Crimean People on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
According to the
2021 Russian census
The 2021 Russian census () was the first census of the Russia, Russian Federation population since 2010 Russian census, 2010 and the third after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, dissolution of the Soviet Union. It took place between October 1 ...
, the total population of the Republic of Crimea
Crimea, or the Crimean Peninsula, historically also known as the ''Tauric Chersonese'' (Tauric Peninsula, Tauric, Taurica, or Tauris), is a major peninsula in the north of the Black Sea.
Crimea may also refer to:
Places Crimean Peninsula Republic ...
and Sevastopol
Sevastopol ( ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea and a major port on the Black Sea. Due to its strategic location and the navigability of the city's harbours, Sevastopol has been an important port and naval base th ...
was at 2,482,450 (Crimea: 1,934,630, Sevastopol: 547,820). This is up from the 2001 Ukrainian census
The 2001 Ukrainian census is to date the only census of the population of independent Ukraine. It was conducted by the State Statistics Committee of Ukraine on 5 December 2001, twelve years after the last Soviet Union census in 1989.Autonomous Republic of Crimea
The Autonomous Republic of Crimea is a ''de jure'' administrative division of Ukraine encompassing most of Crimea that was unilaterally annexed by Russia in 2014. The Autonomous Republic of Crimea occupies most of the peninsula, and the local census conducted by Russia in December 2014, which found 2,248,400 people (Republic of Crimea: 1,889,485, Sevastopol: 395,000). According to the Ukrainian census,
(
 Other minorities are
Other minorities are  Currently two thirds of migrants into Crimea are from other regions of Ukraine; every fifth migrant is from elsewhere in the former Soviet Union and every 40th from outside of it. Three quarters of those leaving Crimea move to other areas in Ukraine. Every 20th migrates to the West.
The number of Crimean residents who consider Ukraine their
Currently two thirds of migrants into Crimea are from other regions of Ukraine; every fifth migrant is from elsewhere in the former Soviet Union and every 40th from outside of it. Three quarters of those leaving Crimea move to other areas in Ukraine. Every 20th migrates to the West.
The number of Crimean residents who consider Ukraine their
File:Life expectancy in Russian subject -Crimea.png, Life expectancy in Crimea
File:Life expectancy in Russian subject -Crimea -diff.png, Life expectancy with calculated differences
File:Life expectancy in Russian subject -Republic of Crimea -diff.png, Life expectancy in
File:Life expectancy in Russian subject -Sevastopol -diff.png, Life expectancy in Sevastopol
File:Life expectancy in Russia -Crimea.png, Life expectancy in Crimea and neighboring regions of the country
Perekop
Perekop ( Ukrainian & Russian: Перекоп; ; ) is a village located on the Perekop Isthmus connecting the Crimean peninsula to the Ukrainian mainland. It is known for the Or Qapi fortress, which served as the gateway to Crimea. The villa ...
and Pervomaisky districts had a Ukrainian ethnic plurality, while the rest of Crimea had a simple or absolute majority of ethnic Russians.
History
The Crimean interior has been ethnically diverse throughout its recorded history, changing hands numerous times, while the south coast was held continuously for most of the last two millennia by various Roman (andEastern Roman
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
) states. The interior was dominated by a succession of Scytho-Sarmatian
The Scythian languages are a group of Eastern Iranic languages of the classical and late antique period (the Middle Iranic period), spoken in a vast region of Eurasia by the populations belonging to the Scythian cultures and their desce ...
, Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, a Germanic people
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Gothic alphabet, an alphabet used to write the Gothic language
** Gothic ( ...
, Hunnic, Turkic, Mongol
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China (Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of M ...
and Slavic
Slavic, Slav or Slavonic may refer to:
Peoples
* Slavic peoples, an ethno-linguistic group living in Europe and Asia
** East Slavic peoples, eastern group of Slavic peoples
** South Slavic peoples, southern group of Slavic peoples
** West Slav ...
conquests. Its south coast was Greek speaking first as Greek colonies
Greek colonisation refers to the expansion of Archaic Greeks, particularly during the 8th–6th centuries BC, across the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea.
The Archaic expansion differed from the Iron Age migrations of the Greek Dark Ages ...
