With a population of about 129 million in 2022,
Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
is the
10th most populated country in the world. It is the largest Spanish-speaking country in the world and the third-most populous country in the Americas after the United States and Brazil, the most populous city in the country is the capital,
Mexico City
Mexico City is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Mexico, largest city of Mexico, as well as the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North America. It is one of the most important cultural and finan ...
, with a population of 9.2 million and its
metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region consisting of a densely populated urban area, urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories which share Industry (economics), industries, commercial areas, Transport infrastructure, transport network ...
is also the most populated with 21.8 million as of 2020.
Approximately 53% of the population lives in one of the 48 large metropolitan areas in the country.
In total, about 76% of the population of the country lives in urban areas and 23% lives in rural ones.
[
Demographic censuses are performed by the ]Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía
The National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI from its former name in ) is an autonomous agency of the Mexican Government dedicated to coordinate the National System of Statistical and Geographical Information of the country. It w ...
. The National Population Council (CONAPO) is an institution under the Ministry of Interior
An interior ministry or ministry of the interior (also called ministry of home affairs or ministry of internal affairs) is a government department that is responsible for domestic policy, public security and law enforcement.
In some states, th ...
in charge of the analysis and research of population dynamics. The National Institute of Indigenous Peoples
The National Institute of Indigenous Peoples (, INPI, Tzotzil language, Tzotzil: ''Instituto Ta Sjunul Jlumaltik Sventa Batsi Jnaklometik,'' Qʼeqchiʼ language, Q'eqchi': ''Molam Tk’anjelaq Chi Rixeb’ Laj Ralch’och’'', Ixil language, Ixil ...
also undertakes research and analysis of the sociodemographic and linguistic indicators of the indigenous peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
. Throughout most of the 20th century Mexico's population was characterized by rapid growth. Although this tendency has been reversed and average annual population growth over the last five years was less than 1%, the demographic transition is still in progress; Mexico still has a large youth cohort.
Demographic dynamics

 Estimates vary for the Pre-Columbian population of Mexico from 1.5 million to 21 million, but the most accepted figure is about 12 million people, including the population of the
Estimates vary for the Pre-Columbian population of Mexico from 1.5 million to 21 million, but the most accepted figure is about 12 million people, including the population of the Aztec Empire
The Aztec Empire, also known as the Triple Alliance (, Help:IPA/Nahuatl, �jéːʃkaːn̥ t͡ɬaʔtoːˈlóːjaːn̥ or the Tenochca Empire, was an alliance of three Nahuas, Nahua altepetl, city-states: , , and . These three city-states rul ...
which is estimated at 6 million people. In 1600, the population was estimated to have been around 1 to 2 million, having drastically declined due to disease and warfare following Spanish conquest
The Spanish Empire, sometimes referred to as the Hispanic Monarchy or the Catholic Monarchy, was a colonial empire that existed between 1492 and 1976. In conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, it ushered in the European Age of Discovery. It ...
. By 1700, the population was estimated to be around 4 million.
In 1900, the Mexican population was 13.6 million. During the period of economic prosperity that was dubbed by economists as the "Mexican Miracle", the government invested in efficient social programs that reduced the infant mortality
Infant mortality is the death of an infant before the infant's first birthday. The occurrence of infant mortality in a population can be described by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the number of deaths of infants under one year of age ...
rate and increased life expectancy
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where '' ...
. These measures jointly led to an intense demographic increase between 1930 and 1980.
Intense population growth in the northern states, especially along the US-Mexican border, changed the country's demographic profile in the second half of the 20th century, as the 1967 US-Mexico maquiladora
A (), or (), is a factory that is largely duty (economics), duty free and tariff free. These factories take raw materials and assemble, manufacture, or process them and export the finished product. These factories and systems are present thro ...
agreement through which all products manufactured in the border cities could be imported duty-free to the US. Since the adoption of NAFTA in 1994, however, which allows all products to be imported duty-free regardless of their place of origin within Mexico, the non-border maquiladora share of exports has increased while that of border cities has decreased. This has led to decentralization and rapid economic growth in Mexican states (and cities), such as Quintana Roo (Cancun), Baja California Sur (La Paz), Nuevo León (Monterrey), Querétaro, and Aguascalientes whose population grew by more than one-third from 2000 to 2015, while the whole of Mexico grew by 22.6% in this period.
While the national annual growth rate was still positive (1.0%) in the early years of the 2000s, the national net migration rate was negative (-4.75/1000 inhabitants), in the 2010s, however, the net migration rate reached 0, given the strong economy of Mexico, changes in US Immigration Policy & Enforcement, US Legislative and CFR-8 decisions, plus the (then) slowly recovering US economy, causing many of its former residents to return. Given the former strong flow of immigrants to the United States; an estimated 5.3 million undocumented Mexican immigrants lived in the United States in 2004 and 18.2 million American citizens in the 2000 Census declared having Mexican ancestry.
The population's annual growth rate has been reduced from a 3.5% peak in 1965 to 0.99% in 2005. While Mexico is now transitioning to the third phase of demographic transition
In demography, demographic transition is a phenomenon and theory in the Social science, social sciences referring to the historical shift from high birth rates and high Mortality rate, death rates to low birth rates and low death rates as societi ...
, close to 50% of the population in 2009 was 25 years old or younger. Fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were t ...
s have also decreased from 5.7 children per woman in 1976 to 1.9 in 2020.COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
. The Mexican government projects that the country's population will grow to about 123 million by 2042 and then start declining slowly. Assumptions underlying this projection include fertility stabilizing at 1.85 children per woman and continued high net emigration (slowly decreasing from 583,000 in 2005 to 393,000 in 2050).
Mexico is composed of 32 federal entities which include 31 states and Mexico City, the five most populous federal entities in 2020 were the State of Mexico
The State of Mexico, officially just Mexico, is one of the 32 federal entities of the United Mexican States. Colloquially known as Edomex (from , the abbreviation of , and ), to distinguish it from the name of the whole country, it is the mo ...
(16.9 million), Mexico City (9.2 million), Jalisco
Jalisco, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Jalisco, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is located in western Mexico and is bordered by s ...
(8.3 million), Veracruz (8.0 million) and Puebla
Puebla, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Puebla, is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its capital is Puebla City. Part of east-centr ...
(6.5 million), which collectively contain around 40% of the national population.Greater Mexico City
Greater Mexico City is the conurbation around Mexico City, officially called the Metropolitan Area of the Valley of Mexico (). It encompasses Mexico City itself and 60 adjacent municipalities of Mexico, municipalities of the State of Mexico and Hi ...
metro area
Metro Area is a Brooklyn-based house and nu-disco duo formed in 1998 by Morgan Geist and Darshan Jesrani.
History
Geist grew up in Wayne, New Jersey, Spring Arts Clubs: Electro-Shock by Tricia Romano">village voice > nyclife > Spring Arts ...
, which includes Mexico City and adjacent municipalities of surrounding states, is the most populous in the country and is estimated to be the second most populous in the world (after Tokyo), according to the UN Urbanization Report.
The average annual population growth rate of Mexico City
Mexico City is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Mexico, largest city of Mexico, as well as the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North America. It is one of the most important cultural and finan ...
was 0.2%. The state with the lowest population growth rate over the same period was Michoacán
Michoacán, formally Michoacán de Ocampo, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Michoacán de Ocampo, is one of the 31 states which, together with Mexico City, compose the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. The stat ...
(-0.1%), whereas the states with the highest population growth rates were Quintana Roo
Quintana Roo, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Quintana Roo, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, constitute the 32 administrative divisions of Mexico, federal entities of Mexico. It is divided into municipalities of ...
(4.7%) and Baja California Sur
Baja California Sur, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California Sur, is a state in Mexico. It is the 31st and last state to be admitted, in 1974. It is also the second least populated Mexican state and the ninth-largest state by ...
(3.4%), both of which are two of the least populous states and the last to be admitted to the Union in the 1970s. The average annual net migration rate
The net migration rate is the difference between the number of immigrants (people coming into an area) and the number of emigrants (people leaving an area) per year divided by the population. When the number of immigrants is larger than the num ...
of Mexico City over the same period was negative and the lowest of all political divisions of Mexico
Mexico is a federal republic composed of 32 federative entities (): 31 states and Mexico City. According to the Constitution of Mexico, the states of the federation are free and sovereign in all matters concerning their internal affairs. Sin ...
, whereas the states with the highest net migration rate were Quintana Roo (2.7), Baja California
Baja California, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California, is a state in Mexico. It is the northwesternmost of the 32 federal entities of Mexico. Before becoming a state in 1952, the area was known as the North Territory of B ...
(1.8) and Baja California Sur (1.6).
UN estimates
According to the 2012 revision of the World Population Prospects, the total population was 117,886,000 in 2010, compared to only 28,296,000 in 1950. The proportion of children below the age of 15 in 2010 was 30%, 64% of the population was between 15 and 65 years of age, and 6% was 65 years or older.
Structure of the population
Population by Sex and Age Group (Census 12.VI.2010; including an estimation of 1 334 585 people corresponding to 448 195 housing units without information of the occupants):
Population by Sex and Age Group (Census 15.III.2020) (Including an estimation of 6 337 751 persons corresponding to 1 588 422 housing units without information of the occupants.):
Vital statistics
Registered births and deaths
Source: Instituto Nacional de Estadística, Geografía e Informática
The National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI from its former name in ) is an autonomous agency of the Mexican Government dedicated to coordinate the National System of Statistical and Geographical Information of the country. It w ...
