Data Reduction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Data reduction is the transformation of numerical or alphabetical

digital information
Digital data, in information theory and information systems, is information represented as a string of Discrete mathematics, discrete symbols, each of which can take on one of only a finite number of values from some alphabet (formal languages ...
derived empirically or experimentally into a corrected, ordered, and simplified form. The purpose of data reduction can be two-fold: reduce the number of data records by eliminating invalid data or produce summary data and statistics at different aggregation levels for various applications. Data reduction does not necessarily mean loss of information.
When information is derived from instrument readings there may also be a transformation from analog to digital form. When the data are already in digital form the 'reduction' of the data typically involves some editing, scaling
Scaling may refer to:
Science and technology
Mathematics and physics
* Scaling (geometry), a linear transformation that enlarges or diminishes objects
* Scale invariance, a feature of objects or laws that do not change if scales of length, energ ...
, encoding
In communications and Data processing, information processing, code is a system of rules to convert information—such as a letter (alphabet), letter, word, sound, image, or gesture—into another form, sometimes data compression, shortened or ...
, sorting
Sorting refers to ordering data in an increasing or decreasing manner according to some linear relationship among the data items.
# ordering: arranging items in a sequence ordered by some criterion;
# categorizing: grouping items with similar p ...
, collating, and producing tabular summaries. When the observations are discrete but the underlying phenomenon is continuous then smoothing and interpolation
In the mathematics, mathematical field of numerical analysis, interpolation is a type of estimation, a method of constructing (finding) new data points based on the range of a discrete set of known data points.
In engineering and science, one ...
are often needed. The data reduction is often undertaken in the presence of reading or measurement error
Observational error (or measurement error) is the difference between a measured value of a quantity and its unknown true value.Dodge, Y. (2003) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', OUP. Such errors are inherent in the measurement pr ...
s. Some idea of the nature of these errors is needed before the most likely value may be determined.
An example in astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
is the data reduction in the ''Kepler'' satellite. This satellite records 95-megapixel images once every six seconds, generating dozens of megabytes of data per second, which is orders-of-magnitudes more than the downlink bandwidth of 550 kB/s. The on-board data reduction encompasses co-adding the raw frames for thirty minutes, reducing the bandwidth by a factor of 300. Furthermore, interesting targets are pre-selected and only the relevant pixels are processed, which is 6% of the total. This reduced data is then sent to Earth where it is processed further.
Research has also been carried out on the use of data reduction in wearable (wireless) devices for health monitoring and diagnosis applications. For example, in the context of epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of Non-communicable disease, non-communicable Neurological disorder, neurological disorders characterized by a tendency for recurrent, unprovoked Seizure, seizures. A seizure is a sudden burst of abnormal electrical activit ...
diagnosis, data reduction has been used to increase the battery lifetime of a wearable EEG device by selecting and only transmitting EEG data that is relevant for diagnosis and discarding background activity.
Types of Data Reduction
Dimensionality Reduction
When dimensionality increases, data becomes increasingly sparse while density and distance between points, critical to clustering and outlier analysis, becomes less meaningful.Dimensionality reduction
Dimensionality reduction, or dimension reduction, is the transformation of data from a high-dimensional space into a low-dimensional space so that the low-dimensional representation retains some meaningful properties of the original data, ideally ...
helps reduce noise in the data and allows for easier visualization, such as the example below where 3-dimensional data is transformed into 2 dimensions to show hidden parts. One method of dimensionality reduction is wavelet transform, in which data is transformed to preserve relative distance between objects at different levels of resolution, and is often used for image compression
Image compression is a type of data compression applied to digital images, to reduce their cost for computer data storage, storage or data transmission, transmission. Algorithms may take advantage of visual perception and the statistical properti ...
.

Numerosity Reduction
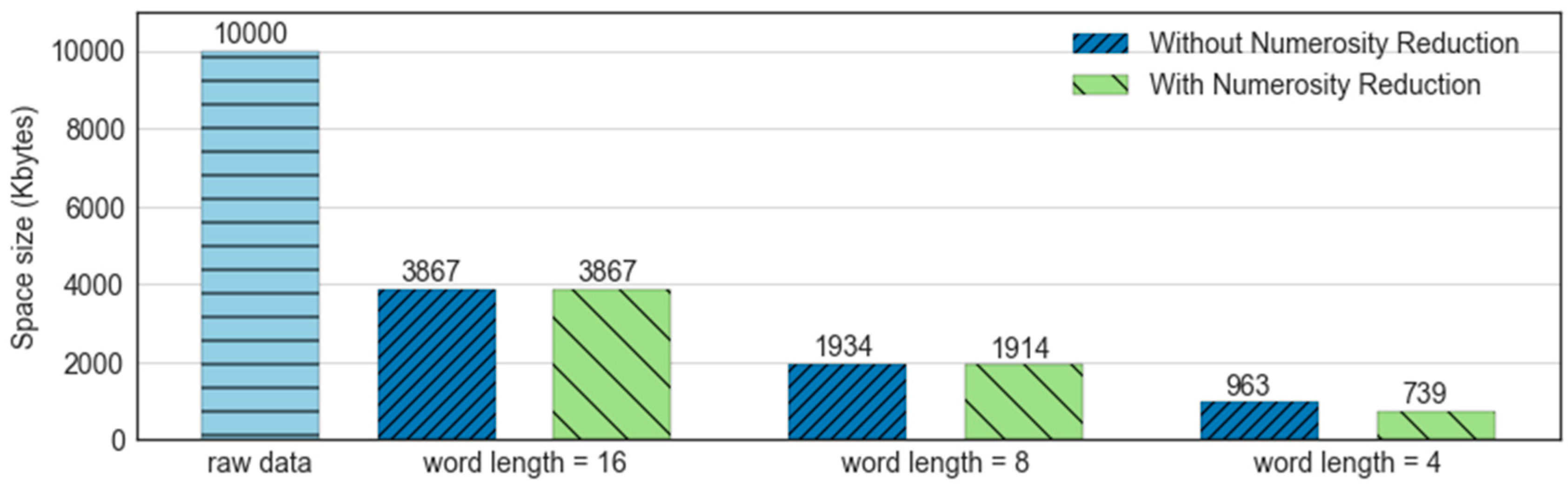
This method of data reduction reduces the data volume by choosing alternate, smaller forms of data representation. Numerosity reduction can be split into 2 groups: parametric and non-parametric methods. Parametric methods (regression, for example) assume the data fits some model, estimate model parameters, store only the parameters, and discard the data. One example of this is in the image below, where the volume of data to be processed is reduced based on more specific criteria. Another example would be a log-linear model, obtaining a value at a point in m-D space as the product on appropriate marginal subspaces. Non-parametric methods do not assume models, some examples being histograms, clustering, sampling, etc.
Statistical modelling
Data reduction can be obtained by assuming a statistical model for the data. Classical principles of data reduction include sufficiency,likelihood
A likelihood function (often simply called the likelihood) measures how well a statistical model explains observed data by calculating the probability of seeing that data under different parameter values of the model. It is constructed from the j ...
, conditionality and equivariance.
See also
*Data cleansing
Data cleansing or data cleaning is the process of identifying and correcting (or removing) corrupt, inaccurate, or irrelevant records from a dataset, table, or database. It involves detecting incomplete, incorrect, or inaccurate parts of the dat ...
* Data editing
* Data preprocessing
* Data wrangling
References
Further reading
* {{data *