demographics of hungary on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Hungary's population has been slowly declining since 1980. The population composition at the foundation of Hungary (895) depends on the size of the arriving Hungarian population and the size of the Slavic (and remains of Avar-Slavic) population at the time. One source mentions 200,000 Slavs and 400,000 Hungarians, while other sources often don't give estimates for both, making comparison more difficult. The size of the Hungarian population around 895 is often estimated between 120,000 and 600,000, with a number of estimates in the 400-600,000 range.Edgar C. Polomé, Essays on Germanic religion, Institute for the Study of Man, 1989, p. 15
Hungary's population has been slowly declining since 1980. The population composition at the foundation of Hungary (895) depends on the size of the arriving Hungarian population and the size of the Slavic (and remains of Avar-Slavic) population at the time. One source mentions 200,000 Slavs and 400,000 Hungarians, while other sources often don't give estimates for both, making comparison more difficult. The size of the Hungarian population around 895 is often estimated between 120,000 and 600,000, with a number of estimates in the 400-600,000 range.Edgar C. Polomé, Essays on Germanic religion, Institute for the Study of Man, 1989, p. 15
/ref> Other sources only mention a fighting force of 25,000 Magyar warriors used in the attack, while declining to estimate the total population including women and children and warriors not participating in the invasion. In the historical demographics the largest earlier shock was the Mongol Invasion of Hungary, several plagues also took a toll on the country's population. According to demographers, about 80 percent of the population was made up of Hungarians before the

File:Ethnic map of 11th century.jpg, Kniezsa's (1938) view on the ethnic map of the Kingdom of Hungary in the 11th century, based on toponyms. Kniezsa's view has been criticized by many scholars, because of its non-compliance with later archaeological and onomastics research, but his map is still regularly cited in modern reliable sources. One of the most prominent critics of this map was Emil Petrovici.
File:Kingdom of Hungary - Ethnic Map - 1495.jpg, Estimated ethnic map of the
 The
The


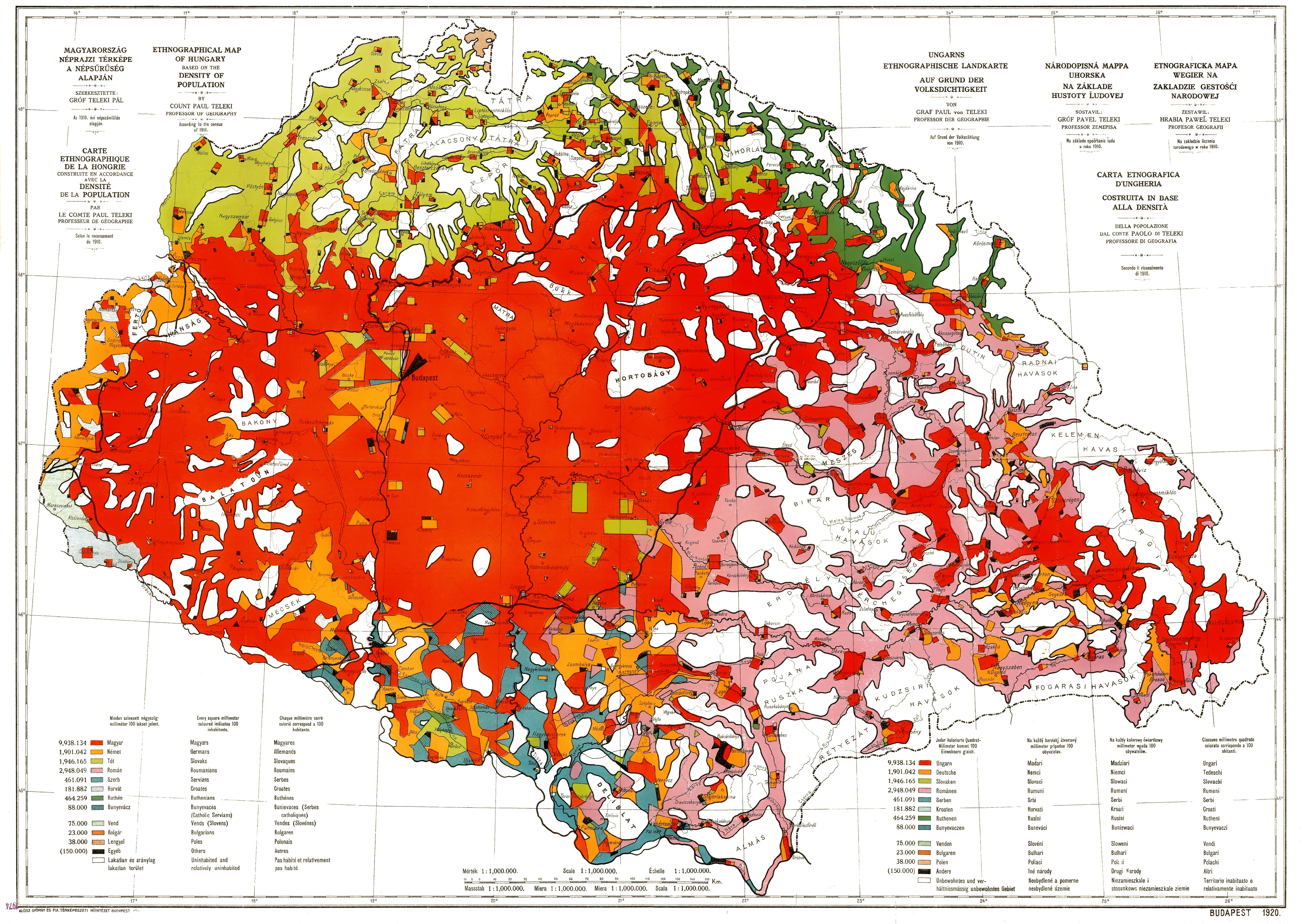 Hungary lost 64% of its total population in consequence of the
Hungary lost 64% of its total population in consequence of the
The territory of Bácska had 789,705 inhabitants, and 45,4% or 47,2% declared themselves to be Hungarian native speakers or ethnic Hungarians. The percentage of Hungarian speakers was 84% in southern Czechoslovakia and 25% in the Sub-Carpathian Rus. After WW II: 1949–1990 After World War II, about 200,000 Germans were deported to Germany according to the decree of the Potsdam Conference. Under the forced exchange of population between Czechoslovakia and Hungary, approximately 73,000 Slovaks left Hungary. After these population movements Hungary became an ethnically almost homogeneous country except the rapidly growing number of

 When the
When the
/ref> showed up in Făgăraş, Fogaras and this area was mentioned under different name (Olachi) in 1285. The first appearance of a probably Romanian name 'Ola' in Hungary derives from a charter (1258). They were a significant population in Transylvania,
ONE LAND — TWO NATIONS TRANSYLVANIA AND THE THEORY OF DACO-ROMAN-RUMANIAN CONTINUITY
COMMITTEE OF TRANSYLVANIA INC. (This is a special issue of the CARPATHIAN OBSERVER Volume 8, Number 1. Library of Congress Catalog Card Number; 80-81573), 1980, p. 10 The number of Romanians started to increase significantly from the
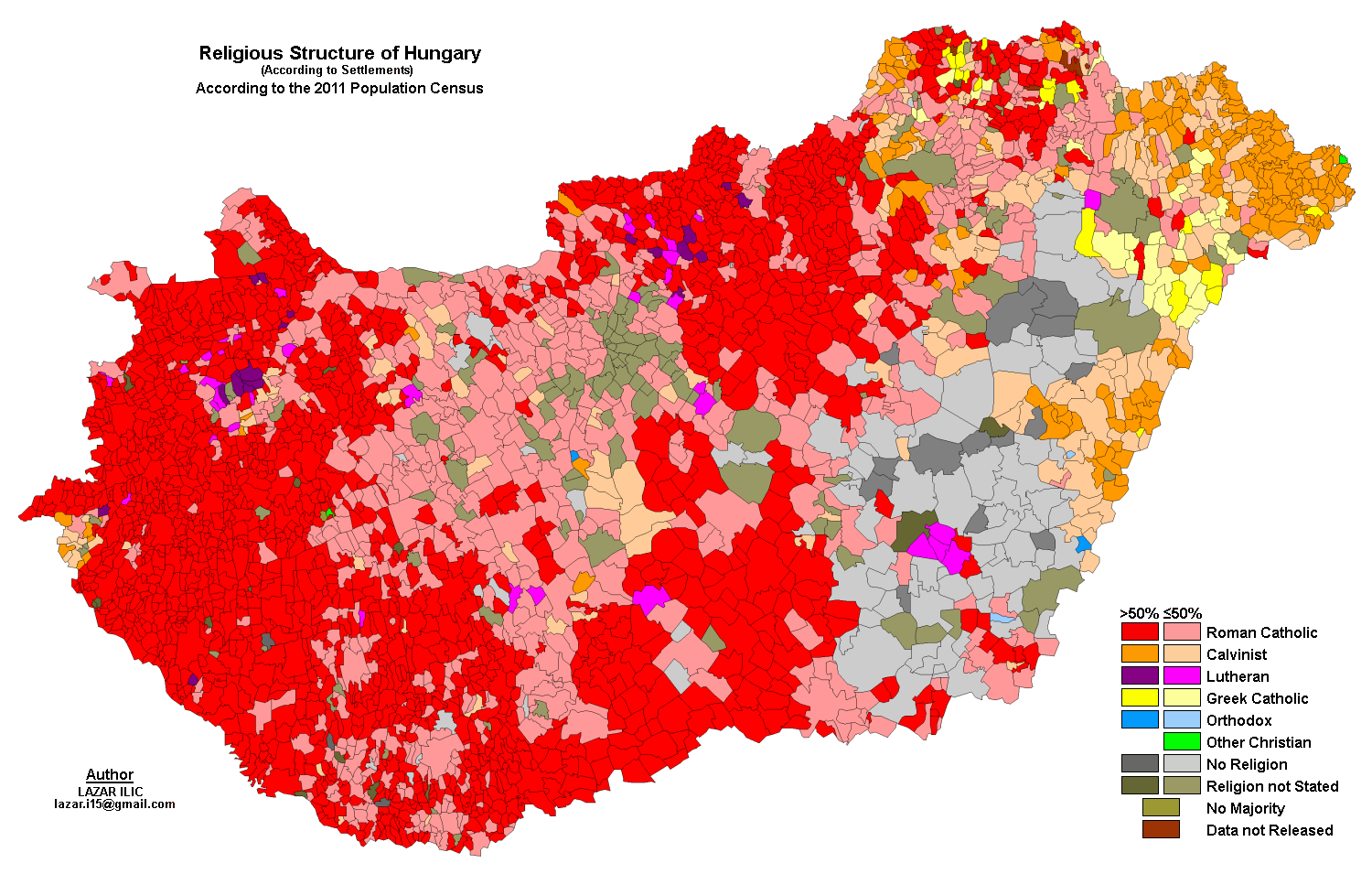 According to 2011 census data,
