Diaminopimelate Pathway on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Diaminopimelic acid (DAP) is an
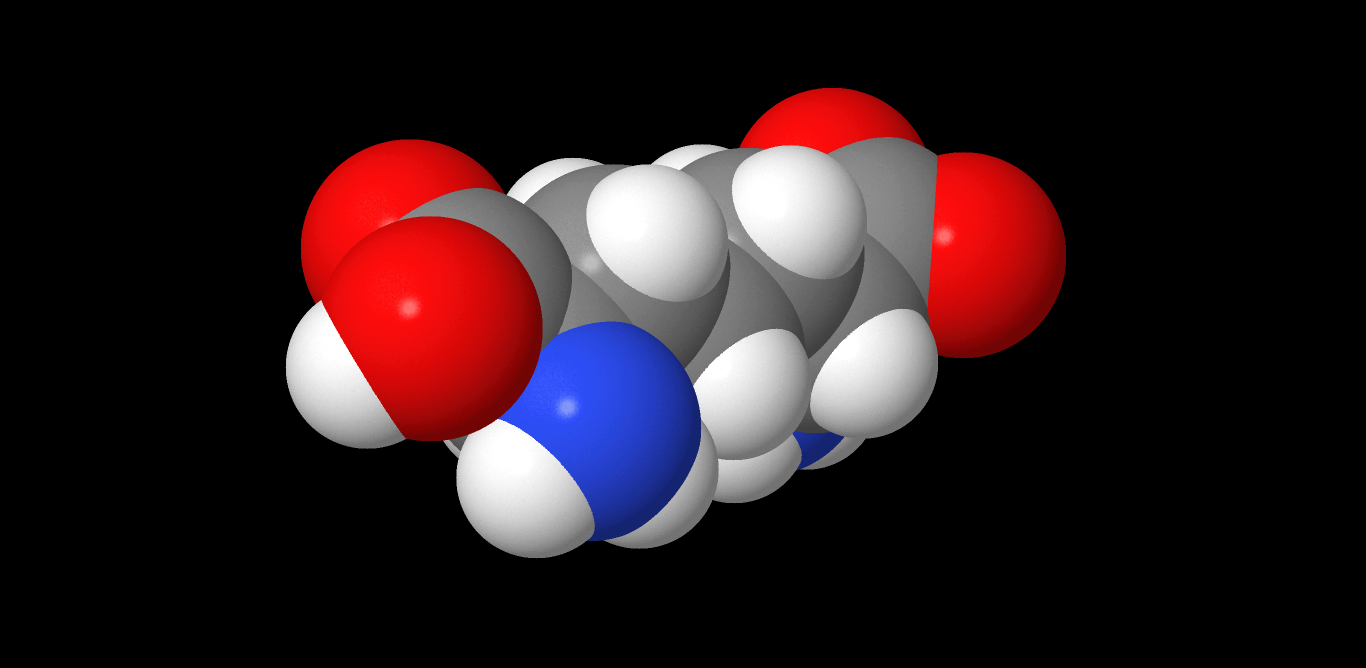
amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
, representing an epsilon
Epsilon (, ; uppercase , lowercase or ; ) is the fifth letter of the Greek alphabet, corresponding phonetically to a mid front unrounded vowel or . In the system of Greek numerals it also has the value five. It was derived from the Phoenic ...
-carboxy
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl group (e.g. ...
derivative of lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. Lysine contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form when the lysine is dissolved in water at physiological pH), an α-carboxylic acid group ( ...
. ''meso''-α,ε-Diaminopimelic acid is the last intermediate in the biosynthesis of lysine and undergoes decarboxylation
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide (CO2). Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is ...
by diaminopimelate decarboxylase to give the final product.
DAP is a characteristic of certain cell wall
A cell wall is a structural layer that surrounds some Cell type, cell types, found immediately outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. Primarily, it provides the cell with structural support, shape, protection, ...
s of some bacteria. DAP is often found in the peptide linkages of NAM- NAG chains that make up the cell wall of gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelope consists ...
bacteria. When provided, they exhibit normal growth. When in deficiency, they still grow but with the inability to make new cell wall peptidoglycan.
This is also the attachment point for Braun's lipoprotein.
See also
* Aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, an enzyme involved in DAP synthesis *Peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like layer (sacculus) that surrounds the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. The sugar component consists of alternating ...
* Pimelic acid
Pimelic acid is the organic compound with the formula HO2C(CH2)5CO2H. Pimelic acid is one unit longer than a related dicarboxylic acid, adipic acid, a precursor to many polyesters and polyamides. However compared to adipic acid, pimelic acid is ...
Images

References
Alpha-Amino acids Dicarboxylic acids Non-proteinogenic amino acids {{OrganicAcid-stub