Crocodile Safari Man on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Crocodiles (


 * Subfamily
* Subfamily
 A total of 18
A total of 18
Morphology And Physiology Of The Crocodylia
, in Fauna of Australia Vol 2A Amphibia and Reptilia, chapter 40, pp. 326–336. Australian Government Publishing Service, Canberra. Their tongues are not free, but held in place by a membrane that limits movement; as a result, crocodiles are unable to stick out their tongues. Crocodiles have smooth skin on their bellies and sides, while their dorsal surfaces are armoured with large osteoderms. The armoured skin has scales and is thick and rugged, providing some protection. They are still able to absorb heat through this armour, as a network of small capillaries allows blood through the scales to absorb heat. The osteoderms are highly vascularised and aid in calcium balance, both to neutralize acids while the animal cannot breathe underwater and to provide calcium for eggshell formation. Crocodilian tegument have pores believed to be sensory in function, analogous to the lateral line in fishes. They are particularly seen on their upper and lower jaws. Another possibility is that they are secretory, as they produce an oily substance which appears to flush mud off.
 Size greatly varies among species, from the
Size greatly varies among species, from the
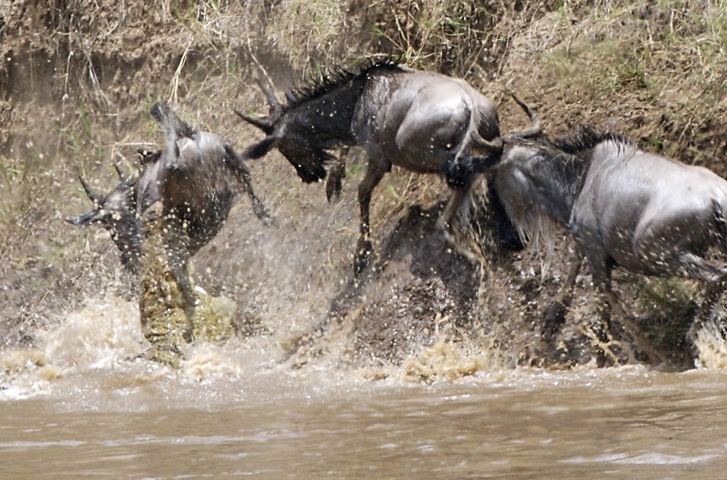

 Crocodiles are ambush predators, waiting for fish or land animals to come close, then rushing out to attack. Crocodiles mostly eat
Crocodiles are ambush predators, waiting for fish or land animals to come close, then rushing out to attack. Crocodiles mostly eat
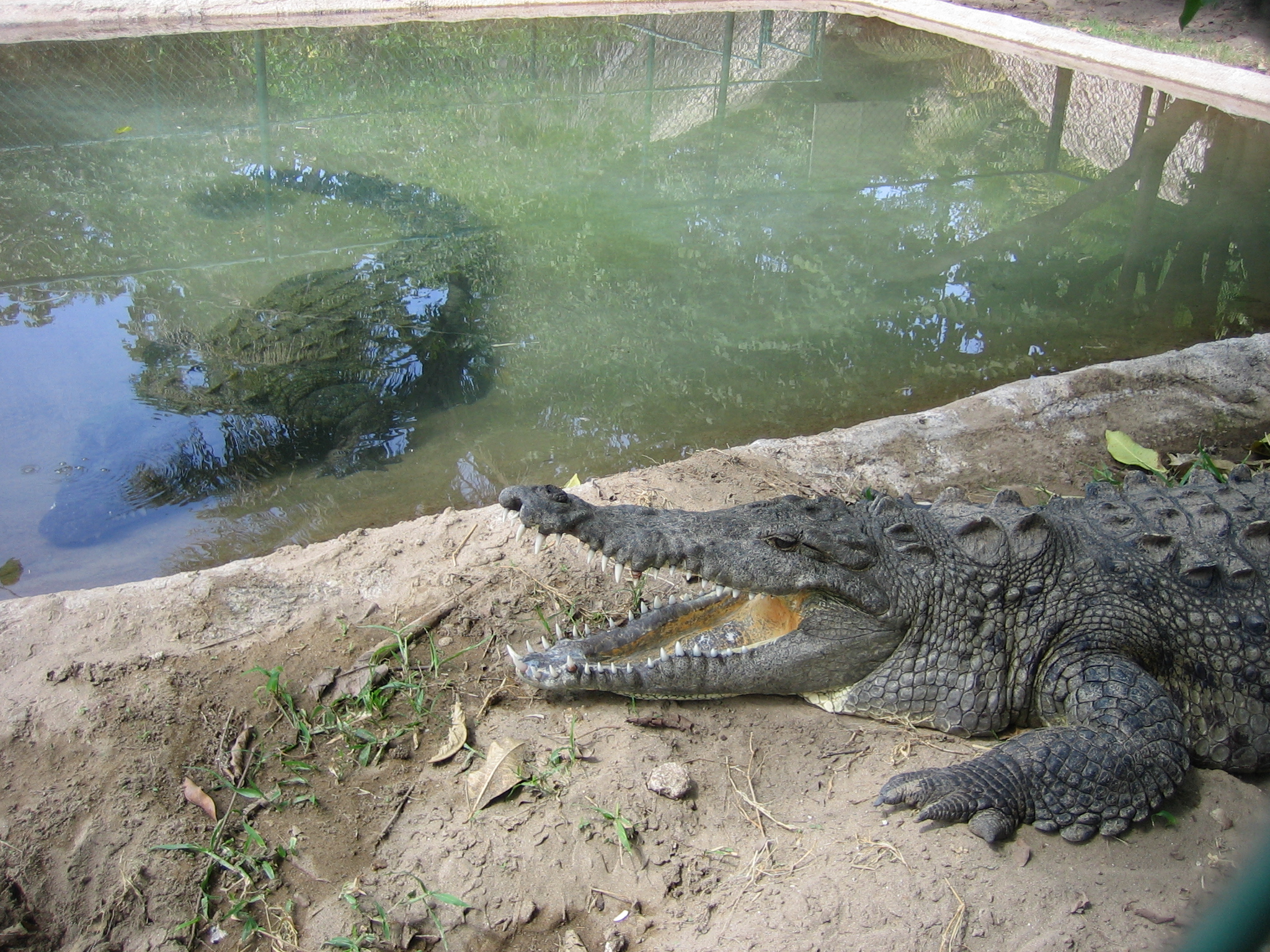 Crocodiles can move quickly over short distances, even out of water. The land speed record for a crocodile is measured in a galloping Freshwater crocodile, Australian freshwater crocodile. Maximum speed varies between species. Some species can gallop, including Cuban crocodiles, Johnston's crocodiles, New Guinea crocodiles, Dwarf crocodile, African dwarf crocodiles, and even small Nile crocodiles. The fastest means by which most species can move is a "belly run", in which the body moves in a snake-like (sinusoidal) fashion, limbs splayed out to either side paddling away frantically while the tail whips to and fro. Crocodiles can reach speeds of when they "belly run", and often faster if slipping down muddy riverbanks. When a crocodile walks quickly, it holds its legs in a straighter and more upright position under its body, which is called the "high walk". This walk allows a speed of up to 5 km/h.
Crocodiles may possess a homing instinct. In northern Australia, three rogue saltwater crocodiles were relocated by helicopter, but returned to their original locations within three weeks, based on data obtained from tracking devices attached to them.
Crocodiles can move quickly over short distances, even out of water. The land speed record for a crocodile is measured in a galloping Freshwater crocodile, Australian freshwater crocodile. Maximum speed varies between species. Some species can gallop, including Cuban crocodiles, Johnston's crocodiles, New Guinea crocodiles, Dwarf crocodile, African dwarf crocodiles, and even small Nile crocodiles. The fastest means by which most species can move is a "belly run", in which the body moves in a snake-like (sinusoidal) fashion, limbs splayed out to either side paddling away frantically while the tail whips to and fro. Crocodiles can reach speeds of when they "belly run", and often faster if slipping down muddy riverbanks. When a crocodile walks quickly, it holds its legs in a straighter and more upright position under its body, which is called the "high walk". This walk allows a speed of up to 5 km/h.
Crocodiles may possess a homing instinct. In northern Australia, three rogue saltwater crocodiles were relocated by helicopter, but returned to their original locations within three weeks, based on data obtained from tracking devices attached to them.
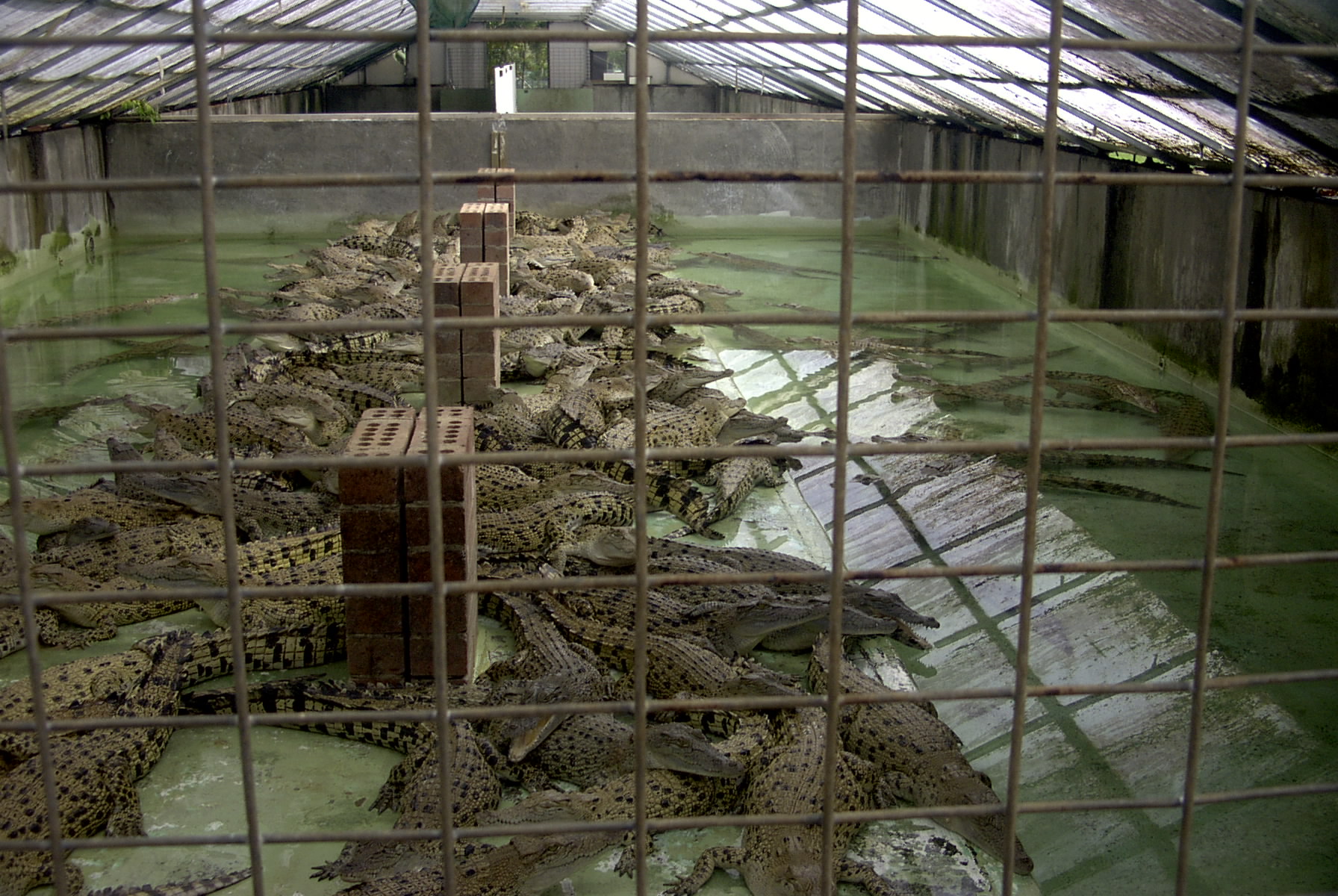
 Crocodiles are the most social of reptiles. Even though they do not form social groups, many species congregate in certain sections of
Crocodiles are the most social of reptiles. Even though they do not form social groups, many species congregate in certain sections of
 courtship display, Courtship takes place in a series of behavioural interactions that include a variety of snout rubbing and submissive display that can take a long time. Mating always takes place in water, where the pair can be observed mating several times.
