Cross Of Jesus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 According to Christian tradition, the True Cross is the real
According to Christian tradition, the True Cross is the real

 The rediscovery of the True Cross, called the "Invention of the True Cross" (from the Latin ''inventio,'' "finding," a meaning obsolete in English except in this phrase), was traditionally attributed to Saint
The rediscovery of the True Cross, called the "Invention of the True Cross" (from the Latin ''inventio,'' "finding," a meaning obsolete in English except in this phrase), was traditionally attributed to Saint
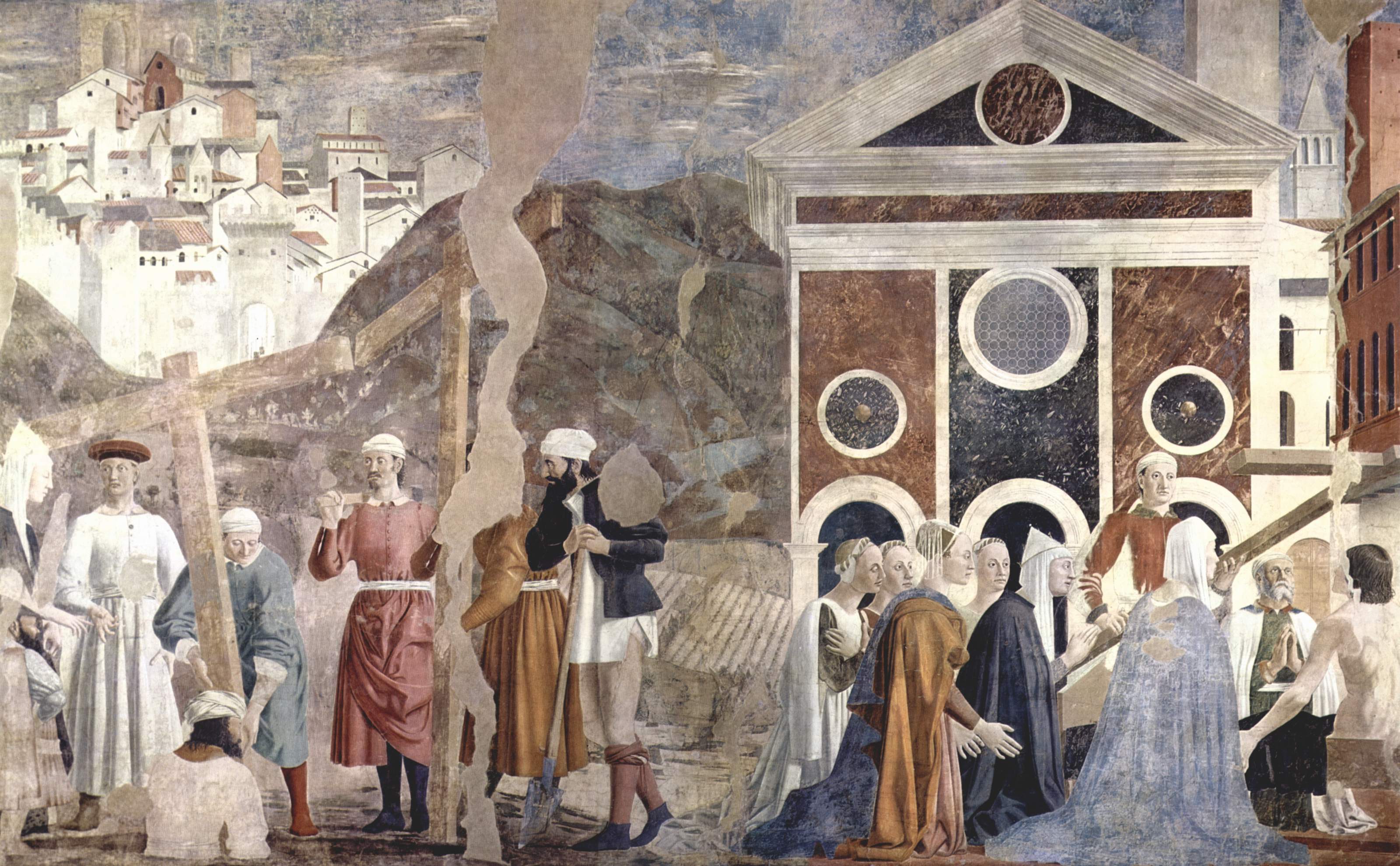 In his ''Ecclesiastical History'', nearly a century after Eusebius and forty years after Rufinus,
In his ''Ecclesiastical History'', nearly a century after Eusebius and forty years after Rufinus,
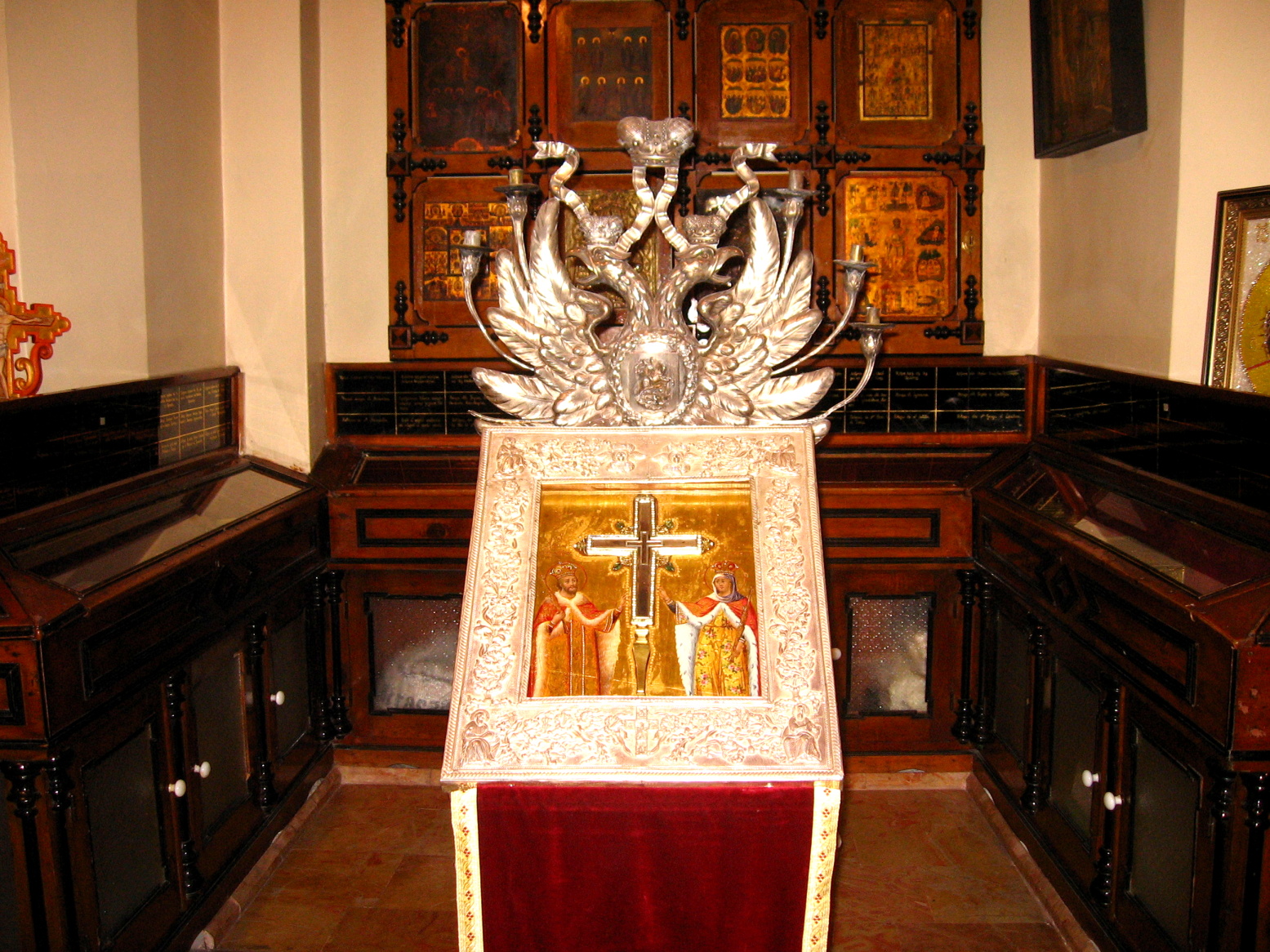
 When Jerusalem fell to the Muslims in 638, Heraclius retrieved the True Cross but did not attempt to retake the city.