(INEGI)
Current vital statistics
CBR and CDR estimates
The following estimates were prepared by the Instituto Nacional de Estadística, Geografía e Informatica:

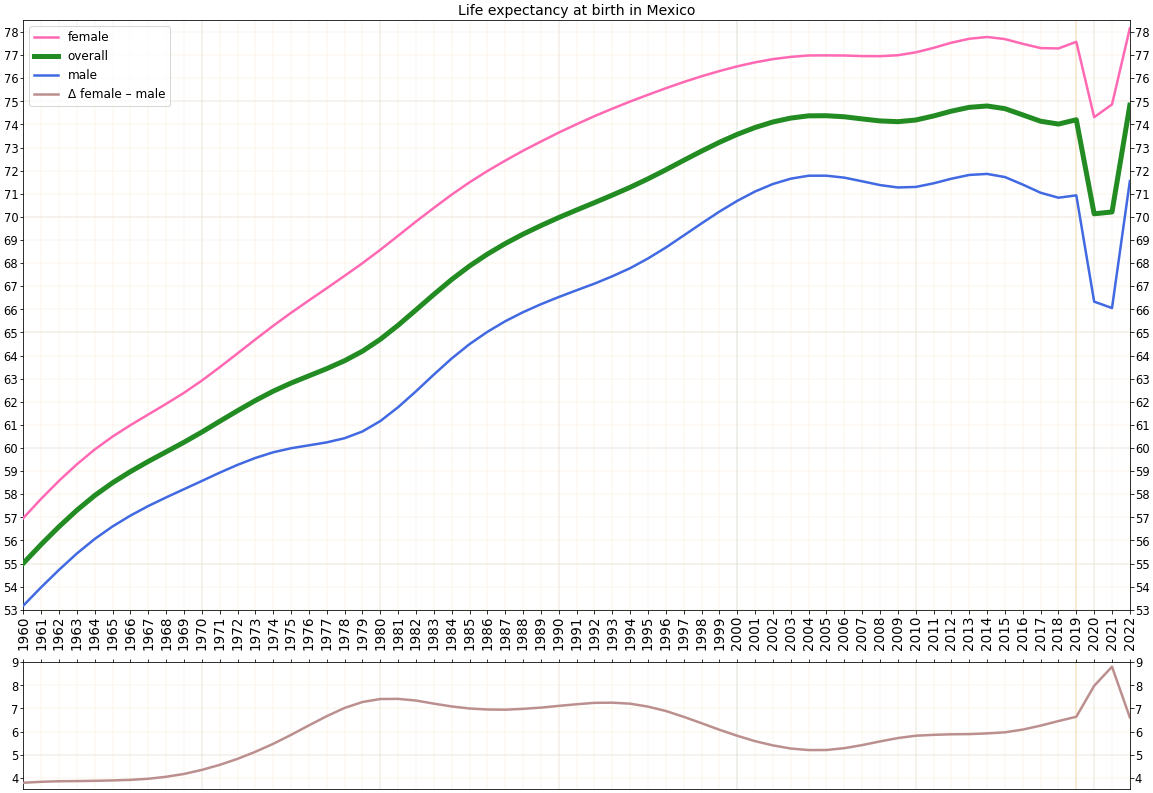
Life expectancy from 1893 to 1950
Life expectancy
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where '' ...
in Mexico from 1893 to 1950. Source: Our World In Data
Our World in Data (OWID) is a scientific online publication that focuses on large global problems such as poverty, disease, hunger, war, climate change, population growth, existential risks, and inequality.
It is a project of the Global Cha ...
UN estimates
The Population Department of the United Nations prepared the following estimates.
International migration
Immigration to Mexico
Aside from the original Spanish colonists, many Europeans immigrated to Mexico in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Non-Spanish immigrant groups included British, Irish, Italian, German, French and Dutch.[Conmemoran 100 años de inmigración coreana](_blank)
The PRI governments, in power for most of the 20th century, had a policy of granting asylum to fellow Latin Americans fleeing political persecution in their home countries. This led to the arrival of immigrants, mainly political refugees from Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
, Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America. It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica, stretching along a narrow strip of land between the Andes, Andes Mountains and the Paci ...
, Cuba
Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the ...
, Peru
Peru, officially the Republic of Peru, is a country in western South America. It is bordered in the north by Ecuador and Colombia, in the east by Brazil, in the southeast by Bolivia, in the south by Chile, and in the south and west by the Pac ...
, Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuel ...
and Central America during the 1970s and 1980s.
A second wave of immigrants has come to Mexico as a result of the economic crises experienced by some countries in the region. The Argentine community is quite significant estimated to be somewhere between 11,000 and 30,000. Due to the 2008–2014 Spanish financial crisis
The 2008–2014 Spanish financial crisis, also known as the Great Recession in Spain or the Great Spanish Depression, began in 2008 during the 2008 financial crisis. In 2012, it made Spain a late participant in the European sovereign debt crisi ...
, many Spaniards have been emigrating to Mexico to seek new opportunities. For example, during the last quarter of 2012, a number of 7,630 work permits were granted to Spaniards. In recent time, the country has also received increasing numbers of refugees and migrants from the Caribbean and Central America.North American Free Trade Agreement
The North American Free Trade Agreement (, TLCAN; , ALÉNA), referred to colloquially in the Anglosphere as NAFTA, ( ) was an agreement signed by Canada, Mexico, and the United States that created a trilateral trade bloc in North America. The ...
(NAFTA), but also by the fact that Mexico has become a popular destination for retirees, especially the small towns: just in the State of Guanajuato, in San Miguel de Allende
San Miguel de Allende () is the principal city in the Municipalities of Mexico, municipality of San Miguel de Allende (municipality), San Miguel de Allende, located in the far eastern part of Guanajuato, Mexico. A part of the Bajío region, the t ...
and its surroundings, 10,000 Americans have their residence.
Discrepancies between the figures of official legal immigrants and all foreign-born residents is quite large. The official figure for foreign-born residents in Mexico in 2020 was 1,212,252,Chiapas
Chiapas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas, is one of the states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises Municipalities of Chiapas, 124 municipalities and its capital and large ...
, where the majority of immigrants are from Central America.
Emigration from Mexico
 The national
The national net migration rate
The net migration rate is the difference between the number of immigrants (people coming into an area) and the number of emigrants (people leaving an area) per year divided by the population. When the number of immigrants is larger than the num ...
of Mexico is negative, estimated at 1.8 migrants per 1,000 population .
The great majority of Mexican emigrants have moved to the United States of America, this migration phenomenon has been a defining feature in the relationship of both countries for most of the 20th century.[ In the year 2000 approximately 20 million American residents identified themselves as either Mexican, Mexican-Americans or of Mexican origin, making "Mexican" the sixth-most cited ancestry of all US residents.
In the year 2000 the INEGI estimated that about eight million Mexican-born people, which then was equivalent to 8.7% of the population of Mexico itself, lived in the United States of America and according to the Pew Hispanic Center in 2006, an estimated ten percent of all Mexican citizens lived in the United States. For the 2015-2020 period the states who sent the highest percentages of migrants to the United States were Guanajuato (7.8%), Jalisco (7.5%), Michoacán (6.3%) y el Estado de México (5.4%), with the total number of migrants being 803 thousand people,]2008 financial crisis
The 2008 financial crisis, also known as the global financial crisis (GFC), was a major worldwide financial crisis centered in the United States. The causes of the 2008 crisis included excessive speculation on housing values by both homeowners ...
, which reduced available jobs, and to the introduction of stricter immigration laws in many States. According to the Pew Hispanic Center the total number of Mexican-born people had stagnated in 2010 and then began to fall. After the Mexican-American community, Mexican Canadian
Mexican Canadians (, ) are Canadians, Canadian citizens of Mexican origin, either through birth or ethnicity, who reside in Canada. According to the 2021 Census, 155,380 Canadians indicated they were of full or partial Mexican ancestry (0.42% of ...
s are the second-largest group of emigrant Mexicans, with a population of over 90,000.Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
during the era of the Viceroyalty of New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( ; Nahuatl: ''Yankwik Kaxtillan Birreiyotl''), originally the Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain. It was one of several ...
, when the Philippines was a territory under the rule of Mexico city. Mexicans live throughout Latin America as well as in Australia, France, Germany, Italy, and the United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE), or simply the Emirates, is a country in West Asia, in the Middle East, at the eastern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is a Federal monarchy, federal elective monarchy made up of Emirates of the United Arab E ...
.
Cities and metropolitan areas
Settlements, cities and municipalities
 In 2010, Mexico had more than 189,432 ''localidades'' (lit. "localities" or "settlements"), which are census-designated places defined as a small town, a large city, or simply as a single unit housing in a rural area whether situated remotely or close to an urban area.
In 2010, Mexico had more than 189,432 ''localidades'' (lit. "localities" or "settlements"), which are census-designated places defined as a small town, a large city, or simply as a single unit housing in a rural area whether situated remotely or close to an urban area.["Proyecto para dotar de conectividad a una región marginada en México"]
page 4, retrieved on September 7, 2024. Localities with more than 2,500 inhabitants are considered urban settlements whereas thos with less than 2500 inhabitants are considered rural settlements. In 2010 there were 3,021 cities with a population between 2,500 and 15,000 inhabitants, 413 with a population between 15,000 and 50,000 inhabitants, 86 with a population between 50,000 and 100,000, 95 with a population between 100,000 and 500,000, 25 with a population between 500,000 and one million and 11 with a population of more than one million. Urban areas contain 76.81% of Mexico's total population and rural settlements contain 23% of the population.["Programa Nacional de Ordenamiento Territorial y Urbano"]
page 27, retrieved in August 28, 2024.
Municipalities
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality' ...
(''municipios'' in Spanish) and boroughs
A borough is an administrative division in various English language, English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
...
