DC Brushless Motor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A brushless DC electric motor (BLDC), also known as an electronically commutated motor, is a
A brushless DC electric motor (BLDC), also known as an electronically commutated motor, is a
 Brushless motors can be constructed in several different physical configurations. In the conventional
Brushless motors can be constructed in several different physical configurations. In the conventional
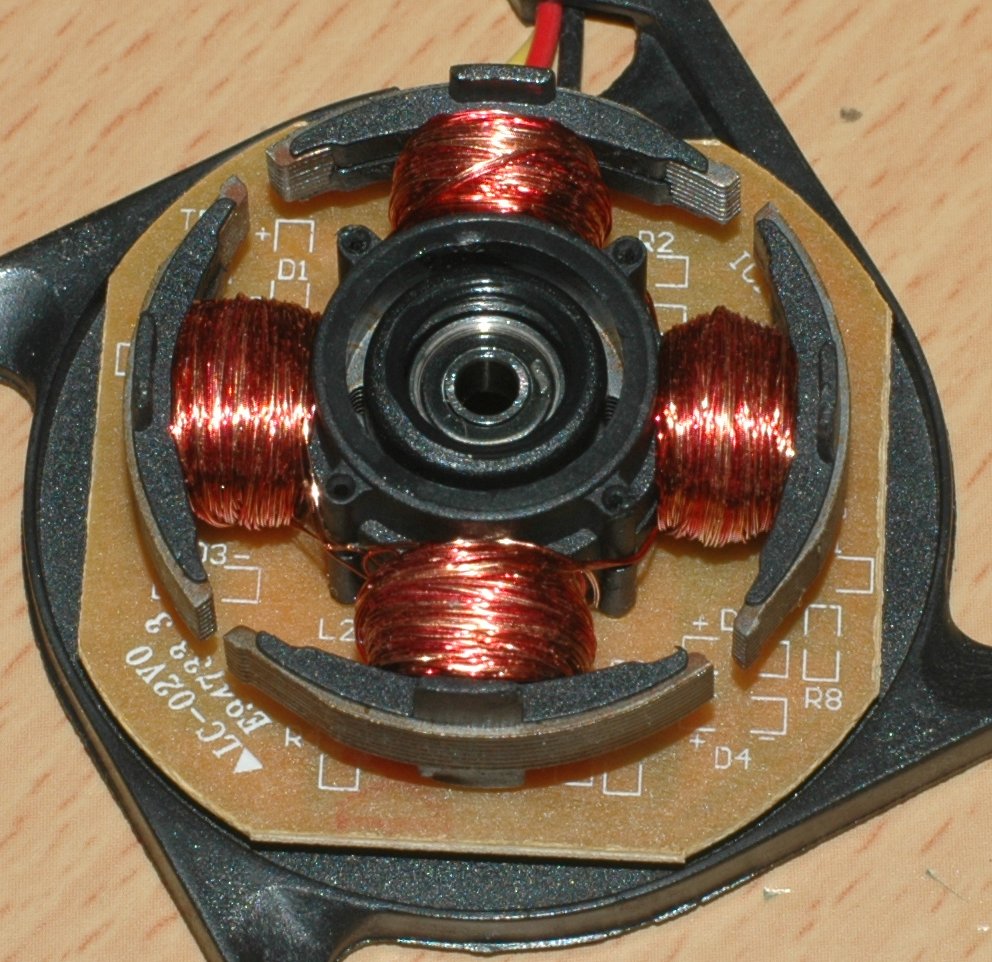 Brushless motors fulfill many functions originally performed by brushed DC motors, but cost and control complexity prevents brushless motors from replacing brushed motors completely in the lowest-cost areas. Nevertheless, brushless motors have come to dominate many applications, particularly devices such as computer
Brushless motors fulfill many functions originally performed by brushed DC motors, but cost and control complexity prevents brushless motors from replacing brushed motors completely in the lowest-cost areas. Nevertheless, brushless motors have come to dominate many applications, particularly devices such as computer
performance
 Brushless motors have become a popular motor choice for
Brushless motors have become a popular motor choice for
Electric Drives – Brushless DC / AC and Reluctance Motors
with useful diagrams
How Brushless Motor and ESC Work
– Video explanation how Brushless DC Motor works, plus how to control one with an Arduino micro-controller. {{Authority control DC motors Electric motors 20th-century inventions
 A brushless DC electric motor (BLDC), also known as an electronically commutated motor, is a
A brushless DC electric motor (BLDC), also known as an electronically commutated motor, is a synchronous motor
A synchronous electric motor is an AC electric motor in which, at steady state,
the rotation of the shaft is synchronized with the frequency of the supply current; the rotation period is exactly equal to an integer number of AC cycles. Sync ...
using a direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional electric current, flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor (material), conductor such as a wire, but can also flow throug ...