(7th or 6th century BC and following), then under the Bosporan Kingdom
The Bosporan Kingdom, also known as the Kingdom of the Cimmerian Bosporus (; ), was an ancient Greco-Scythians, Scythian state located in eastern Crimea and the Taman Peninsula on the shores of the Cimmerian Bosporus, centered in the present-day ...
(480 BC - 63 BC), Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
s (47 BC -330 AD) and their successor states, the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
(330 AD - 1204 AD), the Empire of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond or the Trapezuntine Empire was one of the three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire that existed during the 13th through to the 15th century. The empire consisted of the Pontus, or far northeastern corner of A ...
(1204 AD - 1461 AD), and the independent Principality of Theodoro
The Principality of Theodoro (), also known as Gothia () or the Principality of Theodoro-Mangup, was a Greek principality in the southern part of Crimea, specifically on the foothills of the Crimean Mountains. It represented one of the final rump ...
(1461 AD - 1475 AD). In 1475 the region was conquered by the Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks () were a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group in Anatolia. Originally from Central Asia, they migrated to Anatolia in the 13th century and founded the Ottoman Empire, in which they remained socio-politically dominant for the e ...
. During the late Middle Ages a few coastal cities were ruled by Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
city states. A number of Englishmen
The English people are an ethnic group and nation native to England, who speak the English language, a West Germanic language, and share a common ancestry, history, and culture. The English identity began with the Anglo-Saxons, when they we ...
, fleeing England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
after the Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Norman, French people, French, Flemish people, Flemish, and Bretons, Breton troops, all led by the Du ...
, were said to have settled in Crimea with the Byzantine Emperor’s permission, and comprised a majority of his Varangian Guard
The Varangian Guard () was an elite unit of the Byzantine army from the tenth to the fourteenth century who served as personal bodyguards to the Byzantine emperors. The Varangian Guard was known for being primarily composed of recruits from Nort ...
until the Empire’s collapse.
The Crimean Tatars
Crimean Tatars (), or simply Crimeans (), are an Eastern European Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group and nation indigenous to Crimea. Their ethnogenesis lasted thousands of years in Crimea and the northern regions along the coast of the Blac ...
emerged as a Turkic-speaking ethnic group native to Crimea in the early modern period, during the lifetime of the Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate, self-defined as the Throne of Crimea and Desht-i Kipchak, and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary, was a Crimean Tatars, Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the longest-lived of th ...
, and by the annexation of the Crimean Khanate by the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
in 1783, they formed the clear majority of Crimean population. The colonization "New Russia
Novorossiya rus, Новороссия, Novorossiya, p=nəvɐˈrosʲːɪjə, a=Ru-Новороссия.ogg; , ; ; ; "New Russia". is a historical name, used during the era of the Russian Empire for an administrative area that would later becom ...
" (the Novorossiysk Governorate
Novorossiya Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit ('' guberniya'') of the Russian Empire, which existed in 1764–1783 and again in 1796–1802. It was created and governed according to the "Plan for the Colonization of New Russi ...
, of which the later Taurida Governorate
Taurida Governorate was an administrative-territorial unit ('' guberniya'') of the Russian Empire. It included the territory of the Crimean Peninsula and the mainland between the lower Dnieper River with the coasts of the Black Sea and Sea o ...
formed a part) at the end of the 18th century was led by Prince
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. The ...
Grigori Potemkin
Prince Grigory Aleksandrovich Potemkin-Tauricheski (A number of dates as late as 1742 have been found on record; the veracity of any one is unlikely to be proved. This is his "official" birth-date as given on his tombstone.) was a Russian mi ...
who was granted the powers of an absolute ruler over the area by Catherine the Great
Catherine II. (born Princess Sophie of Anhalt-Zerbst; 2 May 172917 November 1796), most commonly known as Catherine the Great, was the reigning empress of Russia from 1762 to 1796. She came to power after overthrowing her husband, Peter I ...
. The lands were generously given to the Russian ''dvoryanstvo
The Russian nobility or ''dvoryanstvo'' () arose in the Middle Ages. In 1914, it consisted of approximately 1,900,000 members, out of a total population of 138,200,000. Up until the February Revolution of 1917, the Russian noble estates staffed ...
