Datapath VisionRGB-E2s Dual Port Capture Card on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A data path is a collection of 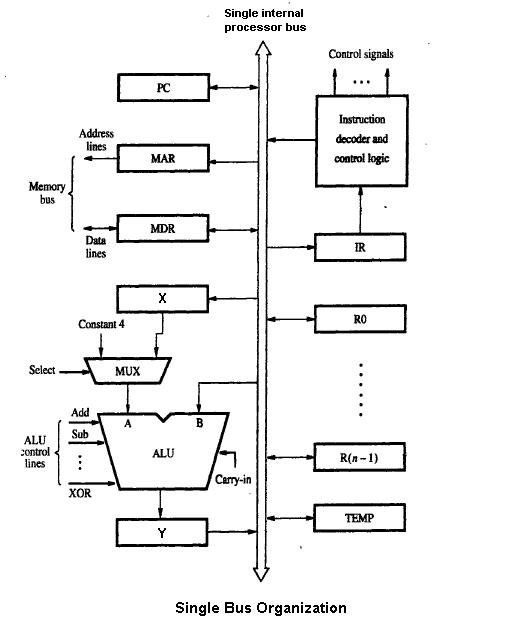 The simplest design for a CPU uses one common internal bus.
Efficient addition requires a slightly more complicated three-internal-bus structure.
Many relatively simple CPUs have a 2-read, 1-write
The simplest design for a CPU uses one common internal bus.
Efficient addition requires a slightly more complicated three-internal-bus structure.
Many relatively simple CPUs have a 2-read, 1-write
functional unit
In computer engineering, an execution unit (E-unit or EU) is a part of a processing unit that performs the operations and calculations forwarded from the instruction unit. It may have its own internal control sequence unit (not to be confused wi ...
s such as arithmetic logic unit
In computing, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is a Combinational logic, combinational digital circuit that performs arithmetic and bitwise operations on integer binary numbers. This is in contrast to a floating-point unit (FPU), which operates on ...
s (ALUs) or multiplier Multiplier may refer to:
Mathematics
* Multiplier (arithmetic), the number of multiples being computed in multiplication
* Constant multiplier, a constant factor with units of measurement
* Lagrange multiplier, a scalar variable used in mathema ...
s that perform data processing operations, register
Register or registration may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Music
* Register (music), the relative "height" or range of a note, melody, part, instrument, etc.
* ''Register'', a 2017 album by Travis Miller
* Registration (organ), ...
s, and buses
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a motor vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van, but fewer than the average rail transport. It is most commonly used ...
. Along with the control unit
The control unit (CU) is a component of a computer's central processing unit (CPU) that directs the operation of the processor. A CU typically uses a binary decoder to convert coded instructions into timing and control signals that direct the op ...
it composes the central processing unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor, or just processor, is the primary Processor (computing), processor in a given computer. Its electronic circuitry executes Instruction (computing), instructions ...
(CPU). A larger data path can be made by joining more than one data paths using multiplexers
In electronics, a multiplexer (or mux; spelled sometimes as multiplexor), also known as a data selector, is a device that selects between several analog or digital input signals and forwards the selected input to a single output line. The sel ...
.
A data path is the ALU, the set of registers, and the CPU's internal bus(es) that allow data to flow between them.
 The simplest design for a CPU uses one common internal bus.
Efficient addition requires a slightly more complicated three-internal-bus structure.
Many relatively simple CPUs have a 2-read, 1-write
The simplest design for a CPU uses one common internal bus.
Efficient addition requires a slightly more complicated three-internal-bus structure.
Many relatively simple CPUs have a 2-read, 1-write register file
A register file is an array of processor registers in a central processing unit (CPU). The instruction set architecture of a CPU will almost always define a set of registers which are used to stage data between memory and the functional units on ...
connected to the 2 inputs and 1 output of the ALU.
During the late 1990s, there was growing research in the area of reconfigurable data paths—data paths that may be re-purposed at run-time using programmable fabric—as such designs may allow for more efficient processing as well as substantial power savings.
Finite-state machine with data path
A finite-state machine with data path (FSMD) is a mathematical abstraction which combines afinite-state machine
A finite-state machine (FSM) or finite-state automaton (FSA, plural: ''automata''), finite automaton, or simply a state machine, is a mathematical model of computation. It is an abstract machine that can be in exactly one of a finite number o ...
, which controls the program flow
In computer science, control flow (or flow of control) is the order in which individual Statement (computer science), statements, Instruction (computer science), instructions or function calls of an imperative programming, imperative computer pro ...
, with a data path. It can be used to design digital logic
A logic gate is a device that performs a Boolean function, a logical operation performed on one or more binary inputs that produces a single binary output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gate, one that has, for ...
or computer program
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to Execution (computing), execute. It is one component of software, which also includes software documentation, documentation and other intangibl ...
s.
FSMDs are essentially sequential programs in which statements have been scheduled into states, thus resulting in more complex state diagrams. Here, a program is converted into a complex state diagram in which states and arcs may include arithmetic expression
In mathematics, an expression is a written arrangement of symbols following the context-dependent, syntactic conventions of mathematical notation. Symbols can denote numbers, variables, operations, and functions. Other symbols include punctu ...
s, and those expressions may use external inputs and outputs as well as variables. The FSMD level of abstraction is often referred to as the register-transfer level
In digital circuit design, register-transfer level (RTL) is a design abstraction which models a synchronous digital circuit in terms of the flow of digital signals (data) between hardware registers, and the logical operations performed on th ...
.
FSMs do not use variables or arithmetic operations/conditions, thus FSMDs are more powerful than FSMs. An FSMD is equivalent to a Turing machine
A Turing machine is a mathematical model of computation describing an abstract machine that manipulates symbols on a strip of tape according to a table of rules. Despite the model's simplicity, it is capable of implementing any computer algori ...
in expressiveness.
References
Central processing unit Digital electronics {{CPU technologies