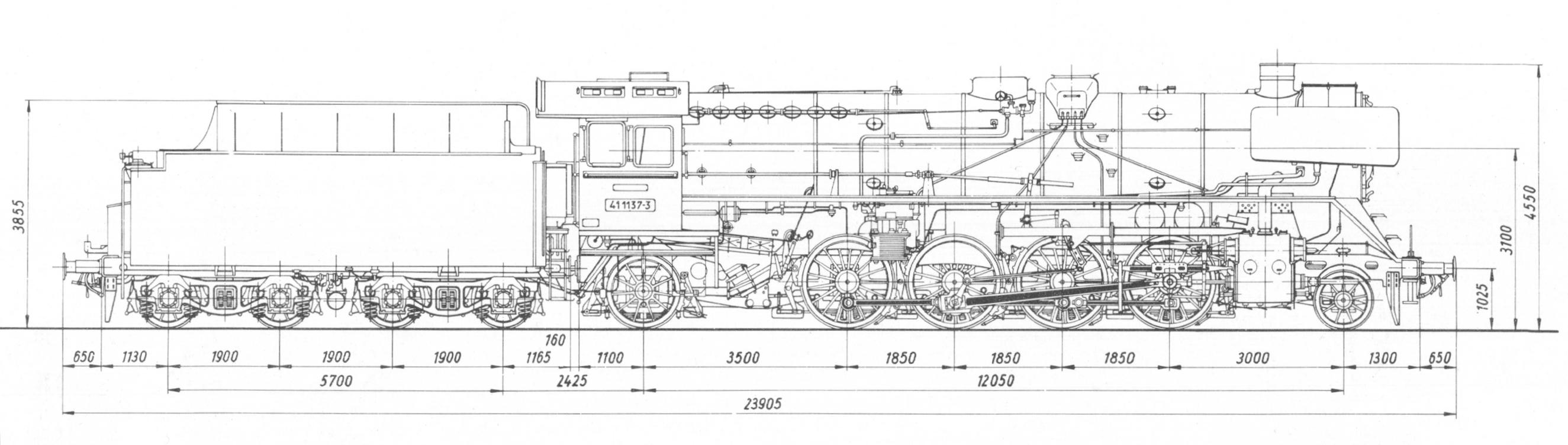
DRG Class 41 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The German Class 41
Dampflok-Gesellschaft München e.V.
* 41 096 oil-fired
Dampflok-Gemeinschaft 41 096 e.V.

 The DR too had difficulties with
The DR too had difficulties with  Regardless of that, DR engineers worked on a "reconstruction programme for the recovery of the steam locomotive fleet". This envisaged, amongst other things, the modernisation of 102 Class 41 locomotives. The German term used for reconstruction was ''Rekonstruktion'' or ''Reko'' for short, hence the subsequent designation of the locomotives as '' Rekolokomotiven'' or ''Rekoloks''.
Demarcation disputes, disagreements over the detail of the reconstruction programme and the continued non-delivery of the ''Reko'' boiler, delayed the start of work still further. Only the explosion of 03 1046's ''St47K'' boiler in 1958 at Wünsdorf led to pressure from the then transport minister, Erwin Kramer (1902–1979), to get started on the ''Reko'' programme.
Regardless of that, DR engineers worked on a "reconstruction programme for the recovery of the steam locomotive fleet". This envisaged, amongst other things, the modernisation of 102 Class 41 locomotives. The German term used for reconstruction was ''Rekonstruktion'' or ''Reko'' for short, hence the subsequent designation of the locomotives as '' Rekolokomotiven'' or ''Rekoloks''.
Demarcation disputes, disagreements over the detail of the reconstruction programme and the continued non-delivery of the ''Reko'' boiler, delayed the start of work still further. Only the explosion of 03 1046's ''St47K'' boiler in 1958 at Wünsdorf led to pressure from the then transport minister, Erwin Kramer (1902–1979), to get started on the ''Reko'' programme.