courtship display, Courtship takes place in a series of behavioural interactions that include a variety of snout rubbing and submissive display that can take a long time. Mating always takes place in water, where the pair can be observed mating several times.
 The larger species of crocodiles are very dangerous to humans, mainly because of their ability to strike before the person can react. The
The larger species of crocodiles are very dangerous to humans, mainly because of their ability to strike before the person can react. The

 Crocodiles are protected in many parts of the world, but are also farmed commercially. Their hides are tanned and used to make leather goods such as shoes and handbags; crocodile meat is also considered a delicacy. The most commonly farmed species are the saltwater and Nile crocodiles, while a hybrid of the saltwater and the rare
Crocodiles are protected in many parts of the world, but are also farmed commercially. Their hides are tanned and used to make leather goods such as shoes and handbags; crocodile meat is also considered a delicacy. The most commonly farmed species are the saltwater and Nile crocodiles, while a hybrid of the saltwater and the rare
 Crocodiles have appeared in various forms in religions across the world. Ancient Egypt had Sobek, the crocodile-headed god, with his cult-city Crocodilopolis, as well as Taweret, the goddess of childbirth and fertility, with the back and tail of a crocodile. The Wukari Federation#Religion, Jukun shrine in the Wukari Federation, Nigeria is dedicated to crocodiles in thanks for their aid during migration. In Madagascar various peoples such as the Sakalava people, Sakalava and Antandroy see crocodiles as ancestor spirits and under local ''Fady (taboo), fady'' often offer them food;Campbell, Gwyn (2012). David Griffiths and the Missionary "History of Madagascar". Leiden, The Netherlands: Brill. . in the case of the latter at least a crocodile features prominently as an ancestor deity.
Crocodiles appear in different forms in Hinduism. Varuna, a Historical Vedic religion, Vedic and Hindu god, rides a part-crocodile Makara (Hindu mythology), makara; his consort Varuni rides a crocodile. Similarly the goddess personifications of the Ganges, Ganga and Yamuna rivers are often depicted as riding crocodiles. Also in India, in Goa, crocodile worship is practised, including the annual ''Mannge Thapnee'' ceremony.
Sikh warriors known as nihang also have connections with crocodiles. ''Nihang'' may come from the Persian word for a mythical sea creature (). The term owes its origin to Mughal Empire, Mughal historians, who compared the ferocity of the Akali with that of crocodiles. In Sikhism however, ''Akali'' refers to the immortal army of Akal (god).
In Latin America, Cipactli was the giant earth crocodile of the Aztec and other Nahua peoples.
Crocodiles have appeared in various forms in religions across the world. Ancient Egypt had Sobek, the crocodile-headed god, with his cult-city Crocodilopolis, as well as Taweret, the goddess of childbirth and fertility, with the back and tail of a crocodile. The Wukari Federation#Religion, Jukun shrine in the Wukari Federation, Nigeria is dedicated to crocodiles in thanks for their aid during migration. In Madagascar various peoples such as the Sakalava people, Sakalava and Antandroy see crocodiles as ancestor spirits and under local ''Fady (taboo), fady'' often offer them food;Campbell, Gwyn (2012). David Griffiths and the Missionary "History of Madagascar". Leiden, The Netherlands: Brill. . in the case of the latter at least a crocodile features prominently as an ancestor deity.
Crocodiles appear in different forms in Hinduism. Varuna, a Historical Vedic religion, Vedic and Hindu god, rides a part-crocodile Makara (Hindu mythology), makara; his consort Varuni rides a crocodile. Similarly the goddess personifications of the Ganges, Ganga and Yamuna rivers are often depicted as riding crocodiles. Also in India, in Goa, crocodile worship is practised, including the annual ''Mannge Thapnee'' ceremony.
Sikh warriors known as nihang also have connections with crocodiles. ''Nihang'' may come from the Persian word for a mythical sea creature (). The term owes its origin to Mughal Empire, Mughal historians, who compared the ferocity of the Akali with that of crocodiles. In Sikhism however, ''Akali'' refers to the immortal army of Akal (god).
In Latin America, Cipactli was the giant earth crocodile of the Aztec and other Nahua peoples.
 The name of Surabaya, Indonesia, is locally believed to be derived from the words "''suro"'' (shark) and "''boyo"'' (crocodile), two creatures which, in a local mythology, myth, fought each other in order to gain the title of "the strongest and most powerful animal" in the area. It was said that the two powerful animals agreed for a truce and set boundaries; that the shark's domain would be in the sea while the crocodile's domain would be on the land. However one day the shark swam into the river estuary to hunt; this angered the crocodile, who declared it his territory. The Shark argued that the river was a water-realm which meant that it was shark territory, while the crocodile argued that the river flowed deep inland, so it was therefore crocodile territory. The two animals bit each other and a ferocious fight ensued. Finally the shark, badly bitten, fled to the open sea, and in the end the crocodile ruled the estuarine area that today is the city. Another source alludes to a Jayabaya prophecy—a 12th-century psychic king of Kediri Kingdom—as he foresaw a fight between a giant white shark and a giant white crocodile taking place in the area. This is sometimes interpreted as a foretelling of the Mongol invasion of Java, a major conflict between the forces of the Kublai Khan, Mongol Empire, Mongol ruler of China, and those of Raden Wijaya's Majapahit in 1293. The two animals are now used as the city's symbol, with the two facing and circling each other, as depicted in a statue appropriately located near the entrance to the Surabaya Zoo, city zoo (see photo on the Surabaya page).
The name of Surabaya, Indonesia, is locally believed to be derived from the words "''suro"'' (shark) and "''boyo"'' (crocodile), two creatures which, in a local mythology, myth, fought each other in order to gain the title of "the strongest and most powerful animal" in the area. It was said that the two powerful animals agreed for a truce and set boundaries; that the shark's domain would be in the sea while the crocodile's domain would be on the land. However one day the shark swam into the river estuary to hunt; this angered the crocodile, who declared it his territory. The Shark argued that the river was a water-realm which meant that it was shark territory, while the crocodile argued that the river flowed deep inland, so it was therefore crocodile territory. The two animals bit each other and a ferocious fight ensued. Finally the shark, badly bitten, fled to the open sea, and in the end the crocodile ruled the estuarine area that today is the city. Another source alludes to a Jayabaya prophecy—a 12th-century psychic king of Kediri Kingdom—as he foresaw a fight between a giant white shark and a giant white crocodile taking place in the area. This is sometimes interpreted as a foretelling of the Mongol invasion of Java, a major conflict between the forces of the Kublai Khan, Mongol Empire, Mongol ruler of China, and those of Raden Wijaya's Majapahit in 1293. The two animals are now used as the city's symbol, with the two facing and circling each other, as depicted in a statue appropriately located near the entrance to the Surabaya Zoo, city zoo (see photo on the Surabaya page).
FLMNH.ufl.edu
"How long do crocodiles live for?" Adam Britton. * Crocodilian Biology Database, FAQ
"How fast can a crocodile run?" Adam Britton.
Crocodilian Online
Crocodile Attacks in Australia
BBC news finds powerful agent in crocodile blood
World's most expensive handbag sells in Hong Kong for over US$377,000 – a Hermès white crocodile
(31 May 2017), ''South China Morning Post''
292 New Guinea crocodiles massacred
in West Papua (province), West Papua, Indonesia {{DEFAULTSORT:Crocodile Crocodylidae, Extant Ypresian first appearances Taxa named by Georges Cuvier Crocodilian families
family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large, semiaquatic
In biology, being semi-aquatic refers to various macroorganisms that live regularly in both aquatic and terrestrial environments. When referring to animals, the term describes those that actively spend part of their daily time in water (in ...
reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
s that live throughout the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
, Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
, the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
. The term "crocodile" is sometimes used more loosely to include all extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
members of the order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* A socio-political or established or existing order, e.g. World order, Ancien Regime, Pax Britannica
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
...
Crocodilia
Crocodilia () is an order of semiaquatic, predatory reptiles that are known as crocodilians. They first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and are the closest living relatives of birds. Crocodilians are a type of crocodylomorph pseudosuchia ...
, which includes the alligator
An alligator, or colloquially gator, is a large reptile in the genus ''Alligator'' of the Family (biology), family Alligatoridae in the Order (biology), order Crocodilia. The two Extant taxon, extant species are the American alligator (''A. mis ...
s and caiman
A caiman ( (also spelled cayman) from Taíno language, Taíno ''kaiman'') is an alligatorid belonging to the subfamily Caimaninae, one of two primary lineages within the Alligatoridae family (biology), family, the other being alligators. ...
s (both members of the family Alligatoridae
The family (biology), family Alligatoridae of crocodylians includes alligators, caimans and their extinct relatives.