According to 2011 census data,
KSH, vital statistics, 1960-2012Hungarian Central Statistical Office (in English)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Demographics Of Hungary Society of Hungary
Demographic
Demography () is the statistics, statistical study of human populations: their size, composition (e.g., ethnic group, age), and how they change through the interplay of fertility (births), mortality (deaths), and migration.
Demographic analy ...
features of the population of Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
include population density
Population density (in agriculture: Standing stock (disambiguation), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geog ...
, ethnicity
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they Collective consciousness, collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, ...
, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects.
Population
 Hungary's population has been slowly declining since 1980. The population composition at the foundation of Hungary (895) depends on the size of the arriving Hungarian population and the size of the Slavic (and remains of Avar-Slavic) population at the time. One source mentions 200,000 Slavs and 400,000 Hungarians, while other sources often don't give estimates for both, making comparison more difficult. The size of the Hungarian population around 895 is often estimated between 120,000 and 600,000, with a number of estimates in the 400-600,000 range.Edgar C. Polomé, Essays on Germanic religion, Institute for the Study of Man, 1989, p. 15
Hungary's population has been slowly declining since 1980. The population composition at the foundation of Hungary (895) depends on the size of the arriving Hungarian population and the size of the Slavic (and remains of Avar-Slavic) population at the time. One source mentions 200,000 Slavs and 400,000 Hungarians, while other sources often don't give estimates for both, making comparison more difficult. The size of the Hungarian population around 895 is often estimated between 120,000 and 600,000, with a number of estimates in the 400-600,000 range.Edgar C. Polomé, Essays on Germanic religion, Institute for the Study of Man, 1989, p. 15/ref> Other sources only mention a fighting force of 25,000 Magyar warriors used in the attack, while declining to estimate the total population including women and children and warriors not participating in the invasion. In the historical demographics the largest earlier shock was the Mongol Invasion of Hungary, several plagues also took a toll on the country's population. According to demographers, about 80 percent of the population was made up of Hungarians before the
Battle of Mohács
The Battle of Mohács (; , ) took place on 29 August 1526 near Mohács, in the Kingdom of Hungary. It was fought between the forces of Hungary, led by King Louis II of Hungary, Louis II, and the invading Ottoman Empire, commanded by Suleima ...
. However, the Hungarian ethnic group became a minority in its own country in the 18th century due to centuries long Ottoman and Habsburg wars, the resettlement policies and continuous immigration from neighboring countries. Major territorial changes made Hungary ethnically homogeneous after World War I. Nowadays, more than nine-tenths of the population is ethnically Hungarian and speaks Hungarian as the mother tongue.Hungary. (2009). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved May 11, 2009, from Encyclopædia Britannica Online: https://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/276730/Hungary
Population over time
Note: The data refer to the territory of theKingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
, and not that of the present-day republic.
