Dephasing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 In
In physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
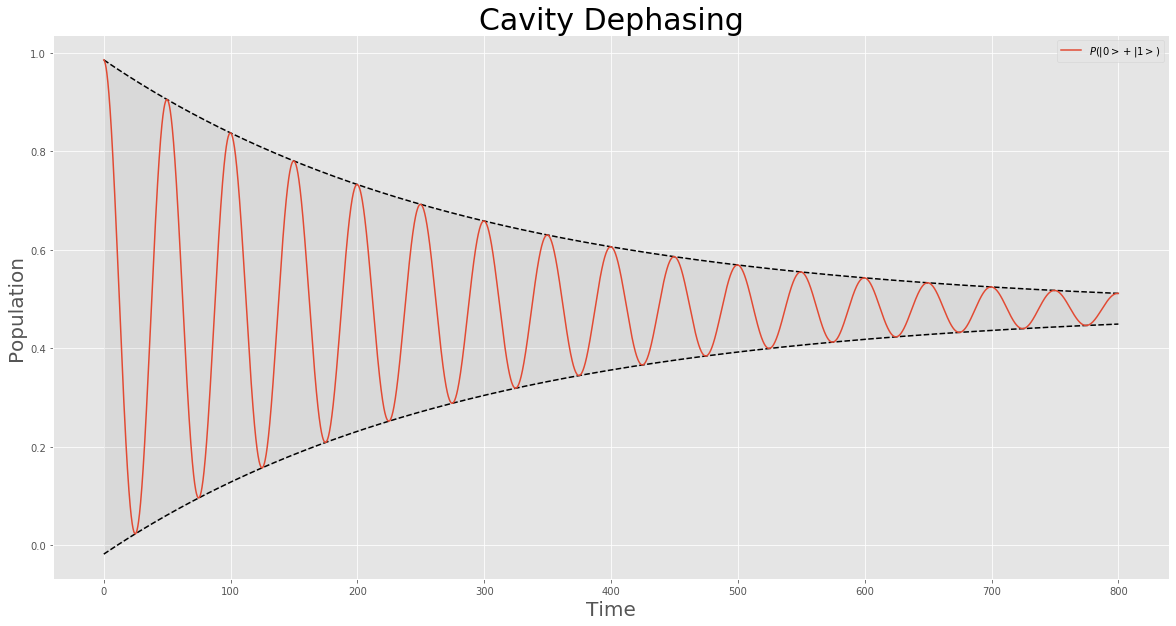
, dephasing is a mechanism that recovers classical behaviour from a quantum
In physics, a quantum (: quanta) is the minimum amount of any physical entity (physical property) involved in an interaction. The fundamental notion that a property can be "quantized" is referred to as "the hypothesis of quantization". This me ...
system. It refers to the ways in which coherence
Coherence is, in general, a state or situation in which all the parts or ideas fit together well so that they form a united whole.
More specifically, coherence, coherency, or coherent may refer to the following:
Physics
* Coherence (physics ...
caused by perturbation decays over time, and the system returns to the state before perturbation. It is an important effect in molecular and atomic spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets electromagnetic spectra. In narrower contexts, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Spectro ...
, and in the condensed matter physics
Condensed matter physics is the field of physics that deals with the macroscopic and microscopic physical properties of matter, especially the solid and liquid State of matter, phases, that arise from electromagnetic forces between atoms and elec ...
of mesoscopic
Mesoscopic physics is a subdiscipline of condensed matter physics that deals with materials of an intermediate size. These materials range in size between the nanoscale for a quantity of atoms (such as a molecule) and of materials measuring mic ...
devices.
The reason can be understood by describing the conduction in metals as a classical phenomenon with quantum effects all embedded into an effective mass that can be computed quantum mechanically, as also happens to resistance that can be seen as a scattering
In physics, scattering is a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities (including particles and radiat ...
effect of conduction electrons
In solid-state physics, the valence band and conduction band are the bands closest to the Fermi level, and thus determine the electrical conductivity of the solid. In nonmetals, the valence band is the highest range of electron energies in w ...
