Count Kaunitz on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Wenzel Anton, Prince of Kaunitz-Rietberg (, ; 2 February 1711 – 27 June 1794) was an Austrian and Czech
 From 1749, Kaunitz served as a ''
From 1749, Kaunitz served as a ''
 Kaunitz's most important and influential office was that of State Chancellor and minister of foreign affairs, which he held from 1753 to 1792 and where he had Empress Maria Theresa's full trust—against the opposition of her husband, Francis Stephen. He had reluctantly accepted his appointment and demanded complete freedom to re-organise the foreign office on
Kaunitz's most important and influential office was that of State Chancellor and minister of foreign affairs, which he held from 1753 to 1792 and where he had Empress Maria Theresa's full trust—against the opposition of her husband, Francis Stephen. He had reluctantly accepted his appointment and demanded complete freedom to re-organise the foreign office on 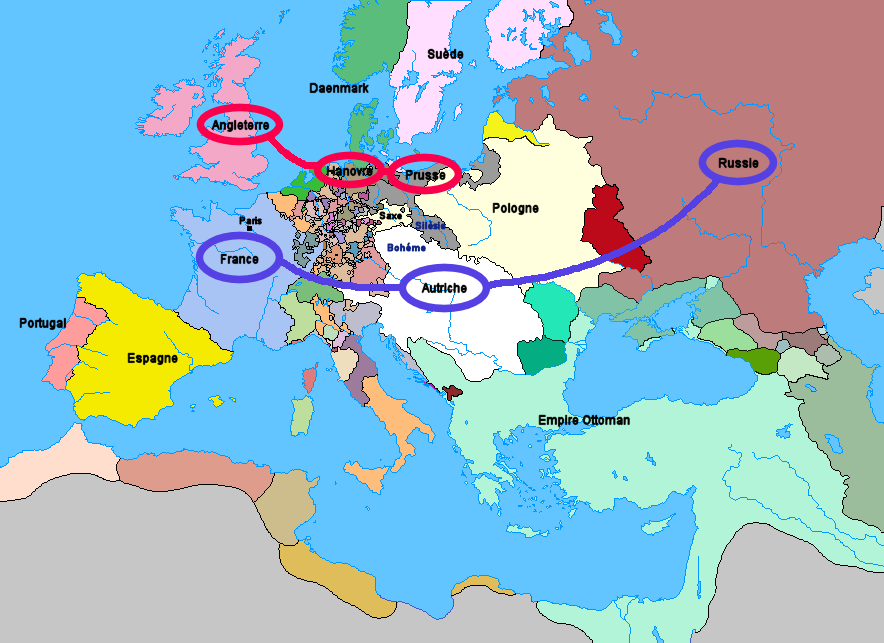
 The State Chancellor was a liberal patron of education and art, a notable collector, one of the founders of the
The State Chancellor was a liberal patron of education and art, a notable collector, one of the founders of the
diplomat
A diplomat (from ; romanization, romanized ''diploma'') is a person appointed by a state (polity), state, International organization, intergovernmental, or Non-governmental organization, nongovernmental institution to conduct diplomacy with one ...
and statesman in the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
. A proponent of enlightened absolutism
Enlightened absolutism, also called enlightened despotism, refers to the conduct and policies of European absolute monarchs during the 18th and early 19th centuries who were influenced by the ideas of the Enlightenment, espousing them to enhanc ...
, he held the office of State Chancellor for about four decades and was responsible for the foreign policies during the reigns of Maria Theresa
Maria Theresa (Maria Theresia Walburga Amalia Christina; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was the ruler of the Habsburg monarchy from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position suo jure, in her own right. She was the ...
, Joseph II, and Leopold II. In 1764, he was elevated to the noble rank of a Prince of the Holy Roman Empire
Prince of the Holy Roman Empire (, , cf. ''Fürst'') was a title attributed to a hereditary ruler, nobleman or prelate recognised by the Holy Roman Emperor.
Definition
Originally, possessors of the princely title bore it as immediate vassal ...
('' Reichfürst'').
