Distributaries on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A distributary, or a distributary channel is a
A distributary, or a distributary channel is a
 In
In
 *The
*The

 A distributary, or a distributary channel is a
A distributary, or a distributary channel is a stream
A stream is a continuous body of water, body of surface water Current (stream), flowing within the stream bed, bed and bank (geography), banks of a channel (geography), channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a strea ...
channel that branches off and flows a main stream channel. It is the opposite of a ''tributary
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream (''main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which they ...
'', a stream that flows another stream or river. Distributaries are a result of river bifurcation
River bifurcation (from , fork) occurs when a river (a ''bifurcating river'') flowing in a single channel (hydrology), channel separates into two or more separate streams (called distributary, ''distributaries'') which then continue downstream ( ...
and are often found where a river approaches a lake
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from ...
or an ocean
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian Ocean, Indian, Southern Ocean ...
and divides into distributary networks; as such they are a common feature of river delta
A river delta is a landform, archetypically triangular, created by the deposition of the sediments that are carried by the waters of a river, where the river merges with a body of slow-moving water or with a body of stagnant water. The creat ...
s. They can also occur inland, on alluvial fan
An alluvial fan is an accumulation of sediments that fans outwards from a concentrated source of sediments, such as a narrow canyon emerging from an escarpment. They are characteristic of mountainous terrain in arid to Semi-arid climate, semiar ...
s, or where a tributary stream bifurcates as it nears its confluence
In geography, a confluence (also ''conflux'') occurs where two or more watercourses join to form a single channel (geography), channel. A confluence can occur in several configurations: at the point where a tributary joins a larger river (main ...
with a larger stream. In some cases, a minor distributary can divert so much water from the main channel that it can later become the main route.
Related terms
Common terms to name individual river distributaries inEnglish-speaking countries
The English-speaking world comprises the 88 countries and territories in which English is an official, administrative, or cultural language. In the early 2000s, between one and two billion people spoke English, making it the largest language ...
are ''arm'' and ''channel''. These terms may refer to a distributary that does not rejoin the channel from which it has branched (e.g., the North, Middle, and South Arms of the Fraser River
The Fraser River () is the longest river within British Columbia, Canada, rising at Fraser Pass near Blackrock Mountain (Canada), Blackrock Mountain in the Rocky Mountains and flowing for , into the Strait of Georgia just south of the City of V ...
, or the West Channel of the Mackenzie River
The Mackenzie River (French: ; Slavey language, Slavey: ' èh tÊʰò literally ''big river''; Inuvialuktun: ' uËkpÉk literally ''great river'') is a river in the Canadian Canadian boreal forest, boreal forest and tundra. It forms, ...
), or to one that does (e.g. Annacis Channel and Annieville Channel of the Fraser River
The Fraser River () is the longest river within British Columbia, Canada, rising at Fraser Pass near Blackrock Mountain (Canada), Blackrock Mountain in the Rocky Mountains and flowing for , into the Strait of Georgia just south of the City of V ...
, separated by Annacis Island).
In Australia, the term ''anabranch
An anabranch is a section of a river or stream that diverts from the main channel or stem of the watercourse and rejoins the main stem downstream. Local anabranches can be the result of small islands in the watercourse. In larger anabranches, ...
'' is used to refer to a distributary that diverts from the main course of the river and rejoins it later. In North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
such a branching river is called a ''braided river
A braided river (also called braided channel or braided stream) consists of a network of river channel (geography), channels separated by small, often temporary, islands called ''braid bars'' or, in British English usage, ''aits'' or ''eyots''.
...
''.
North America
 In
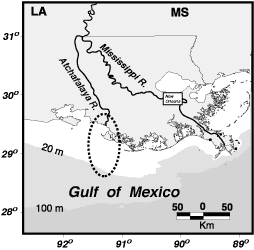
In Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
, the Atchafalaya River
The Atchafalaya River () is a distributary of the Mississippi River and Red River of the South, Red River in south central Louisiana in the United States. It flows south, just west of the Mississippi River, and is the fifth largest river in N ...
is an important distributary of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
. Because the Atchafalaya takes a steeper route to the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southw ...
than does the Mississippi, over several decades the Atchafalaya has captured more and more of the Mississippi's flow, after the Mississippi meandered into the Red River of the South
The Red River is a major river in the Southern United States. It was named for its reddish water color from passing through red-bed country in its watershed. It also is known as the Red River of the South to distinguish it from the Red River ...
