forecasting
Forecasting is the process of making predictions based on past and present data. Later these can be compared with what actually happens. For example, a company might Estimation, estimate their revenue in the next year, then compare it against the ...
method that relies on a panel of experts. Delphi has been widely used for business forecasting and has certain advantages over another structured forecasting approach, prediction markets.
Delphi can also be used to help reach expert consensus and develop professional guidelines. It is used for such purposes in many health-related fields, including clinical medicine, public health, and research.
Delphi is based on the principle that forecasts (or decisions) from a structured group of individuals are more accurate than those from unstructured groups. The experts answer questionnaires in two or more rounds. After each round, a facilitator
A facilitator is a person who helps a Social group, group of people to work together better, understand their common objectives, and plan how to achieve these objectives, during meetings or discussions. In doing so, the facilitator remains "neut ...
or change agent provides an anonymised summary of the experts' forecasts from the previous round as well as the reasons they provided for their judgments. Thus, experts are encouraged to revise their earlier answers in light of the replies of other members of their panel. It is believed that during this process the range of the answers will decrease and the group will converge towards the "correct" answer. Finally, the process is stopped after a predefined stopping criterion (e.g., number of rounds, achievement of consensus, stability of results), and the mean
A mean is a quantity representing the "center" of a collection of numbers and is intermediate to the extreme values of the set of numbers. There are several kinds of means (or "measures of central tendency") in mathematics, especially in statist ...
or median
The median of a set of numbers is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a Sample (statistics), data sample, a statistical population, population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as the “ ...
scores of the final rounds determine the results.
Special attention has to be paid to the formulation of the Delphi theses and the definition and selection of the experts in order to avoid methodological weaknesses that severely threaten the validity and reliability of the results.
Ensuring that the participants have requisite expertise and that more domineering participants do not overwhelm weaker-willed participants, as the first group tends to be less inclined to change their minds and the second group is more motivated to fit in, can be a barrier to reaching true consensus.
History
The name ''Delphi'' derives from theOracle of Delphi
An oracle is a person or thing considered to provide insight, wise counsel or prophecy, prophetic predictions, most notably including precognition of the future, inspired by Deity, deities. If done through occultic means, it is a form of divina ...
, although the authors of the method were unhappy with the oracular connotation of the name, "smacking a little of the occult". The Delphi method assumes that group judgments are more valid than individual judgments.
The Delphi method was developed at the beginning of the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
to forecast the impact of technology on war
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or between such organi ...
fare. In 1944, General Henry H. Arnold ordered the creation of the report for the U.S. Army Air Corps on the future technological capabilities that might be used by the military.
Different approaches were tried, but the shortcomings of traditional forecasting
Forecasting is the process of making predictions based on past and present data. Later these can be compared with what actually happens. For example, a company might Estimation, estimate their revenue in the next year, then compare it against the ...
methods, such as theoretical approach, quantitative models or trend extrapolation, quickly became apparent in areas where precise scientific laws have not been established yet. To combat these shortcomings, the Delphi method was developed by Project RAND during the 1950-1960s (1959) by Olaf Helmer, Norman Dalkey, and Nicholas Rescher
Nicholas Rescher (; ; 15 July 1928 – 5 January 2024) was a German-born American philosopher, polymath, and author, who was a professor of philosophy at the University of Pittsburgh from 1961. He was chairman of the Center for Philosophy of Sc ...
. It has been used ever since, together with various modifications and reformulations, such as the Imen-Delphi procedure.
Experts were asked to give their opinion on the probability, frequency, and intensity of possible enemy attacks. Other experts could anonymously give feedback. This process was repeated several times until a consensus emerged.
In 2021, a cross-disciplinary study by Beiderbeck et al. focused on new directions and advancements of the Delphi method, including Real-time Delphi formats. The authors provide a methodological toolbox for designing Delphi surveys including among others sentiment analyses of the field of psychology.
Key characteristics
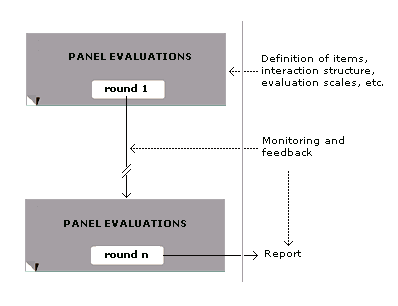 The following key characteristics of the Delphi method help the participants to focus on the issues at hand and separate Delphi from other methodologies: in this technique a panel of experts is drawn from both inside and outside the organisation. The panel consists of experts having knowledge of the area requiring decision making. Each expert is asked to make anonymous predictions.