Family
Kaunitz was born inVienna
Vienna ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital, List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city, and one of Federal states of Austria, nine federal states of Austria. It is Austria's primate city, with just over two million inhabitants. ...
, Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
, one of 19 children of Maximilian Ulrich, third Count of Kaunitz (1679–1746), and his consort Marie Ernestine, ''née'' Countess of Ostfriesland and Rietberg
Rietberg () is a town in the district of Gütersloh in the state of North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located approximately 10 km south of Gütersloh and 25 km north-west of Paderborn in the region Ostwestfalen-Lippe. The town is l ...
(1687–1758), an heiress of the House of Cirksena. The Kaunitz family (''Kounicové'') belonged to an ancient Czech
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus
*Czech (surnam ...
nobility and, like the related Martinic dynasty, derived its lineage from the medieval Vršovci clan in the Kingdom of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia (), sometimes referenced in English literature as the Czech Kingdom, was a History of the Czech lands in the High Middle Ages, medieval and History of the Czech lands, early modern monarchy in Central Europe. It was the pr ...
. First mentioned in the 14th century, they originally lived in the Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
n duchy of Troppau
Opava (; , ) is a city in the Moravian-Silesian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 55,000 inhabitants. It lies on the Opava River. Opava is one of the historical centres of Silesia and was a historical capital of Czech Silesia.
Administr ...
, but in 1509, they moved to Slavkov (''Austerlitz'') Castle near Brno
Brno ( , ; ) is a Statutory city (Czech Republic), city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava (river), Svitava and Svratka (river), Svratka rivers, Brno has about 403,000 inhabitants, making ...
.
Wenzel Anton's grandfather, Dominik Andreas von Kaunitz (1655–1705), served as a Habsburg ''Geheimrat
was the title of the highest advising officials at the imperial, royal, or princely courts of the Holy Roman Empire, who jointly formed the ''Geheimer Rat'' reporting to the ruler. The term remained in use during subsequent monarchic reigns in Ge ...
'' and envoy. Elevated to the hereditary rank of a Count (''Graf
(; feminine: ) is a historical title of the German nobility and later also of the Russian nobility, usually translated as "count". Considered to be intermediate among noble ranks, the title is often treated as equivalent to the British title ...
'') in 1683, his diplomacy contributed to the 1686 League of Augsburg against King Louis XIV of France
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
and the 1697 Treaty of Ryswick
The Peace of Ryswick, or Rijswijk, was a series of treaties signed in the Dutch city of Rijswijk between 20 September and 30 October 1697. They ended the 1688 to 1697 Nine Years' War between France and the Grand Alliance, which included the Dutc ...
that ended the Nine Years' War
The Nine Years' War was a European great power conflict from 1688 to 1697 between Kingdom of France, France and the Grand Alliance (League of Augsburg), Grand Alliance. Although largely concentrated in Europe, fighting spread to colonial poss ...
. Wenzel Anton's father, Count Maximilian Ulrich, was appointed a member of the Aulic Council
The Aulic Council (; ; literally "Court Council of the Empire", sometimes abbreviated in academic writing as "RHR") was one of the two supreme courts of the Holy Roman Empire, the other being the ''Reichskammergericht'' (Imperial Chamber Court). ...
(''Reichshofrat'') in 1706; he served as Imperial envoy and as governor (''Landeshauptmann
The Landeshauptmann (if male) or Landeshauptfrau (if female) (, "state captain", plural ''Landeshauptleute,'' ) is the chairman of a state government and the supreme official of an Austrian state and the Italian autonomous provinces of South Ty ...
'') of Moravia
Moravia ( ; ) is a historical region in the eastern Czech Republic, roughly encompassing its territory within the Danube River's drainage basin. It is one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The medieval and early ...
from 1720. By his marriage with Marie Ernestine in 1699, he inherited the immediate County of Rietberg in Westphalia
Westphalia (; ; ) is a region of northwestern Germany and one of the three historic parts of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It has an area of and 7.9 million inhabitants.
The territory of the region is almost identical with the h ...
.