(''delegaciones'' in Spanish) are incorporated places in Mexico, that is, second or third-level political divisions with internal autonomy, legally prescribed limits, powers and functions. In terms of second-level political divisions there are 2,477 municipalities, including 16 semi-autonomous boroughs all within Mexico city.["Mexico en cifras"]
INEGI, retrieved in September 1, 2024. A municipality can be constituted by one or more cities one of which is the ''cabecera municipal'' (municipal seat). Cities are usually contained within the limits of a single municipality, with a few exceptions in which small areas of one city may extend to other adjacent municipalities ''without'' incorporating the city which serves as the municipal seat of the adjacent municipality. Some municipalities or cities within municipalities are further divided into ''delegaciones'' or boroughs. However, unlike the boroughs of the Federal District, these are third-level administrative divisions; they have very limited autonomy and no elective representatives.
Municipalities in central Mexico are usually very small in area and thus coextensive with cities (as is the case of Guadalajara, Puebla and León), whereas municipalities in northern and southeastern Mexico are much larger and usually contain more than one city or town that may not necessarily conform a single urban agglomeration (as is the case of Tijuana).
Metropolitan areas
 A metropolitan area in Mexico is defined as a group of municipalities that heavily interact with each other, usually around a core city.
A metropolitan area in Mexico is defined as a group of municipalities that heavily interact with each other, usually around a core city.[CONAPO Áreas Metropolitanas](_blank)
In 2004, a joint effort between CONAPO, INEGI
The National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI from its former name in ) is an autonomous agency of the Government of Mexico, Mexican Government dedicated to coordinate the National System of Statistical and Geographical Information ...
and the Ministry of Social Development (SEDESOL) agreed to define metropolitan areas as either:["Metropolis de México 2020"]
Retrieved September 7, 2024. The most populous metropolitan area in Mexico is the ''Metropolitan Area of the Valley of Mexico'', or Greater Mexico City
Greater Mexico City is the conurbation around Mexico City, officially called the Metropolitan Area of the Valley of Mexico (). It encompasses Mexico City itself and 60 adjacent municipalities of Mexico, municipalities of the State of Mexico and Hi ...
, which in 2020 had a population of 21.8 million, or around 18% of the nation's population. The next four largest metropolitan areas in Mexico are Greater Monterrey (5.3 million), Greater Guadalajara (5.2 million), Greater Puebla (3.2 million) and Greater Toluca
Greater Toluca or the Metropolitan Area of Toluca is the conurbation formed by Toluca, as the core city, and 12 adjacent municipalities of the state of Mexico, namely Almoloya de Juárez, Calimaya, Chapultepec, Lerma, Metepec, Mexicaltzingo ...
(2.3 million),
Other demographic statistics
 Demographic statistics according to the
Demographic statistics according to the CIA World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the United States' Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print ve ...
, unless otherwise indicated.
Median age
:total: 30.6 years (2023 est.). Country comparison to the world: 130th
:male: 28.2 years
:female: 30.4 years (2020 est.)
:total: 28.6 years Country comparison to the world: 135th
:male: 27.5 years
:female: 29.7 years (2018 est.)
Contraceptive prevalence rate
:73.1% (2018)
:66.9% (2015)
Mother's mean age at first birth
:21.3 years (2008 est.)
Major infectious diseases
:degree of risk: intermediate (2020)
:food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea and hepatitis A
:vectorborne diseases: dengue fever
Note: a new coronavirus is causing sustained community spread of respiratory illness (COVID-19) in Mexico; sustained community spread means that people have been infected with the virus, but how or where they became infected is not known, and the spread is ongoing; illness with this virus has ranged from mild to severe with fatalities reported; as of June 6, 2022, Mexico has reported a total of 5,782,405 cases of COVID-19 or 4,484.8 cumulative cases of COVID-19 per 100,000 population with a total of 324,966 cumulative deaths or a rate of 252 cumulative deaths per 100,000 population; as of May 20, 2022, 66.68% of the population has received at least one dose of COVID-19 vaccine.
Dependency ratio
The dependency ratio is an age-population ratio of those typically not in the labor force (the ''dependent'' part ages 0 to 14 and 65+) and those typically in the labor force (the ''productive'' part ages 15 to 64). It is used to measure the press ...
s
:total dependency ratio: 51.4 (2015 est.)
:youth dependency ratio: 41.6 (2015 est.)
:elderly dependency ratio: 9.8 (2015 est.)
: potential support ratio: 10.2 (2015 est.)
Urbanization
:urban population: 81.3% of total population (2022)
:rate of urbanization: 1.4% annual rate of change (2020–25 est.)
:urban population: 80.2% of total population (2018)
:rate of urbanization: 1.59% annual rate of change (2015–20 est.)
Obesity – adult prevalence rate
:28.9% (2016) Country comparison to the world: 29th
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
:4.7% (2018/19) Country comparison to the world: 80th
:4.2% (2016) Country comparison to the world: 87th
Education expenditures
:4.3% of GDP (2018) Country comparison to the world: 92nd
:5.2% of GDP (2015) Country comparison to the world: 59th
Literacy
definition: age 15 and over can read and write (2016 est.)
:total population: 95.2%
:male: 96.1%
:female: 94.5% (2020)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
:total: 15 years
:male: 15 years
:female: 15 years (2019)
Unemployment, youth ages 15–24
:total: 8.1%
:male: 7.8%
:female: 8.7% (2020 est.)
Ethnic groups
 Although Mexico is an ethnically diverse country, for most of the 20th century and early 21st century the Mexican government has not conducted surveys regarding the ethnic origin of the population, except for indigenous peoples. However, recently the Mexican National Institute of Statistics and Geography has begun conducting surveys to quantify the percentage of Afro-descendant Mexicans, as well as Euro-descendant Mexicans living in the country. However, the results of surveys on the population of Euro-descendants has never been published.
Regardless of ethnicity, the majority of Mexicans are united under the same national identity.
Although Mexico is an ethnically diverse country, for most of the 20th century and early 21st century the Mexican government has not conducted surveys regarding the ethnic origin of the population, except for indigenous peoples. However, recently the Mexican National Institute of Statistics and Geography has begun conducting surveys to quantify the percentage of Afro-descendant Mexicans, as well as Euro-descendant Mexicans living in the country. However, the results of surveys on the population of Euro-descendants has never been published.
Regardless of ethnicity, the majority of Mexicans are united under the same national identity.[Wimmer, Andreas, 2002. ''Nationalist Exclusion and Ethnic Conflict: Shadows of Modernity'', Cambridge University Press page 115] This is the product of an ideology strongly promoted by Mexican academics such as Manuel Gamio and José Vasconcelos
José Vasconcelos Calderón (28 February 1882 – 30 June 1959), called the "cultural " of the Mexican Revolution, was an important Mexicans, Mexican writer, philosopher, and politician. He is one of the most influential and controversial pers ...
known as mestizaje
( , ; fem. , literally 'mixed person') is a term primarily used to denote people of mixed Ethnic groups in Europe, European and Indigenous ancestry in the former Spanish Empire. In certain regions such as Latin America, it may also refer to ...
, whose goal was that of Mexico becoming a racially and culturally homogeneous country.Latin American
Latin Americans (; ) are the citizenship, citizens of Latin American countries (or people with cultural, ancestral or national origins in Latin America).
Latin American countries and their Latin American diaspora, diasporas are Metroethnicity, ...
countries, Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
does not have a dominant ethnic group at the national level since many areas have different ethnic groups in majority and minority. Several genetic and anthropological studies have shown that the miscegenation in Mexico
Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar ...
is very diverse and different in each region of the country, for example, in the central regions where large Mesoamerican cultures flourished, and where there was a great fusion between Spaniards and Amerindians, a mostly balanced mestizaje is noted, while in the more rural southern regions, Amerindian ancestry predominates, while in the northern and western regions of the country, the population is predominantly of European ancestry, because the native populations existed in a much smaller number, leading to those territories being inhabited mainly by Spanish settlers and their descendants. Each region of the Mexican territory is different in society, culture and traditions.
During most of the 20th century these censuses' results were taken as fact, with extraofficial international publications often using them as a reference to estimate Mexico's racial composition,["México sin mestizaje: una reinterpretación de nuestra historia"](_blank)
''UNAM'', 2016. Retrieved March 13, 2019.[Bartolomé, Miguel Alberto. (1996) "Pluralismo cultural y redefinicion del estado en México". in Coloquio sobre derechos indígenas, Oaxaca, IO]
p. 2 arguing that an alteration so drastic of population trends compared to earlier censuses such as New Spain's 1793 census (on which Europeans were estimated to be 18% to 22% of the population, Mestizos 21% to 25%, and Indigenous peoples 51% to 61%)
Mestizo Mexicans
A large majority of Mexicans have been classified as "Mestizos", meaning in modern Mexican usage that they neither identify fully with any indigenous culture nor with a Spanish cultural heritage, but rather identify as having cultural traits incorporating elements from both indigenous and Spanish traditions. By the deliberate efforts of post-revolutionary governments, the "Mestizo identity" was constructed as the base of the modern Mexican national identity, through a process of cultural synthesis referred to as ''mestizaje'' . Mexican politicians and reformers such as José Vasconcelos
José Vasconcelos Calderón (28 February 1882 – 30 June 1959), called the "cultural " of the Mexican Revolution, was an important Mexicans, Mexican writer, philosopher, and politician. He is one of the most influential and controversial pers ...
and Manuel Gamio were instrumental in building a Mexican national identity upon this concept, [Wade (1981:32)] which were designed with the main goal of "helping" indigenous peoples to achieve the same level of progress as the rest of society by transforming indigenous communities into Mestizo ones, eventually assimilating them into the Mestizo Mexican society.
