Costochondritis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Costochondritis, also known as chest wall pain syndrome or costosternal syndrome, is a benign
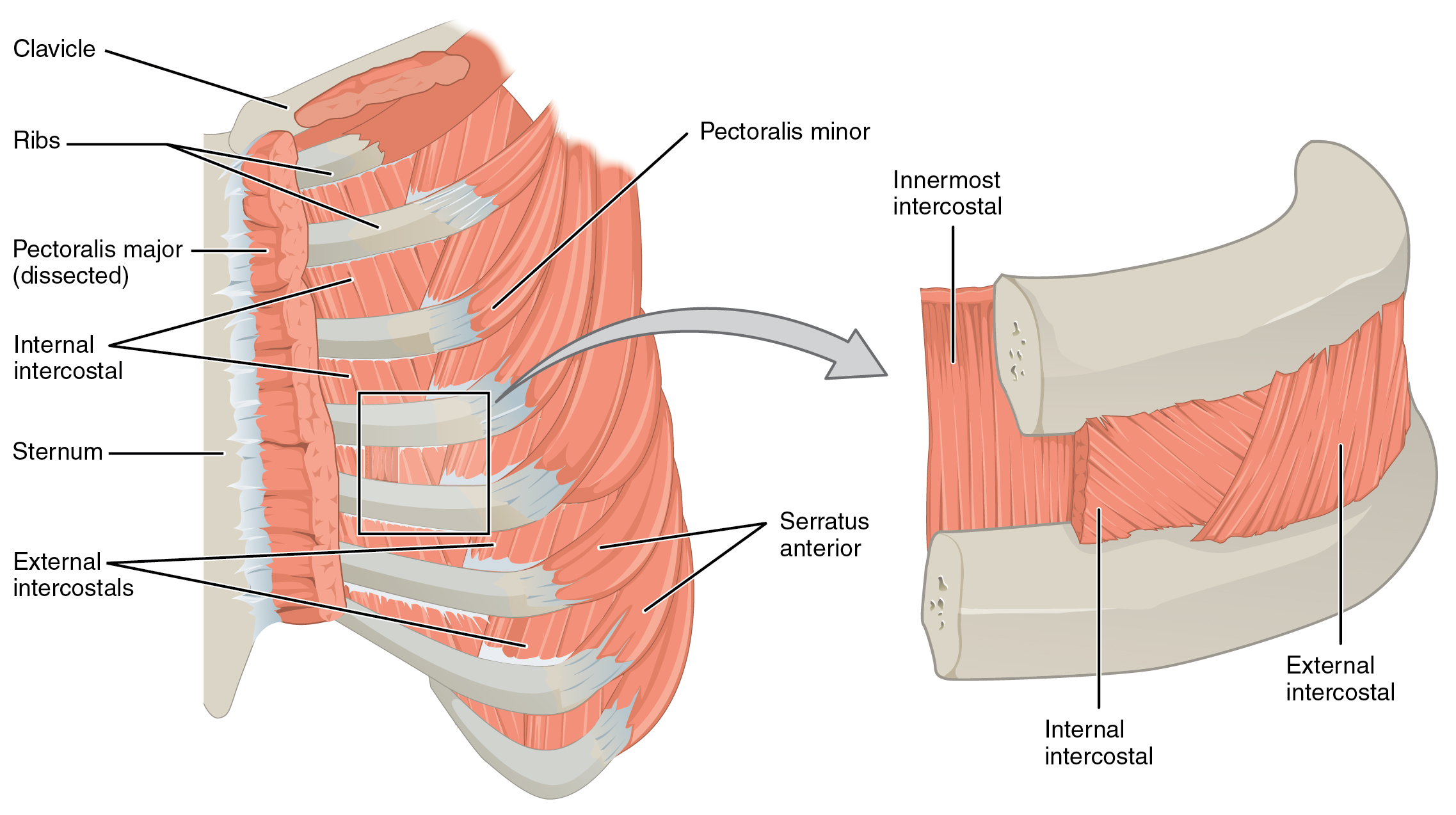
 Costochondritis typically presents unilaterally (one side), which is typically the left side. It affects primarily the 2nd to 5th ribs at the sternocostal and costochondral joints. The most commonly reported symptom of costochondritis is chest pain that is often exacerbated by movement and deep breathing. Pain is typically widespread and reproducible with palpation of the anterior (front) chest at the affected joints. Pain from costochondritis can vary between individuals, and is typically described as a sharp, aching, dull, or pressure-like pain. It may also be accompanied by a radiating pain to the shoulder, arm, front neck, or
Costochondritis typically presents unilaterally (one side), which is typically the left side. It affects primarily the 2nd to 5th ribs at the sternocostal and costochondral joints. The most commonly reported symptom of costochondritis is chest pain that is often exacerbated by movement and deep breathing. Pain is typically widespread and reproducible with palpation of the anterior (front) chest at the affected joints. Pain from costochondritis can vary between individuals, and is typically described as a sharp, aching, dull, or pressure-like pain. It may also be accompanied by a radiating pain to the shoulder, arm, front neck, or
inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
of the upper costochondral (rib to cartilage) and sternocostal (cartilage to sternum) joints. 90% of patients are affected in multiple ribs on a single side, typically at the 2nd to 5th ribs. Chest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
, the primary symptom of costochondritis, is considered a symptom of a medical emergency
A medical emergency is an acute injury or illness that poses an immediate risk to a person's life or long-term health, sometimes referred to as a situation risking "life or limb". These emergencies may require assistance from another, qualified ...
, making costochondritis a common presentation in the emergency department
An emergency department (ED), also known as an accident and emergency department (A&E), emergency room (ER), emergency ward (EW) or casualty department, is a medical treatment facility specializing in emergency medicine, the Acute (medicine), ...
. One study found costochondritis was responsible for 30% of patients with chest pain in an emergency department
