CumFreq on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 CumFreq uses the
CumFreq uses the
ILRI website
or from
/ref> The computer program allows determination of the best fitting During the input phase, the user can select the number of intervals needed to determine the
During the input phase, the user can select the number of intervals needed to determine the
/ref> provides examples of application to magnitudes like
 The confidence belt around an experimental cumulative frequency or return period curve gives an impression of the region in which the true distribution may be found.
Also, it clarifies that the experimentally found best fitting probability distribution may deviate from the true distribution.
The confidence belt around an experimental cumulative frequency or return period curve gives an impression of the region in which the true distribution may be found.
Also, it clarifies that the experimentally found best fitting probability distribution may deviate from the true distribution.
 The software offers the option to use a probability distribution calculator. The cumulative frequency and the
The software offers the option to use a probability distribution calculator. The cumulative frequency and the
statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a s ...
and data analysis
Data analysis is the process of inspecting, Data cleansing, cleansing, Data transformation, transforming, and Data modeling, modeling data with the goal of discovering useful information, informing conclusions, and supporting decision-making. Da ...
the application software
Application software is any computer program that is intended for end-user use not operating, administering or programming the computer. An application (app, application program, software application) is any program that can be categorized as ...
CumFreq is a tool for cumulative frequency analysis of a single variable and for probability distribution fitting
Probability distribution fitting or simply distribution fitting is the fitting of a probability distribution to a series of data concerning the repeated measurement of a variable phenomenon.
The aim of distribution fitting is to prediction, predic ...
.
Originally the method was developed for the analysis of hydrological
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and drainage basin sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is called a hydro ...
measurements of spatially varying magnitudes (e.g. hydraulic conductivity
In science and engineering, hydraulic conductivity (, in SI units of meters per second), is a property of porous materials, soils and Rock (geology), rocks, that describes the ease with which a fluid (usually water) can move through the porosity, ...
of the soil) and of magnitudes varying in time (e.g. rainfall, river discharge
In hydrology, discharge is the volumetric flow rate (volume per time, in units of m3/h or ft3/h) of a stream. It equals the product of average flow velocity (with dimension of length per time, in m/h or ft/h) and the cross-sectional area (in m2 o ...
) to find their return period
A return period, also known as a recurrence interval or repeat interval, is an average time or an estimated average time between events such as earthquakes, floods, landslides, or river discharge flows to occur.
The reciprocal value of return p ...
s. However, it can be used for many other types of phenomena, including those that contain negative values.
Software features
 CumFreq uses the
CumFreq uses the plotting position
Plot or Plotting may refer to:
Art, media and entertainment
* Plot (narrative), the connected story elements of a piece of fiction
Music
* ''The Plot'' (album), a 1976 album by jazz trumpeter Enrico Rava
* The Plot (band), a band formed in 2003 ...
approach to estimate the ''cumulative frequency'' of each of the observed magnitudes in a data series of the variable.''Frequency and Regression Analysis''. Chapter 6 in: H.P.Ritzema (ed., 1994), ''Drainage Principles and Applications'', Publ. 16, pp. 175–224, International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement (ILRI), Wageningen, The Netherlands. . Free download as PDF from ILRI website
or from
/ref> The computer program allows determination of the best fitting
probability distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is a Function (mathematics), function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of possible events for an Experiment (probability theory), experiment. It is a mathematical descri ...
. Alternatively it provides the user with the option to select the probability distribution to be fitted. The following probability distributions are included: normal
Normal(s) or The Normal(s) may refer to:
Film and television
* ''Normal'' (2003 film), starring Jessica Lange and Tom Wilkinson
* ''Normal'' (2007 film), starring Carrie-Anne Moss, Kevin Zegers, Callum Keith Rennie, and Andrew Airlie
* ''Norma ...
, lognormal
In probability theory, a log-normal (or lognormal) distribution is a continuous probability distribution of a random variable whose logarithm is normal distribution, normally distributed. Thus, if the random variable is log-normally distributed ...
, logistic, loglogistic, exponential
Exponential may refer to any of several mathematical topics related to exponentiation, including:
* Exponential function, also:
**Matrix exponential, the matrix analogue to the above
*Exponential decay, decrease at a rate proportional to value
* Ex ...
, Cauchy
Baron Augustin-Louis Cauchy ( , , ; ; 21 August 1789 – 23 May 1857) was a French mathematician, engineer, and physicist. He was one of the first to rigorously state and prove the key theorems of calculus (thereby creating real a ...
, Fréchet, Gumbel, Pareto, Weibull, Generalized extreme value distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the generalized extreme value (GEV) distribution
is a family of continuous probability distributions developed within extreme value theory to combine the Gumbel distribution, Gumbel, Fréchet distribution, F ...