According to many 20th- and 21st-century academics, large scale intermixing between the European immigrants and the native Indigenous peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
would result in Mestizos making up the vast majority of Mexico's population by the time of the Mexican Revolution
The Mexican Revolution () was an extended sequence of armed regional conflicts in Mexico from 20 November 1910 to 1 December 1920. It has been called "the defining event of modern Mexican history". It saw the destruction of the Federal Army, its ...
.colonial times
The ''Colonial Times'' was a newspaper in what is now the Australian state of Tasmania. It was established as the ''Colonial Times, and Tasmanian Advertiser'' in 1825 in Hobart, Van Diemen's Land
Van Diemen's Land was the colon ...
show that the majority of Spanish men married with Spanish women. Said registers also put in question other assumptions held by contemporary academics, such as the claim that European immigrants who arrived to Mexico were almost exclusively men, or that "pure Spanish" people were part of a small powerful elite, as Spaniards were often the most numerous ethnic group in the colonial citiesEncyclopædia Britannica
The is a general knowledge, general-knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It has been published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. since 1768, although the company has changed ownership seven times. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, ...
'', which uses a biology-based approach, around three-fifths of the Mexican population is Mestizo[R. Martínez & C. De La Torre (2008)]
"Racial Appearance And Income In Contemporary Mexico, pag 9 note 1"
, ''Journal of Diversity Management'', 2008. Retrieved April 1, 2021. with "static" racial labels such as White, Indian, Black etc. being more commonly used. The use of variated methods and criteria to quantify the number of Mestizos in Mexico is not new: Since several decades ago, many authors have analyzed colonial censuses data and have made different conclusions regarding the ethnic composition of the population of colonial Mexico/New Spain. Some historians, such as Gonzalo Aguirre-Beltrán who claimed in 1972 that practically the totality of New Spain's population, in reality, were Mestizos, using to back up his claims arguments such as that affairs of Spaniards with non-Europeans due to the alleged absence of female European immigrants were widespread as well as there being a huge desire of Mestizos to "pass" as Spaniards, this because Spanishness was seen as a symbol of high status.
The use of variated methods and criteria to quantify the number of Mestizos in Mexico is not new: Since several decades ago, many authors have analyzed colonial censuses data and have made different conclusions regarding the ethnic composition of the population of colonial Mexico/New Spain. Some historians, such as Gonzalo Aguirre-Beltrán who claimed in 1972 that practically the totality of New Spain's population, in reality, were Mestizos, using to back up his claims arguments such as that affairs of Spaniards with non-Europeans due to the alleged absence of female European immigrants were widespread as well as there being a huge desire of Mestizos to "pass" as Spaniards, this because Spanishness was seen as a symbol of high status.["Racismo, falso mestizaje y desigualdad social en México"](_blank)
''Revista Cuadrivio'', 2016. Retrieved March 13, 2019. According to some 21st-century historians, Aguirre Beltran also disregards facts such as the population dynamics of New Spain being different depending on the region at hand (i.e. miscegenation could not happen in a significant amount in regions where the native population was openly hostile until the early 20th century, such as most of New Spain's internal provinces, which nowadays are the northern and western regions of Mexico),
According to some 21st-century historians, Aguirre Beltran also disregards facts such as the population dynamics of New Spain being different depending on the region at hand (i.e. miscegenation could not happen in a significant amount in regions where the native population was openly hostile until the early 20th century, such as most of New Spain's internal provinces, which nowadays are the northern and western regions of Mexico),
Indigenous peoples
 The 2003 General Law of Linguistic Rights of the Indigenous Peoples recognizes 62
The 2003 General Law of Linguistic Rights of the Indigenous Peoples recognizes 62 indigenous languages
An indigenous language, or autochthonous language, is a language that is native to a region and spoken by its indigenous peoples. Indigenous languages are not necessarily national languages but they can be; for example, Aymara is both an indigeno ...
as "national languages" which have the same validity as Spanish in all territories in which they are spoken.["Ley General de Derechos Lingüísticos de los Pueblos Indígenas"](_blank)
The recognition of indigenous languages and the protection of indigenous cultures is granted not only to the ethnic groups indigenous to modern-day Mexican territory, but also to other North American indigenous groups that migrated to Mexico from the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, such as the KikapúGuatemala
Guatemala, officially the Republic of Guatemala, is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico, to the northeast by Belize, to the east by Honduras, and to the southeast by El Salvador. It is hydrologically b ...
in the 1980s.["Encuesta Intercensal 2015"](_blank)
, "INEGI
The National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI from its former name in ) is an autonomous agency of the Government of Mexico, Mexican Government dedicated to coordinate the National System of Statistical and Geographical Information ...
", Mexico, December 2015. Retrieved April 28, 2017. According to the 2020 national Mexican census, 19.4% of the population self-identified as Indigenous. Surveys made by the Mexican government do count as Indigenous all persons who speak an indigenous language and people who do not speak indigenous languages nor live in indigenous communities but self-identify as Indigenous. According to these criteria, the (Comisión Nacional para el Desarrollo de los Pueblos Indígenas, or CDI in Spanish) and the
Surveys made by the Mexican government do count as Indigenous all persons who speak an indigenous language and people who do not speak indigenous languages nor live in indigenous communities but self-identify as Indigenous. According to these criteria, the (Comisión Nacional para el Desarrollo de los Pueblos Indígenas, or CDI in Spanish) and the INEGI
The National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI from its former name in ) is an autonomous agency of the Government of Mexico, Mexican Government dedicated to coordinate the National System of Statistical and Geographical Information ...
(Mexico's National Institute of Statistics and Geography), state that there are 15.7 million indigenous people in Mexico of many different ethnic groups,Yucatán
Yucatán, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Yucatán, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, constitute the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 106 separate municipalities, and its capital city is Mérida.
...
(59%), Oaxaca
Oaxaca, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca, is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of the Mexico, United Mexican States. It is divided into municipalities of Oaxaca, 570 munici ...
(48%), Quintana Roo
Quintana Roo, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Quintana Roo, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, constitute the 32 administrative divisions of Mexico, federal entities of Mexico. It is divided into municipalities of ...
(39%), Chiapas
Chiapas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas, is one of the states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises Municipalities of Chiapas, 124 municipalities and its capital and large ...
(28%), Campeche
Campeche, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Campeche, is one of the 31 states which, with Mexico City, make up the Administrative divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. Located in southeast Mexico, it is bordered by the sta ...
(27%), Hidalgo (24%), Puebla
Puebla, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Puebla, is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its capital is Puebla City. Part of east-centr ...
(19%), Guerrero
Guerrero, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guerrero, is one of the 32 states that compose the administrative divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Guerrero, 85 municipalities. The stat ...
(17%), San Luis Potosí
San Luis Potosí, officially the Free and Sovereign State of San Luis Potosí, is one of the 32 states which compose the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 59 municipalities and is named after its capital city, San Luis Potosí.
It ...
(15%) and Veracruz
Veracruz, formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entit ...
(15%). Oaxaca is the state with the greatest number of distinct indigenous peoples and languages in the country.
White Mexicans
White Mexicans are Mexicans
Mexicans () are the citizens and nationals of the Mexico, United Mexican States. The Mexican people have varied origins with the most spoken language being Spanish language, Spanish, but many also speak languages from 68 different Languages o ...
of total or predominantly European or West Asian
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian ...
ancestry, and/or those with a European phenotype.[en el año de 1808 aproximadamente el 60% de la población de lo que sería México pertenecía a la categoría étnica de indígena, el 18% eran europeos o de origen europeo (de los cuales la inmensa mayoría eran criollos nacidos en México)](_blank)
. Spaniards and other Europeans began arriving in Mexico during the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire
The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire was a pivotal event in the history of the Americas, marked by the collision of the Aztec Triple Alliance and the Spanish Empire. Taking place between 1519 and 1521, this event saw the Spanish conquistad ...
and continued immigrating to the country during colonial and independent Mexico. This ethnic group contrasts with the Afro-Mexican and Indigenous Mexican groups in the fact that phenotype (hair color, skin color etc.) is often used as the main criterion to delineate it.["Por estas razones el color de piel determina las oportunidades de los mexicanos"]
, ''Huffington post'', July 26, 2017. Retrieved April 30, 2018.["Presenta INEGI estudio que relaciona color de piel con oportunidades"]
, ''El Universal'', June 16, 2017. Retrieved April 30, 2018.The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a Reference work, reference resource produced by the United States' Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The off ...
, which uses the 1921 census results as the base of its estimations, calculates this population as only 10%,American Sociological Association
The American Sociological Association (ASA) is a non-profit organization dedicated to advancing the discipline and profession of sociology. Founded in December 1905 as the American Sociological Society at Johns Hopkins University by a group of fi ...
obtained a percentage of 18.8% among the general population, having its higher frequency on the North region (22.3%–23.9%) followed by the Center region (18.4%–21.3%) and the South region (11.9%). Another study made by the University College London
University College London (Trade name, branded as UCL) is a Public university, public research university in London, England. It is a Member institutions of the University of London, member institution of the Federal university, federal Uni ...
in collaboration with Mexico's National Institute of Anthropology and History found that the frequencies of blond hair and light eyes in Mexicans are of 18% and 28% respectively,National Council to Prevent Discrimination
The National Council to Prevent Discrimination (; CONAPRED) is a Mexican government agency created in 2003 by Federal Law to Prevent and Eliminate Discrimination and to promote policies and measures to contribute to the cultural and social develop ...
and the National Institute of Statistics and Geography
The National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI from its former name in ) is an autonomous agency of the Mexican Government dedicated to coordinate the National System of Statistical and Geographical Information of the country. It w ...
reporting results that estimate light skinned Mexicans at about one-third of the country's population.Mestizo
( , ; fem. , literally 'mixed person') is a term primarily used to denote people of mixed European and Indigenous ancestry in the former Spanish Empire. In certain regions such as Latin America, it may also refer to people who are culturall ...
s, while having a very low frequency (5–10%) in Caucasian children.Mexican Social Security Institute
The Mexican Institute of Social Security (, IMSS) is a Federal government of the United Mexican States, governmental organization that assists public health, pensions and social security in Mexico operating under the Secretariat of Health (Mexic ...
