are a feature of genetic connective tissue disorders such as hypermobility spectrum disorder or Ehlers–Danlos syndrome
Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) is a group of 14 genetic connective-tissue disorders. Symptoms often include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar formation. These may be noticed at birth or in early childhood. Co ...
(EDS). Until new diagnostic criteria were introduced, hypermobility syndrome was sometimes considered identical to hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome (hEDS), formerly called EDS Type 3. As no genetic test can distinguish the two conditions and because of the similarity of the diagnostic criteria
Medical diagnosis (abbreviated Dx, Dx, or Ds) is the process of determining which disease or condition explains a person's symptoms and signs. It is most often referred to as a diagnosis with the medical context being implicit. The information r ...
and recommended treatments, many experts recommend they be recognized as the same condition until further research is undertaken.
In 2016 the diagnostic criteria for hEDS were re-written to be more restrictive, with the intent of narrowing the pool of hEDS patients in the hope of making it easier to identify a common genetic mutation, hEDS being the only EDS variant without a diagnostic DNA test. At the same time, joint hypermobility syndrome was renamed as hypermobility spectrum disorder and redefined as a hypermobility disorder that does not meet the diagnostic criteria for hEDS, other types of Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome, or other heritable Connective Tissue Disorder (such as Marfan's, Loeys–Dietz, or osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta (; OI), colloquially known as brittle bone disease, is a group of genetic disorders that all result in bones that bone fracture, break easily. The range of symptoms—on the skeleton as well as on the body's other Or ...
).
Signs and symptoms
People with joint hypermobility may develop other conditions caused by their unstable joints. These conditions include: *Subluxation
A subluxation is an incomplete or partial dislocation of a joint or organ. According to the World Health Organization, a subluxation is a "significant structural displacement" and is therefore visible on static imaging studies, such as X-rays. ...
s or dislocation
In materials science, a dislocation or Taylor's dislocation is a linear crystallographic defect or irregularity within a crystal structure that contains an abrupt change in the arrangement of atoms. The movement of dislocations allow atoms to sli ...
s, especially in the shoulder
The human shoulder is made up of three bones: the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone) as well as associated muscles, ligaments and tendons.
The articulations between the bones of the shoulder m ...
* Joint instability causing frequent sprains
A sprain is a soft tissue injury of the ligaments within a joint, often caused by a sudden movement abruptly forcing the joint to exceed its functional range of motion. Ligaments are tough, inelastic fibers made of collagen that connect two or m ...
, tendinitis
Tendinopathy is a type of tendon disorder that results in pain, swelling, and impaired function. The pain is typically worse with movement. It most commonly occurs around the shoulder ( rotator cuff tendinitis, biceps tendinitis), elbow ( tenn ...
, or bursitis
Bursitis is the inflammation of one or more bursae (synovial sacs) of synovial fluid in the body. They are lined with a synovial membrane that secretes a lubricating synovial fluid. There are more than 150 bursae in the human body. The bursae (bu ...
when doing activities that would not affect others. However, a 2018 study reports that while hypermobile individuals are more likely to suffer dislocations doing sports, they are less likely to suffer muscle and tendon sprains. The overall chances of sports injury are not significantly different.
* Joint pain
* Early-onset osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of articular cartilage, joint cartilage and underlying bone. A form of arthritis, it is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world, affect ...
(as early as during teen years)
* Fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
, even after short periods of exercise
* Back pain
Back pain (Latin: ''dorsalgia'') is pain felt in the back. It may be classified as neck pain (cervical), middle back pain (thoracic), lower back pain (lumbar) or coccydynia (tailbone or sacral pain) based on the segment affected. The lumbar area ...
, prolapsed disc
A disc herniation or spinal disc herniation is an injury to the intervertebral disc between two vertebrae, usually caused by excessive Strain (injury), strain or trauma to the Vertebral column, spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensatio ...
s or spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis is when one spinal vertebra slips out of place compared to another. While some medical dictionaries define spondylolisthesis specifically as the forward or anterior displacement of a vertebra over the vertebra inferior to it (o ...