 From 1959 onwards, 80 Class 41 locomotives were to be given the new ''39E'' ''Reko'' boilers in the
From 1959 onwards, 80 Class 41 locomotives were to be given the new ''39E'' ''Reko'' boilers in the
 Currently the locomotives listed below have been preserved such that they are able to be displayed. Three are operational. A further 8 ''Rekolokomotiven'' are in varying states of repair. See the list of preserved steam locomotives in Germany
* 41 1144-9, IGE "Werrabahn Eisenach" (
Currently the locomotives listed below have been preserved such that they are able to be displayed. Three are operational. A further 8 ''Rekolokomotiven'' are in varying states of repair. See the list of preserved steam locomotives in Germany
* 41 1144-9, IGE "Werrabahn Eisenach" (
steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, Fuel oil, oil or, rarely, Wood fuel, wood) to heat ...
s were standard goods train engines ('' Einheitslokomotiven'') operated by the Deutsche Reichsbahn
The ''Deutsche Reichsbahn'' (), also known as the German National Railway, the German State Railway, German Reich Railway, and the German Imperial Railway, was the Weimar Republic, German national Rail transport, railway system created after th ...
(DRB) and built from 1937 to 1941.
History
In the search for a new, fast, goods train locomotive, theDeutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft
The ''Deutsche Reichsbahn'' (), also known as the German National Railway, the German State Railway, German Reich Railway, and the German Imperial Railway, was the German national railway system created after the end of World War I from the re ...
(DRG) in 1934 was attracted by the proposal from the Berliner Maschinenbau (BMAG, formerly Louis Schwartzkopff) for a 2-8-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and two trailing wh ...
(1D1h2) engine. The design, produced by Friedrich Wilhelm Eckhardt (1892–1961), differed from the DRG's original requirement for a 2-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels. ...
(1D) engine, because the required performance with an 18-ton axle load
The axle load of a wheeled vehicle is the total weight bearing on the roadway for all wheels connected to a given axle. Axle load is an important design consideration in the engineering of roadways and railways, as both are designed to tolerate a m ...
was easier to generate on a 2-8-2 engine rather than one with a 2-8-0 wheel configuration. Continued adherence to this instruction would in the end have given the new engine no significant advantage over the Prussian goods train locomotives which were to be withdrawn. The Reichsbahn Central Office Engineering Works (RZM) eventually agreed to this proposal; the BMAG was tasked to develop the proposed design and produce two prototypes
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and software programming. A prototype is generally used to ...
.
In January 1937 the two prototype locomotives, 41 001 and 41 002, were delivered to the DRG, who subsequently tested them thoroughly and bought them. The prototypes soon proved themselves, with their power, performance and quiet riding qualities, as well as their exceptional acceleration.
In developing the Class 41, the principle of having standard locomotives ('' Einheitsloks'') demonstrated the financial advantages of standardization. For example, the construction costs of the engine, through the use of components from the simultaneously developed Class 03, 06 and 45 engines, was under 10,000 Reichsmark
The (; sign: ℛ︁ℳ︁; abbreviation: RM) was the currency of Germany from 1924 until the fall of Nazi Germany in 1945, and in the American, British and French occupied zones of Germany, until 20 June 1948. The Reichsmark was then replace ...
s.
From October 1938, the first full-scale production Class 41 locomotives were ordered by the now renamed (since February 1937) Deutsche Reichsbahn
The ''Deutsche Reichsbahn'' (), also known as the German National Railway, the German State Railway, German Reich Railway, and the German Imperial Railway, was the Weimar Republic, German national Rail transport, railway system created after th ...
(DRB). All the well-known locomotive manufacturers in Germany participated in the building of the locomotives, including BMAG, Borsig Borsig is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* (1867–1897), German entrepreneur
* August Borsig (1804–1854), German businessman
* Conrad von Borsig (1873–1945), German mechanical engineer
* Ernst Borsig (1869–1933) ...
, Maschinenfabrik Esslingen
Maschinenfabrik Esslingen (ME) was a German engineering firm that manufactured locomotives, tramways, railway wagons, roll-blocks, technical equipment for the railways, (turntable (rail), turntables and traverser (railway), traversers), bridges, s ...
, Henschel & Sohn, Arnold Jung Lokomotivfabrik
The Arnold Jung Lokomotivfabrik (Arnold Jung Locomotive Works) was a locomotive manufacturer, in particular of Feldbahn locomotives, in Kirchen, Rhineland-Palatinate, Rheinland-Pfalz, Germany.
History
The firm was founded on 13 February ...
, Krauss-Maffei
KraussMaffei is a German manufacturing company. It is a manufacturer of injection molding machines, machines for plastics extrusion technology, and reaction process machinery. It was acquired by ChemChina in 2016.
History
KraussMaffei was forme ...
, Krupp
Friedrich Krupp AG Hoesch-Krupp (formerly Fried. Krupp AG and Friedrich Krupp GmbH), trade name, trading as Krupp, was the largest company in Europe at the beginning of the 20th century as well as Germany's premier weapons manufacturer dur ...