Around 1009, the year in which Fatimid caliph
When Jerusalem fell to the Muslims in 638, Heraclius retrieved the True Cross but did not attempt to retake the city.
Around 1009, the year in which Fatimid caliph

Fernand Cabrol, "The true Cross"
a Catholic view
Relic of the True Cross in Wrocław, Poland
{{Authority control Catholic Church in Jerusalem Christian folklore Christian mythology Christian relics Christian terminology Christianity in Jerusalem Crucifixion of Jesus Jesus and history Relics associated with Jesus Individual crosses and crucifixes Church of the Holy Sepulchre Helena, mother of Constantine I
 According to Christian tradition, the True Cross is the real
According to Christian tradition, the True Cross is the real cross
A cross is a religious symbol consisting of two Intersection (set theory), intersecting Line (geometry), lines, usually perpendicular to each other. The lines usually run vertically and horizontally. A cross of oblique lines, in the shape of t ...
on which Jesus of Nazareth
Jesus ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the central figure of Christianity, the world's largest religi ...
was crucified.
It is related by numerous historical accounts and legends that Helen, the mother of Roman emperor Constantine the Great
Constantine I (27 February 27222 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a Constantine the Great and Christianity, pivotal ro ...
, recovered the True Cross at the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, also known as the Church of the Resurrection, is a fourth-century church in the Christian Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem. The church is the seat of the Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Jerusalem. Some ...
in Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
, when she travelled to the Holy Land
The term "Holy Land" is used to collectively denote areas of the Southern Levant that hold great significance in the Abrahamic religions, primarily because of their association with people and events featured in the Bible. It is traditionall ...
in the years 326–328. The late fourth-century historians Gelasius of Caesarea and Tyrannius Rufinus
Tyrannius Rufinus, also called Rufinus of Aquileia (; 344/345–411), was an early Christian monk, philosopher, historian, and theologian who worked to translate Greek patristic material, especially the work of Origen, into Latin.
Life
Rufinus ...
wrote that while Helen was there, she discovered the hiding place of three crosses that were believed to have been used at the crucifixion of Jesus and the two thieves, Dismas and Gestas, who were executed with him. To one cross was affixed the titulus bearing Jesus' name, but according to Rufinus, Helen was unsure of its legitimacy until a miracle
A miracle is an event that is inexplicable by natural or scientific lawsOne dictionary define"Miracle"as: "A surprising and welcome event that is not explicable by natural or scientific laws and is therefore considered to be the work of a divi ...
revealed that it was the True Cross. This event is celebrated on the liturgical calendar
The liturgical year, also called the church year, Christian year, ecclesiastical calendar, or kalendar, consists of the cycle of liturgical days and seasons that determines when feast days, including celebrations of saints, are to be obs ...
as the Feast of the Exaltation of the Cross (Roodmas
Roodmas (from Old English ''rood'' "rod", "cross" and ''mas'', Mass (liturgy), Mass; similar to the Christmas#Etymology, etymology of Christmas) is a name for the celebration of the Feast of the Cross. It has been applied to both historical comme ...
) by the Oriental Orthodox
The Oriental Orthodox Churches are Eastern Christianity, Eastern Christian churches adhering to Miaphysitism, Miaphysite Christology, with approximately 50 million members worldwide. The Oriental Orthodox Churches adhere to the Nicene Christian ...
, Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
, Persian, Roman Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
, Lutheran, and Anglican churches.
The Roman Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, and Oriental Orthodox churches, as well as denominations of the Church of the East
The Church of the East ( ) or the East Syriac Church, also called the Church of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, the Persian Church, the Assyrian Church, the Babylonian Church, the Chaldean Church or the Nestorian Church, is one of three major branches o ...
, have all claimed to possess relics
In religion, a relic is an object or article of religious significance from the past. It usually consists of the physical remains or personal effects of a saint or other person preserved for the purpose of veneration as a tangible memorial. Reli ...
of the True Cross as objects of veneration
Veneration (; ), or veneration of saints, is the act of honoring a saint, a person who has been identified as having a high degree of sanctity or holiness. Angels are shown similar veneration in many religions. Veneration of saints is practiced, ...
. Historians generally dispute the authenticity of the relic
In religion, a relic is an object or article of religious significance from the past. It usually consists of the physical remains or personal effects of a saint or other person preserved for the purpose of veneration as a tangible memorial. Reli ...
s, as do Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
and other Christian churches, who do not hold them in high regard.
Provenance

''The Golden Legend''
In the Latin-speaking traditions of Western Europe, the story of the True Cross was well established by the 13th century when, in 1260, it was recorded byJacobus de Voragine
Jacobus de Voragine, OP (13/16 July 1298) was an Italian chronicler and archbishop of Genoa. He was the author, or more accurately the compiler, of the '' Golden Legend'', a collection of the legendary lives of the greater saints of the mediev ...
, Bishop of Genoa, in the ''Golden Legend
The ''Golden Legend'' ( or ''Legenda sanctorum'') is a collection of 153 hagiographies by Jacobus de Voragine that was widely read in Europe during the Late Middle Ages. More than a thousand manuscripts of the text have survived.Hilary Maddo ...
''.
''The Golden Legend'' contains several versions of the origin of the True Cross. In ''The Life of Adam'', Voragine writes that the True Cross came from three trees which grew from three seeds from the "Tree of Mercy" which Seth
Seth, in the Abrahamic religions, was the third son of Adam and Eve. The Hebrew Bible names two of his siblings (although it also states that he had others): his brothers Cain and Abel. According to , Seth was born after Abel's murder by Cain, ...
collected and planted in the mouth of Adam
Adam is the name given in Genesis 1–5 to the first human. Adam is the first human-being aware of God, and features as such in various belief systems (including Judaism, Christianity, Gnosticism and Islam).
According to Christianity, Adam ...
's corpse.
In another account contained in "Of the Invention of the Holy Cross", Voragine writes that the True Cross came from a tree that grew from part of the Tree of Knowledge of Good and Evil
In Christianity and Judaism, the tree of the knowledge of good and evil (, ; ) is one of two specific trees in the story of the Garden of Eden in Genesis 2–3, along with the tree of life. Alternatively, some scholars have argued that the tre ...
, "the tree that Adam ate of", that Seth planted on Adam's grave where it "endured there unto the time of Solomon
Solomon (), also called Jedidiah, was the fourth monarch of the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), Kingdom of Israel and Judah, according to the Hebrew Bible. The successor of his father David, he is described as having been the penultimate ...
". Alternatively, it reached Solomon via Moses
In Abrahamic religions, Moses was the Hebrews, Hebrew prophet who led the Israelites out of slavery in the The Exodus, Exodus from ancient Egypt, Egypt. He is considered the most important Prophets in Judaism, prophet in Judaism and Samaritani ...