An emergency department (ED), also known as an accident and emergency department (A&E), emergency room (ER), emergency ward (EW) or casualty department, is a medical treatment facility specializing in emergency medicine, the Acute (medicine), ...
setting.
The exact cause of costochondritis is not known; however, it is believed to be due to repetitive minor trauma, called microtrauma. In rarer cases, costochondritis may develop as a result of an infectious factor. Diagnosis is predominantly clinical and based on physical examination, medical history, and ruling other conditions out. Costochondritis is often confused with Tietze syndrome, due to the similarity in location and symptoms, but with Tietze syndrome being differentiated by swelling of the costal cartilage.
Costochondritis is considered a self-limited condition that will resolve on its own. Treatment options usually involve rest, pain medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a Indication (medicine), therapeutic drug class which Analgesic, reduces pain, Anti-inflammatory, decreases inflammation, Antipyretic, decreases fever, and Antithrombotic, prevents bl ...
s (NSAIDs), ice
Ice is water that is frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 ° C, 32 ° F, or 273.15 K. It occurs naturally on Earth, on other planets, in Oort cloud objects, and as interstellar ice. As a naturally oc ...
, heat
In thermodynamics, heat is energy in transfer between a thermodynamic system and its surroundings by such mechanisms as thermal conduction, electromagnetic radiation, and friction, which are microscopic in nature, involving sub-atomic, ato ...
, and manual therapy
Manual therapy, or manipulative therapy, is a treatment primarily used by physical therapists, occupational therapists, and massage therapists to treat musculoskeletal pain and disability. It mostly includes kneading and manipulation of muscle ...
. Cases with persistent discomfort may be managed with an intercostal nerve blocking injection utilizing a combination of corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
s and local anesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of all sensation (including pain) in a specific body part without loss of consciousness, providing local anesthesia, as opposed to a general anesthetic, which eliminates all sensati ...
. The condition predominantly affects women over the age of 40, though some studies have found costochondritis to still be common among adolescents presenting with chest pain.