, Orenstein & Koppel and Schichau.
Unlike the prototype locomotives, corner valve pressure compensators were omitted from the production locos and ''Nicolai'' pressure compensating tubular valves (later ''Karl Schultz valves'') were used to give a better ride when running light. On the valve gear
The valve gear of a steam engine is the mechanism that operates the inlet and exhaust valves to admit steam into the cylinder and allow exhaust steam to escape, respectively, at the correct points in the cycle. It can also serve as a reversing ...
, the normal lifting link (''Hängeeisen'') replaced the '' Kuhn slides'' of the prototypes which were expensive to manufacture.
As with Classes 03, 45 and 50, the boiler made of St 47 K steel, which aged and embrittled rapidly, soon caused major problems. As early as 1941, the DRB decreed a reduction of the permissible operating pressure to . In this way the wear and tear on the boiler could at least be slowed.
The axle load
The axle load of a wheeled vehicle is the total weight bearing on the roadway for all wheels connected to a given axle. Axle load is an important design consideration in the engineering of roadways and railways, as both are designed to tolerate a m ...
of the locomotive could be switched between 18 t and 20 t by inserting bolts into different sockets in the equalising beams. This was supposed to enable the locomotive to be more versatile in its use. Little or no use was made of this flexibility however. The Deutsche Bundesbahn
Deutsche Bundesbahn (, ) or DB () was formed as the state railway of the newly established West Germany (FRG) on 7 September 1949 as a successor of the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft (DRG). The DB remained the state railway of West Germany u ...
and East German DR later left the bolts in the 18 t setting.
The locomotives were, with the exception of the prototypes, coupled to 22 T 34 tenders. The prototypes, 41 001 and 41 002, had 22 T 32 tenders on delivery. From their use of turntable
A phonograph, later called a gramophone, and since the 1940s a record player, or more recently a turntable, is a device for the mechanical and analogue reproduction of sound. The sound vibration waveforms are recorded as corresponding phys ...
s, it is also known that some engines were running with 22 T 30 tenders.
The advent of war increasingly stifled the purchase of fast goods train locomotives until, in January 1941, the existing orders were cancelled completely. On 2 June 1941, MF Esslingen delivered the last Class 41 locomotive, no. 41 352, to the DRB. With that a total of 366 engines of this class had been built in just under four years.
Preserved locomotives
After theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, 216 engines went into the Deutsche Bundesbahn
Deutsche Bundesbahn (, ) or DB () was formed as the state railway of the newly established West Germany (FRG) on 7 September 1949 as a successor of the Deutsche Reichsbahn-Gesellschaft (DRG). The DB remained the state railway of West Germany u ...
fleet and 122 were left in the hands of the DR in East Germany
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from Foundation of East Germany, its formation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on ...
. There is evidence that, in addition, 22 locomotives were left in the former Reichsbahn railway division of Breslau in Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
and later incorporated into the Polish State Railways
The Polish State Railways ( , abbr.: PKP S.A.) is a Polish state-owned holding company (legally a sole-shareholder company of the State Treasury) comprising the rail transport holdings of the country's formerly dominant namesake railway oper ...
(PKP) as Ot 1-1 to Ot 1-19. Number 41 153 was listed on the books of the Czechoslovakian State Railways (CSD) after 1945. Number 41 034 as well as other locomotives (41 076, 41 082 and 41 312) from locomotive convoys ( reparations) were left in the territory of the Soviet State Railway ( SZD) and later transferred to the PKP. The fate of other locomotives is unknown.
As a result of the employment of the two prototype locomotives at Schneidemühl (present-day Piła) locomotive shed in heading express cattle trains to Berlin, the engines were unflatteringly christened Ochsenlok (''Oxen loco'').
DB rebuild
Because the boiler of these engines suffered from metal fatigue, they began to be repaired in the 1950s. Between 1957 and 1961, 107 vehicles were fitted with fully welded boilers, like those installed on the Class 03.10. In addition the front part of theframe
A frame is often a structural system that supports other components of a physical construction and/or steel frame that limits the construction's extent.
Frame and FRAME may also refer to:
Physical objects
In building construction
*Framing (con ...
