Cystoviridae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Cystovirus'' is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses which infects bacteria. It is the only genus in the family ''Cystoviridae.'' The name of the group c''ysto'' derives from Greek ''kystis'' which means bladder or sack. There are seven species in this genus.
 Cystovirus particles are enveloped, with icosahedral and spherical geometries, and T=13, T=2 symmetry. The virion diameter is around 85 nm. Cystoviruses are distinguished by their outer layer protein and lipid envelope. No other
Cystovirus particles are enveloped, with icosahedral and spherical geometries, and T=13, T=2 symmetry. The virion diameter is around 85 nm. Cystoviruses are distinguished by their outer layer protein and lipid envelope. No other
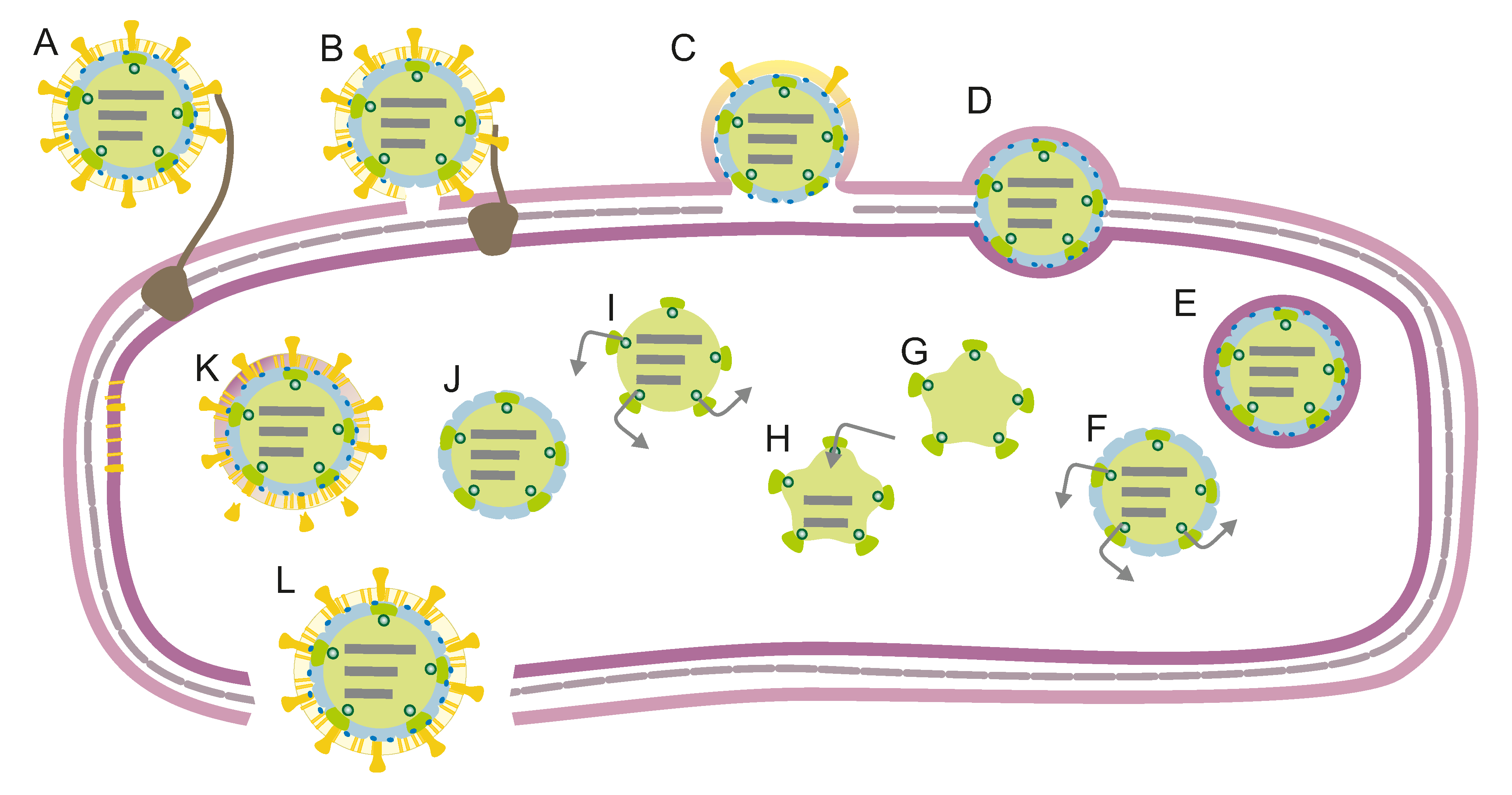 Cytoviruses enter the bacteria by adsorption on its pilus and then membrane fusion. Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Replication follows the double-stranded RNA virus replication model. Double-stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. The progeny viruses are released from the cell by
Cytoviruses enter the bacteria by adsorption on its pilus and then membrane fusion. Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Replication follows the double-stranded RNA virus replication model. Double-stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. The progeny viruses are released from the cell by
Hyperexpansion of RNA Bacteriophage Diversity
PlosOne. '' Microvirgula'',Xiaoyao Cai, Fengjuan Tian, Li Teng, Hongmei Liu, Yigang Tong Tong, Shuai Le, Tingting Zhang (2021)
Cultivation of a Lytic Double-Stranded RNA Bacteriophage Infecting Microvirgula aerodenitrificans Reveals a Mutualistic Parasitic Lifestyle
American Society for Microbiology. '' Acinetobacter'',Clay S. Crippen, Bibi Zhou, and Christine M. Szymanski (2021)
RNA and Sugars, Unique Properties of Bacteriophages Infecting Multidrug Resistant Acinetobacter radioresistens Strain LH6
NCBI. '' Lactococcus'', ''
NCBI Taxonomy. and possibly other bacterial genera.
