Despotate Of Epiros on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Despotate of Epirus () was one of the Greek
 Theodore Komnenos Doukas immediately set out to attack
Theodore Komnenos Doukas immediately set out to attack

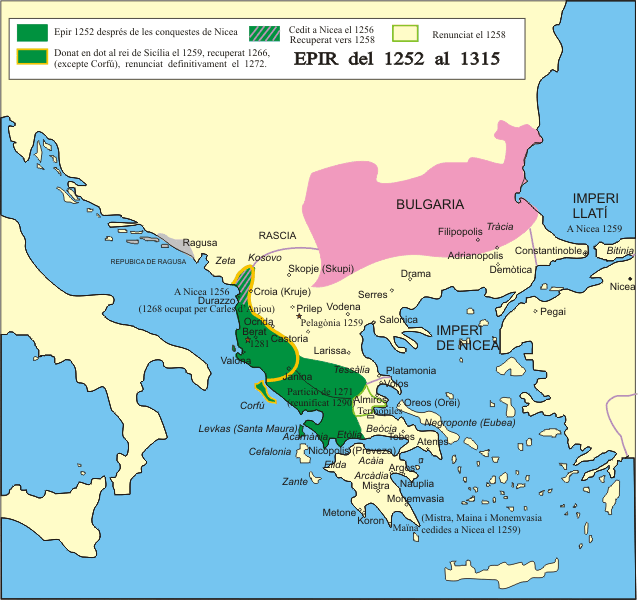 Thessalonica never regained its power after the battle of Klokotnitsa. Theodore's younger son Demetrios Angelos Doukas lost Thessalonica to Nicaea in 1246 and Michael II of Epirus allied with the Latins against the Nicaeans. In 1248
Thessalonica never regained its power after the battle of Klokotnitsa. Theodore's younger son Demetrios Angelos Doukas lost Thessalonica to Nicaea in 1246 and Michael II of Epirus allied with the Latins against the Nicaeans. In 1248
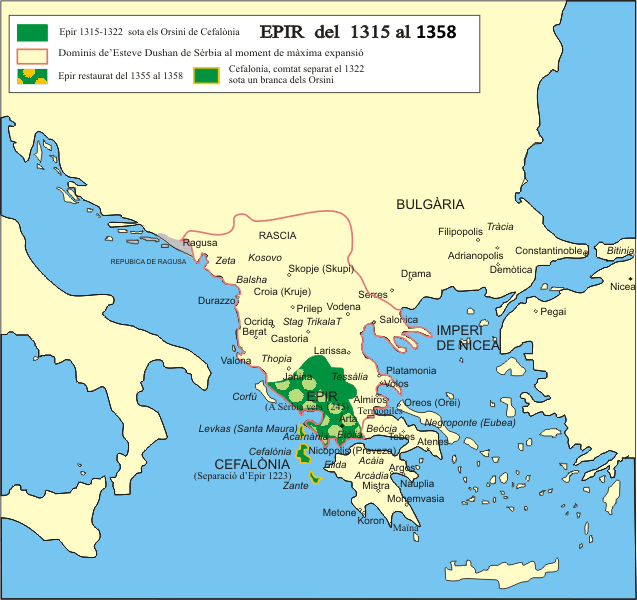 Anna succeeded in marrying off Thomas to a daughter of Michael IX, but Thomas was assassinated in 1318 by his cousin Nicholas Orsini, who married his widow and claimed to rule not only Epirus, but all of Greece; his rule was limited only to Akamania, or the southern part of Epirus. In 1323 he was overthrown by his brother
Anna succeeded in marrying off Thomas to a daughter of Michael IX, but Thomas was assassinated in 1318 by his cousin Nicholas Orsini, who married his widow and claimed to rule not only Epirus, but all of Greece; his rule was limited only to Akamania, or the southern part of Epirus. In 1323 he was overthrown by his brother
successor states
Succession of states is a concept in international relations regarding a successor state that has become a sovereign state over a territory (and populace) that was previously under the sovereignty of another state. The theory has its roots in 19th ...
of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
established in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
in 1204 by a branch of the Angelos dynasty. It claimed to be the legitimate successor of the Byzantine Empire during the subsequent struggle for Constantinople, along with the Empire of Nicaea
The Empire of Nicaea (), also known as the Nicene Empire, was the largest of the three Byzantine Greeks, Byzantine Greek''A Short history of Greece from early times to 1964'' by Walter Abel Heurtley, W. A. Heurtley, H. C. Darby, C. W. Crawley, C ...
and the Empire of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond or the Trapezuntine Empire was one of the three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire that existed during the 13th through to the 15th century. The empire consisted of the Pontus, or far northeastern corner of A ...
