Dance History on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The history of dance is difficult to access because
The history of dance is difficult to access because

 There is a long recorded history of Chinese dances. Some of the dances mentioned in ancient texts, such as dancing with sleeve movements are still performed today. Some of the early dances were associated with shamanic rituals.
There is a long recorded history of Chinese dances. Some of the dances mentioned in ancient texts, such as dancing with sleeve movements are still performed today. Some of the early dances were associated with shamanic rituals.
Ballets Russes brought together great music, design and dance together in a one complete performanc
African dance refers mainly to the dance styles of
Ntongela Masilela's essay.
/ref> artist
Historic Illustrations of Dancing from 3300 B.C. to 1911 A.D.
from
The history of pointe shoes and technique (ballet)
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Dance Dance research

 The history of dance is difficult to access because
The history of dance is difficult to access because dance
Dance is an The arts, art form, consisting of sequences of body movements with aesthetic and often Symbol, symbolic value, either improvised or purposefully selected. Dance can be categorized and described by its choreography, by its repertoir ...
does not often leave behind clearly identifiable physical artifacts that last over millennia, such as stone tool
Stone tools have been used throughout human history but are most closely associated with prehistoric cultures and in particular those of the Stone Age. Stone tools may be made of either ground stone or knapped stone, the latter fashioned by a ...
s, hunting implements or cave paintings
In archaeology, cave paintings are a type of parietal art (which category also includes petroglyphs, or engravings), found on the wall or ceilings of caves. The term usually implies prehistoric origin. These paintings were often created by ''Hom ...
. It is not possible to identify with exact precision when dance becomes part of human culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
. Dance is filled with aesthetic values, making it distinct from one society to another and is shrouded in symbolism that expounds on the cultural heritage of a community accordingly being unique from one society to another. Dance can help tell a story, convey feelings and emotions, and connect with others and ourselves.
Early dance
The natural impulse to dance may have existed in early primates before they evolved into humans. Dance has been an important part ofceremony
A ceremony (, ) is a unified ritualistic event with a purpose, usually consisting of a number of artistic components, performed on a special occasion.
The word may be of Etruscan language, Etruscan origin, via the Latin .
Religious and civil ...
, ritual
A ritual is a repeated, structured sequence of actions or behaviors that alters the internal or external state of an individual, group, or environment, regardless of conscious understanding, emotional context, or symbolic meaning. Traditionally ...
s, celebrations and entertainment
Entertainment is a form of activity that holds the attention and Interest (emotion), interest of an audience or gives pleasure and delight. It can be an idea or a task, but it is more likely to be one of the activities or events that have deve ...
since before the birth of the earliest human civilization
A civilization (also spelled civilisation in British English) is any complex society characterized by the development of state (polity), the state, social stratification, urban area, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyon ...
s. Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
delivers traces of dance from prehistoric times
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use o ...
such as the 10,000-year-old Bhimbetka rock shelters
The Bhimbetka rock shelters are an archaeological site in central India that spans the Paleolithic and Mesolithic periods, as well as the historic period. It exhibits the earliest traces of human life in India and evidence of the Stone Age star ...
paintings in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
and Egyptian
''Egyptian'' describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of year ...
tomb depicting dancing figures from c. 3300 BC. Many contemporary dance
Contemporary dance is a genre of Concert dance, dance performance that developed during the mid-twentieth century and has since grown to become one of the dominant genres for formally trained dancers throughout the world, with particularly stron ...
forms can be traced back to historical
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categ ...
, traditional
A tradition is a system of beliefs or behaviors (folk custom) passed down within a group of people or society with symbolic meaning or special significance with origins in the past. A component of cultural expressions and folklore, common examp ...
, ceremonial
A ceremony (, ) is a unified ritualistic event with a purpose, usually consisting of a number of artistic components, performed on a special occasion.
The word may be of Etruscan origin, via the Latin .
Religious and civil (secular) ceremoni ...
and ethnic
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, re ...
dances of the ancient period.
Means of social communication and bonding
Dance may have been used as a tool of social interaction that promoted cooperation essential for survival among earlyhuman
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s. Studies found that today's best dancers share two specific genes associated with a predisposition for being good social communicators.
Also, the term "kinesthetic" is the right term to help understanding how dance makes communication, and it means recognition of movement of one's own body, this word is a combination of two words (Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
: ''kinein'' "to move", ''aesthesis'' "perception"). So dance moves and background sounds play a big role too. When there is a group performance by holding hands or shoulders or even dancing opposite each other makes them feel communicated and bonded.
