Die (integrated circuit) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
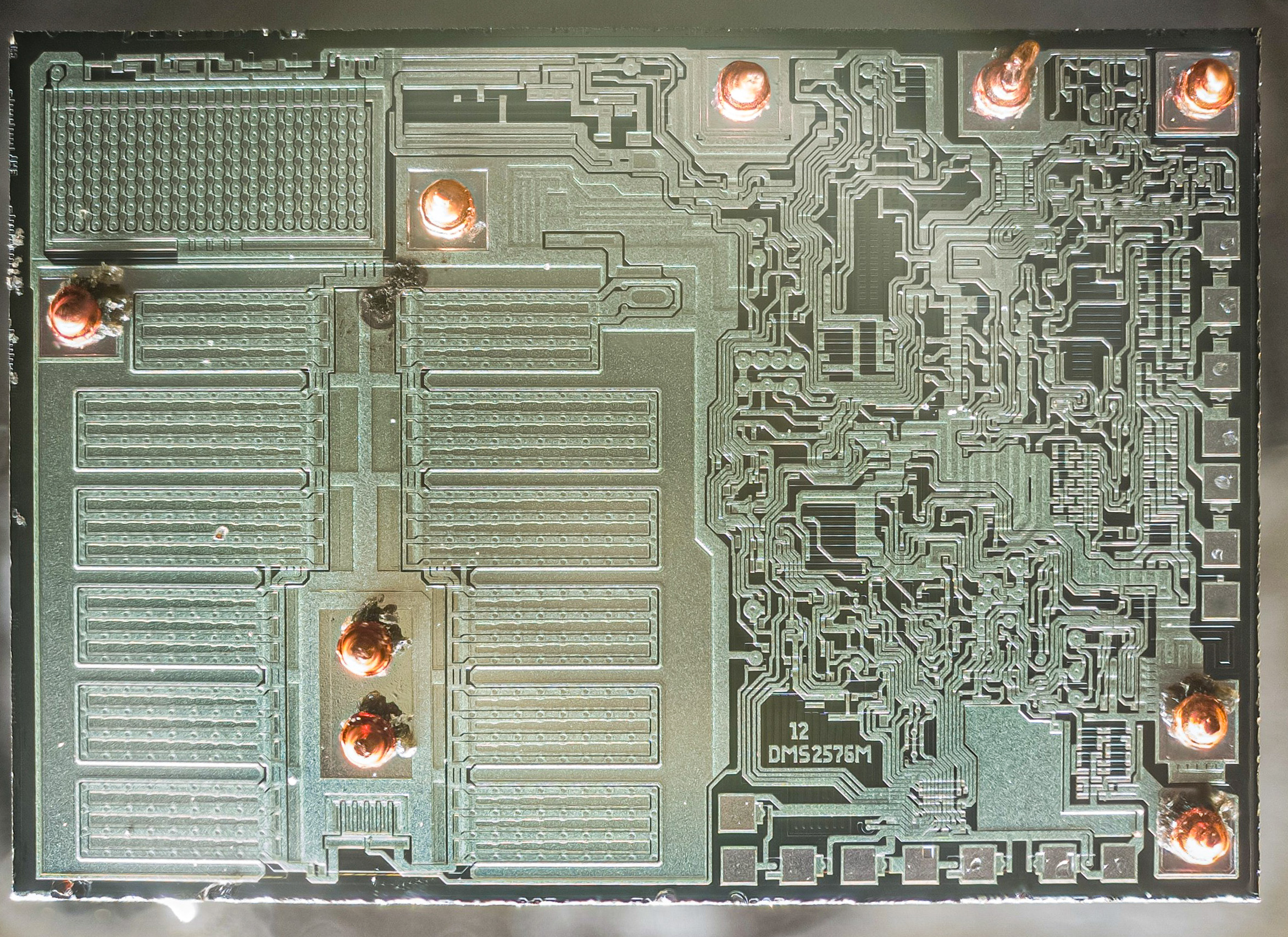 A die, in the context of
A die, in the context of  There are three commonly used plural forms: ''dice'', ''dies,'' and ''die''. To simplify handling and integration onto a
There are three commonly used plural forms: ''dice'', ''dies,'' and ''die''. To simplify handling and integration onto a
From Sand to Silicon “Making of a Chip” Illustrations
(n.d.) These wafers are then polished to a mirror finish before going through
These wafers are then polished to a mirror finish before going through
File:2N2222.jpg, Single NPN
 A die, in the context of
A die, in the context of integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
s, is a small block of semiconducting material on which a given functional circuit is fabricated. Typically, integrated circuits are produced in large batches on a single wafer of electronic-grade silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
(EGS) or other semiconductor (such as GaAs
Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is a III-V direct band gap semiconductor with a zinc blende crystal structure.
Gallium arsenide is used in the manufacture of devices such as microwave frequency integrated circuits, monolithic microwave integrated circui ...