; its rulers briefly proclaiming themselves as Emperors in 1227–1242 (during which it is most often called the Empire of Thessalonica). The term "Despotate of Epirus" is, like "Byzantine Empire" itself, a modern historiographic convention and not a name in use at the time.
The Despotate was centred on the region of Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
, encompassing also Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
and the western portion of Greek Macedonia
Macedonia ( ; , ) is a geographic and former administrative region of Greece, in the southern Balkans. Macedonia is the largest and geographic region in Greece, with a population of 2.36 million (as of 2020). It is highly mountainous, wit ...
and also included Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
and western Greece as far south as Nafpaktos. Through a policy of aggressive expansion under Theodore Komnenos Doukas the Despotate of Epirus also briefly came to incorporate central Macedonia
Macedonia (, , , ), most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a former administr ...
, with the establishment of the Empire of Thessalonica in 1224, and Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
as far east as Didymoteicho
Didymoteicho ( ) is a town located on the eastern edge of the Evros (regional unit), Evros regional unit of Eastern Macedonia and Thrace, in northeastern Greece. It is the seat of the municipality of the same name. The town (pop. 8,681 in 2021 ...
and Adrianople
Edirne (; ), historically known as Orestias, Adrianople, is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the Edirne Province, province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, Edirne was the second c ...
, and was on the verge of recapturing Constantinople and restoring the Byzantine Empire before the Battle of Klokotnitsa
The Battle of Klokotnitsa (, ''Bitkata pri Klokotnitsa'') occurred on 9 March 1230 near the village of Klokotnitsa (Haskovo), Klokotnitsa (today in Haskovo Province, Bulgaria) between the Second Bulgarian Empire and the Empire of Thessalonica. ...
in 1230 where he was defeated by the Bulgarian Empire Bulgarian Empire may refer to:
* First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire (; was a medieval state that existed in Southeastern Europe between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. It was founded in 680–681 after part of the Bulgars, led b ...
. After that, the Epirote state contracted to its core in Epirus and Thessaly, and was forced into vassalage to other regional powers. It nevertheless managed to retain its autonomy until being conquered by the restored Palaiologan Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
in ca. 1337. In the 1410s, Carlo I Tocco, Count Palatine of Cephalonia and Zakynthos
The County Palatine of Cephalonia and Zakynthos existed from 1185 to 1479 as part of the Kingdom of Sicily. The title and the right to rule the Ionian islands of Cephalonia and Zakynthos was originally given to Margaritus of Brindisi for his ser ...
, managed to reunite the core of the Epirote state, but his successors gradually lost it to the advancing Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
, with the last stronghold, Vonitsa
Vonitsa () is a town in the northwestern part of Aetolia-Acarnania in Greece, seat of the municipality of Aktio-Vonitsa. The beach town is situated on the south coast of the Ambracian Gulf, and is dominated by a Venetian fortress on a hill. Von ...
, falling to the Ottomans in 1479.
Nomenclature
In traditional and modernhistoriography
Historiography is the study of the methods used by historians in developing history as an academic discipline. By extension, the term ":wikt:historiography, historiography" is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiog ...
, the Epirote state is usually termed the "Despotate of Epirus" and its rulers are summarily attributed the title of " Despot" from its inception, but this use is not strictly accurate. First of all, the title of "Despot" was not borne by all Epirote rulers: the state's founder, Michael I Komnenos Doukas
Michael I Komnenos Doukas, Latinized as Comnenus Ducas (), and in modern sources often recorded as Michael I Angelos, a name he never used, was the founder and first ruler of the Despotate of Epirus from until his assassination in 1214/15.
Bor ...
, never used it, and is only anachronistically referred to as "Despot of Epirus
The Despot of Epirus was the ruler of the Despotate of Epirus, one of the rump states of the Byzantine Empire in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade. The name "Despotate of Epirus" and the title "despot of Epirus" are modern historiographical name ...
" in 14th-century Western European sources. His successor Theodore Komnenos Doukas did not use it either, and actually crowned himself emperor (''basileus
''Basileus'' () is a Greek term and title that has signified various types of monarchs throughout history. In the English language, English-speaking world, it is perhaps most widely understood to mean , referring to either a or an . The title ...
'') at Thessalonica
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area) and the capital city, capital of the geographic reg ...
. The first ruler of Epirus to receive the title of Despot was Michael II
Michael II (, ; 770 – 2 October 829), called the Amorian (, ) and the Stammerer (, or , ), reigned as Byzantine emperor from 25 December 820 to his death on 2 October 829, the first ruler of the Amorian dynasty.
Born in Amorium, Michael was ...
