DUOX2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dual oxidase 2, also known as DUOX2 or ThOX2 (for
thyroid
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by ...
oxidase
In biochemistry, an oxidase is an oxidoreductase (any enzyme that catalyzes a redox reaction) that uses dioxygen (O2) as the electron acceptor. In reactions involving donation of a hydrogen atom, oxygen is reduced to water (H2O) or hydrogen peroxid ...
), is an enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
that in humans is encoded by the ''DUOX2'' gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
. Dual oxidase is an enzyme that was first identified in the mammalian thyroid gland
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by ...
. In humans, two isoforms are found; hDUOX1 and hDUOX2 (this enzyme). The protein location is not exclusive to thyroid tissue; hDUOX1 is prominent in airway epithelial cells and hDUOX2 in the salivary glands and gastrointestinal tract.
Function
Investigations into reactive oxygen species ( ROS) in biological systems have, until recently, focused on characterization of phagocytic cell processes. It is now well accepted that production of such species is not restricted tophagocytic
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell (biology), cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs ph ...
cells and can occur in eukaryotic non-phagocytic cell types via NADPH oxidase
NADPH oxidase (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase) is a membrane-bound enzyme complex that faces the extracellular space. It can be found in the plasma membrane as well as in the membranes of phagosomes used by neutrophil white ...
(NOX) or dual oxidase (DUOX). This new family of proteins, termed the NOX/DUOX family or NOX family of NADPH oxidases, consists of homologs to the catalytic moiety of phagocytic NADPH-oxidase, gp91phox. Members of the NOX/DUOX family have been found throughout eukaryotic species, including invertebrates, insects, nematodes, fungi, amoeba, algae, and plants (not found in prokaryotes). These enzymes clearly demonstrate regulated production of ROS as their sole function. Genetic analyses have implicated NOX/DUOX derived ROS in biological roles and pathological conditions including hypertension (NOX1
NADPH oxidase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''NOX1'' gene.
NOX1 is a homolog of the catalytic subunit of the superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase of phagocytes, gp91phox. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms
A p ...
), innate immunity ( NOX2/DUOX), otoconia formation in the inner ear ( NOX3) and thyroid hormone biosynthesis (DUOX1/2).DUOX2 is the isoform that generates H2O2 utilized by thyroid peroxidase
Thyroid peroxidase, also called thyroperoxidase (TPO), thyroid specific peroxidase or iodide peroxidase, is an enzyme expressed mainly in the thyroid where it is secreted into colloid. Thyroid peroxidase oxidizes iodide ions to form iodine atoms ...
(TPO) for the biosynthesis of thyroid hormone
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones triiodothyronine, T3 and T4
rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone
rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone
rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus
r ...
s,Visser, T. J. (2018). Regulation of Thyroid Function, Synthesis, and Function of Thyroid Hormones. In P. Vitti & L. Hegedüs (Eds.), Thyroid Diseases Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Springer.
supported by the discovery of congenital hypothyroidism resultant from an inactivating mutation in the ''DUOX2'' gene.
The family currently has seven members including NOX1
NADPH oxidase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''NOX1'' gene.
NOX1 is a homolog of the catalytic subunit of the superoxide-generating NADPH oxidase of phagocytes, gp91phox. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms
A p ...
, NOX2 (formerly known as gp91phox), NOX3, NOX4, NOX5
NADPH oxidase, EF-hand calcium binding domain 5, also known as NOX5, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''NOX5'' gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene ...
, DUOX1 and DUOX2.
This protein is known as a dual oxidase because it has both a peroxidase homology domain and a gp91phox domain.
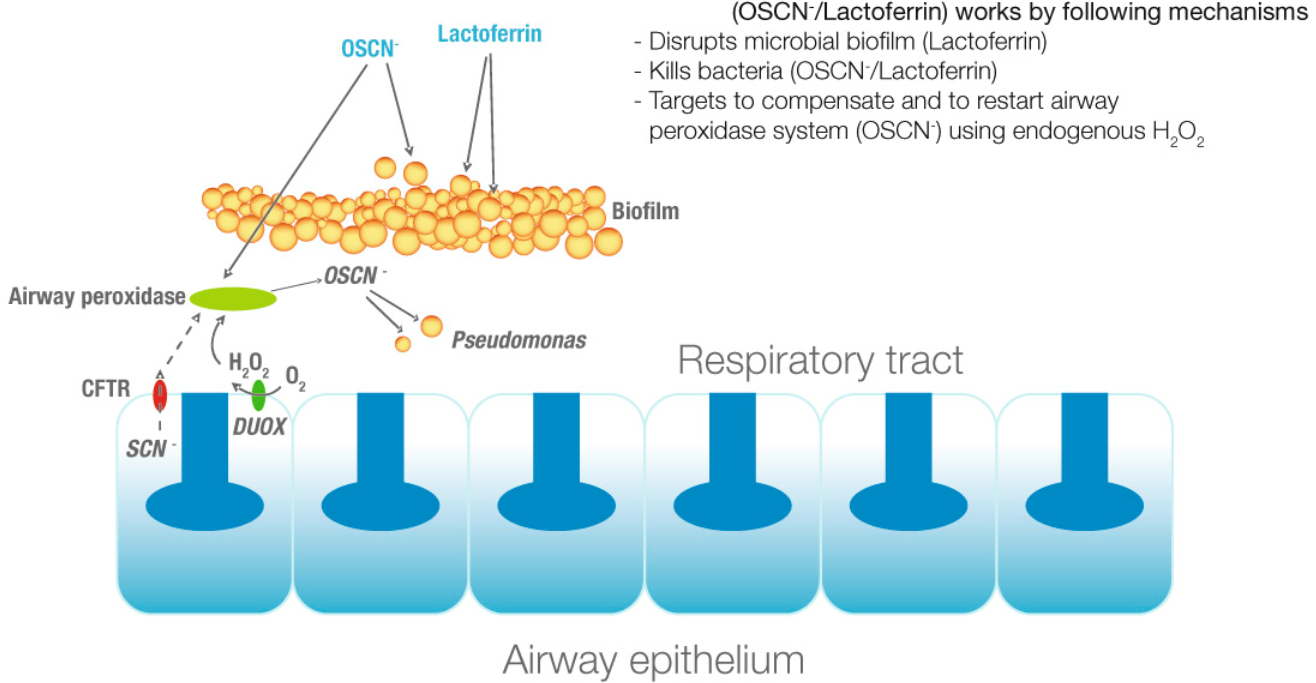
Duox are also implicated in lung defence system and especially in cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive manner that impairs the normal clearance of Sputum, mucus from the lungs, which facilitates the colonization and infection of the lungs by bacteria, notably ''Staphy ...
.
Schema of duox implication in human lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
defence system

References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Thyroid hormone metabolism enzymes and transporters EF-hand-containing proteins