Demographics of Kingdom of Hungary, (1910 Census)
Demographic changes in pre-Trianon Hungary (1867–1914)
Population and ethnic composition (1869–1910)

Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
in 1495, created by the Hungarian Academy of Sciences
The Hungarian Academy of Sciences ( , MTA) is Hungary’s foremost and most prestigious learned society. Its headquarters are located along the banks of the Danube in Budapest, between Széchenyi rakpart and Akadémia utca. The Academy's primar ...
based on their research. Hungarians are depicted in orange. The date 1495 is based on a nationwide registry conducted in the Kingdom of Hungary by commission of the royal treasury. The map shows the estimated absolute or relative linguistic majority of the local population based on the family names of taxpayers recorded in national or domanial registers, the linguistic analysis of the names of geographic objects and on various scholarly sources.
File:Kingdom of Hungary - Ethnic Map - 1784.jpg, Ethnic map of the Kingdom of Hungary in 1784 by the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, based on their researches. Hungarians are depicted in orange. The ethnic pattern of Hungary changed due to the centuries long wars and migration movements.
File:Ethnographic map of hungary 1910 by teleki carte rouge.jpg, The Red Map. Ethnic map of the Hungary proper publicized by the Hungarian delegation. Regions with population density below 20 persons/km2Spatiul istoric si ethnic romanesc, Editura Militara, Bucuresti, 1992 are left blank and the corresponding population is represented in the nearest region with population density above that limit. The vibrant, dominant red color was deliberately chosen to mark Hungarians while the light purple color of the Romanians, who were already the majority in the whole of Transylvania back then, is shadow-like.
File:1910 census in Hungary.png, In the Kingdom of Hungary, the 1910 census was based on mother tongue. According to the census, 54.4% of the inhabitants of Hungary were recorded to speak Hungarian as their native language. This number included the Jewish ethnic group (around 5% of the population according to a separate census on religion and about 23% of Budapest's citizenry) who were overwhelmingly Hungarian-speaking (the Jews tending to declare German as mother tongue due to the immigration of Jews of Yiddish/German mother tongue).
File:Ethnic Map of Hungary 1910 with Counties.png, Ethnic Map of Hungary 1910 with Counties
Fertility
 The
The total fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were t ...
is the number of children born per woman. It is based on fairly good data for the entire period in the present-day Hungary. Sources: Our World In Data
Our World in Data (OWID) is a scientific online publication that focuses on large global problems such as poverty, disease, hunger, war, climate change, population growth, existential risks, and inequality.
It is a project of the Global Cha ...
and Gapminder Foundation.
Total Fertility Rate by county
Source: 2011 census
Life expectancy

Infant mortality rate
The infant mortality rate (IMR) decreased considerably after WW II. In 1949, the IMR was 91.0. The rate decreased to 47.6 in 1960, 35.9 in 1970, 23.2 in 1980, 14.8 in 1990, 9.2 in 2000 and reached an all-time low in 2023 at 3.1 per 1000 live born children.Vital statistics
Source: Hungarian Central Statistical OfficeCurrent vital statistics
Structure of the population
Vital statistics by county
There are large variations in the birth rates as of 2016:Zala County
Zala (, ; ; ) is an administrative county (Counties of Hungary, comitatus or ''vármegye'') in south-western Hungary. It is named after the Zala River. It shares borders with Croatia (Koprivnica–Križevci County, Koprivnica–Križevci and Me� ...
has the lowest birth rate with 7.5 births per thousand inhabitants, while Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg County has the highest birth rate with 11.2 births per thousand inhabitants.
The death rates also differ greatly from as low as 11.3 deaths per thousand inhabitants in Pest County to as high as 15.7 deaths per thousand inhabitants in Békés County
Békés (, , ) is an administrative division (county or ''vármegye'') in south-eastern Hungary, on the border with Romania. It shares borders with the Hungarian counties Csongrád-Csanád, Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok, and Hajdú-Bihar. The capital ...
.
Ethnic groups and language
History and census numbers
Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon (4 June 1920) Hungary lost 64% of its total population in consequence of the
Hungary lost 64% of its total population in consequence of the Treaty of Trianon
The Treaty of Trianon (; ; ; ), often referred to in Hungary as the Peace Dictate of Trianon or Dictate of Trianon, was prepared at the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace Conference. It was signed on the one side by Hungary ...
, decreasing from 20.9 million to 7.6 million, and 31% (3.3 out of 10.7 million) of its ethnic Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former pa ...
, Hungary lost five of its ten most populous cities.
According to the census of 1910, the largest ethnic group in the Kingdom of Hungary were Hungarians, who were 54.5% of the population of Kingdom of Hungary, excluding Croatia-Slavonia.
Although the territories of the former Kingdom of Hungary that were assigned by the treaty to neighbouring states in total had a majority of non-Hungarian population, they also included areas of Hungarian majority and significant Hungarian minorities, numbering 3,318,000 in total.
The number of Hungarians in the different areas based on census data of 1910. The present day location of each area is given in parentheses.
* In Upper Hungary
Upper Hungary (, "Upland"), is the area that was historically the northern part of the Kingdom of Hungary, now mostly present-day Slovakia. The region has also been called ''Felső-Magyarország'' ( literally: "Upper Hungary"; ).
During the ...
(mostly Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
): 885,000 - 30%
* In Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
(Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
): 1,658,045 - 31.6%
* In Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( ; sr-Cyrl, Војводина, ), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an Autonomous administrative division, autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia, located in Central Europe. It lies withi ...
(Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
): 425,672 - 28.1%
* In Transcarpathia
Transcarpathia (, ) is a historical region on the border between Central and Eastern Europe, mostly located in western Ukraine's Zakarpattia Oblast.
From the Hungarian Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin, conquest of the Carpathian Basin ...
(Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
): 183,000 - 30%
* In Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
: 121,000 - 3.5%
* In Prekmurje
Prekmurje (; Prekmurje Slovene: ''Prèkmürsko'' or ''Prèkmüre''; ) is a geographically, linguistically, culturally, and ethnically defined region of Slovenia, settled by Slovenes and a Hungarians in Slovenia, Hungarian minority, lying betwee ...
(Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
): 14,065 - 15%
* In Burgenland
Burgenland (; ; ; Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian: ''Burgnland''; Slovene language, Slovene: ''Gradiščanska''; ) is the easternmost and least populous Bundesland (Austria), state of Austria. It consists of two statutory city (Austria), statut ...
(Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
): 26,200 - 9%
Non-Hungarian population in the Kingdom of Hungary, based on 1910 census data
Romanians, Slovaks, Ruthenians, Serbs, Croats and Germans, who represented the majority of the populations of the above-mentioned territories:
* In Upper Hungary
Upper Hungary (, "Upland"), is the area that was historically the northern part of the Kingdom of Hungary, now mostly present-day Slovakia. The region has also been called ''Felső-Magyarország'' ( literally: "Upper Hungary"; ).
During the ...