Phylogeny
The superfamily Alligatoroidea includes all crocodilians (fossil and extant) that are more closely related to the Am ...
), the gharial
The gharial (''Gavialis gangeticus''), also known as gavial or fish-eating crocodile, is a crocodilian in the family (biology), family Gavialidae and among the longest of all living crocodilians. Mature females are long, and males . Adult males ...
and false gharial
The false gharial (''Tomistoma schlegelii''), also known by the names Malayan gharial, Sunda gharial and tomistoma is a freshwater crocodilian of the Family (biology), family Gavialidae native to Peninsular Malaysia, Borneo, Sumatra and Java. It ...
(both members of the family Gavialidae
Gavialidae is a family of large semiaquatic crocodilians with elongated, narrow snouts. Gavialidae consists of two living species, the gharial (''Gavialis gangeticus'') and the false gharial (''Tomistoma schlegelii''), both occurring in Asia. Man ...
) as well as other extinct taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
.
Crocodile size
Size in general is the Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude or dimensions of a thing. More specifically, ''geometrical size'' (or ''spatial size'') can refer to three geometrical measures: length, area, or volume. Length can be generalized ...
, morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
*Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
*Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies, ...
, behaviour
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions of Individual, individuals, organisms, systems or Artificial intelligence, artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or or ...
and ecology
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their Natural environment, environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community (ecology), community, ecosystem, and biosphere lev ...
differ among species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
. However, they have many similarities in these areas as well. All crocodiles are semiaquatic
In biology, being semi-aquatic refers to various macroorganisms that live regularly in both aquatic and terrestrial environments. When referring to animals, the term describes those that actively spend part of their daily time in water (in ...
and tend to congregate in freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include non-salty mi ...
habitats such as river
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of ...
s, lake
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from ...
s, wetland
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially ...
s and sometimes in brackish
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuari ...
water and saltwater
Saline water (more commonly known as salt water) is water that contains a high concentration of dissolved salts (mainly sodium chloride). On the United States Geological Survey (USGS) salinity scale, saline water is saltier than brackish wat ...
. They are carnivorous
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose nutrition and energy requirements are met by consumption of animal tissues (mainly mu ...
animals, feeding mostly on vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s such as fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
, reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
s, bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
s and mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s, and sometimes on invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
s such as mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s and crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s, depending on species and age. All crocodiles are tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the equator, where the sun may shine directly overhead. This contrasts with the temperate or polar regions of Earth, where the Sun can never be directly overhead. This is because of Earth's ax ...
species that, unlike alligators, are very sensitive to cold
Cold is the presence of low temperature, especially in the atmosphere. In common usage, cold is often a subjectivity, subjective perception. A lower bound to temperature is absolute zero, defined as 0.00K on the Kelvin scale, an absolute t ...
. Many species are at the risk of extinction
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
, some being classified as critically endangered
An IUCN Red List critically endangered (CR or sometimes CE) species is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as facing an extremely high risk of extinction in the wild. As of December 2023, of t ...
.
Etymology
The word ''crocodile'' (''croc.'') was derived during theMiddle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman Conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English pe ...
period from the transliteration
Transliteration is a type of conversion of a text from one script to another that involves swapping letters (thus '' trans-'' + '' liter-'') in predictable ways, such as Greek → and → the digraph , Cyrillic → , Armenian → or L ...
krokódilos of a Greek word which translates as: "stones worm". Through Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically r ...
the English language
English is a West Germanic language that developed in early medieval England and has since become a English as a lingua franca, global lingua franca. The namesake of the language is the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples th ...
word has developed from Grecian origination in Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
.
A very early extant Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
source is an Aesop's Fable named Ἀλώπηξ καὶ κροκόδειλος of the sixth century BCE. Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
a century after in consideration of the Greek word thought it was from the Ionic period.
The Latin language
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
word ''crocodilus'' existed in first century a.d. in the work ''Naturalis Historia
The ''Natural History'' () is a Latin work by Pliny the Elder. The largest single work to have survived from the Roman Empire to the modern day, the ''Natural History'' compiles information gleaned from other ancient authors. Despite the work' ...
'' of Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
. Examples in writing in the sixth and seventh century a.d., and existed, though and
were forms in Medieval Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. It was also the administrative language in the former Western Roman Empire, Roman Provinces of Mauretania, Numidi ...
. The Latin form is found as ''cocodrille'' c. the 13th century in the Old French
Old French (, , ; ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France approximately between the late 8th -4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ...
work Li livres dou tresor, in which the croc. is ''jaune'' (yellow).
The earliest known source in the English language is within the work Kyng Alisaunder from towards the beginning of the 14th century, a Magic (supernatural), magical Romance (prose fiction)#Medieval romance, romance poetry work of rhyming couplets, where the word is found line 5720:
:Forth went the kyng wondres sekynde :
:A griselich hest he gonne fynde ;
:So mychel seigh he neuere, ne non swiche ;
:Two heudes it had wel ferlich
:To a cokedrill that on was liche,
:That others the monoceros selcouthliche.
Writing sometime after 1483 on his visit to the Holy Land
The term "Holy Land" is used to collectively denote areas of the Southern Levant that hold great significance in the Abrahamic religions, primarily because of their association with people and events featured in the Bible. It is traditionall ...
s Felix Fabri
Felix Fabri (also spelt Faber; 1441 – 1502) was a Swiss Dominican theologian. He left vivid and detailed descriptions of his pilgrimages to Palestine and also in 1489 authored a book on the history of Swabia, entitled ''Historia Suevorum''.
...
in German and Latin mentions the Cocodrillen and ''cocodrillos'' respectively. By 1538 the exact same form of the modern word as the current English is found in French
French may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France
** French people, a nation and ethnic group
** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices
Arts and media
* The French (band), ...
; ''croc''. is within a poem of Edmund Spenser
Edmund Spenser (; – 13 January 1599 Old Style and New Style dates, O.S.) was an English poet best known for ''The Faerie Queene'', an epic poem and fantastical allegory celebrating the House of Tudor, Tudor dynasty and Elizabeth I. He is re ...
, thought written in 1579-80, and in the works of William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 23 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
whose lifetime was 1564 - 1616. The similitude of the English word formation to a Latin source was caused at least by the transmission of a relevant ancient science from the influx of the publication of translations of Pliny the Elder some time towards the end of fourteenth and, or, beginning of fifteenth century. The publication of concrete realization in the anatomical work of Andreas Vesalius
Andries van Wezel (31 December 1514 – 15 October 1564), latinized as Andreas Vesalius (), was an anatomist and physician who wrote '' De Humani Corporis Fabrica Libri Septem'' (''On the fabric of the human body'' ''in seven books''), which is ...
during 1543 inspired the creation of monographs and books of animals contributing to new science in zoology
Zoology ( , ) is the scientific study of animals. Its studies include the anatomy, structure, embryology, Biological classification, classification, Ethology, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinction, extinct, and ...
.
Taxonomy and phylogeny
Crocodylidae was named as afamily
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
by Georges Cuvier
Jean Léopold Nicolas Frédéric, baron Cuvier (23 August 1769 – 13 May 1832), known as Georges Cuvier (; ), was a French natural history, naturalist and zoology, zoologist, sometimes referred to as the "founding father of paleontology". Cuv ...
in 1807. It belongs to the larger superfamily
SUPERFAMILY is a database and search platform of structural and functional annotation for all proteins and genomes. It classifies amino acid sequences into known structural domains, especially into SCOP superfamilies. Domains are functional, str ...
Crocodyloidea
Crocodyloidea is one of three superfamilies of crocodilians, the other two being Alligatoroidea and Gavialoidea, and it includes the crocodiles. Crocodyloidea may also include the extinct Mekosuchinae, native to Australasia from the Eocene to ...
, which also includes additional extinct crocodile relatives. These all belong to the order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* A socio-political or established or existing order, e.g. World order, Ancien Regime, Pax Britannica
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
...
Crocodilia
Crocodilia () is an order of semiaquatic, predatory reptiles that are known as crocodilians. They first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and are the closest living relatives of birds. Crocodilians are a type of crocodylomorph pseudosuchia ...
, which also includes alligators
An alligator, or colloquially gator, is a large reptile in the genus ''Alligator'' of the family Alligatoridae in the order Crocodilia. The two extant species are the American alligator (''A. mississippiensis'') and the Chinese alligator (''A ...
and gharials
Gavialidae is a family of large semiaquatic crocodilians with elongated, narrow snouts. Gavialidae consists of two living species, the gharial (''Gavialis gangeticus'') and the false gharial (''Tomistoma schlegelii''), both occurring in Asia. Man ...
.
Although crocodiles, alligators, and the gharial are similar in appearance, they belong to separate biological families. The gharial, with its narrow snout
A snout is the protruding portion of an animal's face, consisting of its nose, mouth, and jaw. In many animals, the structure is called a muzzle, Rostrum (anatomy), rostrum, beak or proboscis. The wet furless surface around the nostrils of the n ...
, is easier to distinguish, while morphological differences are more difficult to spot in crocodiles and alligators. The most obvious external differences are visible in the head, with crocodiles having narrower and longer heads, with a more V-shaped than a U-shaped snout compared to alligators and caimans. Another obvious trait is that the upper and lower jaws of the crocodiles are the same width, and the teeth
A tooth (: teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tear ...
in the lower jaw fall along the edge or outside the upper jaw when the mouth is closed; therefore, all teeth are visible, unlike an alligator, which possesses in the upper jaw small depressions into which the lower teeth fit. Also, when the crocodile's mouth is closed, the large fourth tooth in the lower jaw fits into a constriction in the upper jaw. For hard-to-distinguish specimens, the protruding tooth is the most reliable feature to define the species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
' family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
. Crocodiles have more webbing
file:Webbing.jpg, red, blue and black nylon webbing as used in auto racing harnesses
Webbing is a strong Textile, fabric weaving, woven as a flat strip or tube of varying width and fibres, often used in place of rope. It is a versatile componen ...
on the toes of the hind feet
The foot (: feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is an organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of ...
and can better tolerate saltwater
Saline water (more commonly known as salt water) is water that contains a high concentration of dissolved salts (mainly sodium chloride). On the United States Geological Survey (USGS) salinity scale, saline water is saltier than brackish wat ...
due to specialized salt gland
The salt gland is an organ (anatomy), organ for excreting excess salt (chemistry), salts. It is found in the cartilaginous fishes subclass elasmobranchii (sharks, rays, and skates), seabirds, and some reptiles. Salt glands can be found in the r ...
s for filtering out salt, which are present, but non-functioning, in alligators. Another trait that separates crocodiles from other crocodilians is their much higher levels of aggression
Aggression is behavior aimed at opposing or attacking something or someone. Though often done with the intent to cause harm, some might channel it into creative and practical outlets. It may occur either reactively or without provocation. In h ...