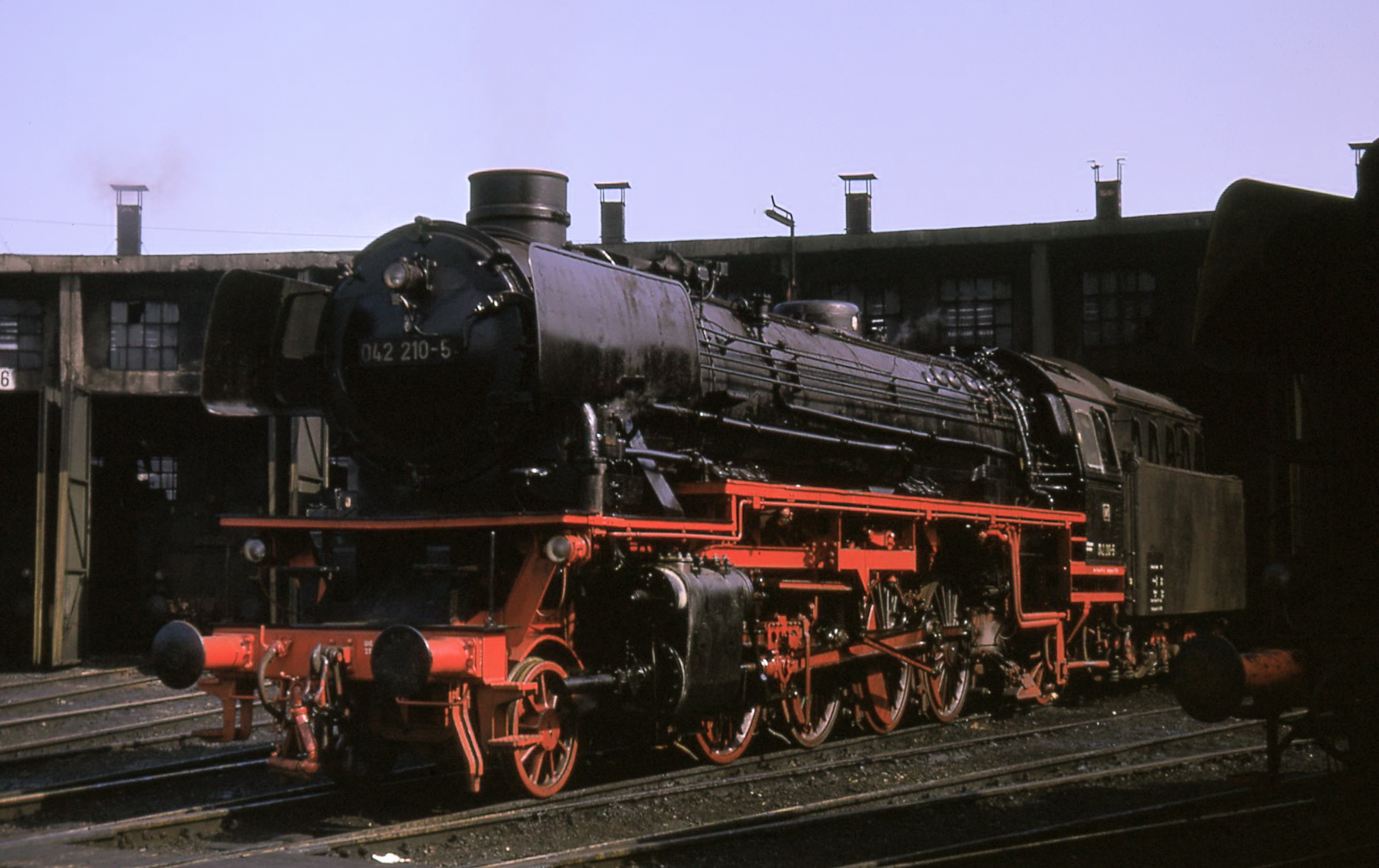
and the running plate were changed. Forty examples were converted to oil-firing with heavy oil. From 1968, these were designated as Class 042. The last Class 042 steam locomotives were retired in 1977 at Rheine
Rheine () is a city in the district of Steinfurt (district), Steinfurt in Westphalia, Germany. It is the largest city in the district and the location of Rheine Air Base.
Geography
Rheine is on the river Ems (river), Ems, about north of Münster ...
locomotive shed. The photograph (right) shows one as a museum loco, now reclassified to Class 41 (the pre-1968 designation).
