Cruciate Ligament Of Atlas on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The cruciate ligament of the atlas (cruciform ligament) is a cross-shaped (thus the name) 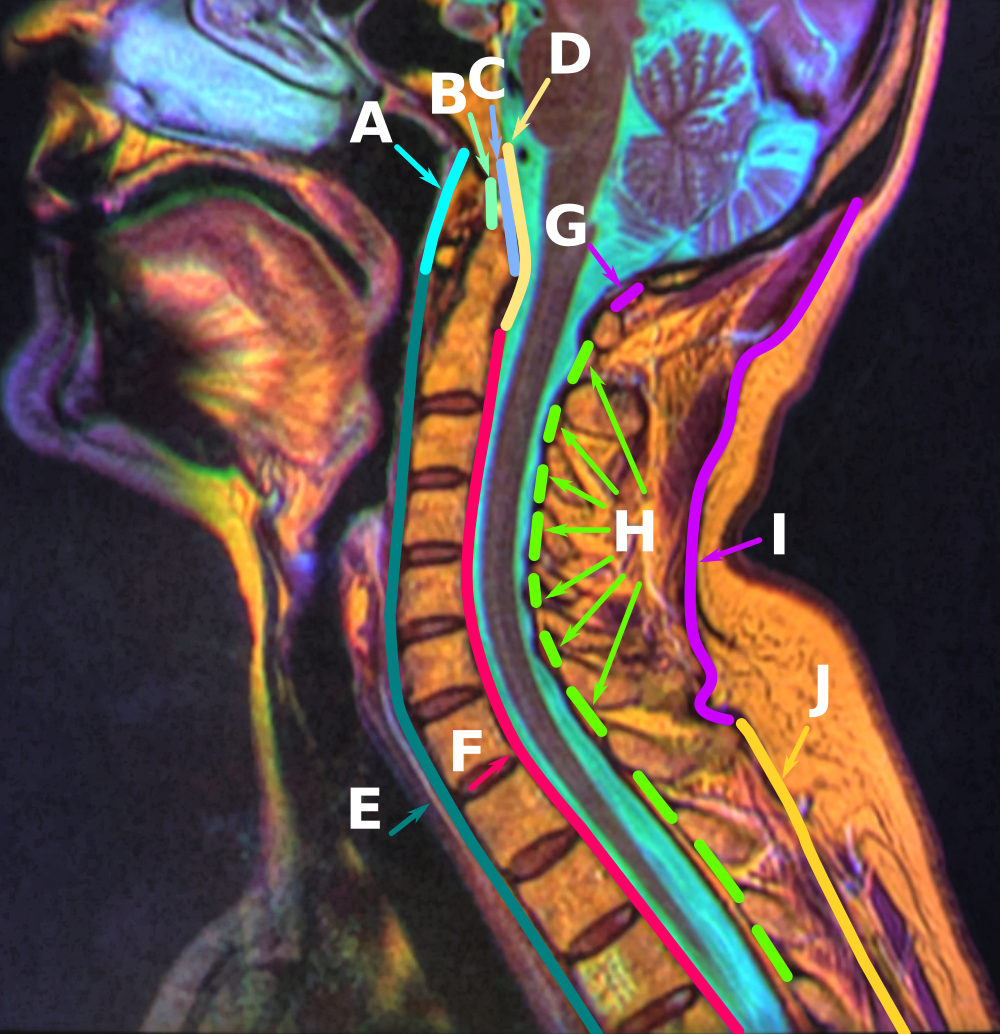
ligament
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have liga ...
in the neck
The neck is the part of the body in many vertebrates that connects the head to the torso. It supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that transmit sensory and motor information between the brain and the rest of the body. Addition ...
forming part of the atlanto-axial joint
The atlanto-axial joint is a joint in the upper part of the neck between the atlas bone and the axis bone, which are the first and second cervical vertebrae. It is a pivot joint, that can start from C2 To C7.
Structure
The atlanto-axial joint ...
. It consists of the transverse ligament of atlas
In anatomy, the transverse ligament of the atlas is a broad, tough ligament which arches across the ring of the atlas (first cervical vertebra) posterior to the dens to keep the dens (odontoid process) in contact with the atlas. It forms the tra ...
