Cumbrians on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Hen Ogledd (), meaning the Old North, is the
Hen Ogledd (), meaning the Old North, is the
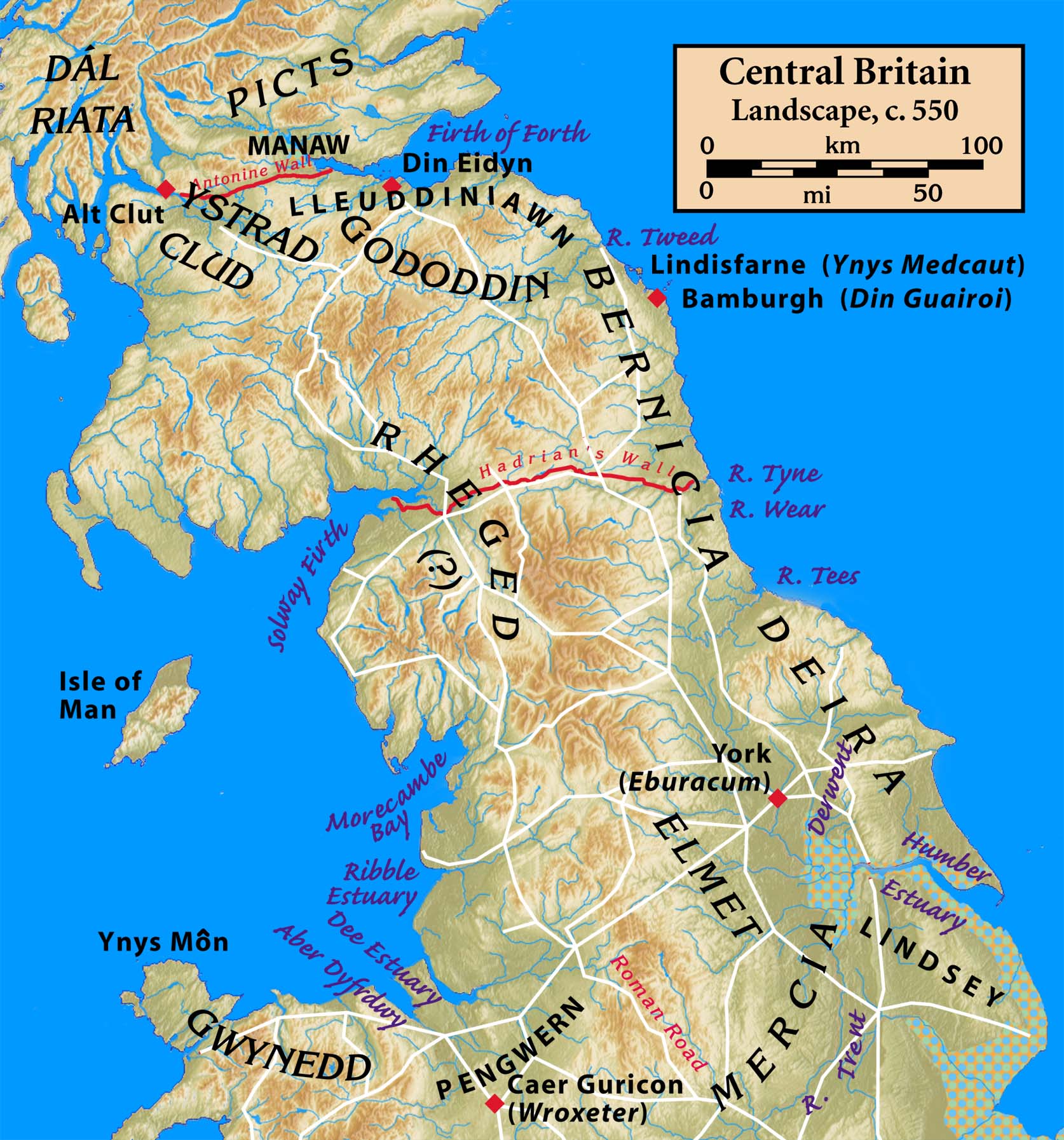
 The interests of kingdoms of this era were not restricted to their immediate vicinity. Alliances were not made only within the same ethnic groups, nor were enmities restricted to nearby different ethnic groups. An alliance of Britons fought against another alliance of Britons at the Battle of Arfderydd.
The interests of kingdoms of this era were not restricted to their immediate vicinity. Alliances were not made only within the same ethnic groups, nor were enmities restricted to nearby different ethnic groups. An alliance of Britons fought against another alliance of Britons at the Battle of Arfderydd.
"What's in a name? Britons, Angles, ethnicity and material culture from the fourth to seventh centuries."
''Heroic Age'' 4 (Winter 2001). {{Barbarian kingdoms Celtic Britons Medieval history of England 1st millennium in Scotland Sub-Roman Britain Anglo-Saxon England Medieval history of Wales Northern England History of Cumbria History of Dumfries and Galloway History of Northumberland History of the Scottish Borders History of Yorkshire Barbarian kingdoms Regions of England Regions of Scotland Historical regions in the United Kingdom Scottish Lowlands
 Hen Ogledd (), meaning the Old North, is the
Hen Ogledd (), meaning the Old North, is the historical region
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the Human history, human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some t ...
that was inhabited by the Brittonic people of sub-Roman Britain
Sub-Roman Britain, also called post-Roman Britain or Dark Age Britain, is the period of late antiquity in Great Britain between the end of Roman rule and the founding of Anglo-Saxon kingdoms. The term was originally used to describe archae ...
in the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th to the 10th century. They marked the start o ...
, now Northern England
Northern England, or the North of England, refers to the northern part of England and mainly corresponds to the Historic counties of England, historic counties of Cheshire, Cumberland, County Durham, Durham, Lancashire, Northumberland, Westmo ...
and the southern Scottish Lowlands
The Lowlands ( or , ; , ) is a cultural and historical region of Scotland.
The region is characterised by its relatively flat or gently rolling terrain as opposed to the mountainous landscapes of the Scottish Highlands. This area includes ci ...
, alongside the fellow Brittonic Celtic Kingdom of Elmet, in Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ) is an area of Northern England which was History of Yorkshire, historically a county. Despite no longer being used for administration, Yorkshire retains a strong regional identity. The county was named after its county town, the ...
. Its population spoke a variety of the Brittonic language known as Cumbric
Cumbric is an extinct Celtic language of the Brittonic subgroup spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North", in Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands. It was closely related to Old Welsh and the ot ...
which is closely related to, if not a dialect of Old Welsh
Old Welsh () is the stage of the Welsh language from about 800 AD until the early 12th century when it developed into Middle Welsh.Koch, p. 1757. The preceding period, from the time Welsh became distinct from Common Brittonic around 550, ha ...
. The people of Wales and the Hen Ogledd considered themselves to be one people, and both were referred to as Cymry
The Welsh () are an ethnic group and nation native to Wales who share a common ancestry, history and culture. Wales is one of the four countries of the United Kingdom. The majority of people living in Wales are British citizens.
In Wales, ...
('fellow-countrymen') from the Brittonic word ''combrogi''. The Hen Ogledd was distinct from the parts of Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
inhabited by the Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples in what is now Scotland north of the Firth of Forth, in the Scotland in the early Middle Ages, Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and details of their culture can be gleaned from early medieval texts and Pic ...
, Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
, and Scoti
''Scoti'' or ''Scotti'' is a Latin name for the Gaels,Duffy, Seán. ''Medieval Ireland: An Encyclopedia''. Routledge, 2005. p.698 first attested in the late 3rd century. It originally referred to all Gaels, first those in Ireland and then those ...