. The Old River Control Structure
The Old River Control Structure is a floodgate system in a branch of the Mississippi River in central Louisiana. It regulates the flow of water from the Mississippi into the Atchafalaya River, thereby preventing the Mississippi River from chang ...
, a dam
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aqua ...
which regulates the outflow from the Mississippi into the Atchafalaya, was completed by the Army Corps of Engineers in 1963. The dam is intended to prevent the Atchafalaya from capturing the main flow of the Mississippi and stranding the ports of Baton Rouge
Baton Rouge ( ; , ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the U.S. state of Louisiana. It had a population of 227,470 at the 2020 United States census, making it List of municipalities in Louisiana, Louisiana's second-m ...
and New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
.
In British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
, Canada, the Fraser River
The Fraser River () is the longest river within British Columbia, Canada, rising at Fraser Pass near Blackrock Mountain (Canada), Blackrock Mountain in the Rocky Mountains and flowing for , into the Strait of Georgia just south of the City of V ...
has numerous sloughs and side-channels which may be defined as distributaries. This river's final stretch has three main distributaries: the North Arm and the South Arm, and a few smaller ones adjoining them.
Examples of inland distributaries:
* Teton Riverâa tributary of Henrys Fork in Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest and Mountain states, Mountain West subregions of the Western United States. It borders Montana and Wyoming to the east, Nevada and Utah to the south, and Washington (state), ...
âsplits into two distributary channels, the North Fork and South Fork, which join Henrys Fork miles apart.
* Parting of the Waters National Landmark within Wyoming's Teton Wilderness on the Continental Divide
A continental divide is a drainage divide on a continent such that the drainage basin on one side of the divide feeds into one ocean or sea, and the basin on the other side either feeds into a different ocean or sea, or else is endorheic, not ...
where North Two Ocean Creek splits into two distributaries, Pacific Creek and Atlantic Creek, which ultimately flow into their respective oceans.
* Kings River (California)
The Kings River () is a river draining the Sierra Nevada mountain range in central California in the United States. Its headwaters originate along the Sierra Crest in and around Kings Canyon National Park and form Kings Canyon, one of the dee ...
has deposited a large alluvial fan at the transition from its canyon in the Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada ( ) is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primari ...
mountains to the flat Central Valley. Distributaries flow north into the Pacific Ocean via the San Joaquin River
The San Joaquin River ( ; ) is the longest river of Central California. The long river starts in the high Sierra Nevada and flows through the rich agricultural region of the northern San Joaquin Valley before reaching Suisun Bay, San Francis ...
and south into an endorheic basin
An endorheic basin ( ; also endoreic basin and endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water (e.g. rivers and oceans); instead, the water drainage flows into permanent ...
surrounding Tulare Lake
Tulare Lake () or Tache Lake ( Yokuts: ''Pah-áh-su'', ''Pah-áh-sÄ'') is a freshwater lake in the southern San Joaquin Valley, California, United States. Historically, Tulare Lake was once the largest freshwater lake west of the Mississippi R ...
.
* The Qu'Appelle River
The Qu'Appelle River is a river in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba that flows east from Lake Diefenbaker in south-western Saskatchewan to join the Assiniboine River in Manitoba, just s ...
, in Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada. It is bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and to the south by the ...
and Manitoba
Manitoba is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population ...
, is a distributary of the South Saskatchewan River
The South Saskatchewan River is a major river in the Canadian provinces of Alberta and Saskatchewan. The river begins at the confluence of the Bow River, Bow and Oldman Rivers in southern Alberta and ends at the Saskatchewan River Forks in ce ...