, from his uncle Manuel of Thessalonica in the 1230s, and then again, as a sign of submission and vassalage, from the Nicaean emperor John III Vatatzes. Earlier historians assumed that Michael I was indeed named "Despot" by the deposed emperor Alexios III Angelos
Alexios III Angelos (; 1211), Latinized as Alexius III Angelus, was Byzantine Emperor from March 1195 to 17/18 July 1203. He reigned under the name Alexios Komnenos (; Aléxios Komnēnós) associating himself with the Komnenos dynasty (from whi ...
after ransoming him from Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
captivity in or ; this has been disproven by more recent research.
Furthermore, even after Michael II, speaking of the Epirote rulers as "Despots ''of'' Epirus" is technically incorrect. The title of Despot did not imply any specific territorial jurisdiction, nor was it hereditary; it was merely the highest rank in the Byzantine court hierarchy, awarded by a reigning emperor to close relatives, usually his sons. Consequently, it was often borne by the princes sent to govern semi-autonomous appanage
An appanage, or apanage (; ), is the grant of an estate, title, office or other thing of value to a younger child of a monarch, who would otherwise have no inheritance under the system of primogeniture (where only the eldest inherits). It was ...
s and only later came to be associated with these territories as the practice became regularized (aside from Epirus, the Despotate of the Morea
The Despotate of the Morea () or Despotate of Mystras () was a province of the Byzantine Empire which existed between the mid-14th and mid-15th centuries. Its territory varied in size during its existence but eventually grew to include almost a ...
is the most notable case). The territorial term "despotate" itself (in Greek , ) was first used in contemporary sources for Epirus only from the 14th century on, e.g. in the '' Chronicle of the Morea'', in the history of John Kantakouzenos, the hagiography of St. Niphon, or the '' Chronicle of the Tocco'', where the inhabitants of the Despotate are referred to as the ''Despotatoi''. The term "Despotate of Epirus" is thus sometimes replaced by "(Independent) State of Epirus" in more recent historiography.
The Epirote realm itself did not have an official name. Contemporaries, particularly in Western Europe, used the term ''Romania'' (), which generally referred to the whole Byzantine Empire, to refer specifically to Epirus, as seen in the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
title of ''Despotus Romanie'' claimed by Philip I of Taranto and his son Philip of Apulia, Nicholas Orsini, and later Carlo I Tocco. In the Byzantine world, the term ''Dysis'' (), meaning "West", which historically referred to Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
, Macedonia
Macedonia (, , , ), most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a former administr ...
and Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
, or even the entire European part of the Empire, also came into use already in the 13th century when juxtaposing Epirus to its eastern rival, the Empire of Nicaea
The Empire of Nicaea (), also known as the Nicene Empire, was the largest of the three Byzantine Greeks, Byzantine Greek''A Short history of Greece from early times to 1964'' by Walter Abel Heurtley, W. A. Heurtley, H. C. Darby, C. W. Crawley, C ...
, which was then called ''Anatolē'' (), "East". Moreover, the term "Hellenes
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Albania, Anatolia, parts of Italy and Egypt, and to a lesser extent, other countries surrounding the Eastern Mediterranean and Black Sea. They also f ...
" was widely used instead of the earlier "Romans" by the 13th-century court of the Despotate to describe its population.
Foundation
The Epirote state was founded in 1205 by Michael Komnenos Doukas, a cousin of theByzantine emperor
The foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, which Fall of Constantinople, fell to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised s ...
s Isaac II Angelos
Isaac II Angelos or Angelus (; September 1156 – 28 January 1204) was Byzantine Emperor from 1185 to 1195, and co-Emperor with his son Alexios IV Angelos from 1203 to 1204. In a 1185 revolt against the Emperor Andronikos Komnenos, Isaac ...
and Alexios III Angelos
Alexios III Angelos (; 1211), Latinized as Alexius III Angelus, was Byzantine Emperor from March 1195 to 17/18 July 1203. He reigned under the name Alexios Komnenos (; Aléxios Komnēnós) associating himself with the Komnenos dynasty (from whi ...
. At first, Michael allied with Boniface of Montferrat, but having lost the Morea
Morea ( or ) was the name of the Peloponnese peninsula in southern Greece during the Middle Ages and the early modern period. The name was used by the Principality of Achaea, the Byzantine province known as the Despotate of the Morea, by the O ...
(Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridg ...
