cultural evolutionism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sociocultural evolution, sociocultural evolutionism or social evolution are theories of
sociobiology
Sociobiology is a field of biology that aims to explain social behavior in terms of evolution. It draws from disciplines including psychology, ethology, anthropology, evolution, zoology, archaeology, and population genetics. Within the study of ...
and cultural evolution
Cultural evolution is an evolutionary theory of social change. It follows from the definition of culture as "information capable of affecting individuals' behavior that they acquire from other members of their species through teaching, imitation ...
that describe how societies
A society () is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. ...
and culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
change over time. Whereas sociocultural development traces processes that tend to increase the complexity
Complexity characterizes the behavior of a system or model whose components interact in multiple ways and follow local rules, leading to non-linearity, randomness, collective dynamics, hierarchy, and emergence.
The term is generally used to c ...
of a society or culture, sociocultural evolution also considers process that can lead to decreases in complexity ( degeneration) or that can produce variation or proliferation without any seemingly significant changes in complexity (cladogenesis
Cladogenesis is an evolutionary splitting of a parent species into two distinct species, forming a clade.
This event usually occurs when a few organisms end up in new, often distant areas or when environmental changes cause several extinctions, ...
). Sociocultural evolution is "the process by which structural reorganization is affected through time, eventually producing a form or structure that is qualitatively different from the ancestral form".
Most of the 19th-century and some 20th-century approaches to socioculture aimed to provide models for the evolution of humankind
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are great apes characterized by their hairlessness, bipedalism, and high intelligen ...
as a whole, arguing that different societies have reached different stages of social development. The most comprehensive attempt to develop a general theory of social evolution centering on the development of sociocultural systems, the work of Talcott Parsons
Talcott Parsons (December 13, 1902 – May 8, 1979) was an American sociologist of the classical tradition, best known for his social action theory and structural functionalism. Parsons is considered one of the most influential figures in soci ...
(1902–1979), operated on a scale which included a theory of world history
Human history or world history is the record of humankind from prehistory to the present. Early modern human, Modern humans evolved in Africa around 300,000 years ago and initially lived as hunter-gatherers. They Early expansions of hominin ...
. Another attempt, on a less systematic scale, originated from the 1970s with the world-systems approach of Immanuel Wallerstein (1930–2019) and his followers.
More recent approaches focus on changes specific to individual societies and reject the idea that cultures differ primarily according to how far each one has moved along some presumed linear scale of social progress
Progress is movement towards a perceived refined, improved, or otherwise desired state. It is central to the philosophy of progressivism, which interprets progress as the set of advancements in technology, science, and social organization effic ...
. Most modern archaeologists
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
and cultural anthropologists work within the frameworks of neoevolutionism, sociobiology
Sociobiology is a field of biology that aims to explain social behavior in terms of evolution. It draws from disciplines including psychology, ethology, anthropology, evolution, zoology, archaeology, and population genetics. Within the study of ...
, and modernization theory
Modernization theory or modernisation theory holds that as societies become more economically modernized, wealthier and more educated, their political institutions become increasingly liberal democratic and rationalist. The "classical" theories ...
.
Introduction
Anthropologists
An anthropologist is a scientist engaged in the practice of anthropology. Anthropologists study aspects of humans within past and present societies. Social anthropology, cultural anthropology and philosophical anthropology study the norms, values ...
and sociologists
This list of sociologists includes people who have made notable contributions to sociological theory or to research in one or more areas of sociology.
A
* Peter Abell, British sociologist
* Andrew Abbott, American sociologist
* Margaret ...
often assume that human beings have natural
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the laws, elements and phenomena of the physical world, including life. Although humans are part ...
social tendencies but that particular human social behaviours have non- genetic causes and dynamics (i.e. people learn them in a social environment
The social environment, social context, sociocultural context or milieu refers to the immediate physical and social setting in which people live or in which something happens or develops. It includes the culture that the individual was educated ...
and through social interaction
A social relation is the fundamental unit of analysis within the social sciences, and describes any voluntary or involuntary interpersonal relationship between two or more conspecifics within and/or between groups. The group can be a language or ...
).
Societies exist in complex social environments (for example: with differing natural resources and constraints) and adapt themselves to these environments. It is thus inevitable that all societies change.
Specific theories of social or cultural evolution often attempt to explain differences between coeval
{{Short pages monitor Thus  In his 1877 classic ''Ancient Societies'', Lewis H. Morgan, an anthropologist whose ideas have had much impact on sociology, differentiated between three eras: savagery, barbarism and
In his 1877 classic ''Ancient Societies'', Lewis H. Morgan, an anthropologist whose ideas have had much impact on sociology, differentiated between three eras: savagery, barbarism and  Anthropologists Sir E.B. Tylor in England and Lewis Henry Morgan in the United States worked with data from
Anthropologists Sir E.B. Tylor in England and Lewis Henry Morgan in the United States worked with data from  Émile Durkheim, another of the "fathers" of sociology, developed a dichotomal view of social progress. His key concept was
Émile Durkheim, another of the "fathers" of sociology, developed a dichotomal view of social progress. His key concept was
 Weber's major works in
Weber's major works in
 When the critique of classical social evolutionism became widely accepted, modern anthropological and sociological approaches changed respectively. Modern theories are careful to avoid unsourced, ethnocentric speculation, comparisons, or value judgments; more or less regarding individual societies as existing within their own historical contexts. These conditions provided the context for new theories such as
When the critique of classical social evolutionism became widely accepted, modern anthropological and sociological approaches changed respectively. Modern theories are careful to avoid unsourced, ethnocentric speculation, comparisons, or value judgments; more or less regarding individual societies as existing within their own historical contexts. These conditions provided the context for new theories such as
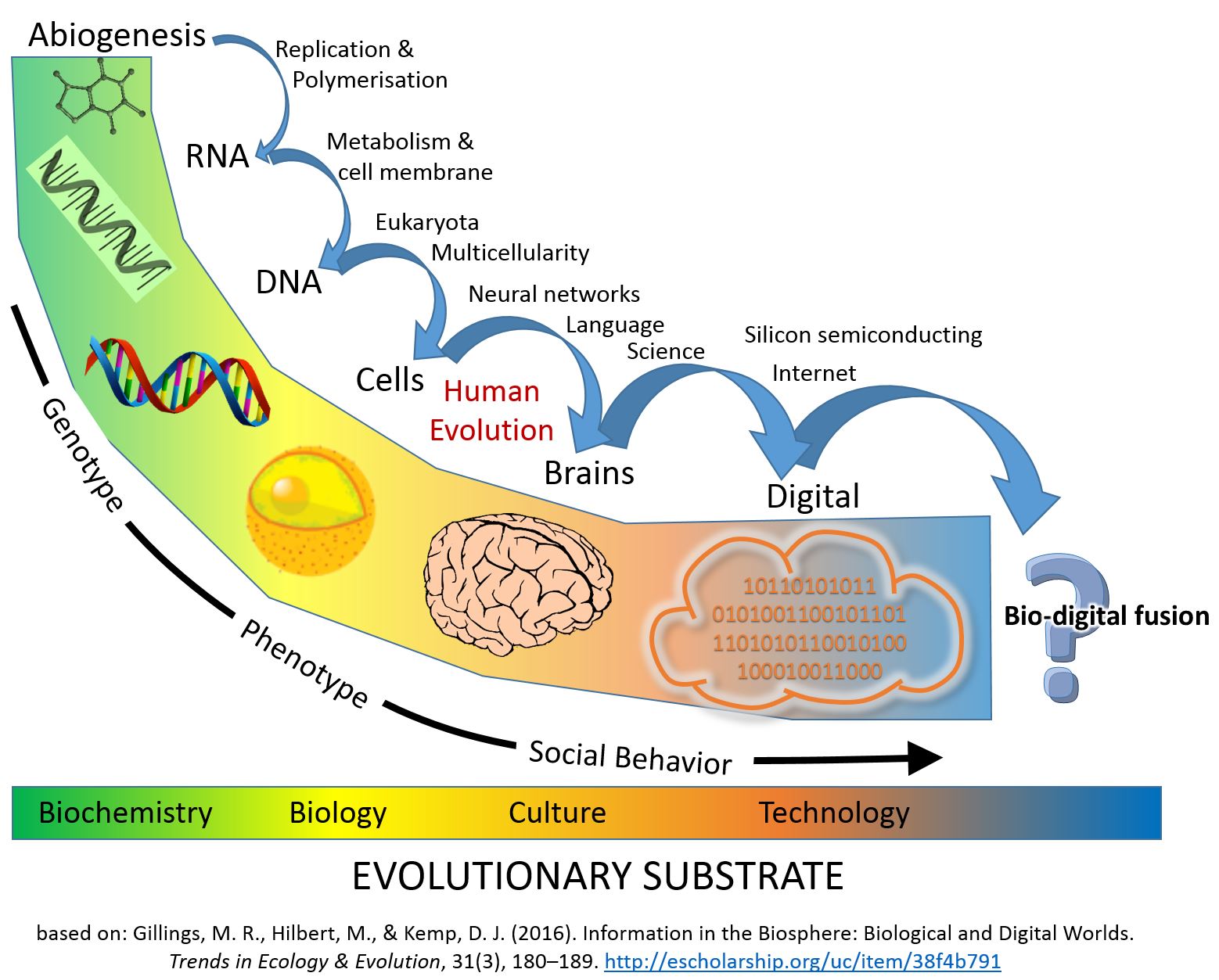 Many argue that the next stage of sociocultural evolution consists of a merger with technology, especially information processing technology. Several cumulative major transitions of evolution have transformed life through key innovations in information storage and replication, including
Many argue that the next stage of sociocultural evolution consists of a merger with technology, especially information processing technology. Several cumulative major transitions of evolution have transformed life through key innovations in information storage and replication, including
The Philosophy of Positivism
* Robert Carneiro, ''Evolutionism in Cultural Anthropology: A Critical History''. Westview Press, Boulder, CO, 2003. *
Full text
* Mesoudi, A.
Cultural Evolution: How Darwinian Theory Can Explain Human Culture and Synthesize the Social Sciences
', 2011, University of Chicago Press, * Morgan, John Henry, ''In the Beginning: The Paleolithic Origins of Religious Consciousness'' 2007 Cloverdale Books, South Bend. * Raoul Naroll and William T. Divale. 1976. Natural Selection in Cultural Evolution: Warfare versus Peaceful Diffusion. ''American Ethnologist'' 3: 97–128.
Segal, Daniel
(2000)
Western Civ" and the Staging of History in American Higher Education
' ''
Evolutionary Anthropology: Issues, News, and Reviews Volume 12, Issue 2, Pages 57–108 (April 2003)
**
The evolution of culture: New perspectives and evidence
(p 57–60) Charles H. Janson, Eric A. Smith **
Making space for traditions
(p 61–70) Dorothy Fragaszy *** Traditions in monkeys (p 71–81) Susan Perry, Joseph H. Manson **
Is culture a golden barrier between human and chimpanzee?
(p 82–91) Christophe Boesch *** Cultural panthropology (p 92–105) Andrew Whiten, Victoria Horner, Sarah Marshall-Pescini **
The fossil record – Human and nonhuman
(p 106–108) Eric Delson *
Evolutionary Anthropology: Issues, News, and Reviews Volume 12, Issue 3, Pages 109–159 (2003)
**
On stony ground: Lithic technology, human evolution, and the emergence of culture
(p 109–122) Robert Foley, Marta Mirazón Lahr **
The evolution of cultural evolution
(p 123–135) Joseph Henrich, Richard McElreath **
The adaptive nature of culture
(p 136–149) Michael S. Alvard **
Do animals have culture?
(p 150–159) Kevin N. Laland, William Hoppitt
Sociocultural evolution on Principia Cybernetica Web
Secular Cycles and Millennial Trends
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sociocultural Evolution Cultural concepts Memetics Anthropology Sociological theories
progressivism
Progressivism is a Left-right political spectrum, left-leaning political philosophy and Reformism, reform political movement, movement that seeks to advance the human condition through social reform. Adherents hold that progressivism has unive ...
became one of the basic ideas underlying the theory of sociocultural evolutionism.
However, Spencer's theories were more complex than just a romp up the great chain of being
The great chain of being is a hierarchical structure of all matter and life, thought by medieval Christianity to have been decreed by God. The chain begins with God and descends through angels, Human, humans, Animal, animals and Plant, plants to ...