As folk celebrations
Many dances of the early periods were performed as a ritual to the gods who ancestors believed needed to be kept entertained for world peace. Dance used in many celebrations and until now. Throughout history we can notice that dance had many uses such as also community dance, harvesting and worship. Dance evolution started as folk origins to court presentations and now theater or even cinema movies.In ceremonies and rituals
Dance may be performed in religious or shamanic rituals, for example inrain dance
Rainmaking is a weather modification ritual that attempts to invoke rain. It is based on the belief that humans can influence nature, spirits, or the ancestors who withhold or bring rain.
Among the best known examples of weather modification ...
performed in times of drought. Shamans dancing for rain is mentioned in ancient Chinese texts. Dance is an important aspect of some religious rites in ancient Egypt, similarly dance is also integral to many ceremonies and rites among African people. Ritual dances may also be performed in temples and during religious festivals, for example the Rasa ritual dances of India (a number of Indian classical dance
Indian classical dance, or ''Shastriya Nritya'', is an umbrella term for different regionally-specific Indian classical dance traditions, rooted in predominantly Hindu musical theatre performance,, Quote: All of the dances considered to be part ...
s may have their origin in ritual dances), and the Cham dance
The cham dance () entry: 'cham. is a lively masked and costumed dance associated with some sects of Tibetan Buddhism and Buddhist festivals. The dance is accompanied by music played by bhikkhu, monks using traditional Tibetan musical instruments ...
s of Tibet.
As a method of healing
Another early use of dance may have been as a precursor to ecstatic trance states in healing rituals. Dance is used for this purpose by many cultures from the Brazilianrainforest
Rainforests are forests characterized by a closed and continuous tree Canopy (biology), canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforests can be generally classified as tropi ...
to the Kalahari Desert
The Kalahari Desert is a large semiarid climate, semiarid sandy savanna in Southern Africa covering including much of Botswana as well as parts of Namibia and South Africa.
It is not to be confused with the Angolan, Namibian, and South African ...
.Guenther, Mathias Georg. 'The San Trance Dance: Ritual and Revitalization Among the Farm Bushmen of the Ghanzi District, Republic of Botswana.' Journal, South West Africa Scientific Society, v30, 1975–76. Medieval European '' danses macabres'' were thought to have protected participants from disease; however, the hysteria and duration of these dances sometimes led to death due to exhaustion.
According to a Sinhalese legend, Kandyan dance
Kandyan dance (Sinhala language, Sinhala: උඩරට නැටුම්) encompasses various dance forms popular and native to the area called Kandy of the Central Hills region known as Udarata in Sri Lanka, which have today spread to other pa ...
s originated 2500 years ago from a magic dance ritual that broke the spell on a bewitched king to cure the king of a mysterious illness.
As a method of expression
One of the earliest structured uses of dances may have been in the performance and in the telling of myths. It was also sometimes used to show feelings for one of the opposite gender. It is also linked to the origin of "lovemaking". Before the production of written languages, dance was one of the methods of passing these stories down from generation to generation.Nathalie Comte. "Europe, 1450 to 1789: Encyclopedia of the Early Modern World". Ed. Jonathan Dewald. Vol. 2. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons, 2004. p94-108. In European culture, one of the earliest records of dancing is byHomer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
, whose ''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; , ; ) is one of two major Ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odyssey'', the poem is divided into 24 books and ...
'' describes chorea
Chorea, or (rarely) choreia, () is an abnormal involuntary movement disorder, characterized by quick movements of the hands or feet. It is one of a group of neurological disorders called dyskinesias. The term ''chorea'' is derived , as the move ...
(χορεία ''khoreia''). The early Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
s made the art of dancing into a system, expressive of all the different passions. For example, the dance of the Furies
The Erinyes ( ; , ), also known as the Eumenides (, the "Gracious ones"), are chthonic goddesses of vengeance in ancient Greek religion and mythology. A formulaic oath in the ''Iliad'' invokes them as "the Erinyes, that under earth take v ...
, so represented, would create complete terror among those who witnessed them. The Greek philosopher, Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
, ranked dancing with poetry
Poetry (from the Greek language, Greek word ''poiesis'', "making") is a form of literature, literary art that uses aesthetics, aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language to evoke meaning (linguistics), meanings in addition to, or in ...
