Darya-i-Noor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
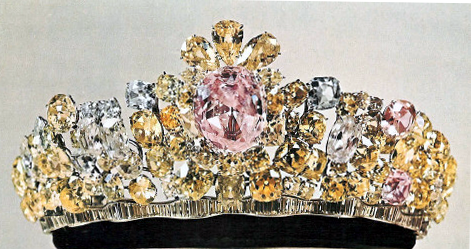
The or 'Ocean of Light'), also spelled Darya-ye Noor and Daria-i-Nur, is one of the largest cut diamonds in the world, weighing an estimated 182 carats (36 g). Its colour, pale pink, is one of the rarest to be found in diamonds. The diamond is currently in the
 In 1965, a Canadian team conducting research on the
In 1965, a Canadian team conducting research on the
Treasury of National Jewels of Iran
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140226222210/https://cbi.ir/page/2091.aspx , date=2014-02-26 Iranian National Jewels Jewels of the Mughal Empire Individual diamonds Pink diamonds Golconda diamonds Dhaka Nawab family Wars involving Afsharid Iran
Iranian National Jewels
The Iranian National Jewels (, ''Javāherāt-e Melli-ye Irān''), originally the Iranian Crown Jewels (, ''Javāherāt-e Saltanati-ye Irān''), include elaborate crowns, thirty tiaras, and numerous aigrettes, a dozen bejeweled swords and shields ...
collection of the Central Bank of Iran
The Central Bank of the Islamic Republic of Iran (CBI; ; SWIFT Code: BMJIIRTH), also known as ''Bank Markazi'', was established under the Iranian Banking and Monetary Act in 1960. It serves as the banker to the Iranian government and has the e ...
in Tehran
Tehran (; , ''Tehrân'') is the capital and largest city of Iran. It is the capital of Tehran province, and the administrative center for Tehran County and its Central District (Tehran County), Central District. With a population of around 9. ...
. During the reign of Naser al-Din Shah
Naser al-Din Shah Qajar (; ; 17 July 1831 – 1 May 1896) was the fourth Shah of Qajar Iran from 5 September 1848 to 1 May 1896 when he was assassinated. During his rule there was internal pressure from the people of Iran, as well as external ...
, an elaborate frame was crafted from 457 smaller diamonds and four rubies, crowned by Iran's imperial insignia. However, another diamond with the same name is in a private collection in Bangladesh.
Dimensions
It is and weighs around 182 metric carats. It is the world's largest known pink diamond. It may have been cut originally from an even larger stone.History
This diamond, as is also presumed for theKoh-i-Noor
The ; ), also spelled Koh-e-Noor, Kohinoor and Koh-i-Nur, is one of the largest cut diamonds in the world, weighing . It is currently set in the Crown of Queen Elizabeth The Queen Mother.
The diamond originated in the Kollur mine in present ...
, was mined in Kollur mine
The Kollur Mine was a series of gravel-clay pits on the south bank of the Krishna River in the state of Andhra Pradesh, India. It has produced many large diamonds, known as Golconda diamonds, several of which are or have been a part of crown je ...
in the Golcanda region of Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (ISO 15919, ISO: , , AP) is a States and union territories of India, state on the East Coast of India, east coast of southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, seventh-largest state and th ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
. Its early origins are shrouded in mystery, but it is believed to have been one of the eyes of the Mughal
Mughal or Moghul may refer to:
Related to the Mughal Empire
* Mughal Empire of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries
* Mughal dynasty
* Mughal emperors
* Mughal people, a social group of Central and South Asia
* Mughal architecture
* Mug ...
Peacock Throne
The Peacock Throne ( Hindustani: ''Mayūrāsana'', Sanskrit: मयूरासन, Urdu: تخت طاؤس, , ''Takht-i Tāvūs'') was the imperial throne of Hindustan. The throne is named after the dancing peacocks at its rear and was the seat ...
.