, who used it as the staff of Moses
The Staff of Moses, also known as the Rod of Moses or Staff of God, is mentioned in the Bible and Quran as a walking stick used by Moses. According to the Book of Exodus, the staff (, translated "rod" in the King James Bible) was used to produce ...
, and David
David (; , "beloved one") was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the third king of the United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament.
The Tel Dan stele, an Aramaic-inscribed stone erected by a king of Aram-Dam ...
, who planted it at Jerusalem. It was felled by Solomon to be a beam in his temple but not found suitable in the end.
After many centuries, the tree was cut down and the wood used to build a bridge over which the Queen of Sheba
The Queen of Sheba, also known as Bilqis in Arabic and as Makeda in Geʽez, is a figure first mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. In the original story, she brings a caravan of valuable gifts for Solomon, the fourth King of Israel and Judah. This a ...
passed on her journey to meet Solomon. So struck was she by the portent contained in the timber of the bridge that she fell on her knees and revered it. On her visit to Solomon, she told him that a piece of wood from the bridge would bring about the replacement of God's covenant with the Jewish people by a new order. Solomon, fearing the eventual destruction of his people, had the timber buried.
After fourteen generations, the wood taken from the bridge was fashioned into the Cross used to crucify
Crucifixion is a method of capital punishment in which the condemned is tied or nailed to a large wooden cross, beam or stake and left to hang until eventual death. It was used as a punishment by the Achaemenid Empire, Persians, Ancient Carthag ...
Jesus Christ. Voragine then goes on to describe its rediscovery by Helena, mother of the Emperor Constantine
Constantine I (27 February 27222 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a pivotal role in elevating the status of Christ ...
.
In the Late Middle Ages
The late Middle Ages or late medieval period was the Periodization, period of History of Europe, European history lasting from 1300 to 1500 AD. The late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period ( ...
and Early Renaissance
Renaissance art (1350 – 1620) is the painting, sculpture, and decorative arts of the period of European history known as the Renaissance, which emerged as a distinct style in Italy in about AD 1400, in parallel with developments which occurr ...
, there was wide general acceptance of the account of the cross's history as presented by Voragine. This general acceptance is displayed in numerous artworks on the subject, culminating in one of the most famous fresco
Fresco ( or frescoes) is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plaster, the painting become ...
cycles of the Renaissance, the '' Legend of the True Cross'' by Piero della Francesca
Piero della Francesca ( , ; ; ; – 12 October 1492) was an Italian Renaissance painter, Italian painter, mathematician and List of geometers, geometer of the Early Renaissance, nowadays chiefly appreciated for his art. His painting is charact ...
, which he painted on the walls of the chancel
In church architecture, the chancel is the space around the altar, including the Choir (architecture), choir and the sanctuary (sometimes called the presbytery), at the liturgical east end of a traditional Christian church building. It may termi ...
of the Church of San Francesco in Arezzo
Arezzo ( , ; ) is a city and ''comune'' in Italy and the capital of the Province of Arezzo, province of the same name located in Tuscany. Arezzo is about southeast of Florence at an elevation of Above mean sea level, above sea level. As of 2 ...
between 1452 and 1466, faithfully reproducing the episodes of ''The Golden Legend''.
Eastern Christianity
According to thesacred tradition
Sacred tradition, also called holy tradition, Anno Domini tradition or apostolic tradition, is a theological term used in Christian theology. According to this theological position, sacred Tradition and Scripture form one ''deposit'', so sacred T ...
of the Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, officially the Orthodox Catholic Church, and also called the Greek Orthodox Church or simply the Orthodox Church, is List of Christian denominations by number of members, one of the three major doctrinal and ...
the True Cross was made from three different types of wood: cedar, pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae.
''World Flora Online'' accepts 134 species-rank taxa (119 species and 15 nothospecies) of pines as cu ...
and cypress
Cypress is a common name for various coniferous trees or shrubs from the ''Cupressus'' genus of the '' Cupressaceae'' family, typically found in temperate climates and subtropical regions of Asia, Europe, and North America.
The word ''cypress'' ...
. This is an allusion to : "The glory of Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
shall come unto thee, the fir tree, the pine tree, and the box ypresstogether to beautify the place of my sanctuary, and I will make the place of my feet glorious." The link between this verse and the crucifixion lies in the words "the place of my feet", which is interpreted as referring to the footrest () on which Jesus' feet were nailed and which appears on the Orthodox cross. (Compare with the Jewish concepts of the Ark of the Covenant
The Ark of the Covenant, also known as the Ark of the Testimony or the Ark of God, was a religious storage chest and relic held to be the most sacred object by the Israelites.
Religious tradition describes it as a wooden storage chest decorat ...
or the Jerusalem Temple
The Temple in Jerusalem, or alternatively the Holy Temple (; , ), refers to the two religious structures that served as the central places of worship for Israelites and Jews on the modern-day Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem. Accor ...
as being God's footstool, and the prescribed Three Pilgrimage Festivals
The Three Pilgrimage Festivals or Three Pilgrim Festivals, sometimes known in English by their Hebrew name ''Shalosh Regalim'' (, or ), are three major festivals in Judaism—two in spring; Passover, 49 days later Shavuot (literally 'weeks', or ...
, in Hebrew ''aliya la-regel'', lit. ''ascending to the foot'').
Tradition of Lot's triple tree
A further tradition holds that these three trees from which the True Cross was constructed grew together in one spot. A traditional Orthodoxicon
An icon () is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, in the cultures of the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, Catholic Church, Catholic, and Lutheranism, Lutheran churches. The most common subjects include Jesus, Mary, mother of ...
in the Monastery of the Cross depicts Lot, the nephew of Abraham
Abraham (originally Abram) is the common Hebrews, Hebrew Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father who began the Covenant (biblical), covenanta ...
, watering the trees. According to tradition, these trees were used to construct the Temple in Jerusalem
The Temple in Jerusalem, or alternatively the Holy Temple (; , ), refers to the two religious structures that served as the central places of worship for Israelites and Jews on the modern-day Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem. Accord ...
("to beautify the place of my sanctuary"). Later, during Herod's reconstruction of the Temple, the wood from these trees was removed from the Temple and discarded, eventually being used to construct the cross on which Jesus was crucified ("and I will make the place of my feet glorious").
Empress Helena and the Cross
 The rediscovery of the True Cross, called the "Invention of the True Cross" (from the Latin ''inventio,'' "finding," a meaning obsolete in English except in this phrase), was traditionally attributed to Saint
The rediscovery of the True Cross, called the "Invention of the True Cross" (from the Latin ''inventio,'' "finding," a meaning obsolete in English except in this phrase), was traditionally attributed to Saint Helena, mother of Constantine I
Flavia Julia Helena (; , ''Helénē''; – 330), also known as Helena of Constantinople and in Christianity as Saint Helena, was an ''List of Augustae, Augusta'' of the Roman Empire and mother of Emperor Constantine the Great. She was b ...
, an account that emerged over time.
Eusebius
The ''Life of Constantine
''Life of Constantine the Great'' (; ) is a panegyric written in Greek in honor of Constantine the Great by Eusebius of Caesarea in the 4th century AD. It was never completed due to the death of Eusebius in 339. The work provides scholars with ...
'' by Eusebius of Caesarea
Eusebius of Caesarea (30 May AD 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilius, was a historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christian polemicist from the Roman province of Syria Palaestina. In about AD 314 he became the bishop of Caesarea Maritima. ...