Wenzel Anton himself married Countess Maria Ernestine von Starhemberg (1717–1749), a granddaughter of Imperial Chamber president Count Gundaker Thomas von Starhemberg (1663–1745), on 6 May 1736. Four sons were born of the marriage, among them the Austrian general Count Franz Wenzel von Kaunitz-Rietberg (1742–1825). Wenzel Anton's granddaughter Eleonora (daughter of his eldest son, Ernest) married a successor in the office of State Chancellor, Prince Klemens von Metternich
Klemens Wenzel Nepomuk Lothar, Prince of Metternich-Winneburg zu Beilstein ( ; 15 May 1773 – 11 June 1859), known as Klemens von Metternich () or Prince Metternich, was a German statesman and diplomat in the service of the Austrian Empire. ...
.
Early life
As the second son, it was at first intended that Wenzel Anton should become a clergyman, and at thirteen he held acanonry
Canon () is a Christian title usually used to refer to a member of certain bodies in subject to an canon law, ecclesiastical rule.
Originally, a canon was a cleric living with others in a clergy house or, later, in one of the houses within the p ...
at the Westphalian Diocese of Münster. With the death of his elder brother, however, he decided on a secular career, and studied law and diplomacy at the universities of Vienna
Vienna ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital, List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city, and one of Federal states of Austria, nine federal states of Austria. It is Austria's primate city, with just over two million inhabitants. ...
, Leipzig
Leipzig (, ; ; Upper Saxon: ; ) is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Saxony. The city has a population of 628,718 inhabitants as of 2023. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, eighth-largest city in Ge ...
and Leiden
Leiden ( ; ; in English language, English and Archaism, archaic Dutch language, Dutch also Leyden) is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Provinces of the Nethe ...
. He became a chamberlain of the Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
emperor Charles VI, and continued his education for some years by a '' Grand Tour'' to Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
, the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
, and England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
.
Back in Vienna, he was appointed a member of the Imperial Aulic Council in 1735. At the Imperial Diet of Regensburg
Regensburg (historically known in English as Ratisbon) is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the rivers Danube, Naab and Regen (river), Regen, Danube's northernmost point. It is the capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the ...
(''Ratisbon'') in 1739, he was one of the emperor's commissaries. During the War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession was a European conflict fought between 1740 and 1748, primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italian Peninsula, Italy, the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea. Related conflicts include King Ge ...
, in March 1741, he was sent on a diplomatic mission to Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025.
Florence ...
, Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
, and to the Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia, also referred to as the Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica among other names, was a State (polity), country in Southern Europe from the late 13th until the mid-19th century, and from 1297 to 1768 for the Corsican part of ...
. In August 1742, he was appointed ambassador at Turin
Turin ( , ; ; , then ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital from 1861 to 1865. The city is main ...
and reached the support of King Charles Emmanuel III
Charles Emmanuel III (27 April 1701 – 20 February 1773) was Duke of Savoy, List of monarchs of Sardinia, King of Sardinia and ruler of the Savoyard states from his Victor Amadeus II, father's abdication on 3 September 1730 until his death ...
for Maria Theresa
Maria Theresa (Maria Theresia Walburga Amalia Christina; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was the ruler of the Habsburg monarchy from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position suo jure, in her own right. She was the ...
.
In October 1744, he was appointed minister plenipotentiary
An envoy extraordinary and minister plenipotentiary, usually known as a minister, was a diplomatic head of mission who was ranked below ambassador. A diplomatic mission headed by an envoy was known as a legation rather than an embassy. Under the ...
in the Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The period began with the acquisition by the Austrian Habsburg monarchy of the former Spanish Netherlands under the Treaty of Ras ...
, while its governor
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political regions, political region, in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the ...
, Prince Charles of Lorraine, fought in the Silesian Wars
The Silesian Wars () were three wars fought in the mid-18th century between Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia (under King Frederick the Great) and Habsburg monarchy, Habsburg Austria (under Empress Maria Theresa) for control of the Central European ...
