Digi-Comp II on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
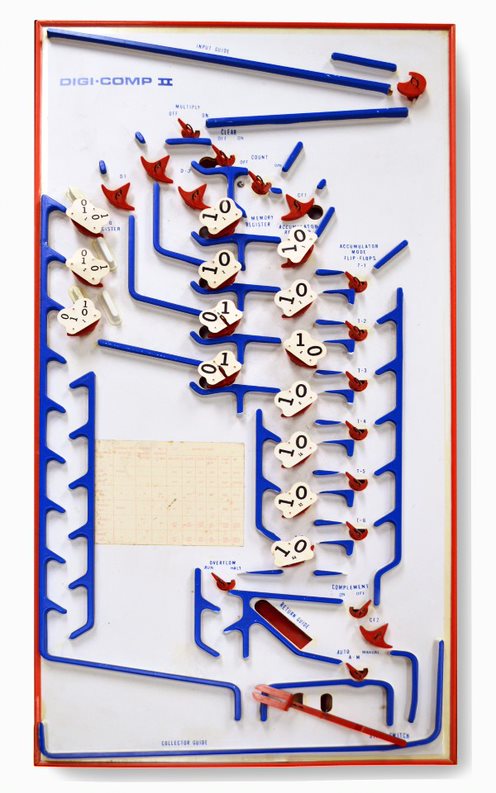 The Digi-Comp II was a toy computer invented by John "Jack" Thomas Godfrey (1924–2009) in 1965 and manufactured by E.S.R., Inc. in the late 1960s that used
The Digi-Comp II was a toy computer invented by John "Jack" Thomas Godfrey (1924–2009) in 1965 and manufactured by E.S.R., Inc. in the late 1960s that used
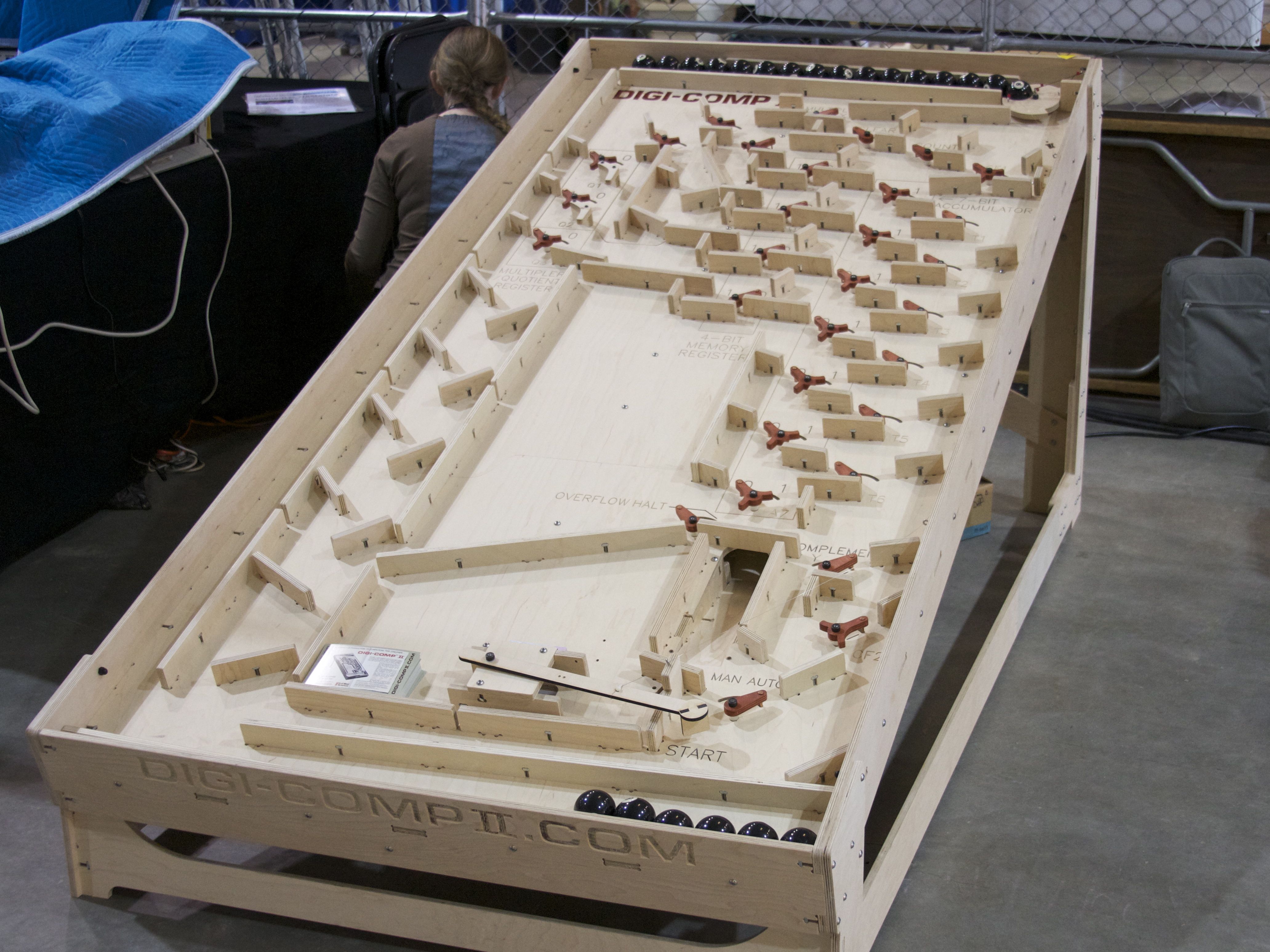 A slightly downscaled reproduction of the Digi-Comp II, made from plywood, is available from Evil Mad Scientist since 2011. This reproduction uses steel pachinko balls, and measures .
In 2011, Evil Mad Scientist also created a giant variant measuring around in size that uses billiard balls. The
A slightly downscaled reproduction of the Digi-Comp II, made from plywood, is available from Evil Mad Scientist since 2011. This reproduction uses steel pachinko balls, and measures .
In 2011, Evil Mad Scientist also created a giant variant measuring around in size that uses billiard balls. The
The Old Computer Museum
- Collection of old analog, digital and mechanical computers.
System Source Computer Museum
">System Source Computer Museum">System Source Computer Museum
providing a web simulator
Extra-large recreation
video showing the multiplication of 13 × 3 on a scaled-up re-creation. * {{anchor, DIGI-TRAN
Original Instruction Manual
Digi-Comp II Replica
- Instructions and files for creating your own Digi-Comp II Mechanical computers Educational toys