Terminology
The word "costochondritis" is derived from "Costo-" (Latin "costa," meaning "rib"), "Chondr-" (Greek "chondros," which means "cartilage") and "-itis" (Greek suffix that denotes inflammation).Presentation
 Costochondritis typically presents unilaterally (one side), which is typically the left side. It affects primarily the 2nd to 5th ribs at the sternocostal and costochondral joints. The most commonly reported symptom of costochondritis is chest pain that is often exacerbated by movement and deep breathing. Pain is typically widespread and reproducible with palpation of the anterior (front) chest at the affected joints. Pain from costochondritis can vary between individuals, and is typically described as a sharp, aching, dull, or pressure-like pain. It may also be accompanied by a radiating pain to the shoulder, arm, front neck, or
Costochondritis typically presents unilaterally (one side), which is typically the left side. It affects primarily the 2nd to 5th ribs at the sternocostal and costochondral joints. The most commonly reported symptom of costochondritis is chest pain that is often exacerbated by movement and deep breathing. Pain is typically widespread and reproducible with palpation of the anterior (front) chest at the affected joints. Pain from costochondritis can vary between individuals, and is typically described as a sharp, aching, dull, or pressure-like pain. It may also be accompanied by a radiating pain to the shoulder, arm, front neck, or scapula
The scapula (: scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side ...
(shoulder blade).
The condition usually onsets gradually following repetitive coughing, strenuous physical activity, or trauma to the chest. Symptoms of costochondritis may be recurrent and last weeks to months; however, refractory
In materials science, a refractory (or refractory material) is a material that is resistant to decomposition by heat or chemical attack and that retains its strength and rigidity at high temperatures. They are inorganic, non-metallic compound ...
cases of the condition can persist to over a year.
Costochondritis does not present with heat, erythema
Erythema (, ) is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia (increased blood flow) in superficial capillaries. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not associated with pathology inc ...
, or swelling of the affected area, the presence of which would indicate Tietze syndrome. Additionally, symptoms such as tachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal ...
, hypotension
Hypotension, also known as low blood pressure, is a cardiovascular condition characterized by abnormally reduced blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood and is ...
, radiating pain, shortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that con ...
, fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
, nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. It can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat.
Over 30 d ...
, or a productive cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages which can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex following three ...
are unrelated to costochondritis. These signs warrant further investigation for other, more serious causes of chest pain.
Comorbidity
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a functional somatic syndrome with symptoms of widespread chronic pain, accompanied by fatigue, sleep disturbance including awakening unrefreshed, and Cognitive deficit, cognitive symptoms. Other symptoms can include he ...
may increase the pain effects of costochondritis.
Cause
The exactetiology
Etiology (; alternatively spelled aetiology or ætiology) is the study of causation or origination. The word is derived from the Greek word ''()'', meaning "giving a reason for" (). More completely, etiology is the study of the causes, origins ...
of costochondritis is unknown. Repetitive minor trauma is proposed to be a likely cause, with risk factors such as strenuous coughing, exercise, and lifting identified.
Infection of the costosternal joint may cause costochondritis in rare cases. Most cases of infectious costochondritis are caused by ''Actinomyces
''Actinomyces'' is a genus of the Actinomycetia class of bacteria. They all are Gram-positive and facultatively anaerobic, growing best under anaerobic conditions. ''Actinomyces'' species may form endospores, and while individual bacteria are r ...
'', ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posi ...
'', ''Candida albicans
''Candida albicans'' is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usu ...
'', and ''Salmonella
''Salmonella'' is a genus of bacillus (shape), rod-shaped, (bacillus) Gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two known species of ''Salmonella'' are ''Salmonella enterica'' and ''Salmonella bongori''. ''S. enterica'' ...
''. In rare cases, ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly fo ...
'' can be a cause of infectious costochondritis.
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis underlying the development of costochondritis remains unclear. Proposed mechanisms of pain include neurogenic inflammation, muscular imbalances,neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropa ...
of the intercostal nerves
The intercostal nerves are part of the somatic nervous system, and arise from the anterior rami of the thoracic spinal nerves from T1 to T11. The intercostal nerves are distributed chiefly to the thoracic pleura and abdominal peritoneum, and dif ...