) to the Franks
file:Frankish arms.JPG, Aristocratic Frankish burial items from the Merovingian dynasty
The Franks ( or ; ; ) were originally a group of Germanic peoples who lived near the Rhine river, Rhine-river military border of Germania Inferior, which wa ...
at the battle of the Olive Grove of Koundouros, he went to Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
, where he considered himself the Byzantine governor of the old province of Nicopolis
Nicopolis () or Actia Nicopolis was the capital city of the Roman province of Epirus (Roman province), Epirus. Its site, near Preveza, Greece, still contains impressive ruins. The city was founded in 29 BC by Octavian in commemoration of his ...
and revolted against Boniface. Epirus soon became the new home of many refugees from Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
, Thessaly
Thessaly ( ; ; ancient Aeolic Greek#Thessalian, Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic regions of Greece, geographic and modern administrative regions of Greece, administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient Thessaly, a ...
, and the Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridg ...
, and Michael was described as a second Noah
Noah (; , also Noach) appears as the last of the Antediluvian Patriarchs (Bible), patriarchs in the traditions of Abrahamic religions. His story appears in the Hebrew Bible (Book of Genesis, chapters 5–9), the Quran and Baháʼí literature, ...
, rescuing men from the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
flood. John X Kamateros, the Patriarch of Constantinople
The ecumenical patriarch of Constantinople () is the archbishop of Constantinople and (first among equals) among the heads of the several autocephalous churches that comprise the Eastern Orthodox Church. The ecumenical patriarch is regarded as ...
, did not consider him a legitimate successor and instead joined Theodore I Laskaris
Theodore I Laskaris or Lascaris (; 1175November 1221) was the first emperor of Nicaea—a successor state of the Byzantine Empire—from 1205 to his death. Although he was born to an obscure aristocratic family, his mother was related t ...
in Nicaea
Nicaea (also spelled Nicæa or Nicea, ; ), also known as Nikaia (, Attic: , Koine: ), was an ancient Greek city in the north-western Anatolian region of Bithynia. It was the site of the First and Second Councils of Nicaea (the first and seve ...
; Michael instead recognized the authority of Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III (; born Lotario dei Conti di Segni; 22 February 1161 – 16 July 1216) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 8 January 1198 until his death on 16 July 1216.
Pope Innocent was one of the most power ...
over Epirus, cutting ties to the Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, officially the Orthodox Catholic Church, and also called the Greek Orthodox Church or simply the Orthodox Church, is List of Christian denominations by number of members, one of the three major doctrinal and ...
.
Henry of Flanders demanded that Michael submit to the Latin Empire
The Latin Empire, also referred to as the Latin Empire of Constantinople, was a feudal Crusader state founded by the leaders of the Fourth Crusade on lands captured from the Byzantine Empire. The Latin Empire was intended to replace the Byzantin ...
, which he did, at least nominally, by allowing his daughter to marry Henry's brother Eustace in 1209. Michael did not honour this alliance, assuming that mountainous Epirus would be mostly impenetrable by any Latins with whom he made and broke alliances. Meanwhile, Boniface's relatives from Montferrat
Montferrat ( , ; ; , ; ) is a historical region of Piedmont, in northern Italy. It comprises roughly (and its extent has varied over time) the modern provinces of Province of Alessandria, Alessandria and Province of Asti, Asti. Montferrat ...
made claims to Epirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
as well, and in 1210 Michael allied with the Venetians and attacked Boniface's Kingdom of Thessalonica
The Kingdom of Thessalonica () was a short-lived Crusader State founded after the Fourth Crusade over conquered Byzantine lands in today's territory of Northern Greece and Thessaly.
History
Background
After the fall of Constantinople to the ...
. Pope Innocent III excommunicated him in response. Henry forced Michael into a renewed nominal alliance later that year.
Michael turned his attention to capturing other strategically important Latin-held towns, including Larissa
Larissa (; , , ) is the capital and largest city of the Thessaly region in Greece. It is the fifth-most populous city in Greece with a population of 148,562 in the city proper, according to the 2021 census. It is also the capital of the Larissa ...
and Dyrrhachium. He also took control of the ports on the Gulf of Corinth
The Gulf of Corinth or the Corinthian Gulf (, ) is a deep inlet of the Ionian Sea, separating the Peloponnese from western mainland Greece. It is bounded in the east by the Isthmus of Corinth which includes the shipping-designed Corinth Canal and ...
. In 1214 he captured Corcyra
Corfu ( , ) or Kerkyra (, ) is a Greece, Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands; including its Greek islands, small satellite islands, it forms the margin of Greece's northwestern frontier. The island is part of the Corfu (regio ...
from Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
, but he was assassinated
Assassination is the willful killing, by a sudden, secret, or planned attack, of a personespecially if prominent or important. It may be prompted by political, ideological, religious, financial, or military motives.
Assassinations are orde ...
later that year and was succeeded by his half-brother Theodore.