. Spencer based his arguments on an analogy between the evolution of societies and the ontogeny of an animal. Accordingly, he searched for "general principles of development and structure" or "fundamental principles of organization", rather than being content simply ascribing progress between social stages to the direct intervention of some beneficent deity. Moreover, he accepted that these conditions are "far less specific, far more modifiable, far more dependent on conditions that are variable": in short, that they are a messy biological process.
Though Spencer's theories transcended the label of 'stagism' and appreciate biological complexity, they still accepted a strongly fixed direction and morality to natural development. p. 297-8. For Spencer, interference with the natural process of evolution was dangerous and had to be avoided at all costs. Such views were naturally coupled to the pressing political and economic questions of the time. Spencer clearly thought society's evolution brought about a racial hierarchy with Caucasians at the top and Africans at the bottom. This notion is deeply linked to the colonial projects European powers were pursuing at the time, and the idea of European superiority used paternalistically to justify those projects. The influential German zoologist Ernst Haeckel even wrote that 'natural men are closer to the higher vertebrates than highly civilized Europeans', including not just a racial hierarchy but a civilizational one. Likewise, Spencer's evolutionary argument advanced a theory of statehood: "until spontaneously fulfilled a public want should not be fulfilled at all" sums up Spencer's notion about limited government and the free operation of market forces.
This is not to suggest that stagism was useless or entirely motivated by colonialism and racism. Stagist theories were first proposed in contexts where competing epistemologies were largely static views of the world. Hence "progress" had in some sense to be invented, conceptually: the idea that human society would move through stages was a triumphant invention. Moreover, stages were not always static entities. In Buffon's theories, for example, it was possible to regress between stages, and physiological changes were species' reversibly adapting to their environment rather than irreversibly transforming.
In addition to progressivism, economic analyses influenced classical social evolutionism. Adam Smith
Adam Smith (baptised 1723 – 17 July 1790) was a Scottish economist and philosopher who was a pioneer in the field of political economy and key figure during the Scottish Enlightenment. Seen by some as the "father of economics"——— or ...
(1723–1790), who held a deeply evolutionary view of human society, identified the growth of freedom as the driving force in a process of stadial societal development. According to him, all societies pass successively through four stages: the earliest humans lived as hunter-gatherers, followed by pastoralists and nomads, after which society evolved to agriculturalists and ultimately reached the stage of commerce. With the strong emphasis on specialisation and the increased profits stemming from a division of labour, Smith's thinking also exerted some direct influence on Darwin himself. Both in Darwin's theory of the evolution of species and in Smith's accounts of political economy, competition between selfishly functioning units plays an important and even dominating rôle. Similarly occupied with economic concerns as Smith, Thomas R. Malthus (1766–1834) warned that given the strength of the sex drive inherent in all animals, Malthus argued, populations tend to grow geometrically, and population growth is only checked by the limitations of economic growth, which, if there would be growth at all, would quickly be outstripped by population growth, causing hunger, poverty, and misery. Far from being the consequences of economic structures or social orders, this "struggle for existence" is an inevitable natural law, so Malthus.
Auguste Comte, known as "the father of sociology", formulated the law of three stages: human development progresses from the theological
Theology is the study of religious belief from a religious perspective, with a focus on the nature of divinity. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of an ...
stage, in which nature was myth
Myth is a genre of folklore consisting primarily of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society. For scholars, this is very different from the vernacular usage of the term "myth" that refers to a belief that is not true. Instead, the ...
ically conceived and man sought the explanation of natural phenomena from supernatural beings; through a metaphysical stage in which nature was conceived of as a result of obscure forces and man sought the explanation of natural phenomena from them; until the final positive stage in which all abstract and obscure forces are discarded, and natural phenomena are explained by their constant relationship. This progress is forced through the development of human mind, and through increasing application of thought, reasoning and logic to the understanding of the world. Comte saw the science-valuing society as the highest, most developed type of human organization.
Herbert Spencer, who argued against government intervention
A market intervention is a policy or measure that modifies or interferes with a market, typically done in the form of state action, but also by philanthropic and political-action groups. Market interventions can be done for a number of reas ...
as he believed that society should evolve toward more individual freedom, followed Lamarck
Jean-Baptiste Pierre Antoine de Monet, chevalier de Lamarck (1 August 1744 – 18 December 1829), often known simply as Lamarck (; ), was a French naturalist, biologist, academic, and soldier. He was an early proponent of the idea that biolo ...
in his evolutionary thinking, in that he believed that humans do over time adapt to their surroundings. He differentiated between two phases of development as regards societies' internal regulation: the "military" and "industrial" societies. The earlier (and more primitive) military society has the goal of conquest and defense, is centralised
Centralisation or centralization (American English) is the process by which the activities of an organisation, particularly those regarding planning, decision-making, and framing strategies and policies, become concentrated within a particular ...
, economically self-sufficient, collectivistic, puts the good of a group over the good of an individual, uses compulsion, force and repression, and rewards loyalty, obedience and discipline. The industrial society, in contrast, has a goal of production and trade
Trade involves the transfer of goods and services from one person or entity to another, often in exchange for money. Economists refer to a system or network that allows trade as a market.
Traders generally negotiate through a medium of cr ...
, is decentralised, interconnected with other societies via economic relations, works through voluntary cooperation and individual self-restraint, treats the good of individual as of the highest value, regulates the social life via voluntary relations; and values initiative, independence and innovation. The transition process from the military to industrial society is the outcome of steady evolutionary processes within the society. Spencer "imagined a kind of feedback loop between mental and social evolution: the higher the mental powers the greater the complexity of the society that the individuals could create; the more complex the society, the greater the stimulus it provided for further mental development. Everything cohered to make progress inevitable or to weed out those who did not keep up."
Regardless of how scholars of Spencer interpret his relation to Darwin, Spencer became an incredibly popular figure in the 1870s, particularly in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
. Authors such as Edward L. Youmans, William Graham Sumner
William Graham Sumner (October 30, 1840 – April 12, 1910) was an American clergyman, social scientist, and neoclassical liberal. He taught social sciences at Yale University, where he held the nation's first professorship in sociology and bec ...
, John Fiske, John W. Burgess, Lester Frank Ward, Lewis H. Morgan (1818–1881) and other thinkers of the gilded age
In History of the United States, United States history, the Gilded Age is the period from about the late 1870s to the late 1890s, which occurred between the Reconstruction era and the Progressive Era. It was named by 1920s historians after Mar ...
all developed theories of social evolutionism as a result of their exposure to Spencer as well as to Darwin.
 In his 1877 classic ''Ancient Societies'', Lewis H. Morgan, an anthropologist whose ideas have had much impact on sociology, differentiated between three eras: savagery, barbarism and
In his 1877 classic ''Ancient Societies'', Lewis H. Morgan, an anthropologist whose ideas have had much impact on sociology, differentiated between three eras: savagery, barbarism and civilization
A civilization (also spelled civilisation in British English) is any complex society characterized by the development of state (polity), the state, social stratification, urban area, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyon ...
, which are divided by technological inventions, like fire, bow, pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other raw materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. The place where such wares are made by a ''potter'' is al ...
in the savage era, domestication of animals
The domestication of vertebrates is the mutual relationship between vertebrate animals, including birds and mammals, and the humans who influence their care and reproduction.
Charles Darwin recognized a small number of traits that made domestica ...
, agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
, metalworking
Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals in order to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term, it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on e ...
in the barbarian era and alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letter (alphabet), letters written to represent particular sounds in a spoken language. Specifically, letters largely correspond to phonemes as the smallest sound segments that can distinguish one word from a ...
and writing
Writing is the act of creating a persistent representation of language. A writing system includes a particular set of symbols called a ''script'', as well as the rules by which they encode a particular spoken language. Every written language ...
in the civilization era. Thus Morgan drew a link between social progress and technological progress. Morgan viewed technological progress as a force behind social progress, and held that any social change
Social change is the alteration of the social order of a society which may include changes in social institutions, social behaviours or social relations. Sustained at a larger scale, it may lead to social transformation or societal transformat ...
—in social institution
An institution is a humanly devised structure of rules and norms that shape and constrain social behavior. All definitions of institutions generally entail that there is a level of persistence and continuity. Laws, rules, social conventions and ...
s, organizations or ideologies—has its beginnings in technological change. Morgan's theories were popularized by Friedrich Engels
Friedrich Engels ( ;"Engels"
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''.The Origin of the Family, Private Property and the State ''The Origin of the Family, Private Property and the State: in the Light of the Researches of Lewis H. Morgan'' () is an 1884 anthropological treatise by Friedrich Engels. It is partially based on notes by Karl Marx to Lewis H. Morgan's book ''Anc ...
'' on them. For Engels and other Marxists this theory was important, as it supported their conviction that materialistic factors—economic and technological—are decisive in shaping the fate of humanity.
Edward Burnett Tylor (1832–1917), a pioneer of anthropology, focused on the evolution of culture worldwide, noting that culture is an important part of every society and that it is also subject to a process of evolution. He believed that societies were at different stages of cultural development and that the purpose of anthropology was to reconstruct the evolution of culture, from primitive beginnings to the modern state.
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''.The Origin of the Family, Private Property and the State ''The Origin of the Family, Private Property and the State: in the Light of the Researches of Lewis H. Morgan'' () is an 1884 anthropological treatise by Friedrich Engels. It is partially based on notes by Karl Marx to Lewis H. Morgan's book ''Anc ...
 Anthropologists Sir E.B. Tylor in England and Lewis Henry Morgan in the United States worked with data from
Anthropologists Sir E.B. Tylor in England and Lewis Henry Morgan in the United States worked with data from indigenous people
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
, who (they claimed) represented earlier stages of cultural evolution that gave insight into the process and progression of evolution of culture. Morgan had a significant influence on Karl Marx
Karl Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, political theorist, economist, journalist, and revolutionary socialist. He is best-known for the 1848 pamphlet '' The Communist Manifesto'' (written with Friedrich Engels) ...
and on Friedrich Engels, who developed a theory of sociocultural evolution in which the internal contradictions in society generated a series of escalating stages that ended in a socialist society (see Marxism
Marxism is a political philosophy and method of socioeconomic analysis. It uses a dialectical and materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to analyse class relations, social conflict, ...
). Tylor and Morgan elaborated the theory of unilinear evolution, specifying criteria for categorising cultures according to their standing within a fixed system of growth of humanity as a whole and examining the modes and mechanisms of this growth. Theirs was often a concern with culture in general, not with individual cultures.
Their analysis of cross-cultural data was based on three assumptions:
# contemporary societies may be classified and ranked as more "primitive" or more "civilized"
# there are a determinate number of stages between "primitive" and "civilized" (e.g. band, tribe
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide use of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. The definition is contested, in part due to conflict ...
, chiefdom
A chiefdom is a political organization of people representation (politics), represented or government, governed by a tribal chief, chief. Chiefdoms have been discussed, depending on their scope, as a stateless society, stateless, state (polity) ...
, and state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
)
# all societies progress through these stages in the same sequence, but at different rates
Theorists usually measured progression (that is, the difference between one stage and the next) in terms of increasing social complexity (including class differentiation and a complex division of labour), or an increase in intellectual, theological, and aesthetic sophistication. These 19th-century ethnologists
Ethnology (from the , meaning 'nation') is an academic field and discipline that compares and analyzes the characteristics of different peoples and the relationships between them (compare cultural, social, or sociocultural anthropology).
Scien ...
used these principles primarily to explain differences in religious beliefs and kinship terminologies among various societies.
Lester Frank Ward (1841–1913), sometimes referred to as the "father" of American sociology, rejected many of Spencer's theories regarding the evolution of societies. Ward, who was also a botanist and a paleontologist, believed that the law of evolution functioned much differently in human societies than it did in the plant and animal kingdoms, and theorized that the "law of nature" had been superseded by the "law of the mind". He stressed that humans, driven by emotions, create goals for themselves and strive to realize them (most effectively with the modern scientific method
The scientific method is an Empirical evidence, empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has been referred to while doing science since at least the 17th century. Historically, it was developed through the centuries from the ancient and ...
) whereas there is no such intelligence and awareness guiding the non-human world. Plants and animals adapt to nature; man shapes nature. While Spencer believed that competition and "survival of the fittest" benefited human society and sociocultural evolution, Ward regarded competition as a destructive force, pointing out that all human institutions, traditions and laws were tools invented by the mind of man and that that mind designed them, like all tools, to "meet and checkmate" the unrestrained competition of natural forces. Ward agreed with Spencer that authoritarian governments repress the talents of the individual, but he believed that modern democratic societies, which minimized the role of religion and maximized that of science, could effectively support the individual in his or her attempt to fully utilize their talents and achieve happiness. He believed that the evolutionary processes have four stages:
* First comes cosmogenesis, creation and evolution of the world.