 Members of the ''Cystoviridae'' appear to be most closely related to the '' Reoviridae'', but also share
Members of the ''Cystoviridae'' appear to be most closely related to the '' Reoviridae'', but also share
ICTV Online Report: ''Cystoviridae''
{{Authority control Cystoviridae Riboviria Virus genera
Discovery
''Pseudomonas virus phi6
Φ6 (Phi 6) is the best-studied bacteriophage of the virus family Cystoviridae. It infects ''Pseudomonas'' bacteria (typically plant-pathogenic '' P. syringae''). It has a three-part, segmented, double-stranded RNA genome, totalling ~13.5 k ...
'' was the first virus in this family to be discovered and was initially characterized in 1973 by Anne Vidaver at the University of Nebraska. She found that when she cultured the bacterial strain '' Pseudomonas phaseolicola'' HB1OY with halo blight
Halo blight of bean is a bacterial disease caused by '' Pseudomonas syringae pv. phaseolicola''. Halo blight’s pathogen is a gram-negative, aerobic, polar-flagellated and non-spore forming bacteria. This bacterial disease was first discovered in ...
infected bean straw, cytopathic effects were detected in cultured lawns, indicating that there was a lytic microbe or bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteri ...
present.
In 1999, phi7–14 were identified by the laboratory of Leonard Mindich at the Public Health Research Institute associated with New York University. They did this by culturing various leaves in Lysogeny Broth and then plating the broth on lawns of '' Pseudomonas syringae pv phaseolicola''. They were able to identify viral plaques from this and then subsequently sequence their genomes.
Microbiology
Structure
 Cystovirus particles are enveloped, with icosahedral and spherical geometries, and T=13, T=2 symmetry. The virion diameter is around 85 nm. Cystoviruses are distinguished by their outer layer protein and lipid envelope. No other
Cystovirus particles are enveloped, with icosahedral and spherical geometries, and T=13, T=2 symmetry. The virion diameter is around 85 nm. Cystoviruses are distinguished by their outer layer protein and lipid envelope. No other bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteri ...
has any lipid in its outer coat, though the '' Tectiviridae'' and the ''Corticoviridae
''Corticovirus'' is a genus of viruses in the family '' Corticoviridae''. Corticoviruses are bacteriophages; that is, their natural hosts are bacteria. The genus contains two species. The name is derived from Latin ''cortex'', ''corticis'' (mea ...
'' have lipids within their capsids.
Genome
Cystoviruses have a tripartite double-stranded RNA genome which is approximately 14 kbp in total length. The genome is linear and segmented, and labeled as large (L) 6.4 kbp, medium (M) 4 kbp, and small (S) 2.9 kb in length. The genome codes for twelve proteins.Life cycle
 Cytoviruses enter the bacteria by adsorption on its pilus and then membrane fusion. Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Replication follows the double-stranded RNA virus replication model. Double-stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. The progeny viruses are released from the cell by
Cytoviruses enter the bacteria by adsorption on its pilus and then membrane fusion. Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Replication follows the double-stranded RNA virus replication model. Double-stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. The progeny viruses are released from the cell by lysis
Lysis ( ) is the breaking down of the membrane of a cell, often by viral, enzymic, or osmotic (that is, "lytic" ) mechanisms that compromise its integrity. A fluid containing the contents of lysed cells is called a ''lysate''. In molecular bio ...
.
Most identified cystoviruses infect '' Pseudomonas'' species, but this is likely biased due to the method of screening and enrichment. There are many proposed members of this family. Pseudomonas viruses φ7, φ8, φ9, φ10, φ11, φ12, and φ13 have been identified and named, but other cystovirus-like viruses have also been isolated. These seven putative relatives are classified as either close (φ7, φ9, φ10, φ11) or distant (φ8, φ12, φ13) relatives to φ6, with the distant relatives thought to infect via the LPS
LPS may refer to:
Science and medicine
* Lipopolysaccharide (Endotoxin)
* Levator palpebrae superioris muscle
Schools
* Leighton Park School in Reading, England
* Lexington Public Schools, a school district in Massachusetts, USA
* Lincoln P ...
rather than the pili.