(shortened as IMSS) nationwide, around half of Mexican babies have the Mongolian spot.
 Mexico's northern and western regions have the highest percentages of
Mexico's northern and western regions have the highest percentages of white
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no chroma). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully (or almost fully) reflect and scatter all the visible wa ...
population, with the majority of the people being of predominantly European ancestry.["Nómadas y sedentarios, El pasado prehispánico de Zacatecas"](_blank)
''Mesoweb'', Mexico, page 10, retrieved on July 7, 2024. This eventually led the northeast region of the country to become the region with the highest proportion of whites during the Spanish colonial period, albeit recent migration waves have been changing its demographic trends.["Transición migratoria y demográfica de México. Nuevos patrones"](_blank)
page 17, retrieved on September 12, 2024.
 While the majority of European immigration to Mexico has been Spanish with the first wave starting with the colonization of America and the last one being a consequence of the
While the majority of European immigration to Mexico has been Spanish with the first wave starting with the colonization of America and the last one being a consequence of the Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War () was a military conflict fought from 1936 to 1939 between the Republican faction (Spanish Civil War), Republicans and the Nationalist faction (Spanish Civil War), Nationalists. Republicans were loyal to the Left-wing p ...
of 1937, immigrants from other European countries have arrived to Mexico as well. During the Second Mexican Empire
The Second Mexican Empire (; ), officially known as the Mexican Empire (), was a constitutional monarchy established in Mexico by Mexican monarchists with the support of the Second French Empire. This period is often referred to as the Second ...
, the immigration was mostly French. Then, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, spurred by government policies of Porfirio Díaz
José de la Cruz Porfirio Díaz Mori (; ; 15 September 1830 – 2 July 1915) was a General (Mexico), Mexican general and politician who was the dictator of Mexico from 1876 until Mexican Revolution, his overthrow in 1911 seizing power in a Plan ...
, migrants came mainly from Italy, Germany, the United Kingdom, and Ireland, taking advantage of the liberal policies then valid in Mexico, and went into merchant, industrial and educational ventures while others arrived with no or limited capital, as employees or farmers.Puebla
Puebla, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Puebla, is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its capital is Puebla City. Part of east-centr ...
. Significant numbers of German immigrants also arrived during and after the First and Second World Wars.Ashkenazi Jews
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; also known as Ashkenazic Jews or Ashkenazim) form a distinct subgroup of the Jewish diaspora, that emerged in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium CE. They traditionally speak Yiddish, a language ...
came.Sephardic
Sephardic Jews, also known as Sephardi Jews or Sephardim, and rarely as Iberian Peninsular Jews, are a Jewish diaspora population associated with the historic Jewish communities of the Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal) and their descendant ...
community that lived in Mexico since colonial times, though many lived as Crypto-Jews
Crypto-Judaism is the secret adherence to Judaism while publicly professing to be of another faith; practitioners are referred to as "crypto-Jews" (origin from Greek ''kryptos'' – , 'hidden').
The term is especially applied historically to Spani ...
, mostly in the northern states of Nuevo León
Nuevo León, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Nuevo León, is a Administrative divisions of Mexico, state in northeastern Mexico. The state borders the Mexican states of Tamaulipas, Coahuila, Zacatecas, and San Luis Potosí, San Luis ...
and Tamaulipas
Tamaulipas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tamaulipas, is a state in Mexico; one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It is divided into 43 municipalities.
It is located in nor ...
. Some communities of European immigrants have remained isolated from the rest of the general population since their arrival, among them the German-speaking Mennonites from Russia of Chihuahua and Durango
Durango, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Durango, is one of the 31 states which make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico, situated in the northwest portion of the country. With a population of 1,832,650 ...
, and the Veneto
Veneto, officially the Region of Veneto, is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the Northeast Italy, north-east of the country. It is the fourth most populous region in Italy, with a population of 4,851,851 as of 2025. Venice is t ...
s of Chipilo
Chipilo, officially known as Chipilo de Francisco Javier Mina, is a small city in the state of Puebla, Mexico. It is located south of the state capital Puebla, Puebla, at a height of above sea level. The name itself derives from Náhuatl, meani ...
, Puebla, which have retained their original languages.
Afro-Mexicans
Afro-Mexicans are an ethnic group that predominate in certain areas of Mexico such as the Costa Chica of Oaxaca and the Costa Chica of Guerrero
The Costa Chica of Guerrero (Spanish language, Spanish for “small coast of Guerrero") is an area along the south coast of the state of Guerrero, Mexico, extending from just south of Acapulco to the Oaxaca border. Geographically, it consists of p ...
, Veracruz (e.g. Yanga) and in some towns in northern Mexico, mainly in Múzquiz Municipality, Coahuila. The existence of individuals of Sub-Saharan African descent in Mexico has its origins in the slave trade that took place during colonial times and that did not end until 1829 after the consummation of the Mexican independence. The institution was not as prominent as elsewhere in the Americas and was already in decay by the late 1700s, which led to the number of free black people eventually surpassing that of enslaved ones. Although Mexico did not abolish slavery immediately after independence, the expansion of Anglo-American settlement in Texas with their Black slaves became a point of contention between the US and Mexico. The northern territory had been claimed by the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire, sometimes referred to as the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy or the Catholic Monarchy, was a colonial empire that existed between 1492 and 1976. In conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, it ushered ...
but not settled beyond a few missions. The Mexican government saw a solution to the problem of Indian attacks in the north by inviting immigration by US Americans. Rather than settling in the territory contested by northern Indian groups, the Anglo-Americans and their Black slaves established farming in eastern Texas, contiguous to US territory in Louisiana. Mexican President Anastasio Bustamante
Trinidad Anastasio de Sales Ruiz Bustamante y Oseguera (; 27 July 1780 – 6 February 1853) was a Mexican physician, general, and politician who served as the 4th President of Mexico three times from 1830 to 1832, 1837 to 1839, and 1839 to 1841. ...
, concerned that the US would annex Texas, sought to limit Anglo-American immigration in 1830 and mandated no new slaves in the territory.
Historically, the presence of this ethnic group within the country has been difficult to assess for a number of reasons: their small numbers, heavy intermarriage with other ethnic groups, and Mexico's tradition of defining itself as a Mestizo society or mixing of European and indigenous only. Nowadays this ethnic group also includes people from Africa, the Caribbean and elsewhere in the Americas who have been arriving in recent migration waves to the country.indigenous languages
An indigenous language, or autochthonous language, is a language that is native to a region and spoken by its indigenous peoples. Indigenous languages are not necessarily national languages but they can be; for example, Aymara is both an indigeno ...
.
Arab Mexicans
 An Arab Mexican is a Mexican citizen of
An Arab Mexican is a Mexican citizen of Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
-speaking origin who can be of various ancestral origins. The vast majority of Mexico's 1.1 million Arabs are from either Lebanese, Syrian, Iraqi, or Palestinian
Palestinians () are an Arab ethnonational group native to the Levantine region of Palestine.
*: "Palestine was part of the first wave of conquest following Muhammad's death in 632 CE; Jerusalem fell to the Caliph Umar in 638. The indigenous p ...
background.Kibbeh
Kibbeh (, also kubba and other spellings; ; ) is a popular dish in the Arab world and the Levant in particular based on spiced lean ground meat and bulgur wheat. Kibbeh is considered to be a national dish of Lebanon and Syria.
In Levantine ...
, Tabbouleh
Tabbouleh (), also transcribed tabouleh, tabbouli, tabouli, or taboulah, is a Levantine salad of finely chopped parsley, soaked bulgur, tomatoes, mint, and onion, seasoned with olive oil, lemon juice, salt and sweet pepper. Some variations a ...
and even created recipes such as '' Tacos Árabes''. By 1765, Dates, which originated from the Middle East, were introduced into Mexico by the Spaniards. The fusion between Arab and Mexican food has highly influenced the Yucatecan cuisine.
Arab immigration to Mexico started in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Roughly 100,000 Arabic-speakers settled in Mexico during this time period. They came mostly from Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
, Syria, Palestine
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is a country in West Asia. Recognized by International recognition of Palestine, 147 of the UN's 193 member states, it encompasses the Israeli-occupied West Bank, including East Jerusalem, and th ...
, and Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
and settled in significant numbers in Nayarit
Nayarit, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Nayarit, is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in Municipalities of Nayarit, 20 municipalit ...
, Puebla
Puebla, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Puebla, is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its capital is Puebla City. Part of east-centr ...
, Mexico City and the northern part of the country (mainly in the states of Baja California
Baja California, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California, is a state in Mexico. It is the northwesternmost of the 32 federal entities of Mexico. Before becoming a state in 1952, the area was known as the North Territory of B ...
, Tamaulipas
Tamaulipas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tamaulipas, is a state in Mexico; one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It is divided into 43 municipalities.
It is located in nor ...
, Nuevo León
Nuevo León, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Nuevo León, is a Administrative divisions of Mexico, state in northeastern Mexico. The state borders the Mexican states of Tamaulipas, Coahuila, Zacatecas, and San Luis Potosí, San Luis ...