.
Crocodylidae is cladistic
Cladistics ( ; from Ancient Greek 'branch') is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups ("clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is ...
ally defined as a crown group
In phylogenetics, the crown group or crown assemblage is a collection of species composed of the living representatives of the collection, the most recent common ancestor of the collection, and all descendants of the most recent common ancestor ...
composed of the last common ancestor
A most recent common ancestor (MRCA), also known as a last common ancestor (LCA), is the most recent individual from which all organisms of a set are inferred to have descended. The most recent common ancestor of a higher taxon is generally assu ...
of the Nile crocodile
The Nile crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'') is a large crocodilian native to freshwater habitats in Africa, where it is present in 26 countries. It is widely distributed in sub-Saharan Africa, occurring mostly in the eastern, southern, and ce ...
(''Crocodylus niloticus''), the Dwarf crocodile
The dwarf crocodile (''Osteolaemus tetraspis''), also known as the African dwarf crocodile, broad-snouted crocodile (a name more often used for the Asian mugger crocodile) or bony crocodile, is an African crocodile that is also the smallest extan ...
(''Osteolaemus tetraspis''), and all of its descendants. It contains two subfamilies
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end botanical subfamily names with "-oideae", and zool ...
: Crocodylinae
Crocodylinae is a subfamily of true crocodiles within the family Crocodylidae, and is the sister taxon to Osteolaeminae ( dwarf crocodiles and slender-snouted crocodiles).
Taxonomy
Crocodylinae was cladistically defined by Christopher Brochu ...
and Osteolaeminae
Osteolaeminae is a subfamily of true crocodiles within the family Crocodylidae containing the dwarf crocodiles and slender-snouted crocodiles, and is the sister taxon to Crocodylinae.
Taxonomy
Osteolaeminae was named by Christopher Brochu in ...
. Crocodylinae contains 13-14 living species, as well as 6 extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
species. Osteolaeminae was named by Christopher Brochu in 2003 as a subfamily of Crocodylidae separate from Crocodylinae, and contains the two extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
genera
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial s ...
''Osteolaemus
''Osteolaemus'' is a genus of crocodiles. They are small, secretive crocodiles that occur in wetlands of West and Middle Africa. They are commonly known as the African dwarf crocodiles. Unlike other crocodiles, ''Osteolaemus'' are strictly noctur ...
'' and ''Mecistops
''Mecistops'' is a genus of crocodiles, the slender-snouted crocodiles, native to sub-Saharan Africa.
Taxonomy and etymology
Traditionally placed in '' Crocodylus'', recent studies in DNA and morphology have shown that it is in fact basal to '' ...
'', along with several extinct genera. The number of extant species within Osteolaeminae is currently in question.



Crocodylinae
Crocodylinae is a subfamily of true crocodiles within the family Crocodylidae, and is the sister taxon to Osteolaeminae ( dwarf crocodiles and slender-snouted crocodiles).
Taxonomy
Crocodylinae was cladistically defined by Christopher Brochu ...
** Genus ''Crocodylus
''Crocodylus'' is a genus of true crocodiles in the family Crocodylidae.
Taxonomy
The Genus, generic name, ''Crocodylus'', was proposed by Josephus Nicolaus Laurenti in 1768. ''Crocodylus'' contains 13–14 extant taxon, extant (living) species ...
''
***''Crocodylus acutus
''Crocodylus'' is a genus of true crocodiles in the family Crocodylidae.
Taxonomy
The generic name, ''Crocodylus'', was proposed by Josephus Nicolaus Laurenti in 1768. ''Crocodylus'' contains 13–14 extant (living) species and 5 extinct specie ...
'', American crocodile
The American crocodile (''Crocodylus acutus'') is a species of crocodilian found in the Neotropics. It is the most widespread of the four Extant taxon, extant species of crocodiles from the Americas, with populations present from South Florida, ...
***''Crocodylus halli
''Crocodylus halli'', also known as Hall's New Guinea crocodile, is a species of crocodile endemic to the island of New Guinea. It is found on the southern half of the island, south of the New Guinea highlands. It is named after Philip M. Hall, a ...
'', Hall's New Guinea crocodile found South of the New Guinea Highlands
The New Guinea Highlands, also known as the Central Range or Central Cordillera, is a long chain of mountain ranges on the island of New Guinea, including the island's highest peak, Puncak Jaya, Indonesia, , the highest mountain in Oceania. The r ...
***'' Crocodylus intermedius'', Orinoco crocodile
The Orinoco crocodile (''Crocodylus intermedius'') is a critically endangered crocodile. Its population is very small, and they can only be found in the Orinoco river basin in Venezuela and Colombia. Extensively hunted for their skins in the 19t ...
***'' Crocodylus johnsoni'', freshwater crocodile
The freshwater crocodile (''Crocodylus johnstoni)'', also known Common name, commonly as the Australian freshwater crocodile, Johnstone's crocodile, and the freshie, is a species of crocodile native to the northern regions of Australia. Unlike ...
, or Johnstone's crocodile
***''Crocodylus mindorensis
''Crocodylus'' is a genus of true crocodiles in the family Crocodylidae.
Taxonomy
The generic name, ''Crocodylus'', was proposed by Josephus Nicolaus Laurenti in 1768. ''Crocodylus'' contains 13–14 extant (living) species and 5 extinct specie ...
'', Philippine crocodile
The Philippine crocodile (''Crocodylus mindorensis''), also known as the Mindoro crocodile, the Philippine freshwater crocodile, the ''bukarot'' in Ilocano language, Ilocano, and more generally as a ''buwaya'' in most Filipino lowland cultures, i ...
***'' Crocodylus moreletii'', Morelet's crocodile
Morelet's crocodile (''Crocodylus moreletii''), also known as the Mexican crocodile or Belize crocodile, is a modest-sized crocodilian found only in the Atlantic regions of Mexico, Belize and Guatemala. It usually grows to about in length. It i ...
or Mexican crocodile
***''Crocodylus niloticus
The Nile crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'') is a large crocodilian native to freshwater habitats in Africa, where it is present in 26 countries. It is widely distributed in sub-Saharan Africa, occurring mostly in the eastern, southern, and ce ...
'', Nile crocodile
The Nile crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'') is a large crocodilian native to freshwater habitats in Africa, where it is present in 26 countries. It is widely distributed in sub-Saharan Africa, occurring mostly in the eastern, southern, and ce ...
or African crocodile (the subspecies found in Madagascar is sometimes called the black crocodile)
***''Crocodylus novaeguineae
The New Guinea crocodile (''Crocodylus novaeguineae'') is a small species of crocodile found on the island of New Guinea north of the mountain ridge that runs along the centre of the island. The population found south of the mountain ridge, form ...
'', New Guinea crocodile
The New Guinea crocodile (''Crocodylus novaeguineae'') is a small species of crocodile found on the island of New Guinea north of the mountain ridge that runs along the centre of the island. The population found south of the mountain ridge, form ...
found North of the New Guinea Highlands
The New Guinea Highlands, also known as the Central Range or Central Cordillera, is a long chain of mountain ranges on the island of New Guinea, including the island's highest peak, Puncak Jaya, Indonesia, , the highest mountain in Oceania. The r ...
***'' Crocodylus palustris'', mugger, marsh or Indian crocodile
***''Crocodylus porosus
The saltwater crocodile (''Crocodylus porosus'') is a crocodilian native to saltwater habitats, brackish wetlands and freshwater rivers from India's east coast across Southeast Asia and the Sundaland to northern Australia and Micronesia. It h ...
'', saltwater crocodile
The saltwater crocodile (''Crocodylus porosus'') is a crocodilian native to saltwater habitats, brackish wetlands and freshwater rivers from India's east coast across Southeast Asia and the Sundaland to northern Australia and Micronesia. It ha ...
or estuarine crocodile
****'' Crocodylus raninus'', the Borneo crocodile, is currently considered to be a synonym of ''Crocodylus porosus''; whether or not it is a distinct species remains unclear.
***'' Crocodylus rhombifer'', Cuban crocodile
The Cuban crocodile (''Crocodylus rhombifer'') is a small-medium species of crocodile endemic to Cuba. Typical length is and typical weight . Large males can reach as much as in length and weigh more than . Despite its smaller size, it is a hig ...
***'' Crocodylus siamensis'', Siamese crocodile
The Siamese crocodile (''Crocodylus siamensis'') is a medium-sized freshwater crocodile native to Indonesia (Borneo and possibly Java), Brunei, East Malaysia, Laos, Cambodia, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam. The species is critically endangered and ...
(may be extinct in the wild)
***''Crocodylus suchus
The West African crocodile, desert crocodile, or sacred crocodile (''Crocodylus suchus'') is a species of crocodile related to, and often confused with, the larger and more aggressive Nile crocodile (''C. niloticus'').
Taxonomy
The species wa ...
'', West African crocodile
The West African crocodile, desert crocodile, or sacred crocodile (''Crocodylus suchus'') is a species of crocodile related to, and often confused with, the larger and more aggressive Nile crocodile (''C. niloticus'').
Taxonomy
The species wa ...
, desert or sacred crocodile
***''Crocodylus anthropophagus
''Crocodylus anthropophagus'' is an extinct species of crocodile from the Pleistocene of Tanzania. It lived 1.84 million years ago. It was a large-sized predator reaching a length of .
Etymology
''Crocodylus anthropophagus'' was first named by ...
''
***''Crocodylus checchiai
''Crocodylus checchiai'' is an extinct species of crocodile from the Miocene to Pliocene of Libya and Kenya. ''C. checchiai'' was named in 1947 based on a skull from the Sahabi Formation. Remains from the lower Nawata Formation in the Turkana Bas ...
''
***''Crocodylus falconensis
''Crocodylus falconensis'' is an extinct species of crocodile known from the early Pliocene of the lower
part of the Vergel Member of the San Gregorio Formation of Venezuela. ''C. falconensis'' was named in 2013 after Falcón State and is though ...
''
***''Crocodylus palaeindicus
''Crocodylus palaeindicus'' is an extinct species of crocodile from southern Asia. ''C. palaeindicus'' lived from the Miocene to the Pliocene. It may be an ancestor of the living Mugger crocodile.