* Then, when life arises, there is biogenesis
Spontaneous generation is a Superseded scientific theories, superseded scientific theory that held that living creatures could arise from abiotic component, non-living matter and that such processes were commonplace and regular. It was Hypoth ...
.
* Development of humanity leads to anthropogenesis, which is influenced by the human mind
The mind is that which thinks, feels, perceives, imagines, remembers, and wills. It covers the totality of mental phenomena, including both conscious processes, through which an individual is aware of external and internal circumstances, ...
.
* Finally there arrives sociogenesis, which is the science of shaping the evolutionary process itself to optimize progress, human happiness and individual self-actualization.
Ward regarded modern societies as superior to "primitive" societies (one need only look to the impact of medical science on health and lifespan) and shared theories of white supremacy
White supremacy is the belief that white people are superior to those of other races. The belief favors the maintenance and defense of any power and privilege held by white people. White supremacy has roots in the now-discredited doctrine ...
. Though he supported the Out-of-Africa theory of human evolution, he did not believe that all races and social classes were equal in talent. When a Negro rapes a white woman, Ward declared, he is impelled not only by lust but also by the instinctive drive to improve his own race. Ward did not think that evolutionary progress was inevitable and he feared the degeneration of societies and cultures, which he saw as very evident in the historical record. Ward also did not favor the radical reshaping of society as proposed by the supporters of the eugenics movement or by the followers of Karl Marx; like Comte, Ward believed that sociology was the most complex of the sciences and that true sociogenesis was impossible without considerable research and experimentation.
 Émile Durkheim, another of the "fathers" of sociology, developed a dichotomal view of social progress. His key concept was
Émile Durkheim, another of the "fathers" of sociology, developed a dichotomal view of social progress. His key concept was social solidarity
Solidarity or solidarism is an awareness of shared interests, objectives, standards, and sympathies creating a psychological sense of unity of groups or classes. True solidarity means moving beyond individual identities and single issue politics ...
, as he defined social evolution in terms of progressing from mechanical solidarity
In sociology, mechanical solidarity and organic solidarity are the two types of social solidarity that were formulated by Émile Durkheim, introduced in his '' Division of Labour in Society'' (1893) as part of his theory on the development of socie ...
to organic solidarity
In sociology, mechanical solidarity and organic solidarity are the two types of social solidarity that were formulated by Émile Durkheim, introduced in his '' Division of Labour in Society'' (1893) as part of his theory on the development of socie ...
. In mechanical solidarity, people are self-sufficient, there is little integration and thus there is the need for the use of force and repression to keep society together. In organic solidarity, people are much more integrated and interdependent and specialisation and cooperation are extensive. Progress from mechanical to organic solidarity is based firstly on population growth
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. The World population, global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to 8.2 billion in 2025. Actual global human population growth amounts to aroun ...
and increasing population density
Population density (in agriculture: Standing stock (disambiguation), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geog ...
, secondly on increasing "morality density" (development of more complex social interactions) and thirdly on increasing specialisation in the workplace. To Durkheim, the most important factor in social progress is the division of labour
The division of labour is the separation of the tasks in any economic system or organisation so that participants may specialise ( specialisation). Individuals, organisations, and nations are endowed with or acquire specialised capabilities, a ...
. This was later used in the mid-1900s by the economist Ester Boserup
Ester Boserup (18 May 1910 – 24 September 1999) was a Danish economist. She studied economic and agricultural development, worked at the United Nations as well as other international organizations, and wrote seminal books on agrarian change an ...
(1910–1999) to attempt to discount some aspects of Malthusian theory.
Ferdinand Tönnies
Ferdinand Tönnies (; 26 July 1855 – 8 April 1936) was a German sociologist, economist, and philosopher. He was a significant contributor to sociological theory and field studies, best known for distinguishing between two types of social gro ...
(1855–1936) describes evolution as the development from informal society, where people have many liberties and there are few laws and obligations, to modern, formal rational society, dominated by traditions and laws, where people are restricted from acting as they wish. He also notes that there is a tendency to standardisation
Standardization (American English) or standardisation (British English) is the process of implementing and developing technical standards based on the consensus of different parties that include firms, users, interest groups, standards organiza ...
and unification, when all smaller societies are absorbed into a single, large, modern society. Thus Tönnies can be said to describe part of the process known today as globalization
Globalization is the process of increasing interdependence and integration among the economies, markets, societies, and cultures of different countries worldwide. This is made possible by the reduction of barriers to international trade, th ...
. Tönnies was also one of the first sociologists to claim that the evolution of society is not necessarily going in the right direction, that social progress is not perfect, and it can even be called a regression as the newer, more evolved societies are obtained only after paying a high cost, resulting in decreasing satisfaction of the individuals making up that society. Tönnies' work became the foundation of neoevolutionism.
Although Max Weber
Maximilian Carl Emil Weber (; ; 21 April 186414 June 1920) was a German Sociology, sociologist, historian, jurist, and political economy, political economist who was one of the central figures in the development of sociology and the social sc ...
is not usually counted as a sociocultural evolutionist, his theory of tripartite classification of authority
The German sociologist Max Weber (1864-1920) distinguished three ideal types of legitimate political leadership/domination/ authority ().
He wrote about these three types of domination both in his essay "The Three Types of Legitimate Rule", whi ...
can be viewed as an evolutionary theory as well. Weber distinguishes three ideal type
Ideal type (), also known as pure type, is a typological term most closely associated with the sociologist Max Weber (1864–1920). For Weber, the conduct of social science depends upon the construction of abstract, hypothetical concepts. The "id ...
s of political leadership
Leadership, is defined as the ability of an individual, group, or organization to "", influence, or guide other individuals, teams, or organizations.
"Leadership" is a contested term. Specialist literature debates various viewpoints on the co ...
, domination and authority
Authority is commonly understood as the legitimate power of a person or group of other people.
In a civil state, ''authority'' may be practiced by legislative, executive, and judicial branches of government,''The New Fontana Dictionary of M ...
:
# charismatic domination
# traditional domination (patriarchs, patrimonialism, feudalism)
# legal (rational) domination (modern law and state, bureaucracy)
Weber also notes that legal domination is the most advanced, and that societies evolve from having mostly traditional
A tradition is a system of beliefs or behaviors (folk custom) passed down within a group of people or society with symbolic meaning or special significance with origins in the past. A component of cultural expressions and folklore, common examp ...
and charismatic authorities to mostly rational and legal ones.
Critique and impact on modern theories
The early 20th-century inaugurated a period of systematic critical examination, and rejection of the sweeping generalisations of the unilineal theories of sociocultural evolution. Cultural anthropologists such asFranz Boas
Franz Uri Boas (July 9, 1858 – December 21, 1942) was a German-American anthropologist and ethnomusicologist. He was a pioneer of modern anthropology who has been called the "Father of American Anthropology". His work is associated with the mov ...
(1858–1942), along with his students, including Ruth Benedict
Ruth Fulton Benedict (June 5, 1887 – September 17, 1948) was an American anthropologist and folklorist.
She was born in New York City, attended Vassar College, and graduated in 1909. After studying anthropology at the New School of Social ...
and Margaret Mead
Margaret Mead (December 16, 1901 – November 15, 1978) was an American cultural anthropologist, author and speaker, who appeared frequently in the mass media during the 1960s and the 1970s.
She earned her bachelor's degree at Barnard Col ...
, are regarded as the leader
Leadership, is defined as the ability of an individual, group, or organization to "", influence, or guide other individuals, teams, or organizations.
"Leadership" is a contested term. Specialist literature debates various viewpoints on the co ...
s of anthropology's rejection of classical social evolutionism.
However, the school of Boas ignore some of the complexity in evolutionary theories that emerged outside Herbert Spencer's influence. Charles Darwin's ''On the Origin of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life'')The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by M ...
'' gave a mechanistic account of the origins and development of animals, quite apart from Spencer's theories that emphasized the inevitable human development through stages. Consequently, many scholars developed more sophisticated understandings of how cultures evolve, relying on deep cultural analogies, than the theories in Herbert Spencer's tradition. Walter Bagehot (1872) applied selection and inheritance to the development of human political institutions. Samuel Alexander (1892) discusses the natural selection of moral principles in society. William James (1880) considered the 'natural selection' of ideas in learning and scientific development. In fact, he identified a 'remarkable parallel ��between the facts of social evolution on the one hand, and of zoological evolution as expounded by Mr Darwin on the other'. Charles Sanders Peirce
Charles Sanders Peirce ( ; September 10, 1839 – April 19, 1914) was an American scientist, mathematician, logician, and philosopher who is sometimes known as "the father of pragmatism". According to philosopher Paul Weiss (philosopher), Paul ...
(1898) even proposed that the current laws of nature we have exist because they have evolved over time. Darwin himself, in Chapter 5 of the Descent of Man, proposed that human moral sentiments were subject to group selection:
"A tribe including many members who, from possessing in a high degree the spirit of patriotism, fidelity, obedience, courage, and sympathy, were always ready to aid one another, and to sacrifice themselves for the common good, would be victorious over most other tribes; and this would be natural selection."
Through the mechanism of imitation, cultures as well as individuals could be subject to natural selection.
While these theories involved evolution applied to social questions, except for Darwin's group selection the theories reviewed above did not advance a precise understanding of how Darwin's mechanism extended and applied to cultures beyond a vague appeal to competition. Ritchie's Darwinism and Politics (1889) breaks this trend, holding that "language and social institutions make it possible to transmit experience
quite independently of the continuity of race." Hence Ritchie saw cultural evolution as a process that could operate independently of and on different scales to the evolution of species, and gave it precise underpinnings: he was 'extending its range', in his own words, to ideas, cultures and institutions.
Thorstein Veblen, around the same time, came to a similar insight: that humans evolve to their social environment, but their social environment in turn also evolves. Veblen's mechanism for human progress was the evolution of human intentionality: Veblen labelled men 'a creature of habit' and thought that habits were 'mentally digested' from those who influenced him. In short, as Hodgson and Knudsen point out, Veblen thinks:
"the changing institutions in their turn make for a further selection of individuals endowed with the fittest temperament, and a further adaptation of individual temperament and habits to the changing environment through the formation of new institutions."
Thus, Veblen represented an extension of Ritchie's theories, where evolution operates at multiple levels, to a sophisticated appreciation of how each level interacts with the other.
This complexity notwithstanding, Boas and Benedict used sophisticated ethnography
Ethnography is a branch of anthropology and the systematic study of individual cultures. It explores cultural phenomena from the point of view of the subject of the study. Ethnography is also a type of social research that involves examining ...
and more rigorous empirical methods to argue that Spencer, Tylor, and Morgan's theories were speculative and systematically misrepresented ethnographic data. Theories regarding "stages" of evolution were especially criticised as illusions. Additionally, they rejected the distinction between "primitive" and "civilized" (or "modern"), pointing out that so-called primitive contemporary societies have just as much history, and were just as evolved, as so-called civilized societies. They therefore argued that any attempt to use this theory to reconstruct the histories of non-literate (i.e. leaving no historical documents) peoples is entirely speculative and unscientific.
They observed that the postulated progression, which typically ended with a stage of civilization identical to that of modern Europe, is ethnocentric
Ethnocentrism in social science and anthropology—as well as in colloquial English discourse—means to apply one's own culture or ethnicity as a frame of reference to judge other cultures, practices, behaviors, beliefs, and people, instead of ...
. They also pointed out that the theory assumes that societies are clearly bounded and distinct, when in fact cultural traits and forms often cross social boundaries and diffuse among many different societies (and are thus an important mechanism of change). Boas in his culture-history approach focused on anthropological fieldwork in an attempt to identify factual processes instead of what he criticized as speculative stages of growth. His approach greatly influenced American anthropology in the first half of the 20th century, and marked a retreat from high-level generalization and from "systems building".
Later critics observed that the assumption of firmly bounded societies was proposed precisely at the time when European powers were colonising non-Western societies, and was thus self-serving. Many anthropologists and social theorists now consider unilineal cultural and social evolution a Western myth
Myth is a genre of folklore consisting primarily of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society. For scholars, this is very different from the vernacular usage of the term "myth" that refers to a belief that is not true. Instead, the ...
seldom based on solid empirical grounds. Critical theorists argue that notions of social evolution are simply justifications for power by the élites of society. Finally, the devastating World Wars that occurred between 1914 and 1945 crippled Europe's self-confidence. After millions of deaths, genocide, and the destruction of Europe's industrial infrastructure, the idea of progress seemed dubious at best.