Conflict with Nicaea and Bulgaria
 Theodore Komnenos Doukas immediately set out to attack
Theodore Komnenos Doukas immediately set out to attack Thessalonica
Thessaloniki (; ), also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, Salonika, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece (with slightly over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area) and the capital city, capital of the geographic reg ...
, and he fought with the Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
ns along the way. Henry of Flanders died on the way to counterattack, and in 1217 Theodore captured his successor Peter of Courtenay, most likely executing him. The Latin Empire fell into disarray after losing the Battle of Poimanenon
The Battle of Poimanenon or Poemanenum was fought in early 1224 (or possibly late 1223) between the forces of the two main successor states of the Byzantine Empire; the Latin Empire and the Byzantine Greek Empire of Nicaea. The opposing forces me ...
to the Nicaeans, and could not stop Theodore from capturing Thessalonica in 1224. Theodore now challenged Nicaea for the imperial title and crowned himself emperor, founding the short-lived Empire of Thessalonica. In 1225, after John III Doukas Vatatzes
John III Doukas Vatatzes, Latinized as Ducas Vatatzes (; 1192 – 3 November 1254), was Emperor of Nicaea from 1221 to 1254. He was succeeded by his son, known as Theodore II Doukas Laskaris.
Life
John Doukas Vatatzes, born in about 1192 i ...
of Nicaea had taken Adrianople
Edirne (; ), historically known as Orestias, Adrianople, is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the Edirne Province, province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, Edirne was the second c ...
, Theodore arrived and took it back from him. Theodore also allied with the Bulgarians
Bulgarians (, ) are a nation and South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and its neighbouring region, who share a common Bulgarian ancestry, culture, history and language. They form the majority of the population in Bulgaria, ...
and drove the Latins out of Thrace
Thrace (, ; ; ; ) is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe roughly corresponding to the province of Thrace in the Roman Empire. Bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Se ...
. In 1227 Theodore crowned himself Byzantine emperor, although this was not recognized by most Greeks, especially not the Patriarch in Nicaea.
In 1230 Theodore broke the truce with Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
, hoping to remove Ivan Asen II
Ivan Asen II, also known as John Asen II (, ; 1190s – May/June 1241), was Emperor (Tsar) of Second Bulgarian Empire, Bulgaria from 1218 to 1241. He was still a child when his father Ivan Asen I of Bulgaria, Ivan Asen I one of the founders of th ...
, who had held him back from attacking Constantinople. In the battle of Klokotnitsa
The Battle of Klokotnitsa (, ''Bitkata pri Klokotnitsa'') occurred on 9 March 1230 near the village of Klokotnitsa (Haskovo), Klokotnitsa (today in Haskovo Province, Bulgaria) between the Second Bulgarian Empire and the Empire of Thessalonica. ...
(near Haskovo in Bulgaria) the Bulgarian emperor defeated Theodore, capturing and later blinding him. His brother Manuel Komnenos Doukas took power in Thessalonica, but Epirus itself soon broke away under Michael I's illegitimate son, Michael II Komnenos Doukas
Michael II Komnenos Doukas, Latinized as Comnenus Ducas (, ''Mikhaēl II Komnēnos Doukas''), often called Michael Angelos in narrative sources, was from 1230 until his death in 1266/68 the ruler of the Despotate of Epirus, which included Epirus ...
. Manuel awarded Michael the title of Despot—making Michael the first Epirote ruler to bear the title—as a sign of his nominal dependency on Thessalonica, but Michael was ''de facto'' independent, which he demonstrated by seizing Corfu in ca. 1236. In the rump Empire of Thessalonica, after Theodore was released in 1237, he overthrew his brother Manuel, and set up his son John Komnenos Doukas as ruler of Thessalonica.
Nicaean and Byzantine suzerainty

 Thessalonica never regained its power after the battle of Klokotnitsa. Theodore's younger son Demetrios Angelos Doukas lost Thessalonica to Nicaea in 1246 and Michael II of Epirus allied with the Latins against the Nicaeans. In 1248
Thessalonica never regained its power after the battle of Klokotnitsa. Theodore's younger son Demetrios Angelos Doukas lost Thessalonica to Nicaea in 1246 and Michael II of Epirus allied with the Latins against the Nicaeans. In 1248 John III Doukas Vatatzes
John III Doukas Vatatzes, Latinized as Ducas Vatatzes (; 1192 – 3 November 1254), was Emperor of Nicaea from 1221 to 1254. He was succeeded by his son, known as Theodore II Doukas Laskaris.