'' (nobility), and the enserfed peasantry
A peasant is a pre-industrial agricultural laborer or a farmer with limited land-ownership, especially one living in the Middle Ages under feudalism and paying rent, tax, fees, or services to a landlord. In Europe, three classes of peasan ...
mostly from Ukraine and fewer from Russia were transferred to cultivate what was a sparsely populated steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without closed forests except near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the tropical and subtropica ...
. Catherine the Great also invited European settlers to these newly conquered lands: Crimea Germans
The Crimea Germans (, , ) were ethnic German settlers who were invited by Russia to colonize the Crimea as part of the ''Ostsiedlung'' ("East Settlement").
History
From 1783 onwards, there was a systematic settlement of Russians, Ukrainians, and ...
, Poles in Russia
There are currently more than 22,000 ethnic Polish people, Poles living in the Russian Federation. This includes native Poles as well as those forcibly deported during and after World War II. When including all of the countries of the former Sovie ...
, Italians of Crimea
The Italians of Crimea (; ; ) are an ethnic minority residing in Crimea, whose ancestors were Italians who emigrated to Crimea during the Italian diaspora, the largest nucleus of which is found in the city of Kerch. Ancient Romans, who are the an ...
, and others.
Crimea is geographically and demographically divided into three regions, the steppe interior, the mountains, and the coast. The Tatars were the predominant portion of the population in the mountainous area and about half of the steppe population, while Russians were concentrated most heavily in the Feodosiya district.
Germans and settled in the Crimea at the beginning of the 19th century, receiving a large allotment and fertile land.
Wealthy colonists later bought substantial portions of land, mainly in Perekopsky and Yevpatoria
Yevpatoria (; ; ; ) is a city in western Crimea, north of Kalamita Bay. Yevpatoria serves as the administrative center of Yevpatoria Municipality, one of the districts (''raions'') into which Crimea is divided. It had a population of
His ...
districts.
At the beginning of the 19th century, Italian emigration to the Crimea came from various Italian regions (Liguria
Liguria (; ; , ) is a Regions of Italy, region of north-western Italy; its Capital city, capital is Genoa. Its territory is crossed by the Alps and the Apennine Mountains, Apennines Mountain chain, mountain range and is roughly coextensive with ...
, Campania
Campania is an administrative Regions of Italy, region of Italy located in Southern Italy; most of it is in the south-western portion of the Italian Peninsula (with the Tyrrhenian Sea to its west), but it also includes the small Phlegraean Islan ...
, Apulia
Apulia ( ), also known by its Italian language, Italian name Puglia (), is a Regions of Italy, region of Italy, located in the Southern Italy, southern peninsular section of the country, bordering the Adriatic Sea to the east, the Strait of Ot ...
), with immigrants settling mainly in the coastal cities of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
and the Sea of Azov
The Sea of Azov is an inland Continental shelf#Shelf seas, shelf sea in Eastern Europe connected to the Black Sea by the narrow (about ) Strait of Kerch, and sometimes regarded as a northern extension of the Black Sea. The sea is bounded by Ru ...
, as well as in Odesa
Odesa, also spelled Odessa, is the third most populous List of cities in Ukraine, city and List of hromadas of Ukraine, municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern ...
, Mykolaiv
Mykolaiv ( ), also known as Nikolaev ( ) is a List of cities in Ukraine, city and a hromada (municipality) in southern Ukraine. Mykolaiv is the Administrative centre, administrative center of Mykolaiv Raion (Raions of Ukraine, district) and Myk ...
, Sevastopol
Sevastopol ( ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea and a major port on the Black Sea. Due to its strategic location and the navigability of the city's harbours, Sevastopol has been an important port and naval base th ...
, Mariupol
Mariupol is a city in Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine. It is situated on the northern coast (Pryazovia) of the Sea of Azov, at the mouth of the Kalmius, Kalmius River. Prior to the Russian invasion of Ukraine, it was the tenth-largest city in the coun ...
, Berdiansk
Berdiansk or Berdyansk (, ; , ) is a port city in Zaporizhzhia Oblast, south-eastern Ukraine. It is on the northern coast of the Sea of Azov, which is connected to the Black Sea. It serves as the administrative center of Berdiansk Raion. The c ...
and Taganrog
Taganrog (, ) is a port city in Rostov Oblast, Russia, on the north shore of Taganrog Bay in the Sea of Azov, several kilometers west of the mouth of the Don (river), Don River. It is in the Black Sea region. Population:
Located at the site of a ...