, and said that certain dancers, with rhythm applied to gesture, could express manners, passions, and actions. The most eminent Greek sculptors studied the attitude
Attitude or Attitude may refer to:
Philosophy and psychology
* Attitude (psychology), a disposition or state of mind
** Attitude change
* Propositional attitude, a mental state held towards a proposition
Science and technology
* Orientation ...
of the dancers for their art of imitating the passion.
Cultural traditions
Asia

Indian classical dance
An early manuscript describing dance is the ''Natya Shastra
The ''Nāṭya Shāstra'' (, ''Nāṭyaśāstra'') is a Sanskrit treatise on the performing arts. The text is attributed to sage Bharata, and its first complete compilation is dated to between 200 BCE and 200 CE, but estimates vary b ...
'' on which is based the modern interpretation of classical Indian dance
Indian classical dance, or ''Shastriya Nritya'', is an umbrella term for different regionally-specific Indian classical dance traditions, rooted in predominantly Hindu musical theatre performance,, Quote: All of the dances considered to be part ...
(e.g. Bharathanatyam).
During the reign of the last Mughals
The Mughal Empire was an early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to the highlands of pre ...
and Nawab
Nawab is a royal title indicating a ruler, often of a South Asian state, in many ways comparable to the Western title of Prince. The relationship of a Nawab to the Emperor of India has been compared to that of the Kingdom of Saxony, Kings of ...
s of Oudh
The Kingdom of Awadh (, , also Oudh State, Kingdom of Oudh, Awadh Subah, or Awadh State) was a Mughal subah, then an independent kingdom, and lastly a British protectorate in the Awadh region of North India until its annexation by the Br ...
, dance fell down to the status of 'nautch
The nautch (, meaning "dance" or "dancing" from Hindustani: "naach")Scott A. Kugle, 2016When Sun Meets Moon: Gender, Eros, and Ecstasy in Urdu Poetry p.230. was a popular court dance performed by girls (known as "nautch girls") in later Mug ...
', an unethical sensuous thing of courtesans.
Later, linking dance with immoral trafficking and prostitution, British rule prohibited public performance of dance. Many disapproved of it. In 1947, India won its freedom and created for dance an ambience where it could regain its past glory. Classical forms and regional distinctions were re-discovered, ethnic specialties were honored, and by synthesizing them with the individual talents of the masters in the line and fresh innovations, emerged dance with a new face but with classicism of the past.
In Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
, the ancient Sinhalese chronicle '' Mahavamsa'' states that when King Vijaya landed in Sri Lanka in 543 BCE he heard sounds of music and dancing from a wedding ceremony. The origins of the dances of Sri Lanka
There are several styles of classical and folk dance in Sri Lanka.
cultivators) -->
Classical dances
There are three main styles of Sri Lankan classical dance:
*The Kandyan dances of the Hill Country, known as Kandyan dance, Uda Rata Natum;
*T ...
are dated back to the aboriginal tribes, and to the mythological times of aboriginal yingyang twins and " yakkas" (devils). The classical dances of Sri Lanka (Kandyan dances) feature a highly developed system of tala (rhythm) and provided by cymbals called thalampataa.
Chinese dance
 There is a long recorded history of Chinese dances. Some of the dances mentioned in ancient texts, such as dancing with sleeve movements are still performed today. Some of the early dances were associated with shamanic rituals.
There is a long recorded history of Chinese dances. Some of the dances mentioned in ancient texts, such as dancing with sleeve movements are still performed today. Some of the early dances were associated with shamanic rituals. Folk dance
A folk dance is a dance that reflects the life of the people of a certain country or region. Not all ethnic dances are folk dances. For example, Ritual, ritual dances or dances of ritual origin are not considered to be folk dances. Ritual dances ...
s of the early period were also developed into court dances. The important dances of the ancient period were the ceremonial ''yayue
''Yayue'' () was a form of classical music and dance performed at the royal court and temples in ancient China. The basic conventions of ''yayue'' were established in the Western Zhou. Together with law and rites, it formed the formal represent ...
'' dated to the Zhou dynasty
The Zhou dynasty ( ) was a royal dynasty of China that existed for 789 years from until 256 BC, the longest span of any dynasty in Chinese history. During the Western Zhou period (771 BC), the royal house, surnamed Ji, had military ...
of the first millennium BC. The art of dance in China reached its peak during the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed ...