* Joint
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
s that make clicking noises (also a symptom of osteoarthritis)
* Susceptibility to whiplash
* Temporomandibular joint dysfunction
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMD, TMJD) is an umbrella term covering pain and dysfunction of the muscles of mastication (the muscles that move the jaw) and the temporomandibular joints (the joints which connect the Human mandible, mand ...
, also known as TMD
* Increased nerve compression
Nerve compression syndrome, or compression neuropathy, or nerve entrapment syndrome, is a medical condition caused by chronic, direct pressure on a peripheral nerve. It is known colloquially as a ''trapped nerve'', though this may also refer to n ...
disorders (such as carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a nerve compression syndrome associated with the collected signs and symptoms of Pathophysiology of nerve entrapment#Compression, compression of the median nerve at the carpal tunnel in the wrist. Carpal tunn ...
)
* Poor response to local anaesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of all sense, sensation (including pain) in a specific body part without loss of consciousness, providing local anesthesia, as opposed to a general anesthetic, which eliminates all sen ...
(especially in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome) or pain medication
* "Growing pains
''Growing Pains'' is an American television sitcom created by Neal Marlens that ran on ABC for seven seasons from September 24, 1985, to April 25, 1992. The series follows the misadventures of the Seaver family, including psychiatrist and fathe ...
" as described in children in late afternoon or night
Associated conditions
Those with hypermobile joints are more likely to haveADHD
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by symptoms of inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and emotional dysregulation that are excessive and pervasive, impairing in multiple ...
, autism
Autism, also known as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by differences or difficulties in social communication and interaction, a preference for predictability and routine, sensory processing d ...
, dyspraxia
Developmental coordination disorder (DCD), also known as developmental motor coordination disorder, developmental dyspraxia, or simply dyspraxia (from Ancient Greek ''praxis'' 'activity'), is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by impair ...
, fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a functional somatic syndrome with symptoms of widespread chronic pain, accompanied by fatigue, sleep disturbance including awakening unrefreshed, and Cognitive deficit, cognitive symptoms. Other symptoms can include he ...
, hereditary connective tissue disorders, mitral valve prolapse
Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is a valvular heart disease characterized by the displacement of an abnormally thickened mitral valve leaflet into the atria of the heart, left atrium during Systole (medicine), systole. It is the primary form of myxom ...
, and anxiety disorders
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental disorders characterized by significant and uncontrollable feelings of anxiety and fear such that a person's social, occupational, and personal functions are significantly impaired. Anxiety may cause phys ...
such as panic disorder
Panic disorder is a mental disorder, specifically an anxiety disorder, characterized by reoccurring unexpected panic attacks. Panic attacks are sudden periods of intense fear that may include palpitations, sweating, shaking, shortness of breath ...
.
Causes
 Hypermobility generally results from one or more of the following:
* Abnormally shaped ends of one or more bones at a joint or increased angle of the bone such as in
Hypermobility generally results from one or more of the following:
* Abnormally shaped ends of one or more bones at a joint or increased angle of the bone such as in coxa valga
Coxa valga is a deformity of the hip where the angle formed between the head and neck of the femur and its shaft is increased, usually above 135 degrees.
The deformity may develop in children with neuromuscular disorders (i.e. cerebral palsy, spi ...
* A mutation in collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a trip ...
or collagen-related genes (as found in certain types of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome) or other connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, a group of cells that are similar in structure, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops mostly from the mesenchyme, derived from the mesod ...
(as found in Loeys–Dietz syndrome
Loeys–Dietz syndrome (LDS) is an autosomal dominant genetic connective tissue disorder. It has features similar to Marfan syndrome and Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. The disorder is marked by aneurysms in the aorta, often in children, and the aorta m ...
and Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with dolichostenomelia, long arms, legs, Arachnodactyly, fingers, and toes. They also typically ha ...
) resulting in weakened ligaments
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have ligam ...
/ligamentous laxity, muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
s and tendons
A tendon or sinew is a tough band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It sends the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system, while withstanding tension.
Tendons, like ligaments, are made of ...
. Type 1 collagen defects may also result in weakened bones, which may result in osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
and fractures
Fracture is the appearance of a crack or complete separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress (mechanics), stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacemen ...