, a superior longitudinal band, and an inferior longitudinal band.
The cruciate ligament of the atlas prevents abnormal movement of the atlanto-axial joint.
It may be torn, such as by fractures
Fracture is the appearance of a crack or complete separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress (mechanics), stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacemen ...
of the atlas bone
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a continent or region of Earth. Advances in astronomy have also resulted in atlases of the celestial sphere or of other planets.
Atlases have traditionally been ...
.

Structure
The cruciate ligament of theatlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of world map, maps of Earth or of a continent or region of Earth. Advances in astronomy have also resulted in atlases of the celestial sphere or of other planets.
Atlases have traditio ...
consists of the transverse ligament of the atlas, a superior longitudinal band, and an inferior longitudinal band. The superior longitudinal band connects the transverse ligament to the anterior side of the foramen magnum
The foramen magnum () is a large, oval-shaped opening in the occipital bone of the skull. It is one of the several oval or circular openings (foramina) in the base of the skull. The spinal cord, an extension of the medulla oblongata, passes thro ...
(near the basilar part) in the occipital bone
The occipital bone () is a neurocranium, cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone lies over the occipital lob ...
of the skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
. The inferior longitudinal band connects the transverse ligament to the body of the axis bone
In anatomy, the axis (from Latin ''axis'', "axle") is the second cervical vertebra (C2) of the spine, immediately inferior to the atlas, upon which the head rests. The spinal cord passes through the axis.
The defining feature of the axis is its ...
(C2).
Variation
The inferior longitudinal band may be absent in some people; the rest of the ligament is invariably present.Gerber's ligament
In about half of individuals, an additional band - ''Gerber's ligament'' - arises at the junction of the transverse ligament and superior band, and is situated deep to the superior band.Function
The cruciate ligament of the atlas prevents abnormal movements of theatlanto-axial joint
The atlanto-axial joint is a joint in the upper part of the neck between the atlas bone and the axis bone, which are the first and second cervical vertebrae. It is a pivot joint, that can start from C2 To C7.
Structure
The atlanto-axial joint ...
. The longitudinal bands prevent hyperflexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relativ ...
and hyperextension
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relativ ...
of the occipital bone
The occipital bone () is a neurocranium, cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone lies over the occipital lob ...
, and hold the transverse ligament of the atlas in a normal position.
Clinical significance
Any part of the cruciate ligament of the atlas may tear, which is a significant injury. This may be caused byfractures
Fracture is the appearance of a crack or complete separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress (mechanics), stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacemen ...
of the atlas bone
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a continent or region of Earth. Advances in astronomy have also resulted in atlases of the celestial sphere or of other planets.
Atlases have traditionally been ...
. Ligament tears may be imaged with radiography
Radiography is an imaging technology, imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical ("diagnostic" radiog ...
, a CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
, or magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
.
Ossification
Very rarely, the cruciate ligament of the atlas mayossify
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in the ...
. This may lead to cervical myelopathy
Myelopathy describes any neurologic deficit related to the spinal cord.
When due to Physical trauma, trauma, myelopathy is known as (acute) spinal cord injury. When inflammatory, it is known as myelitis. Disease that is vascular in nature is kno ...
, that is, damage to the spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the lower brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal c ...
.
Etymology
The terms "cruciform" and "cruciate" refer to thecross
A cross is a religious symbol consisting of two Intersection (set theory), intersecting Line (geometry), lines, usually perpendicular to each other. The lines usually run vertically and horizontally. A cross of oblique lines, in the shape of t ...
shape of the ligament
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have liga ...
. Both terms are frequently used, although the term "cruciate" may be confusing due to confusion with the anterior cruciate ligament
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of a pair of cruciate ligaments (the other being the posterior cruciate ligament) in the human knee. The two ligaments are called "cruciform" ligaments, as they are arranged in a crossed formation. In ...
and the posterior cruciate ligament
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is a ligament in each knee of humans and various other animals. It works as a counterpart to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). It connects the posterior intercondylar area of the tibia to the Medial condyl ...
of the knee
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the hu ...
.
References
{{Authority control Ligaments of the head and neck Bones of the vertebral column