. With the October Revolution
The October Revolution, also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution (in Historiography in the Soviet Union, Soviet historiography), October coup, Bolshevik coup, or Bolshevik revolution, was the second of Russian Revolution, two r ...
of 1917, with which the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
became the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, a bitter period began for minorities in Russia. Italians of Crimea
The Italians of Crimea (; ; ) are an ethnic minority residing in Crimea, whose ancestors were Italians who emigrated to Crimea during the Italian diaspora, the largest nucleus of which is found in the city of Kerch. Ancient Romans, who are the an ...
therefore faced much repression. Between 1936 and 1938, during Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Dzhugashvili; 5 March 1953) was a Soviet politician and revolutionary who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until Death and state funeral of Joseph Stalin, his death in 1953. He held power as General Secret ...
's Great Purge
The Great Purge, or the Great Terror (), also known as the Year of '37 () and the Yezhovshchina ( , ), was a political purge in the Soviet Union that took place from 1936 to 1938. After the Assassination of Sergei Kirov, assassination of ...
, many Italians were accused of espionage
Espionage, spying, or intelligence gathering, as a subfield of the intelligence field, is the act of obtaining secret or confidential information ( intelligence). A person who commits espionage on a mission-specific contract is called an ...
and were arrested, tortured, deported or executed. The few survivors were allowed to return to Kerch in the 1950s and 1960s during Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and the Premier of the Soviet Union, Chai ...
's administration. The descendants of the surviving Italians of Crimea currently account for people, mainly residing in Kerch.
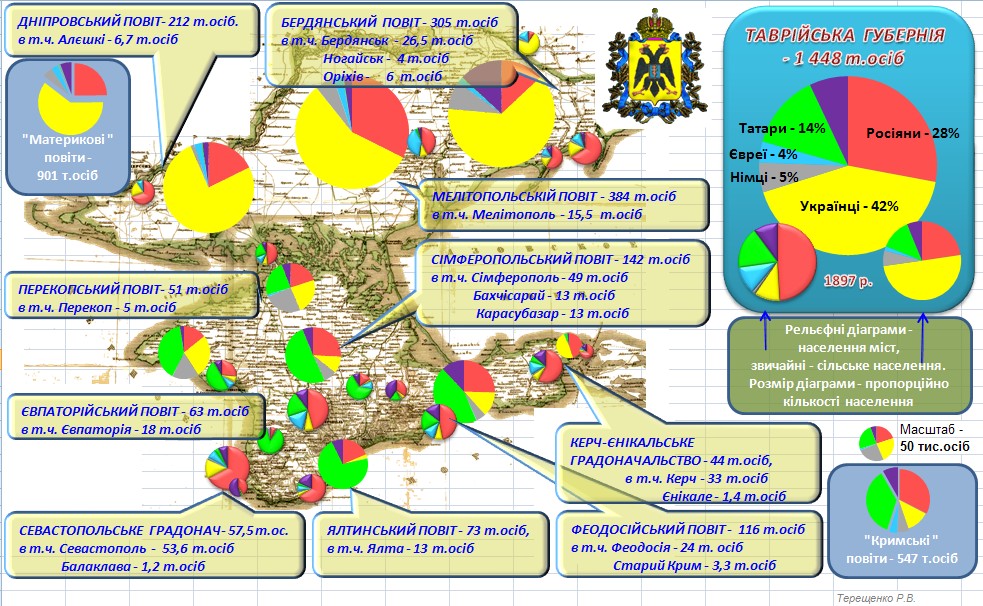
By the 1897 Russian Empire Census, Crimean Tatars continued to form a slight plurality (35%) of Crimea's still largely rural population, but there were large numbers of Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
(33%) and Ukrainians (11%), as well as smaller numbers of Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
, Jews (including Krymchaks
Krymchaks ( Krymchak: , , , ) are Jewish ethno-religious communities of Crimea derived from Turkic-speaking adherents of Rabbinic Judaism.Crimean Karaites
Crimean Karaites or simply Karaites (Crimean Karaim language, Karaim: Кърымкъарайлар, ''Qrımqaraylar'', singular къарай, ''qaray''; Trakai dialect: ''karajlar'', singular ''karaj''; ; ; ), also known more broadly as Eastern E ...