(died 339) is the earliest and main historical source on the rediscovery of the Tomb of Jesus and the construction of the first church at the site, but does not mention anything concerning the True Cross. Eusebius describes how the site of the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, also known as the Church of the Resurrection, is a fourth-century church in the Christian Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem. The church is the seat of the Greek Orthodox Patriarchate of Jerusalem. Some ...
, once a site of veneration for the early Christian Church in Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
, had been covered over with earth and a temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a place of worship, a building used for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. By convention, the specially built places of worship of some religions are commonly called "temples" in Engli ...
of Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
had been built on top. Although Eusebius does not say as much, this would probably have been done as part of Hadrian
Hadrian ( ; ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. Hadrian was born in Italica, close to modern Seville in Spain, an Italic peoples, Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his branch of the Aelia gens, Aelia '' ...
's 130 reconstruction of Jerusalem into the Roman city of Aelia Capitolina
Aelia Capitolina (Latin: ''Colonia Aelia Capitolina'' ɔˈloːni.a ˈae̯li.a kapɪtoːˈliːna was a Roman colony founded during the Roman emperor Hadrian's visit to Judaea in 129/130 CE. It was founded on the ruins of Jerusalem, which had b ...
, following Jerusalem's destruction at the end of the Jewish Revolt in the year 70, and in connection with Bar Kokhba's revolt of 132–135. Following his conversion to Christianity, Emperor Constantine ordered in about 325–326 that the site be uncovered and instructed Macarius Macarius is a Latinization (literature), Latinized form of the old Greek given name Makários (Μακάριος), meaning "happy, fortunate, blessed"; compare the Latin Beatus (disambiguation), ''beatus'' and Felix (name) , ''felix''. Ancient Gree ...
, Bishop of Jerusalem, to build a church on the site. Eusebius' work contains details about the demolition of the pagan temple and the erection of the church, but does not mention anywhere the finding of the True Cross.
Cyril of Jerusalem
Perhaps the earliest witness to the tradition of the True Cross wasCyril
Cyril (also Cyrillus or Cyryl) is a masculine given name. It is derived from the Greek language, Greek name (''Kýrillos''), meaning 'lordly, masterful', which in turn derives from Greek (''kýrios'') 'lord'. There are various variant forms of t ...
, Bishop of Jerusalem (c. 350-386). In the fourth of his Catechetical Lectures, which are dated to around the year 350, he says that "the whole world has since been filled with pieces of the wood of the Cross." This text relates that pieces of the cross were dispersed as relics, but offers no information about the discovery of the cross itself. Elsewhere, in a letter to Emperor Constantius Constantius may refer to:
__NOTOC__ Roman people
* Constantius I "Chlorus" (–306), Western Roman emperor from 305 to 306
* Julius Constantius (died 337), consul in 335, son of Constantius I
* Constantius Gallus (325–354), ''caesar'' from 351 to ...
, Cyril only relates that the cross was found during the reign of Constantine..
Gelasius and Rufinus
About forty years after Cyril, there was a fully developed story about how the True Cross was discovered. Cyril's nephew Gelasius of Caesarea recorded the account in a now lost Greek Ecclesiastical History prior to his death in 395. This version was adapted circa 402 in Rufinus of Aquileia's Latin additions to Eusebius' Church History. In this narrative, Helena went to Jerusalem in search of the relic and was made aware of its location by a heavenly sign. She tore down the temple ofAphrodite
Aphrodite (, ) is an Greek mythology, ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, procreation, and as her syncretism, syncretised Roman counterpart , desire, Sexual intercourse, sex, fertility, prosperity, and ...
that had been built there, and beneath the rubble found three crosses. The cross of Jesus was identified, with the aid of Bishop Macarius of Jerusalem
Macarius I ( ''Makarios I Hierosolymōn'') was Bishop of Jerusalem from 312 to shortly before 335, according to Sozomen. He is venerated as a saint within the Eastern Orthodox Church and Roman Catholic Church.
Athanasius, in one of his ora ...
, by its miraculous affecting of a cure for a mortally ill woman. A Church was then built on the spot and the relic was divided, with part staying in Jerusalem and part given to Constantine along with the nails.
Socrates Scholasticus
 In his ''Ecclesiastical History'', nearly a century after Eusebius and forty years after Rufinus,
In his ''Ecclesiastical History'', nearly a century after Eusebius and forty years after Rufinus, Socrates Scholasticus
Socrates of Constantinople ( 380 – after 439), also known as Socrates Scholasticus (), was a 5th-century Greek Christian church historian, a contemporary of Sozomen and Theodoret.
He is the author of a ''Historia Ecclesiastica'' ("Church Hi ...
(died c. 440) gives a description of the discovery later repeated by Sozomen
Salamanes Hermias Sozomenos (; ; c. 400 – c. 450 AD), also known as Sozomen, was a Roman lawyer and historian of the Christian Church.
Family and home
Sozoman was born around 400 in Bethelia, a small town near Gaza, into a wealthy Christia ...
and Theodoret
Theodoret of Cyrus or Cyrrhus (; AD 393 – 458/466) was an influential theologian of the School of Antioch, biblical commentator, and Christian bishop of Cyrrhus (423–457).
He played a pivotal role in several 5th-century Byzantine ...
. Socrates' account is very similar to Rufinus'. In it he describes how Helena Augusta, Constantine's aged mother, had the pagan temple destroyed and the Sepulchre uncovered, whereupon three crosses, the titulus, and the nails from Jesus's crucifixion were uncovered as well. In Socrates's version of the story, Macarius had the three crosses placed in turn on a deathly ill woman. This woman recovered at the touch of the third cross, which was taken as a sign that this was the cross of Christ, the new Christian symbol. Socrates also reports that, having also found the cross's nails, Helena sent these to Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
, where they were incorporated into the emperor's helmet and the bridle of his horse.
Sozomen
In his ''Ecclesiastical History'',Sozomen
Salamanes Hermias Sozomenos (; ; c. 400 – c. 450 AD), also known as Sozomen, was a Roman lawyer and historian of the Christian Church.
Family and home
Sozoman was born around 400 in Bethelia, a small town near Gaza, into a wealthy Christia ...
(died ) gives essentially the same version as Socrates. Without further attribution, he also adds that it was said that the location of the Sepulchre was "disclosed by a Hebrew who dwelt in the East and who derived his information from some documents which had come to him by paternal inheritance"although Sozomen himself disputes this accountso that a dead person was also revived by the touch of the Cross. Later popular versions of this story state that the Jew who assisted Helena was named Jude or Judas but later converted to Christianity and took the name Kyriakos.
Theodoret

Theodoret
Theodoret of Cyrus or Cyrrhus (; AD 393 – 458/466) was an influential theologian of the School of Antioch, biblical commentator, and Christian bishop of Cyrrhus (423–457).
He played a pivotal role in several 5th-century Byzantine ...
(died ) in his ''Ecclesiastical History'' Chapter xvii gives what would become the standard version of the finding of the True Cross:
With the Cross were also found the Holy Nails, which Helena took with her back to Constantinople. According to Theodoret, "She had part of the cross of our Saviour conveyed to the palace. The rest was enclosed in a covering of silver, and committed to the care of the bishop of the city, whom she exhorted to preserve it carefully, in order that it might be transmitted uninjured to posterity."
Syriac tradition
Another popular ancient version from the Syriac tradition replaced Helena with a fictitious first-century empress named Protonike, who is said to be the wife of emperorClaudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; ; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54), or Claudius, was a Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus and Ant ...