. Its flow is controlled by the Qu'Appelle River Dam. This dam forms the southern arm of Lake Diefenbaker
Lake Diefenbaker is a reservoir and bifurcation lake in the southern part of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It was formed by the construction of the Gardiner Dam and the Qu'Appelle River Dam across ...
.
South America
The Casiquiare canal is an inland distributary of the upperOrinoco
The Orinoco () is one of the longest rivers in South America at . Its drainage basin, sometimes known as the Orinoquia, covers approximately 1 million km2, with 65% of it in Venezuela and 35% in Colombia. It is the List of rivers by discharge, f ...
, which flows southward into the Rio Negro, forming a unique natural canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface ...
between the Orinoco and Amazon river systems. It is the largest river on the planet that links two major river systems.
Europe
 *The
*The IJssel
The IJssel (; ) is a Dutch distributary of the river Rhine that flows northward and ultimately discharges into the IJsselmeer (before the 1932 completion of the Afsluitdijk known as the Zuiderzee), a North Sea natural harbour. It more immediatel ...
, the Waal
WAAL (99.1 FM broadcasting, FM; "The Whale") is a commercial radio, commercial radio station licensed to Binghamton, New York. It airs a classic rock radio format and is owned by Townsquare Media. WAAL is the oldest FM radio station continuou ...
and the Nederrijn
300px, Course of the Nederrijn
The Nederrijn (; "Lower Rhine"; distinct from the Lower Rhine or further upstream) is the Dutch part of the Rhine from the confluence at the town of Angeren of the cut-off Rhine bend of Oude Rijn (Gelderland ...
(Lower Rhine) are the three principal distributaries of the Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the AustriaâSwit ...
. These are formed by two separate bifurcations within the RhineâMeuseâScheldt delta
The RhineâMeuseâScheldt delta is a river delta in the Netherlands formed by the confluence of the Rhine, the Meuse () and the Scheldt rivers. In some cases, the Scheldt delta is considered a separate delta to the RhineâMeuse delta. The resu ...
.
*The Akhtuba River
The Akhtuba (); also transliterated ''Achtuba'' on some maps) is a left distributary of the Volga in southern Russia.
The Akhtuba splits off the Volga shortly before the city of Volgograd (at ), and flows toward the Volga Delta and Caspian Sea ...
is a major distributary of the Volga
The Volga (, ) is the longest river in Europe and the longest endorheic basin river in the world. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment ...
. The bifurcation occurs close to, but before, the Volga Delta
The Volga Delta is the largest river delta in Europe and occurs where Europe's largest river system, the Volga River, drains into the Caspian Sea in Russia's Astrakhan Oblast, north-east of the republic of Kalmykia. The delta is located in the ...
.
* The Tärendö River
The Tärendö River (Swedish language, Swedish: ''Tärendö älv'', Meänkieli: ''Täränönväylä'') is a small distributary river to the Kalix River in Norrbotten County, Norrbotten, Sweden.
It is the second largest river bifurcation, bifurcatio ...
in northern Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
is an inland distributary, far from the mouth of the river. It begins at the Torne River and ends at the Kalix River
The Kalix River (in Kalix dialect: ''kölisälva'', Swedish language, Swedish: proper ''Kalix älv'' or in everyday language ''Kalixälven'', Northern Sami: ''Gáláseatnu'', In Meänkieli the lower part of the river is called ''Kaihnuunväylä'', ...
.
* The Little Danube in Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
branches off from the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
near Bratislava, and flows into the Vah before rejoining the main river near Komárno
Komárno (, , ), colloquially also called ''Révkomárom'', ''Ãregkomárom'', ''Ãszak-Komárom'' in Hungarian language, Hungarian, is a town in Slovakia at the confluence of the Danube and the Váh rivers. Historically it was formed by the "old ...
. The area in the middle is the largest freshwater island in Europe.
* The Abbey River, Limerick
Limerick ( ; ) is a city in western Ireland, in County Limerick. It is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Munster and is in the Mid-West Region, Ireland, Mid-West which comprises part of the Southern Region, Ireland, Southern Region. W ...