) through processes such as photolithography
Photolithography (also known as optical lithography) is a process used in the manufacturing of integrated circuits. It involves using light to transfer a pattern onto a substrate, typically a silicon wafer.
The process begins with a photosensiti ...
. The wafer is cut ( diced) into many pieces, each containing one copy of the circuit. Each of these pieces is called a die.
 There are three commonly used plural forms: ''dice'', ''dies,'' and ''die''. To simplify handling and integration onto a
There are three commonly used plural forms: ''dice'', ''dies,'' and ''die''. To simplify handling and integration onto a printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a Lamination, laminated sandwich structure of electrical conduction, conductive and Insulator (electricity), insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes ...
, most dies are packaged in various forms.
Manufacturing process
Most dies are composed of silicon and used for integrated circuits. The process begins with the production of monocrystalline siliconingot
An ingot is a piece of relatively pure material, usually metal, that is Casting, cast into a shape suitable for further processing. In steelmaking, it is the first step among semi-finished casting products. Ingots usually require a second procedu ...
s. These ingots are then sliced into disks with a diameter of up to 300 mm.(n.d.)
 These wafers are then polished to a mirror finish before going through
These wafers are then polished to a mirror finish before going through photolithography
Photolithography (also known as optical lithography) is a process used in the manufacturing of integrated circuits. It involves using light to transfer a pattern onto a substrate, typically a silicon wafer.
The process begins with a photosensiti ...
. In many steps the transistors are manufactured and connected with metal interconnect layers. These prepared wafers then go through wafer testing
A wafer is a crisp, often sweet, very thin, flat, light biscuit, often used to decorate ice cream, and also used as a Garnish (food), garnish on some sweet dishes. They frequently have a waffle surface pattern but may also be patterned with insi ...
to test their functionality. The wafers are then sliced and sorted to filter out the faulty dies. Functional dies are then packaged and the completed integrated circuit is ready to be shipped.
Uses
A die can host many types of circuits. One common use case of an integrated circuit die is in the form of acentral processing unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions ...
(CPU). Through advances in modern technology, the size of the transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
within the die has shrunk exponentially, following Moore's law
Moore's law is the observation that the Transistor count, number of transistors in an integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years. Moore's law is an observation and Forecasting, projection of a historical trend. Rather than a law of ...
. Other uses for dies can range from LED
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresp ...
lighting to power semiconductor device
A power semiconductor device is a semiconductor device used as a switch or rectifier in power electronics (for example in a switch-mode power supply). Such a device is also called a power device or, when used in an integrated circuit, a power IC ...
s.
Images
Images of dies are commonly called die shots.bipolar junction transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor (FET), uses only one kind of charge carrier. A ...
die
File:Die of an infrared receiver..jpg, Die of an infrared receiver
File:RGB-SMD-LED.jpg, Close-up of an RGB light-emitting diode
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corre ...
, showing the three individual dies
File:MC14053B internal view.jpg, A small-scale integrated-circuit die, with bond wire
Wire bonding is a method of making interconnections between an integrated circuit (IC) or other semiconductor device and its integrated circuit packaging, packaging during Fabrication (semiconductor), semiconductor device fabrication. Wire bon ...
s attached
File:Diopsis.jpg, A VLSI integrated-circuit die
File:Pentiumpro moshen.jpg, Two dies bonded onto one chip carrier
In electronics, a chip carrier is one of several kinds of surface-mount technology packages for integrated circuits (commonly called "chips"). Connections are made on all four edges of a square package; compared to the internal cavity for mount ...
File:Burr-Brown OPA103.jpg, A monolithic IC operational amplifier
File:ICM7107.jpg, 3 1/2 Digit Single Chip A/D Converter
File:SN7400 1965.jpg, SN7400 Quad NAND gate in flat pack package. 1965.
File:CD-ROM Drive head die.jpg, CD-ROM Drive head die
File:Security camera CCD sensor.jpg, An old security camera CCD sensor
File:1 watt 9 volt SMD LED.jpg, 1 watt 9 volt SMD LED.
File:3 watt power LED after removing phosphor.jpg, 6-volt 3-watt power LED. Wire bonds damaged in removing phosphor.
See also
*Die preparation
Die preparation is a step of semiconductor device fabrication during which a wafer is prepared for IC packaging and IC testing. The process of die preparation typically consists of two steps: wafer mounting and wafer dicing.
Wafer mounting
...
* Integrated circuit design
Integrated circuit design, semiconductor design, chip design or IC design, is a sub-field of electronics engineering, encompassing the particular Boolean logic, logic and circuit design techniques required to design integrated circuits (ICs). A ...
* Wire bonding
Wire bonding is a method of making interconnections between an integrated circuit (IC) or other semiconductor device and its packaging during semiconductor device fabrication. Wire bonding can also be used to connect an IC to other electronics ...
and ball bonding
References
External links
* – animation {{Authority control Integrated circuits