 The Digi-Comp II was a toy computer invented by John "Jack" Thomas Godfrey (1924–2009) in 1965 and manufactured by E.S.R., Inc. in the late 1960s that used
The Digi-Comp II was a toy computer invented by John "Jack" Thomas Godfrey (1924–2009) in 1965 and manufactured by E.S.R., Inc. in the late 1960s that used marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite. Marble is typically not foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorpho ...
s rolling down a ramp to perform basic calculations. A two-level masonite
Masonite is a type of hardboard, a kind of engineered wood, which is made of steam-cooked and pressure-molded wood fibers in a process patented by William H. Mason. It is also called Quartrboard, Isorel, hernit, karlit, torex, treetex, and ...
platform with blue plastic guides served as the medium for a supply of marbles that rolled down an inclined plane moving plastic cams as they went. The red plastic cams played the part of flip-flops in an electronic computer - as a marble passed one of the cams, it would flip the cam around - in one position, the cam would allow the marble to pass in one direction, in the other position, it would cause the marble to drop through a hole and roll to the bottom of the ramp. The Digi-Comp II platform measures .
The Digi-Comp II was not programmable, unlike the Digi-Comp I, an earlier offering in the E.S.R. product line that used an assortment of plastic slides, tubes, and bent metal wires to solve simple logic problems.
