Crown Firecoach on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Crown Firecoach is a nameplate used for various types of
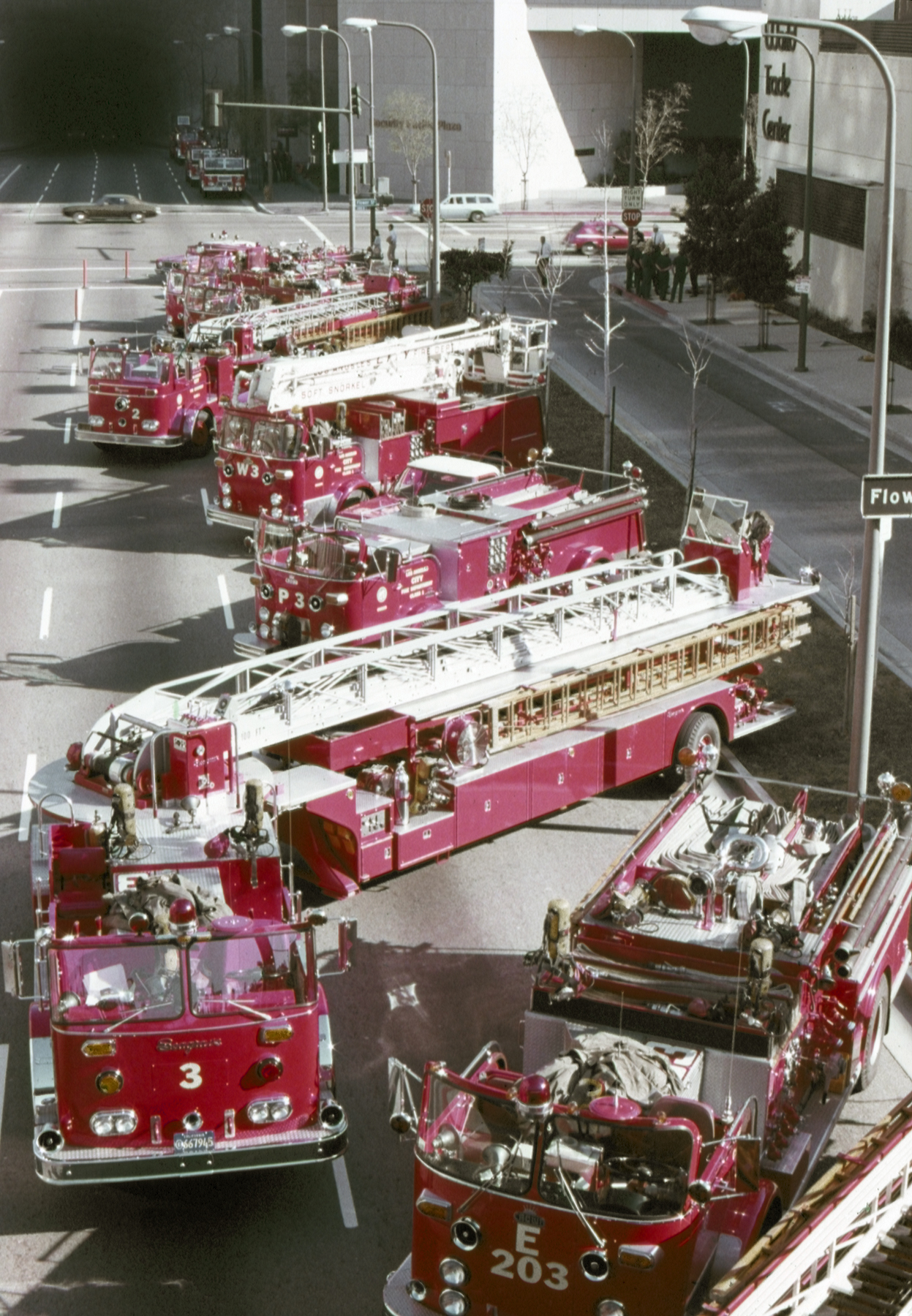 The production of fire apparatus by Crown Coach can be traced back to World War II. As was the case with other vehicle manufacturers, all production was diverted towards the armed forces following the outbreak of the war. In the case of Crown Coach, the company was asked to produce fire engine bodies for a chassis produced by Ford/Marmon-Herrington. In the postwar era, though Crown Coach concentrated its resources on updating its bus products (on what would become the 1949 Crown Supercoach school bus), the company built a few more chassis-based fire engines in the late 1940s.