(mostly Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
): 1,687,977 Slovaks and 1,233,454 others (mostly Hungarians - 886,044, Germans, Ruthenians and Roma). However, according to the Czechoslovak census in 1921, there were 2,025,003 (67,5%) Slovaks, 650,597 (21,7%) Hungarians, 145,844 (4,9%) Germans, 88,970 (3,0%) Ruthenians and 90,456 (3,0%) others including Jews.
* In Carpathian Ruthenia
Transcarpathia (, ) is a historical region on the border between Central and Eastern Europe, mostly located in western Ukraine's Zakarpattia Oblast.
From the Hungarian Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin, conquest of the Carpathian Basin ...
(Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
): 330,010 Ruthenians and 275,932 others (mostly Hungarians, Germans, Romanians, and Slovaks)
* In Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
(Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
): 2,831,222 Romanians (53.8%) and 2,431,273 others (mostly Hungarians - 1,662,948 (31.6%) and Germans - 563,087 (10.7%). The 1919 and 1920 Transylvanian censuses indicate a greater percentage of Romanians (57.1%/57.3%) and a smaller Hungarian minority (26.5%/25.5%)
* In Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( ; sr-Cyrl, Војводина, ), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an Autonomous administrative division, autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia, located in Central Europe. It lies withi ...
and Croatia-Slavonia (Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
, Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
): 2,756,000 Croats and Serbs and 1,366,000 others (mostly Hungarians and Germans)
* In Prekmurje
Prekmurje (; Prekmurje Slovene: ''Prèkmürsko'' or ''Prèkmüre''; ) is a geographically, linguistically, culturally, and ethnically defined region of Slovenia, settled by Slovenes and a Hungarians in Slovenia, Hungarian minority, lying betwee ...
(Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
): 74,199 Slovenes (80%), 14,065 Hungarians (15,2%), 2,540 Germans (2,7%)
* In Burgenland
Burgenland (; ; ; Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian: ''Burgnland''; Slovene language, Slovene: ''Gradiščanska''; ) is the easternmost and least populous Bundesland (Austria), state of Austria. It consists of two statutory city (Austria), statut ...
(Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
): 217,072 Germans and 69,858 others (mainly Croatian and Hungarian)
Post-Trianon Hungary
According to the 1920 census 10.4% of the population spoke one of the minority languages as mother language:
* 551,212 German (6.9%)
* 141,882 Slovak (1.8%)
* 23,760 Romanian (0.3%)
* 36,858 Croatian (0.5%)
* 23,228 Bunjevac and Šokci
Šokci ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Šokci, Шокци, , ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, label=, separator=" / ", Šokac, Шокац, sh-Latn-Cyrl, label=, separator=" / ", Šokica, Шокица; ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native t ...
(0.3%)
* 17,131 Serb (0.2%)
* 7,000 Slovenes (0,08%)
The number of bilingual people was much higher, for example 1,398,729 people spoke German (17%), 399,176 people spoke Slovak (5%), 179,928 people spoke Croatian (2.2%) and 88,828 people spoke Romanian (1.1%). Hungarian was spoken by 96% of the total population and was the mother language of 89%. The percentage and the absolute number of all non-Hungarian nationalities decreased in the next decades, although the total population of the country increased.
Note: 300.000 Hungarian refugees fled to Hungary from the territory of successor states (Romania, Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia) after the WW I.
From 1938 to 1945
Hungary expanded its borders with territories from Czechoslovakia, Romania and Yugoslavia following the First Vienna Award
The First Vienna Award was a treaty signed on 2 November 1938 pursuant to the Vienna Arbitration, which took place at Vienna's Belvedere Palace. The arbitration and award were direct consequences of the previous month's Munich Agreement, whic ...
(1938) and Second Vienna Award
The Second Vienna Award was the second of two territorial disputes that were arbitrated by Nazi Germany and the Kingdom of Italy. On 30 August 1940, they assigned the territory of Northern Transylvania, including all of Maramureș and part of Cri ...
(1940). The remainder of Carpathian Ruthenia and parts of Yugoslavia were occupied and annexed in 1939 and 1941, respectively. Regarding Northern Transylvania
Northern Transylvania (, ) was the region of the Kingdom of Romania that during World War II, as a consequence of the August 1940 territorial agreement known as the Second Vienna Award, became part of the Kingdom of Hungary (1920-1946), Kingdom ...
, the Romanian census from 1930 counted 38% Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former pa ...
and 49% Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, ...
, while the Hungarian census from 1941 counted 53.5% Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former pa ...
and 39.1% Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, ...
.Károly Kocsis, Eszter Kocsisné Hodosi, Ethnic Geography of the Hungarian Minorities in the Carpathian Basin, Simon Publications LLC, 1998, p. 116-15The territory of Bácska had 789,705 inhabitants, and 45,4% or 47,2% declared themselves to be Hungarian native speakers or ethnic Hungarians. The percentage of Hungarian speakers was 84% in southern Czechoslovakia and 25% in the Sub-Carpathian Rus. After WW II: 1949–1990 After World War II, about 200,000 Germans were deported to Germany according to the decree of the Potsdam Conference. Under the forced exchange of population between Czechoslovakia and Hungary, approximately 73,000 Slovaks left Hungary. After these population movements Hungary became an ethnically almost homogeneous country except the rapidly growing number of
Romani people
{{Infobox ethnic group
, group = Romani people
, image =
, image_caption =
, flag = Roma flag.svg
, flag_caption = Romani flag created in 1933 and accepted at the 1971 World Romani Congress
, po ...
in the second half of the 20th century.
For historical reasons, significant Hungarian minority populations can be found in the surrounding countries, notably in Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
(in Transcarpathia
Transcarpathia (, ) is a historical region on the border between Central and Eastern Europe, mostly located in western Ukraine's Zakarpattia Oblast.
From the Hungarian Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin, conquest of the Carpathian Basin ...
), Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
, Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
(in Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
), and Serbia
, image_flag = Flag of Serbia.svg
, national_motto =
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Serbia.svg
, national_anthem = ()
, image_map =
, map_caption = Location of Serbia (gree ...
(in Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( ; sr-Cyrl, Војводина, ), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an Autonomous administrative division, autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia, located in Central Europe. It lies withi ...
). Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
(in Burgenland
Burgenland (; ; ; Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian: ''Burgnland''; Slovene language, Slovene: ''Gradiščanska''; ) is the easternmost and least populous Bundesland (Austria), state of Austria. It consists of two statutory city (Austria), statut ...
), Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
, and Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
(Prekmurje
Prekmurje (; Prekmurje Slovene: ''Prèkmürsko'' or ''Prèkmüre''; ) is a geographically, linguistically, culturally, and ethnically defined region of Slovenia, settled by Slovenes and a Hungarians in Slovenia, Hungarian minority, lying betwee ...
) are also host to a number of ethnic Hungarians.
2001–2022
*Note: In 2001 570,537, in 2011 1,398,731 people did not give answer for ethnicity. Moreover, people were able to give more than one answer on the question asking for the minorities (for example, people were allowed to write Hungarian as their first ethnic identity and German as an ethnic identity being influenced by), hence the sum of the above exceeds the number of population.