(DC) electric
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
power supply. It uses an electronic controller to switch DC currents to the motor windings, producing magnetic fields that effectively rotate in space and which the permanent magnet rotor follows. The controller adjusts the phase and amplitude of the current pulses that control the speed
In kinematics, the speed (commonly referred to as ''v'') of an object is the magnitude of the change of its position over time or the magnitude of the change of its position per unit of time; it is thus a non-negative scalar quantity. Intro ...
and torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. Wh ...
of the motor. It is an improvement on the mechanical commutator
In mathematics, the commutator gives an indication of the extent to which a certain binary operation fails to be commutative. There are different definitions used in group theory and ring theory.
Group theory
The commutator of two elements, ...
(brushes) used in many conventional electric motors.
The construction of a brushless motor system is typically similar to a permanent magnet synchronous motor
A synchronous electric motor is an AC electric motor in which, at steady state,
the rotation of the shaft is synchronized with the frequency of the supply current; the rotation period is exactly equal to an integer number of AC cycles. Synch ...
(PMSM), but can also be a switched reluctance motor
The switched reluctance motor (SRM) is a type of reluctance motor. Unlike brushed DC motors, power is delivered to windings in the stator (case) rather than the rotor. This simplifies mechanical design because power does not have to be delivere ...
, or an induction (asynchronous) motor. They may also use neodymium magnets
A nickel-plated neodymium magnet on a bracket from a hard disk drive
file:Nd-magnet.jpg">Nickel-plated neodymium magnet cubes
Left: high-resolution transmission electron microscopy image of Nd2Fe14B; right: crystal structure with unit cell mar ...
and be outrunners (the stator
The stator is the stationary part of a rotary system, found in electric generators, electric motors, sirens, mud motors, or biological rotors (such as bacterial flagella or ATP synthase). Energy flows through a stator to or from the rotat ...
is surrounded by the rotor), inrunner
The term inrunner refers to an electric motor where the rotor (runner) is inside the stator. The term is in particular used for brushless motors to differentiate them from outrunners that have their rotor outside the stator. The vast majority ...
s (the rotor is surrounded by the stator), or axial (the rotor and stator are flat and parallel).
The advantages of a brushless motor over brushed motors are high power-to-weight ratio, high speed, nearly instantaneous control of speed (rpm) and torque, high efficiency, and low maintenance. Brushless motors find applications in such places as computer peripherals (disk drives, printers), hand-held power tools, and vehicles ranging from model aircraft to automobiles. In modern washing machines, brushless DC motors have allowed replacement of rubber belts and gearboxes by a direct-drive design.
Background
Brushed DC motor
A brushed DC electric motor is an internally commutated electric motor designed to be run from a direct current power source and utilizing an electric brush for contact.
Brushed motors were the first commercially important application of electr ...
s were invented in the 20th century and are still common. Brushless DC motors were made possible by the development of solid-state electronics
Solid-state electronics are semiconductor electronics: electronic equipment that use semiconductor devices such as transistors, diodes and integrated circuits (ICs). The term is also used as an adjective for devices in which semiconductor elec ...
in the 1960s.
An electric motor develops torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational analogue of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. Wh ...
by keeping the magnetic fields of the rotor
ROTOR was an elaborate air defence radar system built by the British Government in the early 1950s to counter possible attack by Soviet bombers. To get it operational as quickly as possible, it was initially made up primarily of WWII-era syst ...
(the rotating part of the machine) and the stator
The stator is the stationary part of a rotary system, found in electric generators, electric motors, sirens, mud motors, or biological rotors (such as bacterial flagella or ATP synthase). Energy flows through a stator to or from the rotat ...