, as seen in osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta (; OI), colloquially known as brittle bone disease, is a group of genetic disorders that all result in bones that bone fracture, break easily. The range of symptoms—on the skeleton as well as on the body's other Or ...
, a genetic disorder which also commonly involves joint hypermobility
* Abnormal joint proprioception
Proprioception ( ) is the sense of self-movement, force, and body position.
Proprioception is mediated by proprioceptors, a type of sensory receptor, located within muscles, tendons, and joints. Most animals possess multiple subtypes of propri ...
(an impaired ability to locate body parts in space and/or monitor an extended joint)
These abnormalities cause abnormal joint stress, meaning that the joints can wear out, leading to osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of articular cartilage, joint cartilage and underlying bone. A form of arthritis, it is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world, affect ...
.
The condition tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic basis for at least some forms of hypermobility. The term ''double jointed'' is often used to describe hypermobility; however, the name is a misnomer and should not be taken literally, as hypermobile joints are not doubled/extra in any sense.
Most people have hypermobility with no other symptoms. Approximately 5% of the healthy population have one or more hypermobile joints. However, people with symptomatic hypermobility are subject to many difficulties. For example, their joints may be easily injured, be more prone to complete or partial dislocation due to the weakly stabilized joint and they may develop problems from muscle fatigue
Muscle fatigue is when muscles that were initially generating a normal amount of force, then experience a declining ability to generate force. It can be a result of vigorous exercise, but abnormal fatigue may be caused by barriers to or interfer ...
(as muscles must work harder to compensate for weakness in the ligaments that support the joints). Hypermobility syndromes can lead to chronic pain or even disability in severe cases. Musical instrumentalists with hypermobile fingers may have difficulties when fingers collapse into the finger locking position. Or, conversely, they may display superior abilities due to their increased range of motion for fingering, such as in playing a violin or cello.
Hypermobility may be symptomatic of a serious medical condition, such as Stickler syndrome
Stickler syndrome (hereditary progressive arthro-ophthalmodystrophy) is a group of rare genetic disorders affecting connective tissue, specifically collagen. Stickler syndrome is a subtype of collagenopathy, types II and XI. Stickler syndrome i ...
, Ehlers–Danlos syndrome
Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) is a group of 14 genetic connective-tissue disorders. Symptoms often include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar formation. These may be noticed at birth or in early childhood. Co ...
, Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with dolichostenomelia, long arms, legs, Arachnodactyly, fingers, and toes. They also typically ha ...
, Loeys–Dietz syndrome
Loeys–Dietz syndrome (LDS) is an autosomal dominant genetic connective tissue disorder. It has features similar to Marfan syndrome and Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. The disorder is marked by aneurysms in the aorta, often in children, and the aorta m ...
, rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
, osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta (; OI), colloquially known as brittle bone disease, is a group of genetic disorders that all result in bones that bone fracture, break easily. The range of symptoms—on the skeleton as well as on the body's other Or ...
, lupus
Lupus, formally called systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Common ...
, polio
Poliomyelitis ( ), commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 75% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe ...
, Fragile X syndrome
Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is a genetic neurodevelopmental disorder. The average IQ in males with FXS is under 55, while affected females tend to be in the borderline to normal range, typically around 70–85. Physical features may include a lo ...
, Down syndrome, Morquio syndrome
Morquio syndrome, also known as mucopolysaccharidosis type IV (MPS IV), is a rare metabolic disorder in which the body cannot process certain types of sugar molecules called glycosaminoglycans (AKA GAGs, or mucopolysaccharides). In Morquio syndro ...
, cleidocranial dysostosis
Cleidocranial dysostosis (CCD), also called cleidocranial dysplasia, is a congenital disorder, birth defect that mostly affects the bones and teeth. The collarbones are typically either poorly developed or absent, which allows the shoulders to be ...
or myotonia congenita
''Myotonia congenita'' is a congenital neuromuscular channelopathy that affects skeletal muscles (muscles used for movement). It is a genetic disorder. The hallmark of the disease is the failure of initiated contraction to terminate, often refe ...
.
Hypermobility has been associated with myalgic encephalomyelitis (chronic fatigue syndrome) and fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a functional somatic syndrome with symptoms of widespread chronic pain, accompanied by fatigue, sleep disturbance including awakening unrefreshed, and Cognitive deficit, cognitive symptoms. Other symptoms can include he ...