), Bulgarians
Bulgarians (, ) are a nation and South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and its neighbouring region, who share a common Bulgarian ancestry, culture, history and language. They form the majority of the population in Bulgaria, ...
, Belarusians, Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic of Turkey
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic lang ...
, Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
, Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
and Roma (gypsies).
The upheavals and ethnic cleansing of the 20th century vastly changed Crimea's ethnic composition. In 1944, 200,000 Crimean Tatars were deported from Crimea to Central Asia and Siberia, along with 70,000 Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
and 14,000 Bulgarians and other nationalities.The Persecution of Pontic Greeks in the Soviet Union(
PDF
Portable document format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe Inc., Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, computer hardware, ...
)" By the latter 20th century, Russians and Ukrainians made up almost the entire population. However, with the fall of the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
, exiled Crimean Tatars began returning to their homeland and accounted for 10% of the population by the beginning of the 21st century.
Ethnicities and languages
Crimean Gothic
Crimean Gothic was a Germanic languages, Germanic, probably East Germanic languages, East Germanic, language spoken by the Crimean Goths in some isolated locations in Crimea until the late 18th century. Crimea was inhabited by the Goths in Late ...
, an East Germanic language, became extinct around the 18th century, while the Crimean Goths
The Crimean Goths were either a Greuthungi- Gothic tribe or a Western Germanic tribe that bore the name '' Gothi'', a title applied to various Germanic tribes that remained in the lands around the Black Sea, especially in Crimea. They were the ...
diffused into other ethnicities much earlier on. Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
was also spoken by settlers from England, who were eventually absorbed into the Tatar population. According to Ukraine's 2001 census, the ethnic makeup of Crimea's population consisted primarily of the following self-reported groups: Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
(1.450 million, 60.4%), Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
(576,600; 24.0%), Crimean Tatars
Crimean Tatars (), or simply Crimeans (), are an Eastern European Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group and nation indigenous to Crimea. Their ethnogenesis lasted thousands of years in Crimea and the northern regions along the coast of the Blac ...
(258,400; 10.8%), Belarusians
Belarusians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Belarus. They natively speak Belarusian language, Belarusian, an East Slavic language. More than 9 million people proclaim Belarusian ethnicity worldwide. Nearly 7.99&n ...
(25,000; 1.5%), Armenians
Armenians (, ) are an ethnic group indigenous to the Armenian highlands of West Asia.Robert Hewsen, Hewsen, Robert H. "The Geography of Armenia" in ''The Armenian People From Ancient to Modern Times Volume I: The Dynastic Periods: From Antiq ...
(10,000; 0.4%), and Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
(5,500; 0.2%).
 Other minorities are
Other minorities are Black Sea Germans
The Black Sea Germans (; ; ) are ethnic Germans who left their homelands (starting in the late-18th century, but mainly in the early-19th century at the behest of Emperor Alexander I of Russia, ), and settled in territories off the north coast ...
, Roma
Roma or ROMA may refer to:
People, characters, figures, names
* Roma or Romani people, an ethnic group living mostly in Europe and the Americas.
* Roma called Roy, ancient Egyptian High Priest of Amun
* Roma (footballer, born 1979), born ''Paul ...
, Bulgarians
Bulgarians (, ) are a nation and South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and its neighbouring region, who share a common Bulgarian ancestry, culture, history and language. They form the majority of the population in Bulgaria, ...
, Poles
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
, Azerbaijanis
Azerbaijanis (; , ), Azeris (, ), or Azerbaijani Turks (, ) are a Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group living mainly in the Azerbaijan (Iran), Azerbaijan region of northwestern Iran and the Azerbaijan, Republic of Azerbaijan. They are predomin ...
, Koreans
Koreans are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula. The majority of Koreans live in the two Korean sovereign states of North and South Korea, which are collectively referred to as Korea. As of 2021, an estimated 7.3 m ...
, Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
and Italians of Crimea
The Italians of Crimea (; ; ) are an ethnic minority residing in Crimea, whose ancestors were Italians who emigrated to Crimea during the Italian diaspora, the largest nucleus of which is found in the city of Kerch. Ancient Romans, who are the an ...
. The number of Crimea Germans
The Crimea Germans (, , ) were ethnic German settlers who were invited by Russia to colonize the Crimea as part of the ''Ostsiedlung'' ("East Settlement").