(the fixed part of the machine) misaligned. One or both sets of magnets are electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Electromagnets usually consist of wire (likely copper) wound into a electromagnetic coil, coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic ...
s, made of a coil of wire wound around an iron core. DC running through the wire winding creates the magnetic field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
, providing the power that runs the motor. The misalignment generates a torque that tries to realign the fields. As the rotor moves and the fields come into alignment, it is necessary to move either the rotor's or stator's field to maintain the misalignment and continue to generate torque and movement. The device that moves the fields based on the position of the rotor is called a commutator
In mathematics, the commutator gives an indication of the extent to which a certain binary operation fails to be commutative. There are different definitions used in group theory and ring theory.
Group theory
The commutator of two elements, ...
.
Brush commutator
In brushed motors this is done with a rotary switch on the motor's shaft called a commutator. It consists of a rotating cylinder or disc divided into multiple metal contact segments on the rotor. The segments are connected to conductor windings on the rotor. Two or more stationary contacts called ''brushes
A brush is a common tool with bristles, wire or other filaments. It generally consists of a handle or block to which filaments are affixed in either a parallel or perpendicular orientation, depending on the way the brush is to be gripped during u ...
'', made of a soft conductor such as graphite
Graphite () is a Crystallinity, crystalline allotrope (form) of the element carbon. It consists of many stacked Layered materials, layers of graphene, typically in excess of hundreds of layers. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable ...
, press against the commutator, making sliding electrical contact with successive segments as the rotor turns. The brushes selectively provide electric current to the windings. As the rotor rotates, the commutator selects different windings and the directional current is applied to a given winding such that the rotor's magnetic field remains misaligned with the stator and creates a torque in one direction.
The brush commutator has disadvantages that has led to a decline in use of brushed motors. These disadvantages are:
*The friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. Types of friction include dry, fluid, lubricated, skin, and internal -- an incomplete list. The study of t ...
of the brushes sliding along the rotating commutator segments causes power losses that can be significant in a low-power motor.
*The soft brush material wears down due to friction, creating dust, and eventually the brushes must be replaced. This makes commutated motors unsuitable for low particulate or sealed applications like hard disk
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating hard disk drive platter, pla ...
motors and for applications that require maintenance-free operation.
*The electrical resistance of the sliding brush contact causes a voltage drop in the motor circuit called , which consumes energy.
*The repeated abrupt switching of the current through the inductance
Inductance is the tendency of an electrical conductor to oppose a change in the electric current flowing through it. The electric current produces a magnetic field around the conductor. The magnetic field strength depends on the magnitude of the ...
of the windings causes sparks at the commutator contacts, which is a fire hazard in explosive atmospheres and a source of electronic noise
In electronics, noise is an unwanted disturbance in an electrical signal.
Noise generated by electronic devices varies greatly as it is produced by several different effects.
In particular, noise is inherent in physics and central to thermod ...
, which can cause electromagnetic interference in nearby microelectronic circuits.
During the last hundred years, high-power DC brushed motors, once the mainstay of industry, were replaced by alternating current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in w ...
(AC) synchronous motor
A synchronous electric motor is an AC electric motor in which, at steady state,
the rotation of the shaft is synchronized with the frequency of the supply current; the rotation period is exactly equal to an integer number of AC cycles. Sync ...
s. Today, brushed motors are used only in low-power applications or where only DC is available, but the above drawbacks limit their use even in these applications.
Brushless solution
In brushless DC motors, an electronic controller replaces the brush commutator contacts. An electronic sensor detects the angle of the rotor and controlssemiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
switches such as transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
s that switch current through the windings, either reversing the direction of the current or, in some motors turning it off, at the correct angle so the electromagnets create torque in one direction. The elimination of the sliding contact allows brushless motors to have less friction and longer life; their working life is limited only by the lifetime of their bearings.
Brushed DC motors develop a maximum torque when stationary, linearly decreasing as velocity increases. Some limitations of brushed motors can be overcome by brushless motors; they include higher efficiency and lower susceptibility to mechanical wear. These benefits come at the cost of potentially less rugged, more complex, and more expensive control electronics.
A typical brushless motor has permanent magnets that rotate around a fixed armature, eliminating problems associated with connecting current to the moving armature. An electronic controller replaces the commutator assembly of the brushed DC motor, which continually switches the phase to the windings to keep the motor turning. The controller performs similar timed power distribution by using a solid-state circuit rather than the commutator system.
Brushless motors offer several advantages over brushed DC motors, including high torque to weight ratio, increased efficiency producing more torque per watt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of Power (physics), power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantification (science), quantify the rate of Work ...