, commanding the Austrian army in Bohemia against King Frederick II of Prussia
Frederick II (; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was the monarch of Prussia from 1740 until his death in 1786. He was the last Hohenzollern monarch titled ''King in Prussia'', declaring himself '' King of Prussia'' after annexing Royal Prus ...
. Upon the December 1744 death of Charles' consort and co-governor, Archduchess Maria Anna, a sister of Maria Theresa, Kaunitz was virtually the head of government.
In 1746, however, he was forced to leave Brussels
Brussels, officially the Brussels-Capital Region, (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) is a Communities, regions and language areas of Belgium#Regions, region of Belgium comprising #Municipalit ...
after it was besieged by French forces under Count Maurice de Saxe
Maurice, Count of Saxony (, ; 28 October 1696 – 20 November 1750) was a notable soldier, officer and a famed military commander of the 18th century. The illegitimate son of Augustus II the Strong, King of Poland, Grand Duke of Lithuania ...
. He moved with the government of the Austrian Netherlands, first to Antwerp
Antwerp (; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of Antwerp Province, and the third-largest city in Belgium by area at , after ...
, then to Aachen
Aachen is the List of cities in North Rhine-Westphalia by population, 13th-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, 27th-largest city of Germany, with around 261,000 inhabitants.
Aachen is locat ...
. His request to be recalled from his difficult situation was heeded in June 1746. On a journey to Westphalia in September 1746, he laid the foundation stone of the parish church in the village of . Two years later, he represented Maria Theresa at the Congress of Aachen at the close of the War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession was a European conflict fought between 1740 and 1748, primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italian Peninsula, Italy, the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea. Related conflicts include King Ge ...
. Extremely displeased with the provisions that deprived Austria of the provinces of Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
and Glatz and guaranteed them to the warlike King of Prussia, he reluctantly signed the resulting Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle on 23 October 1748. Both fearing a nascent Prussia, the Austrian and French sides began to make overtures to each other.
 From 1749, Kaunitz served as a ''
From 1749, Kaunitz served as a ''Geheimrat
was the title of the highest advising officials at the imperial, royal, or princely courts of the Holy Roman Empire, who jointly formed the ''Geheimer Rat'' reporting to the ruler. The term remained in use during subsequent monarchic reigns in Ge ...
'' at the court of Maria Theresa. The empress appealed to all her counsellors for advice as to the policy Austria ought to pursue in view of the changed conditions produced by the rise of Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
. The great majority of them, including her husband Francis Stephen of Lorraine, were of the opinion that the old alliance with the sea powers, England and Holland, should be maintained. Kaunitz had long been a strong opponent of the Anglo-Austrian Alliance, which had existed since 1731, and gave his opinion that Frederick II was now the "most wicked and dangerous enemy of Austria," that it was hopeless to expect the support of Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
nations against him, and that the only way of recovering Silesia was by an alliance with Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
and France. The empress eagerly accepted views which were already her own, and entrusted the adviser with the execution of his own plans. Thus, Kaunitz was made Imperial ambassador at the French court in Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; ) is a former royal residence commissioned by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, about west of Paris, in the Yvelines, Yvelines Department of Île-de-France, Île-de-France region in Franc ...
in 1750, where he had extensive contact with the ''Lumières
The Lumières (literally in English: ''The Lights'') was a cultural, philosophical, literary and intellectual movement beginning in the second half of the 17th century, originating in France, then western Europe and spreading throughout the rest ...
'' movement and several ''Encyclopédistes
The Encyclopédistes () (also known in British English as Encyclopaedists, or in U.S. English as Encyclopedists) were members of the , a French writers' society, who contributed to the development of the ''Encyclopédie'' from June 1751 to Dece ...
''. Staying in France until 1752, he co-operated in laying the groundwork for the future Bourbon-Habsburg alliance.