, Sinaloa
Sinaloa (), officially the (), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, compose the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 18 municipalities, and its capital city is Culiacán Rosales.
It is located in northwest Mexic ...
, Chihuahua, Coahuila
Coahuila, formally Coahuila de Zaragoza, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Coahuila de Zaragoza, is one of the 31 states of Mexico. The largest city and State Capital is the city of Saltillo; the second largest is Torreón and the thi ...
, and Durango
Durango, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Durango, is one of the 31 states which make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico, situated in the northwest portion of the country. With a population of 1,832,650 ...
, as well as the city of Tampico
Tampico is a city and port in the southeastern part of the Mexican state of Tamaulipas. It is located on the north bank of the Pánuco River, about inland from the Gulf of Mexico, and directly north of the state of Veracruz. Tampico is the fif ...
and Guadalajara
Guadalajara ( ; ) is the capital and the most populous city in the western Mexican List of states of Mexico, state of Jalisco, as well as the most densely populated municipality in Jalisco. According to the 2020 census, the city has a population ...
. During the 1948 Israel-Lebanon war and the Six-Day War, thousands of Lebanese left Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
for Mexico. They first arrived in Veracruz
Veracruz, formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entit ...
. Although Arabs made up less than 5% of the total immigrant population in Mexico during the 1930s, they constituted half of the immigrant economic activity.[ Another concentration of Arab-Mexicans is in ]Baja California
Baja California, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California, is a state in Mexico. It is the northwesternmost of the 32 federal entities of Mexico. Before becoming a state in 1952, the area was known as the North Territory of B ...
facing the U.S.-Mexican border, esp. in cities of Mexicali
Mexicali (; ) is the capital city of the States of Mexico, Mexican state of Baja California. The city, which is the seat of the Mexicali Municipality, has a population of 689,775, according to the 2010 census, while the Calexico–Mexicali, Cale ...
in the Imperial Valley
The Imperial Valley ( or ''Valle Imperial'') of Southern California lies in Imperial and Riverside counties, with an urban area centered on the city of El Centro. The Valley is bordered by the Colorado River to the east and, in part, the S ...
U.S./Mexico, and Tijuana
Tijuana is the most populous city of the Mexican state of Baja California, located on the northwestern Pacific Coast of Mexico. Tijuana is the municipal seat of the Tijuana Municipality, the hub of the Tijuana metropolitan area and the most popu ...
across from San Diego with a large Arab American
Arab Americans ( or ) are Americans who trace ancestry to any of the various waves of immigrants from the Arabic-speaking countries. In the United States census, Arabs are racially classified as White Americans which is defined as "A person ha ...
community (about 280,000), some of whose families have relatives in Mexico. 45% of Arab Mexicans are of Lebanese descent.
 The majority of Arab-Mexicans are Christians who belong to the
The majority of Arab-Mexicans are Christians who belong to the Maronite Church
The Maronite Church (; ) is an Eastern Catholic '' sui iuris'' particular church in full communion with the pope and the worldwide Catholic Church, with self-governance under the Code of Canons of the Eastern Churches. The head of the Maronit ...
, Roman Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
, Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
and Eastern Rite Catholic Churches
The Eastern Catholic Churches or Oriental Catholic Churches, also known as the Eastern-Rite Catholic Churches, Eastern Rite Catholicism, or simply the Eastern Churches, are 23 Eastern Christian autonomous ('' sui iuris'') particular churches of ...
and a scant number are Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
, The term "Arab Mexican" may include ethnic groups that do not in fact identify as Arab. The inter-ethnic marriage in the Arab community, regardless of religious affiliation, is very high; most community members have only one parent of Arab ancestry. As a result, the Arab community in Mexico shows marked language shift
Language shift, also known as language transfer, language replacement or language assimilation, is the process whereby a speech community shifts to a different language, usually over an extended period of time. Often, languages that are perceived ...
away from Arabic. Only a few speak any Arabic, and such knowledge is often limited to a few basic words. Instead, the majority, especially those of younger generations, speak Spanish as a first language. Today, the most common Arabic surnames
In many societies, a surname, family name, or last name is the mostly hereditary portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family. It is typically combined with a given name to form the full name of a person, although several giv ...
in Mexico include Nader, Hayek, Ali, Haddad, Nasser, Malik, Abed, Mansoor, Harb, and Elias.
Asian Mexicans
 Although Asian Mexicans make up less than 1% of the total population of modern Mexico, they are nonetheless a notable minority. Due to the historical and contemporary perception in Mexican society of what constitutes Asian culture (associated with the Far East rather than the
Although Asian Mexicans make up less than 1% of the total population of modern Mexico, they are nonetheless a notable minority. Due to the historical and contemporary perception in Mexican society of what constitutes Asian culture (associated with the Far East rather than the Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
), Asian Mexicans typically refers to those of East Asian
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Ja ...
descent, and may also include those of South
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both west and east.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþa ...
and Southeast Asian
Southeast Asia is the geographical southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Australian mainland, which is part of Oceania. Southeast Asia is ...
descent while Mexicans of West Asian
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian ...
descent are referred to as Arab Mexicans.
Asian immigration began with the arrival of Filipinos
Filipinos () are citizens or people identified with the country of the Philippines. Filipinos come from various Austronesian peoples, all typically speaking Filipino language, Filipino, Philippine English, English, or other Philippine language ...
to Mexico during the colonial period. For two and a half centuries, between 1565 and 1815, many Filipinos and Mexicans sailed back and forth between Mexico and the Philippines as crews, prisoners, adventurers and soldiers in the Manila-Acapulco Galleon assisting Spain in its trade between Asia and the Americas. Also, on these voyages, thousands of Asian individuals (mostly males) were brought to Mexico as slaves and were called "Chino",New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( ; Nahuatl: ''Yankwik Kaxtillan Birreiyotl''), originally the Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain. It was one of several ...
and eventually she gave rise to the " China Poblana".
These early individuals are not very apparent in modern Mexico for two main reasons: the widespread ''mestizaje
( , ; fem. , literally 'mixed person') is a term primarily used to denote people of mixed Ethnic groups in Europe, European and Indigenous ancestry in the former Spanish Empire. In certain regions such as Latin America, it may also refer to ...
'' of Mexico during the Spanish period and the common practice of ''Chino'' slaves to " pass" as ''Indios'' (the indigenous people of Mexico) to attain freedom. As had occurred with a large portion of Mexico's black population, over generations the Asian populace was absorbed into the general Mestizo
( , ; fem. , literally 'mixed person') is a term primarily used to denote people of mixed European and Indigenous ancestry in the former Spanish Empire. In certain regions such as Latin America, it may also refer to people who are culturall ...
population. Facilitating this miscegenation
Miscegenation ( ) is marriage or admixture between people who are members of different races or ethnicities. It has occurred many times throughout history, in many places. It has occasionally been controversial or illegal. Adjectives describin ...
was the assimilation of Asians into the indigenous population. The indigenous people were legally protected from chattel slavery
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
, and by being recognized as part of this group, Asian slaves could claim they were wrongly enslaved.
Asians, predominantly Chinese, became Mexico's fastest-growing immigrant group from the 1880s to the 1920s, exploding from about 1,500 in 1895 to more than 20,000 in 1910.
Romani Mexicans
Romani people
{{Infobox ethnic group
, group = Romani people
, image =
, image_caption =
, flag = Roma flag.svg
, flag_caption = Romani flag created in 1933 and accepted at the 1971 World Romani Congress
, po ...
have settled in Mexico since the colonial era. There are around 50,000 Vlax Romani
Vlax Romani varieties are spoken mainly in Southeastern Europe by the Romani people.Norbert Boretzky and Birgit Igla. Kommentierter Dialektatlas des Romani. Wiesbaden:
Harrassowitz Verlag 2004. Teil 1: Vergleich der Dialekte. Vlax Romani can also ...
in Mexico.
Official censuses
Historically, population studies and censuses have never been up to the standards that a population as diverse and numerous such as Mexico's require: the first racial census was made in 1793, being also Mexico's (then known as New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( ; Nahuatl: ''Yankwik Kaxtillan Birreiyotl''), originally the Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain. It was one of several ...
) first ever nationwide population census. Since only part of its original datasets survive, most of what is known of it comes from essays made by researchers who back in the day used the census' findings as reference for their own works.
More than a century would pass until the Mexican government conducted a new racial census in 1921 (some sources assert that the census of 1895 included a comprehensive racial classification;["censo General de la Republica Mexicana 1895"](_blank)
, "INEGI
The National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI from its former name in ) is an autonomous agency of the Government of Mexico, Mexican Government dedicated to coordinate the National System of Statistical and Geographical Information ...
", Mexico. Retrieved July 24, 2017. While the 1921 census was the last time the Mexican government conducted a census that included a comprehensive racial classification, in recent years it has conducted nationwide surveys to quantify most of the ethnic groups who inhabit the country as well as the social dynamics and inequalities between them.
1793 census
Also known as the "Revillagigedo census" from the name of the Count who ordered that it be conducted, this census was the first nationwide population census of Mexico (then known as the Viceroyalty of New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( ; Nahuatl: ''Yankwik Kaxtillan Birreiyotl''), originally the Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain. It was one of several ...
). Most of its original datasets have reportedly been lost, so most of what is known about it nowadays comes from essays and field investigations made by academics who had access to the census data and used it as reference for their works, such as Prussian geographer Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 1769 – 6 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, natural history, naturalist, List of explorers, explorer, and proponent of Romanticism, Romantic philosophy and Romanticism ...
.