However, cystoviruses do not only infect ''Pseudomonas''. But also bacteria of the genera ''Streptomyces
''Streptomyces'' is the largest genus of Actinomycetota and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 500 species of ''Streptomyces'' bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positive, ...
'',Siddharth R. Krishnamurthy, Andrew B. Janowski,Guoyan Zhao, Dan Barouch, David Wang (2016)Hyperexpansion of RNA Bacteriophage Diversity
PlosOne. '' Microvirgula'',Xiaoyao Cai, Fengjuan Tian, Li Teng, Hongmei Liu, Yigang Tong Tong, Shuai Le, Tingting Zhang (2021)
Cultivation of a Lytic Double-Stranded RNA Bacteriophage Infecting Microvirgula aerodenitrificans Reveals a Mutualistic Parasitic Lifestyle
American Society for Microbiology. '' Acinetobacter'',Clay S. Crippen, Bibi Zhou, and Christine M. Szymanski (2021)
RNA and Sugars, Unique Properties of Bacteriophages Infecting Multidrug Resistant Acinetobacter radioresistens Strain LH6
NCBI. '' Lactococcus'', ''
Pectobacterium
''Pectobacterium'' is a bacterial genus of the family Pectobacteriaceae; it used to be a member of the genus ''Erwinia'', which was split into three genera: ''Erwinia'', ''Pectobacterium'', and ''Brenneria''.
Species include ''Pectobacterium c ...
'',CystoviridaeNCBI Taxonomy. and possibly other bacterial genera.
Taxonomy
 Members of the ''Cystoviridae'' appear to be most closely related to the '' Reoviridae'', but also share
Members of the ''Cystoviridae'' appear to be most closely related to the '' Reoviridae'', but also share homology
Homology may refer to:
Sciences
Biology
*Homology (biology), any characteristic of biological organisms that is derived from a common ancestor
* Sequence homology, biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences
*Homologous chrom ...
with the '' Totiviridae''. In particular, the structural genes of cystoviruses are highly-similar to those used by a number of dsRNA viruses that infect eukaryotes. The genus ''Cystovirus'' has seven species:
* ''Pseudomonas virus phi6
Φ6 (Phi 6) is the best-studied bacteriophage of the virus family Cystoviridae. It infects ''Pseudomonas'' bacteria (typically plant-pathogenic '' P. syringae''). It has a three-part, segmented, double-stranded RNA genome, totalling ~13.5 k ...
''
* '' Pseudomonas virus phi8''
* ''Pseudomonas virus phi12
''Pseudomonas'' is a genus of Gram-negative, Gammaproteobacteria, belonging to the family Pseudomonadaceae and containing 191 described species. The members of the genus demonstrate a great deal of metabolic diversity and consequently are able ...
''
* '' Pseudomonas virus phi13''
* '' Pseudomonas virus phi2954''
* '' Pseudomonas virus phiNN''
* ''Pseudomonas virus phiYY
''Pseudomonas'' is a genus of Gram-negative, Gammaproteobacteria, belonging to the family Pseudomonadaceae and containing 191 described species. The members of the genus demonstrate a great deal of metabolic diversity and consequently are able ...
''
Other unassigned phages:
* ''Microvirgula virus phiNY
''Microvirgula'' is a Gram-negative bacteria genus from the family of Neisseriaceae
The Neisseriaceae are a family of Pseudomonadota, within the ''Neisseriales'' order. While many organisms in the family are mammalian commensals or part of t ...
''
* '' Streptomyces virus phi0''
* '' Lactococcus virus phi7-4''
* ''Pectobacterium virus MA14
''Pectobacterium'' is a bacterial genus of the family Pectobacteriaceae; it used to be a member of the genus ''Erwinia'', which was split into three genera: ''Erwinia'', ''Pectobacterium'', and ''Brenneria''.
Species include ''Pectobacterium ...
''
* ''Acinetobacter virus CAP3
''Acinetobacter'' is a genus of gram-negative bacteria belonging to the wider class of Gammaproteobacteria. ''Acinetobacter'' species are oxidase-negative, exhibit twitching motility, and occur in pairs under magnification.
They are importan ...
''
* '' Acinetobacter virus CAP4''
* '' Acinetobacter virus CAP5''
* '' Acinetobacter virus CAP6''
* ''Acinetobacter virus CAP7
''Acinetobacter'' is a genus of gram-negative bacteria belonging to the wider class of Gammaproteobacteria. ''Acinetobacter'' species are oxidase-negative, exhibit twitching motility, and occur in pairs under magnification.
They are importan ...
''
References
External links
ICTV Online Report: ''Cystoviridae''
{{Authority control Cystoviridae Riboviria Virus genera