Dnieper Balts on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Dnieper Balts were a subgroup of the
The Dnieper Balts were a subgroup of the
 Various archeological monuments and the prevalence of Baltic
Various archeological monuments and the prevalence of Baltic
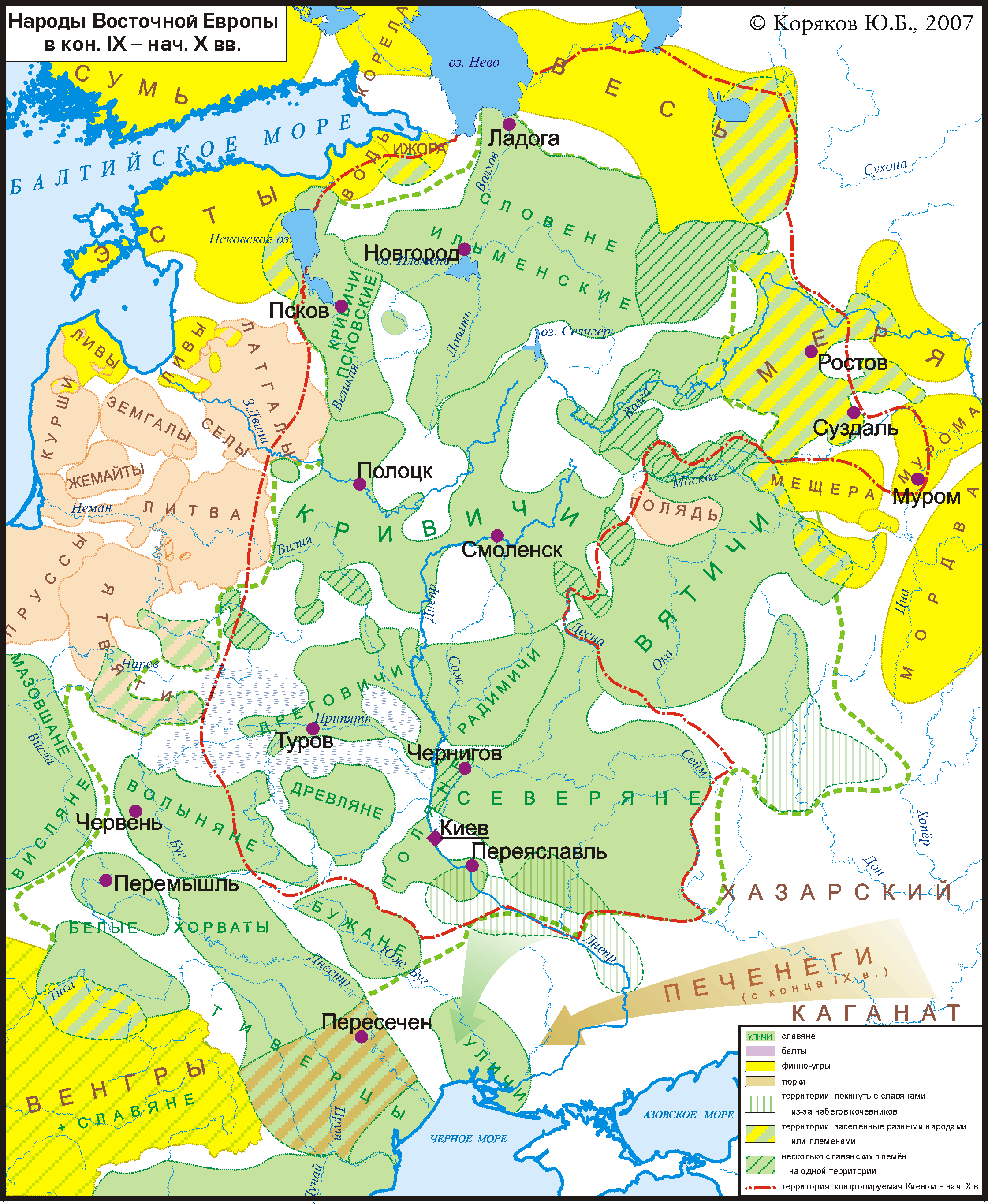 In the middle of the 1st millennium, Slavs began to invade the Baltic territory of the Dnieper Balts along the Dnieper and its tributaries. In the 7th century, the Slavs, that previously only lived in
In the middle of the 1st millennium, Slavs began to invade the Baltic territory of the Dnieper Balts along the Dnieper and its tributaries. In the 7th century, the Slavs, that previously only lived in
Balts
The Balts or Baltic peoples (, ) are a group of peoples inhabiting the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea who speak Baltic languages. Among the Baltic peoples are modern-day Lithuanians (including Samogitians) and Latvians (including Latgalians ...