, myofascial pain, or mechanical dysfunction.
Diagnosis
Costochondritis is predominately aclinical diagnosis
Medical diagnosis (abbreviated Dx, Dx, or Ds) is the process of determining which disease or condition explains a person's symptoms and signs. It is most often referred to as a diagnosis with the medical context being implicit. The information ...
only after life-threatening conditions have been ruled out, with physical examination and medical history being considered. Before a costochondritis diagnosis is made, other serious causes of chest pain are investigated. Further evaluation for cardiopulmonary
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart an ...
or neoplastic
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
causes is typically based on history, age, and risk factor
In epidemiology, a risk factor or determinant is a variable associated with an increased risk of disease or infection.
Due to a lack of harmonization across disciplines, determinant, in its more widely accepted scientific meaning, is often use ...
s, with diagnostic imaging and tests, completed to assess for life-threatening emergencies. If there is a suspicion of infection or a rheumatoid condition, laboratory work may be conducted.
A physical exam will assess for tenderness or pain upon palpation
Palpation is the process of using one's hands to check the body, especially while perceiving/diagnosing a disease or illness. Usually performed by a health care practitioner, it is the process of feeling an object in or on the body to determine ...
, with an absence of heat, erythema
Erythema (, ) is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia (increased blood flow) in superficial capillaries. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not associated with pathology inc ...
, or swelling. The physical exam may assess if the pain is worsened with movements of the upper body or breathing, and may be reproduced upon using the crowing rooster maneuver, the hooking maneuver, or the horizontal flexion maneuver. Medical history is considered in diagnosing costochondritis, such as inquiry regarding any recent trauma, coughing, exercise, or activity involving the upper body that may have caused the symptoms.
Differential diagnosis
Cardiopulmonary
Life-threatening medical emergencies that may be associated with chest wall pain includeacute coronary syndrome
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is a syndrome due to decreased blood flow in the coronary arteries such that part of the heart muscle is unable to function properly or dies. The most common symptom is centrally located pressure-like chest pain, ...
, aortic dissection
Aortic dissection (AD) occurs when an injury to the innermost layer of the aorta allows blood to flow between the layers of the aortic wall, forcing the layers apart. In most cases, this is associated with a sudden onset of agonizing ches ...
, pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and dyspnea, shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve is ...
, or pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an pulmonary artery, artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include dyspnea, shortness of breath, chest pain ...
. Other cardiopulmonary causes of chest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
similar to that produced by costochondritis may include but are not limited to myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
, angina
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease.
Angina is typically the result of parti ...
, and pericarditis
Pericarditis () is inflammation of the pericardium, the fibrous sac surrounding the heart. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp chest pain, which may also be felt in the shoulders, neck, or back. The pain is typically less severe whe ...
. With costochondritis, the pain is typically worse with respiration, with movement, or within certain positions. Typically with other causes of chest pain, individuals will likely have radiating pain, shortness of breath, fever, a productive cough, nausea, dizziness, tachycardia, or hypotension.
These conditions will be ruled out using tests such as X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
s, which will help assess for pneumonia, pneumothorax, lung mass, and other concerns. Other tests such as an electrocardiogram (ECG) can be performed to exclude infection, ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems ...
, and other conditions. A laboratory workup can rule out acute coronary syndrome, pulmonary embolism, and pneumonia. Costochondritis will yield normal results for these tests.

Musculoskeletal
There are severalmusculoskeletal
The human musculoskeletal system (also known as the human locomotor system, and previously the activity system) is an organ system that gives humans the ability to move using their muscular and skeletal systems. The musculoskeletal system provid ...
conditions similar to costochondritis that are often confused. One such condition includes Tietze syndrome, which is often confused with costochondritis due to the similarity in location and symptomatology. Typically, costochondritis is a more common condition that is not associated with any swelling, affects multiple joints (usually of the 2nd to 5th ribs), and is usually seen in individuals older than 40 years of age. Tietze syndrome is a rarer condition that usually has visible swelling, commonly affecting a single joint (usually of the 2nd or 3rd rib), and typically seen in individuals younger than 40 years of age.