, a period when dancers from many parts of the world also performed at the imperial court. However, Chinese opera
Traditional Chinese opera (), or ''Xiqu'', is a form of musical theatre in China with roots going back to the early periods in China. It is an amalgamation of various art forms that existed in ancient China, and evolved gradually over more tha ...
became popular during the Song and Yuan dynasty, and many dances were merged into Chinese opera. The art of dance in women also declined from the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv ...
onward as a result of the increasing popularity of footbinding
Foot binding (), or footbinding, was the Chinese custom of breaking and tightly binding the feet of young girls to change their shape and size. Feet altered by foot binding were known as lotus feet and the shoes made for them were known as lotus ...
, a practice that ironically may have originated from dancing when a dancer wrapped her feet so she may dance ballet-fashion. The best-known of the Chinese traditional dances are the dragon dance
Dragon dance () is a form of traditional dance and performance in China, Chinese culture of China, culture. Like the lion dance, it is most often seen during festive celebrations. The dance is performed by a team of experienced dancers who man ...
and lion dance
Lion dance ( zh, s=舞狮, t=舞獅, p=wǔshī, c=, first=t) is a form of traditional dance in Culture of China, Chinese culture and other Asian countries in which performers mimic a Asiatic lion, lion's movements in a lion costume to bring good l ...
. Lion dance was described in the Tang dynasty in form that resembles today's dance.
Iranian dance
= Prehistory
= The people of the Iranian plateau have known dance in the forms of music, play, drama or religious rituals and have used instruments like mask, costumes of animals or plants, and musical instruments for rhythm, at least since the 6th millennium BC. Cultural mixed forms of dance, play and drama have served rituals like celebration, mourning and worship. And the actors have been masters of music, dance, physical acts and manners of expression. Artifacts with pictures of dancers, players or actors were found in many archaeological prehistoric sites in Iran, like Tepe Sabz, Ja'far Abad, Chogha Mish, Tall-e Jari, Cheshmeh Ali, Ismaeel Abad, Tal-e bakun, Tepe Sialk, Tepe Musian, tepe Yahya, Shahdad, Tepe Gian, Kul Farah, Susa, Kok Tepe, Cemeteries of Luristan, etc.= History
= The earliest researched dance from historic Iran is a dance worshipingMithra
Mithra ( ; ) is an ancient Iranian deity ('' yazata'') of covenants, light, oaths, justice, the Sun, contracts, and friendship. In addition to being the divinity of contracts, Mithra is also a judicial figure, an all-seeing protector of Truth ( ...
(as in the Cult of Mithras) in which a bull was sacrificed. This cult later became highly adhered in the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
. This dance was to promote vigor in life. Ancient Persian dance was significantly researched by Greek historian from Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
of Halikarnassos, in his work ''Book IX (Calliope)'', in which he describes the history of Asian empires and Persian wars until 478 BC. Ancient Persia was occupied by foreign powers, first Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
, then Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of yea ...
, and then Mongols
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China ( Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family o ...
and in turn political instability and civil wars occurred. Throughout these changes a slow disappearance of heritage dance traditions occurred.
Religious prohibition of dancing in Iran came with the spread of Islam, but it was spurred by historical events. Religious prohibition to dancing waxed and waned over the years, but after the Iranian Revolution
The Iranian Revolution (, ), also known as the 1979 Revolution, or the Islamic Revolution of 1979 (, ) was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dynasty in 1979. The revolution led to the replacement of the Impe ...
in 1979 dancing was no longer allowed due to its frequent mixing of the sexes. The Islamic Revolution of 1979 was the end of a successful era for dancing and the art of ballet in Iran. The Iranian national ballet company was dissolved and its members emigrated to different countries. According to the principles of the "cultural revolution" in Iran, dancing was considered to be perverse, a great sin, immoral and corrupting. As a result, many of the talented Persian dancers moved to the West and spread out mainly in Europe and the United States and a new generation of Iranian dancers and ballet artists have grown up in the Diaspora.
Europe
15th–19th centuries: from court dancing to Romanticism
The origins of ballet dancing can be traced to the Italian Renaissance courts of the 15th century. Dance masters would teach the steps to nobility and the court would participate in performances as a form of social entertainment. This practice continued for several centuries. In the 17th century, courtly ballet reached its peak under the rule of KingLouis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
.