that lived in the Dnieper
The Dnieper or Dnepr ( ), also called Dnipro ( ), is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. Approximately long, with ...
river basin for millennia until the Late Middle Ages
The late Middle Ages or late medieval period was the Periodization, period of History of Europe, European history lasting from 1300 to 1500 AD. The late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period ( ...
, when they were partly destroyed and partly assimilated by the Slavs
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and ...
by the 13th century. To the north and northeast of the Dnieper Balts were the Volga Finns
The Volga Finns are a historical group of peoples living in the vicinity of the Volga, who speak Uralic languages. Their modern representatives are the Mari people, the Erzya and the Moksha (commonly grouped together as Mordvins) as well as ...
, and to the southeast and south were the ancient Iranians
Iranian peoples, or Iranic peoples, are the collective ethnolinguistic groups who are identified chiefly by their native usage of any of the Iranian languages, which are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages within the Indo-European langu ...
, the Scythians
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranian Eurasian noma ...
.
The Dnieper Balts have been studied by many researchers, such as the Lithuanian linguist Kazimieras Būga
Kazimieras Būga (; November 6, 1879 – December 2, 1924) was a Lithuanian linguist and philologist. He was a professor of linguistics, who mainly worked on the Lithuanian language.
He was born at Pažiegė, near Dusetos, then part of the Russ ...
, the German linguist Max Vasmer
Max Julius Friedrich Vasmer (; ; 28 February 1886 – 30 November 1962) was a Russian and German linguist. He studied problems of etymology in Indo-European, Finno-Ugric and Turkic languages and worked on the history of Slavic, Baltic, ...
, and the Russian linguists Vladimir Toporov
Vladimir Nikolayevich Toporov (; 5 July 1928 in Moscow5 December 2005 in Moscow) was a Russian philologist associated with the Tartu–Moscow Semiotic School. His wife was Tatyana Elizarenkova. He is also recognized as a prominent Balticist. ...
and Oleg Trubachyov.
History
In the early 20th century, the Lithuanian linguistKazimieras Būga
Kazimieras Būga (; November 6, 1879 – December 2, 1924) was a Lithuanian linguist and philologist. He was a professor of linguistics, who mainly worked on the Lithuanian language.
He was born at Pažiegė, near Dusetos, then part of the Russ ...
showed that essentially all names in the upper Nemunas and upper Dnieper basins were Baltic. In 1962, the Russian linguists Vladimir Toporov
Vladimir Nikolayevich Toporov (; 5 July 1928 in Moscow5 December 2005 in Moscow) was a Russian philologist associated with the Tartu–Moscow Semiotic School. His wife was Tatyana Elizarenkova. He is also recognized as a prominent Balticist. ...
and Oleg Trubachyov, in their work, the "Linguistic analysis of the hydronyms of the Upper Dnieper region" (), demonstrated that more than a thousand names in the Dnieper basin were of Baltic origin, due to their morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
*Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
*Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies, ...
and etymology
Etymology ( ) is the study of the origin and evolution of words—including their constituent units of sound and meaning—across time. In the 21st century a subfield within linguistics, etymology has become a more rigorously scientific study. ...