Life
John Doukas Vatatzes, born in about 1192 i ...
of Nicaea forced Michael to recognize him as emperor, and officially recognized him in turn as ''despotēs'' in Epirus. Vatatzes' granddaughter Maria later (in 1256) married Michael's son Nikephoros, although she died in 1258. Also in 1248 Michael's daughter Anna married William II, Prince of Achaea
The Prince of Achaea was the ruler of the Principality of Achaea, one of the crusader states Frankokratia, founded in Greece in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade (1202–1204). The principality witnessed various overlords during its more than tw ...
, and Michael decided to honour this alliance over his obligations to Vatatzes. The allies were defeated in the ensuing conflict at the Battle of Pelagonia in 1259.
Emperor Theodore II Laskaris
Theodore II Laskaris or Ducas Lascaris (; November 1221/1222 – 16 August 1258) was Emperor of Nicaea from 1254 to 1258. He was the only child of Emperor John III Doukas Vatatzes and Empress Irene Laskarina. His mother was the eldest da ...
allied with Michael II, and their children, betrothed by John years before, finally married in 1256, with Theodore receiving Dyrrhachium in return. Michael did not accept this transfer of land, and in 1257 he revolted, defeating a Nicaean army led by George Acropolites. As Michael marched on Thessalonica, he was attacked by King Manfred of Sicily
Manfred (; 123226 February 1266) was the last King of Sicily from the Hohenstaufen dynasty, reigning from 1258 until his death. The natural son of the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II, Manfred became regent over the Kingdom of Sicily on b ...
, who conquered Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
and Corcyra
Corfu ( , ) or Kerkyra (, ) is a Greece, Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands; including its Greek islands, small satellite islands, it forms the margin of Greece's northwestern frontier. The island is part of the Corfu (regio ...
. However, Michael immediately allied with him by marrying his daughter Helena to him. After Theodore II died, Michael, Manuel, and William II fought the new Nicaean emperor, Michael VIII Palaiologos
Michael VIII Palaiologos or Palaeologus (; 1224 – 11 December 1282) reigned as Byzantine emperor from 1261 until his death in 1282, and previously as the co-emperor of the Empire of Nicaea from 1259 to 1261. Michael VIII was the founder of th ...
. The alliance was very unstable and in 1259 William was captured at the disastrous Battle of Pelagonia. Michael VIII went on to capture Michael II's capital of Arta, leaving Epirus with only Ioannina
Ioannina ( ' ), often called Yannena ( ' ) within Greece, is the capital and largest city of the Ioannina (regional unit), Ioannina regional unit and of Epirus (region), Epirus, an Modern regions of Greece, administrative region in northwester ...
and Vonitsa. Arta was recovered by 1260 while Michael VIII was occupied against Constantinople.
Italian invasions
After Michael VIII restored the empire in Constantinople in 1261 he frequently harassed Epirus, and forced Michael's son Nikephoros to marry his niece Anna Palaiologina Kantakouzene in 1265. Michael considered Epirus avassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain ...
state, although Michael II and Nikephoros continued to ally with the Princes of Achaea and the Dukes of Athens
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and above sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they ...
. In 1267 Corcyra and much of Epirus were taken by Charles of Anjou
Charles I (early 1226/12277 January 1285), commonly called Charles of Anjou or Charles d'Anjou, was King of Sicily from 1266 to 1285. He was a member of the royal Capetian dynasty and the founder of the House of Anjou-Sicily. Between 1246 a ...
, and in 1267/68 Michael II died. Michael VIII did not attempt to annex Epirus directly, and allowed Nikephoros I to succeed his father and deal with Charles, who captured Dyrrhachium in 1271. In 1279 Nikephoros allied with Charles against Michael VIII, agreeing to become Charles' vassal. With Charles' defeat soon after Nikephoros lost Albania to the Byzantines.
Under Andronikos II Palaiologos
Andronikos II Palaiologos (; 25 March 1259 – 13 February 1332), Latinization of names, Latinized as Andronicus II Palaeologus, reigned as Byzantine emperor from 1282 to 1328. His reign marked the beginning of the recently restored em ...
, son of Michael VIII, Nikephoros renewed the alliance with Constantinople. Nikephoros, however, was persuaded to ally with Charles II of Naples
Charles II, also known as Charles the Lame (; ; 1254 – 5 May 1309), was King of Naples, Count of Provence and Forcalquier (1285–1309), Prince of Achaea (1285–1289), and Count of Anjou and Maine (1285–1290); he also was King of Albania ( ...
in 1292, although Charles was defeated by Andronikos's fleet. Nikephoros married his daughter to Charles's son Philip I of Taranto and sold much of his territory to him. After Nikephoros's death in c. 1297 Byzantine influence grew under his widow Anna, Andronikos's cousin, who ruled as regent for her young son Thomas I Komnenos Doukas. In 1306 she revolted against Philip in favour of Andronikos; the Latin inhabitants were expelled but she was forced to return some territory to Philip. In 1312 Philip abandoned his claim to Epirus and claimed the defunct Latin Empire of Constantinople instead as the inheritance of his wife Catherine II of Valois, Princess of Achaea.