State Chancellor
 Kaunitz's most important and influential office was that of State Chancellor and minister of foreign affairs, which he held from 1753 to 1792 and where he had Empress Maria Theresa's full trust—against the opposition of her husband, Francis Stephen. He had reluctantly accepted his appointment and demanded complete freedom to re-organise the foreign office on
Kaunitz's most important and influential office was that of State Chancellor and minister of foreign affairs, which he held from 1753 to 1792 and where he had Empress Maria Theresa's full trust—against the opposition of her husband, Francis Stephen. He had reluctantly accepted his appointment and demanded complete freedom to re-organise the foreign office on Ballhausplatz
Ballhausplatz is a town square, square in central Vienna containing the building (with the address Ballhausplatz 2) that for over two hundred years has been the official residence of the most senior Austrian Cabinet Minister, the State Chancellor ...
. Thanks in large part to him, Habsburg Austria established itself as a sovereign great power
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power ...
, entering into the Treaty of Versailles (1756) with her old enemy, the French ancien régime
''Ancien'' may refer to
* the French word for " ancient, old"
** Société des anciens textes français
* the French for "former, senior"
** Virelai ancien
** Ancien Régime
** Ancien Régime in France
{{disambig ...
, commonly known as Diplomatic Revolution (''renversement des alliances''). The new Franco-Austrian Alliance was considered a great feat of diplomacy, and it established Kaunitz as the recognized master of the art.
The Diplomatic Revolution of 1756
Kaunitz was the mastermind of the Diplomatic Revolution of 1756, which involved the dramatic shakeup of traditional military alliances in Europe. Austria went from an ally of Britain to an ally of France and Russia. Prussia became an ally of Britain, along with Hanover. The result was the basic lineup of forces in the Seven Years' War.Seven Years' War
Once he was State Chancellor, Kaunitz pursued his policies seeking ''rapprochement'' with France. Upon the outbreak of theFrench and Indian War
The French and Indian War, 1754 to 1763, was a colonial conflict in North America between Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of France, France, along with their respective Native Americans in the United States, Native American ...
overseas in 1754, he had the Austrian ambassador in Paris, Prince Georg Adam of Starhemberg, raise the topic of forming a defensive league. King Louis XV finally accepted, after the Anglo-Prussian Treaty of Westminster was signed in 1756. The alliance was expanded in 1757
Events
January–March
* January 2 – Seven Years' War: The British East India Company Army, under the command of Robert Clive, captures Calcutta, India.
* January 5 – Robert-François Damiens makes an unsuccessful assa ...
to include Russia and Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
.
Thus began the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...
in Europe, which ultimately failed to bring the lost provinces back to Austria. On 29 August 1756, King Frederick's Prussian Army invaded the Electorate of Saxony
The Electorate of Saxony, also known as Electoral Saxony ( or ), was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire from 1356 to 1806 initially centred on Wittenberg that came to include areas around the cities of Dresden, Leipzig and Chemnitz. It was a ...
in a preemptive strike
A preemptive war is a war that is commenced in an attempt to repel or defeat a perceived imminent offensive or invasion, or to gain a strategic advantage in an impending (allegedly unavoidable) war ''shortly before'' that attack materializes. I ...
; they rolled over the Saxon forces and occupied Dresden
Dresden (; ; Upper Saxon German, Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; , ) is the capital city of the States of Germany, German state of Saxony and its second most populous city after Leipzig. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, 12th most p ...
. While the Austrian allies were not able to reach agreement on joint action, the politico-military situation remained inconclusive. Kaunitz urged for the replacement of the hesitant field marshal Count Leopold Joseph von Daun by Ernst Gideon von Laudon
Ernst Gideon von Laudon, since 1759 Freiherr von Laudon (originally Laudohn or Loudon; 13 February 171714 July 1790), was a Baltic German-born Austrian military officer and one of the most successful opponents of the Prussian king Frederick the ...
, however, a decisive victory was not achieved.