, increased reliability, reduced noise, longer lifetime by eliminating brush and commutator erosion, elimination of ionizing sparks from the commutator, and an overall reduction of electromagnetic interference (EMI). With no windings on the rotor, they are not subjected to centrifugal forces, and because the windings are supported by the housing, they can be cooled by conduction, requiring no airflow inside the motor for cooling. This in turn means that the motor's internals can be entirely enclosed and protected from dirt or other foreign matter.
Brushless motor commutation can be implemented in software using a microcontroller
A microcontroller (MC, uC, or μC) or microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Pro ...
, or may alternatively be implemented using analog or digital circuits. Commutation with electronics instead of brushes allows for greater flexibility and capabilities not available with brushed DC motors, including speed limiting, microstepping operation for slow and fine motion control, and a holding torque when stationary. Controller software can be customized to the specific motor being used in the application, resulting in greater commutation efficiency.
The maximum power that can be applied to a brushless motor is limited almost exclusively by heat; too much heat weakens the magnets and damages the windings' insulation.
When converting electricity into mechanical power, brushless motors are more efficient than brushed motors primarily due to the absence of brushes, which reduces mechanical energy loss due to friction. The enhanced efficiency is greatest in the no-load and low-load regions of the motor's performance curve.
Environments and requirements in which manufacturers use brushless-type DC motors include maintenance-free operation, high speeds, and operation where sparking is hazardous (i.e. explosive environments) or could affect electronically sensitive equipment.
The construction of a brushless motor resembles a stepper motor
A stepper motor, also known as step motor or stepping motor,Clarence W. de Silva. Mechatronics: An Integrated Approach (2005). CRC Press. p. 675. "The terms ''stepper motor'', ''stepping motor'', and ''step motor'' are synonymous and are often u ...
, but the motors have important differences in implementation and operation. While stepper motors are frequently stopped with the rotor in a defined angular position, a brushless motor is usually intended to produce continuous rotation. Both motor types may have a rotor position sensor for internal feedback. Both a stepper motor and a well-designed brushless motor can hold finite torque at zero RPM.
Controller implementations
Because the controller implements the traditional brushes' functionality, it needs to know the rotor's orientation relative to the stator coils. This is automatic in a brushed motor due to the fixed geometry of the rotor shaft and brushes. Some designs useHall effect sensor
A Hall effect sensor (also known as a Hall sensor or Hall probe) is any sensor incorporating one or more Hall elements, each of which produces a voltage proportional to one axial component of the Magnetic field#The B-field, magnetic field vector ...
s or a rotary encoder
A rotary encoder, also called a shaft encoder, is an electro-mechanical device that converts the angle, angular position or motion of a shaft or axle to Analog signal, analog or Digital signal, digital output signals.
There are two main types of ...
to directly measure the rotor's position. Others measure the back-EMF
Counter-electromotive force (counter EMF, CEMF, back EMF),Graf, "counterelectromotive force", Dictionary of Electronics is the electromotive force (EMF) manifesting as a voltage that opposes the change in current which induced it. CEMF is the EMF ...
in the undriven coils to infer the rotor position, eliminating the need for separate Hall effect sensors. These are therefore often called ''sensorless'' controllers.
Controllers that sense rotor position based on back-EMF have extra challenges in initiating motion because no back-EMF is produced when the rotor is stationary. This is usually accomplished by beginning rotation from an arbitrary phase, and then skipping to the correct phase if it is found to be wrong. This can cause the motor to run backwards briefly, adding even more complexity to the startup sequence. Other sensorless controllers are capable of measuring winding saturation caused by the position of the magnets to infer the rotor position.
A typical controller contains three polarity-reversible outputs controlled by a logic circuit. Simple controllers employ comparator
In electronics, a comparator is a device that compares two voltages or currents and outputs a digital signal indicating which is larger. It has two analog input terminals V_+ and V_- and one binary digital output V_\text. The output is ideally
...
s working from the orientation sensors to determine when the output phase should be advanced. More advanced controllers employ a microcontroller to manage acceleration, control motor speed and fine-tune efficiency.
Two key performance parameters of brushless DC motors are the motor constants
The motor size constant (K_\text) and motor velocity constant (K_\text, alternatively called the back EMF constant) are values used to describe characteristics of electrical motors.