Collapse of the despotate
 Anna succeeded in marrying off Thomas to a daughter of Michael IX, but Thomas was assassinated in 1318 by his cousin Nicholas Orsini, who married his widow and claimed to rule not only Epirus, but all of Greece; his rule was limited only to Akamania, or the southern part of Epirus. In 1323 he was overthrown by his brother
Anna succeeded in marrying off Thomas to a daughter of Michael IX, but Thomas was assassinated in 1318 by his cousin Nicholas Orsini, who married his widow and claimed to rule not only Epirus, but all of Greece; his rule was limited only to Akamania, or the southern part of Epirus. In 1323 he was overthrown by his brother John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second E ...
, who attempted to balance submission to Constantinople with cooperation with the Angevins of Naples, who also claimed Greece as part of their domains. John was poisoned around 1335 by his wife Anna, who became regent for their son Nikephoros II
Nikephoros II Phokas (; – 11 December 969), Latinized Nicephorus II Phocas, was Byzantine emperor from 963 to 969. His career, not uniformly successful in matters of statecraft or of war, nonetheless greatly contributed to the resurgence of t ...
. In 1337 the new Emperor, Andronikos III Palaiologos
Andronikos III Palaiologos (; 25 March 1297 – 15 June 1341), commonly Latinized as Andronicus III Palaeologus, was the Byzantine emperor from 1328 to 1341. He was the son of Michael IX Palaiologos and Rita of Armenia. He was proclaimed c ...
, arrived in northern Epirus with an army partly composed of 2,000 Turks contributed by his ally Umur of Aydın. Andronikos first dealt with unrest due to attacks by Albanians and then turned his interest to the Despotate. Anna tried to negotiate and obtain the Despotate for her son when he came of age, but Andronikos demanded the complete surrender of the Despotate to which she finally agreed. Thus Epirus came peacefully under imperial rule, with Theodore Synadenos as governor.
The imperials had insisted that Nikephoros would be engaged to one of the daughters of the emperor's right-hand man, John Kantakouzenos. When the time of the engagement came, Nikephoros had vanished. Andronikos learned that Nikephoros had fled to Italy, with the help of members of the Epirote aristocracy who supported an independent Epirus. He stayed in Taranto
Taranto (; ; previously called Tarent in English) is a coastal city in Apulia, Southern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Taranto, serving as an important commercial port as well as the main Italian naval base.
Founded by Spartans ...
, Italy, in the court of Catherine II of Valois (Philip of Taranto's widow), the titular
Titular may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Title character in a narrative work, the character referred to in its title
Religion
* Titular (Catholicism), a cardinal who holds a titulus, one of the main churches of Rome
** Titular bisho ...
empress of Constantinople.
In 1339 a revolt began, supported by Catherine of Valois, who had previously moved to the Peloponnese, and by Nikephoros who had returned to Epirus, based in Thomokastron. By the end of the year the imperial army returned to the area, and in the following year, 1340, Andronikos III himself arrived together with John Kantakouzenos. Nikephoros was persuaded through diplomacy to recognize the authority of the emperor. He surrendered Thomokastron, married Maria Kantakouzene, the daughter of John Kantakouzenos, and received the title of '' panhypersebastos''.
The Empire soon fell into a civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
between John V Palaiologos
John V Palaiologos or Palaeologus (; 18 June 1332 – 16 February 1391) was Byzantine emperor from 1341 to 1391, with interruptions. His long reign was marked by constant civil war, the spread of the Black Death and several military defea ...
and John VI Kantakouzenos, and Epirus was conquered by the Serbian tsar Stefan Dušan
Stephen (honorific), Stefan Uroš IV Dušan ( sr-Cyrl, Стефан Урош IV Душан), also known as Dušan the Mighty ( sr-Cyrl, Душан Силни; – 20 December 1355), was the King of Serbia from 8 September 1331 and Emperor of th ...
in 1348, who appointed his brother, despot Simeon Nemanjić-Palailogos as governor of the province. Nikephoros II took advantage of the Byzantine civil war and the death of Dušan (1355) to escape and to reestablish himself in Epirus in 1356, to which he also added Thessaly. Nikephoros was killed in battle putting down an Albanian
Albanian may refer to:
*Pertaining to Albania in Southeast Europe; in particular:
**Albanians, an ethnic group native to the Balkans
**Albanian language
**Albanian culture
**Demographics of Albania, includes other ethnic groups within the country ...
revolt in 1359, and the territory of the former despotate became a component part of the personal Empire of Dušan's brother Simeon Nemanjić-Palailogos. Simeon was also governing Thessaly at the time, and, as the ''Chronicle of Ioannina'' shows, he left much of the territory under the control of Albanian clans establishing short-lived entities: the clan of Pjetër Losha held Arta, and the clan of Muriq Shpata held Aetoloacarnania, with Angelokastron as its capital.