The former DB locomotives, 41 105 and 41 241, have been preserved as representatives of their class by '' Stoom Stichting Nederland'' in the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
. Number 41 018, an operational loco owned by the Munich Steam Locomotive Company, is stabled at the Augsburg Railway Park and 41 113 is exhibited in the Technical Museum at Sinsheim. The ''Osnabrück Steam Engine Friends'' are working hard to restore 41 052 to operational status, after it had stood for a long time as a monument at Osnabrück
Osnabrück (; ; archaic English: ''Osnaburg'') is a city in Lower Saxony in western Germany. It is situated on the river Hase in a valley penned between the Wiehen Hills and the northern tip of the Teutoburg Forest. With a population of 168 ...
-Schinkel. Number 41 096 is preserved as operational loco at Klein-Mahner. Number 41 360 is operated by the Dampflok-Tradition Oberhausen e.V. Since the end of ban on steam locomotives, she has provided a comprehensive programme of journeys on the Deutsche Bahn
(, ; abbreviated as DB or DB AG ) is the national railway company of Germany, and a state-owned enterprise under the control of the German government. Headquartered in the Bahntower in Berlin, it is a joint-stock company ( AG).
DB was fou ...
's railway network.
* 41 018 oil-firedDampflok-Gesellschaft München e.V.
* 41 096 oil-fired
Dampflok-Gemeinschaft 41 096 e.V.

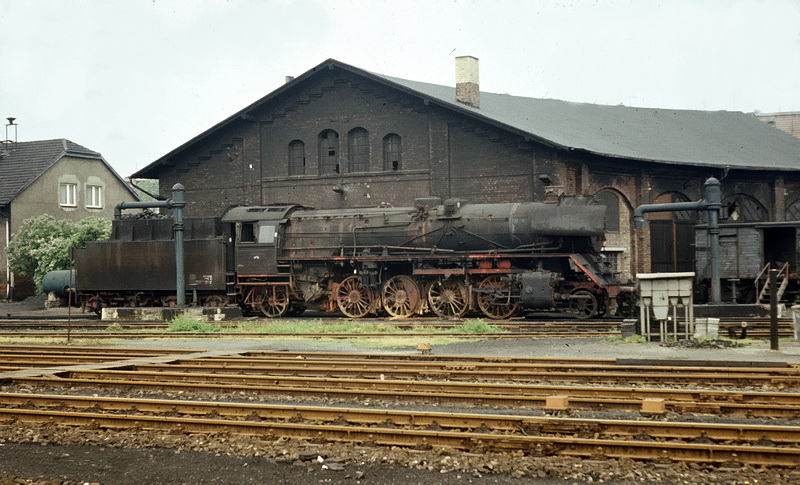
DR Class 41 and DR ''Rekolok''
 The DR too had difficulties with
The DR too had difficulties with boiler
A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, centra ...
s made of ''St 47 K'' steel. The reduction of boiler overpressure
Overpressure (or blast overpressure) is the pressure caused by a shock wave over and above normal atmospheric pressure. The shock wave may be caused by sonic boom or by explosion
An explosion is a rapid expansion in volume of a given amoun ...
from 20 to 16 bar had certainly slowed their susceptibility to damage, but could not prevent it entirely. Of the 112 locomotives recorded in the DR fleet in 1955, only 12 had already been equipped with a '1943 Type' replacement boiler and were therefore safe. Problems with the ''St 47 K'' boilers, however, increased massively. Repair welding did not produce the desired effect, but made the material even more brittle and the danger of cracks developing and boiler explosion
A boiler explosion is a catastrophic failure of a boiler.
There are two types of boiler explosions. One type is a failure of the pressure parts of the steam and water sides. There can be many different causes, such as failure of the safety val ...
s was greater than before. And it was not just the Class 41 that was affected. Classes 03, 03.10 and 50, with boilers made of non-aging ''St 47 K'', were also prone to damage. As a result of increasing difficulties the DR had to withdraw over 300 locomotives from service in 1956 which abruptly led to an enormous shortage of engines. The urgent call for action which then resulted led at last to the development and subsequent ordering of a new boiler (later called the ''39E'') that, with a few minor alterations, was also usable on locomotive classe 03, 03.10 and 39.
Because the delivery of the new boilers kept being delayed, 21 Class 41 locomotives were simply fitted with replacement boilers to the old design by January 1959. Even the Meiningen repair shop made a complete copy of the old boiler for 41 075. Other damaged boilers were fully repaired and many parts replaced.
 Regardless of that, DR engineers worked on a "reconstruction programme for the recovery of the steam locomotive fleet". This envisaged, amongst other things, the modernisation of 102 Class 41 locomotives. The German term used for reconstruction was ''Rekonstruktion'' or ''Reko'' for short, hence the subsequent designation of the locomotives as '' Rekolokomotiven'' or ''Rekoloks''.