. When the temperature is lowered and the dimensions of the device are meaningfully reduced, this classical behaviour should disappear and the laws of quantum mechanics should govern the behavior of conducting electrons seen as waves that move ballistically
Ballistics is the field of mechanics concerned with the launching, flight behaviour and impact effects of projectiles, especially weapon munitions such as bullets, unguided bombs, rockets and the like; the science or art of designing and acceler ...
inside the conductor without any kind of dissipation. Most of the time this is what one observes. But it appeared as a surprise to uncover that the so-called dephasing time, that is the time it takes for the conducting electrons to lose their quantum behavior, becomes finite rather than infinite when the temperature approaches zero in mesoscopic devices violating the expectations of the theory of Boris Altshuler, Arkady Aronov and David E. Khmelnitskii. This kind of saturation of the dephasing time at low temperatures is an open problem
In science and mathematics, an open problem or an open question is a known problem which can be accurately stated, and which is assumed to have an objective and verifiable solution, but which has not yet been solved (i.e., no solution for it is kno ...
even as several proposals have been put forward.
The coherence of a sample is explained by the off-diagonal elements of a density matrix
In quantum mechanics, a density matrix (or density operator) is a matrix used in calculating the probabilities of the outcomes of measurements performed on physical systems. It is a generalization of the state vectors or wavefunctions: while th ...
. An external electric
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
or magnetic field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
can create coherences between two quantum state
In quantum physics, a quantum state is a mathematical entity that embodies the knowledge of a quantum system. Quantum mechanics specifies the construction, evolution, and measurement of a quantum state. The result is a prediction for the system ...
s in a sample if the frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
corresponds to the energy gap between the two states. The coherence terms decay with the dephasing time or spin–spin relaxation, ''T''2.
After coherence is created in a sample by light, the sample emits a polarization wave, the frequency of which is equal to and the phase
Phase or phases may refer to:
Science
*State of matter, or phase, one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist
*Phase (matter), a region of space throughout which all physical properties are essentially uniform
*Phase space, a mathematica ...
of which is inverted from the incident light. In addition, the sample is excited by the incident light and a population of molecules in the excited state
In quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Add ...
is generated. The light passing through the sample is absorbed because of these two processes, and it is expressed by an absorption spectrum
Absorption spectroscopy is spectroscopy that involves techniques that measure the absorption of electromagnetic radiation, as a function of frequency or wavelength, due to its interaction with a sample. The sample absorbs energy, i.e., photons, ...
. The coherence decays with the time constant
In physics and engineering, the time constant, usually denoted by the Greek language, Greek letter (tau), is the parameter characterizing the response to a step input of a first-order, LTI system theory, linear time-invariant (LTI) system.Concre ...
, ''T''2, and the intensity of the polarization wave is reduced. The population of the excited state also decays with the time constant of the longitudinal relaxation, ''T''1. The time constant ''T''2 is usually much smaller than ''T''1, and the bandwidth of the absorption spectrum is related to these time constants by the Fourier transform
In mathematics, the Fourier transform (FT) is an integral transform that takes a function as input then outputs another function that describes the extent to which various frequencies are present in the original function. The output of the tr ...
, so the time constant ''T''2 is a main contributor to the bandwidth. The time constant ''T''2 has been measured with ultrafast time-resolved spectroscopy directly, such as in photon echo experiments.
What is the dephasing rate of a particle that has an energy ''E'' if it is subject to a fluctuating environment that has a temperature ''T''? In particular what is the dephasing rate close to equilibrium (''E~T''), and what happens in the zero temperature limit? This question has fascinated the mesoscopic community during the last two decades (see references below).
See also
*Dephasing rate SP formula
The ''SP'' formula for the dephasing rate \Gamma_ of a particle that moves in a fluctuating environment unifies various results that have been obtained, notably in condensed matter physics, with regard to the motion of electrons in a metal. The g ...
References
Other
* (And references therein.) * * * * * *{{cite journal , last1=Frasca , first1=M. , year=2003 , title=Saturation of dephasing time in mesoscopic devices produced by a ferromagnetic state , journal=Physical Review B
''Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics'' (also known as PRB) is a peer-reviewed, scientific journal, published by the American Physical Society (APS). The Lead Editor of PRB is Stephen E. Nagler and the Chief Editor is Sarma ...
, volume=68 , issue=19 , pages=193413 , arxiv=cond-mat/0308377 , bibcode=2003PhRvB..68s3413F , doi=10.1103/PhysRevB.68.193413, s2cid=119498061
Wave mechanics
Quantum optics
Quantum information science
Mesoscopic physics