.
The former ethnic Balticness of the Dnieper basin
The Dnieper Basin is the drainage basin of the Dnieper River, covering an area of . Its water resources compose around 80% of the total for all Ukraine.
Geography
The Dnieper Basin lies within Ukraine, Belarus, and Russia. It borders on the Vol ...
is evidenced by numerous archaeological finds, as well as hydronyms. For example, the hydronyms Yauza, and Moskva, are of Baltic origin according to Toporov. In the late Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
, the Balts lived in territories from what is now the western border of Poland to the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ),; , ; , or simply the Urals, are a mountain range in Eurasia that runs north–south mostly through Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the river Ural (river), Ural and northwestern Kazakhstan.
. However, some propose a smaller territory of Baltic inhabitation from the Vistula
The Vistula (; ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest in Europe, at in length. Its drainage basin, extending into three other countries apart from Poland, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra i ...
in the west to at least as far as Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
in the east and as far south as Kyiv
Kyiv, also Kiev, is the capital and most populous List of cities in Ukraine, city of Ukraine. Located in the north-central part of the country, it straddles both sides of the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2022, its population was 2, ...
.
Ancient history
 Various archeological monuments and the prevalence of Baltic
Various archeological monuments and the prevalence of Baltic hydronyms
A hydronym (from , , "water" and , , "name") is a type of toponym that designates a proper name of a body of water. Hydronyms include the proper names of rivers and streams, lakes and ponds, swamps and marshes, seas and oceans. As a subset of top ...
indicate that by the end of the Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
period (), there were several closely related, at least hypothetically Baltic, cultures in Central and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
, which were the Pamariai, (Late) Narva
Narva is a municipality and city in Estonia. It is located in the Ida-Viru County, at the Extreme points of Estonia, eastern extreme point of Estonia, on the west bank of the Narva (river), Narva river which forms the Estonia–Russia border, E ...
, and (Late) Nemunas cultures. The earliest of them is the Pamariai culture, which covered only a narrow part of the southeastern coast of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
.
During the Bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
() and Iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
() Ages, in the lands to the east and south of modern-day Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
and Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to t ...
, there were Baltic (Late) Narva
Narva is a municipality and city in Estonia. It is located in the Ida-Viru County, at the Extreme points of Estonia, eastern extreme point of Estonia, on the west bank of the Narva (river), Narva river which forms the Estonia–Russia border, E ...
and the Brushed Pottery cultures (the areas of these two cultures included the east of present-day Lithuania and Latvia), the , Milograd, and the later Dyakovo cultures.
In the 3rd and 5th centuries AD, the aforementioned Baltic cultures of the Dnieper
The Dnieper or Dnepr ( ), also called Dnipro ( ), is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. Approximately long, with ...
, Daugava
The Daugava ( ), also known as the Western Dvina or the Väina River, is a large river rising in the Valdai Hills of Russia that flows through Belarus and Latvia into the Gulf of Riga of the Baltic Sea. The Daugava rises close to the source of ...
and Oka basins transformed into the Kolochin, and Moshchiny cultures, which existed until the 8th–10th centuries. This transformation was due to the strong influence of the culture of the Western Balts
The Western Baltic culture (; also known as (West Baltic circle), ) was the Western Baltic languages, westernmost branch of the Balts, representing a distinct archaeological culture of the Bronze Age and Iron Age, along the southern coast of th ...
(of the Zarubintsy culture
The Zarubintsy, Zarubyntsi or Zarubinets culture was a culture that, from the 3rd century BC until the 1st century AD, flourished in the area north of the Black Sea along the upper and middle Dnieper and Pripyat Rivers, stretching west towards t ...
), which moved from the territory of what is now Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
deep into the Dnieper basin as early as the 2nd and 1st centuries BC.
Moshchiny culture is considered to be the ancestor of the Eastern Galindians, who lived in the lands near Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
and within the Protva river basin.