, Laplace distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the Laplace distribution is a continuous probability distribution named after Pierre-Simon Laplace. It is also sometimes called the double exponential distribution, because it can be thought of as two exponen ...
, Burr distribution
In probability theory, statistics and econometrics, the Burr Type XII distribution or simply the Burr distribution is a continuous probability distribution for a non-negative random variable. It is also known as the Singh–Maddala distribution a ...
(Dagum mirrored), Dagum distribution
The Dagum distribution (or Mielke Beta-Kappa distribution) is a continuous probability distribution defined over positive real numbers. It is named after Camilo Dagum, who proposed it in a series of papers in the 1970s. The Dagum distribution ar ...
(Burr mirrored), Gompertz distribution
In probability and statistics, the Gompertz distribution is a continuous probability distribution, named after Benjamin Gompertz. The Gompertz distribution is often applied to describe the distribution of adult lifespans by demographers and actu ...
, Student distribution and other.
Another characteristic of CumFreq is that it provides the option to use two different probability distributions, one for the lower data range, and one for the higher. The ranges are separated by a break-point. The use of such composite (discontinuous) probability distributions can be useful when the data of the phenomenon studied were obtained under different conditions.
 During the input phase, the user can select the number of intervals needed to determine the
During the input phase, the user can select the number of intervals needed to determine the histogram
A histogram is a visual representation of the frequency distribution, distribution of quantitative data. To construct a histogram, the first step is to Data binning, "bin" (or "bucket") the range of values— divide the entire range of values in ...
. He may also define a threshold to obtain a truncated distribution
In statistics, a truncated distribution is a conditional distribution that results from restricting the domain of some other probability distribution. Truncated distributions arise in practical statistics in cases where the ability to record, or ...
.
The output section provides a calculator to facilitate interpolation
In the mathematics, mathematical field of numerical analysis, interpolation is a type of estimation, a method of constructing (finding) new data points based on the range of a discrete set of known data points.
In engineering and science, one ...
and extrapolation
In mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. ...
.
Further it gives the option to see the Q–Q plot
In statistics, a Q–Q plot (quantile–quantile plot) is a probability plot, a List of graphical methods, graphical method for comparing two probability distributions by plotting their ''quantiles'' against each other. A point on the plot ...
in terms of calculated and observed cumulative frequencies.
ILRI''Drainage research in farmers' fields: analysis of data'', 2002. Contribution to the project "Liquid Gold" of the International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement (ILRI), Wageningen, The Netherlands/ref> provides examples of application to magnitudes like
crop yield
In agriculture, the yield is a measurement of the amount of a crop grown, or product such as wool, meat or milk produced, per unit area of land. The seed ratio is another way of calculating yields.
Innovations, such as the use of fertilizer, the ...
, watertable depth
In geotechnical engineering, watertable control is the practice of controlling the height of the water table by drainage. Its main applications are in agricultural land (to improve the crop yield using drainage system (agriculture), agricultural d ...
, soil salinity
Soil salinity is the salt (chemistry), salt content in the soil; the process of increasing the salt content is known as salinization (also called salination in American and British English spelling differences, American English). Salts occur nat ...
, hydraulic conductivity
In science and engineering, hydraulic conductivity (, in SI units of meters per second), is a property of porous materials, soils and Rock (geology), rocks, that describes the ease with which a fluid (usually water) can move through the porosity, ...
, rainfall, and river discharge
In hydrology, discharge is the volumetric flow rate (volume per time, in units of m3/h or ft3/h) of a stream. It equals the product of average flow velocity (with dimension of length per time, in m/h or ft/h) and the cross-sectional area (in m2 o ...
.
Generalizing distributions
The program can produce generalizations of the normal, logistic, and other distributions by transforming the data using anexponent
In mathematics, exponentiation, denoted , is an operation involving two numbers: the ''base'', , and the ''exponent'' or ''power'', . When is a positive integer, exponentiation corresponds to repeated multiplication of the base: that is, i ...
that is optimized to obtain the best fit
Curve fitting is the process of constructing a curve, or mathematical function, that has the best fit to a series of data points, possibly subject to constraints. Curve fitting can involve either interpolation, where an exact fit to the data is ...
.
This feature is not common in other distribution-fitting software which normally include only a logarithmic transformation of data obtaining distributions like the lognormal
In probability theory, a log-normal (or lognormal) distribution is a continuous probability distribution of a random variable whose logarithm is normal distribution, normally distributed. Thus, if the random variable is log-normally distributed ...
and loglogistic.
Generalization of symmetrical distributions (like the normal
Normal(s) or The Normal(s) may refer to:
Film and television
* ''Normal'' (2003 film), starring Jessica Lange and Tom Wilkinson
* ''Normal'' (2007 film), starring Carrie-Anne Moss, Kevin Zegers, Callum Keith Rennie, and Andrew Airlie
* ''Norma ...
