Dascylium on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
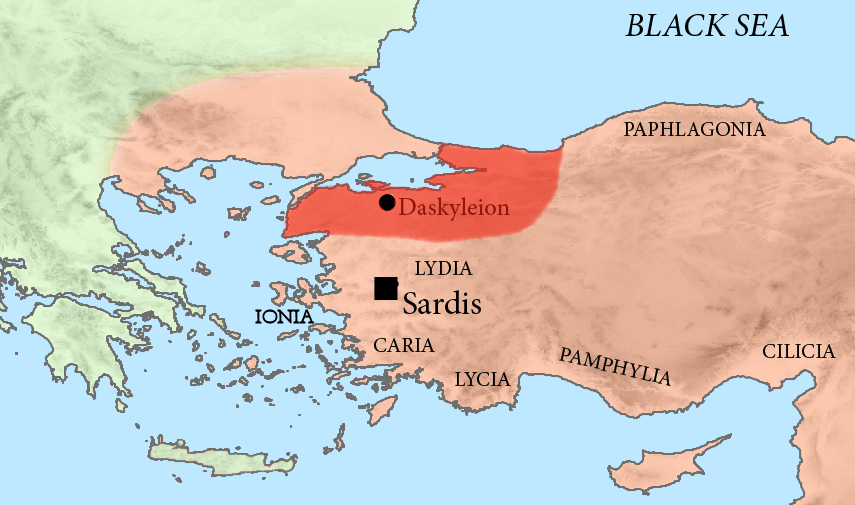 Dascylium, Dascyleium, or Daskyleion (), also known as Dascylus, was a town in
Dascylium, Dascyleium, or Daskyleion (), also known as Dascylus, was a town in
/ref>
 Dascylium, Dascyleium, or Daskyleion (), also known as Dascylus, was a town in
Dascylium, Dascyleium, or Daskyleion (), also known as Dascylus, was a town in Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
some inland from the coast of the Propontis, at modern Ergili, Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
. Its site was rediscovered in 1952 and has since been excavated.Dascylium (Ergili)/ref>
History
Excavations have shown that the site was inhabited in theBronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
.
Iron Age
Phrygian period
Phrygians settled there before 750 BC. It came under the control ofLydia
Lydia (; ) was an Iron Age Monarchy, kingdom situated in western Anatolia, in modern-day Turkey. Later, it became an important province of the Achaemenid Empire and then the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sardis.
At some point before 800 BC, ...
. It was then said to be named after Dascylus, the father of Gyges.
Persian period
After the Conquests of Cyrus the Great in 547 BC, Dascylium was chosen as the seat of the Persian satrapy of Hellespontine Phrygia, comprising lands of the Troad,Mysia
Mysia (UK , US or ; ; ; ) was a region in the northwest of ancient Asia Minor (Anatolia, Asian part of modern Turkey). It was located on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara. It was bounded by Bithynia on the east, Phrygia on the southeast, Lyd ...
and Bithynia.
Hellenistic period
Pharnabazus was satrap of Darius III there, untilAlexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
appointed Calas, who was replaced by Arrhidaeus in the Treaty of Triparadisus. According to Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
, Hellespontine Phrygia and Phrygia Epictetus comprised Lesser Phrygia (Mysia
Mysia (UK , US or ; ; ; ) was a region in the northwest of ancient Asia Minor (Anatolia, Asian part of modern Turkey). It was located on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara. It was bounded by Bithynia on the east, Phrygia on the southeast, Lyd ...
). Others geographers arranged it differently.
It was a member of the Delian League
The Delian League was a confederacy of Polis, Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, founded in 478 BC under the leadership (hegemony) of Classical Athens, Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Achaemenid Empire, Persian ...
.
When Alexander of Macedon invaded Asia in 334 BC, the first of the major battles by which he overthrew the Achaemenid Empire was fought at the Granicus river on his way to Dascylium from Abydos on the coast.
Bishopric
Dascylium appears as aChristian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
bishopric
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
in the mid-7th-century ''Notitia Episcopatuum The ''Notitiae Episcopatuum'' (singular: ''Notitia Episcopatuum'') were official documents that furnished for Eastern countries the list and hierarchical rank of the metropolitan and suffragan bishoprics of a church.
In the Roman Church (the mos ...
'' of Pseudo-Epiphanius. It was a suffragan
A suffragan bishop is a type of bishop in some Christian denominations.
In the Catholic Church, a suffragan bishop leads a diocese within an ecclesiastical province other than the principal diocese, the metropolitan archdiocese; the diocese led ...
of the metropolitan see
Metropolitan may refer to:
Areas and governance (secular and ecclesiastical)
* Metropolitan archdiocese, the jurisdiction of a metropolitan archbishop
** Metropolitan bishop or archbishop, leader of an ecclesiastical "mother see"
* Metropolitan ...
of Nicomedia
Nicomedia (; , ''Nikomedeia''; modern İzmit) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek city located in what is now Turkey. In 286, Nicomedia became the eastern and most senior capital city of the Roman Empire (chosen by the emperor Diocletian who rul ...
, capital of the Roman province
The Roman provinces (, pl. ) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as Roman g ...
of Bithynia.
The first bishop of Dascylium whose name appears in an extant document is Ioannes, who took part in the Third Council of Constantinople in 680 and in the Trullan Council
The Quinisext Council (; , literally meaning, ''Fifth-Sixth Meeting''), i.e., the Fifth-Sixth Council, often called the Council ''in Trullo'', Trullan Council, or the Penthekte Synod, was a church council held in 692 at Constantinople under Ju ...
of 692. The priest Basilius acted as representative of an unnamed bishop of the see at the Second Council of Nicaea
The Second Council of Nicaea is recognized as the last of the first seven ecumenical councils by the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Catholic Church. In addition, it is also recognized as such by Old Catholic Church, Old Catholics and others. ...
in 787. Georgius was at the Council of Constantinople (869) and Germanus at the Photian Council of Constantinople (879)
The Fourth Council of Constantinople was held in 879–880. It confirmed the reinstatement of Photius I as patriarch of Constantinople.
The result of this council is accepted by the Eastern Orthodox as having the authority of an ecumenical c ...
.
Archaeology
In 2020, archaeologists found a 4th century BC terracotta mask, representing the godDionysus
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, myth, Dionysus (; ) is the god of wine-making, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, festivity, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, and theatre. He was also known as Bacchus ( or ; ...
, in the city’s acropolis. From 1988 to 2010 the excavations were directed by Tomris Bakır. In August 2021, archaeologists led by Kaan Iren have announced the discovery of Ancient relief described Greek-Persian wars at Dascylium. Explorer Kaan Iren said: "there are Greek soldiers fighting and Persians on horseback fighting them. Greek soldiers are depicted under the hoofs of Persian horses. There is a propaganda scene here under the pretext of war".
See also
* Ancient sites of BalıkesirReferences
Further reading
* * * {{Coord, 40, 07, 44, N, 28, 04, 18, E, display=title Populated places established in the 8th century BC 1952 archaeological discoveries Populated places in ancient Mysia Populated places in Bithynia Catholic titular sees in Asia Achaemenid cities Hellespontine Phrygia Former populated places in Turkey Members of the Delian League