In 1949, Crown engineer Roy Hardy (a former Mack executive) commenced work on a dedicated design for a company-produced fire engine. The Crown fire engine would compete with the recently introduced American LaFrance 700 cab-forward fire engine, but built to Crown Coach standards and quality. A key part of the design behind the new fire engine was adapting the chassis and front bodywork of the mid-engine Supercoach school bus for the vehicle.
With the blessing of company president M.M. Brockway, construction of the first prototype was completed in 1951. Taking on the name "Crown Firecoach" in relation to its configuration and its relation to the Supercoach bus, the Firecoach would remain a demonstration vehicle for two years, as Crown both completed its development and marketed it to potential customers.
In 1965, following an increase in school bus production, Firecoach production was split into its own division within the company.
The production of fire apparatus by Crown Coach can be traced back to World War II. As was the case with other vehicle manufacturers, all production was diverted towards the armed forces following the outbreak of the war. In the case of Crown Coach, the company was asked to produce fire engine bodies for a chassis produced by Ford/Marmon-Herrington. In the postwar era, though Crown Coach concentrated its resources on updating its bus products (on what would become the 1949 Crown Supercoach school bus), the company built a few more chassis-based fire engines in the late 1940s.
In 1949, Crown engineer Roy Hardy (a former Mack executive) commenced work on a dedicated design for a company-produced fire engine. The Crown fire engine would compete with the recently introduced American LaFrance 700 cab-forward fire engine, but built to Crown Coach standards and quality. A key part of the design behind the new fire engine was adapting the chassis and front bodywork of the mid-engine Supercoach school bus for the vehicle.
With the blessing of company president M.M. Brockway, construction of the first prototype was completed in 1951. Taking on the name "Crown Firecoach" in relation to its configuration and its relation to the Supercoach bus, the Firecoach would remain a demonstration vehicle for two years, as Crown both completed its development and marketed it to potential customers.
In 1965, following an increase in school bus production, Firecoach production was split into its own division within the company.
firefighting apparatus
A firefighting apparatus (North American English) or firefighting appliance (UK English) describes any vehicle that has been customized for use during firefighting operations. These vehicles are highly customized depending on their needs and the d ...
manufactured and marketed by Crown Coach Corporation
The Crown Coach Corporation (founded as the Crown Carriage Company) is a defunct American bus manufacturer. Founded in 1904, the company was best known for its Supercoach range of yellow school buses and motorcoaches; the former vehicles wer ...
in Los Angeles, California
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, ...
, from 1951 to 1985. Although sold primarily in the West Coast region of the United States (California, Oregon, Washington, Idaho, Arizona, and Nevada), other examples of the Firecoach were sold to fire departments in Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
, Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its ...
, and New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
, as well as in Mexico and Kuwait.
Using the mid-engine chassis of the Crown Supercoach
The Crown Supercoach is a bus that was constructed and marketed by Crown Coach Corporation from 1948 to 1991. While most examples were sold as yellow school buses, the Supercoach formed the basis for motorcoaches and other specialty vehicles usi ...
school bus as a basis, the Firecoach was produced in several configurations for fire departments. In addition, Crown Coach served as a second-stage manufacturer, producing fire apparatus bodies for a variety of customer-supplied chassis upon request.
Shortly after the sale of Crown Coach
The Crown Coach Corporation (founded as the Crown Carriage Company) is a defunct American bus manufacturer. Founded in 1904, the company was best known for its Supercoach range of yellow school buses and motorcoaches; the former vehicles wer ...
in 1979, the Firecoach line was discontinued in favor of bus manufacturing. In 1991, Crown ended operations altogether.
Background
 The production of fire apparatus by Crown Coach can be traced back to World War II. As was the case with other vehicle manufacturers, all production was diverted towards the armed forces following the outbreak of the war. In the case of Crown Coach, the company was asked to produce fire engine bodies for a chassis produced by Ford/Marmon-Herrington. In the postwar era, though Crown Coach concentrated its resources on updating its bus products (on what would become the 1949 Crown Supercoach school bus), the company built a few more chassis-based fire engines in the late 1940s.