. Hypermobility causes physical trauma (in the form of joint dislocations, joint subluxation
A subluxation is an incomplete or partial dislocation of a joint or organ. According to the World Health Organization, a subluxation is a "significant structural displacement" and is therefore visible on static imaging studies, such as X-rays. ...
s, joint instability, sprain
A sprain is a soft tissue injury of the ligaments within a joint, often caused by a sudden movement abruptly forcing the joint to exceed its functional range of motion. Ligaments are tough, inelastic fibers made of collagen that connect two or ...
s, etc.). These conditions often, in turn, cause physical and/or emotional trauma and are possible triggers for conditions such as fibromyalgia.
People with hypermobility may experience particular difficulties when pregnant. During pregnancy, the body releases relaxin
Relaxin is a protein hormone of about 6000 Da, first described in 1926 by Frederick Hisaw.
The relaxin family peptide hormones belong to the insulin superfamily and consists of seven peptides of high structural but low sequence similarity; re ...
and certain hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
s that alter ligament physiology, easing the stretching needed to accommodate fetal growth as well as the birthing process. The combination of hypermobility and pregnancy-related pelvic girdle during pregnancy can be debilitating. The pregnant person with hypermobile joints will often be in significant pain as muscles and joints adapt to the pregnancy. Pain often inhibits such people from standing or walking during pregnancy. Some pregnant people who have one of these disorders find they need to use a bedpan
A bedpan or bed pan is a device used as a receptacle for the urine and/or Human feces, feces of a person who is confined to a bed and therefore not able to use a toilet or chamber pot.
Bedpans can be either reusable or disposable, and include s ...
and/or a wheelchair
A wheelchair is a mobilized form of chair using two or more wheels, a footrest, and an armrest usually cushioned. It is used when walking is difficult or impossible to do due to illnesses, injury, disabilities, or age-related health conditio ...
during pregnancy. Some may experience permanent disability.
Syndromes
 Hypermobility syndrome is generally considered to comprise hypermobility together with other symptoms, such as
Hypermobility syndrome is generally considered to comprise hypermobility together with other symptoms, such as myalgia
Myalgia or muscle pain is a painful sensation evolving from muscle tissue. It is a symptom of many diseases. The most common cause of acute myalgia is the overuse of a muscle or group of muscles; another likely cause is viral infection, espec ...
and arthralgia
Arthralgia () literally means ' joint pain'. Specifically, arthralgia is a symptom of injury, infection, illness (in particular arthritis), or an allergic reaction to medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceuti ...
. It is relatively common among children and affects more females than males.
Current thinking suggests four causative factors:
* The shape of the ends of the bones—Some joints normally have a large range of movement, such as the shoulder and hip. Both are ball-and-socket joint
The ball-and-socket joint (or spheroid joint) is a type of synovial joint in which the ball-shaped surface of one rounded bone fits into the cup-like depression of another bone. The distal bone is capable of motion around an indefinite number of ...
s. If a shallow rather than a deep socket is inherited, a relatively large range of movement will be possible. If the socket is particularly shallow, then the joint may dislocate easily.
* Protein deficiency or hormone problems—Ligaments are made up of several types of protein fibre. These proteins include elastin
Elastin is a protein encoded by the ''ELN'' gene in humans and several other animals. Elastin is a key component in the extracellular matrix of gnathostomes (jawed vertebrates). It is highly Elasticity (physics), elastic and present in connective ...
, which gives elasticity and which may be altered in some people. Female sex hormones alter collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix of the connective tissues of many animals. It is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up 25% to 35% of protein content. Amino acids are bound together to form a trip ...
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s. Women are generally more supple just before a period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Period (punctuation)
* Era, a length or span of time
*Menstruation, commonly referred to as a "period"
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (o ...
and even more so in the latter stages of pregnancy, because of a hormone called relaxin
Relaxin is a protein hormone of about 6000 Da, first described in 1926 by Frederick Hisaw.
The relaxin family peptide hormones belong to the insulin superfamily and consists of seven peptides of high structural but low sequence similarity; re ...
that allows the pelvis
The pelvis (: pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of an Anatomy, anatomical Trunk (anatomy), trunk, between the human abdomen, abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also c ...
to expand so the head of the baby can pass.