A similar condition known as slipping rib syndrome is also associated with chest pain and inflammation of the costal cartilage
Costal cartilage, also known as rib cartilage, are bars of hyaline cartilage that serve to prolong the ribs forward and contribute to the elasticity of the walls of the thorax. Costal cartilage is only found at the anterior ends of the ribs, pr ...
. Unlike costochondritis, the pain associated with slipping rib syndrome is often felt in the lower ribs, abdomen, and back, commonly affecting the interchondral junctions of the false 8th to 10th ribs. Costochondritis is typically experienced within the sternocostal junctions of the true
True most commonly refers to truth, the state of being in congruence with fact or reality.
True may also refer to:
Places
* True, West Virginia, an unincorporated community in the United States
* True, Wisconsin, a town in the United States
* ...
2nd to 5th ribs.
Other musculoskeletal conditions that may cause chest pain similar to costochondritis includes but are not limited to, painful xiphoid syndrome, muscle strain
A strain is an acute or Chronic condition, chronic soft tissue injury that occurs to a muscle, tendon, or both. The equivalent injury to a ligament is a sprain. Generally, the muscle or tendon overstretches and partially tears, under more phys ...
, myofascial pain syndrome
Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS), also known as chronic myofascial pain (CMP), is a syndrome characterized by chronic pain in multiple myofascial trigger points ("knots") and fascial (connective tissue) constrictions. It can appear in any body part. ...
, thoracic disk herniation, and rib fracture
A rib fracture is a break in a rib bone. This typically results in chest pain that is worse with inspiration. Bruising may occur at the site of the break. When several ribs are broken in several places a flail chest results. Potential complicat ...
.
Other
* Rheumatologic conditions such asfibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a functional somatic syndrome with symptoms of widespread chronic pain, accompanied by fatigue, sleep disturbance including awakening unrefreshed, and Cognitive deficit, cognitive symptoms. Other symptoms can include he ...
, SAPHO syndrome
SAPHO syndrome includes a variety of inflammatory bone disorders that may be associated with skin changes. These diseases share some clinical, radiologic, and pathologic characteristics.
An entity initially known as chronic recurrent multifocal ...
, ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis from the disease spectrum of axial spondyloarthritis. It is characterized by long-term inflammation of the joints of the spine, typically where the spine joins the pelvis. With AS, eye and bow ...
, rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
, and psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a long-term inflammatory arthritis that may occur in some people affected by the autoimmune disease psoriasis. The classic features of psoriatic arthritis include dactylitis (sausage-like swelling of the fingers ...
can cause symptoms similar to costochondritis.
* Oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the study, treatment, diagnosis, and prevention of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an ''oncologist''. The name's Etymology, etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγ ...
-related conditions, namely neoplasm
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s and myelomatous pleural effusion have been associated with chest pain.
* Chest pain is occasionally experienced with respiratory
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies gr ...
-related conditions such as pleuritis, precordial catch syndrome, and pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
.
* Psychogenic
A psychogenic effect is one that originates from the brain instead of other physical organs (i.e. the cause is psychological rather than physiological) and may refer to:
*Psychogenic pain
*Psychogenic disease
*Psychogenic amnesia
*Psychogenic coug ...
conditions such as anxiety disorder
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental disorders characterized by significant and uncontrollable feelings of anxiety and fear such that a person's social, occupational, and personal functions are significantly impaired. Anxiety may cause phys ...
s, panic disorder
Panic disorder is a mental disorder, specifically an anxiety disorder, characterized by reoccurring unexpected panic attacks. Panic attacks are sudden periods of intense fear that may include palpitations, sweating, shaking, shortness of breath ...
s, and hyperventilation syndrome
Hyperventilation syndrome (HVS), also known as chronic hyperventilation syndrome (CHVS), dysfunctional breathing hyperventilation syndrome, cryptotetany, spasmophilia, latent tetany, and central neuronal hyper excitability syndrome (NHS), is a r ...
may cause chest pain.