Thus modern sociocultural evolutionism rejects most of classical social evolutionism due to various theoretical problems:
# The theory was deeply ethnocentric
Ethnocentrism in social science and anthropology—as well as in colloquial English discourse—means to apply one's own culture or ethnicity as a frame of reference to judge other cultures, practices, behaviors, beliefs, and people, instead of ...
—it makes heavy value judgments about different societies, with Western civilization
Western culture, also known as Western civilization, European civilization, Occidental culture, Western society, or simply the West, refers to the internally diverse culture of the Western world. The term "Western" encompasses the social no ...
seen as the most valuable.
# It assumed all cultures follow the same path or progression and have the same goals.
# It equated civilization with material culture
Material culture is culture manifested by the Artifact (archaeology), physical objects and architecture of a society. The term is primarily used in archaeology and anthropology, but is also of interest to sociology, geography and history. The fie ...
(technology, cities, etc.)
Because social evolution was posited as a scientific theory, it was often used to support unjust and often racist
Racism is the belief that groups of humans possess different behavioral traits corresponding to inherited attributes and can be divided based on the superiority of one Race (human categorization), race or ethnicity over another. It may also me ...
social practices – particularly colonialism, slavery, and the unequal economic conditions present within industrialized Europe. Social Darwinism is especially criticised, as it purportedly led to some philosophies used by the Nazis
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During H ...
.
Max Weber, disenchantment, and critical theory
 Weber's major works in
Weber's major works in economic sociology
Economic sociology is the study of the social cause and effect of various economic phenomena. The field can be broadly divided into a classical period and a contemporary one, known as "new economic sociology".
The classical period was concerned ...
and the sociology of religion
Sociology of religion is the study of the beliefs, practices and organizational forms of religion using the tools and methods of the discipline of sociology. This objective investigation may include the use both of Quantitative research, quantit ...
dealt with the rationalization, secularisation
In sociology, secularization () is a multilayered concept that generally denotes "a transition from a religious to a more worldly level." There are many types of secularization and most do not lead to atheism or irreligion, nor are they automatica ...
, and so called "disenchantment
In social science, disenchantment () is the cultural rationalization and devaluation of religion apparent in modern society. The term was borrowed from Friedrich Schiller by Max Weber to describe the character of a modernized, bureaucratic, ...
" which he associated with the rise of capitalism and modernity
Modernity, a topic in the humanities and social sciences, is both a historical period (the modern era) and the ensemble of particular Society, socio-Culture, cultural Norm (social), norms, attitudes and practices that arose in the wake of the ...
. In sociology, rationalization is the process whereby an increasing number of social action
In sociology, social action, also known as Weberian social action, is an act which takes into account the actions and reactions of individuals (or ' agents'). According to Max Weber, "Action is 'social' insofar as its subjective meaning takes acc ...
s become based on considerations of teleological efficiency or calculation rather than on motivations derived from morality
Morality () is the categorization of intentions, Decision-making, decisions and Social actions, actions into those that are ''proper'', or ''right'', and those that are ''improper'', or ''wrong''. Morality can be a body of standards or principle ...
, emotion
Emotions are physical and mental states brought on by neurophysiology, neurophysiological changes, variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavior, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or suffering, displeasure. There is ...
, custom, or tradition
A tradition is a system of beliefs or behaviors (folk custom) passed down within a group of people or society with symbolic meaning or special significance with origins in the past. A component of cultural expressions and folklore, common e ...
. Rather than referring to what is genuinely "rational" or "logical", rationalization refers to a relentless quest for goals that might actually function to the ''detriment'' of a society. Rationalization is an ambivalent aspect of modernity, manifested especially in Western society
Western culture, also known as Western civilization, European civilization, Occidental culture, Western society, or simply the West, refers to the Cultural heritage, internally diverse culture of the Western world. The term "Western" encompas ...
– as a behaviour of the capitalist market, of rational administration in the state
A state is a political entity that regulates society and the population within a definite territory. Government is considered to form the fundamental apparatus of contemporary states.
A country often has a single state, with various administrat ...
and bureaucracy
Bureaucracy ( ) is a system of organization where laws or regulatory authority are implemented by civil servants or non-elected officials (most of the time). Historically, a bureaucracy was a government administration managed by departments ...
, of the extension of modern science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
, and of the expansion of modern technology.
Weber's thought regarding the rationalizing and secularizing tendencies of modern Western society (sometimes described as the " Weber Thesis") would blend with Marxism to facilitate critical theory, particularly in the work of thinkers such as Jürgen Habermas
Jürgen Habermas ( , ; ; born 18 June 1929) is a German philosopher and social theorist in the tradition of critical theory and pragmatism. His work addresses communicative rationality and the public sphere.
Associated with the Frankfurt S ...
(born 1929). Critical theorists, as antipositivist
In social science, antipositivism (also interpretivism, negativism or antinaturalism) is a theoretical stance which proposes that the social realm cannot be studied with the methods of investigation utilized within the natural sciences, and th ...
s, are critical of the idea of a hierarchy of sciences or societies, particularly with respect to the sociological positivism
Positivism is a philosophical school that holds that all genuine knowledge is either true by definition or positivemeaning '' a posteriori'' facts derived by reason and logic from sensory experience.John J. Macionis, Linda M. Gerber, ''Soci ...
originally set forth by Comte. Jürgen Habermas has critiqued the concept of pure instrumental rationality
"Instrumental" and "value rationality" are terms scholars use to identify two ways individuals act in order to optimize their behavior. Instrumental rationality recognizes means that "work" efficiently to achieve ends. Value rationality recognize ...
as meaning that scientific-thinking becomes something akin to ideology
An ideology is a set of beliefs or values attributed to a person or group of persons, especially those held for reasons that are not purely about belief in certain knowledge, in which "practical elements are as prominent as theoretical ones". Form ...
itself. For theorists such as Zygmunt Bauman
Zygmunt Bauman (; ; 19 November 1925 – 9 January 2017) was a Polish–British sociologist and philosopher. He was driven out of the Polish People's Republic during the 1968 Polish political crisis and forced to give up his Polish citizenship. ...
(1925–2017), rationalization as a manifestation of modernity may be most closely and regrettably associated with the events of the Holocaust
The Holocaust (), known in Hebrew language, Hebrew as the (), was the genocide of History of the Jews in Europe, European Jews during World War II. From 1941 to 1945, Nazi Germany and Collaboration with Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy ...
.
Modern theories
 When the critique of classical social evolutionism became widely accepted, modern anthropological and sociological approaches changed respectively. Modern theories are careful to avoid unsourced, ethnocentric speculation, comparisons, or value judgments; more or less regarding individual societies as existing within their own historical contexts. These conditions provided the context for new theories such as
When the critique of classical social evolutionism became widely accepted, modern anthropological and sociological approaches changed respectively. Modern theories are careful to avoid unsourced, ethnocentric speculation, comparisons, or value judgments; more or less regarding individual societies as existing within their own historical contexts. These conditions provided the context for new theories such as cultural relativism
Cultural relativism is the view that concepts and moral values must be understood in their own cultural context and not judged according to the standards of a different culture. It asserts the equal validity of all points of view and the relati ...
and multilineal evolution.
In the 1920s and 1930s, Gordon Childe
Vere Gordon Childe (14 April 189219 October 1957) was an Australian archaeologist who specialised in the study of European prehistory. He spent most of his life in the United Kingdom, working as an academic for the University of Edinburgh and ...
revolutionized the study of cultural evolutionism. He conducted a comprehensive pre-history account that provided scholars with evidence for African and Asian cultural transmission into Europe. He combated scientific racism by finding the tools and artifacts of the indigenous people from Africa and Asia and showed how they influenced the technology of European culture. Evidence from his excavations countered the idea of Aryan supremacy and superiority. Adopting "Kosinna's basic concept of the archaeological culture and his identification of such cultures as the remains of prehistoric peoples" and combining it with the detailed chronologies of European prehistory developed by Gustaf Oscar Montelius, Childe argued that each society needed to be delineated individually on the basis of constituent artefacts which were indicative of their practical and social function. Childe explained cultural evolution by his theory of divergence with modifications of convergence. He postulated that different cultures form separate methods that meet different needs, but when two cultures were in contact they developed similar adaptations, solving similar problems. Rejecting Spencer's theory of parallel cultural evolution, Childe found that interactions between cultures contributed to the convergence of similar aspects most often attributed to one culture. Childe placed emphasis on human culture as a social construct
A social construct is any category or thing that is made real by convention or collective agreement. Socially constructed realities are contrasted with natural kinds, which exist independently of human behavior or beliefs.
Simple examples of s ...
rather than products of environmental or technological contexts. Childe coined the terms "Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, also known as the First Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period in Afro-Eurasia from a lifestyle of hunter-gatherer, hunting and gathering to one of a ...
", and " Urban Revolution" which are still used today in the branch of pre-historic anthropology.
In 1941 anthropologist Robert Redfield
Robert Redfield (December 4, 1897 – October 16, 1958) was an American anthropologist and ethnolinguist, whose ethnographic work in Tepoztlán, Mexico, is considered a landmark of Latin American ethnography. He was associated with the Universi ...
wrote about a shift from 'folk society' to 'urban society'. By the 1940s cultural anthropologists such as Leslie White and Julian Steward
Julian Haynes Steward (January 31, 1902 – February 6, 1972) was an American anthropologist known best for his role in developing "the concept and method" of cultural ecology, as well as a scientific theory of culture change.
Early life and ed ...
sought to revive an evolutionary model on a more scientific basis, and succeeded in establishing an approach known as neoevolutionism. White rejected the opposition between "primitive" and "modern" societies but did argue that societies could be distinguished based on the amount of energy they harnessed, and that increased energy allowed for greater social differentiation (White's law). Steward on the other hand rejected the 19th-century notion of progress, and instead called attention to the Darwinian notion of "adaptation", arguing that all societies had to adapt to their environment in some way.
The anthropologists Marshall Sahlins
Marshall David Sahlins ( ; December 27, 1930April 5, 2021) was an American cultural anthropologist best known for his ethnographic work in the Pacific and for his contributions to anthropological theory. He was the Charles F. Grey Distinguishe ...
and Elman Service
Elman Rogers Service (May 18, 1915 – November 14, 1996) was an American cultural anthropologist.
Biography
He was born on May 18, 1915, in Tecumseh, Michigan and died on November 14, 1996, in Santa Barbara, California. He earned a bachelor' ...
prepared an edited volume, ''Evolution and Culture'', in which they attempted to synthesise White's and Steward's approaches. Other anthropologists, building on or responding to work by White and Steward, developed theories of cultural ecology and ecological anthropology. The most prominent examples are Peter Vayda and Roy Rappaport
Roy Abraham Rappaport (1926–1997) was an American anthropologist known for his contributions to the anthropological study of ritual and to ecological anthropology.
Biography
Rappaport was born in New York City on 25 March 1926. He received hi ...
. By the late 1950s, students of Steward such as Eric Wolf and Sidney Mintz turned away from cultural ecology to Marxism, world systems theory
World-systems theory (also known as world-systems analysis or the world-systems perspective)Immanuel Wallerstein, (2004), "World-systems Analysis." In ''World System History'', ed. George Modelski, in ''Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems'' (E ...
, dependency theory
Dependency theory is the idea that resources flow from a " periphery" of poor and exploited states to a " core" of wealthy states, enriching the latter at the expense of the former. A central contention of dependency theory is that poor states ...
and Marvin Harris's cultural materialism.
Today most anthropologists reject 19th-century notions of progress and the three assumptions of unilineal evolution. Following Steward, they take seriously the relationship between a culture and its environment to explain different aspects of a culture. But most modern cultural anthropologists have adopted a general systems approach, examining cultures as emergent systems and arguing that one must consider the whole social environment, which includes political and economic relations among cultures. As a result of simplistic notions of "progressive evolution", more modern, complex cultural evolution theories (such as dual inheritance theory
Dual inheritance theory (DIT), also known as gene–culture coevolution or biocultural evolution, was developed in the 1960s through early 1980s to explain how human behavior is a product of two different and interacting evolutionary processes: g ...