* Muscle tone—The tone of muscles is controlled by the nervous system, and influences range of movement. Special techniques can change muscle tone and increase flexibility. Yoga
Yoga (UK: , US: ; 'yoga' ; ) is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines that originated with its own philosophy in ancient India, aimed at controlling body and mind to attain various salvation goals, as pra ...
, for example, can help to relax muscles and make the joints more supple. However, yoga is not recommended by most medical professionals for people with Joint Hypermobility Syndrome, due to the likelihood of damage to the joints. Gymnasts and athletes can sometimes acquire hypermobility in some joints through activity.
* Proprioception—Compromised ability to detect exact joint/body position with closed eyes, may lead to overstretching and hypermobile joints.
Hypermobility can also be caused by connective tissue disorders, such as Ehlers–Danlos syndrome
Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) is a group of 14 genetic connective-tissue disorders. Symptoms often include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar formation. These may be noticed at birth or in early childhood. Co ...
(EDS) and Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with dolichostenomelia, long arms, legs, Arachnodactyly, fingers, and toes. They also typically ha ...
. Joint hypermobility is a common symptom for both. EDS has numerous sub-types; most include hypermobility in some degree. When hypermobility is the main symptom, then EDS/hypermobility type is likely. People with EDS-HT experience frequent joint dislocations and subluxations (partial/incomplete dislocations), with or without trauma, sometimes spontaneously. Commonly, hypermobility is dismissed by medical professionals as nonsignificant.
Ehlers–Danlos syndrome hypermobility type
Joint hypermobility is often correlated with hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome (hEDS, known also by EDS type III or Ehlers–Danlos syndrome hypermobility type (EDS-HT)).Ehlers–Danlos syndrome
Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) is a group of 14 genetic connective-tissue disorders. Symptoms often include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar formation. These may be noticed at birth or in early childhood. Co ...
is a genetic disorder caused by mutations or hereditary genes, but the genetic defect that produced hEDS is largely unknown. In conjunction with joint hypermobility, a common symptom for hEDS is smooth, velvety, and stretchy skin; a symptom largely unique to the syndrome. When diagnosing hEDS, the Beighton Criteria are used, but are not always able to distinguish between generalized hypermobility and hEDS.
Ehlers–Danlos hypermobility type can have severe musculoskeletal effects, including:
* Jaw laxity that may make an individual's jaw open and close like a hinge, as well as open further than the average.
* Neck pain that can lead to chronic headaches and is usually associated with a crackling or grinding sensation (crepitus
Crepitus is "a grating sound or sensation produced by friction between bone and cartilage or the fractured parts of a bone".
Various types of crepitus that can be heard in joint pathologies are:
*Bone crepitus: This can be heard when two frag ...
).
* The spine may end up in a "round back" or inversely may extend too much into hyperlordosis. Individuals may also experience scoliosis.
* Joints commonly associated with hypermobility (wrists, knees, ankles, elbows, shoulders) may be at more severe risk to dislocate or strain.
Diagnosis
Joint hypermobility syndrome shares symptoms with other conditions such as Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, andosteogenesis imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta (; OI), colloquially known as brittle bone disease, is a group of genetic disorders that all result in bones that bone fracture, break easily. The range of symptoms—on the skeleton as well as on the body's other Or ...
. Experts in connective tissue disorders formally agreed that severe forms of Hypermobility Syndrome and mild forms of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Hypermobility Type are the same disorder.
Generalized hypermobility is a common feature in all these hereditary connective tissue disorders and many features overlap, but often features are present that enable differentiating these disorders.
The inheritance pattern of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome varies by type. The arthrochalasia, classic, hypermobility and vascular forms usually have an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. Autosomal dominant inheritance
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the Phenotype, effect of a different variant of the same gene on Homologous chromosome, the other copy of the chromosome. The firs ...
occurs when one copy of a gene in each cell is sufficient to cause a disorder. In some cases, an affected person inherits the mutation from one affected parent. Other cases result from new (sporadic) gene mutations. Such cases can occur in people with no history of the disorder in their family.