In 1949, Crown engineer Roy Hardy (a former Mack executive) commenced work on a dedicated design for a company-produced fire engine. The Crown fire engine would compete with the recently introduced American LaFrance 700 cab-forward fire engine, but built to Crown Coach standards and quality. A key part of the design behind the new fire engine was adapting the chassis and front bodywork of the mid-engine Supercoach school bus for the vehicle.
With the blessing of company president M.M. Brockway, construction of the first prototype was completed in 1951. Taking on the name "Crown Firecoach" in relation to its configuration and its relation to the Supercoach bus, the Firecoach would remain a demonstration vehicle for two years, as Crown both completed its development and marketed it to potential customers.
In 1965, following an increase in school bus production, Firecoach production was split into its own division within the company.
The production of fire apparatus by Crown Coach can be traced back to World War II. As was the case with other vehicle manufacturers, all production was diverted towards the armed forces following the outbreak of the war. In the case of Crown Coach, the company was asked to produce fire engine bodies for a chassis produced by Ford/Marmon-Herrington. In the postwar era, though Crown Coach concentrated its resources on updating its bus products (on what would become the 1949 Crown Supercoach school bus), the company built a few more chassis-based fire engines in the late 1940s.
In 1949, Crown engineer Roy Hardy (a former Mack executive) commenced work on a dedicated design for a company-produced fire engine. The Crown fire engine would compete with the recently introduced American LaFrance 700 cab-forward fire engine, but built to Crown Coach standards and quality. A key part of the design behind the new fire engine was adapting the chassis and front bodywork of the mid-engine Supercoach school bus for the vehicle.
With the blessing of company president M.M. Brockway, construction of the first prototype was completed in 1951. Taking on the name "Crown Firecoach" in relation to its configuration and its relation to the Supercoach bus, the Firecoach would remain a demonstration vehicle for two years, as Crown both completed its development and marketed it to potential customers.
In 1965, following an increase in school bus production, Firecoach production was split into its own division within the company.
Design overview
As with its Supercoach counterpart, the Firecoach saw only gradual changes during its production run. Built largely to order for individual fire departments, the firm produced the Firecoach in a variety of different types and configurations, including pumpers, tillers, aerial trucks, and tender trucks.Mechanical layout
While nearly all Firecoaches were two-axle configurations, several "tractor" units were built to tow aerial devices and for various specialty uses. Derived from the Crown Supercoach product line, the cab-forward Firecoach was of a mid-engine layout. Although equipped withHall-Scott
Hall-Scott Motor Car Company was an American manufacturing company based in Berkeley, California. It was among the most significant builders of water-cooled aircraft engines before World War I.
History
1910–21
The company was founded in 1910 ...
gasoline engines like the Supercoach, the Firecoach was equipped with much larger versions (935 and 1091 cubic inches vs. 590). In 1958, to improve braking ability, Firecoaches (alongside all other Crown Coach vehicles) were equipped with 10-inch wide brake drums. For 1963, an automatic transmission became an option. The first diesel-engine Firecoach was assembled in 1964 (a decade after its introduction in Crown buses).
Cab design
In 1954, Crown Coach produced its first Firecoach with an enclosed cab; a 4-door cab made its debut in 1963. Although an enclosed cab had been introduced as an option, into the mid-1960s, the majority of Crown Firecoaches were constructed with open-air cabs. Following theWatts riots
The Watts riots, sometimes referred to as the Watts Rebellion or Watts Uprising, took place in the Watts neighborhood and its surrounding areas of Los Angeles from August 11 to 16, 1965. The riots were motivated by anger at the racist and abus ...
of 1965, in order to provide better security for firefighters, Crown Coach introduced a compartment roof design for its open-air cabs; the design became retrofitted to many in-service Firecoaches as well.
During the 1970s, fully enclosed cabs grew in popularity. In 1977, Crown Coach made the first major change to the Firecoach cab with the introduction of a "wide-cab" configuration; sold alongside its predecessor, the wide-cab Firecoach became standard in 1979.