By the 18th century, ballet
Ballet () is a type of performance dance that originated during the Italian Renaissance in the fifteenth century and later developed into a concert dance form in France and Russia. It has since become a widespread and highly technical form of ...
had migrated from the French and Italian royal courts to the Paris Opéra
The Paris Opera ( ) is the primary opera and ballet company of France. It was founded in 1669 by Louis XIV as the , and shortly thereafter was placed under the leadership of Jean-Baptiste Lully and officially renamed the , but continued to be kn ...
under the careful direction of composer/dancer Jean-Baptiste Lully
Jean-Baptiste Lully ( – 22 March 1687) was a French composer, dancer and instrumentalist of Italian birth, who is considered a master of the French Baroque music style. Best known for his operas, he spent most of his life working in the court o ...
. Lully sought to develop ballet into more serious art. Under his influence, ballet was turned into a recognized art that was performed by professional dancers rather than courtiers.
During the 18th century, ballet transitioned from a courtly dance of moving images as a spectacle to performance art in its own right. Ballet performances developed around a central narrative and contained an expressive movement that revealed the relationships between characters. This dramatic style of ballet became known as the ballet d'action
Ballet d'action is a hybrid genre of expressive and symbolic ballet
Ballet () is a type of performance dance that originated during the Italian Renaissance in the fifteenth century and later developed into a concert dance form in France and ...
. The ballet d'action strove to express, for the first time, human emotions drawn directly from the dancers themselves. Masks previously worn by performers were removed so that emotional content could be derived from facial expressions.
Costumes during this time were very restricting for dancers. Although a more expressive use of the body was encouraged, dancers' movements were still restricted due to heavy materials and corseted dresses. Costumes often covered a dancer's physique and made it difficult to see complex or intricate choreography. It was not until choreographer Jean Georges Noverre called for dance reforms in 1760 with his ''Letters on Dancing and Ballets'' that costumes became more conducive. Noverre urged that costumes be crafted using lightweight fabrics that move fluidly with the body, complementing a dancer's figure. In addition, dancers wore soft slippers that fit snugly along the foot. This shoe design instilled confidence within the ballerina
A ballet dancer is a person who practices the art of classical ballet. Both females and males can practice ballet. They rely on years of extensive training and proper technique to become a part of a professional ballet company. Ballet dancer ...
, daring her to dance on her toes. Naturalistic costuming allowed dancers to push the boundaries of movement, eventually rising en pointe
Because ballet became formalized in France, a significant part of ballet terminology is in the French language.
A
À la seconde
() (Literally "to second") If a step is done "à la seconde", it is done to the side. 'Second position'. It can also ...
.
The era of Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century. The purpose of the movement was to advocate for the importance of subjec ...
produced ballets inspired by fantasy, mystique, and the unfamiliar cultures of exotic places. Ballets that focused more on the emotions, the fantasy and the spiritual worlds and heralded the beginning of true pointe-work. Now, on her toes, the deified ballerina (embodied in this period by the legendary ballerina Marie Taglioni
Marie Taglioni, Comtesse de Voisins (23 April 1804 – 22 April 1884) was a Swedish-born ballet dancer of the Romantic ballet era partially of Italian descent, a central figure in the history of European dance. She spent most of her life in t ...
) seemed to magically skim the surface of the stage, an ethereal being never quite touching the ground. It was during this period that the ascending star of the ballerina quite eclipsed the presence of the poor male dancer, who was in many cases reduced to the status of a moving statue, present only in order to lift the ballerina. This sad state was really only redressed by the rise of the male ballet star Vaslav Nijinsky
Vaslav or Vatslav Nijinsky (12 March 1889/18908 April 1950) was a Russian ballet dancer and choreographer of Polish ancestry. He is regarded as the greatest male dancer of the early 20th century.
Nijinsky was celebrated for his virtuosity and f ...
, with the Ballets Russes
The Ballets Russes () was an itinerant ballet company begun in Paris that performed between 1909 and 1929 throughout Europe and on tours to North and South America. The company never performed in Russia, where the Russian Revolution, Revolution ...