.
The major kingdoms of the Hen Ogledd were Elmet
Elmet (), sometimes Elmed or Elmete, was an independent Brittonic Celtic
Cumbric-speaking kingdom between about the 4th century and mid-7th century.
The people of Elmet survived as a distinctly recognised Brittonic Celtic group for centuri ...
, Gododdin
The Gododdin () were a Brittonic people of north-eastern Britannia, the area known as the Hen Ogledd or Old North (modern south-east Scotland and north-east England), in the sub-Roman period. Descendants of the Votadini, they are best known ...
, Rheged
Rheged () was one of the kingdoms of the ('Old North'), the Brittonic-speaking region of what is now Northern England and southern Scotland, during the post-Roman era and Early Middle Ages. It is recorded in several poetic and bardic sources, ...
, and the Kingdom of Strathclyde
Strathclyde (, "valley of the River Clyde, Clyde"), also known as Cumbria, was a Celtic Britons, Brittonic kingdom in northern Britain during the Scotland in the Middle Ages, Middle Ages. It comprised parts of what is now southern Scotland an ...
(Welsh: ''Ystrad Clud''). Smaller kingdoms included Aeron and Calchfynydd. Eidyn
Eidyn was the region around modern Edinburgh in sub-Roman and early medieval Britain, approximately during the 5th–7th centuries. It centred on the stronghold of Din Eidyn, thought to have been at Castle Rock, now the site of Edinburgh Cast ...
, Lleuddiniawn, and Manaw Gododdin
Manaw Gododdin was the narrow coastal region on the south side of the Firth of Forth, part of the Brythonic-speaking Kingdom of Gododdin in the post-Roman Era. It is notable as the homeland of Cunedda prior to his conquest of North Wales, and ...
were evidently parts of Gododdin. The later Anglian kingdoms of Deira
Deira ( ; Old Welsh/ or ; or ) was an area of Post-Roman Britain, and a later Anglian kingdom.
Etymology
The name of the kingdom is of Brythonic origin, and is derived from the Proto-Celtic , meaning 'oak' ( in modern Welsh), in which case ...
and Bernicia
Bernicia () was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom established by Anglian settlers of the 6th century in what is now southeastern Scotland and North East England.
The Anglian territory of Bernicia was approximately equivalent to the modern English cou ...
both had Brittonic-derived names, suggesting they may have been Brittonic kingdoms originally. All the kingdoms of the Hen Ogledd except Strathclyde were gradually either integrated or subsumed by the emerging Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, Gaelic Scots and fellow Brittonic Picts by about 800; Strathclyde was eventually incorporated into the rising Middle Irish
Middle Irish, also called Middle Gaelic (, , ), is the Goidelic language which was spoken in Ireland, most of Scotland and the Isle of Man from AD; it is therefore a contemporary of Late Old English and Early Middle English. The modern Goideli ...
-speaking Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland was a sovereign state in northwest Europe, traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a Anglo-Sc ...
in the 11th century.
The memory of the Hen Ogledd remained strong in Wales after its fall, and indeed the term came into being in Wales after the destruction of the Brittonic kingdoms of the north. Welsh tradition included genealogies of the ''Gwŷr y Gogledd'', or Men of the North, and several important Welsh dynasties traced their lineage to them. A number of important early Welsh texts were attributed to the Men of the North, such as Taliesin
Taliesin ( , ; 6th century AD) was an early Britons (Celtic people), Brittonic poet of Sub-Roman Britain whose work has possibly survived in a Middle Welsh manuscript, the ''Book of Taliesin''. Taliesin was a renowned bard who is believed to ...
, Aneirin
Aneirin (), also rendered as Aneurin or Neirin and Aneurin Gwawdrydd, was an early Medieval Brythonic war poet who lived during the 6th century. He is believed to have been a bard or court poet in one of the Cumbric kingdoms of the Hen Ogledd ...
, Myrddin Wyllt
Myrddin Wyllt (—"Myrddin the Wild", , ) is a figure in medieval Welsh legend. In Middle Welsh poetry he is accounted a chief bard, the speaker of several poems in The Black Book of Carmarthen and The Red Book of Hergest. He is called ''Wyl ...
, and the Cynfeirdd poets. Heroes of the north such as Urien
Urien ap Cynfarch Oer () or Urien Rheged (, Old Welsh: or , ) was a powerful sixth-century Brittonic-speaking figure who was possibly the ruler of the territory or kingdom known as Rheged. He is one of the best-known and best documented o ...
, Owain mab Urien
Owain mab Urien (Middle Welsh Owein) (died c. 595) was the son of Urien, king of Rheged c. 590, and fought with his father against the Angles of Bernicia. The historical figure of Owain became incorporated into the Arthurian cycle of legends w ...
, and Coel Hen
Coel (Old Welsh: ''Coil''), also called ''Coel Hen'' (Coel the Old) and King Cole, is a figure prominent in Welsh literature and legend since the Middle Ages. Early Welsh tradition knew of a Coel Hen, a 4th-century leader in Roman Britain, Ro ...
and his descendants feature in Welsh poetry and the Welsh Triads
The Welsh Triads (, "Triads of the Island of Britain") are a group of related texts in medieval manuscripts which preserve fragments of Welsh folklore, mythology and traditional history in groups of three. The triad is a rhetorical form whereby o ...
.
Background
Almost nothing is reliably known of Central Britain before . There had never been a period of long-term, effectiveRoman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
control north of the Tyne– Solway line, and south of that line effective Roman control began to erode before the traditionally given date of departure of the Roman military from Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the territory that became the Roman province of ''Britannia'' after the Roman conquest of Britain, consisting of a large part of the island of Great Britain. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410.
Julius Caes ...
in 407. It was noted in the writings of Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus, occasionally anglicized as Ammian ( Greek: Αμμιανός Μαρκελλίνος; born , died 400), was a Greek and Roman soldier and historian who wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from antiquit ...
and others that there was ever-decreasing Roman control from about 100 onward, and in the years after 360 there was widespread disorder and the large-scale permanent abandonment of territory by the Romans.
By 550, the region was controlled by native Brittonic-speaking peoples except for the eastern coastal areas, which were controlled by the Anglian peoples of Bernicia
Bernicia () was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom established by Anglian settlers of the 6th century in what is now southeastern Scotland and North East England.
The Anglian territory of Bernicia was approximately equivalent to the modern English cou ...
and Deira
Deira ( ; Old Welsh/ or ; or ) was an area of Post-Roman Britain, and a later Anglian kingdom.
Etymology
The name of the kingdom is of Brythonic origin, and is derived from the Proto-Celtic , meaning 'oak' ( in modern Welsh), in which case ...
. To the north were the Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples in what is now Scotland north of the Firth of Forth, in the Scotland in the early Middle Ages, Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and details of their culture can be gleaned from early medieval texts and Pic ...
(now also accepted as Brittonic speakers prior to Gaelicisation) with the Gaelic
Gaelic (pronounced for Irish Gaelic and for Scots Gaelic) is an adjective that means "pertaining to the Gaels". It may refer to:
Languages
* Gaelic languages or Goidelic languages, a linguistic group that is one of the two branches of the Insul ...
kingdom of Dál Riata
Dál Riata or Dál Riada (also Dalriada) () was a Gaels, Gaelic Monarchy, kingdom that encompassed the Inner Hebrides, western seaboard of Scotland and north-eastern Ireland, on each side of the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North ...
to the northwest. All of these peoples would play a role in the history of the Old North.