From about 1760, gradual exhaustion of all forces became obvious, and Kaunitz reacted by depriving his long-time foe Court Chancellor Count Friedrich Wilhelm von Haugwitz of his powers. He replaced the office by founding the Austrian Council of State (''Staatsrat'') in 1761, overseeing the reorganization of the Austrian Army. Nevertheless, when the new tsar Peter III of Russia
Peter III Fyodorovich (; ) was Emperor of Russia from 5 January 1762 until 9 July of the same year, when he was overthrown by his wife, Catherine II (the Great). He was born in the German city of Kiel as Charles Peter Ulrich of Schleswig-Holst ...
left the alliance in 1762, Kaunitz entered into peace negotiations that led to the 1763 Treaty of Hubertusburg. Following the end of war, Kaunitz gained the title of ''Reichsfürst'' (Prince of the Holy Roman Empire). The lack of a navy during the war had demonstrated Austria's vulnerability at sea, and he was instrumental in the creation of a small Austrian navy to boost the state's presence in the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
, laying the foundations for the future Austro-Hungarian Navy
The Austro-Hungarian Navy or Imperial and Royal War Navy (, in short ''k.u.k. Kriegsmarine'', ) was the navy, naval force of Austria-Hungary. Ships of the Austro-Hungarian Navy were designated ''SMS'', for ''Seiner Majestät Schiff'' (His Majes ...
.
Josephinism
 The State Chancellor was a liberal patron of education and art, a notable collector, one of the founders of the
The State Chancellor was a liberal patron of education and art, a notable collector, one of the founders of the Royal Academy
The Royal Academy of Arts (RA) is an art institution based in Burlington House in Piccadilly London, England. Founded in 1768, it has a unique position as an independent, privately funded institution led by eminent artists and architects. Its ...
in Brussels, and sponsor of Christoph Willibald Gluck
Christoph Willibald (Ritter von) Gluck (; ; 2 July 1714 – 15 November 1787) was a composer of Italian and French opera in the early classical period (music), classical period. Born in the Upper Palatinate and raised in Bohemia, both part of th ...
and one of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 1756 – 5 December 1791) was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition and proficiency from an early age ...
’s first and lifelong patrons. He worked towards the goal of subjecting the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
to the state, most notably against tax exemption and the traditional institution of mortmain
Mortmain () is the perpetual, inalienable ownership of real estate by a corporation or legal institution; the term is usually used in the context of its prohibition. Historically, the land owner usually would be the religious office of a church ...
ownership of real estates. Kaunitz followed the thoughts of Jansenism
Jansenism was a 17th- and 18th-century Christian theology, theological movement within Roman Catholicism, primarily active in Kingdom of France, France, which arose as an attempt to reconcile the theological concepts of Free will in theology, f ...
and the Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment (also the Age of Reason and the Enlightenment) was a Europe, European Intellect, intellectual and Philosophy, philosophical movement active from the late 17th to early 19th century. Chiefly valuing knowledge gained th ...
; among his aims was also the better education of the commoners.
Although Maria Theresa's son and heir, Emperor Joseph II generally shared such ideas, his reforms moved too fast and too thoroughly for Kaunitz. The ongoing disputes between the two men led to several resignation requests by the state chancellor. Kaunitz advocated a reconciliation with the former enemy Prussia; he accompanied Joseph II when he met Frederick II two times in 1769 and 1770. The Prussian king was annoyed by Kaunitz' arrogance and patronising manners, nevertheless the approach realised in the First Partition of Poland
The First Partition of Poland took place in 1772 as the first of three partitions that eventually ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth by 1795. The growth of power in the Russian Empire threatened the Kingdom of Prussia an ...
in 1772, backed by both Kaunitz and Joseph II against the concerns of Maria Theresa ("good faith is lost for all time").
In 1777, Joseph's hasty military action led to the War of the Bavarian Succession
The War of the Bavarian Succession (; 3 July 1778 – 13 May 1779) was a dispute between the Austrian Habsburg monarchy and an alliance of Electorate of Saxony, Saxony and Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia over succession to the Electorate of Bavaria ...
. When the Austrian position became untenable, Kaunitz carried the peace negotiations on his own initiative; by the 1779 Treaty of Teschen, he won the Bavarian Innviertel
The Innviertel (literally German language, German for "Inn Quarter"; officially called the ; ) is a traditional Austrian region southeast of the Inn (river), Inn river. It forms the western part of the States of Austria, state of Upper Austria a ...
region for Austria. In Imperial matters, he was able to dominate the Perpetual Diet of Regensburg
The Perpetual Diet of Regensburg or the Eternal Diet of Regensburg, () also commonly called in English the Perpetual Diet of Ratisbon,Jean Berenger, C.A. Simpson, ''The Habsburg Empire 1700-1918'' (2014), p. 134 from the city's Latin name, was a ...