, in the early 20th century. Ballet as we know it had well and truly evolved by this time, with all the familiar conventions of costume, choreographic form, plot, pomp, and circumstance firmly fixed in place. Nijinsky brought athleticism into ballet. Although at that time his choreography was considered as controversial, now they are considered as one of the first contemporary balletEarly 20th century: from ballet to contemporary dance
Since the Ballets Russes began revolutionizing ballet in the early 20th century, there have been continued attempts to break the mold of classical ballet. Currently the artistic scope of ballet technique (and its accompanying music, jumper, andmultimedia
Multimedia is a form of communication that uses a combination of different content forms, such as Text (literary theory), writing, Sound, audio, images, animations, or video, into a single presentation. T ...
) is more all-encompassing than ever. The boundaries that classify a work of classical ballet are constantly being stretched, muddied and blurred until perhaps all that remains today are traces of technique idioms such as turnout.
The 20th century was indeed a period of breaking away from everything that ballet stood for. It was a time of unprecedented creative growth, for dancers and choreographers. It was also a time of the broadening of the definition of dance. Ballets Russes was a turning point to the future of ballet in the West and in the world. Collaborating with that era geniuses, such as Coco Chanel, Pablo Picasso and otherBallets Russes brought together great music, design and dance together in a one complete performanc
Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the list of sovereign states and ...
, of which many are based on traditional rhythms and music traditions of the region. Modern African dance styles are deeply rooted in culture and tradition. Many tribes have a role solely for the purpose of passing on the tribe's dance traditions; dances which have been passed down through the centuries, often unchanged, with little to no room for improvisation. Each tribe developed its own unique style of dance, falling into three categories based on purpose. The first is religious dancing, which many tribes purport enhances peace, health, and prosperity. Religious dances often involved masqueraders, performing as both the spirits and those who placated them. Religion and spirituality infused every part of traditional African life, and continues to affect African dance today. The second is griotic, and was a type of dance that told a story. It is named after a ''griot
A griot (; ; Manding languages, Manding: or (in N'Ko script, N'Ko: , or in French spelling); also spelt Djali; or / ; ) is a West African historian, storyteller, praise singer, poet, and/or musician. Griots are masters of communicatin ...
'', which is a term for a traditional storyteller in West Africa. Certain griotic dances were only danced by the tribe's ''griot;'' today, troupes perform the same dances that were once exclusive to the ''griot''. The third type is ceremonial. These dances are performed at ceremonies such as weddings, anniversaries, and rites of passage. However, many dances did not have only one purpose. Rather, there was often one primary purpose, that blended into many secondary purposes. Dance was often very important to the maintenance of a ruler's status in the tribal society. Colonialism and globalization have resulted in the eradication of certain styles of African dance. Other styles have been blended together, or mixed with dance styles outside of Africa.
African dance in the context of slavery
As people were taken from Africa to be sold as slaves, especially starting in the 1500s, they brought their dance styles with them. Entire cultures were imported into the New World, especially those areas where slaves were given more flexibility to continue their cultures and where there were more African slaves than Europeans or indigenous Americans, such asBrazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
. African dance styles were merged with new cultural experiences to form new styles of dance. For example, slaves responded to the fears of their masters about high-energy styles of dance with changing stepping to shuffling. However, in North America, slaves did not have as much freedom to continue their culture and dance. In many cases, these dances have evolved into modern dance styles, such as African-American dance
African-American dance is a form of dance that was created by Africans in the Diaspora, specifically the United States. It has developed within various spaces throughout African-American communities in the United States, rather than studios, sc ...