, discussed below) receive little attention in the social sciences, having given way in some cases to a series of more humanist approaches. Some reject the entirety of evolutionary thinking and look instead at historical contingencies, contacts with other cultures, and the operation of cultural symbol systems. In the area of development studies, authors such as Amartya Sen
Amartya Kumar Sen (; born 3 November 1933) is an Indian economist and philosopher. Sen has taught and worked in England and the United States since 1972. In 1998, Sen received the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his contributions ...
have developed an understanding of 'development' and 'human flourishing' that also question more simplistic notions of progress, while retaining much of their original inspiration.
Neoevolutionism
Neoevolutionism was the first in a series of modern multilineal evolution theories. It emerged in the 1930s and extensively developed in the period following theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
and was incorporated into both anthropology and sociology in the 1960s. It bases its theories on empirical evidence from areas of archaeology, palaeontology
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure geo ...
, and historiography
Historiography is the study of the methods used by historians in developing history as an academic discipline. By extension, the term ":wikt:historiography, historiography" is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiog ...
and tries to eliminate any references to systems of values
In ethics and social sciences, value denotes the degree of importance of some thing or action, with the aim of determining which actions are best to do or what way is best to live ( normative ethics), or to describe the significance of different a ...
, be it moral or cultural, instead trying to remain objective and simply descriptive.
While 19th-century evolutionism explained how culture develops by giving general principles of its evolutionary process, it was dismissed by the Historical Particularists as unscientific in the early 20th century. It was the neo-evolutionary thinkers who brought back evolutionary thought and developed it to be acceptable to contemporary anthropology.
Neo-evolutionism discards many ideas of classical social evolutionism, namely that of social progress, so dominant in previous sociology evolution-related theories. Then neo-evolutionism discards the determinism
Determinism is the Metaphysics, metaphysical view that all events within the universe (or multiverse) can occur only in one possible way. Deterministic theories throughout the history of philosophy have developed from diverse and sometimes ov ...
argument and introduces probability
Probability is a branch of mathematics and statistics concerning events and numerical descriptions of how likely they are to occur. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1; the larger the probability, the more likely an e ...
, arguing that accidents and free will greatly affect the process of social evolution. It also supports counterfactual history
Counterfactual history (also virtual history) is a form of historiography that attempts to answer the ''wikt:what if, What if?'' questions that arise from counterfactuals, counterfactual conditions. Counterfactual history seeks by "conjecturing ...
—asking "what if" and considering different possible paths that social evolution may take or might have taken, and thus allows for the fact that various cultures may develop in different ways, some skipping entire stages others have passed through. Neo-evolutionism stresses the importance of empirical
Empirical evidence is evidence obtained through sense experience or experimental procedure. It is of central importance to the sciences and plays a role in various other fields, like epistemology and law.
There is no general agreement on how t ...
evidence. While 19th-century evolutionism used value judgments and assumptions for interpreting data, neo-evolutionism relies on measurable information for analysing the process of sociocultural evolution.
Leslie White, author of ''The Evolution of Culture: The Development of Civilization to the Fall of Rome'' (1959), attempted to create a theory explaining the entire history of humanity. The most important factor in his theory is technology. ''Social system
In sociology, a social system is the patterned network of relationships constituting a coherent whole that exist between individuals, groups, and institutions. It is the formal Social structure, structure of role and status that can form in a smal ...
s are determined by technological systems'', wrote White in his book, echoing the earlier theory of Lewis Henry Morgan. He proposes a society's energy consumption
Energy consumption is the amount of energy used.
Biology
In the body, energy consumption is part of energy homeostasis. It derived from food energy. Energy consumption in the body is a product of the basal metabolic rate and the physical acti ...
as a measure of its advancement. He differentiates between five stages of human development. In the first, people use the energy of their own muscles. In the second, they use the energy of domesticated animals. In the third, they use the energy of plants (so White refers to agricultural revolution here). In the fourth, they learn to use the energy of natural resources: coal, oil, gas. In the fifth, they harness nuclear energy
Nuclear energy may refer to:
*Nuclear power, the use of sustained nuclear fission or nuclear fusion to generate heat and electricity
*Nuclear binding energy, the energy needed to fuse or split a nucleus of an atom
*Nuclear potential energy, the pot ...
. White introduced a formula, P=E·T, where E is a measure of energy consumed, and T is the measure of efficiency of technical factors utilising the energy. This theory is similar to Russian astronomer Nikolai Kardashev's later theory of the Kardashev scale
The Kardashev scale () is a method of measuring a civilization's level of technology, technological advancement based on the amount of energy it is capable of harnessing and using. The measure was proposed by Soviet astronomer Nikolai Kardashev i ...
.
Julian Steward
Julian Haynes Steward (January 31, 1902 – February 6, 1972) was an American anthropologist known best for his role in developing "the concept and method" of cultural ecology, as well as a scientific theory of culture change.
Early life and ed ...
, author of ''Theory of Culture Change: The Methodology of Multilinear Evolution'' (1955, reprinted 1979), created the theory of "multilinear" evolution which examined the way in which societies adapted to their environment. This approach was more nuanced than White's theory of "unilinear evolution." Steward rejected the 19th-century notion of progress, and instead called attention to the Darwinian notion of "adaptation", arguing that all societies had to adapt to their environment in some way. He argued that different adaptations could be studied through the examination of the specific resources a society exploited, the technology the society relied on to exploit these resources, and the organization of human labour. He further argued that different environments and technologies would require different kinds of adaptations, and that as the resource base or technology changed, so too would a culture. In other words, cultures do not change according to some inner logic, but rather in terms of a changing relationship with a changing environment. Cultures therefore would not pass through the same stages in the same order as they changed—rather, they would change in varying ways and directions. He called his theory "multilineal evolution". He questioned the possibility of creating a social theory encompassing the entire evolution of humanity; however, he argued that anthropologists are not limited to describing specific existing cultures. He believed that it is possible to create theories analysing typical common culture, representative of specific eras or regions. As the decisive factors determining the development of given culture he pointed to technology and economics, but noted that there are secondary factors, like political system, ideologies and religion. All those factors push the evolution of a given society in several directions at the same time; hence the application of the term "multilinear" to his theory of evolution.
Marshall Sahlins
Marshall David Sahlins ( ; December 27, 1930April 5, 2021) was an American cultural anthropologist best known for his ethnographic work in the Pacific and for his contributions to anthropological theory. He was the Charles F. Grey Distinguishe ...
, co-editor with Elman Service of ''Evolution and Culture'' (1960), divided the evolution of societies into 'general' and 'specific'. General evolution is the tendency of cultural and social systems to increase in complexity, organization and adaptiveness to environment. However, as the various cultures are not isolated, there is interaction and a diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
of their qualities (like technological invention
An invention is a unique or novelty (patent), novel machine, device, Method_(patent), method, composition, idea, or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, or process for increasing efficiency or lowering cost. It m ...
s). This leads cultures to develop in different ways (specific evolution), as various elements are introduced to them in different combinations and at different stages of evolution.
In his ''Power and Prestige'' (1966) and ''Human Societies: An Introduction to Macrosociology'' (1974), Gerhard Lenski
Gerhard Emmanuel "Gerry" Lenski, Jr. (August 13, 1924 – December 7, 2015) was an American sociologist known for contributions to the sociology of religion, social inequality, and introducing the ecological-evolutionary theory. He spent much of ...
expands on the works of Leslie White and Lewis Henry Morgan, developing the ecological-evolutionary theory. He views technological progress as the most basic factor in the evolution of societies and cultures. Unlike White, who defined technology as the ability to create and utilise energy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
, Lenski focuses on information
Information is an Abstraction, abstract concept that refers to something which has the power Communication, to inform. At the most fundamental level, it pertains to the Interpretation (philosophy), interpretation (perhaps Interpretation (log ...
—its amount and uses. The more information and knowledge (especially allowing the shaping of natural environment) a given society has, the more advanced it is. He distinguishes four stages of human development, based on advances in the history of communication
The history of communication technologies (media and appropriate inscription tools) have evolved in tandem with shifts in political and economic systems, and by extension, systems of power. Communication can range from very subtle processes of exc ...
. In the first stage, information is passed by gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s. In the second, when humans gain sentience
Sentience is the ability to experience feelings and sensations. It may not necessarily imply higher cognitive functions such as awareness, reasoning, or complex thought processes. Some writers define sentience exclusively as the capacity for ''v ...
, they can learn
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, value (personal and cultural), values, Attitude (psychology), attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, non-human animals, and ...
and pass information through by experience. In the third, humans start using sign
A sign is an object, quality, event, or entity whose presence or occurrence indicates the probable presence or occurrence of something else. A natural sign bears a causal relation to its object—for instance, thunder is a sign of storm, or me ...
s and develop logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises based on the structure o ...
. In the fourth, they can create symbol
A symbol is a mark, Sign (semiotics), sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, physical object, object, or wikt:relationship, relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by cr ...
s and develop language
Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed language, signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing syste ...
and writing. Advancements in the technology of communication translate into advancements in the economic system
An economic system, or economic order, is a system of production, resource allocation and distribution of goods and services within an economy. It includes the combination of the various institutions, agencies, entities, decision-making proces ...
and political system
In political science, a political system means the form of Political organisation, political organization that can be observed, recognised or otherwise declared by a society or state (polity), state.
It defines the process for making official gov ...
, distribution of goods
In economics, goods are anything that is good, usually in the sense that it provides welfare or utility to someone. Alan V. Deardorff, 2006. ''Terms Of Trade: Glossary of International Economics'', World Scientific. Online version: Deardorffs ...
, social inequality
Social inequality occurs when resources within a society are distributed unevenly, often as a result of inequitable allocation practices that create distinct unequal patterns based on socially defined categories of people. Differences in acce ...
and other spheres of social life. He also differentiates societies based on their level of technology, communication and economy: (1) hunters and gatherers, (2) agricultural, (3) industrial, and (4) special (like fishing societies).
Talcott Parsons
Talcott Parsons (December 13, 1902 – May 8, 1979) was an American sociologist of the classical tradition, best known for his social action theory and structural functionalism. Parsons is considered one of the most influential figures in soci ...
, author of ''Societies: Evolutionary and Comparative Perspectives'' (1966) and ''The System of Modern Societies'' (1971) divided evolution into four subprocesses: (1) division, which creates functional subsystems from the main system; (2) adaptation, where those systems evolve into more efficient versions; (3) inclusion of elements previously excluded from the given systems; and (4) generalization of values, increasing the legitimization of the ever more complex system. He shows those processes on 4 stages of evolution: (I) primitive or foraging, (II) archaic agricultural, (III) classical or "historic" in his terminology, using formalized and universalizing theories about reality and (IV) modern empirical cultures. However, these divisions in Parsons' theory are the more formal ways in which the evolutionary process is conceptualized, and should not be mistaken for Parsons' actual theory. Parsons develops a theory where he tries to reveal the complexity of the processes which take form between two points of necessity, the first being the cultural "necessity," which is given through the values-system of each evolving community; the other is the environmental necessities, which most directly is reflected in the material realities of the basic production system and in the relative capacity of each industrial-economical level at each window of time. Generally, Parsons highlights that the dynamics and directions of these processes is shaped by the cultural imperative embodied in the cultural heritage, and more secondarily, an outcome of sheer "economic" conditions.
Michel Foucault
Paul-Michel Foucault ( , ; ; 15 October 192625 June 1984) was a French History of ideas, historian of ideas and Philosophy, philosopher who was also an author, Literary criticism, literary critic, Activism, political activist, and teacher. Fo ...
's recent, and very much misunderstood, concepts such as biopower
Biopower (or ''biopouvoir'' in French), coined by French social theorist Michel Foucault, refers to various means by which modern nation states control of populations, control their populations. In Foucault's work, it has been used to refer ...
, biopolitics
Biopolitics is a concept popularized by the French philosopher Michel Foucault in the mid-20th century. At its core, biopolitics explores how governmental power operates through the management and regulation of a population's bodies and lives.