History
From 1783 onwards, there was a systematic settlement of Russians, Ukrainians, and ...
was 45,000 in 1941. In 1944, 70,000 Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
and 14,000 Bulgarians from the Crimea were deported to Central Asia and Siberia, along with 200,000 Crimean Tatars and other nationalities.
According to the 2001 census, 77% of Crimean inhabitants named Russian as their native language, 11.4% – Crimean Tatar, and 10.1% – Ukrainian. Of the Ukrainians in Crimea, 40% gave Ukrainian as their native language, with 60% identifying as ethnic Ukrainians while giving Russian as their primary language. 93% of Crimean Tatars gave Crimean Tatar as their native language, 6% were Russophone
This article details the geographical distribution of Russian-speakers. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, the status of the Russian language often became a matter of controversy. Some Post-Soviet states adopted policies of Derus ...
. In 2013, however, the Crimean Tatar language was estimated to be on the brink of extinction, being taught in Crimea only in around 15 schools at that point of time. Turkey has provided the greatest support to Ukraine, which has been unable to resolve the problem of education in the mother tongue in Crimea, by bringing the schools to a modern state. Ukrainian was until 2014 the single official state language countrywide, but in Crimea government business was carried out mainly in Russian
Russian(s) may refer to:
*Russians (), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*A citizen of Russia
*Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages
*''The Russians'', a b ...
. Attempts to expand the usage of Ukrainian in education and government affairs have been less successful in Crimea than in other areas of the nation. motherland
A homeland is a place where a national or ethnic identity has formed. The definition can also mean simply one's country of birth. When used as a proper noun, the Homeland, as well as its equivalents in other languages, often has ethnic natio ...
increased sharply from 32% to 71.3% from 2008 through 2011; according to a poll by Razumkov Center
Razumkov Centre (), or fully the Ukrainian Centre for Economic and Political Studies named after Olexander Razumkov (), is a Ukrainian non-governmental public policy think tank.
Overview
The Razumkov Center carries out research in domestic, econ ...
in March 2011, although this is the lowest number in all Ukraine (93% on average across the country).Poll: Most Crimean residents consider Ukraine their motherlandKyiv Post
The ''Kyiv Post'' is Ukraine’s first and most prominent English-language newspaper. It was founded in 1995 in Kyiv by American businessman Jed Sunden.
In 2018, the publication was acquired by prominent Ukrainian businessman Adnan Kivan, foun ...
(11 April 2011) Surveys of regional identities in Ukraine have shown that around 30% of Crimean residents claim to have retained a self-identified "Soviet
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
identity".
Since the independence of Ukraine in 1991, 3.8 million former citizens of Russia have applied for Ukrainian citizenship.
In 2014 after Russian annexation of Crimea ocupational authorities conducted a census. According to the census result the population of the Crimean Federal District
The Crimean Federal District () was a federal district of Russia. It was established on March 21, 2014 after the annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation. The federal district included both the Republic of Crimea and the federal city o ...
is 2.2844 million people. The ethnic composition is as follows: Russians
Russians ( ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Eastern Europe. Their mother tongue is Russian language, Russian, the most spoken Slavic languages, Slavic language. The majority of Russians adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church ...
: 1.49 million (65.3%), Ukrainians
Ukrainians (, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. Their native tongue is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, and the majority adhere to Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, forming the List of contemporary eth ...
: 0.35 million (15.1%), Crimean Tatars
Crimean Tatars (), or simply Crimeans (), are an Eastern European Turkic peoples, Turkic ethnic group and nation indigenous to Crimea. Their ethnogenesis lasted thousands of years in Crimea and the northern regions along the coast of the Blac ...
: 0.24 million (12.0%). Official Ukrainian authorities and Mejlis of the Crimean Tatar People
The Mejlis of the Crimean Tatar People () is the single highest executive-representative body of the Crimean Tatars in period between sessions of the Qurultay of the Crimean Tatar People. The Mejlis is a member institution of the Platform of E ...
claimed doubts that the results of population census in Crimea represent the facts.
A survey in May 2013, asked respondents what language they spoke at home:
*82% Russian
*10% Crimean Tatar
*3% Russian and Ukrainian equally
*3% Russian and another language equally
*2% Ukrainian
Note that the proportion of people in the survey who gave their ethnicity as Ukrainian was 20%, Crimean Tatar 15%.