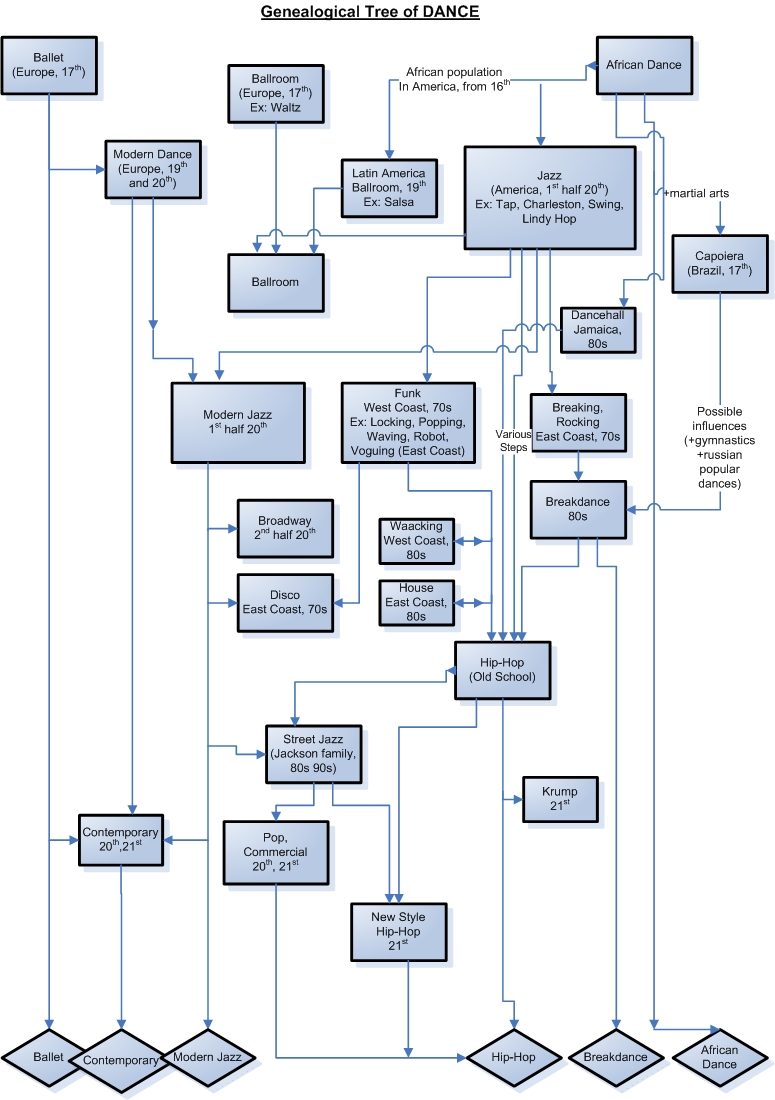
and Brazilian dance. For example, the Calenda evolved in Brazil from tribal dance. The Calenda then evolved into the Cakewalk, which was danced originally to mock plantation owners; it then evolved into the Charleston. Capoeira
Capoeira () is an Afro-Brazilian martial art and game that includes elements of dance, acrobatics, capoeira music, music, and spirituality.
It likely originated from enslaved Mbundu people, of the Kingdom of Ndongo, in present-day Angola. The ...
was a martial art practiced originally in Africa which the enslaved Africans masked as a form of dance in order to not arouse the suspicion of plantation owners.The late 20th and early 21st centuries

Postmodernism
After the explosion of modern dance in the early 20th century, the 1960s saw the growth ofpostmodernism
Postmodernism encompasses a variety of artistic, Culture, cultural, and philosophical movements that claim to mark a break from modernism. They have in common the conviction that it is no longer possible to rely upon previous ways of depicting ...
. Postmodernism veered towards simplicity, the beauty of small things, the beauty of untrained body, and unsophisticated movement. The famous "No" manifesto, by Yvonne Rainer
Yvonne Rainer (born November 24, 1934) is an American dancer, choreographer, and filmmaker, whose work in these disciplines is regarded as challenging and experimental.
, rejecting all costumes, stories and outer trappings in favour of raw and unpolished movement was perhaps the extreme of this wave of thinking. However, it was not long before sets, décor and shock value re-entered the vocabulary of modern choreographers.
Street dance
At the same time,mass culture
Popular culture (also called pop culture or mass culture) is generally recognized by members of a society as a set of practices, beliefs, artistic output (also known as popular art pop_art.html" ;"title="f. pop art">f. pop artor mass art, somet ...
experienced expansion of street dance
Street dance is an umbrella term for a large number of social dance styles such as: breakdancing, popping, Locking (dance), locking, house dance, waacking, voguing, etc. Social dance styles have many accompanying steps and foundations, created o ...
. In 1973, famous group Jackson 5
The Jackson 5, later known as the Jacksons, are an American pop band composed of members of the Jackson family. The group was formed in Gary, Indiana in 1964, and originally consisted of brothers Jackie, Ti ...
performed on television a dance called ''Robot'' (choreographed by postmodern
Postmodernism encompasses a variety of artistic, cultural, and philosophical movements that claim to mark a break from modernism. They have in common the conviction that it is no longer possible to rely upon previous ways of depicting the wo ...
/ref> artist
Michael Jackson
Michael Joseph Jackson (August 29, 1958 – June 25, 2009) was an American singer, songwriter, dancer, and philanthropist. Dubbed the "King of Pop", he is regarded as Cultural impact of Michael Jackson, one of the most culturally significan ...