The dermatosparaxis
Cutaneous asthenia is a skin disorder caused by a collagen defect. Collagen is the protein that binds the cells of the dermis together. It is also called dermatoproxy, hereditary skin fragility or ''cutis elastica'' ("elastic skin") and is found i ...
and kyphoscoliosis
Kyphoscoliosis describes an abnormal curvature of the spine in both the coronal and sagittal planes. It is a combination of kyphosis and scoliosis. This musculoskeletal disorder often leads to other issues in patients, such as under-ventilatio ...
types of EDS and some cases of the classic and hypermobility forms, are inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. In autosomal recessive inheritance
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the Phenotype, effect of a different variant of the same gene on Homologous chromosome, the other copy of the chromosome. The firs ...
, two copies of the gene in each cell are altered. Most often, both parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder are carriers of one copy of the altered gene but do not show signs and symptoms of the disorder.
Beighton criteria
As of July 2000, hypermobility was diagnosed using the Beighton criteria. In 2017, the criteria changed, but still involve the Beighton score. The Beighton criteria do not replace the Beighton score but instead use the previous score in conjunction with other symptoms and criteria. HMS is diagnosed in the presence of either two major criteria, one major and two minor criteria, or four minor criteria. The criteria are:Major criteria
* A Beighton score of 5/9 or more (either current or historic) *Arthralgia
Arthralgia () literally means ' joint pain'. Specifically, arthralgia is a symptom of injury, infection, illness (in particular arthritis), or an allergic reaction to medication
Medication (also called medicament, medicine, pharmaceuti ...
for more than three months in four or more joints
Minor criteria
* A Beighton score of 1, 2 or 3/9 (0, 1, 2 or 3 if aged 50+) * Arthralgia (> 3 months) in one to three joints or back pain (> 3 months),spondylosis
Spondylosis is the degeneration of the vertebral column from any cause. In the more narrow sense, it refers to spinal osteoarthritis, the age-related degeneration of the spinal column, which is the most common cause of spondylosis. The degener ...
, spondylolysis
Spondylolysis also known as a pars defect or pars fracture, is a defect or stress fracture in the pars interarticularis of the vertebral arch. The vast majority of cases occur in the lower lumbar vertebrae (L5), but spondylolysis may also occur ...
/spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis is when one spinal vertebra slips out of place compared to another. While some medical dictionaries define spondylolisthesis specifically as the forward or anterior displacement of a vertebra over the vertebra inferior to it (o ...
.
* Dislocation/subluxation in more than one joint, or in one joint on more than one occasion.
* Soft tissue rheumatism
Rheumatism or rheumatic disorders are conditions causing chronic, often intermittent pain affecting the joints or connective tissue. Rheumatism does not designate any specific disorder, but covers at least 200 different conditions, including a ...
. > 3 lesions (e.g. epicondylitis Epicondylitis is the inflammation of an epicondyle or of adjacent tissues. Epicondyles are on the medial and lateral aspects of the elbow, consisting of the two bony prominences at the distal end of the humerus. These bony projections serve as the a ...
, tenosynovitis
Tenosynovitis is the inflammation of the fluid-filled sheath (called the synovium) that surrounds a tendon, typically leading to joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. Tenosynovitis can be either infectious or noninfectious. Common clinical mani ...
, bursitis
Bursitis is the inflammation of one or more bursae (synovial sacs) of synovial fluid in the body. They are lined with a synovial membrane that secretes a lubricating synovial fluid. There are more than 150 bursae in the human body. The bursae (bu ...
).
* Marfanoid
Marfanoid (or Marfanoid habitus) is a constellation of signs resembling those of Marfan syndrome, including long limbs, with an arm span that is at least 1.03 of the height of the individual, and a crowded oral maxilla, sometimes with a high arch i ...
habitus (tall, slim, span/height ratio >1.03, upper: lower segment ratio less than 0.89, arachnodactyly; positive Steinberg finger / Walker wrist signs).
* Abnormal skin: striae, hyperextensibility, thin skin, papyraceous scarring.