...
and power-knowledge
In critical theory, power-knowledge is a term introduced by the French philosopher Michel Foucault (). According to Foucault's understanding, power is based on knowledge and makes use of knowledge; on the other hand, power reproduces knowledge by ...
has been cited as breaking free from the traditional conception of man as cultural animal. Foucault regards both the terms "cultural animal" and "human nature"as misleading abstractions, leading to a non-critical exemption of man and anything can be justified when regarding social processes or natural phenomena (social phenomena). Foucault argues these complex processes are interrelated, and difficult to study for a reason so those 'truths' cannot be topled or disrupted. For Foucault, the many modern concepts and practices that attempt to uncover "the truth" about human beings (either psychologically, sexually, religion or spiritually) actually create the very types of people they purport to discover. Requiring trained "specialists" and knowledge codes and know how, rigorous pursuit is "put off" or delayed which makes any kind of study not only a 'taboo' subject but deliberately ignored. He cites the concept of 'truth' within many human cultures and the ever flowing dynamics between truth, power, and knowledge as a resultant complex dynamics (Foucault uses the term regimes of truth) and how they flow with ease like water which make the concept of 'truth' impervious to any further rational investigation. Some of the West's most powerful social institutions are powerful for a reason, not because they exhibit powerful structures which inhibit investigation or it is illegal to investigate there historical foundation. It is the very notion of "legitimacy" Foucault cites as examples of "truth" which function as a "Foundationalism
Foundationalism concerns philosophical theories of knowledge resting upon non-inferential justified belief, or some secure foundation of certainty such as a conclusion inferred from a basis of sound premises.Simon Blackburn, ''The Oxford Dict ...
" claims to historical accuracy. Foucault argues, systems such as medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
, prisons
A prison, also known as a jail, gaol, penitentiary, detention center, correction center, correctional facility, or remand center, is a facility where people are imprisoned under the authority of the state, usually as punishment for various cr ...
, and religion
Religion is a range of social system, social-cultural systems, including designated religious behaviour, behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, religious text, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics in religion, ethics, or ...
, as well as groundbreaking works on more abstract theoretical issues of power are suspended or buried into oblivion. Kantorowicz, Ernst (1956) ''The Kings Two Bodies'' He cites as further examples the 'Scientific study' of population biology
The term population biology has been used with different meanings.
In 1971, Edward O. Wilson ''et al''. used the term in the sense of applying mathematical models to population genetics, community ecology, and population dynamics. Alan Hasting ...
and population genetics
Population genetics is a subfield of genetics that deals with genetic differences within and among populations, and is a part of evolutionary biology. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as Adaptation (biology), adaptation, s ...
as both examples of this kind of "Biopower" over the vast majority of the human population giving the new founded political population their 'politics' or polity. With the advent of biology and genetics teamed together as new scientific innovations notions of study of knowledge regarding truth belong to the realm of experts who will never divulge their secrets openly, while the bulk of the population do not know their own biology or genetics this is done for them by the experts. This functions as a truth ignorance mechanism: "where the "subjugated knowledge's", as those that have been both written out of history and submerged in it in a masked form produces what we now know as truth. He calls them "Knowledge's from below" and a "historical knowledge of struggles". Genealogy
Genealogy () is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kin ...
, Foucault suggests, is a way of getting at these knowledge's and struggles; "they are about the insurrection of knowledge's." Foucault tries to show with the added dimension of "Milieu
The social environment, social context, sociocultural context or milieu refers to the immediate physical and social setting in which people live or in which something happens or develops. It includes the culture that the individual was educated ...
" (derived from Newtonian mechanics
Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. These laws, which provide the basis for Newtonian mechanics, can be paraphrased as follows:
# A body r ...
) how this Milieu from the 17th century with the development of the biological
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, and distribution of ...
and physical sciences
Physical science is a branch of natural science that studies non-living systems, in contrast to life science. It in turn has many branches, each referred to as a "physical science", together is called the "physical sciences".
Definition
...
managed to be interwoven into the political, social and biological relationship of men with the arrival of the concept Work
Work may refer to:
* Work (human activity), intentional activity people perform to support themselves, others, or the community
** Manual labour, physical work done by humans
** House work, housework, or homemaking
** Working animal, an ani ...
placed upon the industrial population. Foucault uses the term ''Umwelt
An umwelt (plural: ''umwelten''; from the German wikt:Umwelt, ''Umwelt'', meaning "environment" or "surroundings") is the specific way in which organisms of a particular species perceive and experience the world, shaped by the capabilities of ...
'', borrowed from Jakob von Uexküll
Jakob may refer to:
People
* Jakob (given name), including a list of people with the name
* Jakob (surname), including a list of people with the name Other
* Jakob (band), a New Zealand band, and the title of their 1999 EP
* Max Jakob Memorial ...
, meaning environment within. Technology, production, cartography
Cartography (; from , 'papyrus, sheet of paper, map'; and , 'write') is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can ...
the production of nation states
A nation state, or nation-state, is a political entity in which the State (polity), state (a centralized political organization ruling over a population within a territory) and the nation (a community based on a common identity) are (broadly ...
and government making the efficiency of the body politic
The body politic is a polity—such as a city, realm, or state—considered metaphorically as a physical body. Historically, the sovereign is typically portrayed as the body's head, and the analogy may also be extended to other anatomical part ...
, law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior, with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been variously described as a science and as the ar ...
, heredity
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic infor ...
and consanguine not only sound genuine and beyond historical origin and foundation it can be turned into 'exact truth' where the individual and the societal body are not only subjugated and nullified but dependent upon it. Foucault is not denying that genetic or biological study is inaccurate or is simply not telling the truth what he means is that notions of this newly discovered sciences were extended to include the vast majority (or whole populations) of populations as an exercise in "regimes change".
Foucault argues that the conceptual meaning from the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
and Canon law
Canon law (from , , a 'straight measuring rod, ruler') is a set of ordinances and regulations made by ecclesiastical jurisdiction, ecclesiastical authority (church leadership) for the government of a Christian organization or church and its membe ...
period, the Geocentric model
In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, often exemplified specifically by the Ptolemaic system) is a superseded scientific theories, superseded description of the Universe with Earth at the center. Under most geocentric m ...
, later superseded by the Heliocentrism
Heliocentrism (also known as the heliocentric model) is a superseded astronomical model in which the Earth and planets orbit around the Sun at the center of the universe. Historically, heliocentrism was opposed to geocentrism, which placed t ...
model placing the position of the law of right in the Middle ages (exclusive right
An exclusive right, or exclusivity, is a ''de facto'', non-tangible prerogative existing in law (that is, the power or, in a wider sense, right) to perform an action or acquire a benefit and to permit or deny others the right to perform the same ...
or its correct legal term ''Sui generis
( , ) is a Latin phrase that means "of its/their own kind" or "in a class by itself", therefore "unique". It denotes an exclusion to the larger system an object is in relation to.
Several disciplines use the term to refer to unique entities. ...
'') was the divine right of kings and absolute monarchy where the previous incarnation of truth and rule of political sovereignty was considered absolute and unquestioned by political philosophy
Political philosophy studies the theoretical and conceptual foundations of politics. It examines the nature, scope, and Political legitimacy, legitimacy of political institutions, such as State (polity), states. This field investigates different ...
(monarchs, popes and emperors). However, Foucault noticed that this Pharaonic version of political power
In political science, power is the ability to influence or direct the actions, beliefs, or conduct of actors. Power does not exclusively refer to the threat or use of force (coercion) by one actor against another, but may also be exerted thro ...
was transversed and it was with 18th-century emergence of capitalism and liberal democracy
Liberal democracy, also called Western-style democracy, or substantive democracy, is a form of government that combines the organization of a democracy with ideas of liberalism, liberal political philosophy. Common elements within a liberal dem ...
that these terms began to be "democratized". The modern Pharaonic version represented by the president
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
*'' Præsident ...
, the monarch, the pope
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
and the prime minister
A prime minister or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. A prime minister is not the head of state, but r ...
all became propagandized versions or examples of symbol agents all aimed at towards a newly discovered phenomenon, the population. As symbolic symbol agents of power making the mass population having to sacrifice itself all in the name of the newly formed voting franchise we now call Democracy
Democracy (from , ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which political power is vested in the people or the population of a state. Under a minimalist definition of democracy, rulers are elected through competitiv ...
. However, this was all turned on its head (when the Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
rulers were thrown out and replaced by a more exact apparatus now called the state) when the human sciences suddenly discovered: "The set of mechanisms through which the basic biological features of the human species became an object of a political strategy and took on board the fundamental facts that humans were now a biological species."
Sociobiology
Sociobiology departs perhaps the furthest from classical social evolutionism. It was introduced by Edward Wilson in his 1975 book '' Sociobiology: The New Synthesis'' and followed his adaptation of evolutionary theory to the field of social sciences. Wilson pioneered the attempt to explain the evolutionary mechanics behind social behaviours such asaltruism
Altruism is the concern for the well-being of others, independently of personal benefit or reciprocity.
The word ''altruism'' was popularised (and possibly coined) by the French philosopher Auguste Comte in French, as , for an antonym of egoi ...
, aggression
Aggression is behavior aimed at opposing or attacking something or someone. Though often done with the intent to cause harm, some might channel it into creative and practical outlets. It may occur either reactively or without provocation. In h ...
, and nurturance. In doing so, Wilson sparked one of the greatest scientific controversies
Controversy (, ) is a state of prolonged public dispute or debate, usually concerning a matter of conflicting opinion or point of view. The word was coined from the Latin '' controversia'', as a composite of ''controversus'' – "turned in an opp ...
of the 20th century by introducing and rejuvenating neo-Darwinian modes of thinking in many social sciences and the humanities, leading to reactions ranging from fundamental opposition, not only from social scientists and humanists but also from Darwinists who see it as "excessively simplistic in its approach", to calls for a radical restructuring of the respective disciplines on an evolutionary basis.
The current theory of evolution, the modern evolutionary synthesis (or neo-darwinism), explains that evolution of species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
occurs through a combination of Darwin's mechanism of natural selection and Gregor Mendel
Gregor Johann Mendel Order of Saint Augustine, OSA (; ; ; 20 July 1822 – 6 January 1884) was an Austrian Empire, Austrian biologist, meteorologist, mathematician, Augustinians, Augustinian friar and abbot of St Thomas's Abbey, Brno, St. Thom ...
's theory of genetics as the basis for biological inheritance and mathematical population genetics. Essentially, the modern synthesis introduced the connection between two important discoveries; the units of evolution (genes) with the main mechanism of evolution (selection).
Due to its close reliance on biology, sociobiology is often considered a branch of the biology, although it uses techniques from a plethora of sciences, including ethology
Ethology is a branch of zoology that studies the behavior, behaviour of non-human animals. It has its scientific roots in the work of Charles Darwin and of American and German ornithology, ornithologists of the late 19th and early 20th cen ...
, evolution, zoology
Zoology ( , ) is the scientific study of animals. Its studies include the anatomy, structure, embryology, Biological classification, classification, Ethology, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinction, extinct, and ...
, archaeology, population genetics, and many others. Within the study of human societies
A society () is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. ...
, sociobiology is closely related to the fields of human behavioral ecology and evolutionary psychology
Evolutionary psychology is a theoretical approach in psychology that examines cognition and behavior from a modern evolutionary perspective. It seeks to identify human psychological adaptations with regard to the ancestral problems they evolved ...
.
Sociobiology has remained highly controversial as it contends genes
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
explain specific human behaviours, although sociobiologists describe this role as a very complex and often unpredictable interaction between nature and nurture. The most notable critics of the view that genes play a direct role in human behaviour have been biologists Richard Lewontin
Richard Charles Lewontin (March 29, 1929 – July 4, 2021) was an American evolutionary biologist, mathematician, geneticist, and social commentator. A leader in developing the mathematical basis of population genetics and evolutionary theory, ...
, Steven Rose, and Stephen Jay Gould
Stephen Jay Gould ( ; September 10, 1941 – May 20, 2002) was an American Paleontology, paleontologist, Evolutionary biology, evolutionary biologist, and History of science, historian of science. He was one of the most influential and widely re ...
. Given the convergence of much of sociobiology's claims with right-wing politics, this approach has seen severe opposition both with regard to its research results as well as its basic tenets; this has led even Wilson himself to revisit his claims and state his opposition to some elements of modern sociobiology.
Since the rise of evolutionary psychology, another school of thought, Dual Inheritance Theory
Dual inheritance theory (DIT), also known as gene–culture coevolution or biocultural evolution, was developed in the 1960s through early 1980s to explain how human behavior is a product of two different and interacting evolutionary processes: g ...