), a dance form cultivated in Richmond, CA. This event and later Soul Train
''Soul Train'' is an American musical variety television show. After airing locally on WCIU-TV in Chicago, Illinois, for a year, it aired in syndication from October 2, 1971, to March 25, 2006. In its 35-year history, the show primarily featu ...
performances by black dancers (such as Don Cambell) ignited a street culture revolution, in a sense. B-boying in New York, Locking in L.A., Popping in Fresno, CA, Boogaloo in Oakland, CA, Robot in Richmond, CA, all had their own creative explosions happen around the late '60s–'70s. Each with its own histories, practices, innovators and foundations.
For the emergence of 20th-century modern dance see also: Mary Wigman
Mary Wigman (born Karoline Sophie Marie Wiegmann; 13 November 1886 – 18 September 1973) was a German dancer and choreographer who pioneered expressionist dance, dance therapy, and movement training without pointe shoes. She is considered on ...
, Gret Palucca
Gret Palucca (born Margarethe Paluka; 8 January 1902 – 22 March 1993) was a German dancer and dance teacher, notable for her dance school, the Palucca School of Dance, founded in Dresden in 1925.
Life and work
Margarethe Paluka was born in M ...
, Harald Kreutzberg, Yvonne Georgi, and Isadora Duncan
Angela Isadora Duncan (May 26, 1877, or May 27, 1878 – September 14, 1927) was an American-born dancer and choreographer, who was a pioneer of modern contemporary dance and performed to great acclaim throughout Europe and the United States. Bor ...
.
Hip-hop dance
Hip hop dance is a range of street dance styles primarily performed to hip-hop, hip hop music or that have evolved as part of hip-hop culture, hip hop culture. It is influenced by a wide range of styles that were created in the 1970s and made po ...
started when Clive Campbell, aka Kool DJ Herc
Clive Campbell (born April 16, 1955), better known by his stage name DJ Kool Herc, is a Jamaican-American DJ who is credited with being the founder of hip hop music in the Bronx, New York City, in 1973. Nicknamed the Father of Hip-Hop, Campbe ...
and the father of hip-hop, came to New York from Jamaica in 1967. Toting the seeds of reggae from his homeland, he is credited with being the first DJ to use two turntables and identical copies of the same record to create his jams. But it was his extension of the breaks in these songs—the musical section where the percussive beats were most aggressive—that allowed him to create and name a culture of break boys and break girls who laid it down when the breaks came up. Briefly termed b-boy
A b-boy is a person devoted to breaking or break dancing.
B Boy may also refer to:
Music
* "B-Boy", a song by Tech N9ne featuring Big Scoob, Bumpy Knuckles, Kutt Calhoun, and Skatterman from the album '' K.O.D.'', 2009
* "B Boy" (song) by Meek ...
s and b-girls, these dancers founded breakdancing
Breakdancing or breaking, also called b-boying (when performed by men) or b-girling (women), is a style of street dance originated by African Americans and Nuyorican, Puerto Ricans in The Bronx borough of New York City.
Breakdancing consist ...
, which is now a cornerstone of hip-hop dance.
See also
*History of ballet
Ballet is a formalized dance form with its origins in the Italian Renaissance courts of 15th and 16th centuries. Ballet spread from Italy to France with the help of Catherine de' Medici, where ballet developed even further under her aristocratic ...
* History of figure skating
References
Further reading
* Adshead-Lansdale, J. (ed.) (1994). ''Dance History: An Introduction''. Routledge.. * Charman, S. Kraus, R, G. Chapman, S. and Dixon-Stowall, B. (1990). ''History of the Dance in Art and Education''. Pearson Education. . * Dils, A. (2001). ''Moving History/Dancing Cultures: A Dance History Reader''. Wesleyan University Press. . * * Wood, Melusine (1952). ''Some historical dances twelfth to nineteenth century; their manner of performance and their place in the social life of the time'', London: Imperial Society of Teachers of Dancing.External links
Historic Illustrations of Dancing from 3300 B.C. to 1911 A.D.
from
Project Gutenberg
Project Gutenberg (PG) is a volunteer effort to digitize and archive cultural works, as well as to "encourage the creation and distribution of eBooks."
It was founded in 1971 by American writer Michael S. Hart and is the oldest digital li ...
The history of pointe shoes and technique (ballet)
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Dance Dance research