Craven Fault on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Craven Fault System is the name applied by geologists to the group of crustal faults in the 
 The Craven Faults are major crustal fractures across the
The Craven Faults are major crustal fractures across the
British Geological Survey, Geology of England and IOM, DiGMapGB625, data NERC 2008 The Craven Gap is sometimes called the
 The fault system comprises the North Craven Fault, Middle Craven Fault, South Craven Fault and Feizor Fault along with various other unnamed faults. The Middle Craven Fault moved mainly during
The fault system comprises the North Craven Fault, Middle Craven Fault, South Craven Fault and Feizor Fault along with various other unnamed faults. The Middle Craven Fault moved mainly during
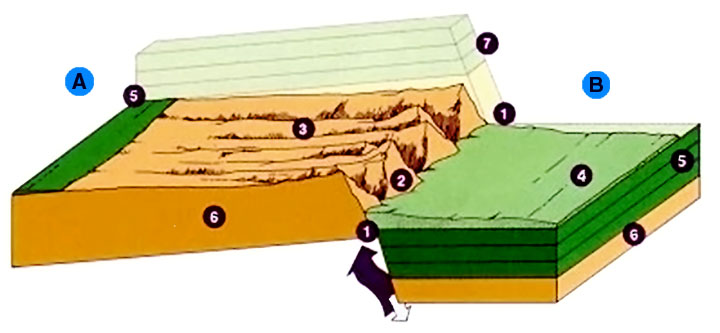 The Great Scar Limestone is over 200 metres thick and the overlying Yoredale Series was over 300 metres thick before
The Great Scar Limestone is over 200 metres thick and the overlying Yoredale Series was over 300 metres thick before
File:Giggleswick Scar - geograph.org.uk - 42107.jpg,
Pennines
The Pennines (), also known as the Pennine Chain or Pennine Hills, are a range of highland, uplands mainly located in Northern England. Commonly described as the "Vertebral column, backbone of England" because of its length and position, the ra ...
that form the southern edge of the Askrigg Block and which partly bounds the Craven Basin. Sections of the system's component faults which include the North, Middle and South Craven faults and the Feizor FaultBritish Geological Survey 1:50,000 scale geological map (England and Wales) sheet 60 ''Settle'' are evident at the surface in the form of degraded faults scarps where Carboniferous Limestone abuts millstone grit
Millstone Grit is any of a number of coarse-grained sandstones of Carboniferous age which occur in the British Isles. The name derives from its use in earlier times as a source of millstones for use principally in watermills. Geologists refer to ...
. The fault system is approximately coincident with the southwestern edge of the Yorkshire Dales
The Yorkshire Dales are a series of valleys, or Dale (landform), dales, in the Pennines, an Highland, upland range in England. They are mostly located in the Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of North Yorkshire, but extend into C ...
National Park and the northeastern edge of the Bowland Fells.

Location
 The Craven Faults are major crustal fractures across the
The Craven Faults are major crustal fractures across the Pennines
The Pennines (), also known as the Pennine Chain or Pennine Hills, are a range of highland, uplands mainly located in Northern England. Commonly described as the "Vertebral column, backbone of England" because of its length and position, the ra ...
. These faults constitute a zone crossing the backbone of England from west to east commencing near Leck, Lancashire at then branching three ways:
* The North Craven Fault extends about to .
* The Mid Craven Fault extends about to .
* The South Craven Fault extends about to .British Geological Survey, Geology of England and IOM, DiGMapGB625, data NERC 2008 The Craven Gap is sometimes called the
Aire Gap
Aire Gap is a pass through the Pennines in England formed by geologic fault (geology), faults and carved out by glaciers. The term is used to describe a geological division, a travel route, or a location that is an entry into the Aire river val ...
, but to do so necessitates including the Aire Fault; that runs from the south end of the South Craven Fault: from Gargrave towards Leeds. Although of less amplitude than the three Craven faults the course of the Aire Fault is made more apparent by the River Aire
The River Aire is a major river in Yorkshire, England, in length. Part of the river below Leeds is canalised, and is known as the Aire and Calder Navigation.
The ''Handbook for Leeds and Airedale'' (1890) notes that the distance from Malha ...
. The broad Aire Gap separates the Yorkshire Dales
The Yorkshire Dales are a series of valleys, or Dale (landform), dales, in the Pennines, an Highland, upland range in England. They are mostly located in the Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of North Yorkshire, but extend into C ...
from the Bowland Fells and the Millstone Grit
Millstone Grit is any of a number of coarse-grained sandstones of Carboniferous age which occur in the British Isles. The name derives from its use in earlier times as a source of millstones for use principally in watermills. Geologists refer to ...
plateaux of the South Pennines
The South Pennines is a region of moorland and hill country in northern England lying towards the southern end of the Pennines. In the west it includes the Rossendale Valley and the West Pennine Moors. It is bounded by the Greater Manchester co ...
.
Geological age
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
times and marks the southern limit of the Askrigg Block. However the North and South Craven faults continued to be active into post-Triassic
The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is t ...
times. The Great Scar Limestone is exposed north of the Middle Craven Fault at Malham Cove
Malham Cove is a large curved limestone formation north of the village of Malham, North Yorkshire, England. It was formed by a waterfall carrying meltwater from glaciers at the end of the last Last glacial period, Ice Age more than 12,000 year ...
and at Gordale Scar and along the South Craven Fault at Giggleswick
Giggleswick, a village and civil parish in North Yorkshire, England, lies on the B6480 road, less than north-west of the town of Settle and divided from it by the River Ribble. It is the site of Giggleswick School.
Until 1974 it was part ...
Scar.
Erosion
 The Great Scar Limestone is over 200 metres thick and the overlying Yoredale Series was over 300 metres thick before
The Great Scar Limestone is over 200 metres thick and the overlying Yoredale Series was over 300 metres thick before weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals (as well as wood and artificial materials) through contact with water, atmospheric gases, sunlight, and biological organisms. It occurs '' in situ'' (on-site, with little or no move ...
. The vertical throw of the fault zone is up to .
Near Ingleton, North Yorkshire
Ingleton is a village and civil parish in North Yorkshire, England. The village is from Kendal and from Lancaster on the western side of the Pennines. It is from Settle. The River Doe and the River Twiss meet to form the source of the ...
the North Craven Fault has a downthrow of about , and a few hundred yards away the South Craven Fault has a downthrow of about . The fault plane of the North Craven Fault is exposed in Swilla Glen.
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English Natural history#Before 1900, naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all speci ...
used the Craven Fault to illustrate how nature can so well conceal dramatic events: "The Craven Fault, for instance, extends for upwards of 30 miles, and along this line the vertical displacement of strata has varied from 600 to 3000 feet."
Gallery
Giggleswick
Giggleswick, a village and civil parish in North Yorkshire, England, lies on the B6480 road, less than north-west of the town of Settle and divided from it by the River Ribble. It is the site of Giggleswick School.
Until 1974 it was part ...
Scar
File: Hillside above Settle and the Langcliffe mills - geograph.org.uk - 782271.jpg, View NW across Ribble to Giggleswick Scar
File:Warrendale Knotts - geograph.org.uk - 114740.jpg, Warrendale Knotts
File:Cross Field Knotts - geograph.org.uk - 1034650.jpg, Cross Field Knotts
References
Bibliography
* *External links
*{{cite web , url=http://www.yorkshire-dales.com/craven-fault.html , title=The Craven Fault , publisher=www.yorkshire-dales.com , accessdate=2009-09-14 Geology of North Yorkshire Geology of the Pennines Geology of Lancashire