Beighton score
The Beighton score is an edited version of the Carter/Wilkinson scoring system which was used for many years as an indicator of widespread hyper-mobility. Medical professionals varied in their interpretations of the results; some accepting as low as 1/9 and some 4/9 as a diagnosis of HMS. Therefore, it was incorporated, with clearer guidelines, into the Beighton Criteria. The Beighton score is measured by adding 1 point for each of the following: * Placing flat hands on the floor with straight legs * Left knee bending backward * Right knee bending backward * Left elbow bending backward * Right elbow bending backward * Left thumb touching the forearm * Right thumb touching the forearm * Left little finger bending backward past 90 degrees * Right little finger bending backward past 90 degrees The Beighton score has been widely used among athletes for screening purposes. It does not appear to be a valid scale when used for this purpose: there exists a statistically significant correlation between the score and the athlete's passive shoulder and hip ranges of motion, but the difference is small enough to be buried by measurement error.
The Beighton score has been widely used among athletes for screening purposes. It does not appear to be a valid scale when used for this purpose: there exists a statistically significant correlation between the score and the athlete's passive shoulder and hip ranges of motion, but the difference is small enough to be buried by measurement error.
Treatments
Physical therapy
It is important that hypermobile individuals remain fit – even more so than the average individual – to prevent recurrent injuries. Regular exercise and exercise that is supervised by a physician and physical therapist can reduce symptoms because strong muscles increase dynamic joint stability. Low-impact exercise such asclosed kinetic chain exercises
Closed kinetic chain exercises or closed chain exercises (CKC) are physical exercises performed where the hand (for arm movement) or foot (for leg movement) is fixed in space and cannot move. The extremity remains in constant contact with the immob ...
are usually recommended as they are less likely to cause injury when compared to high-impact exercise or contact sports.
Heat and cold treatment can help temporarily to relieve the pain of aching joints and muscles but does not address the underlying problems.
Medication
Medication is not the primary treatment for hypermobility, but can be used as an adjunct treatment for related joint pain.Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a Indication (medicine), therapeutic drug class which Analgesic, reduces pain, Anti-inflammatory, decreases inflammation, Antipyretic, decreases fever, and Antithrombotic, prevents bl ...
s are the primary medications of choice. Narcotics are not recommended for primary or long-term treatment and are reserved for short-term use after acute injury.
Lifestyle modification
For some people with hypermobility, lifestyle changes decrease symptom severity. In general, activity that increases pain is to be avoided. For example: * Avoiding hyperextension ** Typing can reduce pain from writing. **Voice control
A voice-user interface (VUI) enables spoken human interaction with computers, using speech recognition to understand spoken commands and answer questions, and typically text to speech to play a reply. A voice command device is a device controlle ...
software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
or a more ergonomic keyboard can reduce pain from typing.
** Bent knees or sitting can reduce pain from standing.
* Strength training to support weak joints with strong muscles
** Weakened ligaments and muscles contribute to poor posture, which may contribute to other medical conditions.
** Isometric exercise
An isometric exercise is an exercise involving the static contraction of a muscle without any visible movement in the angle of the joint. The term "isometric" combines the Greek words ''isos'' (equal) and ''-metria'' (measuring), meaning that i ...
avoids hyperextension and contributes to strength.
** Unwanted symptoms are frequently reduced by some forms of yoga
* Low-impact sports
** Use of low impact elliptical trainer
An elliptical trainer or cross-trainer is a stationary exercise machine used to stair climb, walk, or run without causing excessive pressure to the joints, hence decreasing the risk of impact injuries. For this reason, people with some injuri ...
machines can replace high-impact running.
** Pain-free swimming may require a kickboard or extra care to avoid hyperextending elbow and other joints.
** Bike riding, especially on ergonomic recumbents.
Other treatments
* Bracing can be helpful for temporarily protecting unstable joints. * Physical therapyEpidemiology
Hypermobile joints occur in about 10 to 25% of the population.See also
*Ligamentous laxity
Ligamentous laxity or ligament laxity can appear in a variety of ways and levels of severity.
In most people, ligaments (which are the tissues that connect bones to each other) are naturally tight in such a way that the joints are restricted to ...
References
External links
* {{Soft tissue disorders Arthritis Contortion Disorders of fascia Ehlers–Danlos syndrome Rheumatology Skeletal disorders Syndromes