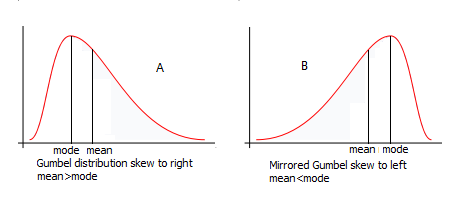
and the logistic) makes them applicable to data obeying a distribution that is skewed to the right (using an exponent <1) as well as to data obeying a distribution that is skewed to the left (using an exponent >1). This enhances the versatility of symmetrical distributions.

Inverting distributions
Skew distributions can be mirrored by distribution inversion (seesurvival function
The survival function is a function that gives the probability that a patient, device, or other object of interest will survive past a certain time.
The survival function is also known as the survivor function
or reliability function.
The term ...
, or complementary distribution function) to change the skewness from positive to negative and vice versa. This amplifies the number of applicable distributions and increases the chance of finding a better fit. CumFreq makes use of that opportunity.
Shifting distributions
When negative data are present that are not supported by a probability distribution, the model performs adistribution shift Distribution may refer to:
Mathematics
*Distribution (mathematics), generalized functions used to formulate solutions of partial differential equations
*Probability distribution, the probability of a particular value or value range of a varia ...
to the positive side while, after fitting, the distribution is shifted back.
Confidence belts
The software employs thebinomial distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the binomial distribution with parameters and is the discrete probability distribution of the number of successes in a sequence of statistical independence, independent experiment (probability theory) ...
to determine the confidence belt of the corresponding cumulative distribution function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a real-valued random variable X, or just distribution function of X, evaluated at x, is the probability that X will take a value less than or equal to x.
Ever ...
.
The prediction of the return period
A return period, also known as a recurrence interval or repeat interval, is an average time or an estimated average time between events such as earthquakes, floods, landslides, or river discharge flows to occur.
The reciprocal value of return p ...
, which is of interest in time series
In mathematics, a time series is a series of data points indexed (or listed or graphed) in time order. Most commonly, a time series is a sequence taken at successive equally spaced points in time. Thus it is a sequence of discrete-time data. ...
, is also accompanied by a confidence belt. The construction of confidence belts is not found in most other software.
The figure to the right shows the variation that may occur when obtaining samples of a variate that follows a certain probability distribution. The data were provided by Benson.Benson, M.A. 1960. Characteristics of frequency curves based on a theoretical 1000 year record. In: T.Dalrymple (ed.), Flood frequency analysis. U.S. Geological Survey Water Supply paper 1543−A, pp. 51–71
 The confidence belt around an experimental cumulative frequency or return period curve gives an impression of the region in which the true distribution may be found.
Also, it clarifies that the experimentally found best fitting probability distribution may deviate from the true distribution.
The confidence belt around an experimental cumulative frequency or return period curve gives an impression of the region in which the true distribution may be found.
Also, it clarifies that the experimentally found best fitting probability distribution may deviate from the true distribution.
Goodness of fit
Cumfreq produces a list of distributions ranked bygoodness of fit
The goodness of fit of a statistical model describes how well it fits a set of observations. Measures of goodness of fit typically summarize the discrepancy between observed values and the values expected under the model in question. Such measur ...
.
Histogram and density function
From thecumulative distribution function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a real-valued random variable X, or just distribution function of X, evaluated at x, is the probability that X will take a value less than or equal to x.
Ever ...
(CDF) one can derive a histogram
A histogram is a visual representation of the frequency distribution, distribution of quantitative data. To construct a histogram, the first step is to Data binning, "bin" (or "bucket") the range of values— divide the entire range of values in ...
and the probability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function (PDF), density function, or density of an absolutely continuous random variable, is a Function (mathematics), function whose value at any given sample (or point) in the sample space (the s ...
(PDF).
Calculator
 The software offers the option to use a probability distribution calculator. The cumulative frequency and the
The software offers the option to use a probability distribution calculator. The cumulative frequency and the return period
A return period, also known as a recurrence interval or repeat interval, is an average time or an estimated average time between events such as earthquakes, floods, landslides, or river discharge flows to occur.
The reciprocal value of return p ...
are give as a function of data value as input. In addition, the confidence intervals are shown. Reversely, the value is presented upon giving the cumulative frequency or the return period.
See also
*Distribution fitting
Probability distribution fitting or simply distribution fitting is the fitting of a probability distribution to a series of data concerning the repeated measurement of a variable phenomenon.
The aim of distribution fitting is to predict the probab ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Cumfreq Statistical software Regression and curve fitting software Freeware