Birth rate, death rate, total fertility rate, life expectancy
;Vital statistics for 2015 *Births: 29 422 (12.8 per 1000) *Deaths: 35 151 (15.3 per 1000) ;Vital statistics for 2020 *Births: 31 105 (13.6 per 1000) *Deaths: 29 890 (13.3 per 1000) ;Fertility rate ;Life expectancyLife expectancy
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where '' ...
at birth for Crimea as a whole, calculated as weighted average
The weighted arithmetic mean is similar to an ordinary arithmetic mean (the most common type of average), except that instead of each of the data points contributing equally to the final average, some data points contribute more than others. The ...
between the Republic of Crimea and the federal city of Sevastopol, according to number of population.
Education
The 2001 Ukrainian census for theAutonomous Republic of Crimea
The Autonomous Republic of Crimea is a ''de jure'' administrative division of Ukraine encompassing most of Crimea that was unilaterally annexed by Russia in 2014. The Autonomous Republic of Crimea occupies most of the peninsula,
*total population 1,203,789 *completed higher education: 175,838 (14.6%) *higher education (partial or complete): 476,793 (39.6%) *completed secondary education: 507,881 (49.7%) *secondary education (partial or complete): 685,855 (57.0%) *no primary education: 1,945 (0.16%) *illiterate: 1,413 (0.11%)
*total population 1,203,789 *completed higher education: 175,838 (14.6%) *higher education (partial or complete): 476,793 (39.6%) *completed secondary education: 507,881 (49.7%) *secondary education (partial or complete): 685,855 (57.0%) *no primary education: 1,945 (0.16%) *illiterate: 1,413 (0.11%)
Religion
The Crimean peninsula was Christianised at an early time, viaGothic Christianity
Gothic Christianity refers to the Christian religion of the Goths and sometimes the Gepids, Vandals, and Burgundians, who may have used the translation of the Bible into the Gothic language and shared common doctrines and practices.
The Gothic ...
, in the 4th century.
In the 9th century, the Goths in Crimea turned to the Greek Orthodox Church
Greek Orthodox Church (, , ) is a term that can refer to any one of three classes of Christian Churches, each associated in some way with Christianity in Greece, Greek Christianity, Antiochian Greek Christians, Levantine Arabic-speaking Christian ...
, under the Metropolitanate of Gothia
:''See Archdiocese of the Goths and the Northlands for the 1994 establishment in Sweden.''
The Metropolitanate of Gothia (also ''of Gothia and Caffa''), also known as the Eparchy of Gothia or Metropolitanate of Doros, was a metropolitan diocese o ...
. In 988, Prince Vladimir I of Kyiv
Vladimir I Sviatoslavich or Volodymyr I Sviatoslavych (; Christian name: ''Basil''; 15 July 1015), given the epithet "the Great", was Prince of Novgorod from 970 and Grand Prince of Kiev from 978 until his death in 1015. The Eastern Orthodox ...
also captured the Byzantine town of Chersonesos (presently part of Sevastopol) where he later converted to Christianity.
Christianity was mostly swept away by the Mongol invasion of Rus'
The Mongol Empire invaded and conquered much of Kievan Rus' in the mid-13th century, sacking numerous cities such as Principality of Ryazan, Ryazan, Principality of Yaroslavl, Yaroslavl, Principality of Pereyaslavl, Pereyaslavl and Vladimi ...
in the 1230s. Islam becomes the state religion of the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as ''Ulug Ulus'' ( in Turkic) was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the division of ...
in the early 14th century. The first mosque in Crimea was built by Ozbeg Khan in Eski Qırım in 1314.
Christianity returned with the annexation of the Crimean Khanate by the Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
in 1783.
A survey of residents of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea in May 2013 found that:
*58% Orthodox
*15% Muslim
*13% Do not know, or not applicable
*10% believed in God but did not belong to any religion
*2% Atheist
*2% Other
The proportion of the population in the survey who were Crimean Tatar was 15%.
Respondents to the same survey said that they attended a religious service:
*3% Several times a week
*7% Weekly
*10% Monthly
*37% Several times a year
*43% Never
References
{{Crimea topics Crimean society Demographics of Ukraine