Demarcation disputes, disagreements over the detail of the reconstruction programme and the continued non-delivery of the ''Reko'' boiler, delayed the start of work still further. Only the explosion of 03 1046's ''St47K'' boiler in 1958 at Wünsdorf led to pressure from the then transport minister, Erwin Kramer (1902–1979), to get started on the ''Reko'' programme.
Regardless of that, DR engineers worked on a "reconstruction programme for the recovery of the steam locomotive fleet". This envisaged, amongst other things, the modernisation of 102 Class 41 locomotives. The German term used for reconstruction was ''Rekonstruktion'' or ''Reko'' for short, hence the subsequent designation of the locomotives as '' Rekolokomotiven'' or ''Rekoloks''.
Demarcation disputes, disagreements over the detail of the reconstruction programme and the continued non-delivery of the ''Reko'' boiler, delayed the start of work still further. Only the explosion of 03 1046's ''St47K'' boiler in 1958 at Wünsdorf led to pressure from the then transport minister, Erwin Kramer (1902–1979), to get started on the ''Reko'' programme.

 From 1959 onwards, 80 Class 41 locomotives were to be given the new ''39E'' ''Reko'' boilers in the
From 1959 onwards, 80 Class 41 locomotives were to be given the new ''39E'' ''Reko'' boilers in the Zwickau
Zwickau (; ) is the fourth-largest city of Saxony, Germany, after Leipzig, Dresden and Chemnitz, with around 88,000 inhabitants,.
The West Saxon city is situated in the valley of the Zwickau Mulde (German: ''Zwickauer Mulde''; progression: ), ...
and Karl Marx Stadt Reichsbahn repair shops (''Reichsbahnausbesserungswerke'' or ''RAW'').
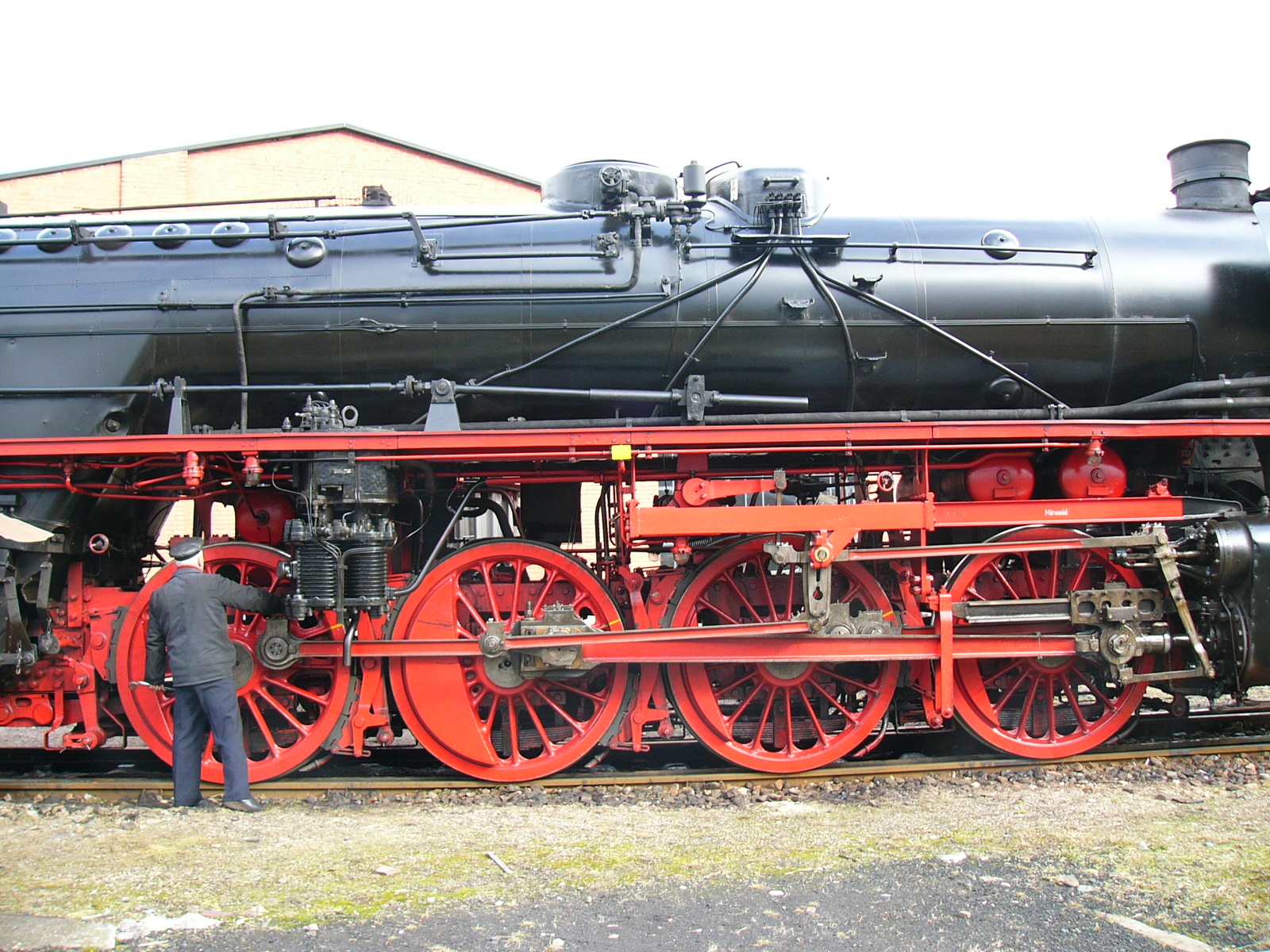
As part of the rebuild, IfS/DR mixer preheaters, pressure-compensating piston valves ( Trofimoff valves) and new ''Stühren'' ash pans were installed. The wider outer firebox needed new front walls to the driver's cab, the front windows of which were equipped with demisting equipment. For the larger and heavier VMP 15-20 compounded mixer pump (''Verbundmischpumpe'') a new pump mount had to be built. This and the new mixer preheater apparatus required a different arrangement for the main air reservoir. The outside cylinders
A cylinder () has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infinite ...
with a diameter of just , originally designed for boiler pressures of 20 bar, were retained however. In the course of the rebuild, the brakes on the front carrying axle were removed.