History
''C. palaeindicus'' was first named by ...
''
***''Crocodylus thorbjarnarsoni
''Crocodylus thorbjarnarsoni'' is an extinct species of crocodile from the Pliocene and Pleistocene of the Turkana Basin in Kenya. It is closely related to the species '' Crocodylus anthropophagus'', which lived during the same time in Tanzania. ...
''
** Genus ''Voay
''Voay'' is an extinct genus of crocodile from Madagascar that lived during the Late Pleistocene to Holocene, containing only one species, ''V. robustus''. Numerous subfossils have been found, including complete skulls, noted for their distinctiv ...
''
***''Voay robustus
''Voay'' is an extinct genus of crocodile from Madagascar that lived during the Late Pleistocene to Holocene, containing only one species, ''V. robustus''. Numerous subfossils have been found, including complete skulls, noted for their distinctiv ...
'' (formerly ''Crocodylus robustus'')
* Subfamily Osteolaeminae
Osteolaeminae is a subfamily of true crocodiles within the family Crocodylidae containing the dwarf crocodiles and slender-snouted crocodiles, and is the sister taxon to Crocodylinae.
Taxonomy
Osteolaeminae was named by Christopher Brochu in ...
** Genus ''Osteolaemus
''Osteolaemus'' is a genus of crocodiles. They are small, secretive crocodiles that occur in wetlands of West and Middle Africa. They are commonly known as the African dwarf crocodiles. Unlike other crocodiles, ''Osteolaemus'' are strictly noctur ...
''
*** ''Osteolaemus tetraspis
The dwarf crocodile (''Osteolaemus tetraspis''), also known as the African dwarf crocodile, broad-snouted crocodile (a name more often used for the Asian mugger crocodile) or bony crocodile, is an African crocodile that is also the smallest extan ...
'', dwarf crocodile
The dwarf crocodile (''Osteolaemus tetraspis''), also known as the African dwarf crocodile, broad-snouted crocodile (a name more often used for the Asian mugger crocodile) or bony crocodile, is an African crocodile that is also the smallest extan ...
(There has been controversy as to whether or not this is actually two species; recent (2010) DNA analysis indicate three distinct species: ''O. tetraspis'', ''O. osborni'' and a third, currently unnamed.)
** Genus ''Mecistops
''Mecistops'' is a genus of crocodiles, the slender-snouted crocodiles, native to sub-Saharan Africa.
Taxonomy and etymology
Traditionally placed in '' Crocodylus'', recent studies in DNA and morphology have shown that it is in fact basal to '' ...
''
***''Mecistops cataphractus
The West African slender-snouted crocodile (''Mecistops cataphractus''), or slender-snouted crocodile, is a critically endangered species of African crocodile. It is one of five species of crocodile in Africa, the other four being the Central Af ...
'' West African slender-snouted crocodile
The West African slender-snouted crocodile (''Mecistops cataphractus''), or slender-snouted crocodile, is a critically endangered species of African crocodile. It is one of five species of crocodile in Africa, the other four being the Central Af ...
*** '' Mecistops leptorhynchus'' Central African slender-snouted crocodile
The Central African slender-snouted crocodile (''Mecistops leptorhynchus'') is one of two species of crocodiles in the genus ''Mecistops''. It was once thought to be a population of the West African slender-snouted crocodile (''Mecistops cataphr ...
** Genus ''Brochuchus
''Brochuchus'' is an extinct genus of crocodile known from the Early Miocene Hiwegi Formation of Rusinga Island in Lake Victoria, Kenya; it was originally named as a species of '' Crocodylus''. It contains two species, ''B. parvidens'' and ''B. ...
''
*** ''Brochuchus pigotti'' (formerly ''Crocodylus pigotti'')
*** ''Brochuchus parvidens''
** Genus ''Euthecodon''
*** ''Euthecodon nitriae''
*** ''Euthecodon brumpti''
*** ''Euthecodon arambourgi''
** Genus ''Rimasuchus''
*** ''Rimasuchus lloydi'' (formerly ''Crocodylus lloydi'')
Phylogeny
Recent molecular studies using DNA sequencing have shown crocodiles to be more closely related to the gavialids rather than toalligator
An alligator, or colloquially gator, is a large reptile in the genus ''Alligator'' of the Family (biology), family Alligatoridae in the Order (biology), order Crocodilia. The two Extant taxon, extant species are the American alligator (''A. mis ...
s, contrary to prior theories based on morphology (biology), morphological studies alone.
Below is a cladogram showing the relationships of the major extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
crocodile groups based on molecular studies, excluding separate extinct taxa:
Below is a more detailed cladogram of Crocodylidae, based on a 2021 study using paleogenomics that extracted DNA from the extinct ''Voay
''Voay'' is an extinct genus of crocodile from Madagascar that lived during the Late Pleistocene to Holocene, containing only one species, ''V. robustus''. Numerous subfossils have been found, including complete skulls, noted for their distinctiv ...
''.
Alternatively, some morphology (biology), morphological studies have recovered ''Mecistops
''Mecistops'' is a genus of crocodiles, the slender-snouted crocodiles, native to sub-Saharan Africa.
Taxonomy and etymology
Traditionally placed in '' Crocodylus'', recent studies in DNA and morphology have shown that it is in fact basal to '' ...
'' as a basal (phylogeny), basal member of Crocodylinae
Crocodylinae is a subfamily of true crocodiles within the family Crocodylidae, and is the sister taxon to Osteolaeminae ( dwarf crocodiles and slender-snouted crocodiles).
Taxonomy
Crocodylinae was cladistically defined by Christopher Brochu ...
, more closely related to ''Crocodylus
''Crocodylus'' is a genus of true crocodiles in the family Crocodylidae.
Taxonomy
The Genus, generic name, ''Crocodylus'', was proposed by Josephus Nicolaus Laurenti in 1768. ''Crocodylus'' contains 13–14 extant taxon, extant (living) species ...
'' than to ''Osteolaemus
''Osteolaemus'' is a genus of crocodiles. They are small, secretive crocodiles that occur in wetlands of West and Middle Africa. They are commonly known as the African dwarf crocodiles. Unlike other crocodiles, ''Osteolaemus'' are strictly noctur ...
'' and the other members of Osteolaeminae
Osteolaeminae is a subfamily of true crocodiles within the family Crocodylidae containing the dwarf crocodiles and slender-snouted crocodiles, and is the sister taxon to Crocodylinae.
Taxonomy
Osteolaeminae was named by Christopher Brochu in ...
, as shown in the cladogram below.
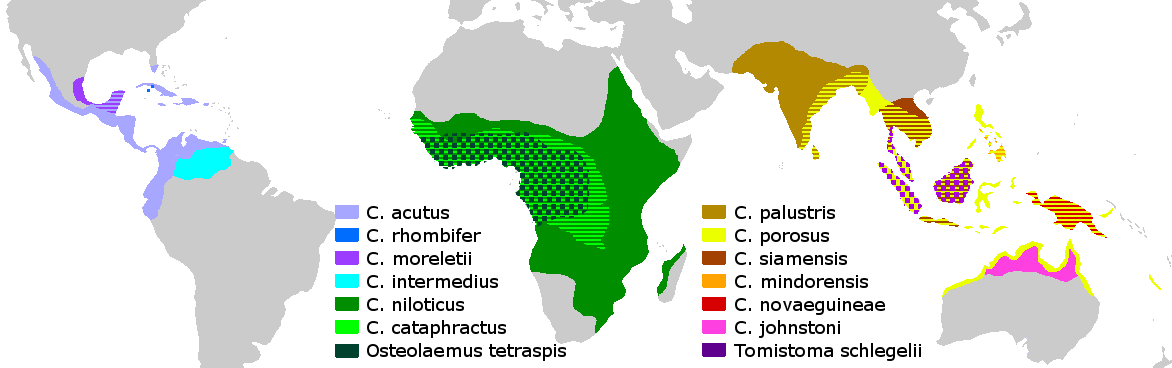
Species
 A total of 18
A total of 18 extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
species have been recognized. Further genetic study is needed for the confirmation of proposed species under the genus ''Osteolaemus
''Osteolaemus'' is a genus of crocodiles. They are small, secretive crocodiles that occur in wetlands of West and Middle Africa. They are commonly known as the African dwarf crocodiles. Unlike other crocodiles, ''Osteolaemus'' are strictly noctur ...
''.
Characteristics
Apart from the advantage conferred by its sufficiently large size relative to other animals in the ecosystem, other physical traits contribute a crocodile's position as predator. Its external morphology (biology), morphology is a sign of its aquatic animal, aquatic and predatory lifestyle. Its Drag (physics), streamlined body enables it to swim swiftly; it also tucks its feet to the side while swimming, making it faster by decreasing water resistance. Crocodiles have webbed feet which, though not used to propel them through the water, allow them to make fast turns and sudden moves in the water or initiate swimming. Webbed feet are an advantage in shallow water, where the animals sometimes move around by walking. Crocodiles have a palatal flap, a rigid tissue at the back of the mouth that blocks the entry of water. The palate has a special path from the nostril to the glottis that bypasses the mouth. The nostrils are closed during submergence. Like other archosaurs, crocodilians are diapsid, although their post-temporal fenestrae are reduced. The walls of the braincase are bony but lack supratemporal and postfrontal bones.Grigg, Gordon and Gans, Carl (1993Morphology And Physiology Of The Crocodylia
, in Fauna of Australia Vol 2A Amphibia and Reptilia, chapter 40, pp. 326–336. Australian Government Publishing Service, Canberra. Their tongues are not free, but held in place by a membrane that limits movement; as a result, crocodiles are unable to stick out their tongues. Crocodiles have smooth skin on their bellies and sides, while their dorsal surfaces are armoured with large osteoderms. The armoured skin has scales and is thick and rugged, providing some protection. They are still able to absorb heat through this armour, as a network of small capillaries allows blood through the scales to absorb heat. The osteoderms are highly vascularised and aid in calcium balance, both to neutralize acids while the animal cannot breathe underwater and to provide calcium for eggshell formation. Crocodilian tegument have pores believed to be sensory in function, analogous to the lateral line in fishes. They are particularly seen on their upper and lower jaws. Another possibility is that they are secretory, as they produce an oily substance which appears to flush mud off.