Motor constant
K_\text is the ''motor constant'' (sometimes, '' ...
(torque constant) and (back-EMF constant, also known as speed constant ).
Variations in construction
inrunner
The term inrunner refers to an electric motor where the rotor (runner) is inside the stator. The term is in particular used for brushless motors to differentiate them from outrunners that have their rotor outside the stator. The vast majority ...
configuration, the permanent magnets are part of the rotor. Three stator windings surround the rotor. In the external-rotor outrunner configuration, the radial relationship between the coils and magnets is reversed; the stator coils form the center (core) of the motor, while the permanent magnets spin within an overhanging rotor that surrounds the core. Outrunners typically have more poles, set up in triplets to maintain the three groups of windings, and have a higher torque at low RPMs. In the flat axial flux type, used where there are space or shape constraints, stator and rotor plates are mounted face to face. In all brushless motors, the coils are stationary.
There are two common electrical winding configurations: the delta configuration connects three windings to each other in a triangle-like circuit, and power is applied at each of the connections. The wye (''Y''-shaped) configuration, sometimes called a star winding, connects all of the windings to a central point, and power is applied to the remaining end of each winding. A motor with windings in delta configuration gives low torque at low speed but can give higher top speed. Wye configuration gives high torque at low speed but not as high top speed. The wye winding is normally more efficient. Delta-connected windings can allow high-frequency parasitic electrical currents to circulate entirely within the motor. A Wye-connected winding does not contain a closed loop in which parasitic currents can flow, preventing such losses. Aside from the higher impedance of the wye configuration, from a controller standpoint, the two winding configurations can be treated exactly the same.
Applications
 Brushless motors fulfill many functions originally performed by brushed DC motors, but cost and control complexity prevents brushless motors from replacing brushed motors completely in the lowest-cost areas. Nevertheless, brushless motors have come to dominate many applications, particularly devices such as computer
Brushless motors fulfill many functions originally performed by brushed DC motors, but cost and control complexity prevents brushless motors from replacing brushed motors completely in the lowest-cost areas. Nevertheless, brushless motors have come to dominate many applications, particularly devices such as computer hard drives
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magnet ...
and CD/DVD players. Small cooling fans in electronic equipment are powered exclusively by brushless motors. They can be found in cordless power tools where the increased efficiency of the motor leads to longer periods of use before the battery needs to be charged. Low speed, low power brushless motors are used in direct-drive turntable
A direct-drive turntable is one of the three main phonograph designs currently being produced. The other styles are the belt-drive turntable and the idler-wheel type. Each name is based upon the type of coupling used between the platter of th ...
s for gramophone record
A phonograph record (also known as a gramophone record, especially in British English) or a vinyl record (for later varieties only) is an analog sound storage medium in the form of a flat disc with an inscribed, modulated spiral groove. The g ...
s. Brushless motors can also be found in marine applications, such as underwater thruster
An underwater thruster is a configuration of marine propellers and hydraulic or electric motor built into or mounted to an underwater robot as a propulsion device. These give the robot movement and maneuverability against sea water resistance. The ...
s. Drones also utilize brushless motors to elevate theiperformance
Transport
Brushless motors are found inelectric vehicle
An electric vehicle (EV) is a motor vehicle whose propulsion is powered fully or mostly by electricity. EVs encompass a wide range of transportation modes, including road vehicle, road and rail vehicles, electric boats and Submersible, submer ...
s, hybrid vehicle
A hybrid vehicle is one that uses two or more distinct types of power, such as submarines that use diesel when surfaced and batteries when submerged. Other means to store energy include pressurized fluid in hydraulic hybrids.
Hybrid powertrai ...
s, personal transporter
A personal transporter (also powered transporter, electric rideable, personal light electric vehicle, personal mobility device, etc.) is any of a class of compact, mostly recent (21st century), motorised micromobility vehicle for transporting an ...
s, and electric aircraft
An electric aircraft is an aircraft powered by electricity.
Electric aircraft are seen as a way to reduce the environmental effects of aviation, providing zero emissions and quieter flights.
Electricity may be supplied by a variety of methods, ...