The 39E ''Reko'' boiler fitted to the engines is a combustion chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the air–fuel ratio, fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the Firebox (steam engine), firebox which is used to allow a mo ...
boiler and can generate 15 tons of steam per hour, thanks to the improved ratio of radiative to tube heating area. This is considerably higher than, for example, the new DB boiler which generates only 13.3 tons of steam per hour. Fitted with this boiler, the engine was able to exceed the performance requirements that it originally had for the 20 bar boilers, in spite of its small cylinders.
The engines rebuilt in this way are classified as '' Rekolokomotiven''. Following their conversion, the DR gave all Class 41 locomotives the extra digit ''1'' under their 1970 renumbering scheme, so that e.g. number 41 122 became number 41 1122-5. In contrast to other classes, the Class 41 was not given a separate sub-class to distinguish ''Reko'' from non-''Reko'' locomotives.
Class 41 '' Rekoloks'' could be seen in regular train service until 1988. The second oil crisis in 1979/80, and its effect on the GDR's economy, granted quite a number of Class 41 engines a short return to operational duties. Even several locomotives earmarked for scrapping were refurbished and were given a new general inspection service. The Meiningen repair shed refurbished a total of 23 locomotives of this class between 1980 and 1983. But by the end of September 1984, Oebisfelde
Oebisfelde () is a town and a former municipality in the Börde district in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Since 1 January 2010, it is part of the town Oebisfelde-Weferlingen.
It is accessed by Bundesstraße (German federal highway) 188.
Geography ...
shed withdrew the 41s and transferred its locomotives to Güsten shed. Göschwitz station, a satellite of Saalfeld
Saalfeld () is a town in Germany, capital of the Saalfeld-Rudolstadt district of Thuringia. It is best known internationally as the ancestral seat of the Saxe-Coburg and Gotha branch of the Saxon House of Wettin.
Geography
The town is situated ...
shed was the next to send its 41s to the storage sidings in November 1986, and at the beginning of May 1988, Staßfurt (Bw Güsten) parted company with the last Class 41 locomotive, 41 1231, in regular service in the DR.
The Class 41 was the most versatile steam locomotive in the DR's engine fleet and hauled high-profile express and fast trains, as well as goods and passenger services.
Number 41 1185 was a DR heritage locomotive, now in the ownership of the Nuremberg Transport Museum.