; in 1780 he was also successful in placing the Habsburg Archduke Maximilian Francis of Austria, Joseph's younger brother, as a coadjutor bishop
A coadjutor bishop (or bishop coadjutor) ("co-assister" in Latin) is a bishop in the Latin Catholic, Anglican and (historically) Eastern Orthodox churches whose main role is to assist the diocesan bishop in administering the diocese.
The coa ...
in the Electorate of Cologne
The Electorate of Cologne (), sometimes referred to as Electoral Cologne (), was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire that existed from the 10th to the early 19th century. It consisted of the Hochstift—the temporal posses ...
and the Prince-Bishopric of Münster
The Prince-Bishopric of Münster (, or ) was a large ecclesiastical principality in the Holy Roman Empire, located in the northern part of today's North Rhine-Westphalia and western Lower Saxony. From the sixteenth to the eighteenth centuries, ...
.
Kaunitz worked around the objections of Joseph II to initiate the Austro-Turkish War of 1788–1791. The goal was to humiliate Austria's old enemy, Prussia. However, it misfired: it proved a costly military operation to help Russia, but it did not achieve any anti-Prussian objective. After Joseph II's death, Leopold II became emperor; the war was ended and Kaunitz's power collapsed.Roider, Karl A. Jr. "Kaunitz, Joseph II and the Turkish War". ''The Slavonic and East European Review
''The Slavonic and East European Review'', the journal of the UCL School of Slavonic and East European Studies (University College London), is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal covering Slavonic and East European Studies. It was estab ...
'' (1976) 54#135 pp. 538–556. The renunciation of Kaunitz' balancing policies led to a serious deterioration of Austria's domestic and international affairs. Meanwhile, Prussia established the Protestant '' Fürstenbund'' league, and the Brabant Revolution
The Brabant Revolution or Brabantine Revolution (, ), sometimes referred to as the Belgian Revolution of 1789–1790 in older writing, was an armed revolution, insurrection that occurred in the Austrian Netherlands (modern-day Belgium) between O ...
broke out in the Austrian Netherlands.
Resignation and death
Joseph II's successor, Leopold II, blamed Kaunitz for the failure and decisively restricted his competences. Kaunitz rejected further ''rapprochement'' with Prussia against Revolutionary France in view of the weak rule of Frederick's successor, King Frederick William II, an assessment that was proved to be correct in theWar of the First Coalition
The War of the First Coalition () was a set of wars that several European powers fought between 1792 and 1797, initially against the Constitutional Cabinet of Louis XVI, constitutional Kingdom of France and then the French First Republic, Frenc ...
.
Kaunitz finally resigned his office upon the accession of Emperor Francis II in July 1792. Kaunitz died in 1794 at his city palace in Vienna and was buried in his family vault beneath the Chapel of St. John the Baptist in Slavkov cemetery.
Ancestry
Notes
Further reading
* McGill, William J. "The roots of policy: Kaunitz in Vienna and Versailles, 1749–1753". ''The Journal of Modern History
''The Journal of Modern History'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal covering European intellectual, political, and cultural history, published by the University of Chicago Press. Established in 1929, the journal covers events from appro ...
'' 43.2 (1971): 228–244.
* Padover, Saul K. "Prince Kaunitz' Résumé of His Eastern Policy, 1763–71". ''The Journal of Modern History'' 5.3 (1933): 352–365.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Kaunitz-Rietberg, Wenzel Anton, Prince of
1711 births
1794 deaths
Politicians from Vienna
Czech politicians
Politicians from the Austrian Empire
Ministers of foreign affairs of Austria
Austrian princes
Habsburg Bohemian nobility
Knights of the Golden Fleece of Austria
Grand Crosses of the Order of Saint Stephen of Hungary
People of the War of the First Coalition