, in Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
is a distributary arm of the River Shannon
The River Shannon ( or archaic ') is the major river on the island of Ireland, and at in length, is the longest river in the British Isles. It drains the Shannon River Basin, which has an area of , â approximately one fifth of the area of I ...
. It rejoins the Shannon to form an island upon which King John's Castle is built.
Asia
Eastern Asia
TheHuai River
The Huai River, formerly romanized as the Hwai, is a major river in East China, about long with a drainage area of . It is located about midway between the Yellow River and Yangtze River, the two longest rivers and largest drainage basins ...
in China splits into three streams. The main stream passes through the Sanhe Sluice, goes out of the Sanhe river, and enters the Yangtze River
The Yangtze or Yangzi ( or ) is the longest river in Eurasia and the third-longest in the world. It rises at Jari Hill in the Tanggula Mountains of the Tibetan Plateau and flows including Dam Qu River the longest source of the Yangtze, i ...
through Baoying Lake and Gaoyou Lake. On the east bank of Hongze Lake, another stream goes out of Gaoliangjian Gate and enters the Yellow Sea
The Yellow Sea, also known as the North Sea, is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean located between mainland China and the Korean Peninsula, and can be considered the northwestern part of the East China Sea.
Names
It is one of four ...
at the port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Hamburg, Manch ...
of Bidan through Subei Guan'gai Zongqu, the main irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ...
channel of Northern Jiangsu
Jiangsu is a coastal Provinces of the People's Republic of China, province in East China. It is one of the leading provinces in finance, education, technology, and tourism, with its capital in Nanjing. Jiangsu is the List of Chinese administra ...
); its total length is 168 kilometers. The third stream leaves the Erhe lock on the northeast bank of Hongze Lake, passes the Huaishuhe River to the north of Lianyungang
Lianyungang () is a prefecture-level city in northeastern Jiangsu province of China, province, China. It borders Yancheng to its southeast, Huai'an and Suqian to its south, Xuzhou to its southwest, and the province of Shandong to its north. Its ...
city, and flows into Haizhou Bay through the Hongkou.
Southeast Asia
The Tha Chin River and Noi River are distributaries of theChao Phraya River
The Chao Phraya River is the major river in Thailand, with its low alluvial plain forming the centre of the country. It flows through Bangkok and then into the Gulf of Thailand.
Etymology
Written evidence of the river being referred to by the ...
in Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
, splitting off from the latter about 200 kilometers upstream from the Bay of Bangkok
The Bay of Bangkok (, , , sometimes informally à¸à¹à¸²à¸§à¸à¸±à¸§ à¸), also known as the Bight of Bangkok, is the northernmost part of the Gulf of Thailand, roughly extending from Hua Hin District to the west and Sattahip District to the e ...
.
The Brantas River
The Brantas is the longest river in East Java, Indonesia. It has a length of 320 km, and drains an area of over 11,000 km2 from the southern slope of Mount Kawi-Kelud-Butak, Mount Wilis, and the northern slopes of Mount Liman-Limas, ...
in East Java
East Java (, , ) is a Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia located in the easternmost third of Java island. It has a land border only with the province of Central Java to the west; the Java Sea and the Indian Ocean border its northern ...
, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
, branches off into two distributaries, Mas River
The Kali Mas ("Golden River" in Javanese language, Javanese), also known as Kali Surabaya, is a distributary of the Brantas River in East Java, flowing north-easterly towards the Madura Strait. This river also forms part of the border between th ...
, also known as Surabaya River, and Porong River.
The Hong River
The Red River or the Hong River (; ; Chữ Nôm: ç§ç´
), also known as the ' (lit. "Main River"; Chữ Nôm: ç§ä¸) in Vietnamese and the (, ') in Chinese, is a -long river that flows from Yunnan in Southwest China through no ...
in Northern Vietnam
Northern Vietnam or '' Tonkin'' () is one of three geographical regions in Vietnam. It consists of three geographic sub-regions: the Northwest (Vùng Tây Bắc), the Northeast (Vùng Äông Bắc), and the Red River Delta (Äá»ng Bằng Sôn ...
has notable distributaries such as the Day River
A day is the time period of a full rotation of the Earth with respect to the Sun. On average, this is 24 hours (86,400 seconds). As a day passes at a given location it experiences morning, afternoon, evening, and night. This daily cycle ...