A further 8 ''Rekolokomotiven'' are in varying states of repair. See the list of preserved steam locomotives in Germany
List of preserved locomotives
 Currently the locomotives listed below have been preserved such that they are able to be displayed. Three are operational. A further 8 ''Rekolokomotiven'' are in varying states of repair. See the list of preserved steam locomotives in Germany
* 41 1144-9, IGE "Werrabahn Eisenach" (
Currently the locomotives listed below have been preserved such that they are able to be displayed. Three are operational. A further 8 ''Rekolokomotiven'' are in varying states of repair. See the list of preserved steam locomotives in Germany
* 41 1144-9, IGE "Werrabahn Eisenach" (Eisenach
Eisenach () is a Town#Germany, town in Thuringia, Germany with 42,000 inhabitants, west of Erfurt, southeast of Kassel and northeast of Frankfurt. It is the main urban centre of western Thuringia, and bordering northeastern Hesse, Hessian re ...
); operational; in service,
* 41 1150-6, Bavarian Railway Museum (Nördlingen
Nördlingen (; Swabian: ''Nearle'' or ''Nearleng'') is a town in the Donau-Ries district, in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany, with a population of approximately 20,674. It is located approximately east of Stuttgart, and northwest of Munich. It was ...
), operational (HU inspection certificate expired)
* 41 052, Osnabrücker Dampflokfreunde (Osnabrück
Osnabrück (; ; archaic English: ''Osnaburg'') is a city in Lower Saxony in western Germany. It is situated on the river Hase in a valley penned between the Wiehen Hills and the northern tip of the Teutoburg Forest. With a population of 168 ...
); being renovated in 2022,
* 41 096, Dampflok-Gemeinschaft 41 096 (Klein Mahner); HU inspection certificate expired,Kjell Sonnemann: ''440 Passagiere fahren ein letztes Mal mit der Dampflok durch die Region.'' in: Salzgitter-Zeitung, 27. März 2018
* 41 105, Stoom Stichting Nederland SSN (Rotterdam
Rotterdam ( , ; ; ) is the second-largest List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city in the Netherlands after the national capital of Amsterdam. It is in the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of South Holland, part of the North S ...
),
* 41 241, Veluwsche Stoomtrein Maatschappij VSM ( Beekbergen) operational in coal,
* 41 271, Rendsburger Eisenbahnfreunde (Neumünster
Neumünster () is a city in the middle of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. With more than 79,000 registered inhabitants, it is the fourth-largest municipality in Schleswig-Holstein (behind Kiel, Lübeck and Flensburg). The ''Holstenhallen'' and ...
),
* 41 360, Eigentümergemeinschaft (Oberhausen
Oberhausen (, ) is a city on the river Emscher in the Ruhr Area, Germany, located between Duisburg and Essen ( ). The city hosts the International Short Film Festival Oberhausen and its Gasometer Oberhausen is an anchor point of the European Rout ...
); not accessible, HU inspection certificate expired, stored due to bankruptcy,
* 41 1231-4, Traditionsbetriebswerk Staßfurt,
* 41 024, Darmstadt-Kranichstein Railway Museum
The Darmstadt-Kranichstein Railway Museum (''Eisenbahnmuseum Darmstadt-Kranichstein'') is a railway museum in the German city of Darmstadt. It is also the largest railway museum in the state of Hesse.
The former Motive power depot, railway depot ...
,
* 41 018, Munich Steam Locomotive Company, location Bahnpark Augsburg (operational)
* 41 226 Tuttlingen Railway Museum
* 41 364 Owned by Bayernbahn, on loan to the Bavarian Railway Museum (Nördlingen
Nördlingen (; Swabian: ''Nearle'' or ''Nearleng'') is a town in the Donau-Ries district, in Swabia, Bavaria, Germany, with a population of approximately 20,674. It is located approximately east of Stuttgart, and northwest of Munich. It was ...
)
* 41 073 EBM Heilbronn
Heilbronn () is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in northern Baden-Württemberg, Germany, surrounded by Heilbronn (district), Heilbronn District.
From the late Middle Ages on, it developed into an important trading centre. At the begi ...
* 41 186 EBM Dieringhausen
* 41 113 Technikmuseum Sinsheim


Video
See also
* List of DRG locomotives and railbusesReferences
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Drg Class 41 41 2-8-2 locomotives 41 Henschel locomotives Krauss-Maffei locomotives Krupp locomotives Railway locomotives introduced in 1937 Borsig locomotives Arnold Jung locomotives Berliner locomotives Esslingen locomotives Standard-gauge locomotives of Germany 1′D1′ h2 locomotives Freight locomotives Schichau-Werke locomotives Orenstein & Koppel locomotives