The following key characteristics of the Delphi method help the participants to focus on the issues at hand and separate Delphi from other methodologies: in this technique a panel of experts is drawn from both inside and outside the organisation. The panel consists of experts having knowledge of the area requiring decision making. Each expert is asked to make anonymous predictions.
Anonymity of the participants
Usually all participants remain anonymous. Their identity is not revealed, even after the completion of the final report. This prevents the authority, personality, or reputation of some participants from dominating others in the process. Arguably, it also frees participants (to some extent) from their personal biases, minimizes the "bandwagon effect
The bandwagon effect is a psychological phenomenon where people adopt certain behaviors, styles, or attitudes simply because others are doing so. More specifically, it is a cognitive bias by which public opinion or behaviours can alter due to ...
" or "halo effect
The halo effect (sometimes called the halo error) is the tendency for positive impressions of a person, company, country, brand, or product in one area to positively influence one's opinion or feelings. The halo effect is "the name given to the p ...
", allows free expression of opinions, encourages open critique, and facilitates admission of errors when revising earlier judgments.
Structuring of information flow
The initial contributions from the experts are collected in the form of answers to questionnaires and their comments to these answers. The panel director controls the interactions among the participants by processing the information and filtering out irrelevant content. This avoids the negative effects of face-to-face panel discussions and solves the usual problems ofgroup dynamics
Group dynamics is a system of behaviors and psychological processes occurring within a social group (''intra''group dynamics), or between social groups ( ''inter''group dynamics). The study of group dynamics can be useful in understanding decision ...
.
Regular feedback
The Delphi method allows participants to comment on the responses of others, the progress of the panel as a whole, and to revise their own forecasts and opinions in real time.Role of the facilitator
The person coordinating the Delphi method is usually known as a ''facilitator'' or Leader, and facilitates the responses of their ''panel of experts'', who are selected for a reason, usually that they hold knowledge on an opinion or view. The facilitator sends out questionnaires, surveys etc. and if the panel of experts accept, they follow instructions and present their views. Responses are collected and analyzed, then common and conflicting viewpoints are identified. If consensus is not reached, the process continues through thesis and antithesis, to gradually work towards synthesis, and building consensus. During the past decades, facilitators have used many different measures and thresholds to measure the degree of consensus or dissent. A comprehensive literature review and summary is compiled in an article by von der Gracht.Applications
Use in forecasting
First applications of the Delphi method were in the field of science and technology forecasting. The objective of the method was to combine expert opinions on likelihood and expected development time, of the particular technology, in a single indicator. One of the first such reports, prepared in 1964 by Gordon and Helmer, assessed the direction of long-term trends in science and technology development, covering such topics as scientific breakthroughs, population control,automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, mainly by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machine ...
, space progress, war prevention and weapon systems. Other forecasts of technology were dealing with vehicle-highway systems, industrial robots, intelligent internet, broadband connections, and technology in education.
Later the Delphi method was applied in other places, especially those related to public policy issues, such as economic trend Economic trend may refer to:
*all the economic indicators that are the subject of economic forecasting
**see also: econometrics
*general trends in the economy, see: economic history
Economic history is the study of history using methodologica ...
s, health and education. It was also applied successfully and with high accuracy in business forecasting. For example, in one case reported by Basu and Schroeder (1977), the Delphi method predicted the sales of a new product during the first two years with inaccuracy of 3–4% compared with actual sales. Quantitative methods produced errors of 10–15%, and traditional unstructured forecast methods had errors of about 20%. (This is only one example; the overall accuracy of the technique is mixed.)
The Delphi method has also been used as a tool to implement multi-stakeholder approaches for participative policy-making in developing countries. The governments of Latin America and the Caribbean have successfully used the Delphi method as an open-ended public-private sector approach to identify the most urgent challenges for their regional ICT-for-development eLAC Action Plans. As a result, governments have widely acknowledged the value of collective intelligence from civil society, academic and private sector participants of the Delphi, especially in a field of rapid change, such as technology policies.