*Methodology had changed in 2001 and 2011 also.
*Roma people is estimated to be around 8.8% Roma
Historical ethnic groups of Hungary

 When the
When the Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former pa ...
invaded the Carpathian Basin
The Pannonian Basin, with the term Carpathian Basin being sometimes preferred in Hungarian literature, is a large sedimentary basin situated in southeastern Central Europe. After the Treaty of Trianon following World War I, the geomorphologic ...
, it was inhabited by Slavic and Avar peoples. Written sources from the 9th century also suggest that some groups of Onogurs and Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic peoples, Turkic Nomad, semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region between the 5th and 7th centu ...
occupied the valley of the river Mureș at the time of the Magyars’ invasion. There is a dispute as to whether Romanian population existed in Transylvania during that time.
The Roma minority
The first Romani groups arrived in Hungary in the fifteenth century from Turkey. Nowadays, the real number of Roma in Hungary is a disputed question.
In the 2001 census only 190 046 (2%) called themselves Roma, but experts and Roma organisations estimate that there are between 450,000 and 1,000,000 Roma living in Hungary. Since then, the size of the Roma population has increased rapidly. Today every fifth or sixth newborn child belongs to the Roma minority. Based on current demographic trends, a 2006 estimate by Central European Management Intelligence claims that the proportion of the Roma population will double by 2050, putting the percentage of its Roma community at around 14-15% of the country's population.
There are problems related to the Roma minority in Hungary, and the very subject is a heated and disputed topic.
Objective problems:
* Slightly more than 80% of Roma children complete primary education, but only one third continue studies into the intermediate (secondary) level. This is far lower than the more than 90% proportion of children of non-Roma families who continue studies at an intermediate level. Less than 1% of Roma hold higher educational certificates.
* Poverty: most of the Roma people live in significantly worse conditions than others.
* Bad health conditions: life expectancy is about 10 years less compared to non-Romas
Kabars
Three Kabar
The Kabars (), also known as Qavars (Qabars) or Khavars, were Khazar rebels who joined Magyar tribes and the Rus' Khaganate confederations in the 9th century CE.
Sources
The Byzantine Emperor Constantine VII is the principal source of the Kaba ...
tribes joined to the Hungarians and participated in the Hungarian conquest of Hungary. They settled mostly in Bihar county.
Böszörménys
The Muslim Böszörmény
Böszörmény, also Izmaelita or Hysmaelita ("Ishmaelites") or Szerecsen ("Saracens"), is a name for the Muslims who lived in Hungary from its foundation at the end of the 9th century until the end of the 13th century. The ''Böszörmény'' were a ...
s migrated to the Carpathian Basin in the course of the 10th-12th centuries and they were composed of various ethnic groups. Most of them must have arrived from Volga Bulgaria
Volga Bulgaria or Volga–Kama Bulgaria (sometimes referred to as the Volga Bulgar Emirate) was a historical Bulgar state that existed between the 9th and 13th centuries around the confluence of the Volga and Kama River, in what is now Europea ...
and Khwarezm
Khwarazm (; ; , ''Xwârazm'' or ''Xârazm'') or Chorasmia () is a large oasis region on the Amu Darya river delta in western Central Asia, bordered on the north by the (former) Aral Sea, on the east by the Kyzylkum Desert, on the south by ...
.
Pechenegs
Communities of Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks, , Middle Turkic languages, Middle Turkic: , , , , , , ka, პაჭანიკი, , , ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Pečenezi, separator=/, Печенези, also known as Pecheneg Turks were a semi-nomadic Turkic peopl ...
(Besenyő in Hungarian) lived in the Kingdom of Hungary from the 11-12th centuries. They were most numerous in the county of Tolna.
Oghuz Turks (Ouzes)
Smaller groups of Oghuz Turk
The Oghuz Turks ( Middle Turkic: , ) were a western Turkic people who spoke the Oghuz branch of the Turkic language family. In the 8th century, they formed a tribal confederation conventionally named the Oghuz Yabgu State in Central Asia ...
settlers ('Úzok' or 'Fekete Kunok/Black Cumans' in Hungarian) came to the Carphatian Basin from the middle of the 11th century. They were settled mostly in Barcaság. The city of Ózd
Ózd () is a town in Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén county, Northern Hungary, from the county seat of Miskolc. Ózd is the second largest municipality in the county.
History
The area has been inhabited since ancient times. The village of Ózd was fir ...
got its name after them.
Jassics
The Jassic (Jász in Hungarian) people were a nomadic tribe which settled -with the Cumans- in the Kingdom of Hungary during the 13th century. Their name is almost certainly related to that of the Iazyges
The Iazyges () were an ancient Sarmatians, Sarmatian tribe that traveled westward in 200BC from Central Asia to the steppes of modern Ukraine. In , they moved into modern-day Hungary and Serbia near the Pannonian steppe between the Danube ...
. Béla IV
Béla may refer to:
* Béla (crater), an elongated lunar crater
* Béla (given name), a common Hungarian male given name
See also
* Bela (disambiguation)
* Belá (disambiguation)
* Bělá (disambiguation) Bělá may refer to:
Places in the Cze ...
, king of Hungary granted them asylum and they became a privileged community with the right of self-government. During the centuries they were fully assimilated to the Hungarian population, their language disappeared, but they preserved their Jassic identity and their regional autonomy until 1876. Over a dozen settlements in Central Hungary (e.g. Jászberény
Jászberény is a city and market centre in Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok county in Hungary.
Location
Jászberény is located in central Hungary, on the Zagyva River, a tributary of the Tisza River. It is about from Budapest.
History
The oldes ...
, Jászárokszállás
Jászárokszállás is a town in Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok county, in the Northern Great Plain region of central Hungary.
Geography
It covers an area of and has a population
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region o ...
, Jászfényszaru
Jászfényszaru is a town in Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok county, in the Northern Great Plain region of central Hungary.
Geography
It covers an area of and has a population of 5567 people (2015).
It is the meeting of three regions: the North-Hungary, t ...
) still bear their name.
Cumans
During the Russian campaign, the Mongols drove some 200,000 Cumans
The Cumans or Kumans were a Turkic people, Turkic nomadic people from Central Asia comprising the western branch of the Cumania, Cuman–Kipchak confederation who spoke the Cuman language. They are referred to as Polovtsians (''Polovtsy'') in Ru ...
, a nomadic tribe who had opposed them, west of the Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe and Southeast Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Ural Mountains, Urals at and the Scandinav ...
. There, the Cumans appealed to King Béla IV of Hungary for protection. In the Kingdom of Hungary, Cumans created two regions named Cumania
The name Cumania originated as the Latin exonym for the Cuman–Kipchak confederation, which was a tribal confederation in the western part of the Eurasian Steppe, between the 10th and 13th centuries. The confederation was dominated by two Turk ...