. Most electric bicycle
An electric bicycle, e-bike, electrically assisted pedal cycle, or electrically power assisted cycle is a bicycle with an integrated electric motor used to assist propulsion. Many kinds of e-bikes are available worldwide, but they generally fa ...
s use brushless motors that are sometimes built into the wheel hub itself, with the stator fixed solidly to the axle and the magnets attached to and rotating with the wheel. The same principle is applied in self-balancing scooter
A self-balancing scooter (also hoverboard, self-balancing board, electric scooter board, or swegway) is a self-balancing personal transporter consisting of two motorized wheels connected to a pair of articulated pads on which the rider places the ...
wheels. Most electrically powered radio-controlled model
A radio-controlled model (or RC model) is a model that is steerable with the use of radio control (RC). All types of model vehicles have had RC systems installed in them, including ground vehicles, boats, planes, helicopters and even submarine ...
s use brushless motors because of their high efficiency.
Cordless tools
Brushless motors are found in many modern cordless tools, including somestring trimmer
A string trimmer, also known by the portmanteau strimmer and the trademarks Weedwacker, Weed Eater and Whipper Snipper, is a garden power tool for cutting grass, small weeds, and groundcover. It uses a whirling monofilament line instead of a b ...
s, leaf blower
A leaf blower, commonly known as a blower, is a device that propels air out of a nozzle to move debris such as leaves and grass cuttings. Leaf blowers are powered by electric or gasoline motors. Gasoline models have traditionally been two-s ...
s, saws (circular
Circular may refer to:
* The shape of a circle
* ''Circular'' (album), a 2006 album by Spanish singer Vega
* Circular letter (disambiguation), a document addressed to many destinations
** Government circular, a written statement of government pol ...
and reciprocating), and drill
A drill is a tool used for making round holes or driving fasteners. It is fitted with a drill bit for making holes, or a screwdriver bit for securing fasteners. Historically, they were powered by hand, and later mains power, but cordless b ...
s/ drivers. The weight and efficiency advantages of brushless over brushed motors are more important to handheld, battery-powered tools than to large, stationary tools plugged into an AC outlet.
Heating and ventilation
There is a trend in theheating, ventilation, and air conditioning
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC ) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. H ...
(HVAC) and refrigeration
Refrigeration is any of various types of cooling of a space, substance, or system to lower and/or maintain its temperature below the ambient one (while the removed heat is ejected to a place of higher temperature).IIR International Dictionary of ...
industries to use brushless motors instead of various types of AC motor
An AC motor is an electric motor driven by an alternating current (AC). The AC motor commonly consists of two basic parts, an outside stator having coils supplied with alternating current to produce a rotating magnetic field, and an inside roto ...
s. The most significant reason to switch to a brushless motor is a reduction in power required to operate them versus a typical AC motor. In addition to the brushless motor's higher efficiency, HVAC systems, especially those featuring variable-speed or load modulation, use brushless motors to give the built-in microprocessor continuous control over cooling and airflow.
Industrial engineering
The application of brushless DC motors withinindustrial engineering
Industrial engineering (IE) is concerned with the design, improvement and installation of integrated systems of people, materials, information, equipment and energy. It draws upon specialized knowledge and skill in the mathematical, physical, an ...
primarily focuses on manufacturing engineering
Manufacturing engineering or production engineering is a branch of professional engineering that shares many common concepts and ideas with other fields of engineering such as mechanical, chemical, electrical, and industrial engineering.
Manufac ...
or industrial automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, mainly by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machine ...
design. Brushless motors are ideally suited for manufacturing applications because of their high power density, good speed-torque characteristics, high efficiency, wide speed ranges and low maintenance. The most common uses of brushless DC motors in industrial engineering are motion control
Motion control is a sub-field of automation, encompassing the systems or sub-systems involved in moving parts of machines in a controlled manner. Motion control systems are extensively used in a variety of fields for automation purposes, includi ...
, linear actuator
A linear actuator is an actuator that creates linear motion (i.e., in a straight line), in contrast to the circular motion of a conventional electric motor. Linear actuators are used in machine tools and industrial machinery, in computer perip ...
s, servomotor
A servomotor (or servo motor or simply servo) is a rotary or linear actuator that allows for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration in a mechanical system. It constitutes part of a servomechanism, and consi ...
s, actuators
An actuator is a component of a machine that produces force, torque, or displacement, when an electrical, pneumatic or hydraulic input is supplied to it in a system (called an actuating system). The effect is usually produced in a controlled way. ...
for industrial robots, extruder
Extrusion is a process used to create objects of a fixed cross-sectional profile by pushing material through a die of the desired cross-section. Its two main advantages over other manufacturing processes are its ability to create very complex ...
drive motors and feed drives for CNC machine
Computer numerical control (CNC) or CNC machining is the automated control of machine tools by a computer. It is an evolution of numerical control (NC), where machine tools are directly managed by data storage media such as punched cards or ...
tools.