, has emerged in the past 25 years that applies the mathematical standards of Population genetics to modeling the adaptive and selective principles of culture. This school of thought was pioneered by Robert Boyd at UCLA
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. Its academic roots were established in 1881 as a normal school then known as the southern branch of the C ...
and Peter Richerson at UC Davis
The University of California, Davis (UC Davis, UCD, or Davis) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Davis, California, United States. It is the northernmost of the ten campuses of the University ...
and expanded by William Wimsatt, among others. Boyd and Richerson's book, ''Culture and the Evolutionary Process'' (1985), was a highly mathematical description of cultural change, later published in a more accessible form in ''Not by Genes Alone'' (2004). In Boyd and Richerson's view, cultural evolution, operating on socially learned information, exists on a separate but co-evolutionary track from genetic evolution, and while the two are related, cultural evolution is more dynamic, rapid, and influential on human society than genetic evolution. Dual Inheritance Theory has the benefit of providing unifying territory for a "nature and nurture" paradigm and accounts for more accurate phenomenon in evolutionary theory applied to culture, such as randomness effects (drift), concentration dependency, "fidelity" of evolving information systems, and lateral transmission through communication. Nicholas Christakis also advances similar ideas about "evolutionary sociology" in his 2019 book, Blueprint: The Evolutionary Origins of a Good Society, emphasizing the relevance of underlying evolutionary forces that have helped to shape all societies, whatever their cultural differences.
Theory of modernization
Theories ofmodernization
Modernization theory or modernisation theory holds that as societies become more economically modernized, wealthier and more educated, their political institutions become increasingly liberal democratic and rationalist. The "classical" theories ...
are closely related to the dependency theory and development theory
Development theory is a collection of theories about how desirable change in society is best achieved. Such theories draw on a variety of social science disciplines and approaches. In this article, multiple theories are discussed, as are recent ...
. While they have been developed and popularized in the 1950s and 1960s, their ideological and epistemic ancestors can be traced back until at least the early 20th century when progressivist historians and social scientists, building upon Darwinian ideas that the roots of economic success in the US had to be found in its population structure, which, as an immigrant society, was composed of the strongest and fittest individuals of their respective countries of origin, had started to supply the national myth of US-American manifest destiny with evolutionary reasoning. Explicitly and implicitly, the US became the yardstick of modernisation, and other societies could be measured in the extent of their modernity by how closely they adhered to the US-American example. Modernization Theories combine the previous theories of sociocultural evolution with practical experiences and empirical research, especially those from the era of decolonization
Decolonization is the undoing of colonialism, the latter being the process whereby Imperialism, imperial nations establish and dominate foreign territories, often overseas. The meanings and applications of the term are disputed. Some scholar ...
. The theory states that:
* Western countries are the most developed, and the rest of the world (mostly former colonies) is in the earlier stages of development, and will eventually reach the same level as the Western world.
* Development stages go from the traditional societies to developed ones.
* Third World
The term Third World arose during the Cold War to define countries that remained non-aligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact. The United States, Canada, Taiwan, Japan, South Korea, the Southern Cone, NATO, Western European countries and oth ...
countries have fallen behind with their social progress and need to be directed on their way to becoming more advanced.
Developing from classical social evolutionism theories, the theory of modernization stresses the modernization factor: many societies are simply trying (or need) to emulate the most successful societies and cultures. It also states that it is possible to do so, thus supporting the concepts of social engineering and that the developed countries can and should help those less developed, directly or indirectly.
Among the scientists who contributed much to this theory are Walt Rostow
Walt Whitman Rostow (; October 7, 1916 – February 13, 2003) was an American economist, professor and political theorist who served as national security advisor to president of the United States Lyndon B. Johnson from 1966 to 1969.
Rostow wor ...
, who in his ''The Stages of Economic Growth: A Non-Communist Manifesto'' (1960) concentrates on the economic system side of the modernization, trying to show factors needed for a country to reach the path to modernization in his Rostovian take-off model. David Apter concentrated on the political system and history of democracy, researching the connection between democracy, good governance
Governance is the overall complex system or framework of Process, processes, functions, structures, Social norm, rules, Law, laws and Norms (sociology), norms born out of the Interpersonal relationship, relationships, Social interaction, intera ...
and efficiency and modernization. David McClelland
David Clarence McClelland (May 20, 1917 – March 27, 1998) was an American psychologist, noted for his work on motivation need theory. He published a number of works between the 1950s and the 1990s and developed new scoring systems for the ...
(''The Achieving Society'', 1967) approached this subject from the psychological
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feel ...
perspective, with his motivation
Motivation is an mental state, internal state that propels individuals to engage in goal-directed behavior. It is often understood as a force that explains why people or animals initiate, continue, or terminate a certain behavior at a particul ...
s theory, arguing that modernization cannot happen until given society values innovation, success and free enterprise. Alex Inkeles
Alex Inkeles (March 4, 1920 – July 9, 2010) was an American sociologist and social psychologist. His main areas of research were national character and the culture and society of the Soviet Union. His career was mostly spent at Harvard Un ...
(''Becoming Modern'', 1974) similarly creates a model of ''modern personality'', which needs to be independent, active, interested in public policies and cultural matters, open to new experiences, rational and able to create long-term plans for the future. Some works of Jürgen Habermas are also connected with this subfield.
The theory of modernization has been subject to some criticism similar to that levied against classical social evolutionism, especially for being too ethnocentric, one-sided and focused on the Western world and its culture.
Contemporary perspectives
Political perspectives
TheCold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
period was marked by rivalry between two superpowers, both of which considered themselves to be the most highly evolved cultures on the planet. The USSR
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
painted itself as a socialist
Socialism is an economic ideology, economic and political philosophy encompassing diverse Economic system, economic and social systems characterised by social ownership of the means of production, as opposed to private ownership. It describes ...
society which emerged from class struggle
In political science, the term class conflict, class struggle, or class war refers to the economic antagonism and political tension that exist among social classes because of clashing interests, competition for limited resources, and inequali ...
, destined to reach the state of communism
Communism () is a political sociology, sociopolitical, political philosophy, philosophical, and economic ideology, economic ideology within the history of socialism, socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a ...
, while sociologists in the United States (such as Talcott Parsons) argued that the freedom and prosperity of the United States were a proof of a higher level of sociocultural evolution of its culture and society. At the same time, decolonization created newly independent countries who sought to become more developed—a model of progress and industrialization which was itself a form of sociocultural evolution.
Technological perspectives
 Many argue that the next stage of sociocultural evolution consists of a merger with technology, especially information processing technology. Several cumulative major transitions of evolution have transformed life through key innovations in information storage and replication, including
Many argue that the next stage of sociocultural evolution consists of a merger with technology, especially information processing technology. Several cumulative major transitions of evolution have transformed life through key innovations in information storage and replication, including RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule that is essential for most biological functions, either by performing the function itself (non-coding RNA) or by forming a template for the production of proteins (messenger RNA). RNA and deoxyrib ...
, DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
, multicellularity, and also language
Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning, both in spoken and signed language, signed forms, and may also be conveyed through writing syste ...
and culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
as inter-human information processing systems. in this sense it can be argued that the carbon-based biosphere has generated a system (human society) capable of creating technology that will result in a comparable evolutionary
transition. "Digital information has reached a similar magnitude to information in the biosphere. It increases exponentially, exhibits high-fidelity replication, evolves through differential fitness, is expressed through artificial intelligence (AI), and has facility for virtually limitless recombination. Like previous evolutionary transitions, the potential symbiosis between biological and digital information will reach a critical point where these codes could compete via natural
selection. Alternatively, this fusion could create a higher-level superorganism employing a low-conflict division of labor in performing informational tasks...humans already embrace fusions of biology and technology. We spend most of our waking time communicating through digitally mediated channels, ...most transactions on the stock market are executed by automated trading algorithms, and our electric grids are in the hands of artificial intelligence. With one in three marriages in America beginning online, digital algorithms are also taking a role in human pair bonding and reproduction".
Anthropological perspectives
Current political theories of the new tribalists consciously mimic ecology and the life-ways ofindigenous peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
, augmenting them with modern sciences. Ecoregional Democracy attempts to confine the "shifting groups", or tribes, within "more or less clear boundaries" that a society inherits from the surrounding ecology, to the borders of a naturally occurring ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) is an ecological and geographic area that exists on multiple different levels, defined by type, quality, and quantity of environmental resources. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and c ...
. Progress can proceed by competition between but not within tribes, and it is limited by ecological borders or by Natural Capitalism incentives which attempt to mimic the pressure of natural selection on a human society by forcing it to adapt consciously to scarce energy or materials. Gaians argue that societies evolve deterministically to play a role in the ecology of their biosphere
The biosphere (), also called the ecosphere (), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on the Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to mat ...
, or else die off as failures due to competition from more efficient societies exploiting nature's leverage.
Thus, some have appealed to theories of sociocultural evolution to assert that optimizing the ecology and the social harmony of closely knit groups is more desirable or necessary than the progression to "civilization." A 2002 poll of experts on Neoarctic and Neotropic
The Neotropical realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting Earth's land surface. Physically, it includes the tropical terrestrial ecoregions of the Americas and the entire South American temperate zone.
Definition
In biogeogra ...
indigenous peoples (reported in ''Harper's'' magazine) revealed that ''all of them'' would have preferred to be a typical New World person in the year 1491, prior to any European contact, rather than a typical European of that time. This approach has been criticised by pointing out that there are a number of historical examples of indigenous peoples doing severe environmental damage (such as the deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
of Easter Island
Easter Island (, ; , ) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is renowned for its nearly 1,000 extant monumental statues, ...
and the extinction of mammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus.'' They lived from the late Miocene epoch (from around 6.2 million years ago) into the Holocene until about 4,000 years ago, with mammoth species at various times inhabi ...
s in North America) and that proponents of the goal have been trapped by the European stereotype of the noble savage
In Western anthropology, Western philosophy, philosophy, and European literature, literature, the Myth of the Noble savage refers to a stock character who is uncorrupted by civilization. As such, the "noble" savage symbolizes the innate goodness a ...
.
The role of war in the development of states and societies
Particularly since the end of the Cold War, there has been a growing number of scholars in the social sciences and humanities who came to complement the more presentist neo-evolutionary research with studies into the more distant past and its human inhabitants. A key element in many of these analyses and theories is warfare, which Robert L. Carneiro called the "prime mover in the origin of the state". He theorizes that given the limited availability of natural resources, societies will compete against each other, with the losing group either moving out of the area now dominated by the victorious one, or, if the area is circumscribed by an ocean or a mountain range and re-settlement is thus impossible, will be either subjugated or killed. Thus, societies become larger and larger, but, facing the constant threat of extinction or assimilation, they were also forced to become more complex in their internal organisation both in order to remain competitive as well as to administer a growing territory and a larger population. Carneiro's ideas have inspired great number of subsequent research into the role of war in the process of political, social, or cultural evolution. An example of this is Ian Morris who argues that given the right geographic conditions, war not only drove much of human culture by integrating societies and increasing material well-being, but paradoxically also made the world much less violent. Large-scale states, says Morris, evolved because only they provided enough stability both internally and externally to survive the constant conflicts which characterise the early history of smaller states, and the possibility of war will continue to force humans to invent and evolve. War drove human societies to adapt in a step-wise process, and each development in military technology either requires or leads to comparable developments in politics and society. Many of the underlying assumptions of Morris's thinking can be traced back in some form or another not only to Carneiro but also toJared Diamond
Jared Mason Diamond (born September 10, 1937) is an American scientist, historian, and author. In 1985 he received a MacArthur Genius Grant, and he has written hundreds of scientific and popular articles and books. His best known is '' Guns, G ...
, and particularly his 1997 book ''Guns, Germs, and Steel
''Guns, Germs, and Steel: The Fates of Human Societies'' (subtitled ''A Short History of Everybody for the Last 13,000 Years'' in Britain) is a 1997 transdisciplinary nonfiction book by the American author Jared Diamond. The book attempts to ...
''. Diamond, who explicitly opposes racist evolutionary tales, argues that the ultimate explanation of why different human development on different continents is the presence or absence of domesticable plants and animals as well as the fact that the east-west orientation of Eurasia made migration within similar climates much easier than the south-north orientation of Africa and the Americas. Nevertheless, he also stresses the importance of conflict and warfare as a proximate explanation for how Europeans managed to conquer much of the world, given how societies who fail to innovate will "tend to be eliminated by competing societies".
Similarly, Charles Tilly
Charles Tilly (May 27, 1929 – April 29, 2008) was an American sociologist, political scientist, and historian who wrote on the relationship between politics and society. He was a professor of history, sociology, and social science at the Uni ...
argues that what drove the political, social, and technological change which, after centuries of great variation with regard to states, lead to the European states ultimately all converging on the national state was coercion and warfare: "War wove the European network of national states, and preparation for war created the internal structures of states within it." He describes how war became more expensive and complex due to the introduction of gunpowder and large armies and thus required significantly large states in order to provide the capital and manpower to sustain these, which at the same time were forced to develop new means of extraction and administration.