(''Kunság
Kunság (; ), later also known as Jászkunság or Jászkun kerület (lit. "Jassic–Cuman District"), is a historical, ethnographic and geographical region in Hungary, corresponding to a former political entity created by and for the Cumans or Ku ...
'' in Hungarian): Greater Cumania (''Nagykunság'') and Little Cumania (''Kiskunság''), both located the Great Hungarian Plain. Here, the Cumans maintained their autonomy, language and some ethnic customs well into the modern era
The modern era or the modern period is considered the current historical period of human history. It was originally applied to the history of Europe and Western history for events that came after the Middle Ages, often from around the year 1500 ...
. According to Pálóczi's estimation originally 70–80,000 Cumans settled in Hungary.
Romanians
The oldest extant documents from Transylvania make reference to Vlachs
Vlach ( ), also Wallachian and many other variants, is a term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate speakers of Eastern Romance languages living in Southeast Europe—south of the Danube (the Balkan peninsula ...
too. Regardless of the subject of Romanian
Romanian may refer to:
*anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Romania
**Romanians, an ethnic group
**Romanian language, a Romance language
***Romanian dialects, variants of the Romanian language
**Romanian cuisine, traditional ...
presence/non-presence in Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
prior to the Hungarian conquest, the first chronicles to write of Vlachs in the intra-Carpathian regions is the ''Gesta Hungarorum
''Gesta Hungarorum'', or ''The Deeds of the Hungarians'', is the earliest book about Kingdom of Hungary, Hungarian history which has survived for posterity. Its genre is not chronicle, but ''gesta'', meaning "deeds" or "acts", which is a medie ...
'', while the first written Hungarian sources about Romanian settlements derive from the 13th century, record was written about ''Olahteluk'' village in Bihar County
Bihar was an administrative county (Comitatus (Kingdom of Hungary), comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary and a county of the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom and Principality of Transylvania (1570–1711), Principality of Transylvania (since the 16th c ...
from 1283. The 'land of Romanians', ''Terram Blacorum'' (1222, 1280)Tamás Kis, Magyar nyelvjárások, Volumes 18-21, Nyelvtudományi Intézet, Kossuth Lajos Tudományegyetem (University of Kossuth Lajos). Magyar Nyelvtudományi Tanszék, 1972, p. 8/ref> showed up in Făgăraş, Fogaras and this area was mentioned under different name (Olachi) in 1285. The first appearance of a probably Romanian name 'Ola' in Hungary derives from a charter (1258). They were a significant population in Transylvania,
Banat
Banat ( , ; ; ; ) is a geographical and Historical regions of Central Europe, historical region located in the Pannonian Basin that straddles Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. It is divided among three countries: the eastern part lie ...
, Maramureș
( ; ; ; ) is a geographical, historical and cultural region in northern Romania and western Ukraine. It is situated in the northeastern Carpathians, along parts of the upper Tisza River drainage basin; it covers the Maramureș Depression and the ...
and Partium
Partium (from Latin '' partium'', the genitive plural of '' pars'' "part, portion") or ''Részek'' (in Hungarian) was a historical and geographical region in the Kingdom of Hungary during the early modern and modern periods. It consisted of the ...
(Crișana
Crișana (, , ) is a geographical and historical region of Romania named after the Criș (Körös) River and its three tributaries: the Crișul Alb, Crișul Negru, and Crișul Repede. In Romania, the term is sometimes extended to include areas ...
). There are different estimations in connection with number of Romanians in Kingdom of Hungary. According to a research based on place-names made by István Kniezsa, 511 villages of Transylvania and Banat appear in documents at the end of the 13th century, however only 3 of them bore Romanian names, and around 1400 AD, Transylvania and Banat consisted of 1757 villages, though only 76 (4.3%) of them had names of Romanian origin.Louis L. Lote (editor)ONE LAND — TWO NATIONS TRANSYLVANIA AND THE THEORY OF DACO-ROMAN-RUMANIAN CONTINUITY
COMMITTEE OF TRANSYLVANIA INC. (This is a special issue of the CARPATHIAN OBSERVER Volume 8, Number 1. Library of Congress Catalog Card Number; 80-81573), 1980, p. 10 The number of Romanians started to increase significantly from the
Early modern period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
, and by 1700 the Romanian ethnic group consisted of 40 percent of the Transylvanian population and their number raised even more in the 18th century. Although, in 1574, Pierre Lescalopier, relating his voyage from Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
to Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
, claimed that most of the inhabitants of Transylvania were Romanians and according to other estimates, the Romanian inhabitants who were primarily peasants, consisted of more than 60 percent of the population in 1600. Jean W. Sedlar estimates that Vlachs (Romanians) constituted about two-thirds of Transylvania's population in 1241 on the eve of the Mongol invasion, however according to Károly Kocsis and Eszter Kocsisné Hodosi the Hungarian ethnic group in Transylvania was in decent majority before Battle of Mohács
The Battle of Mohács (; , ) took place on 29 August 1526 near Mohács, in the Kingdom of Hungary. It was fought between the forces of Hungary, led by King Louis II of Hungary, Louis II, and the invading Ottoman Empire, commanded by Suleima ...
and only lost its relative majority by the 17th century. Nevertheless, Grigore Ureche
Grigore Ureche (; 1590–1647) was a Moldavian chronicler who wrote on Moldavian history in his ''Letopisețul Țării Moldovei'' ('' Chronicles of the Land of Moldavia''), covering the period from 1359 to 1594.
Biography
Grigore Ureche was th ...
in ''Letopisețul Țării Moldovei'' (1642 - 1647) noticed that in Transylvania Romanians were more numerous than Hungarians. Official censuses with information on Hungary's ethnic composition have been conducted since the 19th century.
In 1881, Romanian-majority settlements projected to the present-day territory of Hungary were: Bedő
Bedő () is a village in Hajdú-Bihar County, in the Northern Great Plain region of eastern Hungary.
Geography
It covers an area of and has a population
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Governm ...
, Csengerújfalu
Csengerújfalu () is a village in Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg county, in the Northern Great Plain region of eastern Hungary.
Geography
It covers an area of and has a population
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region ...
, Kétegyháza, Körösszakál
Körösszakál () is a village in Hajdú-Bihar county, in the Northern Great Plain region of eastern Hungary. The village is situated along the bank of the Sebes-Körös.
Geography
It covers an area of and has a population
Population is ...
, Magyarcsanád
Magyarcsanád (; ) is a multi-ethnic village located in Csongrád-Csanád County, southeastern Hungary, near the Mureș () River. The river Maros forms the border between southern Hungary and Romania.
The village has an outskirt called Bökén ...
, Méhkerék, Mezőpeterd
Mezőpeterd () is a village in Hajdú-Bihar county, in the Northern Great Plain region of eastern Hungary.
Geography
It covers an area of and has a population
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Go ...
, Pusztaottlaka
Pusztaottlaka (''Puszta-Ott·lak·a''; ) is a village in Békés County, in the Southern Great Plain region of south-east Hungary.