. This story, which originated in Edessa in the 430s, was transmitted in the so-called ''Doctrina Addai'', which was believed to be written by Thaddeus of Edessa
According to Eastern Christian tradition, Addai of Edessa ( Syriac: ܡܪܝ ܐܕܝ, Mar Addai or Mor Aday sometimes Latinized Addeus) or Thaddeus of Edessa was one of the seventy disciples of Jesus.
Life
Based on various Eastern Christian ...
(Addai in Syriac texts), one of the seventy disciples. The narrative retrojected the Helena version to the first century. In the story, Protonike traveled to Jerusalem after she met Simon Peter
Saint Peter (born Shimon Bar Yonah; 1 BC – AD 64/68), also known as Peter the Apostle, Simon Peter, Simeon, Simon, or Cephas, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus and one of the first leaders of the early Christian Church. He appears repe ...
in Rome. She was shown around the city by James, brother of Jesus
James the Just, or a variation of James, brother of the Lord ( from , and , , can also be Anglicized as "Jacob"), was, according to the New Testament, a brother of Jesus. He was the first Jewish bishop of Jerusalem. Traditionally, it is bel ...
, until she discovered the cross after it healed her daughter of some illness. She then converted to Christianity and had a church built on Golgotha
Calvary ( or ) or Golgotha () was a site immediately outside Jerusalem's walls where, according to Christianity's four canonical gospels, Jesus was crucified.
Since at least the early medieval period, it has been a destination for pilgrimage. ...
. Aside from the Syriac tradition, the Protonike version was also cited by Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian diaspora, Armenian communities around the ...
sources.
Catholic commemoration
According to the 1955 Roman Catholic Marian Missal, Helena went to Jerusalem to search for the True Cross and found it 14 September 320. In the 8th century, the Feast of the Finding was transferred to 3 May and 14 September became the celebration of the "Exaltation of the Cross
The Feast of the Holy Cross, or Feast of the Cross, commemorates True Cross, the cross used in the crucifixion of Jesus. In the Christianity, Christian liturgical calendar, there are several different celebrations which honor and celebrate the ...
", the commemoration of a victory over the Persians
Persians ( ), or the Persian people (), are an Iranian ethnic group from West Asia that came from an earlier group called the Proto-Iranians, which likely split from the Indo-Iranians in 1800 BCE from either Afghanistan or Central Asia. They ...
by the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
Heraclius
Heraclius (; 11 February 641) was Byzantine emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the Exarch of Africa, led a revolt against the unpopular emperor Phocas.
Heraclius's reign was ...
, as a result of which the relic was recovered and returned to Jerusalem.
The True Cross in Jerusalem
Late antiquity
The silver reliquary that was left at the Basilica of the Holy Sepulchre in care of the bishop of Jerusalem was exhibited periodically to the faithful. In the 380s a nun named Egeria who was travelling onpilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a travel, journey to a holy place, which can lead to a personal transformation, after which the pilgrim returns to their daily life. A pilgrim (from the Latin ''peregrinus'') is a traveler (literally one who has come from afar) w ...
described the veneration of the True Cross at Jerusalem in a long letter known as her ''Itinerary'' (), which she sent back to her convent:
Before long, but perhaps not until after the visit of Egeria, it was possible also to venerate the crown of thorns
According to the New Testament, a woven crown of thorns ( or ) was placed on the head of Jesus during the Passion of Jesus, events leading up to his crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion. It was one of the Arma Christi, instruments of the Passion, e ...
, the pillar at which Christ was scourged, and the lance
The English term lance is derived, via Middle English '' launce'' and Old French '' lance'', from the Latin '' lancea'', a generic term meaning a wikt:lancea#Noun">lancea'', a generic term meaning a spear">wikt:lancea#Noun">lancea'', a generi ...
that pierced his side.
The Perso-Byzantine Wars
TheSassanid
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranian peoples, Iranians"), was an List of monarchs of Iran, Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, th ...
Emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
Khosrau II
Khosrow II (spelled Chosroes II in classical sources; and ''Khosrau''), commonly known as Khosrow Parviz (New Persian: , "Khosrow the Victorious"), is considered to be the last great Sasanian King of Kings (Shahanshah) of Iran, ruling from 590 ...
("Chosroes") removed the part of the cross held in Jerusalem as a trophy after he captured the city in 614. Thirteen years later, in 628, the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
Heraclius
Heraclius (; 11 February 641) was Byzantine emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the Exarch of Africa, led a revolt against the unpopular emperor Phocas.
Heraclius's reign was ...
defeated Khosrau and regained the relic from Shahrbaraz
Shahrbaraz (also spelled Shahrvaraz or Shahrwaraz; New Persian: ) was shah (king) of the Sasanian Empire from 27 April 630 to 9 June 630. He usurped the throne from Ardashir III, and was killed by Iranian nobles after forty days. Before usurp ...
. He placed the cross in Constantinople at first, before restoring it to Jerusalem on 21 March 630. Some scholars disagree with this narrative, with Constantin Zuckerman going as far as to suggest that the True Cross was actually lost by the Persians and that the wood contained in the allegedly still sealed reliquary brought to Jerusalem by Heraclius in 629 was a fake. In his analysis, the hoax was designed to serve the political purposes of both Heraclius and his former foe, recently turned ally and father-in-law, the Persian general and soon-king Shahrbaraz.
Islamic rule and the Crusades
 When Jerusalem fell to the Muslims in 638, Heraclius retrieved the True Cross but did not attempt to retake the city.
Around 1009, the year in which Fatimid caliph
When Jerusalem fell to the Muslims in 638, Heraclius retrieved the True Cross but did not attempt to retake the city.
Around 1009, the year in which Fatimid caliph Al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah
Abu Ali al-Mansur (; 13 August 985 – 13 February 1021), better known by his regnal name al-Hakim bi-Amr Allah (), was the sixth Fatimid caliph and 16th Ismaili imam (996–1021). Al-Hakim is an important figure in a number of Shia Ism ...
ordered the destruction of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, other churches, synagogues, Torah scrolls and other non-Muslim religious artifacts and buildings in and around Jerusalem, were destroyed starting on 28 September 1009 on the orders of the Fatimid Caliph Al-Haki ...
, Christians in Jerusalem hid part of the cross and it remained hidden until the city was taken by the European soldiers of the First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the Middle Ages. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Muslim conquest ...
. Arnulf Malecorne, the first Latin patriarch of Jerusalem
The Latin Patriarchate of Jerusalem () is the Latin Catholic ecclesiastical patriarchate in Jerusalem, officially seated in the Church of the Holy Sepulchre. The Latin Patriarch of Jerusalem is the archbishop of Latin Church Catholics of th ...
, had the Greek Orthodox priests who were supposedly in possession of the Cross tortured in order to reveal its location. The relic that Arnulf recovered was a small fragment of wood embedded in a golden cross, and it became the most sacred relic of the Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem, also known as the Crusader Kingdom, was one of the Crusader states established in the Levant immediately after the First Crusade. It lasted for almost two hundred years, from the accession of Godfrey of Bouillon in 1 ...
, with none of the controversy that had followed their discovery of the Holy Lance
The Holy Lance, also known as the Spear of Longinus (named after Longinus, Saint Longinus), the Spear of Destiny, or the Holy Spear, is alleged to be the lance that pierced the side of Jesus as he hung on the cross during his Crucifixion of Jes ...
in Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; , ) "Antioch on Daphne"; or "Antioch the Great"; ; ; ; ; ; ; . was a Hellenistic Greek city founded by Seleucus I Nicator in 300 BC. One of the most important Greek cities of the Hellenistic period, it served as ...
. Displayed in a jewel-encrusted housing of gold and silver, it was housed in a northern chapel at the Church of the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, also known as the Church of the Resurrection, is a fourth-century church in the Christian Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem, Old City of Jerusalem. The church is the seat of the Greek Orthodox Patriarchat ...