Historical context
From a historical perspective, wars were frequently internecine, and Britons were aggressors as well as defenders, as was also true of the Angles, Picts, andGaels
The Gaels ( ; ; ; ) are an Insular Celts, Insular Celtic ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland, and the Isle of Man. They are associated with the Goidelic languages, Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic languages comprising ...
. However, those Welsh stories of the Hen Ogledd that tell of Britons fighting Anglians have a counterpart, told from the opposite side. The story of the demise of the kingdoms of the Old North is the story of the rise of the Kingdom of Northumbria
Northumbria () was an early medieval Heptarchy, kingdom in what is now Northern England and Scottish Lowlands, South Scotland.
The name derives from the Old English meaning "the people or province north of the Humber", as opposed to the Sout ...
from two coastal kingdoms to become the premier power in Britain north of the Humber
The Humber is a large tidal estuary on the east coast of Northern England. It is formed at Trent Falls, Faxfleet, by the confluence of the tidal rivers River Ouse, Yorkshire, Ouse and River Trent, Trent. From there to the North Sea, it forms ...
and south of the Firth of Clyde
The Firth of Clyde, is the estuary of the River Clyde, on the west coast of Scotland. The Firth has some of the deepest coastal waters of the British Isles. The Firth is sheltered from the Atlantic Ocean by the Kintyre, Kintyre Peninsula. The ...
and the Firth of Forth
The Firth of Forth () is a firth in Scotland, an inlet of the North Sea that separates Fife to its north and Lothian to its south. Further inland, it becomes the estuary of the River Forth and several other rivers.
Name
''Firth'' is a cognate ...
.

 The interests of kingdoms of this era were not restricted to their immediate vicinity. Alliances were not made only within the same ethnic groups, nor were enmities restricted to nearby different ethnic groups. An alliance of Britons fought against another alliance of Britons at the Battle of Arfderydd.
The interests of kingdoms of this era were not restricted to their immediate vicinity. Alliances were not made only within the same ethnic groups, nor were enmities restricted to nearby different ethnic groups. An alliance of Britons fought against another alliance of Britons at the Battle of Arfderydd. Áedán mac Gabráin
Áedán mac Gabráin (; ), also written as Aedan, was a king of Dál Riata from 574 until c. 609 AD. The kingdom of Dál Riata was situated in modern Argyll and Bute, Scotland, and parts of County Antrim, Ireland. Genealogies record that Áe ...
of Dál Riata
Dál Riata or Dál Riada (also Dalriada) () was a Gaels, Gaelic Monarchy, kingdom that encompassed the Inner Hebrides, western seaboard of Scotland and north-eastern Ireland, on each side of the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North ...
appears in the ''Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd
''Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd'' () is a brief Middle Welsh tract which claims to give the pedigrees of twenty 6th century rulers of the Hen Ogledd, the Brittonic languages, Brittonic-speaking parts of southern Scotland and northern England. It is att ...
'', a genealogy among the pedigrees of the Men of the North. The ''Historia Brittonum
''The History of the Britons'' () is a purported history of early Britain written around 828 that survives in numerous recensions from after the 11th century. The ''Historia Brittonum'' is commonly attributed to Nennius, as some recensions ha ...
'' states that Oswiu
Oswiu, also known as Oswy or Oswig (; c. 612 – 15 February 670), was King of Bernicia from 642 and of Northumbria from 654 until his death. He is notable for his role at the Synod of Whitby in 664, which ultimately brought the church in Northu ...
, king of Northumbria, married a Briton who may have had some Pictish ancestry. A marriage between the Northumbrian and Pictish royal families would produce the Pictish king Talorgan I. Áedán mac Gabráin fought as an ally of the Britons against the Northumbrians. Cadwallon ap Cadfan
Cadwallon ap Cadfan (died 634)A difference in the interpretation of Bede's dates has led to the question of whether Cadwallon was killed in 634 or the year earlier, 633. Cadwallon died in the year after the Battle of Hatfield Chase, which Bede ...
of the Kingdom of Gwynedd
The Kingdom of Gwynedd (Medieval Latin: ; Middle Welsh: ) was a Wales in the Early Middle Ages, Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire Succession of states, successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon ...
allied with Penda of Mercia
Penda (died 15 November 655)Manuscript A of the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' gives the year as 655. Bede also gives the year as 655 and specifies a date, 15 November. R. L. Poole (''Studies in Chronology and History'', 1934) put forward the theor ...
to defeat Edwin of Northumbria
Edwin (; c. 586 – 12 October 632/633), also known as Eadwine or Æduinus, was the King of Deira and Bernicia – which later became known as Northumbria – from around 616 until his death. He was the second monarch to rule bo ...
.
Conquest and defeat did not necessarily mean the extirpation of one culture and its replacement by another. The Brittonic region of northwestern England was absorbed by Anglian Northumbria in the 7th century, yet it would reemerge 300 years later as South Cumbria, joined with North Cumbria (Strathclyde) into a single state.
Societal context
The organisation of the Men of the North wastribal
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide use of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. The definition is contested, in part due to conflict ...
, based on kinship
In anthropology, kinship is the web of social relationships that form an important part of the lives of all humans in all societies, although its exact meanings even within this discipline are often debated. Anthropologist Robin Fox says that ...
groups of extended families, owing allegiance to a dominant "royal" family, sometimes indirectly through client relationships, and receiving protection in return. For Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foot ...
peoples, this organisation was still in effect hundreds of years later, as shown in the Irish Brehon law
Early Irish law, also called Brehon law (from the old Irish word breithim meaning judge), comprised the statutes which governed everyday life in Early Medieval Ireland. They were partially eclipsed by the Norman invasion of 1169, but underwe ...
, the Welsh Laws of Hywel Dda
''Cyfraith Hywel'' (; ''Laws of Hywel''), also known as ''Welsh law'' (), was the system of law practised in medieval Wales before its conquest of Wales by Edward I, final conquest by England. Subsequently, the Welsh law's criminal codes were s ...
, and the Scottish
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
Laws of the Brets and Scots. The Anglo-Saxon law
Anglo-Saxon law (, later ; , ) was the legal system of Anglo-Saxon England from the 6th century until the Norman Conquest of 1066. It was a form of Germanic law based on unwritten custom known as folk-right and on written laws enacted by Histo ...
had culturally different origins, but with many similarities to Celtic law. Like Celtic law, it was based on cultural tradition, without any perceivable debt to the Roman occupation of Britain."Anglo-Saxon law" is a modern neologism
In linguistics, a neologism (; also known as a coinage) is any newly formed word, term, or phrase that has achieved popular or institutional recognition and is becoming accepted into mainstream language. Most definitively, a word can be considered ...
for the Saxon Law of Wessex, the Anglian Law of Mercia, and the Danelaw
The Danelaw (, ; ; ) was the part of History of Anglo-Saxon England, England between the late ninth century and the Norman Conquest under Anglo-Saxon rule in which Danes (tribe), Danish laws applied. The Danelaw originated in the conquest and oc ...
, all of which were sufficiently similar to merit inclusion within this umbrella term. The laws of Anglian Northumbria
Northumbria () was an early medieval Heptarchy, kingdom in what is now Northern England and Scottish Lowlands, South Scotland.
The name derives from the Old English meaning "the people or province north of the Humber", as opposed to the Sout ...
were supplanted by the Danelaw, but were certainly similar to these. The origins of English law
English law is the common law list of national legal systems, legal system of England and Wales, comprising mainly English criminal law, criminal law and Civil law (common law), civil law, each branch having its own Courts of England and Wales, ...
have been much studied. For example, the 12th century '' Tractatus de legibus et consuetudinibus regni Angliae'' (''Treatise on the laws and customs of the Kingdom of England'') is the book of authority on English common law
Common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law primarily developed through judicial decisions rather than statutes. Although common law may incorporate certain statutes, it is largely based on prece ...