Geography
It covers an area of 18.88 km² and has a population
Population is a set of humans or other or ...
and Vekerd
Vekerd () is a village in Hajdú-Bihar County, in the Northern Great Plain region of eastern Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to ...
.
Important communities lived in the villages of Battonya
Battonya (; ) is a town in Békés County, in the Southern Great Plain region of south-east Hungary. Residents are Hungarians, with minority of Serbs and Romanians.
Geography
It covers an area of 145.77 km2 and has a population of 4966 peopl ...
, Elek, Körösszegapáti, Létavértes
Létavértes () is a town in Hajdú-Bihar county, in the Northern Great Plain region of eastern Hungary.
Geography
It covers an area of and has a population of 7061 people (2015).
International relations
Twin towns – Sister cities
Létavé ...
, Nyíradony, Pocsaj, Sarkadkeresztúr, Zsáka and in the town of Gyula.
Slovaks
The Slovak people lived mainly in Upper Hungary
Upper Hungary (, "Upland"), is the area that was historically the northern part of the Kingdom of Hungary, now mostly present-day Slovakia. The region has also been called ''Felső-Magyarország'' ( literally: "Upper Hungary"; ).
During the ...
, northern parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. Due to post-Ottoman resettlements, the regions of Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( ; sr-Cyrl, Војводина, ), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an Autonomous administrative division, autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia, located in Central Europe. It lies withi ...
, Banat
Banat ( , ; ; ; ) is a geographical and Historical regions of Central Europe, historical region located in the Pannonian Basin that straddles Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. It is divided among three countries: the eastern part lie ...
and Békés county
Békés (, , ) is an administrative division (county or ''vármegye'') in south-eastern Hungary, on the border with Romania. It shares borders with the Hungarian counties Csongrád-Csanád, Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok, and Hajdú-Bihar. The capital ...
received bigger Slovak communities in the 18th century, which revitalized many deserted villages and towns, such as Békéscsaba
Békéscsaba (; ; see also #Name, other alternative names) is a city with county rights in southeast Hungary, the capital of Békés County.
Geography
Békéscsaba is located in the Great Hungarian Plain, southeast from Budapest. Highway 44, 47 ...
, where Slovaks became the biggest ethnic group, or Nyíregyháza
Nyíregyháza (, ) is a city with county rights in northeastern Hungary and the county capital of Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg. With a population of 118,001, it is the seventh-largest city in Hungary and the second largest in the Northern Great ...
, where they comprised more than a third of the population in 1881. After WWII a major population exchange with Czechoslovakia was carried out: 71,787 or 73,200 Slovaks from Hungary were transferred to Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
– the exact number depends on source consulted – were resettled in South Slovakia in exchange for, according to different estimations, 45,000 or 120,000 Hungarians.
Serbs
From the 14th century, escaping from the Ottoman threat, a large number of Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Southeastern Europe who share a common Serbian Cultural heritage, ancestry, Culture of Serbia, culture, History of Serbia, history, and Serbian lan ...
migrated to the Hungarian Kingdom. After the Battle of Mohács
The Battle of Mohács (; , ) took place on 29 August 1526 near Mohács, in the Kingdom of Hungary. It was fought between the forces of Hungary, led by King Louis II of Hungary, Louis II, and the invading Ottoman Empire, commanded by Suleima ...
, most of the territory of Hungary got into Ottoman rule. In that time, especially in the 17th century, many Serb, and other Southern Slavic immigrants settled in Hungary. Most of the Ottoman soldiers in the territory of present-day Hungary were South Slavs
South Slavs are Slavic people who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, ...
(the Janissary
A janissary (, , ) was a member of the elite infantry units that formed the Ottoman sultan's household troops. They were the first modern standing army, and perhaps the first infantry force in the world to be equipped with firearms, adopted dur ...
). After the Turkish withdrawal, Kingdom of Hungary came under Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
rule, a new wave of Serb refugees migrated to the area around 1690, as a consequence of the Habsburg-Ottoman war. In the first half of the 18th century, Serbs and South Slavs were ethnic majority in several cities in Hungary.
Germans
Three waves of German migration can be distinguished in Hungary before the 20th century. The first two waves settled in Upper Hungary
Upper Hungary (, "Upland"), is the area that was historically the northern part of the Kingdom of Hungary, now mostly present-day Slovakia. The region has also been called ''Felső-Magyarország'' ( literally: "Upper Hungary"; ).
During the ...
and in Southern Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
(Transylvanian Saxons
The Transylvanian Saxons (; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjer Såksen'' or simply ''Soxen'', singularly ''Sox'' or ''Soax''; Transylvanian Landler dialect, Transylvanian Landler: ''Soxn'' or ''Soxisch''; ; seldom ''sa ...
), with the first being in the 11th century and the second in the 13th century.
The third, largest wave of German-speaking immigrants into Hungary occurred after the withdrawal of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
from Hungarian territory, after the Treaty of Karlowitz
The Treaty of Karlowitz, concluding the Great Turkish War of 1683–1699, in which the Ottoman Empire was defeated by the Holy League at the Battle of Zenta, was signed in Karlowitz, in the Military Frontier of the Habsburg Monarchy (present-day ...
. Between 1711 and 1780, German-speaking settlers immigrated to the regions of Southern Hungary, mostly region of Bánát, Bács-Bodrog, Baranya and Tolna counties (as well as into present-day Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
and Yugoslavia
, common_name = Yugoslavia
, life_span = 1918–19921941–1945: World War II in Yugoslavia#Axis invasion and dismemberment of Yugoslavia, Axis occupation
, p1 = Kingdom of SerbiaSerbia
, flag_p ...
), which had been depopulated by the Ottoman wars. At the end of the 18th century, the Kingdom of Hungary contained over one million German-speaking residents (collectively known as Danube Swabians
The Danube Swabians ( ) is a collective term for the ethnic German-speaking population who lived in the Kingdom of Hungary in east-central Europe, especially in the Danube River valley, first in the 12th century, and in greater numbers in the 17 ...
). In 2011, 131,951 people declared to be German in Hungary (1,6%).
Rusyns
Rusyns
Rusyns, also known as Carpatho-Rusyns, Carpatho-Russians, Ruthenians, or Rusnaks, are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group from the Carpathian Rus', Eastern Carpathians in Central Europe. They speak Rusyn language, Rusyn, an East Slavic lan ...
had lived mostly in Carpathian Ruthenia
Transcarpathia (, ) is a historical region on the border between Central and Eastern Europe, mostly located in western Ukraine's Zakarpattia Oblast.
From the Hungarian Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin, conquest of the Carpathian Basin ...
, Northeast Hungary, however significant Rusyn population appeared in Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( ; sr-Cyrl, Војводина, ), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an Autonomous administrative division, autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia, located in Central Europe. It lies withi ...
from the 18th century.
Croats
Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
was in personal union with Hungary from 1102. Croat
The Croats (; , ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and other neighboring countries in Central Europe, Central and Southeastern Europe who share a common Croatian Cultural heritage, ancest ...
communities were spread mostly in the western and southern part of the country and along the Danube, including Budapest.
