Dieckman Condensation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Dieckmann condensation is the intramolecular 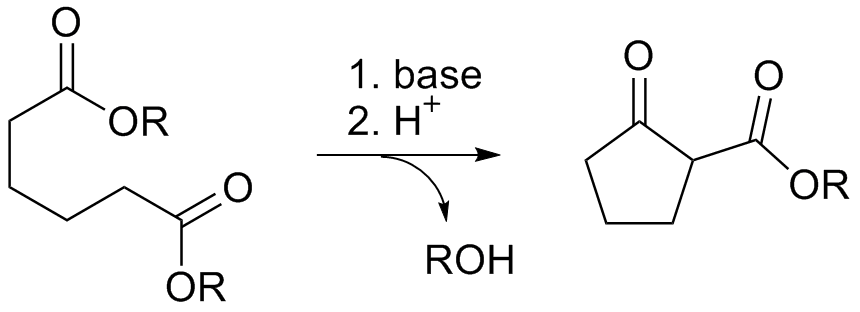
 Due to the steric stability of five- and six-membered rings, these structures will preferentially be formed. 1,6 diesters will form five-membered cyclic β-keto esters, while 1,7 diesters will form six-membered β-keto esters.
Due to the steric stability of five- and six-membered rings, these structures will preferentially be formed. 1,6 diesters will form five-membered cyclic β-keto esters, while 1,7 diesters will form six-membered β-keto esters.
chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, ...
of diesters with base to give β-keto esters. It is named after the German chemist Walter Dieckmann
Walter Dieckmann (8 October 1869 – 12 January 1925) was a German chemist. He is the namesake of the Dieckmann condensation, the intramolecular reaction of diesters with base to give β-keto esters.
Dieckmann studied at the University of Mun ...
(1869–1925). The equivalent intermolecular reaction is the Claisen condensation. Dieckmann condensations are highly effective routes to 5-, 6-, and 7-member rings, but poor for larger rings.
:
Reaction mechanism
Deprotonation of an ester at the α-position generates an enolate ion which then undergoes a 5-exo-trig nucleophilic attack to give a cyclic enol. Protonation with a Brønsted–Lowry acid (H3O+ for example) re-forms the β-keto ester. : Due to the steric stability of five- and six-membered rings, these structures will preferentially be formed. 1,6 diesters will form five-membered cyclic β-keto esters, while 1,7 diesters will form six-membered β-keto esters.
Due to the steric stability of five- and six-membered rings, these structures will preferentially be formed. 1,6 diesters will form five-membered cyclic β-keto esters, while 1,7 diesters will form six-membered β-keto esters.
Further reading
*Dieckmann, W. '' Ber.'' 1894, ''27'', 102 & 965 *Dieckmann, W. ''Ber.'' 1900, ''33'', 595 & 2670 *Dieckmann, W. ''Ann.'' 1901, ''317'', 51 & 93See also
* Claisen condensation * Gabriel–Colman rearrangement * Thorpe reactionReferences
{{Organic reactions Intramolecular condensation reactions Name reactions