Each author gives different estimations for each racial group in the country although they do not vary greatly, with Europeans ranging from 18% to 22% of New Spain's population, Mestizos from 21% to 25%, Indians from 51% to 61%, and Africans from 6,000 and 10,000. The estimations given for the total population range from 3,799,561 to 6,122,354. It is concluded then, that across nearly three centuries of colonization, the population growth trends of whites and mestizos were even, while the total percentage of the indigenous population decreased at a rate of 13%–17% per century. The authors assert that rather than whites and mestizos having higher birthrates, the reason for the indigenous population's numbers decreasing lies in their suffering higher mortality rates due to living in remote locations rather than in cities and towns founded by the Spanish colonists or in being at war with them. For the same reasons, the number of Indigenous Mexicans presents the greatest variation range between publications, as in some cases their numbers in a given location were estimated rather than counted, leading to possible overestimations in some provinces and possible underestimations in others.
~Europeans are included within the Mestizo category.
Regardless of the possible inaccuracies related to the counting of Indigenous peoples living outside of the colonized areas, the effort that New Spain's authorities put into considering them as subjects is worth mentioning, as censuses made by other colonial or post-colonial countries did not consider American Indians to be citizens or subjects; for example, the censuses made by the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata
The Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata or Viceroyalty of Buenos Aires ( or Virreinato de Buenos Aires or ) meaning "River of the Silver", also called the "Viceroyalty of River Plate" in some scholarly writings, in southern South America, was ...
would only count the inhabitants of the colonized settlements.[''Historical Dictionary of Argentina''. London: Scarecrow Press, 1978. pp. 239–40.] Another example is the censuses made by the United States, which did not include Indigenous peoples living among the general population until 1860, and indigenous peoples as a whole until 1900.
1921 census
Made right after the consummation of the Mexican revolution, the social context in which this census was conducted makes it particularly unique, as the government of the time was in the process of rebuilding the country and was looking to unite all Mexicans in a single national identity. The 1921 census' final results in regards to race, which assert that 59.3% of the Mexican population self-identified as Mestizo, 29.1% as Indigenous, and only 9.8% as White, were then essential in cementing the ''mestizaje'' ideology (which asserts that the Mexican population as a whole is product of the admixture of all races), which shaped Mexican identity and culture through the 20th century and remains prominent nowadays, with extraofficial international publications such as ''The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a Reference work, reference resource produced by the United States' Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The off ...
'' using the 1921 census as a reference to estimate Mexico's racial composition up to this day.Mexican Government
The Federal government of Mexico (alternately known as the Government of the Republic or ' or ') is the national government of the United Mexican States, the central government established by its constitution to share sovereignty over the republ ...
conducted a comprehensive racial census with the breakdown by states being the following (foreigners and people who answered "other" not included):
When the 1921 census' results are compared with the results of Mexico's recent censusesEuropean peoples
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common ancestry, language, faith, historical continuity, etc. There are ...
(with the state's Indigenous population showing low European admixture as well).
The present day
Since the end of the Mexican Revolution
The Mexican Revolution () was an extended sequence of armed regional conflicts in Mexico from 20 November 1910 to 1 December 1920. It has been called "the defining event of modern Mexican history". It saw the destruction of the Federal Army, its ...
, the official identity promoted by the government for non-indigenous Mexicans has been the Mestizo one (a mix of European and indigenous culture and heritage),[''About one third'' ]Mexico City
Mexico City is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Mexico, largest city of Mexico, as well as the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North America. It is one of the most important cultural and finan ...
, where the most powerful of the country's elite are located. Despite Mexico's government not using racial terms related to European or
Despite Mexico's government not using racial terms related to European or white people
White is a Race (human categorization), racial classification of people generally used for those of predominantly Ethnic groups in Europe, European ancestry. It is also a Human skin color, skin color specifier, although the definition can var ...
officially for almost a century (resuming using such terms after 2010), the concepts of "white people" (known as ''güeros'' or ''blancos'' in Mexican Spanish
Mexican Spanish () is the variety of dialects and sociolects of the Spanish language spoken in Mexico and its bordering regions. Mexico has the largest number of Spanish speakers, more than double any other country in the world. Spanish is spo ...
) and of "being white" did not disappear [Nutini, Hugo; Barry Isaac (2009). ''Social Stratification in central Mexico 1500 - 2000''. University of Texas Press, p. 55.] and are still present in everyday Mexican culture: different idioms of race are used in Mexico's society that serve as mediating terms between racial groups. It is not strange to see street vendors calling a potential costumer ''Güero'' or ''güerito'', sometimes even when the person is not light-skinned. In this instance it is used to initiate a kind of familiarity, but in cases where social/racial tensions are relatively high, it can have the opposite effect.
Languages
Spanish is the ''de facto'' official language
Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed language, signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing syste ...
in Mexico, being spoken by 98.3% of the population. Mexican Spanish
Mexican Spanish () is the variety of dialects and sociolects of the Spanish language spoken in Mexico and its bordering regions. Mexico has the largest number of Spanish speakers, more than double any other country in the world. Spanish is spo ...
is spoken in a variety of dialects, accents and variations in different regions across the country. Some indigenous languages are still being spoken by around 5% of Mexicans according to the latest census, in 2003 the General Law of Linguistic Rights of the Indigenous Peoples recognized 68 indigenous languages as "national languages", with the "same validity" in all territories and contexts where they are spoken. The indigenous language with the greatest number of speakers is Nahuatl
Nahuatl ( ; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahuas, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller popul ...
(1,586,884 speakers in 2010 or 1.5% of the nation's population), followed by Yucatec Maya
Yucatec Maya ( ; referred to by its speakers as or ) is a Mayan languages, Mayan language spoken in the Yucatán Peninsula, including part of northern Belize. There is also a significant diasporic community of Yucatec Maya speakers in San Fra ...
(796,405 speakers in 2010 0.8%) spoken Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula ( , ; ) is a large peninsula in southeast Mexico and adjacent portions of Belize and Guatemala. The peninsula extends towards the northeast, separating the Gulf of Mexico to the north and west of the peninsula from the C ...
, Mixtecas languages (494,454), Tzeltal (474,298), Zapotecas languages (460,683), Tzotzil (429,168), Otomí (288,052), Totonaca (250,252) Mazateco (230,124), Chol (222,051) and 1,462,857 speakers of other languages. After half a century of rural-to-urban migration, in Mexico City and other major cities large districts and sections use both written and spoken Amerindian languages. Approximately 7,364,645 Mexicans (6.1% of the population) speak an indigenous language according to the 2020 Mexican Census.North American Free Trade Agreement
The North American Free Trade Agreement (, TLCAN; , ALÉNA), referred to colloquially in the Anglosphere as NAFTA, ( ) was an agreement signed by Canada, Mexico, and the United States that created a trilateral trade bloc in North America. The ...
(NAFTA) and the immigration phenomenon and the return of workers and their families from the United States. In border cities, American TV and radio waves in English (and Spanish) are received as much Spanish-speaking radio and TV stations from Mexico on the US side of the border, thus a bilingual cross-cultural exchange is at work. Among the languages brought to the country by immigrants are the Venetian of Chipilo
Chipilo, officially known as Chipilo de Francisco Javier Mina, is a small city in the state of Puebla, Mexico. It is located south of the state capital Puebla, Puebla, at a height of above sea level. The name itself derives from Náhuatl, meani ...
, and Mennonite Low German spoken in Durango
Durango, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Durango, is one of the 31 states which make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico, situated in the northwest portion of the country. With a population of 1,832,650 ...
and Chihuahua.
Mexican nationality and citizenship
 The
The Constitution of Mexico
The current Constitution of Mexico, formally the Political Constitution of the United Mexican States (), was drafted in Santiago de Querétaro, in the State of Querétaro, Mexico, by a constituent convention during the Mexican Revolution. I ...
grants Mexican nationality based on birth and naturalization. Mexican laws regarding nationality by birth are very open. Mexican nationality by birth is granted to:[Artículo 30]
. Constitución Política de los Estados Unidos Mexicanos.
* all those individuals born in Mexican territory,
* all those individuals born outside Mexico, whose father or mother is Mexican by birth,
* all those individuals born outside Mexico, whose father or mother is Mexican by naturalization,
* all those individuals born aboard Mexican aircraft or sea vessels, whether warships or commercial vessels.
Mexican nationality by naturalization is granted to:[
* foreign citizens granted Mexican nationality by the Secretariat of Government (Ministry of the Interior);
* foreign citizens married to a Mexican national, whether by birth or naturalization.
]
Religion
The Mexican population is predominantly Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
(78% of the population aged five and older, according to the 2020 census),Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
or Evangelical, 2.5% were classified as "Non-Evangelical Biblical" (a classification that groups Adventist
Adventism is a branch of Protestant Christianity that believes in the imminent Second Coming (or the "Second Advent") of Jesus Christ. It originated in the 1830s in the United States during the Second Great Awakening when Baptist preacher Willi ...
s, Mormons
Mormons are a Religious denomination, religious and ethnocultural group, cultural group related to Mormonism, the principal branch of the Latter Day Saint movement started by Joseph Smith in upstate New York during the 1820s. After Smith's d ...
and Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a Christian denomination that is an outgrowth of the Bible Student movement founded by Charles Taze Russell in the nineteenth century. The denomination is nontrinitarian, millenarian, and restorationist. Russell co-fou ...
), 0.05% as practicing Jews, and 4.6% without a religion.[Población de 5 años y más por entidad federativa, sexo y religión y su distribución según grupos quinquenales de edad](_blank)
. The largest group of Protestants are Pentecostals
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a movement within the broader Evangelical wing of Protestant Christianity that emphasizes direct personal experience of God through baptism with the Holy Spirit. The term ''Pentecostal'' is derived ...
and Charismatics (classified as Neo-Pentecostals).