Computational power
Computer scientistScott Aaronson
Scott Joel Aaronson (born May 21, 1981) is an American theoretical computer scientist and David J. Bruton Jr. Centennial Professor of Computer Science at the University of Texas at Austin. His primary areas of research are quantum computing a ...
analyzed the computational power of the Digi-Comp II. There are several ways to mathematically model the device's computational capabilities. A natural abstraction is a directed acyclic graph
In mathematics, particularly graph theory, and computer science, a directed acyclic graph (DAG) is a directed graph with no directed cycles. That is, it consists of vertices and edges (also called ''arcs''), with each edge directed from one v ...
in which each internal vertex has an out-degree of 2, representing a toggle cam that routes balls to one of two other vertices. A fixed number of balls are placed at a designated source vertex, and the decision problem
In computability theory and computational complexity theory, a decision problem is a computational problem that can be posed as a yes–no question of the input values. An example of a decision problem is deciding by means of an algorithm whethe ...
is to determine whether any balls ever reach a designated sink vertex. Aaronson showed that this decision problem, given as inputs a description of the DAG and the number of balls to run (encoded in unary), is complete
Complete may refer to:
Logic
* Completeness (logic)
* Completeness of a theory, the property of a theory that every formula in the theory's language or its negation is provable
Mathematics
* The completeness of the real numbers, which implies ...
under log-space reduction for CC, the class of problems log-space reducible to the stable marriage problem
In mathematics, economics, and computer science, the stable marriage problem (also stable matching problem or SMP) is the problem of finding a stable matching between two equally sized sets of elements given an ordering of preferences for each elem ...
. He also showed that the variant of the problem in which the number of balls is encoded in binary
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two digits (0 and 1)
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical operation that ta ...
, allowing the machine to run for an exponentially longer time, is still in P.
Reproductions
 A slightly downscaled reproduction of the Digi-Comp II, made from plywood, is available from Evil Mad Scientist since 2011. This reproduction uses steel pachinko balls, and measures .
In 2011, Evil Mad Scientist also created a giant variant measuring around in size that uses billiard balls. The
A slightly downscaled reproduction of the Digi-Comp II, made from plywood, is available from Evil Mad Scientist since 2011. This reproduction uses steel pachinko balls, and measures .
In 2011, Evil Mad Scientist also created a giant variant measuring around in size that uses billiard balls. The Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a Private university, private Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern t ...
's Stata Center houses one copy of the giant version.
See also
*Geniac
Geniac was an educational toy billed as a "computer" designed and marketed by Edmund Berkeley, with Oliver Garfield from 1955 to 1958, but with Garfield continuing without Berkeley through the 1960s. The name stood for "Genius Almost-automatic Co ...
* Dr. Nim
Dr. Nim is a toy invented by John Thomas Godfrey and manufactured by E.S.R., Inc. in the mid-1960s. It consists of a marble-powered plastic computer capable of playing the game of Nim. The machine selects its moves through the action of the marbl ...
- a Nim
Nim is a mathematical two player game.
Nim or NIM may also refer to:
* Nim (programming language)
* Nim Chimpsky, a signing chimpanzee Acronyms
* Network Installation Manager, an IBM framework
* Nuclear Instrumentation Module
* Negative index met ...
-playing game, based on the Digi-Comp II mechanism
* Turing Tumble
* WDR paper computer
The WDR paper computer or Know-how Computer is an educational model of a computer consisting only of a pen, a sheet of paper, and individual matches in the most simple case. This allows anyone interested to learn how to program without having a ...
* CARDboard Illustrative Aid to Computation
CARDIAC (CARDboard Illustrative Aid to Computation) is a learning aid developed by David Hagelbarger and Saul Fingerman for Bell Telephone Laboratories in 1968 to teach high school students how computers work. The kit consists of an instruction ...
References
External links
The Old Computer Museum
- Collection of old analog, digital and mechanical computers.
System Source Computer Museum
">System Source Computer Museum">System Source Computer Museum
providing a web simulator
Extra-large recreation
video showing the multiplication of 13 × 3 on a scaled-up re-creation. * {{anchor, DIGI-TRAN
Original Instruction Manual
Digi-Comp II Replica
- Instructions and files for creating your own Digi-Comp II Mechanical computers Educational toys