Size
 Size greatly varies among species, from the
Size greatly varies among species, from the dwarf crocodile
The dwarf crocodile (''Osteolaemus tetraspis''), also known as the African dwarf crocodile, broad-snouted crocodile (a name more often used for the Asian mugger crocodile) or bony crocodile, is an African crocodile that is also the smallest extan ...
to the saltwater crocodile
The saltwater crocodile (''Crocodylus porosus'') is a crocodilian native to saltwater habitats, brackish wetlands and freshwater rivers from India's east coast across Southeast Asia and the Sundaland to northern Australia and Micronesia. It ha ...
. Species of the dwarf crocodile ''Osteolaemus'' grow to an adult size of just , whereas the saltwater crocodile can grow to sizes over and weigh over . Several other large species can reach over long and weigh over . Crocodilians show pronounced sexual dimorphism, with males growing much larger and more rapidly than females. Despite their large adult sizes, crocodiles start their lives at around long. The largest species of crocodile is the saltwater crocodile, found in eastern India, northern Australia, throughout South-east Asia, and in the surrounding waters.
The brain volume of two adult crocodiles was 5.6 cm3 for a spectacled caiman and 8.5 cm3 for a larger Nile crocodile
The Nile crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'') is a large crocodilian native to freshwater habitats in Africa, where it is present in 26 countries. It is widely distributed in sub-Saharan Africa, occurring mostly in the eastern, southern, and ce ...
.
The largest crocodile ever held in captivity is a saltwater–Siamese hybrid named Yai (, meaning big; born 10 June 1972) at the Samutprakarn Crocodile Farm and Zoo, Thailand. This animal measures in length and weighs .
The longest crocodile captured alive was Lolong, a saltwater crocodile which was measured at and weighed at by a National Geographic team in Agusan del Sur Province, Philippines.
Teeth
Crocodiles are polyphyodonts; they are able to replace each of their 80 teeth up to 50 times in their 35- to 75-year lifespan. Next to each full-grown tooth, there is a small replacement tooth and an Animal tooth development, odontogenic stem cell in the dental lamina in standby that can be activated if required.Biology and behaviour
Crocodilians are more closely related to birds and dinosaurs than to most animals classified as reptiles, the three families being included in the group Archosauria ('ruling reptiles'). Despite their prehistoric look, crocodiles are among the more biologically complex reptiles. Unlike other reptiles, a crocodile has a cerebral cortex and a four-chambered heart. Crocodilians also have the functional equivalent of a diaphragm by incorporating muscles used for aquatic locomotion into respiration. Salt glands are present in the tongues of crocodiles and they have a pore opening on the surface of the tongue, a trait that separates them from alligators. Salt glands are dysfunctional in Alligatoridae. Their function appears to be similar to that of salt glands in marine turtles. Crocodiles do not have sweat glands and release heat through their mouths. They often sleep with their mouths open and may pant like a dog. Four species of freshwater crocodile climb trees to bask in areas lacking a shoreline.Senses
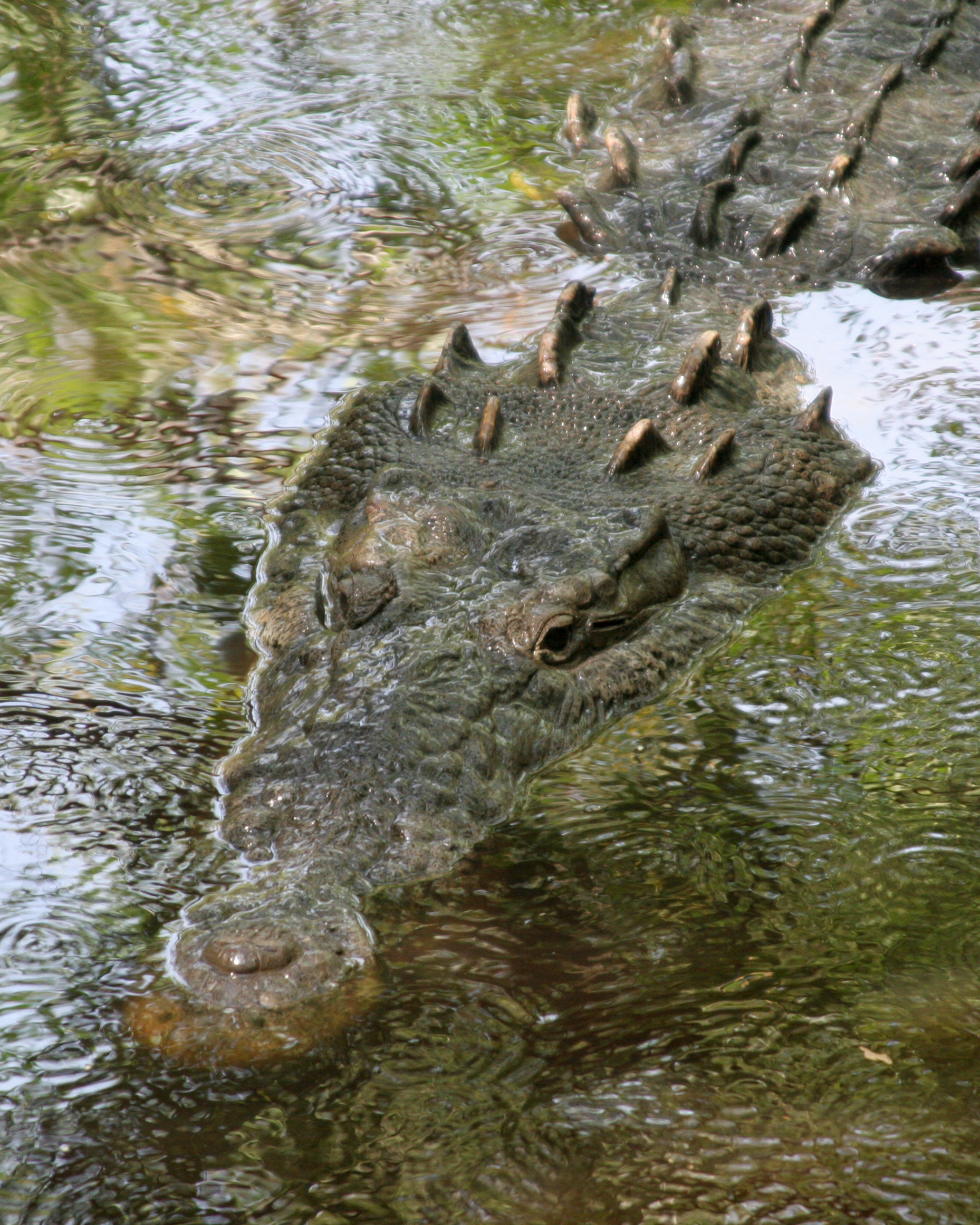
Crocodiles have acute senses, an evolutionary advantage that makes them successful predators. The eyes, ears and nostrils are located on top of the head, allowing the crocodile to lie low in the water, almost totally submerged and hidden from prey.Vision
Crocodiles have very good night vision, and are mostly Nocturnality, nocturnal hunters. They use the disadvantage of most prey animals' poor nocturnal vision to their advantage. The light receptors in crocodilians' eyes include Cone cell, cones and numerous Rod cells, rods, so it is assumed all crocodilians can see colours. Crocodiles have vertical-slit shaped pupils, similar to those of domestic cats. One explanation for the evolution of slit pupils is that they exclude light more effectively than a circular pupil, helping to protect the eyes during daylight. On the rear wall of the eye is a tapetum lucidum, which reflects incoming light back onto the retina, thus utilizing the small amount of light available at night to best advantage. In addition to the protection of the upper and lower eyelids, crocodiles have a nictitating membrane (sometimes called a "third eye-lid") that can be drawn over the eye from the inner corner while the lids are open. The eyeball surface is thus protected under the water while a certain degree of vision is still possible.Olfaction
Crocodilian Olfaction, sense of smell is also very well developed, aiding them to detect prey or animal carcasses that are either on land or in water, from far away. It is possible that crocodiles use olfaction in the egg prior to hatching. Chemoreception in crocodiles is especially interesting because they hunt in both terrestrial and aquatic surroundings. Crocodiles have only one olfactory chamber and the vomeronasal organ is absent in the adults indicating all olfactory perception is limited to the olfactory system. Behavioural and olfactometer experiments indicate that crocodiles detect both air-borne and water-soluble chemicals and use their olfactory system for hunting. When above water, crocodiles enhance their ability to detect volatile odorants by gular pumping, a rhythmic movement of the floor of the pharynx. Crocodiles close their nostrils when submerged, so olfaction underwater is unlikely. Underwater food detection is presumably gustatory and tactile.Hearing
Crocodiles can hear well; their Eardrum, tympanic membranes are concealed by flat flaps that may be raised or lowered by muscles.Touch
The touch sensors, concentrated in crocodile skin, can be thicker than those in human fingerprints. Crocodiles can feel the touch on their skin. Cranial: The upper and lower jaws are covered with sensory pits, visible as small, black speckles on the skin, the crocodilian version of the lateral line organs seen in fish and many amphibians, though arising from a completely different origin. These pigmented nodules encase bundles of Axon, nerve fibers innervated beneath by branches of the trigeminal nerve. They respond to the slightest disturbance in surface water, detecting vibrations and small pressure changes as small as a single drop. This makes it possible for crocodiles to detect prey, danger and intruders, even in total darkness. These sense organs are known as domed pressure receptors (DPRs). Post-Cranial: While alligators and caimans have DPRs only on their jaws, crocodiles have similar organs on almost every scale on their bodies. The function of the DPRs on the jaws is clear; to catch prey, but it is still not clear what the function is of the organs on the rest of the body. The receptors flatten when exposed to increased osmotic pressure, such as that experienced when swimming in sea water hyperosmotic to the body fluids. When contact between the integument and the surrounding sea water solution is blocked, crocodiles are found to lose their ability to discriminate salinities. It has been proposed that the flattening of the sensory organ in hyperosmotic sea water is sensed by the animal as "touch", but interpreted as chemical information about its surroundings. This might be why in alligators they are absent on the rest of the body.Hunting and diet

 Crocodiles are ambush predators, waiting for fish or land animals to come close, then rushing out to attack. Crocodiles mostly eat
Crocodiles are ambush predators, waiting for fish or land animals to come close, then rushing out to attack. Crocodiles mostly eat fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
, amphibians, crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s, mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s, bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
s, reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
s, and mammal
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the Class (biology), class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three ...
s, and they occasionally cannibalize smaller crocodiles. What a crocodile eats varies greatly with species, size and age. From the mostly fish-eating species, like the Slender-snouted crocodile, slender-snouted and freshwater crocodile
The freshwater crocodile (''Crocodylus johnstoni)'', also known Common name, commonly as the Australian freshwater crocodile, Johnstone's crocodile, and the freshie, is a species of crocodile native to the northern regions of Australia. Unlike ...
s, to the larger species like the Nile crocodile
The Nile crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'') is a large crocodilian native to freshwater habitats in Africa, where it is present in 26 countries. It is widely distributed in sub-Saharan Africa, occurring mostly in the eastern, southern, and ce ...
and the saltwater crocodile
The saltwater crocodile (''Crocodylus porosus'') is a crocodilian native to saltwater habitats, brackish wetlands and freshwater rivers from India's east coast across Southeast Asia and the Sundaland to northern Australia and Micronesia. It ha ...
that prey on large mammals, such as Bovinae, buffalo, deer and wild boar, diet shows great diversity. Diet is also greatly affected by the size and age of the individual within the same species. All young crocodiles hunt mostly invertebrates and small fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
, gradually moving on to larger prey. Being ectothermic (cold-blooded) predators, they have a very slow metabolism, so they can survive long periods without food. Despite their appearance of being slow, crocodiles have a very fast strike and are top predators in their environment, and various species have been observed attacking and killing other predators such as sharks and big cats. Crocodiles are also known to be aggressive scavengers who feed upon carrion and steal from other predators. Evidence suggests that crocodiles also feed upon fruits, based on the discovery of seeds in stools and stomachs from many subjects as well as accounts of them feeding.