In 1739, Nader Shah
Nader Shah Afshar (; 6 August 1698 or 22 October 1688 – 20 June 1747) was the founder of the Afsharid dynasty of Iran and one of the most powerful rulers in Iranian history, ruling as shah of Iran (Persia) from 1736 to 1747, when he was a ...
of Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
invaded Northern India and occupied Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
. As payment for returning the crown of India to the Mughal
Mughal or Moghul may refer to:
Related to the Mughal Empire
* Mughal Empire of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries
* Mughal dynasty
* Mughal emperors
* Mughal people, a social group of Central and South Asia
* Mughal architecture
* Mug ...
emperor Muhammad Shah
Mirza Nasir-ud-Din Muḥammad Shah (born Roshan Akhtar; 7 August 1702 – 26 April 1748) was the thirteenth Mughal emperor from 1719 to 1748. He was son of Khujista Akhtar, the fourth son of Bahadur Shah I. After being chosen by the Sayyid ...
, he took possession of the entire fabled treasury of the Mughals, including the ''Daria-i-Noor'', the Koh-i-Noor, and the Peacock Throne
The Peacock Throne ( Hindustani: ''Mayūrāsana'', Sanskrit: मयूरासन, Urdu: تخت طاؤس, , ''Takht-i Tāvūs'') was the imperial throne of Hindustan. The throne is named after the dancing peacocks at its rear and was the seat ...
.
After Nader Shah's death in 1747, the diamond was inherited by his grandson, Shahrokh Mirza. From there, it fell into the hands of Lotf Ali Khan
Lotf Ali Khan (; ) was the last Shah of the Iranian Zand dynasty, ruling from 1789 to 1794.
Early life
Lotf Ali Khan Zand came to power after a decade of infighting among a succession of violent and inept Zand chiefs following the death in 177 ...
. After Lotf Ali Khan's defeat at the hands of Mohammad Khan Qajar
Agha Mohammad Khan Qajar (; 14 March 1742 – 17 June 1797), also known by his regnal name of Agha Mohammad Shah (), was the founder of the Qajar dynasty of Iran, ruling from 1789 to 1797 as Shah. Originally a chieftain of the Quwanlu branch of t ...
, who established the ruling Qajar dynasty
The Qajar family (; 1789–1925) was an Iranian royal family founded by Mohammad Khan (), a member of the Qoyunlu clan of the Turkoman-descended Qajar tribe. The dynasty's effective rule in Iran ended in 1925 when Iran's '' Majlis'', conven ...
of Iran, the Daria-i-Noor entered the Qajar treasury. During this time, Naser al-Din Shah Qajar
Naser al-Din Shah Qajar (; ; 17 July 1831 – 1 May 1896) was the fourth Shah of Qajar Iran from 5 September 1848 to 1 May 1896 when he was assassinated. During his rule there was internal pressure from the people of Iran, as well as external ...
was said to be very fond of the diamond, often wearing it as an arm band, an aigrette, or a brooch, and maintenance of the diamond was an honor bestowed upon higher ranking individuals.
Return to the Indian subcontinent theory
Another theory postulates that the diamond, or another diamond of the same name, had made its way back to the Indian subcontinent by the 19th century. Eventually the diamond made its way into the hands ofMaharaja Ranjit Singh
Ranjit Singh (13 November 1780 – 27 June 1839) was the founder and first maharaja of the Sikh Empire, in the northwest Indian subcontinent, ruling from 1801 until his death in 1839.
Born to Maha Singh, the leader of the Sukerchakia Misl ...
of the Sikh Empire
The Sikh Empire was a regional power based in the Punjab, Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent. It existed from 1799, when Maharaja Ranjit Singh captured Lahore, to 1849, when it was defeated and conquered by the East India Company, Br ...
, where it was kept in the ''Toshakhana'' (treasury). After the annexation of the Sikh Empire into the Company Raj
Company rule in India (also known as the Company Raj, from Hindi , ) refers to regions of the Indian subcontinent under the control of the British East India Company (EIC). The EIC, founded in 1600, established its first trading post in India ...