, overseen by its canons and protected by its knights
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of a knighthood by a head of state (including the pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church, or the country, especially in a military capacity.
The concept of a knighthood ...
. A second chapel beside it was overseen by the Syrian Orthodox
The Syriac Orthodox Church (), also informally known as the Jacobite Church, is an Oriental Orthodox Christian denomination, denomination that originates from the Church of Antioch. The church currently has around 4-5 million followers. The ch ...
and displayed another reliquary holding their fragment of the cross.. The Latin fragment of the cross was repeatedly carried into battle against the Muslims.
Over the course of each liturgical calendar
The liturgical year, also called the church year, Christian year, ecclesiastical calendar, or kalendar, consists of the cycle of liturgical days and seasons that determines when feast days, including celebrations of saints, are to be obs ...
, the Latin patriarch would oversee mass at the various churches around Jerusalem corresponding to the part of Jesus's life being celebrated. The celebrations of Holy Week
Holy Week () commemorates the seven days leading up to Easter. It begins with the commemoration of Triumphal entry into Jerusalem, Christ's triumphal entry into Jerusalem on Palm Sunday, marks the betrayal of Jesus on Spy Wednesday (Holy Wednes ...
closely involved the Holy Sepulchre and its fragment of the True Cross. During lauds
Lauds is a canonical hour of the Divine office. In the Roman Rite Liturgy of the Hours it is one of the major hours, usually held after Matins, in the early morning hours (between 3:00:00 and 5:59:59).
Name
The name is derived from the three la ...
on each Good Friday
Good Friday, also known as Holy Friday, Great Friday, Great and Holy Friday, or Friday of the Passion of the Lord, is a solemn Christian holy day commemorating the crucifixion of Jesus and his death at Calvary (Golgotha). It is observed during ...
, the Latin relic was carried across the church to the chapel of Calvary
Calvary ( or ) or Golgotha () was a site immediately outside Jerusalem's walls where, according to Christianity's four canonical gospels, Jesus was crucified.
Since at least the early medieval period, it has been a destination for pilgrimage. ...
on its south side, the supposed site of Jesus's crucifixion, and then venerated by the barefoot patriarch, the sepulchre's canons, and the assembled pilgrims until sext
Sext is a canonical hour of the Divine Office in the liturgies of many Christian denominations. It consists mainly of psalms and is held around noon. Its name comes from Latin and refers to the sixth hour of the day after dawn. With Terce, None ...
. Prior to the liturgy on Holy Saturday
Holy Saturday (), also known as Great and Holy Saturday, Low Saturday, the Great Sabbath, Hallelujah Saturday, Saturday of the Glory, Easter Eve, Joyous Saturday, the Saturday of Light, Good Saturday, or Black Saturday, among other names, is t ...
, four pilgrims selected by the patriarchpreceded by a thurifer
A thurible (via Old French from Medieval Latin ) is a metal censer, incense burner suspended from chains, in which incense is burned during worship services. It is used in Christian churches, including those of the Catholic Church, Roman Cathol ...
and 2 acolyte
An acolyte is an assistant or follower assisting the celebrant in a religious service or procession. In many Christian denominations, an acolyte is anyone performing ceremonial duties such as lighting altar candles. In others, the term is used f ...
scarried the Latin relic from its chapel to the edicule of the Holy Sepulchre while the congregation waited with unlit candles. A New Fire would "spontaneously" light within the sepulchre. The crossbearer then would light his own candle from it, transit the entire church, and light the candle of the waiting patriarch. The candles of the canons and then the congregation were then lit from one to another, gradually filling the church with light..
After King BaldwinI of Jerusalem presented King SigurdI of Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of the Kingdom of ...
with a splinter of the True Cross following the Norwegian Crusade in 1110, the Cross was captured by Saladin
Salah ad-Din Yusuf ibn Ayyub ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known as Saladin, was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from a Kurdish family, he was the first sultan of both Egypt and Syria. An important figure of the Third Crusade, h ...
during the Battle of Hattin
The Battle of Hattin took place on 4 July 1187, between the Crusader states of the Levant and the forces of the Ayyubid sultan Saladin. It is also known as the Battle of the Horns of Hattin, due to the shape of the nearby extinct volcano of ...
in 1187. While some Christian rulers like Richard the Lionheart
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic language">Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'st ...
of England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
, the Byzantine emperor
The foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, which Fall of Constantinople, fell to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised s ...
IsaacII, and King Tamar of Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
sought to ransom it from Saladin, the cross was not returned. In 1219 the True Cross was offered to the Knights Templar by Al-Kamil in exchange for lifting the siege of Damietta
Damietta ( ' ) is a harbor, port city and the capital of the Damietta Governorate in Egypt. It is located at the Damietta branch, an eastern distributary of the Nile Delta, from the Mediterranean Sea, and about north of Cairo. It was a Cath ...
. The cross was never delivered as Al-Kamil did not, in fact, have it. Subsequently the cross disappeared from historical records. The True Cross was last seen in the city of Damascus following the Battle of Hattin.
21st-century status
The Greek Orthodox church presents a small True Cross relic shown in the Greek Treasury within the Church of the Holy Sepulchre at the foot ofGolgotha
Calvary ( or ) or Golgotha () was a site immediately outside Jerusalem's walls where, according to Christianity's four canonical gospels, Jesus was crucified.
Since at least the early medieval period, it has been a destination for pilgrimage. ...
. The Syriac Orthodox Church also claims a small relic of the True Cross (held in the Monastery of Saint Mark in Jerusalem), as does the Armenian Apostolic Church
The Armenian Apostolic Church () is the Autocephaly, autocephalous national church of Armenia. Part of Oriental Orthodoxy, it is one of the most ancient Christianity, Christian churches. The Armenian Apostolic Church, like the Armenian Catholic ...
(in Armenia). According to the 15th-century ''Book of Ṭeff Grains'', the emperor
The word ''emperor'' (from , via ) can mean the male ruler of an empire. ''Empress'', the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), mother/grandmother (empress dowager/grand empress dowager), or a woman who rules ...
DawitI received four fragments of the True Cross around the year 1400 from Coptic Christians
Copts (; ) are a Christian ethnoreligious group native to Northeast Africa who have primarily inhabited the area of modern Egypt since antiquity. They are, like the broader Egyptian population, descended from the ancient Egyptians. Copts p ...
as thanks for his protection. The Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church
The Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church () is the largest of the Oriental Orthodox Churches. One of the few Christian churches in Africa originating before European colonization of the continent, the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church dates bac ...
claims these relics are still held at either Egziabher Ab or Tekle Maryam, two monasteries near the former imperial cemetery on Amba Geshen.
Dispersion of relics
An inscription of 359 found at Tixter, in the neighbourhood of Sétif inMauretania
Mauretania (; ) is the Latin name for a region in the ancient Maghreb. It extended from central present-day Algeria to the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, encompassing northern present-day Morocco, and from the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean in the ...
(in today Algeria), was said to mention, in an enumeration of relics, a fragment of the True Cross, according to an entry in ''Roman Miscellanies'', X, 441.