Configurations
When first designed in 1951, the Firecoach was initially configured as a 2-axle pumper. During its production run, the Firecoach would be introduced in a variety of other configurations for customer requests. In 1955, the first water tender Firecoach was introduced. In 1956, a Firecoach was introduced as a tiller truck; the Firecoach chassis was a tractor towing an American LaFrance aerial device. In 1961, aerial devices saw a change as Crown introduced its first Firecoach snorkel truck (bucket lift). In 1966, Crown produces its first company-produced tiller-based aerial device, though a 2-axle ladder truck made its debut the same year. In 1969, the first quint version of the Firecoach made its debut as Crown introduced the Firecoach TeleSquirt.Discontinuation
During the late 1970s, sales of the Crown Firecoach began to decline as the design began to age. Following the sale of Crown Coach in 1979, sales largely collapsed, leading to an initial discontinuation of the line in 1982. In 1984, production resumed of cab and chassis vehicles; the bodywork was completed in partnership with a California fire engine manufacturer. In 1985, the final Crown Firecoach chassis was produced, closing a 34-year production run.Variants
Chassis-based apparatus
Crown Coach produced the Firecoach in a variety of different types and configurations, including pumpers, tillers, aerial trucks, and tender trucks. In addition to the fire engines based on its Supercoach bus line, Crown also assembled fire engines on truck chassis (by customer request). During the production of the Firecoach, Crown bodied the following truck chassis: * Chevrolet C30 * Ford C850 (Ford F-Series COE) * Ford C700 (Ford C-Series) * Pierce-Crown * VanPelt-Crown (1984–1985) Crown Coach also built custom-designed fire vehicles from Supercoach and Firecoach chassis: * 1957: 4 fire engines for Kuwait produced with stainless steel water tanks (to use ocean water in pumping). * 1958: 28-foot crew bus for Los Angeles County Fire Department * 1960: Bulldozer transport using Firecoach tractor for Los Angeles City Fire Department * 1965: Two open-cab rescue trucks using Firecoach chassis for Honolulu, Hawaii Fire Department * 1967: Heavy Utility tow truck using Firecoach chassis for Los Angeles Fire Department * 1971: Mobile hospital/ambulance for Walter Reed Army Hospital in Washington DC (using Supercoach body) * 1975: 2-axle trailer water tank/50-foot TeleSqurt for Tulare, California Fire DepartmentIn popular culture
During the first two seasons of the 1972-1977NBC
The National Broadcasting Company (NBC) is an American commercial broadcast television and radio network serving as the flagship property of the NBC Entertainment division of NBCUniversal, a subsidiary of Comcast. It is one of NBCUniversal's ...
/Universal
Universal is the adjective for universe.
Universal may also refer to:
Companies
* NBCUniversal, a media and entertainment company that is a subsidiary of Comcast
** Universal Animation Studios, an American Animation studio, and a subsidiary of N ...
television series ''Emergency!
''Emergency!'' is an American Action fiction, action-adventure medical drama television series jointly produced by Mark VII Limited and Universal Television. Debuting on NBC as a midseason replacement on January 15, 1972, replacing two situatio ...
,'' multiple Firecoaches of the Los Angeles County Fire Department
The Los Angeles County Fire Department (LACoFD) provides firefighting and emergency medical services for the unincorporated parts of Los Angeles County, California, as well as 59 cities through Contract city, contracting, including the city of ...
''(LACoFD)'' served as media props while in active service. On the television show, Engine 51 was portrayed by two different 1965 Firecoach Triple engines. Engine 60 (the fire engine stationed on the Universal set) was used for scenes filmed on the set; Engine 127 was used for scenes where location filming was completed.
In 1973, LACoFD purchased a large number of Ward LaFrance
The Ward LaFrance Truck Corporation was an American manufacturer of trucks and fire apparatus founded by Addison Ward LaFrance in 1916 in Elmira Heights, New York. The company ceased operations in 1979.
LaFrance was a relative of Truckson LaFran ...
P-80 Ambassador pumpers; the company donated an additional P-80 unit to Universal to serve as Engine 51, ending the need to take active fire engines out of service periodically for filming. While Engine #127 was destroyed in a later traffic accident, Engine #60 returned to its permanent assignment on the Universal set until its retirement in 1987.
The two versions of Engine 51, the 1965 Crown Firecoach (assigned as Engine #60; the final open-cab fire engine of Los Angeles) and the 1973 Ward LaFrance (donated to Universal for filming use) are now owned by the County of Los Angeles Fire Museum Association and have been fully restored.
References
{{Reflist Fire service vehicles Vehicles introduced in 1951 Mid-engined vehicles