However, Norman Yoffee has criticised such theorists who, based on general evolutionary frameworks, came to formulate theories of the origins of states and their evolution. He claimed that in no small part due to the prominence of neoevolutionary explanations which group different societies into groups in order to compare them and their progress both to themselves and to modern ethnographic examples, while focusing mostly on political systems and a despotic élite who held together a territorial state by force, "much of what has been said of the earliest states, both in the professional literature as well as in popular writings, is not only factually wrong but also is implausible in the logic of social evolutionary theory".
See also
*Accelerating change
In futures studies and the history of technology, accelerating change is the observed exponential nature of the rate of technological change in recent history, which may suggest faster and more profound change in the future and may or may not ...
* Biocultural evolution
Dual inheritance theory (DIT), also known as gene–culture coevolution or biocultural evolution, was developed in the 1960s through early 1980s to explain how human behavior is a product of two different and interacting evolutionary processes: ...
* Clash of Civilizations
The "Clash of Civilizations" is a thesis that people's cultural and religious identities will be the primary source of conflict in the post–Cold War world. The American political scientist Samuel P. Huntington argued that future wars would be ...
* Critical juncture theory
* Cultural diversity
Cultural diversity is the quality of diverse or different cultures, as opposed to Monoculturalism, monoculture. It has a variety of meanings in different contexts, sometimes applying to cultural products like art works in museums or entertainment ...
* Cultural evolution
Cultural evolution is an evolutionary theory of social change. It follows from the definition of culture as "information capable of affecting individuals' behavior that they acquire from other members of their species through teaching, imitation ...
* Cultural materialism
* Cultural neuroscience
* Cultural selection theory
* Diffusion of innovations
Diffusion of innovations is a theory that seeks to explain how, why, and at what rate new ideas and technology spread. The theory was popularized by Everett Rogers in his book ''Diffusion of Innovations'', first published in 1962. Rogers argue ...
* Dual inheritance theory
Dual inheritance theory (DIT), also known as gene–culture coevolution or biocultural evolution, was developed in the 1960s through early 1980s to explain how human behavior is a product of two different and interacting evolutionary processes: g ...
* Economic determinism
Economic determinism is a socioeconomic theory that economic relationships (such as being an owner or capitalist or being a worker or proletarian) are the foundation upon which all other societal and political arrangements in society are based. T ...
* Edward Burnett Tylor
Sir Edward Burnett Tylor (2 October 18322 January 1917) was an English anthropologist, and professor of anthropology.
Tylor's ideas typify 19th-century cultural evolutionism. In his works '' Primitive Culture'' (1871) and ''Anthropology'' ...
* Evolutionary anthropology
Evolutionary anthropology, the interdisciplinary study of the human evolution, evolution of human physiology and human behaviour and of the relation between hominids and non-hominid primates, builds on natural science and on social science. Vari ...
* Environmental racism
Environmental racism, ecological racism, or ecological apartheid is a form of racism leading to negative environmental outcomes such as landfills, Incineration, incinerators, and hazardous waste disposal disproportionately impacting Community ...
* Extended order
* Franz Boas
Franz Uri Boas (July 9, 1858 – December 21, 1942) was a German-American anthropologist and ethnomusicologist. He was a pioneer of modern anthropology who has been called the "Father of American Anthropology". His work is associated with the mov ...
* Futures studies
Futures studies, futures research or futurology is the systematic, interdisciplinary and holistic study of social and technological advancement, and other environmental trends, often for the purpose of exploring how people will live and wor ...
* Historicism
Historicism is an approach to explaining the existence of phenomena, especially social and cultural practices (including ideas and beliefs), by studying the process or history by which they came about. The term is widely used in philosophy, ant ...
* Institutional memory
Institutional memory is a collective set of facts, concepts, experiences and knowledge held by a group of people.
Concept
Institutional memory has been defined as "the stored knowledge within the organization." Within any organization, tools ...
* Julian Steward
Julian Haynes Steward (January 31, 1902 – February 6, 1972) was an American anthropologist known best for his role in developing "the concept and method" of cultural ecology, as well as a scientific theory of culture change.
Early life and ed ...
* Leslie White
* Lewis Henry Morgan
Lewis Henry Morgan (November 21, 1818 – December 17, 1881) was a pioneering American anthropologist and social theorist who worked as a railroad lawyer. He is best known for his work on kinship and social structure, his theories of social e ...
* Memetics
Memetics is a theory of the evolution of culture based on Darwinian principles with the meme as the unit of culture. The term "meme" was coined by biologist Richard Dawkins in his 1976 book '' The Selfish Gene'', to illustrate the principle that h ...
* Moral progress
* Neoevolutionism
* Neuroculture
* Origin of language
The origin of language, its relationship with human evolution, and its consequences have been subjects of study for centuries. Scholars wishing to study the origins of language draw inferences from evidence such as the fossil record, archaeolog ...
* Origin of speech
The origin of speech differs from the origin of language because language is not necessarily spoken; it could equally be Written language, written or Sign language, signed. Speech is a fundamental aspect of human communication and plays a vital ...
* Origins of society
* Population dynamics
Population dynamics is the type of mathematics used to model and study the size and age composition of populations as dynamical systems. Population dynamics is a branch of mathematical biology, and uses mathematical techniques such as differenti ...
* Punctuated equilibrium
In evolutionary biology, punctuated equilibrium (also called punctuated equilibria) is a Scientific theory, theory that proposes that once a species appears in the fossil record, the population will become stable, showing little evolution, evol ...
* Rationalization (sociology)
In sociology, the term rationalization was coined by Max Weber, a German sociologist, jurist, and economist. Rationalization (or rationalisation) is the replacement of traditions, values, and emotions as motivators for behavior in society with con ...
* Raciolinguistics
* Reformism
Reformism is a political tendency advocating the reform of an existing system or institution – often a political or religious establishment – as opposed to its abolition and replacement via revolution.
Within the socialist movement, ref ...
* Social Darwinism
Charles Darwin, after whom social Darwinism is named
Social Darwinism is a body of pseudoscientific theories and societal practices that purport to apply biological concepts of natural selection and survival of the fittest to sociology, economi ...
* Social cycle theory
Social cycle theories are among the earliest social theories in sociology. Unlike the theory of social evolutionism, which views the evolution of society and human history as progressing in some new, unique direction(s), sociological cycle th ...
* Social dynamics
Social dynamics (or sociodynamics) is the study of the behavior of groups and of the interactions of individual group members, aiming to understand the emergence of complex social behaviors among microorganisms, plants and animals, including h ...
* Social implications of the theory of evolution
* Societal collapse
Societal collapse (also known as civilizational collapse or systems collapse) is the fall of a complex human society characterized by the loss of cultural identity and of social complexity as an Complex adaptive system, adaptive system, the downf ...
* Sociocultural system
* Social progress
Progress is movement towards a perceived refined, improved, or otherwise desired state. It is central to the philosophy of progressivism, which interprets progress as the set of advancements in technology, science, and social organization effic ...
* Symbolic culture
* Technological evolution
References
Cited sources
* Sztompka, Piotr (2002). ''Socjologia''. Znak. .Bibliography
The Philosophy of Positivism
* Robert Carneiro, ''Evolutionism in Cultural Anthropology: A Critical History''. Westview Press, Boulder, CO, 2003. *
Jared Diamond
Jared Mason Diamond (born September 10, 1937) is an American scientist, historian, and author. In 1985 he received a MacArthur Genius Grant, and he has written hundreds of scientific and popular articles and books. His best known is '' Guns, G ...
, '' The World until Yesterday: What Can We Learn from Traditional Societies?'', Penguin Books, 2012 ().
* Evans-Pritchard, Sir Edward, ''A History of Anthropological Thought'', 1981, Basic Books, Inc., New York.
* Graber, Robert B., ''A Scientific Model of Social and Cultural Evolution'', 1995, Thomas Jefferson University Press, Kirksville, MO.
* Harris, Marvin, ''The Rise of Anthropological Theory: A History of Theories of Culture'', 1968, Thomas Y. Crowell, New York.
* Hatch, Elvin, ''Theories of Man and Culture'', 1973, Columbia University Press, New York.
* Hays, H. R., ''From Ape to Angel: An Informal History of Social Anthropology'', 1965, Alfred A. Knopf, New York.
* Johnson, Allen W. and Earle, Timothy, ''The Evolution of Human Societies: From Foraging Group to Agrarian State'', 1987, Stanford University Press.
* Kaplan, David and Manners, Robert, ''Culture Theory'', 1972, Waveland Press, Inc., Prospect Heights, Illinois.
* Kuklick, Henrika, ''The Savage Within: The Social History of British Anthropology, 1885–1945'', 1991, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
* McGilchrist, Iain, '' The Master and His Emissary: The Divided Brain and the Making of the Western World'', 2009, Yale University Press
Yale University Press is the university press of Yale University. It was founded in 1908 by George Parmly Day and Clarence Day, grandsons of Benjamin Day, and became a department of Yale University in 1961, but it remains financially and ope ...
, US and London.
* Mesoudi, A. (2007). Using the methods of experimental social psychology to study cultural evolution. ''Journal of Social, Evolutionary & Cultural Psychology, 1(2),'' 35–58Full text
* Mesoudi, A.
Cultural Evolution: How Darwinian Theory Can Explain Human Culture and Synthesize the Social Sciences
', 2011, University of Chicago Press, * Morgan, John Henry, ''In the Beginning: The Paleolithic Origins of Religious Consciousness'' 2007 Cloverdale Books, South Bend. * Raoul Naroll and William T. Divale. 1976. Natural Selection in Cultural Evolution: Warfare versus Peaceful Diffusion. ''American Ethnologist'' 3: 97–128.
Segal, Daniel
(2000)
Western Civ" and the Staging of History in American Higher Education
' ''
The American Historical Review
''The American Historical Review'' is a quarterly academic history journal published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Historical Association, for which it is an official publication. It targets readers interested in all period ...
'', Vol. 105, No. 3 (Jun., 2000), pp. 770–805
* Seymour-Smith, Charlotte, Macmillan Dictionary of Anthropology, 1986, Macmillan, New York.
* Stocking Jr., George W., ''Race, Culture, and Evolution: Essays in the History of Anthropology'', 1968, The Free Press, New York.
* Stocking Jr., George W., ''After Tylor: British Social Anthropology 1888–1951'', 1995, The University of Wisconsin Press.
* Stocking, George, ''Victorian Anthropology'', Free Press, 1991,
* Sztompka, Piotr, ''The Sociology of Social Change'', Blackwell Publishers, 1994,
* Trigger, Bruce, ''Sociocultural Evolution: Calculation and Contingency (New Perspectives on the Past)'', Blackwell Publishers, 1998,
* Winthrop, Robert H., ''Dictionary of Concepts in Cultural Anthropology'', 1991, Greenwood Press, New York.
* Ovcharov D. A. (2024), ''The problem of the social and natural in man in foreign philosophical thought of the second half of the XX – early XXI centuries: historical and philosophical analytical review'', ''Bulletin of Vyatka State University'', No. 2 (152) (2024), pp. 74-80, .
Readings from an evolutionary anthropological perspective
* Two special issues on the evolution of culture:
*Evolutionary Anthropology: Issues, News, and Reviews Volume 12, Issue 2, Pages 57–108 (April 2003)
**
The evolution of culture: New perspectives and evidence
(p 57–60) Charles H. Janson, Eric A. Smith **
Making space for traditions
(p 61–70) Dorothy Fragaszy *** Traditions in monkeys (p 71–81) Susan Perry, Joseph H. Manson **
Is culture a golden barrier between human and chimpanzee?
(p 82–91) Christophe Boesch *** Cultural panthropology (p 92–105) Andrew Whiten, Victoria Horner, Sarah Marshall-Pescini **
The fossil record – Human and nonhuman
(p 106–108) Eric Delson *
Evolutionary Anthropology: Issues, News, and Reviews Volume 12, Issue 3, Pages 109–159 (2003)
**
On stony ground: Lithic technology, human evolution, and the emergence of culture
(p 109–122) Robert Foley, Marta Mirazón Lahr **
The evolution of cultural evolution
(p 123–135) Joseph Henrich, Richard McElreath **
The adaptive nature of culture
(p 136–149) Michael S. Alvard **
Do animals have culture?
(p 150–159) Kevin N. Laland, William Hoppitt
External links
Sociocultural evolution on Principia Cybernetica Web
Secular Cycles and Millennial Trends
{{DEFAULTSORT:Sociocultural Evolution Cultural concepts Memetics Anthropology Sociological theories