, Ninh Co River and the Luoc River. All of these rivers empty into the Gulf of Tonkin
The Gulf of Tonkin is a gulf at the northwestern portion of the South China Sea, located off the coasts of Tonkin ( northern Vietnam) and South China. It has a total surface area of . It is defined in the west and northwest by the northern co ...
.
Indian Subcontinent
* Kollidam River is a distributary of theKaveri River
The Kaveri (also known as Cauvery) is a major river flowing across Southern India. It is the third largest river in the region after Godavari and Krishna.
The catchment area of the Kaveri basin is estimated to be and encompasses the states o ...
.
* Himalaya
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than 100 pea ...
n rivers including Ganges, Brahmaputra and Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans- Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the dis ...
plus many tributaries form inland distributaries over vast alluvial fans
An alluvial fan is an accumulation of sediments that fans outwards from a concentrated source of sediments, such as a narrow canyon emerging from an escarpment. They are characteristic of mountainous terrain in arid to Semi-arid climate, semiar ...
as they transition from the mountain region to the flat Indo-Gangetic Plain
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the Northern Plain or North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain spanning across the northern and north-eastern part of the Indian subcontinent. It encompasses North India, northern and East India, easte ...
. These areas are highly flood-prone, for example the 2008 Bihar flood
The 2008 Bihar flood was one of the most disastrous floods in the history of Bihar, an impoverished and densely populated state in India. The Koshi embankment near the Indo-Nepal border (at Kusaha VDC, Sunsari district, Nepal) broke on 18 Aug ...
on the Kosi River.
* Padma River
The Padma () is a major river in Bangladesh. It is the eastern and main distributary of the Ganges, flowing generally southeast for to its confluence with the Meghna River, near the Bay of Bengal. The city of Rajshahi is situated on the banks ...
is the main distributary of the Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
in Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
.
* Hoogli River is a Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
distributary that flows through India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, whereas most of the Ganges-Brahmaputra
The Brahmaputra is a trans-boundary river which flows through Southwestern China, Northeastern India, and Bangladesh. It is known as Brahmaputra or Luit in Assamese, Yarlung Tsangpo in Tibetan, the Siang/Dihang River in Arunachali, and ...
complex enters the sea through Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
.
* Nara River is a distributary of the Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayas, Himalayan river of South Asia, South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northw ...
.
Africa
* TheNile River
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the longest river i ...
has two distributaries, the Rosetta
Rosetta ( ) or Rashid (, ; ) is a port city of the Nile Delta, east of Alexandria, in Egypt's Beheira governorate. The Rosetta Stone was discovered there in 1799.
Founded around the 9th century on the site of the ancient town of Bolbitine, R ...
and the Damietta
Damietta ( ' ) is a harbor, port city and the capital of the Damietta Governorate in Egypt. It is located at the Damietta branch, an eastern distributary of the Nile Delta, from the Mediterranean Sea, and about north of Cairo. It was a Cath ...
branches. According to Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
it had in ancient times seven distributaries (east to west):
** The Pelusiac
** The Tanitic
** The Mendesian
** The Phatnitic
** The Sebennytic
** The Bolbitine
** The Canopic
:See History of the Nile Delta.
* The Okavango River
The Okavango River (formerly spelt Okovango or Okovanggo), is a river in southwest Africa. It is known by this name in Botswana, and as Cubango in Angola, and Kavango in Namibia. It is the fourth-longest river system in southern Africa, runni ...
ends in many distributaries in a large inland delta called the Okavango Delta. It is an example of distributaries that do not flow into any other body of water.