Fragments of the Cross were broken up, and the pieces were widely distributed; in 348, in one of his ''Catecheses'', Cyril of Jerusalem remarked that the "whole Earth is full of the relics of the Cross of Christ" and, in another, "The holy wood of the Cross bears witness, seen among us to this day, and from this place now almost filling the whole world, by means of those who in faith take portions from it." Egeria's account testifies to how highly these relics of the crucifixion were prized. John Chrysostom
John Chrysostom (; ; – 14 September 407) was an important Church Father who served as archbishop of Constantinople. He is known for his preaching and public speaking, his denunciation of abuse of authority by both ecclesiastical and p ...
relates that fragments of the True Cross were kept in golden reliquaries, "which men reverently wear upon their persons." Even two Latin inscriptions around 350 from today's Algeria testify to the keeping and admiration of small particles of the cross. Around the year 455, Juvenal
Decimus Junius Juvenalis (), known in English as Juvenal ( ; 55–128), was a Roman poet. He is the author of the '' Satires'', a collection of satirical poems. The details of Juvenal's life are unclear, but references in his works to people f ...
Patriarch of Jerusalem sent to Pope Leo I
Pope Leo I () ( 391 – 10 November 461), also known as Leo the Great (; ), was Bishop of Rome from 29 September 440 until his death on 10 November 461. He is the first of the three Popes listed in the ''Annuario Pontificio'' with the title "the ...
a fragment of the "precious wood", according to the ''Letters'' of Pope Leo. A portion of the cross was taken to Rome in the seventh century by Pope Sergius I
Pope Sergius I (8 September 701) was the bishop of Rome from 15 December 687 to his death on 8 September 701, and is revered as a saint by the Roman Catholic Church. He was elected at a time when two rivals, Paschal and Theodore, were locked ...
, who was of Byzantine origin. "In the small part is power of the whole cross", says an inscription
Epigraphy () is the study of inscriptions, or epigraphs, as writing; it is the science of identifying graphemes, clarifying their meanings, classifying their uses according to dates and cultural contexts, and drawing conclusions about the wr ...
in the Felix Basilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica (Greek Basiliké) was a large public building with multiple functions that was typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek Eas ...
of Nola
Nola is a town and a municipality in the Metropolitan City of Naples, Campania, southern Italy. It lies on the plain between Mount Vesuvius and the Apennines. It is traditionally credited as the diocese that introduced bells to Christian worship.
...
, built by bishop Paulinus at the beginning of 5th century. The cross particle was inserted in the altar.
The Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
poem
Poetry (from the Greek language, Greek word ''poiesis'', "making") is a form of literature, literary art that uses aesthetics, aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language to evoke meaning (linguistics), meanings in addition to, or in ...
''Dream of the Rood
''The'' ''Dream of the Rood'' is one of the Christian poems in the corpus of Old English literature and an example of the genre of dream poetry. Like most Old English poetry, it is written in alliterative verse. The word ''Rood'' is derived f ...
'' mentions the finding of the cross and the beginning of the tradition of the veneration of its relics. The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons.
The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the ninth century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of ...
'' also talks of King Alfred receiving a fragment of the cross from Pope Marinus (see: Annal Alfred the Great, year 883). Although it is possible, the poem need not be referring to this specific relic or have this incident as the reason for its composition. However, there is a later source that speaks of a bequest made to the 'Holy Cross' at Shaftesbury Abbey
Shaftesbury Abbey was an abbey that housed nuns in Shaftesbury, Dorset. It was founded in about 888, and Dissolution of the monasteries, dissolved in 1539 during the English Reformation by the order of Thomas Cromwell, minister to King Henry VI ...
in Dorset; Shaftesbury abbey was founded by King Alfred, supported with a large portion of state funds and given to the charge of his own daughter when he was aliveit is conceivable that if Alfred really received this relic, that he may have given it to the care of the nuns at Shaftesbury.
Most of the very small relics of the True Cross in Europe came from Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
. The city was captured and sacked by the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
in 1204. The ''Chronica Regia Coloniensis
The ''Chronica regia Coloniensis'' ("Royal Chronicle of Cologne", German: ''Kölner Königschronik''), also called the ''Annales Colonienses maximi'', is an anonymous medieval Latin chronicle that covers the years 576 to 1202. The original chronic ...
'' relates that "After the conquest of the city Constantinople inestimable wealth was found: incomparably precious jewels and also a part of the cross of the Lord, which Helena transferred from Jerusalem and hich
Ij () is a village in Golabar Rural District of the Central District in Ijrud County, Zanjan province, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq ...
was decorated with gold and precious jewels. There it attained hehighest admiration. It was carved up by the present bishops and was divided with other very precious relics among the knights; later, after their return to the homeland, it was donated to churches and monasteries." The French knight Robert de Clari wrote that "within this chapel were found many precious relics; for therein were found two pieces of the True Cross, as thick as a man's leg and a fathom
A fathom is a unit of length in the imperial and the U.S. customary systems equal to , used especially for measuring the depth of water. The fathom is neither an international standard (SI) unit, nor an internationally accepted non-SI unit. H ...
in length."
The misplacement of which particular class relics of the Holy Cross (and others in general) belong to, either as a result of confusion or exaggeration; and the outright forgery of relics, was a recurring controversy during the Medieval Age. This happened, often in order to attract pilgrims; or even to facilitate the lucrative practice of simony
Simony () is the act of selling church offices and roles or sacred things. It is named after Simon Magus, who is described in the Acts of the Apostles as having offered two disciples of Jesus payment in exchange for their empowering him to imp ...
.
By the end of the Middle Ages so many churches claimed to possess relics of the True Cross, that John Calvin
John Calvin (; ; ; 10 July 150927 May 1564) was a French Christian theology, theologian, pastor and Protestant Reformers, reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system of C ...
is famously said to have remarked that there was enough wood in them to fill a ship:
Conflicting with this is the finding of Charles Rohault de Fleury, who, in his ''Mémoire sur les instruments de la Passion'' of 1870, made a study of the relics in reference to the criticisms of Calvin and Erasmus
Desiderius Erasmus Roterodamus ( ; ; 28 October c. 1466 – 12 July 1536), commonly known in English as Erasmus of Rotterdam or simply Erasmus, was a Dutch Christian humanist, Catholic priest and Catholic theology, theologian, educationalist ...
. He drew up a catalogue of all known relics of the True Cross showing that, in spite of what various authors have claimed, the fragments of the Cross brought together again would not reach one-third that of a cross which has been supposed to have been in height, with transverse branch of wide, proportions not at all abnormal. He calculated: supposing the Cross to have been of pine-wood (based on his microscopic analysis of the fragments) and giving it a weight of about seventy-five kilogrammes, we find the original volume of the cross to be . The total known volume of known relics of the True Cross, according to his catalogue, amounts to approximately (more specifically 3,942,000 cubic millimetres), leaving a volume of , almost 98%, lost, destroyed, or from which is otherwise unaccounted. Four cross particles – of ten particles with surviving documentary provenances by Byzantine emperors – from European churches, i.e. Santa Croce in Rome, Caravaca de la Cruz, Notre Dame, Paris, Pisa Cathedral
Pisa Cathedral (), officially the Primatial Metropolitan Cathedral of the Assumption of Mary (), is a medieval Catholic cathedral dedicated to the Assumption of the Virgin Mary, in the Piazza dei Miracoli in Pisa, Italy, the oldest of the three s ...
and Florence Cathedral
Florence Cathedral (), formally the Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Flower ( ), is the cathedral of the Catholic Archdiocese of Florence in Florence, Italy. Commenced in 1296 in the Gothic style to a design of Arnolfo di Cambio and completed b ...
, were microscopically examined. "The pieces came all together from olive." It is possible that many alleged pieces of the True Cross are forgeries, created by travelling merchants in the Middle Ages, during which period a thriving trade in manufactured relics went on.
Smyrnakis notes that the largest surviving portion, of 870,760 cubic millimetres, is preserved in the Monastery of Koutloumousiou on Mount Athos
Mount Athos (; ) is a mountain on the Athos peninsula in northeastern Greece directly on the Aegean Sea. It is an important center of Eastern Orthodoxy, Eastern Orthodox monasticism.