, and scholars have held that it owes a debt to Norman law
Norman law (, , ) refers to the customary law of the Duchy of Normandy which developed between the 10th and 13th centuries and which survives today in the legal systems of Jersey and the other Channel Islands. It grew out of a mingling of Frankish ...
and to Germanic law
Germanic law is a scholarly term used to describe a series of commonalities between the various law codes (the ''Leges Barbarorum'', 'laws of the barbarians', also called Leges) of the early Germanic peoples. These were compared with statements i ...
, and not to Roman law
Roman law is the law, legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables (), to the (AD 529) ordered by Eastern Roman emperor Justinian I.
Roman law also den ...
.
A primary ''royal court
A royal court, often called simply a court when the royal context is clear, is an extended royal household in a monarchy, including all those who regularly attend on a monarch, or another central figure. Hence, the word ''court'' may also be app ...
'' () would be maintained as a "capital", but it was not the bureaucratic administrative centre of modern society, nor the settlement or ''civitas
In Ancient Rome, the Latin term (; plural ), according to Cicero in the time of the late Roman Republic, was the social body of the , or citizens, united by Roman law, law (). It is the law that binds them together, giving them responsibilitie ...
'' of Roman rule. As the ruler and protector of his kingdom, the king would maintain multiple courts throughout his territory, travelling among them to exercise his authority and to address the needs of his people, such as in the dispensing of justice. This ancient method of dispensing justice survived as a part of royal procedure until the reforms of Henry II
Henry II may refer to:
Kings
* Saint Henry II, Holy Roman Emperor (972–1024), crowned King of Germany in 1002, of Italy in 1004 and Emperor in 1014
*Henry II of England (1133–89), reigned from 1154
*Henry II of Jerusalem and Cyprus (1271–1 ...
(reigned 1154–1189) modernised the administration of law.
Language
Modern scholarship uses the term "Cumbric" for the Brittonic language spoken in the Hen Ogledd. It appears to have been very closely related toOld Welsh
Old Welsh () is the stage of the Welsh language from about 800 AD until the early 12th century when it developed into Middle Welsh.Koch, p. 1757. The preceding period, from the time Welsh became distinct from Common Brittonic around 550, ha ...
, with some local variances, and more distantly related to Cornish or Breton
Breton most often refers to:
*anything associated with Brittany, and generally
**Breton people
**Breton language, a Southwestern Brittonic Celtic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken in Brittany
** Breton (horse), a breed
**Gale ...
. There are no surviving texts written in the dialect; evidence for it comes from placenames, proper names in a few early inscription
Epigraphy () is the study of inscriptions, or epigraphs, as writing; it is the science of identifying graphemes, clarifying their meanings, classifying their uses according to dates and cultural contexts, and drawing conclusions about the wr ...
s and later non-Cumbric sources, two terms in the '' Leges inter Brettos et Scottos'', and the corpus of poetry by the '' cynfeirdd'', the "early poets", nearly all of which deals with the north.Koch 2006, p. 516.
The ''cynfeirdd'' poetry is the largest source of information, and it is generally accepted that some part of the corpus was first composed in the Hen Ogledd. However, it survives entirely in later manuscripts created in Wales where the oral tradition continued on, and it is unknown how faithful they are to the originals. Still, the texts do contain discernible variances that distinguish the speech from the Welsh dialects. In particular, these texts contain a number of archaism
In language, an archaism is a word, a sense of a word, or a style of speech or writing that belongs to a historical epoch beyond living memory, but that has survived in a few practical settings or affairs. lexicon, Lexical archaisms are single a ...
s – features that appear to have once been common in all Brittonic varieties, but which later vanished from Welsh and the Southwestern Brittonic languages
The Southwestern Brittonic languages (, ) are the Brittonic Celtic languages spoken in what is now South West England and Brittany since the Early Middle Ages. During the period of their earliest attestation, the languages appear to be indisti ...
. In general, however, the differences appear to be slight, and the distinction between Cumbric and Old Welsh is largely geographical rather than linguistic.Koch 2006, p. 517.
Cumbric gradually disappeared as the area was conquered by the Anglo-Saxons, and later the Scots and Norse, though it survived in the Kingdom of Strathclyde
Strathclyde (, "valley of the River Clyde, Clyde"), also known as Cumbria, was a Celtic Britons, Brittonic kingdom in northern Britain during the Scotland in the Middle Ages, Middle Ages. It comprised parts of what is now southern Scotland an ...
, centred at Alt Clut in what is now Dumbarton
Dumbarton (; , or ; or , meaning 'fort of the Britons (historical), Britons') is a town in West Dunbartonshire, Scotland, on the north bank of the River Clyde where the River Leven, Dunbartonshire, River Leven flows into the Clyde estuary. ...
in Scotland. Kenneth H. Jackson suggested that it re-emerged in Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial county in North West England. It borders the Scottish council areas of Dumfries and Galloway and Scottish Borders to the north, Northumberland and County Durham to the east, North Yorkshire to the south-east, Lancash ...
in the 10th century, as Strathclyde established hegemony over that area. It is unknown when Cumbric finally became extinct, but the series of counting systems of Brittonic origin recorded in Northern England since the 18th century have been proposed as evidence of a survival of elements of Cumbric; though the view has been largely rejected on linguistic grounds, with evidence pointing to the fact that it was imported to England after the Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
era.
Welsh tradition
One of the traditional stories relating to the genealogies of Welsh dynasties derived fromCunedda
Cunedda ap Edern, also called Cunedda ''Wledig'' (reigned – c. 460), was an important early Welsh people, Welsh leader, and the progenitor of the royal dynasty of Kingdom of Gwynedd, Gwynedd, one of the very oldest of Western Europe.
Nam ...
and his sons as "Men of the North". Cunedda himself is held to be the progenitor of the royal dynasty of the Kingdom of Gwynedd, one of the largest and most powerful of the medieval Welsh kingdoms, and an ongoing connection to the Hen Ogledd. Cunedda's genealogy shows him as a descendant of one of Magnus Maximus
Magnus Maximus (; died 28 August 388) was Roman emperor in the West from 383 to 388. He usurped the throne from emperor Gratian.
Born in Gallaecia, he served as an officer in Britain under Theodosius the Elder during the Great Conspiracy ...
' generals, Paternus, who Maximus appointed as commander at Alt Clut. The Welsh and the Men of the North may have seen themselves as one people. The Welsh name for themselves, ''Cymry'', derives from this ancient relationship, although this is debatable, as while Gwynedd seemed to have good relationships with them, and with Ceredigion, it is unknown how the other Welsh Kingdoms saw them, since they were not unified themselves, especially the southern Kingdoms like Dyfed
Dyfed () is a preserved county in southwestern Wales, covering the modern counties Carmarthenshire, Ceredigion and Pembrokeshire. It is mostly rural area with a coastline on the Irish Sea and the Bristol Channel. Between 1974 and 1996, Dyfed w ...
and Ystrad Tywi
Ystrad Tywi (, ''Valley of the river Towy'') is a region of southwest Wales situated on both banks of the River Towy (), it contained places such as Cedweli, Carnwyllion, Loughor, Llandeilo, and Gwyr (although this is disputed). Although ...