 The states with the highest percentage of professing Catholics are central states, namely
The states with the highest percentage of professing Catholics are central states, namely Guanajuato
Guanajuato, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guanajuato, is one of the 32 states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Guanajuato, 46 municipalities and its cap ...
(96.4%), Aguascalientes
Aguascalientes, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Aguascalientes, is one of the 32 states which comprise the Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. At 22°N and with an average altitude of above sea level it is pre ...
(95.6%) and Jalisco
Jalisco, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Jalisco, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Political divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. It is located in western Mexico and is bordered by s ...
(95.4%), whereas southeastern states have the lowest percentage of Catholics, namely Chiapas
Chiapas, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Chiapas, is one of the states that make up the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. It comprises Municipalities of Chiapas, 124 municipalities and its capital and large ...
(63.8%), Tabasco
Tabasco, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tabasco, is one of the Political divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into Municipalities of Tabasco, 17 municipalities and its capital city is Villahermosa.
It i ...
(70.4%) and Campeche
Campeche, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Campeche, is one of the 31 states which, with Mexico City, make up the Administrative divisions of Mexico, 32 federal entities of Mexico. Located in southeast Mexico, it is bordered by the sta ...
(71.3%).Ibero-America
Ibero-America (, ) or Iberian America is generally considered to be the region in the Americas comprising countries or territories where Spanish or Portuguese are predominant languages (usually former colony, territories of Spain or Portugal). Sp ...
. The State does not support or provide any economic resource to the Church (as is the case in Spain and Argentina),
See also
* List of municipalities in Mexico by population
* Metropolitan areas of Mexico Metropolitan areas of Mexico have been traditionally defined as the group of municipalities that heavily interact with each other, usually around a core city, in Mexico. The phenomenon of conurbation, metropolization in Mexico is relatively recent, ...
* List of Mexican states by population
The following table is a list of the 31 federal states of Mexico plus Mexico City, ranked in order of their total population based on data from the last three National Population Census in 2020, 2010 and 2000.
See also
* Mexico
* States of Me ...
* List of Mexican states by fertility rate
* Economy of Mexico
The economy of Mexico is a developing mixed-market economy. It is the 13th largest in the world in nominal GDP terms and by purchasing power parity as of 2024. Since the 1994 crisis, administrations have improved the country's macroeconomi ...
* Poverty in Mexico
* Romani Mexicans
References and notes
Further reading
* Merrill, Tim and Ramón Miró. ''Mexico: a country study'' (Library of Congress. Federal Research Division, 1996) US government document; not copyrigh
online free
External links
UN: Fertility in Mexico: Trends and Forecasts
*
Mexico population bureau CONAPO
*
Institute of Statistics, Geography and Informatics, INEGI
Map of Fecundity in Mexico
{{DEFAULTSORT:Demographics Of Mexico


 The national
The national  A metropolitan area in Mexico is defined as a group of municipalities that heavily interact with each other, usually around a core city.CONAPO Áreas Metropolitanas
A metropolitan area in Mexico is defined as a group of municipalities that heavily interact with each other, usually around a core city.CONAPO Áreas Metropolitanas Although Mexico is an ethnically diverse country, for most of the 20th century and early 21st century the Mexican government has not conducted surveys regarding the ethnic origin of the population, except for indigenous peoples. However, recently the Mexican National Institute of Statistics and Geography has begun conducting surveys to quantify the percentage of Afro-descendant Mexicans, as well as Euro-descendant Mexicans living in the country. However, the results of surveys on the population of Euro-descendants has never been published.
Regardless of ethnicity, the majority of Mexicans are united under the same national identity.Wimmer, Andreas, 2002. ''Nationalist Exclusion and Ethnic Conflict: Shadows of Modernity'', Cambridge University Press page 115 This is the product of an ideology strongly promoted by Mexican academics such as Manuel Gamio and
Although Mexico is an ethnically diverse country, for most of the 20th century and early 21st century the Mexican government has not conducted surveys regarding the ethnic origin of the population, except for indigenous peoples. However, recently the Mexican National Institute of Statistics and Geography has begun conducting surveys to quantify the percentage of Afro-descendant Mexicans, as well as Euro-descendant Mexicans living in the country. However, the results of surveys on the population of Euro-descendants has never been published.
Regardless of ethnicity, the majority of Mexicans are united under the same national identity.Wimmer, Andreas, 2002. ''Nationalist Exclusion and Ethnic Conflict: Shadows of Modernity'', Cambridge University Press page 115 This is the product of an ideology strongly promoted by Mexican academics such as Manuel Gamio and  The use of variated methods and criteria to quantify the number of Mestizos in Mexico is not new: Since several decades ago, many authors have analyzed colonial censuses data and have made different conclusions regarding the ethnic composition of the population of colonial Mexico/New Spain. Some historians, such as Gonzalo Aguirre-Beltrán who claimed in 1972 that practically the totality of New Spain's population, in reality, were Mestizos, using to back up his claims arguments such as that affairs of Spaniards with non-Europeans due to the alleged absence of female European immigrants were widespread as well as there being a huge desire of Mestizos to "pass" as Spaniards, this because Spanishness was seen as a symbol of high status.
Other historians, however, argue that Aguirre-Beltran's numbers tend to have inconsistencies and take too many liberties (it is pointed out in the book ''Ensayos sobre historia de la población. México y el Caribe 2'' published in 1998 that on 1646, when according to historic registers the mestizo population was of 1% he estimates it to be 16.6% already, with this being attributed to him interpreting the data in a way convenient for a historic narrative),"Racismo, falso mestizaje y desigualdad social en México"
The use of variated methods and criteria to quantify the number of Mestizos in Mexico is not new: Since several decades ago, many authors have analyzed colonial censuses data and have made different conclusions regarding the ethnic composition of the population of colonial Mexico/New Spain. Some historians, such as Gonzalo Aguirre-Beltrán who claimed in 1972 that practically the totality of New Spain's population, in reality, were Mestizos, using to back up his claims arguments such as that affairs of Spaniards with non-Europeans due to the alleged absence of female European immigrants were widespread as well as there being a huge desire of Mestizos to "pass" as Spaniards, this because Spanishness was seen as a symbol of high status.
Other historians, however, argue that Aguirre-Beltran's numbers tend to have inconsistencies and take too many liberties (it is pointed out in the book ''Ensayos sobre historia de la población. México y el Caribe 2'' published in 1998 that on 1646, when according to historic registers the mestizo population was of 1% he estimates it to be 16.6% already, with this being attributed to him interpreting the data in a way convenient for a historic narrative),"Racismo, falso mestizaje y desigualdad social en México" According to some 21st-century historians, Aguirre Beltran also disregards facts such as the population dynamics of New Spain being different depending on the region at hand (i.e. miscegenation could not happen in a significant amount in regions where the native population was openly hostile until the early 20th century, such as most of New Spain's internal provinces, which nowadays are the northern and western regions of Mexico), or that historic accounts made by investigators at the time consistently observed that New Spain's European population was notoriously concerned with preserving their European heritage, with practices such as inviting relatives and friends directly from Spain or favoring Europeans for marriage even if they were from a lower socioeconomic level than them being common. Newer publications that do cite Aguirre-Beltran's work take those factors into consideration, stating that the Spaniard/Euromestizo/Criollo ethnic label was composed on its majority by descendants of Europeans, albeit the category may have included people with some non-European ancestry.
According to some 21st-century historians, Aguirre Beltran also disregards facts such as the population dynamics of New Spain being different depending on the region at hand (i.e. miscegenation could not happen in a significant amount in regions where the native population was openly hostile until the early 20th century, such as most of New Spain's internal provinces, which nowadays are the northern and western regions of Mexico), or that historic accounts made by investigators at the time consistently observed that New Spain's European population was notoriously concerned with preserving their European heritage, with practices such as inviting relatives and friends directly from Spain or favoring Europeans for marriage even if they were from a lower socioeconomic level than them being common. Newer publications that do cite Aguirre-Beltran's work take those factors into consideration, stating that the Spaniard/Euromestizo/Criollo ethnic label was composed on its majority by descendants of Europeans, albeit the category may have included people with some non-European ancestry.
 The 2003 General Law of Linguistic Rights of the Indigenous Peoples recognizes 62
The 2003 General Law of Linguistic Rights of the Indigenous Peoples recognizes 62  Surveys made by the Mexican government do count as Indigenous all persons who speak an indigenous language and people who do not speak indigenous languages nor live in indigenous communities but self-identify as Indigenous. According to these criteria, the
Surveys made by the Mexican government do count as Indigenous all persons who speak an indigenous language and people who do not speak indigenous languages nor live in indigenous communities but self-identify as Indigenous. According to these criteria, the  While the majority of European immigration to Mexico has been Spanish with the first wave starting with the colonization of America and the last one being a consequence of the
While the majority of European immigration to Mexico has been Spanish with the first wave starting with the colonization of America and the last one being a consequence of the  An Arab Mexican is a Mexican citizen of
An Arab Mexican is a Mexican citizen of  The majority of Arab-Mexicans are Christians who belong to the
The majority of Arab-Mexicans are Christians who belong to the  Although Asian Mexicans make up less than 1% of the total population of modern Mexico, they are nonetheless a notable minority. Due to the historical and contemporary perception in Mexican society of what constitutes Asian culture (associated with the Far East rather than the
Although Asian Mexicans make up less than 1% of the total population of modern Mexico, they are nonetheless a notable minority. Due to the historical and contemporary perception in Mexican society of what constitutes Asian culture (associated with the Far East rather than the  Despite Mexico's government not using racial terms related to European or
Despite Mexico's government not using racial terms related to European or  The
The