Crocodiles have the most acidic stomach of any vertebrate. They can easily digest bones, hooves and horns. The BBC TV reported that a Nile crocodile
The Nile crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'') is a large crocodilian native to freshwater habitats in Africa, where it is present in 26 countries. It is widely distributed in sub-Saharan Africa, occurring mostly in the eastern, southern, and ce ...
that has lurked a long time underwater to catch prey builds up a large oxygen debt. When it has caught and eaten that prey, it closes its right aortic arch and uses its left aortic arch to flush blood loaded with carbon dioxide from its muscles directly to its stomach; the resulting excess acidity in its blood supply makes it much easier for the stomach lining to secrete more stomach acid to quickly dissolve bulks of swallowed prey flesh and bone. Many large crocodilians swallow stones (called gastroliths or stomach stones), which may act as ballast to balance their bodies or assist in crushing food, similar to grit ingested by birds. Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
claimed that Nile crocodiles had a symbiosis, symbiotic relationship with certain birds, such as the Egyptian plover, which enter the crocodile's mouth and pick leeches feeding on the crocodile's blood; with no evidence of this interaction actually occurring in any crocodile species, it is most likely mythical or allegorical fiction.
Bite
Since they feed by grabbing and holding onto their prey, they have Evolution, evolved sharp teeth for piercing and holding onto flesh, and powerful muscles to close the jaws and hold them shut. The teeth are not well-suited to tearing flesh off of large prey items as are the dentition and claws of many mammalian carnivores, the hooked bills and talons of Bird of prey, raptorial birds, or the serrated teeth of sharks. However, this is an advantage rather than a disadvantage to the crocodile since the properties of the teeth allow it to hold onto prey with the least possibility of the prey animal escaping. Cutting teeth, combined with the exceptionally high bite, bite force, would pass through flesh easily enough to leave an escape opportunity for prey. The jaws can bite down with immense force, by far the strongest bite of any animal. The force of a large crocodile's bite is more than , which was measured in aNile crocodile
The Nile crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'') is a large crocodilian native to freshwater habitats in Africa, where it is present in 26 countries. It is widely distributed in sub-Saharan Africa, occurring mostly in the eastern, southern, and ce ...
, in the field; comparing to for a Rottweiler, for a hyena, for an American alligator, and for the largest confirmed great white shark.
A long saltwater crocodile has been confirmed as having the strongest bite, bite force ever recorded for an animal in a laboratory setting. It was able to apply a bite force value of , and thus surpassed the previous record of made by a long American alligator. Taking the measurements of several crocodiles as reference, the bite forces of 6-m individuals were estimated at . The study, led by Dr. Gregory M. Erickson, also shed light on the larger, extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
species of crocodilians. Since crocodile anatomy has changed only slightly over the last 80 million years, current data on modern crocodilians can be used to estimate the bite force of extinct species. An ''Deinosuchus'' would apply a force of , nearly twice that of the latest, higher bite force estimations of ''Tyrannosaurus'' (). The extraordinary bite of crocodilians is a result of their anatomy. The space for the jaw muscle in the skull is very large, which is easily visible from the outside as a bulge at each side. The muscle is so stiff, it is almost as hard as bone to touch, as if it were the continuum of the skull. Another trait is that most of the muscle in a crocodile's jaw is arranged for clamping down. Despite the strong muscles to close the jaw, crocodiles have extremely small and weak muscles to open the jaw. Crocodiles can thus be subdued for study or transport by duct tape, taping their jaws or holding their jaws shut with large rubber bands cut from automobile tire, inner tubes.
Locomotion
Longevity
Measuring crocodile age is unreliable, although several techniques are used to derive a reasonable guess. The most common method is to measure lamellar growth rings in bones and teeth—each ring corresponds to a change in growth rate which typically occurs once a year between dry and wet seasons. Bearing these inaccuracies in mind, it can be safely said that all crocodile species have an average lifespan of at least 30–40 years, and in the case of larger species an average of 60–70 years. The oldest crocodiles appear to be the largest species. Saltwater crocodile, ''C. porosus'' is estimated to live around 70 years on average, with limited evidence of some individuals exceeding 100 years. In captivity, some individuals are claimed to have lived for over a century. A male crocodile lived to an estimated age of 110–115 years in a Russian zoo in Yekaterinburg. Named Kolya, he joined the zoo around 1913 to 1915, fully grown, after touring in an animal show, and lived until 1995. A male freshwater crocodile lived to an estimated age of 120–140 years at the Australia Zoo. Known affectionately as "Mr. Freshie", he was rescued around 1970 by Bob Irwin and Steve Irwin, after being shot twice by hunters and losing an eye as a result, and lived until 2010. Crocworld Conservation Centre, in Scottburgh, South Africa, claims to have a maleNile crocodile
The Nile crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'') is a large crocodilian native to freshwater habitats in Africa, where it is present in 26 countries. It is widely distributed in sub-Saharan Africa, occurring mostly in the eastern, southern, and ce ...
that was born in 1900. Named Henry, the crocodile is said to have lived in Botswana along the Okavango River, according to centre director Martin Rodrigues.
Social behaviour and vocalization
 Crocodiles are the most social of reptiles. Even though they do not form social groups, many species congregate in certain sections of
Crocodiles are the most social of reptiles. Even though they do not form social groups, many species congregate in certain sections of river
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of ...
s, tolerating each other at times of feeding and Body temperature, basking. Most species are not highly territorial, with the exception of the saltwater crocodile, which is a highly territory (animal), territorial and aggressive species: a mature, male saltwater crocodile will not tolerate any other males at any time of the year, but most other species are more flexible. There is a certain form of hierarchy in crocodiles: the largest and heaviest males are at the top, having access to the best basking site, while females are priority during a group feeding of a big kill or carcass. A good example of the hierarchy in crocodiles would be the case of the Nile crocodile
The Nile crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'') is a large crocodilian native to freshwater habitats in Africa, where it is present in 26 countries. It is widely distributed in sub-Saharan Africa, occurring mostly in the eastern, southern, and ce ...
. This species clearly displays all of these behaviours. Studies in this area are not thorough, however, and many species are yet to be studied in greater detail. Mugger crocodiles are also known to show toleration in group feedings and tend to congregate in certain areas. However, males of all species are aggressive towards each other during mating season, to gain access to females.
Crocodiles are also the most vocal of all reptiles, producing a wide variety of sounds during various situations and conditions, depending on species, age, size and sex. Depending on the context, some species can communicate over 20 different messages through Animal communication, vocalizations alone. Some of these vocalizations are made during social communication, especially during territory (animal), territorial displays towards the same sex and courtship display, courtship with the opposite sex; the common concern being reproduction. Therefore most conspecific vocalization is made during the breeding season, with the exception being year-round territorial behaviour in some species and quarrels during feeding. Crocodiles also produce different distress calls and in aggressive displays to their own kind and other animals; notably other predators during Interspecific competition, interspecific predatory confrontations over carcasses and terrestrial kills.
Specific vocalisations include —
* Chirp: When about to hatch, the young make a "peeping" noise, which encourages the female to excavate the nest. The female then gathers the hatchlings in her mouth and transports them to the water, where they remain in a group for several months, protected by the female
* Distress call: A high-pitched call used mostly by younger animals to alert other crocodiles to imminent danger or an animal being attacked.
* Threat call: A hissing sound that has also been described as a coughing noise.
* Hatching call: Emitted by a female when breeding to alert other crocodiles that she has laid eggs in her nest.
* Bellowing: Male crocodiles are especially vociferous. Bellowing choruses occur most often in the spring when breeding groups congregate, but can occur at any time of year. To bellow, males noticeably inflate as they raise the tail and head out of water, slowly waving the tail back and forth. They then puff out the throat and with a closed mouth, begin to vibrate air. Just before bellowing, males project an infrasonic signal at about 10 Hz through the water, which vibrates the ground and nearby objects. These low-frequency vibrations travel great distances through both air and water to advertise the male's presence and are so powerful they result in the water's appearing to "dance".
Reproduction
Mating
 courtship display, Courtship takes place in a series of behavioural interactions that include a variety of snout rubbing and submissive display that can take a long time. Mating always takes place in water, where the pair can be observed mating several times.
courtship display, Courtship takes place in a series of behavioural interactions that include a variety of snout rubbing and submissive display that can take a long time. Mating always takes place in water, where the pair can be observed mating several times.