* Some gastroenterology
Gastroenterology (from the Greek gastḗr- "belly", -énteron "intestine", and -logía "study of") is the branch of medicine focused on the digestive system and its disorders. The digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract, sometime ...
conditions may be associated with costochondritis-like chest pain such as gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic upper gastrointestinal disease in which stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/or ...
, and esophagitis
Esophagitis, also spelled oesophagitis, is a disease characterized by inflammation of the esophagus. The esophagus is a tube composed of a mucosal lining, and longitudinal and circular smooth muscle fibers. It connects the pharynx to the stoma ...
.
*Vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency or hypovitaminosis D is a vitamin D level that is below normal. It most commonly occurs in people when they have inadequate exposure to sunlight, particularly sunlight with adequate ultraviolet B rays (UVB). Vitamin D def ...
can be a differential diagnosis for costochondritis as it may cause chest pain.
*Chest pain has also been reported following the use of cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
, which can increase the risk of various cardiovascular conditions.
Outlook, Treatment and Prevention
Outlook
Costochondritis is usually self-limited, meaning that it will typically resolve on its own without treatment. It may last for several weeks or longer.Treatment
Conservative methods are often the first method to treat the condition. If the condition is a result of trauma or over-use of the upper extremity, individuals will be told to rest and avoid activities. Pain relief medications (analgesics
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic, antalgic, pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used for pain management. Analgesics are conceptually distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily reduce, and in s ...
) such as acetaminophen
Paracetamol, or acetaminophen, is a non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic agent used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. It is a widely available over-the-counter drug sold under various brand names, including Tylenol and Panadol.
Parac ...
, or the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs A nonsteroidal compound is a drug that is not a steroid nor a steroid derivative. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are distinguished from corticosteroids as a class of anti-inflammatory agents.
List of nonsteroidal steroid receptor mod ...
(NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes dysmenorrhea, painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It can be taken oral administration, ...
, naproxen
Naproxen, sold under the brand name Aleve among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain, menstrual cramps, and inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout and fever. It is taken orally. It ...
, or meloxicam
Meloxicam, sold under the brand name Mobic among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain and inflammation in rheumatic diseases and osteoarthritis. It is taken by mouth or given by injection into a vein. ...
may be suggested to relieve discomfort. If the pain is localized, occasionally creams and patches containing compounds such as capsaicin
Capsaicin (8-methyl-''N''-vanillyl-6-nonenamide) (, rarely ) is an active component of chili peppers, which are plants belonging to the genus ''Capsicum''. It is a potent Irritation, irritant for Mammal, mammals, including humans, and produces ...
, NSAIDs, or lidocaine
Lidocaine, also known as lignocaine and sold under the brand name Xylocaine among others, is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type. It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. When used for local anae ...
may be used. Heat or ice compresses may also be used for treatment.
Outpatient follow-up may also be a form of treatment for costochondritis. Manual therapy
Manual therapy, or manipulative therapy, is a treatment primarily used by physical therapists, occupational therapists, and massage therapists to treat musculoskeletal pain and disability. It mostly includes kneading and manipulation of muscle ...
methods such as myofascial release, muscle energy techniques, balanced ligamentous tension (BLT), rib mobilization techniques, and stretching exercises may be used. Additionally, educating the individual with costochondritis about their body mechanics, posture, and activity modification can be beneficial.
In severe cases where symptoms do not resolve and last up to a year or longer, corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
s or local anesthetic injections may be considered.
Prevention
Prevention may be helped by avoiding putting stress on chest and ribs.Epidemiology
Costochondritis is a common condition that is responsible for approximately 13–36% of acute chest pain-related concerns from adults depending on the setting, with 14–39% for adolescents. It is most often seen in individuals who are older than 40 years of age and occurs more often in women than in men.References
External links
{{Osteochondropathy Musculoskeletal disorders