Brushless motors are commonly used as pump, fan and spindle drives in adjustable or variable speed applications as they are capable of developing high torque with good speed response. In addition, they can be easily automated for remote control. Due to their construction, they have good thermal characteristics and high energy efficiency Energy efficiency may refer to:
* Energy efficiency (physics), the ratio between the useful output and input of an energy conversion process
** Electrical efficiency, useful power output per electrical power consumed
** Mechanical efficiency, a rat ...
. To obtain a variable speed response, brushless motors operate in an electromechanical system that includes an electronic motor controller
A motor controller is a device or group of devices that can coordinate in a predetermined manner the performance of an electric motor. A motor controller might include a manual or automatic means for starting and stopping the motor, selecting forw ...
and a rotor position feedback sensor. Brushless DC motors are widely used as servomotors for machine tool servo drives. Servomotors are used for mechanical displacement, positioning or precision motion control. DC stepper motors can also be used as servomotors; however, since they are operated with open loop control, they typically exhibit torque pulsations.
Brushless motors are used in industrial positioning and actuation applications. For assembly robots, Brushless technology may be used to build linear motor
A linear motor is an electric motor that has had its stator and rotor (electric), rotor "unrolled", thus, instead of producing a torque (rotation), it produces a linear force along its length. However, linear motors are not necessarily straight. ...
s. The advantage of linear motors is that they can produce linear motion without the need of a transmission
Transmission or transmit may refer to:
Science and technology
* Power transmission
** Electric power transmission
** Transmission (mechanical device), technology that allows controlled application of power
*** Automatic transmission
*** Manual tra ...
system, such as ballscrews, leadscrew
A leadscrew (or lead screw), also known as a power screw or translation screw,Bhandari, p. 202. is a screw used as a linkage in a machine, to translate turning motion into linear motion. Because of the large area of sliding contact between ...
, rack-and-pinion
rack and pinion is a type of linear actuator that comprises a circular gear (the '' pinion'') engaging a linear gear (the ''rack''). Together, they convert between rotational motion and linear motion: rotating the pinion causes the rack to be ...
, cam
Cam or CAM may refer to:
Science and technology
* Cam (mechanism), a mechanical linkage which translates motion
* Camshaft, a shaft with a cam
* Camera or webcam, a device that records images or video
In computing
* Computer-aided manufacturin ...
, gear
A gear or gearwheel is a rotating machine part typically used to transmit rotational motion and/or torque by means of a series of teeth that engage with compatible teeth of another gear or other part. The teeth can be integral saliences or ...
s or belts, that would be necessary for rotary motors. Transmission systems are known to introduce less responsiveness and reduced accuracy. Direct drive, brushless DC linear motors consist of a slotted stator with magnetic teeth and a moving actuator, which has permanent magnets and coil windings. To obtain linear motion, a motor controller excites the coil windings in the actuator causing an interaction of the magnetic fields resulting in linear motion. Tubular linear motor A tubular linear motor is a type of linear electric motor with a forcer consisting of a series of solenoids wrapped around a cylinder enclosing a movable rod that contains a number of strong cylindrical permanent magnets aligned in alternating and ...
s are another form of linear motor design operated in a similar way.
Aeromodelling
 Brushless motors have become a popular motor choice for
Brushless motors have become a popular motor choice for model aircraft
A model aircraft is a physical model of an existing or imagined aircraft, and is built typically for display, research, or amusement. Model aircraft are divided into two basic groups: flying and non-flying. Non-flying models are also termed s ...
including helicopters
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attribu ...
and drones. Their favorable power-to-weight ratio
Power-to-weight ratio (PWR, also called specific power, or power-to-mass ratio) is a calculation commonly applied to engines and mobile power sources to enable the comparison of one unit or design to another. Power-to-weight ratio is a measurement ...
s and wide range of available sizes have revolutionized the market for electric-powered model flight, displacing virtually all brushed electric motors, except for low powered inexpensive often toy grade aircraft. They have also encouraged growth of simple, lightweight electric model aircraft, rather than the previous internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal comb ...
s powering larger and heavier models. The increased power-to-weight ratio of modern batteries and brushless motors allows models to ascend vertically rather than climb gradually. The low noise and lack of mass compared to small glow fuel
Glow fuel is a fuel source used in model engines – generally the same or similar fuels can be used in model airplanes, helicopters, cars and boats. Glow fuel can be burned by very simple two-stroke engines or by more complicated four-stroke engin ...
internal combustion engines is another reason for their popularity.