, which had heavy Irish presence at the time. 'Cymry' was a term that referred to both the Welsh and the Men of the North but was sometimes applied to others such as the Picts and the Irish as well. It is derived from the Brittonic word c''ombrogoi'', which meant "fellow-countrymen", and it is worth noting in passing that its Breton
Breton most often refers to:
*anything associated with Brittany, and generally
**Breton people
**Breton language, a Southwestern Brittonic Celtic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken in Brittany
** Breton (horse), a breed
**Gale ...
counterpart ''kenvroiz'' still has this original meaning of "compatriots". The word began to be used as an endonym by the Men of the North during the early 7th century (and possibly earlier), and was used throughout the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
to describe the Kingdom of Strathclyde
Strathclyde (, "valley of the River Clyde, Clyde"), also known as Cumbria, was a Celtic Britons, Brittonic kingdom in northern Britain during the Scotland in the Middle Ages, Middle Ages. It comprised parts of what is now southern Scotland an ...
. Before this, and for some centuries after, the traditional as well as the more literary term was ''Brythoniaid'', recalling the still older time when all on the island remained a unity. ''Cymry'' survives today in the native name for Wales (''Cymru'', land of the ''Cymry''), and in the English county name Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial county in North West England. It borders the Scottish council areas of Dumfries and Galloway and Scottish Borders to the north, Northumberland and County Durham to the east, North Yorkshire to the south-east, Lancash ...
, both meaning "homeland", "mother country".
Many of the traditional sources of information about the Hen Ogledd survive in Welsh tradition, and bards such as Aneirin
Aneirin (), also rendered as Aneurin or Neirin and Aneurin Gwawdrydd, was an early Medieval Brythonic war poet who lived during the 6th century. He is believed to have been a bard or court poet in one of the Cumbric kingdoms of the Hen Ogledd ...
(the reputed author of ''Y Gododdin
''Y Gododdin'' () is a medieval Welsh poem consisting of a series of elegies to the men of the Brittonic kingdom of Gododdin and its allies who, according to the conventional interpretation, died fighting the Angles of Deira and Bernicia ...
'') are thought to have been court poets in the Hen Ogledd.
Nature of the sources
A listing of passages from the literary and historical sources, particularly relevant to the Hen Ogledd, can be found in Sir Edward Anwyl's article ''Wales and the Britons of the North''. A somewhat dated introduction to the study of old Welsh poetry can be found in his 1904 article ''Prolegomena to the Study of Old Welsh Poetry''.Literary sources
* Thebard
In Celtic cultures, a bard is an oral repository and professional story teller, verse-maker, music composer, oral historian and genealogist, employed by a patron (such as a monarch or chieftain) to commemorate one or more of the patron's a ...
ic poetry attributed to Taliesin
Taliesin ( , ; 6th century AD) was an early Britons (Celtic people), Brittonic poet of Sub-Roman Britain whose work has possibly survived in a Middle Welsh manuscript, the ''Book of Taliesin''. Taliesin was a renowned bard who is believed to ...
, Aneirin
Aneirin (), also rendered as Aneurin or Neirin and Aneurin Gwawdrydd, was an early Medieval Brythonic war poet who lived during the 6th century. He is believed to have been a bard or court poet in one of the Cumbric kingdoms of the Hen Ogledd ...
, and Llywarch Hen
Llywarch Hen (, "Llywarch the Old"; c. 534 – c. 608), was a prince and poet of the Brythonic kingdom of Rheged, a ruling family in the Hen Ogledd or "Old North" of Britain (modern southern Scotland and northern England). Along with Taliesin, A ...
.
* The genealogical tracts of the Harleian genealogies
__NOTOC__
The Harleian genealogies are a collection of Old Welsh genealogies preserved in British Library, Harley MS 3859. Part of the Harleian Library, the manuscript, which also contains the '' Annales Cambriae'' (Recension A) and a version of ...
, the ''Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd
''Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd'' () is a brief Middle Welsh tract which claims to give the pedigrees of twenty 6th century rulers of the Hen Ogledd, the Brittonic languages, Brittonic-speaking parts of southern Scotland and northern England. It is att ...
'', and the genealogies of Jesus College MS 20.
* The '' Triads of the Island of Britain'' (note that most of the triads published in the notorious third volume of '' The Myvyrian Archaiology of Wales'' are known to be the forgeries of Iolo Morganwg
Edward Williams, better known by his bardic name Iolo Morganwg (; 10March 174718December 1826), was a Welsh antiquarian, poet and collector.Jones, Mary (2004)"Edward Williams/Iolo Morganwg/Iolo Morgannwg" From ''Jones' Celtic Encyclopedia''. R ...
, and are not considered valid sources of historical information). The standard scholarly edition is ''Trioedd Ynys Prydein'' by Rachel Bromwich
Rachel Bromwich (30 July 1915 – 15 December 2010), born Rachel Sheldon Amos, was a British scholar. Her focus was on medieval Welsh literature, and she taught Celtic Languages and Literature in the Department of Anglo-Saxon, Norse and Celtic ...
.
* The other elegies () and songs of praise
''Songs of Praise'' is a BBC Television religious programme that presents Christian hymns, worship songs and inspirational performances in churches of varying denominations from around the UK alongside interviews and stories reflecting how Ch ...
(), as well as certain mythological
Myth is a genre of folklore consisting primarily of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society. For scholars, this is very different from the vernacular usage of the term "myth" that refers to a belief that is not true. Instead, the ...
stories, that have been preserved.
Stories praising a patron and the construction of flattering genealogies are neither unbiased nor reliable sources of historically accurate information. However, while they may exaggerate and make apocryphal assertions, they do not falsify or change the historical facts that were known to the bards' listeners, as that would bring ridicule and disrepute to both the bards and their patrons. In addition, the existence of stories of defeat and tragedy
A tragedy is a genre of drama based on human suffering and, mainly, the terrible or sorrowful events that befall a tragic hero, main character or cast of characters. Traditionally, the intention of tragedy is to invoke an accompanying catharsi ...
, as well as stories of victory, lends additional credibility to their value as sources of history. Within that context, the stories contain useful information, much of it incidental, about an era of British history where very little is reliably known.
Historical sources
* The ''Historia Brittonum
''The History of the Britons'' () is a purported history of early Britain written around 828 that survives in numerous recensions from after the 11th century. The ''Historia Brittonum'' is commonly attributed to Nennius, as some recensions ha ...
'' attributed to Nennius
Nennius – or Nemnius or Nemnivus – was a Welsh monk of the 9th century. He has traditionally been attributed with the authorship of the ''Historia Brittonum'', based on the prologue affixed to that work. This attribution is widely considered ...
* The ''Annales Cambriae
The (Latin for ''Annals of Wales'') is the title given to a complex of Latin chronicles compiled or derived from diverse sources at St David's in Dyfed, Wales. The earliest is a 12th-century presumed copy of a mid-10th-century original; later ...
''
* The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons.
The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the ninth century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of ...
''
* The ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People
The ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People'' (), written by Bede in about AD 731, is a history of the Christian Churches in England, and of England generally; its main focus is on the growth of Christianity. It was composed in Latin, and ...
'' by Bede
Bede (; ; 672/326 May 735), also known as Saint Bede, Bede of Jarrow, the Venerable Bede, and Bede the Venerable (), was an English monk, author and scholar. He was one of the most known writers during the Early Middle Ages, and his most f ...
* The ''Annals of Tigernach
The ''Annals of Tigernach'' (Abbreviation, abbr. AT, ) are chronicles probably originating in Clonmacnoise, Ireland. The language is a mixture of Latin language, Latin and Old Irish, Old and Middle Irish.
Many of the pre-historic entries come f ...