In 1367 a part of the Epirotan Despotate was resurrected under local Serbian nobleman Thomas II Preljubović
Thomas may refer to:
People
* List of people with given name Thomas
* Thomas (name)
* Thomas (surname)
* Saint Thomas (disambiguation)
* Thomas Aquinas (1225–1274) Italian Dominican friar, philosopher, and Doctor of the Church
* Thomas the ...
, who kept Ioannina. After Thomas' death in 1384, his widow remarried in 1385 and transferred the Despotate to homage of Italian nobility. The state tradition was carried on by the Serbian and Italian rulers of Ioannina
Ioannina ( ' ), often called Yannena ( ' ) within Greece, is the capital and largest city of the Ioannina (regional unit), Ioannina regional unit and of Epirus (region), Epirus, an Modern regions of Greece, administrative region in northwester ...
, who solicited aid from the Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks () were a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group in Anatolia. Originally from Central Asia, they migrated to Anatolia in the 13th century and founded the Ottoman Empire, in which they remained socio-politically dominant for the e ...
against the Albanians. In 1399 the Albanian leader of Principality of Gjirokastër, Gjon Zenebishi
John Zenevisi or Gjon Zenebishi ( or ''Gjin Zenebishi''; died 1418) was an Albanian magnate that held the estates in Epirus, such as Gjirokastër and Vagenetia.
Name
Zenevisi can be found with different spellings in historical documents. His n ...
captured the Despot Esau de' Buondelmonti
Esau de' Buondelmonti () was the ruler of Ioannina and its surrounding area (central Epirus) from 1385 until his death in 1411, with the Byzantine title of despot.
Life
Esau was the son of the Florentine nobleman Manente and Lapa Acciaiuoli, ...
and released him after 15 months, when his relatives in Italy offered a huge amount of money as a ransom. By 1416 the Tocco family
The House of Tocco ( ''Tocchi'', Τόκκοι, ''Tokkoi'') was an Italian nobility, Italian noble family from Benevento that came to prominence in the late 14th and 15th centuries, when they ruled various territories in western Greece as County ...
of Cephalonia
Kefalonia or Cephalonia (), formerly also known as Kefallinia or Kephallonia (), is the largest of the Ionian Islands in western Greece and the 6th-largest island in Greece after Crete, Euboea, Lesbos, Rhodes and Chios. It is also a separate regio ...
succeeded in reuniting Epirus, or at least in asserting their control over its towns.
But internal dissension eased the Ottoman conquest, which proceeded with the capture of Ioannina in 1430, Arta in 1449, Angelokastron in 1460, and finally Vonitsa
Vonitsa () is a town in the northwestern part of Aetolia-Acarnania in Greece, seat of the municipality of Aktio-Vonitsa. The beach town is situated on the south coast of the Ambracian Gulf, and is dominated by a Venetian fortress on a hill. Von ...
in 1479. During the Ottoman conquest of the Despotate of Epirus, the islands of Santa Mavra, Cephalonia and Ithaka, the ducal officials were "cut to pieces", the castle of Cephalonia was burned and the peasantry was enslaved and taken to Constantinople as a gift to the sultan, who engaged in "slave breeding" by separating husbands and wives and "mating" them with Ethiopian slaves with the purpose of "producing a race of grey slaves", while other slaves from St Mavra were sold by Ahmed Pascha for ten soldi apiece to slavery in the Ottoman Empire
Chattel slavery was a major institution and a significant part of the Ottoman Empire's economy and traditional society.
The main sources of slaves were wars and politically organized enslavement expeditions in the Caucasus, Eastern Europe, S ...
.Miller, William. The Latins in the Levant: A History of Frankish Greece (1204–1566). London: 1908. p.486
With the exception of several coastal Venetian possessions, this was the end of Frankish rule in mainland Greece.
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Epirus, Despotate Of 1479 disestablishments States and territories established in 1205 Former monarchies of Europe Former countries in the Balkans 13th century in the Byzantine Empire Byzantine rump statesEpirus
Epirus () is a Region#Geographical regions, geographical and historical region, historical region in southeastern Europe, now shared between Greece and Albania. It lies between the Pindus Mountains and the Ionian Sea, stretching from the Bay ...
States and territories disestablished in 1479