Legal restrictions for the use of combustion engine driven model aircraft in some countries, most often due to potential for noise pollution
Noise pollution, or sound pollution, is the propagation of noise or sound with potential harmful effects on humans and animals. The source of outdoor noise worldwide is mainly caused by machines, transport and propagation systems.Senate Publi ...
—even with purpose-designed muffler
A muffler (North American and Australian English) or silencer (British English) is a device for reducing the noise emitted by the exhaust of an internal combustion engine—especially a noise-deadening device forming part of the exhaust syst ...
s for almost all model engines being available over the most recent decades—have also supported the shift to high-power electric systems.
Radio-controlled cars
Their popularity has also risen in the radio-controlled (RC) car area. Brushless motors have been legal in North American RC car racing in accordance withRadio Operated Auto Racing
Remotely Operated Auto Racers (formerly known as Radio Operated Auto Racing), abbreviated as ROAR, is the sanctioning body of competitive radio-controlled car racing in the United States and Canada. It is a US national non profit organization that ...
(ROAR) since 2006. These motors provide a great amount of power to RC racers and, if paired with appropriate gearing and high-discharge lithium polymer
A lithium polymer battery, or more correctly, lithium-ion polymer battery (abbreviated as LiPo, LIP, Li-poly, lithium-poly, and others), is a rechargeable battery derived from lithium-ion and lithium-metal battery technology. The primary differ ...
(Li-Po) or lithium iron phosphate
Lithium iron phosphate or lithium ferro-phosphate (LFP) is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a gray, red-grey, brown or black solid that is insoluble in water. The material has attracted attention as a component of lithium iron phosp ...
(LiFePO4) batteries, these cars can achieve speeds over .
Brushless motors are capable of producing more torque and have a faster peak rotational speed compared to nitro- or gasoline-powered engines. Nitro engine
A nitro engine generally refers to an engine powered with a fuel that contains some portion (usually between 10% and 40%) of nitromethane mixed with methanol. Nitromethane is a highly combustible substance that is generally only used in very spe ...
s peak at around 46,800 r/min and , while a smaller brushless motor can reach 50,000 r/min and . Larger brushless RC motors can reach upwards of and 28,000 r/min to power one-fifth-scale models.
Combat robotics
Brushless motors are widely used as an alternative to brushed motors in the sport ofcombat robotics
Robot combat is a type of robot competition in which custom-built machines fight using various methods to incapacitate each other. The machines have generally been remote-controlled vehicles rather than autonomous robots.
Robot combat competi ...
. They are used in every weight class from 75 grams all the way up to 250 pounds. When used for locomotion, brushless motors are often paired with a planetary gearbox in order to decrease the output speed to make the robot more controllable. Other methods such as friction drive achieve the same result using slightly different means. Brushless motors are also often used to power kinetic weapons (such as a spinning blade). In the lower weight classes, weapons are often mounted directly to the motor while in heavier robots, timing belts, v-belts, and chains are used to transmit power from the motor to the spinning mass.
See also
*Piezoelectric motor
A piezoelectric motor or piezo motor is a type of electric motor based on the change in shape of a piezoelectric material when an electric field is applied, as a consequence of the converse piezoelectric effect. An electrical circuit makes acous ...
*Squirrel-cage rotor
A squirrel-cage rotor is the rotating part of the common squirrel-cage induction motor. It consists of a cylinder of steel laminations, with aluminum or copper conductors cast in its surface. In operation, the non-rotating stator winding is co ...
References
Further reading
* * * * *External links
* * * FlashElectric Drives – Brushless DC / AC and Reluctance Motors
with useful diagrams
How Brushless Motor and ESC Work
– Video explanation how Brushless DC Motor works, plus how to control one with an Arduino micro-controller. {{Authority control DC motors Electric motors 20th-century inventions