''
These sources are not without deficiencies. Both the authors and their later transcribers sometimes displayed a partisanship that promoted their own interests, portraying their own agendas in a positive light, always on the side of justice and moral rectitude. Facts in opposition to those agendas are sometimes omitted, and apocryphal entries are sometimes added.
While Bede was a Northumbrian partisan and spoke with prejudice against the native Britons, his ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People'' is highly regarded for its effort towards an accurate telling of history, and for its use of reliable sources. When passing along "traditional" information that lacks a historical foundation, Bede takes care to note it as such.
The ''De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae
(English: ''On the Ruin and Conquest of Britain'') is a work written in Anglo-Latin literature, Latin in the late fifth or sixth century by the Britons (historical), British religious polemicist Gildas. It is a sermon in three parts condemnin ...
'' by Gildas
Gildas (English pronunciation: , Breton language, Breton: ''Gweltaz''; ) — also known as Gildas Badonicus, Gildas fab Caw (in Middle Welsh texts and antiquarian works) and ''Gildas Sapiens'' (Gildas the Wise) — was a 6th-century Britons (h ...
(c. 516–570) is occasionally relevant in that it mentions early people and places also mentioned in the literary and historical sources. The work was intended to preach Christianity to Gildas' contemporaries and was not meant to be a history. It is one of the few contemporary accounts of his era to have survived.
Place names
Brittonic place names in Scotland south of the Forth and Clyde, and in Cumberland and neighbouring counties, indicate areas of Hen Ogledd inhabited by Britons in the early Middle Ages. Isolated locations of later British presence are also indicated by place names ofOld English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
and Old Norse
Old Norse, also referred to as Old Nordic or Old Scandinavian, was a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants ...
origin. In Yorkshire, the names of Walden
''Walden'' (; first published as ''Walden; or, Life in the Woods'') is an 1854 book by American transcendentalism, transcendentalist writer Henry David Thoreau. The text is a reflection upon the author's simple living in natural surroundings. T ...
, Walton and Walburn, from Old English ''walas'' "Britons or Welshmen", indicate Britons encountered by the Anglo-Saxons, and the name of Birkby, from Old Norse ''Breta'' "Britons", indicates a place where the Vikings met Britons.
Dubious and fraudulent sources
The ''Historia Regum Britanniae
(''The History of the Kings of Britain''), originally called (''On the Deeds of the Britons''), is a fictitious account of British history, written around 1136 by Geoffrey of Monmouth. It chronicles the lives of the List of legendary kings o ...
'' of Geoffrey of Monmouth
Geoffrey of Monmouth (; ; ) was a Catholic cleric from Monmouth, Wales, and one of the major figures in the development of British historiography and the popularity of tales of King Arthur. He is best known for his chronicle '' The History of ...
is disparaged as pseudohistory
Pseudohistory is a form of pseudoscholarship that attempts to distort or misrepresent the historical record, often by employing methods resembling those used in scholarly historical research. The related term cryptohistory is applied to pseud ...
, though it looms large as a source for the largely fictional chivalric romance
As a literary genre, the chivalric romance is a type of prose and verse narrative that was popular in the noble courts of high medieval and early modern Europe. They were fantastic stories about marvel-filled adventures, often of a chivalri ...
stories known collectively as the Matter of Britain
The Matter of Britain (; ; ; ) is the body of medieval literature and legendary material associated with Great Britain and Brittany and the list of legendary kings of Britain, legendary kings and heroes associated with it, particularly King Art ...
. The lack of historical value attributed to the ''Historia'' lies only partly in the fact that it contains so many fictions and falsifications of history; the fact that historical accuracy clearly was not a consideration in its creation makes any references to actual people and places no more than a literary convenience.
The ''Iolo Manuscripts'' are a collection of manuscripts presented in the early 19th century by Edward Williams, who is better known as Iolo Morganwg
Edward Williams, better known by his bardic name Iolo Morganwg (; 10March 174718December 1826), was a Welsh antiquarian, poet and collector.Jones, Mary (2004)"Edward Williams/Iolo Morganwg/Iolo Morgannwg" From ''Jones' Celtic Encyclopedia''. R ...
. Containing various tales, anecdotal material and elaborate genealogies that connect virtually everyone of note with everyone else of note (and with many connections to Arthur
Arthur is a masculine given name of uncertain etymology. Its popularity derives from it being the name of the legendary hero King Arthur.
A common spelling variant used in many Slavic, Romance, and Germanic languages is Artur. In Spanish and Ital ...
and Iolo's native region of Morgannwg), they were at first accepted as genuine, but have since been shown to be an assortment of forged or doctored manuscripts, transcriptions, and fantasies, mainly invented by Iolo himself. A list of works tainted by their reliance on the material presented by Iolo (sometimes without attribution) would be quite long.
Kingdoms and regions
Major kingdoms
Places in the Old North that are mentioned as kingdoms in the literary and historical sources include: * Alt Clut or Ystrad Clud – a kingdom centred at what is nowDumbarton
Dumbarton (; , or ; or , meaning 'fort of the Britons (historical), Britons') is a town in West Dunbartonshire, Scotland, on the north bank of the River Clyde where the River Leven, Dunbartonshire, River Leven flows into the Clyde estuary. ...
in Scotland. Later known as Strathclyde, and possibly even later as Cumbria, it was one of the best attested of the northern British kingdoms. It was also the last surviving, as it operated as an independent realm into the 11th century before it was finally absorbed by the Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland was a sovereign state in northwest Europe, traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a Anglo-Sc ...
.
* Elmet
Elmet (), sometimes Elmed or Elmete, was an independent Brittonic Celtic
Cumbric-speaking kingdom between about the 4th century and mid-7th century.
The people of Elmet survived as a distinctly recognised Brittonic Celtic group for centuri ...
– centred in western Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ) is an area of Northern England which was History of Yorkshire, historically a county. Despite no longer being used for administration, Yorkshire retains a strong regional identity. The county was named after its county town, the ...
in northern England. It was located south of the other northern British kingdoms, and well east of present-day Wales, but managed to survive into the early 7th century.
* Gododdin
The Gododdin () were a Brittonic people of north-eastern Britannia, the area known as the Hen Ogledd or Old North (modern south-east Scotland and north-east England), in the sub-Roman period. Descendants of the Votadini, they are best known ...
– a kingdom in what is now southeastern Scotland and northeastern England, the area previously noted as the territory of the Votadini
The Votadini, also known as the ''Uotadini'', ''Wotādīni'', ''Votādīni'', or ''Otadini'' were a Celtic Britons, Brittonic people of the British Iron Age, Iron Age in Great Britain. Their territory was in what is now south-east Scotland and ...
. They are the subjects of the poem ''Y Gododdin
''Y Gododdin'' () is a medieval Welsh poem consisting of a series of elegies to the men of the Brittonic kingdom of Gododdin and its allies who, according to the conventional interpretation, died fighting the Angles of Deira and Bernicia ...
'', which memorialises a disastrous raid by an army raised by the Gododdin on the Angles of Bernicia
Bernicia () was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom established by Anglian settlers of the 6th century in what is now southeastern Scotland and North East England.
The Anglian territory of Bernicia was approximately equivalent to the modern English cou ...
.Koch 2006, pp. 823–826.
* Rheged
Rheged () was one of the kingdoms of the ('Old North'), the Brittonic-speaking region of what is now Northern England and southern Scotland, during the post-Roman era and Early Middle Ages. It is recorded in several poetic and bardic sources, ...
– a major kingdom that evidently included parts of present-day Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial county in North West England. It borders the Scottish council areas of Dumfries and Galloway and Scottish Borders to the north, Northumberland and County Durham to the east, North Yorkshire to the south-east, Lancash ...
