Cullerlie Stone Circle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cullerlie stone circle, also known as the Standing Stones of Echt, is a small 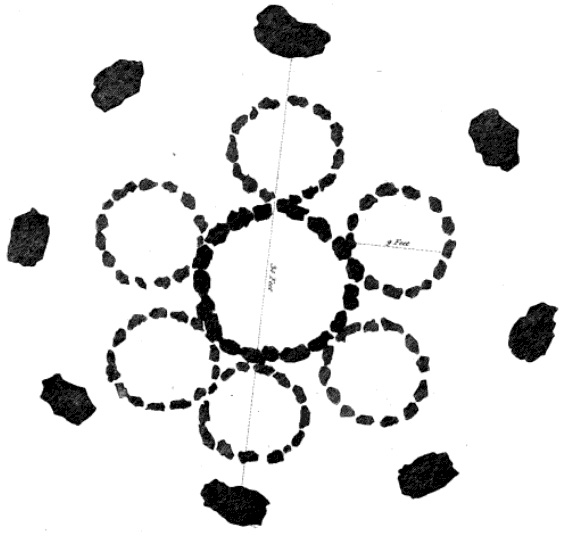 At the time that the circle was built in the second millennium BC, the surrounding landscape was characterised by wet bogs, and the stones were transported to the site from higher ground some distance away. The tallest of the stones marks the north side of the circle. They vary in height from to . A 2004 survey of the site discovered that several of the stones had been carved with previously unnoticed
At the time that the circle was built in the second millennium BC, the surrounding landscape was characterised by wet bogs, and the stones were transported to the site from higher ground some distance away. The tallest of the stones marks the north side of the circle. They vary in height from to . A 2004 survey of the site discovered that several of the stones had been carved with previously unnoticed
stone circle
A stone circle is a ring of standing stones. Most are found in Northwestern Europe – especially in Britain, Ireland, and Brittany – and typically date from the Late Neolithic and Early Bronze Age, with most being built from 3000 BC. The ...
situated near Echt, Aberdeenshire
Echt ( gd, Eicht) is an Aberdeenshire crossroads village in northeast Scotland with a population of approximately 300 people. Echt has a number of prehistoric remains, including the Barmekin of Echt which is on a hill to the northwest. There is ...
. It consists of eight irregular stones of red granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies und ...
arranged at approximately equal intervals to form a circle of diameter, enclosing the same number of small cairns. The cairns are characterised by outer kerbs or rings of stones, with a double ring surrounding the central cairn and a single ring in the others. All but one of the cairns have eleven ringstones, with the last having nine. The whole circle sits on a patch of gravel which forms the end of a low gravel ridge linking the site with Leuchar Moss. It is regarded as "a later development from the recumbent stone circle
A recumbent stone circle is a type of stone circle that incorporates a large monolith, known as a ''recumbent'', lying on its side. They are found in only two regions: in Aberdeenshire in the north-east of Scotland and in the far south-west of Ire ...
", Internet Archive. though its layout with kerbed cairns within the circle makes it unique.
 At the time that the circle was built in the second millennium BC, the surrounding landscape was characterised by wet bogs, and the stones were transported to the site from higher ground some distance away. The tallest of the stones marks the north side of the circle. They vary in height from to . A 2004 survey of the site discovered that several of the stones had been carved with previously unnoticed
At the time that the circle was built in the second millennium BC, the surrounding landscape was characterised by wet bogs, and the stones were transported to the site from higher ground some distance away. The tallest of the stones marks the north side of the circle. They vary in height from to . A 2004 survey of the site discovered that several of the stones had been carved with previously unnoticed cup marks
Cup and ring marks or cup marks are a form of prehistoric art found in the Atlantic seaboard of Europe (Ireland, Wales, Northern England, Scotland, France (Brittany), Portugal, and Spain ( Galicia) – and in Mediterranean Europe – Italy (in Al ...
.
Excavations carried out in 1934 by H. E. Kilbride-Jones on behalf of the Ministry of Works, showed that the circle was built in stages. The entire site had first been cleared, leveled and burned by setting fire to piles of willow twigs. Then came the outer stones, with their bases shaped into points to make them more stable in their gravel bed. They have been somewhat eroded over time by acidic peat eating away the lower portions of the stones. Oak and hazel were burned within the stone rings, leaving charcoal behind, and cremated human bones were deposited in the ashes within five of the rings. They were then filled with smaller stones to create the cairns visible today.
The circle may once have had several companions. In 1820 James Logan wrote: "The small Circles contained in the larger present a curious singularity; and it is also remarkable that, at a short distance to the southwest, are nine others of similar dimensions." However, when the site was excavated in 1934, no trace of these satellite circles could be found.
References
{{reflist Buildings and structures in Aberdeenshire Archaeological sites in Aberdeenshire History of Aberdeenshire Stone circles in Aberdeenshire Stone Age sites in Scotland Scheduled monuments in Scotland