, the stone was confiscated by the British alongside other valuables from the Sikh treasury. A reference is made to it in a list prepared by John Login of confiscated items from the treasury. Login valued the diamond at 63,000 rupees, the equivalent of £6,000 in 1840 which would convert to more than £100 million in 2012. Jewelry associated with the diamond were eleven pearls, eleven additional diamonds, and eleven garnets (known locally as ''choonee''). The total weight was 10.8 ''tolas'' in the local weight measurement system. The Daria-i-Noor would make its way to London but fail to garner the attraction of the British nobility. Thus, two years later it was shipped back to India to be auctioned off, with the Nawab of Dhaka
The Nawab of Dhaka (Bengali: "ঢাকার নবাব"), originally spelt in English Nawab of Dacca, was the title of the head of one of the largest Muslim zamindar in British Bengal and Assam, based in present-day Dhaka, Bangladesh. The t ...
being the winning bidder. To this day it is said to remain in a Bangladeshi bank's vault.
Possible association
 In 1965, a Canadian team conducting research on the
In 1965, a Canadian team conducting research on the Iranian Crown Jewels
The Iranian National Jewels (, ''Javāherāt-e Melli-ye Irān''), originally the Iranian Crown Jewels (, ''Javāherāt-e Saltanati-ye Irān''), include elaborate crowns, thirty tiaras, and numerous aigrettes, a dozen bejeweled swords and shield ...
concluded that the Daria-i-Noor may well have been part of a large pink diamond that had been studded in the throne of the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan
Shah Jahan I, (Shahab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram; 5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), also called Shah Jahan the Magnificent, was the Emperor of Hindustan from 1628 until his deposition in 1658. As the fifth Mughal emperor, his reign marked the ...
, and had been described in the journal of the French jeweller Jean-Baptiste Tavernier
Jean-Baptiste Tavernier (1605–1689) was a 17th-century French gem merchant and traveler. Tavernier, a private individual and merchant traveling at his own expense, covered, by his own account, 60,000 leagues in making six voyages to Persia ...
in 1642, who called it the Great Table diamond ("Diamanta Grande Table"). This diamond may have been cut into two pieces; the larger part is the Daria-i-Noor; the smaller part is believed to be the Noor-ul-Ain
The Noor-ul-Ain () is one of the largest pink diamonds in the world, and the centre piece of the tiara of the same name.
History
The diamond is believed to have been recovered from the mines of Golconda, Hyderabad in India. It was first in poss ...
diamond, presently studded in a tiara also in the Iranian Imperial collection.
See also
* Golconda diamonds * Great Table diamond *Koh-i-Noor
The ; ), also spelled Koh-e-Noor, Kohinoor and Koh-i-Nur, is one of the largest cut diamonds in the world, weighing . It is currently set in the Crown of Queen Elizabeth The Queen Mother.
The diamond originated in the Kollur mine in present ...
* Noor-ul-Ain
The Noor-ul-Ain () is one of the largest pink diamonds in the world, and the centre piece of the tiara of the same name.
History
The diamond is believed to have been recovered from the mines of Golconda, Hyderabad in India. It was first in poss ...
* List of diamonds
Diamond (gemstone), Diamonds occur naturally and vary in size, color, and quality, so the largest of a particular color may not be large in absolute terms, but may still be considered very desirable. Diamonds may also have high valuations in sal ...
* List of largest rough diamonds
This is a partial list of the largest non-synthetic diamonds with a rough stone (uncut) weight of over 200 carats (40 grams). The list is not intended to be complete—e.g., the Cullinan (formerly Premier) mine alone has produced 135 diamonds la ...
Notes
References
External links
Treasury of National Jewels of Iran
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140226222210/https://cbi.ir/page/2091.aspx , date=2014-02-26 Iranian National Jewels Jewels of the Mughal Empire Individual diamonds Pink diamonds Golconda diamonds Dhaka Nawab family Wars involving Afsharid Iran