Slavic invasion
 In the middle of the 1st millennium, Slavs began to invade the Baltic territory of the Dnieper Balts along the Dnieper and its tributaries. In the 7th century, the Slavs, that previously only lived in
In the middle of the 1st millennium, Slavs began to invade the Baltic territory of the Dnieper Balts along the Dnieper and its tributaries. In the 7th century, the Slavs, that previously only lived in Right-bank Ukraine
The Right-bank Ukraine is a historical and territorial name for a part of modern Ukraine on the right (west) bank of the Dnieper River, corresponding to the modern-day oblasts of Vinnytsia, Zhytomyr, Kirovohrad, as well as the western parts o ...
, started invading the Baltic lands in the eastern Dnieper basin. Since the 7th and 8th centuries, the linguistic and cultural Slavicisation
Slavicisation or Slavicization, is the acculturation of something non-Slavic into a Slavic culture, cuisine, region, or nation. The process can either be voluntary or applied through varying degrees of pressure.
The term can also refer to the ...
of Dnieper Balts was accelerated by the conversion of the multilingual tribes living in Ruthenia
''Ruthenia'' is an exonym, originally used in Medieval Latin, as one of several terms for Rus'. Originally, the term ''Rus' land'' referred to a triangular area, which mainly corresponds to the tribe of Polans in Dnieper Ukraine. ''Ruthenia' ...
to Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
. By the early 9th century, only small numbers of Slavs had gone into Upper Dnieper and the majority were still Balts, with the Slavs mostly settling near Gnezdovo
Gnezdovo or Gnyozdovo () is an archeological site located near the village of Gnyozdovo in Smolensky District, Smolensk Oblast, Russia. The site contains extensive remains of a Slavic-Varangian settlement that flourished in the 10th century as ...
.
Some researchers believe that after the Christianization of Kievan Rus'
The Christianization of Kievan Rus' was a long and complicated process that took place in several stages. In 867, Patriarch Photius of Constantinople told other Christian patriarchs that the Rus' people were converting enthusiastically, but his ...
in 988, part of the Dnieper Balts retreated westwards, eventually merging into Lithuanians
Lithuanians () are a Balts, Baltic ethnic group. They are native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,378,118 people. Another two million make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the Lithuanian Americans, United Sta ...
and Latgalians
Latgalians (, , modern ; variant translations also include Latgallians, Lettigalls or Lettigallians) were an ancient Baltic tribe.
They likely spoke a variant of Latvian language, which probably became the ''lingua franca'' in present-day Latvia ...
. In the 9th and 10th centuries, the majority of the Dnieper Balts were separated from the other Balts living in the west by Slavic migrants moving north on the Dnieper banks. In the 11th and 12th centuries, out of the Dnieper Balts, only the Eastern Galindians remained undestroyed by the eastern Slavs.
The Lithuanian professor Zigmas Zinkevičius
Zigmas Zinkevičius (4 January 1925 – 20 February 2018) was a Lithuanian academician, Baltist, linguist, linguistic historian, dialectologist, politician, and the former Minister of Education and Science of Lithuania (1996–1998). Zinkevičiu ...
writes that:It is thought that the Dnieper Balts, just as the other Balts living to the east from present-day Lithuania and Latvia, had an important influence on the Slavs who moved to these lands and the formation of East Slavic as a separate linguistic group.
Religion
According to some researchers, the pagan religion of the Dnieper Balts included the veneration of pillars withbear
Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family (biology), family Ursidae (). They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats ...
heads.
Language
References
Sources
* * * * * * * {{refendSee also
* Eastern Galindians *Neuri
The Neuri or Navari (; ) were an ancient Slavs, Slavic or Balts, Baltic people whose existence was recorded by ancient Greco-Roman world, Graeco-Roman authors.
Identification
The Neuri belonged to a group of northern European peoples of unknown ...
Ancient peoples of Ukraine
Historical Baltic peoples
Bronze Age peoples
Iron Age peoples