Use in patent participation identification
In the early 1980s Jackie Awerman of Jackie Awerman Associates, Inc. designed a modified Delphi method for identifying the roles of various contributors to the creation of a patent-eligible product. (Epsilon Corporation, Chemical Vapor Deposition Reactor) The results were then used by patent attorneys to determine bonus distribution percentage to the general satisfaction of all team members.Use in policy-making
From the 1970s, the use of the Delphi technique in public policy-making introduces a number of methodological innovations. In particular: * the need to examine several types of items (not only ''forecasting'' items but, typically, ''issue'' items, ''goal'' items, and ''option'' items) leads to introducing different evaluation scales which are not used in the standard Delphi. These often include ''desirability'', ''feasibility'' (technical and political) and ''probability'', which the analysts can use to outline different scenarios: the ''desired'' scenario (from desirability), the ''potential'' scenario (from feasibility) and the ''expected'' scenario (from probability); * the complexity of issues posed in public policy-making tends to increase weighting of panelists’ arguments, such as soliciting pros and cons for each item along with new items for panel consideration; * likewise, methods measuring panel evaluations tend to increase sophistication such as multi-dimensional scaling. Further innovations come from the use of computer-based (and later web-based) Delphi conferences. According to Turoff and Hiltz, in computer-based Delphis: * the iteration structure used in the paper Delphis, which is divided into three or more discrete rounds, can be replaced by a process of continuous (roundless) interaction, enabling panelists to change their evaluations at any time; * the statistical group response can be updated in real-time, and shown whenever a panelist provides a new evaluation. According to Bolognini,. A summary is also in web-based Delphis offer two further possibilities, relevant in the context of interactive policy-making ande-democracy
E-democracy (a blend of the terms Electronic publishing, electronic and democracy), also known as digital democracy or Internet democracy, uses information and communication technology (ICT) in politics, political and governance processes. The ...
. These are: Use in health settings
The Delphi technique is widely used to help reach expert consensus in health-related settings. For example, it is frequently employed in the development ofmedical guideline
A medical guideline (also called a clinical guideline, standard treatment guideline, or clinical practice guideline) is a document with the aim of guiding decisions and criteria regarding diagnosis, management, and treatment in specific areas of ...
s and protocols.
Public health
Some examples of its application inpublic health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the de ...
contexts include non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
An alcohol-free or non-alcoholic drink, also known as a temperance drink, is a version of an alcoholic drink made without alcohol, or with the alcohol removed or reduced to almost zero. These may take the form of a non-alcoholic mixed drink or n ...
, iodine deficiency disorders, building responsive health systems for communities affected by migration, the role of health systems in advancing well-being for those living with HIV, on policies and interventions to reduce harmful gambling
Gambling (also known as betting or gaming) is the wagering of something of Value (economics), value ("the stakes") on a Event (probability theory), random event with the intent of winning something else of value, where instances of strategy (ga ...
, on the regulation of electronic cigarettes
An electronic cigarette (e-cigarette), or vape, is a device that simulates smoking. It consists of an Construction of electronic cigarettes#Atomizer and tank, atomizer, a power source such as a battery, and a container such as a cartridge or ...
and on recommendations to end the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
.
Reporting guidelines
Use of the Delphi method in the development of guidelines for the reporting of health research is recommended, especially for experienced developers. Since this advice was made in 2010, two systematic reviews have found that fewer than 30% of published reporting guidelines incorporated Delphi methods into the development process.Online Delphi systems
A number of Delphi forecasts are conducted using web sites that allow the process to be conducted in real-time. For instance, the TechCast Project uses a panel of 100 experts worldwide to forecast breakthroughs in all fields of science and technology. Another example is the Horizon Project, where educational futurists collaborate online using the Delphi method to come up with the technological advancements to look out for in education for the next few years.Variations
Traditionally the Delphi method has aimed at a consensus of the most probable future by iteration. Other versions, such as the Policy Delphi, offer decision support methods aiming at structuring and discussing the diverse views of the preferred future. In Europe, more recent web-based experiments have used the Delphi method as a communication technique for interactivedecision-making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the Cognition, cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be ...
and e-democracy
E-democracy (a blend of the terms Electronic publishing, electronic and democracy), also known as digital democracy or Internet democracy, uses information and communication technology (ICT) in politics, political and governance processes. The ...
.
The Argument Delphi, developed by Osmo Kuusi, focuses on ongoing discussion and finding relevant arguments rather than focusing on the output. The Disaggregative Policy Delphi, developed by Petri Tapio, uses cluster analysis as a systematic tool to construct various scenarios of the future in the latest Delphi round. The respondent's view on the probable and the preferable future are dealt with as separate cases. The computerization of Argument Delphi is relatively difficult because of several problems like argument resolution, argument aggregation and argument evaluation. The computerization of Argument Delphi, developed by Sadi Evren Seker, proposes solutions to such problems.