The mountain and most of the Athos peninsula are governed ...
, and also mentions the preserved relics in Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
(consisting of 537,587 cubic millimetres), in Brussels
Brussels, officially the Brussels-Capital Region, (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) is a Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium#Regions, region of Belgium comprising #Municipalit ...
(516,090 cubic millimetres), in Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
(445,582 cubic millimetres), in Ghent
Ghent ( ; ; historically known as ''Gaunt'' in English) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the Provinces of Belgium, province ...
(436,450 cubic millimetres) and in Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
(237,731 cubic millimetres).
Santo Toribio de Liébana in Spain is also said to hold the largest of these pieces and is one of the most visited Roman Catholic pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a travel, journey to a holy place, which can lead to a personal transformation, after which the pilgrim returns to their daily life. A pilgrim (from the Latin ''peregrinus'') is a traveler (literally one who has come from afar) w ...
sites. In Asia, the only place where the other part of the True Cross is located is in the Monasterio de Tarlac at San Jose, Tarlac, Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
.
The Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church
The Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church () is the largest of the Oriental Orthodox Churches. One of the few Christian churches in Africa originating before European colonization of the continent, the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church dates bac ...
also claims to have the right wing of the true cross buried in the monastery of Gishen Mariam. This piece was gifted by the Venetian Republic
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 ...
to the Ethiopian Empire
The Ethiopian Empire, historically known as Abyssinia or simply Ethiopia, was a sovereign state that encompassed the present-day territories of Ethiopia and Eritrea. It existed from the establishment of the Solomonic dynasty by Yekuno Amlak a ...
in the medieval period and remained in the Atse Emperor's personal possession into the 18th century, even being lost in battle, before being buried atop Amba Geshen.
In 2016, a relic of the True Cross held by the Waterford Cathedral in Ireland was radiocarbon-dated
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for Chronological dating, determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of carbon-14, radiocarbon, a radioactive Isotop ...
to the 11th century by Oxford University
The University of Oxford is a collegiate research university in Oxford, England. There is evidence of teaching as early as 1096, making it the oldest university in the English-speaking world and the second-oldest continuously operating u ...
.
In February 2020, the Sevastopol
Sevastopol ( ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea and a major port on the Black Sea. Due to its strategic location and the navigability of the city's harbours, Sevastopol has been an important port and naval base th ...
district archpriest Sergiy Khalyuta said that a piece of the True Cross was bought by a donor, and was to be placed on board the Russian missile cruiser ''Moskva'', which has a chapel on board. The ship sank in April 2022 during the Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, , starting the largest and deadliest war in Europe since World War II, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, conflict between the two countries which began in 2014. The fighting has caused hundreds of thou ...
. After the sinking, there was speculation that the fragment may have gone down with the ship.
Veneration

John Chrysostom
John Chrysostom (; ; – 14 September 407) was an important Church Father who served as archbishop of Constantinople. He is known for his preaching and public speaking, his denunciation of abuse of authority by both ecclesiastical and p ...
wrote homilies on the three crosses:
The Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
, Oriental Orthodox
The Oriental Orthodox Churches are Eastern Christianity, Eastern Christian churches adhering to Miaphysitism, Miaphysite Christology, with approximately 50 million members worldwide. The Oriental Orthodox Churches adhere to the Nicene Christian ...
, Anglican
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the ...
and some Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
churches celebrate the Feast of the Exaltation of the Cross on September 14, the anniversary of the dedication of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, also known as the Church of the Resurrection, is a fourth-century church in the Christian Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem, Old City of Jerusalem. The church is the seat of the Greek Orthodox Patriarchat ...
. In later centuries, these celebrations also included commemoration of the rescue of the True Cross from the Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
ns in 628. In the Galician usage, beginning about the seventh century, the Feast of the Cross was celebrated on May 3. According to the ''Catholic Encyclopedia
''The'' ''Catholic Encyclopedia: An International Work of Reference on the Constitution, Doctrine, Discipline, and History of the Catholic Church'', also referred to as the ''Old Catholic Encyclopedia'' and the ''Original Catholic Encyclopedi ...
'', when the Galician and Roman practices were combined, the September date, for which the Vatican adopted the official name "Triumph of the Cross" in 1963, was used to commemorate the rescue from the Persians and the May date was kept as the "Invention of the True Cross" to commemorate the finding. The September date is often referred to in the West as Holy Cross Day; the May date (see also Roodmas
Roodmas (from Old English ''rood'' "rod", "cross" and ''mas'', Mass (liturgy), Mass; similar to the Christmas#Etymology, etymology of Christmas) is a name for the celebration of the Feast of the Cross. It has been applied to both historical comme ...
) was dropped from the liturgical calendar
The liturgical year, also called the church year, Christian year, ecclesiastical calendar, or kalendar, consists of the cycle of liturgical days and seasons that determines when feast days, including celebrations of saints, are to be obs ...
of the Catholic Church in 1960 when the Roman Breviary
The Roman Breviary (Ecclesiastical Latin, Latin: ''Breviarium Romanum'') is a breviary of the Roman Rite in the Catholic Church. A liturgical book, it contains public or canonical Catholic prayer, prayers, hymns, the Psalms, readings, and notat ...
was reformed by Pope John XXIII
Pope John XXIII (born Angelo Giuseppe Roncalli; 25 November 18813 June 1963) was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 28 October 1958 until his death on 3 June 1963. He is the most recent pope to take ...
. The Orthodox still commemorate both events on September 14,. one of the Twelve Great Feasts of the liturgical year
The liturgical year, also called the church year, Christian year, ecclesiastical calendar, or kalendar, consists of the cycle of liturgical days and seasons that determines when feast days, including celebrations of saints, are to be obse ...
, and the Procession of the Venerable Wood of the Cross on 1 August, the day on which the relics of the True Cross would be carried through the streets of Constantinople
Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire ...
to bless the city.
In addition to celebrations on fixed days, there are certain days of the variable cycle when the Cross is celebrated. The Catholic Church has a formal Adoration of the Cross during the services for Good Friday
Good Friday, also known as Holy Friday, Great Friday, Great and Holy Friday, or Friday of the Passion of the Lord, is a solemn Christian holy day commemorating the crucifixion of Jesus and his death at Calvary (Golgotha). It is observed during ...
. In Eastern Orthodox churches everywhere, a replica of the cross is brought out in procession during Matins
Matins (also Mattins) is a canonical hour in Christian liturgy, originally sung during the darkness of early morning (between midnight and dawn).
The earliest use of the term was in reference to the canonical hour, also called the vigil, which w ...
of Great and Holy Friday for the people to venerate. The Orthodox also celebrate an additional Veneration of the Cross on the third Sunday of Great Lent
Great Lent, or the Great Fast (Greek language, Greek: Μεγάλη Τεσσαρακοστή, ''Megali Tessarakosti'' or Μεγάλη Νηστεία, ''Megali Nisteia'', meaning "Great 40 Days", and "Great Fast", respectively), is the most impor ...
.
Image gallery
See also
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * . * * * * * * * * * * * * * . * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* . * . * . * . * .External links
Fernand Cabrol, "The true Cross"
a Catholic view
Relic of the True Cross in Wrocław, Poland
{{Authority control Catholic Church in Jerusalem Christian folklore Christian mythology Christian relics Christian terminology Christianity in Jerusalem Crucifixion of Jesus Jesus and history Relics associated with Jesus Individual crosses and crucifixes Church of the Holy Sepulchre Helena, mother of Constantine I