, though its full extent is unknown. It may have covered a vast area at one point, as it is very closely associated with its king Urien
Urien ap Cynfarch Oer () or Urien Rheged (, Old Welsh: or , ) was a powerful sixth-century Brittonic-speaking figure who was possibly the ruler of the territory or kingdom known as Rheged. He is one of the best-known and best documented o ...
, whose name is tied to places all over northwestern Britain.
Minor kingdoms and other regions
Several regions are mentioned in the sources, assumed to be notable regions within one of the kingdoms if not separate kingdoms themselves: * Aeron – a minor kingdom mentioned in sources such as ''Y Gododdin'', its location is uncertain, but several scholars have suggested that it was in theAyrshire
Ayrshire (, ) is a Counties of Scotland, historic county and registration county, in south-west Scotland, located on the shores of the Firth of Clyde. The lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area of Ayrshire and Arran covers the entirety ...
region of southwest Scotland. It is frequently associated with Urien Rheged
Urien ap Cynfarch Oer () or Urien Rheged (, Old Welsh: or , ) was a powerful sixth-century Common Brittonic, Brittonic-speaking figure who was possibly the ruler of the territory or kingdom known as Rheged. He is one of the best-known and b ...
, and may have been part of his realm.
* Calchfynydd ("Chalkmountain") – almost nothing is known about this area, though it was likely somewhere in the Hen Ogledd, as an evident ruler, Cadrawd Calchfynydd, is listed in the ''Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd
''Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd'' () is a brief Middle Welsh tract which claims to give the pedigrees of twenty 6th century rulers of the Hen Ogledd, the Brittonic languages, Brittonic-speaking parts of southern Scotland and northern England. It is att ...
''. William Forbes Skene
William Forbes Skene Writer to the Signet, WS FRSE Society of Antiquaries of Scotland, FSA(Scot) Doctor of Civil Law, DCL Legum Doctor, LLD (7 June 1809 – 29 August 1892), was a Scotland, Scottish lawyer, historian and antiquary.
He co-found ...
suggested an identification with Kelso (formerly Calchow) in the Scottish Borders
The Scottish Borders is one of 32 council areas of Scotland. It is bordered by West Lothian, Edinburgh, Midlothian, and East Lothian to the north, the North Sea to the east, Dumfries and Galloway to the south-west, South Lanarkshire to the we ...
.
* Eidyn
Eidyn was the region around modern Edinburgh in sub-Roman and early medieval Britain, approximately during the 5th–7th centuries. It centred on the stronghold of Din Eidyn, thought to have been at Castle Rock, now the site of Edinburgh Cast ...
– this was the area around the modern city of Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh ...
, then known as Din Eidyn
Eidyn was the region around modern Edinburgh in sub-Roman and early medieval Britain, approximately during the 5th–7th centuries. It centred on the stronghold of Din Eidyn, thought to have been at Castle Rock, now the site of Edinburgh Cast ...
(Fort of Eidyn). It was closely associated with the Gododdin kingdom.Koch 2006, pp. 623–625. Kenneth H. Jackson argued strongly that ''Eidyn'' referred exclusively to Edinburgh, but other scholars have taken it as a designation for the wider area.Williams 1972, p. 64. The name may survive today in toponyms such as Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh ...
(Dunedin in Gaelic, Din Eidyn in Cumbric
Cumbric is an extinct Celtic language of the Brittonic subgroup spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North", in Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands. It was closely related to Old Welsh and the ot ...
, and Carriden (from ''Caer Eidyn'')), located fifteen miles to the west.Dumville, p. 297. Din Eidyn was besieged by the Angles in 638 and was under their control for most of the next three centuries.
* Manaw Gododdin
Manaw Gododdin was the narrow coastal region on the south side of the Firth of Forth, part of the Brythonic-speaking Kingdom of Gododdin in the post-Roman Era. It is notable as the homeland of Cunedda prior to his conquest of North Wales, and ...
– the coastal area south of the Firth of Forth
The Firth of Forth () is a firth in Scotland, an inlet of the North Sea that separates Fife to its north and Lothian to its south. Further inland, it becomes the estuary of the River Forth and several other rivers.
Name
''Firth'' is a cognate ...
, and part of the territory of the Gododdin. The name survives in Slamannan Moor and the village of Slamannan, in Stirlingshire
Stirlingshire or the County of Stirling ( ) is a Shires of Scotland, historic county and registration county of Scotland. Its county town is Stirling.Registers of Scotland. Publications, leaflets, Land Register Counties.
It borders Perthshir ...
. This is derived from ''Sliabh Manann'', the 'Moor of Manann'. It also appears in the name of Dalmeny
Dalmeny () is a village and civil parish in Scotland. It is located on the south side of the Firth of Forth, southeast of South Queensferry and west of Edinburgh city centre. It lies within the traditional boundaries of West Lothian, and ...
, some 5 miles northwest of Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh ...
, and formerly known as Dumanyn, assumed to be derived from ''Dun Manann''. The name also survives north of the Forth in Pictish Manaw as the name of the burgh
A burgh ( ) is an Autonomy, autonomous municipal corporation in Scotland, usually a city, town, or toun in Scots language, Scots. This type of administrative division existed from the 12th century, when David I of Scotland, King David I created ...
of Clackmannan
Clackmannan ( ; , perhaps meaning "Stone of Manau"), is a small town and civil parish set in the Central Lowlands of Scotland. Situated within the Forth Valley, Clackmannan is south-east of Alloa and south of Tillicoultry. The town is within ...
and the eponymous county of Clackmannanshire
Clackmannanshire (; ; ), or the County of Clackmannan, is a Shires of Scotland, historic county, Council areas of Scotland, council area, registration counties, registration county and Lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area in Scotland ...
,, ''Celtic Britain'', The Picts and the Scots. derived from ''Clach Manann'', the 'stone of Manann', referring to a monument stone located there.
* Novant – a kingdom mentioned in ''Y Gododdin'', presumably related to the Iron Age Novantae tribe of southwestern Scotland.
* ''Regio Dunutinga'' – a minor kingdom or region in North Yorkshire
North Yorkshire is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in Northern England.The Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority areas of City of York, York and North Yorkshire (district), North Yorkshire are in Yorkshire and t ...
mentioned in the '' Life of Wilfrid''. It was evidently named for a ruler named Dunaut, perhaps the Dunaut ap Pabo known from the genealogies. Its name may survive in the modern town of Dent, Cumbria.
Kingdoms that were not part of the Old North but are part of its history include:
* Dál Riata
Dál Riata or Dál Riada (also Dalriada) () was a Gaels, Gaelic Monarchy, kingdom that encompassed the Inner Hebrides, western seaboard of Scotland and north-eastern Ireland, on each side of the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North ...
– Though this was a Gaelic
Gaelic (pronounced for Irish Gaelic and for Scots Gaelic) is an adjective that means "pertaining to the Gaels". It may refer to:
Languages
* Gaelic languages or Goidelic languages, a linguistic group that is one of the two branches of the Insul ...
kingdom, the family of Áedán mac Gabráin
Áedán mac Gabráin (; ), also written as Aedan, was a king of Dál Riata from 574 until c. 609 AD. The kingdom of Dál Riata was situated in modern Argyll and Bute, Scotland, and parts of County Antrim, Ireland. Genealogies record that Áe ...
of Dál Riata appears in the ''Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd
''Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd'' () is a brief Middle Welsh tract which claims to give the pedigrees of twenty 6th century rulers of the Hen Ogledd, the Brittonic languages, Brittonic-speaking parts of southern Scotland and northern England. It is att ...