Poles
The Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
lived at the northern borders of Kingdom of Hungary from the arrival of the Hungarians.
Slovenes
The Slovenes
The Slovenes, also known as Slovenians ( ), are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Slovenia and adjacent regions in Italy, Austria and Hungary. Slovenes share a common ancestry, Slovenian culture, culture, and History of Slove ...
(''Vendek'' in Hungarian) lived in the western part of the Carpathian basin before the Hungarian conquest. In the 11th and 12th century, the current linguistic and ethnic border between the Hungarian and Slovene people was established. Nowadays, they live in Vendvidék (''Slovenska krajina'' in Slovenians) between the Mura and the Rába
The Rába (; ; ) is a river in southeastern Austria and western Hungary and a right tributary of the Danube.
Geography
Its source is in Austria, some kilometres east of Bruck an der Mur below Heubodenhöhe Hill. It flows through the Austrian ...
rivers. In 2001, there were around 5,000 Slovenes in Hungary.
Jews
The first historical document about Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
of Hungary is the letter written about 960 to King Joseph of the Khazars by Hasdai ibn Shaprut, the Jewish statesman of Córdoba, in which he says Jews living in "the country of Hungarin". There are Jewish inscriptions on tombs and monuments in Pannonia (Roman Hungary) dated to the second or third century CE.
Armenians
The first Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
came to Hungary from the Balkans in the 10 - 11th century.
Greeks
Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
migrated to Kingdom of Hungary from the 15th and 16th centuries. Mass migrations did not occur until the 17th century, the largest waves being in 1718 and 1760–1770; they were primarily connected to the economic conditions of the period. It is estimated that 10,000 Greeks emigrated to Hungary in the second half of the 18th century. A number of Greeks Communists escaped to Hungary
after the Greek Civil War
The Greek Civil War () took place from 1946 to 1949. The conflict, which erupted shortly after the end of World War II, consisted of a Communism, Communist-led uprising against the established government of the Kingdom of Greece. The rebels decl ...
, notably in the 'Greek' village of Beloiannisz.
Bulgarians
The town of Szentendre
Szentendre, also known as Saint Andrew is a riverside town in Pest County, Hungary, between the capital city Budapest and Pilis Mountains, Pilis-Visegrád Mountains. The town is known for its museums (most notably the :hu: Szentendrei Szabadtéri ...
and the surrounding villages were inhabited by Bulgarians since the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
. However, present day Bulgarians
Bulgarians (, ) are a nation and South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and its neighbouring region, who share a common Bulgarian ancestry, culture, history and language. They form the majority of the population in Bulgaria, ...
are largely descended from gardener
A gardener is someone who practices gardening, either professionally or as a hobby.
Description
A gardener is any person involved in gardening, arguably the oldest occupation, from the hobbyist in a residential garden, the home-owner suppleme ...
s who migrated to Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
from the 18th century.
Religion
The majority of Hungarians becameChristian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
in the 11th century. Hungary remained predominantly Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
until the 16th century, when the Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major Theology, theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the p ...
led to the first Lutherans
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched the Reformation in 15 ...
, and later Calvinists
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Christian, Presbyterian, ...
, which were embraced by nearly the entire Hungarian population at the time.
In the second half of the 16th century, Jesuits
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
led a successful campaign of counterreformation among the Hungarians, although Protestantism survived as the faith of a significant minority, especially in the far east and northeast of the country. Orthodox Christianity
Orthodox, Orthodoxy, or Orthodoxism may refer to:
Religion
* Orthodoxy, adherence to accepted norms, more specifically adherence to creeds, especially within Christianity and Judaism, but also less commonly in non-Abrahamic religions like Neo-pag ...
in Hungary has been the religion mainly of some national minorities in the country, notably Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, ...
, Rusyns
Rusyns, also known as Carpatho-Rusyns, Carpatho-Russians, Ruthenians, or Rusnaks, are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group from the Carpathian Rus', Eastern Carpathians in Central Europe. They speak Rusyn language, Rusyn, an East Slavic lan ...
, Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
, and Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are a South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Southeastern Europe who share a common Serbian Cultural heritage, ancestry, Culture of Serbia, culture, History of Serbia, history, and Serbian lan ...
.
Faith Church, one of Europe's largest Pentecostal
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a movement within the broader Evangelical wing of Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that emphasizes direct personal experience of God in Christianity, God through Baptism with the Holy Spirit#Cl ...
churches, is also located in Hungary. Hungary has historically been home to a significant Jew
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, religion, and community are highly inte ...
ish community.
 According to 2011 census data,
According to 2011 census data, Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
is the largest religion in Hungary, with around 5.2 million adherents (52.9%), while the largest denomination in Hungary is the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
(38.9% — Latin Church
The Latin Church () is the largest autonomous () particular church within the Catholic Church, whose members constitute the vast majority of the 1.3 billion Catholics. The Latin Church is one of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical ...
37.1%; Hungarian Greek Catholic Church
The Hungarian Greek Catholic Church or the Byzantine Catholic Church in Hungary is a '' sui iuris'' (autonomous) Eastern Catholic church based in Hungary. As a particular church of the Catholic Church, it is in full communion with the Holy See. ...
1.8%). There is a significant Calvinist
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Protestantism, Continenta ...
minority (11.6% of the population) and smaller Lutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
(2.2%), Orthodox (0.1%) and Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
(0.1%) minorities. However, these census figures are representative of religious affiliation rather than attendance; around 12% of Hungarians attend religious services more than least once a week and around 50% more than once a year, while 30% of Hungarians do not believe in God at all. The census showed a large drop of religious adherents who wish to answer, from 74.6% to 54.7% in ten years' time, replacing them by people either who do not wish to answer or people who are not following a religion.
Immigration
Hungary migration data, 2001-present
Foreign citizenship population
Largest cities
See also
*Hungarian diaspora
The Hungarian diaspora or Magyar diaspora refers to ethnic Hungarians (''Magyars'') living outside the borders of present-day Hungary. The diaspora can be divided into two main groups: the first group includes those who are autochthonous to their ...
*Demographics of the Kingdom of Hungary by county
The following table shows the linguistic composition of each Hungarian county according to the Hungarian Census of 1910.
See also
*Demographics of Hungary
*Demographic history of Syrmia
References
{{Reflist
Sources
*Révai Nagy LexikonE ...
*History of Hungary
Hungary in its modern (post-1946) borders roughly corresponds to the Great Hungarian Plain (the Carpathian Basin) in Central Europe.
During the Iron Age, it was located at the crossroads between the cultural spheres of Scythian tribes (such a ...
* Demographic history of Syrmia
*Magyarization
Magyarization ( , also Hungarianization; ), after "Magyar"—the Hungarian autonym—was an assimilation or acculturation process by which non-Hungarian nationals living in the Kingdom of Hungary, then part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, adop ...
Notes
Sources
*References
External links
KSH, vital statistics, 1960-2012
{{DEFAULTSORT:Demographics Of Hungary Society of Hungary