A fast-track Delphi was developed to provide consensual expert opinion on the state of scientific knowledge in public health crises. It can provide results within three weeks, while the conventional Delphi can take several months (sometimes years).
Accuracy
Today the Delphi method is a widely accepted forecasting tool and has been used successfully for thousands of studies in areas varying from technology forecasting todrug abuse
Substance misuse, also known as drug misuse or, in older vernacular, substance abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods that are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder, differing definitions ...
.
Overall the track record of the Delphi method is mixed.Khodyakov, D., Grant, S., Kroger, J., Bauman, M. (2023). ''RAND methodological guidance for conducting and critically appraising Delphi panels.'' RAND Corporation. www.rand.org/t/TLA3082-1 https://doi.org/10.7249/tla3082-1 There have been many cases when the method produced poor results. Still, some authors attribute this to poor application of the method and not to the weaknesses of the method itself. The ''RAND Methodological Guidance for Conducting and Critically Appraising Delphi Panels'' is a manual for doing Delphi research which provides guidance for doing research and offers a appraisal tool. This manual gives guidance on best practices that will help to avoid, or mitigate, potential drawbacks of Delphi Method Research; it also helps to understand the confidence that can be given to study results.
It must also be realized that in areas such as science and technology forecasting, the degree of uncertainty is so great that exact and always correct predictions are impossible, so a high degree of error is to be expected. An important challenge for the method is ensuring sufficiently knowledgeable panelists. If panelists are misinformed about a topic, the use of Delphi may only add confidence to their ignorance.
One of the initial problems of the method was its inability to make complex forecasts with multiple factors. Potential future outcomes were usually considered as if they had no effect on each other. Later on, several extensions to the Delphi method were developed to address this problem, such as cross impact analysis, that takes into consideration the possibility that the occurrence of one event may change probabilities of other events covered in the survey. Still the Delphi method can be used most successfully in forecasting single scalar indicators.
Delphi vs. prediction markets
Delphi has characteristics similar to prediction markets as both are structured approaches that aggregate diverse opinions from groups. Yet, there are differences that may be decisive for their relative applicability for different problems. Some advantages of prediction markets derive from the possibility to provide incentives for participation. # They can motivate people to participate over a long period of time and to reveal their true beliefs. # They aggregate information automatically and instantly incorporate new information in the forecast. # Participants do not have to be selected and recruited manually by a facilitator. They themselves decide whether to participate if they think their private information is not yet incorporated in the forecast. Delphi seems to have these advantages over prediction markets: # Participants reveal their reasoning # It is easier to maintain confidentiality # Potentially quicker forecasts if experts are readily available. # Delphi is applicable in situations where the bets involved might affect the value of the currency used in bets (e.g. a bet on the collapse of the dollar made in dollars might have distorted odds). More recent research has also focused on combining both, the Delphi technique and prediction markets. More specifically, in a research study atDeutsche Börse
Deutsche Börse AG (), or the Deutsche Börse Group, is a German multinational corporation that offers a marketplace for organizing the trading of shares and other securities. It is also a transaction services provider, giving companies and inv ...
elements of the Delphi method had been integrated into a prediction market.
See also
* Computer supported brainstorming *DARPA
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military. Originally known as the Adva ...
's Policy Analysis Market
* Horizon scanning
Horizon scanning (HS) or horizon scan is a method from futures studies, sometimes regarded as a part of foresight. It is the early detection and assessment of emerging technologies or threats for mainly policy makers in a domain of choice. Su ...
* Nominal group technique
The nominal group technique (NGT) is a group process involving problem identification, solution generation, and decision-making. It can be used in groups of many sizes, who want to make their decision quickly, as by a vote, but want everyone's opin ...
* Planning poker
* Reference class forecasting
Reference class forecasting or comparison class forecasting is a method of predicting the future by looking at similar past situations and their outcomes. The theories behind reference class forecasting were developed by Daniel Kahneman and Amos ...
* Wideband delphi
* '' The Wisdom of Crowds''
References
Further reading
* This article provides a detailed description of the use of modified Delphi for qualitative, participatory action research. * A cross-validation study replicating one completed in the Netherlands and Belgium, and exploring US experts' views on the diagnosis and treatment of older adults with personality disorders.External links
RAND publications on the Delphi Method
Downloadable documents from RAND concerning applications of the Delphi Technique. {{Authority control Estimation methods Forecasting Systems thinking Futures techniques