''
* Northumbria
Northumbria () was an early medieval Heptarchy, kingdom in what is now Northern England and Scottish Lowlands, South Scotland.
The name derives from the Old English meaning "the people or province north of the Humber", as opposed to the Sout ...
and its predecessor states, Bernicia
Bernicia () was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom established by Anglian settlers of the 6th century in what is now southeastern Scotland and North East England.
The Anglian territory of Bernicia was approximately equivalent to the modern English cou ...
and Deira
Deira ( ; Old Welsh/ or ; or ) was an area of Post-Roman Britain, and a later Anglian kingdom.
Etymology
The name of the kingdom is of Brythonic origin, and is derived from the Proto-Celtic , meaning 'oak' ( in modern Welsh), in which case ...
* Pictish kingdom
Possible kingdoms
The following names appear in historical and literary sources, but it is unknown whether or not they refer to British kingdoms and regions of the ''Hen Ogledd''. *Bryneich
Bernicia () was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom established by Anglian settlers of the 6th century in what is now southeastern Scotland and North East England.
The Anglian territory of Bernicia was approximately equivalent to the modern English coun ...
– this is the British name for the Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
kingdom of Bernicia
Bernicia () was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom established by Anglian settlers of the 6th century in what is now southeastern Scotland and North East England.
The Anglian territory of Bernicia was approximately equivalent to the modern English cou ...
. There was probably a British kingdom in this area before the Anglian kingdom, it this is uncertain.
* Deifr
Deira ( ; Old Welsh/ or ; or ) was an area of Post-Roman Britain, and a later Angles (tribe), Anglian kingdom.
Etymology
The name of the kingdom is of British language (Celtic), Brythonic origin, and is derived from the Proto-Celtic language, ...
or Dewr – this was the British name for Anglo-Saxon Deira
Deira ( ; Old Welsh/ or ; or ) was an area of Post-Roman Britain, and a later Anglian kingdom.
Etymology
The name of the kingdom is of Brythonic origin, and is derived from the Proto-Celtic , meaning 'oak' ( in modern Welsh), in which case ...
, a region between the River Tees
The River Tees (), in England, rises on the eastern slope of Cross Fell in the North Pennines and flows eastwards for to reach the North Sea in the North East of England. The modern-day history of the river has been tied with the industries ...
and the Humber
The Humber is a large tidal estuary on the east coast of Northern England. It is formed at Trent Falls, Faxfleet, by the confluence of the tidal rivers River Ouse, Yorkshire, Ouse and River Trent, Trent. From there to the North Sea, it forms ...
. The name is of British origin, as with Bryneich, it is unknown if it represented an earlier British kingdom.Koch 2006, pp. 584–585.
See also
*Wales in the Early Middle Ages
Wales in the early Middle Ages covers the time between the Roman departure from Wales c. 383 until the middle of the 11th century. In that time there was a gradual consolidation of power into increasingly hierarchical kingdoms. The end of the ea ...
* Scotland in the Early Middle Ages
Scotland was divided into a series of kingdoms in the Early Middle Ages, i.e. between the end of Roman authority in Roman Britain, southern and central Britain from around 400 AD and Origins of the Kingdom of Alba, the rise of the kingdom of Alba ...
* History of Anglo-Saxon England
Anglo-Saxon England or early medieval England covers the period from the end of Roman Empire, Roman imperial rule in Roman Britain, Britain in the 5th century until the Norman Conquest in 1066. Compared to modern England, the territory of the ...
* England in the Middle Ages
England in the Middle Ages concerns the history of England during the Middle Ages, medieval period, from the end of the 5th century through to the start of the Early modern Britain, early modern period in 1485. When England emerged from the co ...
* Northumbria
Northumbria () was an early medieval Heptarchy, kingdom in what is now Northern England and Scottish Lowlands, South Scotland.
The name derives from the Old English meaning "the people or province north of the Humber", as opposed to the Sout ...
* Mercia
Mercia (, was one of the principal kingdoms founded at the end of Sub-Roman Britain; the area was settled by Anglo-Saxons in an era called the Heptarchy. It was centred on the River Trent and its tributaries, in a region now known as the Midlan ...
* Kingdom of Gwynedd
The Kingdom of Gwynedd (Medieval Latin: ; Middle Welsh: ) was a Wales in the Early Middle Ages, Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire Succession of states, successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon ...
* Historical basis for King Arthur
The historicity of King Arthur has been debated both by academics and popular writers. While there have been many claims that King Arthur was a real historical person, the current consensus among specialists on the period holds him to be a mytho ...
* Cumbric language
Cumbric is an extinct Celtic languages, Celtic language of the Brittonic languages, Brittonic subgroup spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North", in Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands. It was clo ...
* King Cole
Notes
Citations
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Alcock, Leslie. ''Kings and Warriors, Craftsmen and Priests in Northern Britain, AD 550–850''. Edinburgh, 2003. * Alcock, Leslie. "Gwyr y Gogledd. An archaeological appraisal." ''Archaeologia Cambrensis
''Archaeologia Cambrensis'' is a Welsh archaeological and historical scholarly journal published annually by the Cambrian Archaeological Association. It contains historical essays, excavation reports, and book reviews, as well as society notes ...
'' 132 (1984 for 1983). pp. 1–18.
* Cessford, Craig. "Northern England and the Gododdin poem." ''Northern History'' 33 (1997). pp. 218–22.
* Clarkson, Tim. ''The Men of the North: the Britons of Southern Scotland.'' Edinburgh: John Donald, Birlinn Ltd, 2010.
* Clarkson, Tim. ''Strathclyde and the Anglo-Saxons in the Viking Age.'' Edinburgh: John Donald, Birlinn Ltd, 2014.
* Dark, Kenneth R. ''Civitas to Kingdom. British political continuity, 300–800.'' London: Leicester UP, 1994.
* Dumville, David N. "Early Welsh Poetry: Problems of Historicity." In ''Early Welsh Poetry: Studies in the Book of Aneirin'', ed. Brynley F. Roberts. Aberystwyth, 1988. 1–16.
* Dumville, David N. "The origins of Northumbria: Some aspects of the British background." In ''The Origins of Anglo-Saxon Kingdoms'', ed. S. Bassett. Leicester: Leicester University Press, 1989. pp. 213–22.
* Higham, N.J. "Britons in Northern England: Through a Thick Glass Darkly." ''Northern History'' 38 (2001). pp. 5–25.
* Macquarrie, A. "The Kings of Strathclyde, c.400–1018." In ''Medieval Scotland: Government, Lordship and Community'', ed. A. Grant and K.J. Stringer. Edinburgh: Edinburgh UP, 1993. pp. 1–19.
* Miller, Molly. "Historicity and the pedigrees of north countrymen." '' Bulletin of the Board of Celtic Studies'' 26 (1975). pp. 255–80.
* Woolf, Alex. "Cædualla Rex Brettonum and the Passing of the Old North." ''Northern History'' 41.1 (2004): 1–20.
External links
* Matthews, Keith J"What's in a name? Britons, Angles, ethnicity and material culture from the fourth to seventh centuries."
''Heroic Age'' 4 (Winter 2001). {{Barbarian kingdoms Celtic Britons Medieval history of England 1st millennium in Scotland Sub-Roman Britain Anglo-Saxon England Medieval history of Wales Northern England History of Cumbria History of Dumfries and Galloway History of Northumberland History of the Scottish Borders History of Yorkshire Barbarian kingdoms Regions of England Regions of Scotland Historical regions in the United Kingdom Scottish Lowlands