Oceania

Australia
A number of the rivers that flow inland from Australia'sGreat Dividing Range
The Great Dividing Range, also known as the East Australian Cordillera or the Eastern Highlands, is a cordillera system in eastern Australia consisting of an expansive collection of mountain ranges, plateaus and rolling hills. It runs roughl ...
form distributaries, most of which flow only intermittently during times of high river levels and end in shallow lakes or simply peter out in the deserts. Yarriambiack Creek
The Yarriambiack Creek, an inland intermittent watercourse of the Wimmera River, Wimmera catchment, is located in the Wimmera region of the Australian state of Victoria, Australia, Victoria. Rising on the northern slopes of the Great Dividing Ran ...
, which flows from the Wimmera River
The Wimmera River, an inland intermittent river of the Wimmera catchment, is located in the Grampians and Wimmera regions of the Australian state of Victoria. Rising in the Pyrenees, on the northern slopes of the Great Dividing Range, the Wimm ...
into Lake Coorong, and Tyrrell Creek, which flows from the Avoca River
The Avoca River, an inland intermittent river of the northcentral catchment, part of the Murray-Darling basin, is located in the lower Riverina bioregion and Central Highlands and Wimmera regions of the Australian state of Victoria. The head ...
into Lake Tyrrell, are two distributaries in Victoria. The Narran River flows from the Balonne River in Queensland
Queensland ( , commonly abbreviated as Qld) is a States and territories of Australia, state in northeastern Australia, and is the second-largest and third-most populous state in Australia. It is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Austr ...
into Narran Lake in New South Wales
New South Wales (commonly abbreviated as NSW) is a States and territories of Australia, state on the Eastern states of Australia, east coast of :Australia. It borders Queensland to the north, Victoria (state), Victoria to the south, and South ...
.
Papua New Guinea
Many of Papua New Guinea's major rivers flow into theGulf of Papua
The Gulf of Papua is located in the southern coast region of New Guinea. It has a total surface area of .
Geography
Some of New Guinea's largest rivers, such as the Fly River, Turama River, Kikori River, Purari River, and Wawoi River flow ...
through marshy, low-lying country, allowing for wide, many-branched deltas. These include the Fly River
The Fly River is the third longest river on the island of New Guinea, after the Sepik and Mamberamo, with a total length of . It is the largest by volume of discharge in Oceania, the largest in the world without a single dam in its catchment, an ...
, which splits into three major and several minor rivers close to its mouth. The Bamu River splits into several channels close to its mouth, among them the ''Bebea'', ''Bina'', ''Dibiri'', and ''Aramia''. The Kikori River also splits into a multitude of channels as it crosses the plains close to the Gulf of Papua. The Purari River
The Purari (also known as Puraari) is a river that originates in the south central highlands especially in Kandep District of Enga Province of Papua New Guinea, flowing though Gulf Province to the Gulf of Papua. The Purari has a drainage bas ...
splits into three major channels as it approaches its mouth.
New Zealand
New Zealand's second-longest river, the Clutha River, splits into two arms, the '' Matau'' and the '' Koua'', some 10 kilometres from the South Island's Pacific Coast. A large island,Inch Clutha
Inch Clutha is a large, flat island sitting in the delta between the Matau (northern) and Koau (southern) branches of the Clutha River, downstream from the town of Balclutha in the South Island of New Zealand. Approximately long and wide, ...
, lies between the two arms. Many of the rivers crossing the Canterbury Plains in the central South Island are braided river
A braided river (also called braided channel or braided stream) consists of a network of river channel (geography), channels separated by small, often temporary, islands called ''braid bars'' or, in British English usage, ''aits'' or ''eyots''.
...
s, and several of these split into separate branches before reaching the coast. Notable among these is the Rangitata River
The Rangitata River is one of the braided rivers of the Canterbury Plains in southern New Zealand. It flows southeast for from the Southern Alps, entering the Pacific Ocean northeast of Timaru. The river has a catchment area of , and a mean ...
, the two arms of which are separated by the low-lying Rangitata Island
Rangitata Island was a long lens-shaped island in the delta of the braided Rangitata River in Canterbury, New Zealand, approximately halfway between Timaru and Ashburton, New Zealand. The island was approximately long and about wide at its wid ...
.
References
Citations
* {{Rivers, streams and springs * River morphology ja:æµè·¯å½¢ç¶#æ´¾å·