Egg-laying & nesting
Egg-laying usually takes place at night and about 30–40 minutes, which are laid in either holes or mound nests, depending on species. The eggs are hard shelled, but translucent at the time of egg-laying. Depending on the species of crocodile, 7 to 95 eggs are laid. Scutes may play a role in calcium storage for eggshell formation. Nesting periods range from a few weeks up to six months. A hole nest is usually excavated in sand and a mound nest is usually constructed out of vegetation. Females can build or dig several trial nests which appear incomplete and abandoned later. Females are highly protective of their nests and young. Crocodile embryos do not have sex chromosomes, and unlike humans, sex is not determined genetically. Temperature-dependent sex determination, Sex is determined by temperature, where at or less most hatchlings are females and at , offspring are of both sexes. A temperature of gives mostly males whereas above in some species continues to give males, but in other species resulting in females, which are sometimes called high-temperature females. Temperature also affects growth and survival rate of the young, which may explain the sexual dimorphism in crocodiles. The average incubation period is around 80 days, and also is dependent on temperature and species that usually ranges from 65 to 95 days. The eggshell structure is very conservative through evolution but there are enough changes to tell different species apart by their eggshell microstructure. At the time of hatching, the young start calling within the eggs. They have an egg-tooth at the tip of their snouts, which is developed from the skin, and that helps them pierce out of the shell. Hearing the calls, the female usually excavates the nest and sometimes takes the unhatched eggs in her mouth, slowly rolling the eggs to help the process. The young is usually carried to the water in the mouth. She would then introduce her hatchlings to the water and even feed them. The mother would then take care of her young for over a year before the next mating season. In the absence of the mother crocodile, the father would act in her place to take care of the young. However, even with a sophisticated Paternal care, parental nurturing, young crocodiles have a very high mortality rate due to their vulnerability to predation. A group of hatchlings is called a pod or Crèche (zoology), crèche and may be protected for months.Cognition
Crocodiles possess some advanced cognitive abilities. 6 December 2013 9 December 2013 Crocodiles cooperative hunting, cooperatively hunt. Large numbers of crocodiles swim in circles to trap fish and take turns snatching them. In hunting larger prey, crocodiles swarm in, with one holding the prey down as the others rip it apart. Vladimir Dinets of the University of Tennessee, observing crocodile's use of Tool use by animals#In reptiles, twigs as bait was inconclusive.Relationship with humans
Danger to humans
saltwater crocodile
The saltwater crocodile (''Crocodylus porosus'') is a crocodilian native to saltwater habitats, brackish wetlands and freshwater rivers from India's east coast across Southeast Asia and the Sundaland to northern Australia and Micronesia. It ha ...
and Nile crocodile
The Nile crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'') is a large crocodilian native to freshwater habitats in Africa, where it is present in 26 countries. It is widely distributed in sub-Saharan Africa, occurring mostly in the eastern, southern, and ce ...
are the most dangerous, killing hundreds of people each year in parts of Southeast Asia and Africa. The mugger crocodile and American crocodile
The American crocodile (''Crocodylus acutus'') is a species of crocodilian found in the Neotropics. It is the most widespread of the four Extant taxon, extant species of crocodiles from the Americas, with populations present from South Florida, ...
are also dangerous to humans.
Crocodile products

 Crocodiles are protected in many parts of the world, but are also farmed commercially. Their hides are tanned and used to make leather goods such as shoes and handbags; crocodile meat is also considered a delicacy. The most commonly farmed species are the saltwater and Nile crocodiles, while a hybrid of the saltwater and the rare
Crocodiles are protected in many parts of the world, but are also farmed commercially. Their hides are tanned and used to make leather goods such as shoes and handbags; crocodile meat is also considered a delicacy. The most commonly farmed species are the saltwater and Nile crocodiles, while a hybrid of the saltwater and the rare Siamese crocodile
The Siamese crocodile (''Crocodylus siamensis'') is a medium-sized freshwater crocodile native to Indonesia (Borneo and possibly Java), Brunei, East Malaysia, Laos, Cambodia, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam. The species is critically endangered and ...
is also bred in Asian farms. Farming has resulted in an increase in the saltwater crocodile population in Australia, as eggs are usually harvested from the wild, so landowners have an incentive to conserve their habitat. Crocodile leather can be made into goods such as wallets, briefcases, purses, handbags, belts, hats, and shoes. Crocodile oil has been used for various purposes. Vietnamese cuisine#Exotic dishes, Crocodiles were eaten by Vietnamese while they were taboo and off limits for Chinese. Vietnamese women who married Chinese men adopted the Chinese taboo.
Crocodile meat is consumed in some countries, such as Australia, Ethiopia, Thailand, South Africa, China, and Cuba (in pickled form). It is also occasionally eaten as an "exotic" delicacy in the western world. Cuts of meat include backstrap and tail fillet.
Due to high demand for crocodile products, Traffic (conservation programme), TRAFFIC states that 1,418,487 Nile Crocodile skins were exported from Africa between 2006 and 2015.
Crocodile hunting and conservation
Aboriginal Australians harvested eggs and hunted crocodiles in a sustainable way for many thousands of years. The Brinkin people (aka Marrithiyal) of the Daly River (Northern Territory), Daly River in the Northern Territory (NT) used harpoons and bamboo, and even their own hands to capture crocodiles for food. After settlement of northern Australia, in the late-19th and early 20th centuries, non-Indigenous Australians, Indigenous people killed individual crocodiles, mostly by locals to protect the population, or novelty-seeking visitors, or just opportunistically, so numbers were not noticeably reduced. From the 1930s, commercial hunting began, with Aboriginal people often employed to kill the crocodiles using traditional methods. From the 1940s to the 1960s, hunting began on a larger scale using .303 rifles. They were hunted for leather, with the skins shipped to plants in capital cities. Western Australia banned hunting freshwater crocodiles in 1962 and saltwater crocodiles in 1970, while NT bans were brought in 1964 and 1971; Queensland did not pass such legislation. The federal government later banned the export of crocodile skins, which brought commercial hunting to an end in Queensland. They have been a protected species since the 1970s, when numbers were down to approximately 3,000 in the NT at the lowest estimate. In 2021, after several attacks on humans by the "salties" and an estimated population of around 200,000 had been reached, Queensland politician Bob Katter called for the reintroduction of hunting.In religion and mythology
 Crocodiles have appeared in various forms in religions across the world. Ancient Egypt had Sobek, the crocodile-headed god, with his cult-city Crocodilopolis, as well as Taweret, the goddess of childbirth and fertility, with the back and tail of a crocodile. The Wukari Federation#Religion, Jukun shrine in the Wukari Federation, Nigeria is dedicated to crocodiles in thanks for their aid during migration. In Madagascar various peoples such as the Sakalava people, Sakalava and Antandroy see crocodiles as ancestor spirits and under local ''Fady (taboo), fady'' often offer them food;Campbell, Gwyn (2012). David Griffiths and the Missionary "History of Madagascar". Leiden, The Netherlands: Brill. . in the case of the latter at least a crocodile features prominently as an ancestor deity.
Crocodiles appear in different forms in Hinduism. Varuna, a Historical Vedic religion, Vedic and Hindu god, rides a part-crocodile Makara (Hindu mythology), makara; his consort Varuni rides a crocodile. Similarly the goddess personifications of the Ganges, Ganga and Yamuna rivers are often depicted as riding crocodiles. Also in India, in Goa, crocodile worship is practised, including the annual ''Mannge Thapnee'' ceremony.
Sikh warriors known as nihang also have connections with crocodiles. ''Nihang'' may come from the Persian word for a mythical sea creature (). The term owes its origin to Mughal Empire, Mughal historians, who compared the ferocity of the Akali with that of crocodiles. In Sikhism however, ''Akali'' refers to the immortal army of Akal (god).
In Latin America, Cipactli was the giant earth crocodile of the Aztec and other Nahua peoples.
Crocodiles have appeared in various forms in religions across the world. Ancient Egypt had Sobek, the crocodile-headed god, with his cult-city Crocodilopolis, as well as Taweret, the goddess of childbirth and fertility, with the back and tail of a crocodile. The Wukari Federation#Religion, Jukun shrine in the Wukari Federation, Nigeria is dedicated to crocodiles in thanks for their aid during migration. In Madagascar various peoples such as the Sakalava people, Sakalava and Antandroy see crocodiles as ancestor spirits and under local ''Fady (taboo), fady'' often offer them food;Campbell, Gwyn (2012). David Griffiths and the Missionary "History of Madagascar". Leiden, The Netherlands: Brill. . in the case of the latter at least a crocodile features prominently as an ancestor deity.
Crocodiles appear in different forms in Hinduism. Varuna, a Historical Vedic religion, Vedic and Hindu god, rides a part-crocodile Makara (Hindu mythology), makara; his consort Varuni rides a crocodile. Similarly the goddess personifications of the Ganges, Ganga and Yamuna rivers are often depicted as riding crocodiles. Also in India, in Goa, crocodile worship is practised, including the annual ''Mannge Thapnee'' ceremony.
Sikh warriors known as nihang also have connections with crocodiles. ''Nihang'' may come from the Persian word for a mythical sea creature (). The term owes its origin to Mughal Empire, Mughal historians, who compared the ferocity of the Akali with that of crocodiles. In Sikhism however, ''Akali'' refers to the immortal army of Akal (god).
In Latin America, Cipactli was the giant earth crocodile of the Aztec and other Nahua peoples.
In language and as symbols
The term "crocodile tears" (and equivalents in other languages) refers to a false, insincere display of emotion, such as a hypocrite crying fake tears of grief. It is derived from an ancient anecdote that crocodiles weep in order to lure their prey, or that they Crying, cry for the victims they are eating, first told in the ''Bibliotheca (Photius), Bibliotheca'' by Photios I of Constantinople. The story is repeated in bestiaries such as List of medieval bestiaries#DeBestiis, ''De bestiis et aliis rebus''. This tale was first spread widely in English in the stories of the ''Travels of Sir John Mandeville'' in the 14th century, and appears in several of Shakespeare's plays. In fact, crocodiles can and do generate tears, but they do not actually cry. In the UK, a row of schoolchildren walking in pairs, or two by two is known as "crocodile".Fashion logos
The French clothing company Lacoste features a crocodile in its logo. The American shoe company Crocs also uses this imagery in its logo.See also
*Alligator meat *''The Crocodile Hunter'' *Crocodilian armor *Game (hunting) *Sewer alligator *Sobek – an ancient Egyptian deity associated with the Nile crocodileReferences
Notes
Further reading
* Iskandar, DT (2000). ''Turtles and Crocodiles of Insular Southeast Asia and New Guinea''. ITB, Bandung. * Crocodilian Biology Database, FAQFLMNH.ufl.edu
"How long do crocodiles live for?" Adam Britton. * Crocodilian Biology Database, FAQ
"How fast can a crocodile run?" Adam Britton.
External links
*Crocodilian Online
Crocodile Attacks in Australia
BBC news finds powerful agent in crocodile blood
World's most expensive handbag sells in Hong Kong for over US$377,000 – a Hermès white crocodile
(31 May 2017), ''South China Morning Post''
292 New Guinea crocodiles massacred
in West Papua (province), West Papua, Indonesia {{DEFAULTSORT:Crocodile Crocodylidae, Extant Ypresian first appearances Taxa named by Georges Cuvier Crocodilian families