Cosmica Sidera on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Galilean moons (), or Galilean satellites, are the four largest
 In 1605, Galileo had been employed as a mathematics tutor for
In 1605, Galileo had been employed as a mathematics tutor for
File:Io Argos MAN Napoli Inv9556.jpg, Io (left) watched by
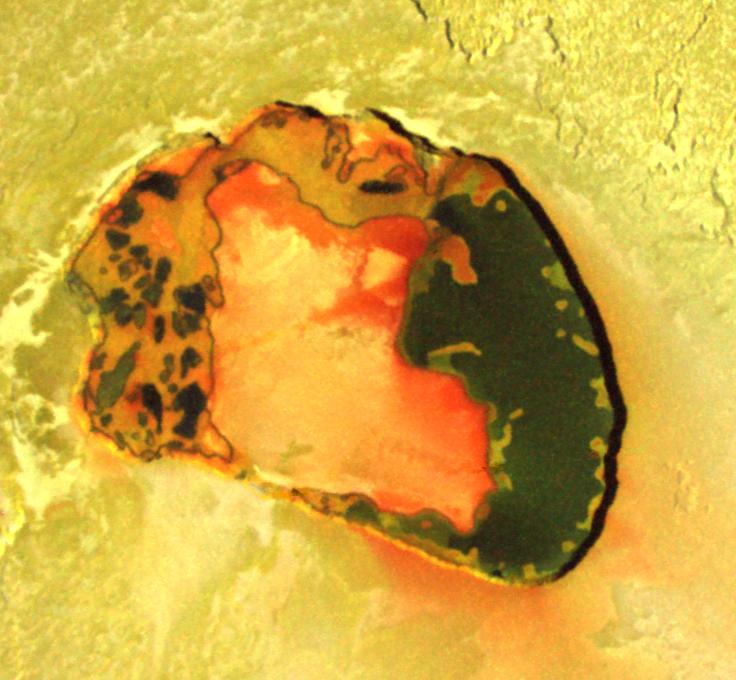 Io (Jupiter I) is the innermost of the four Galilean moons of Jupiter; with a diameter of 3642 kilometers, it is the fourth-largest moon in the Solar System, and is only marginally larger than
Io (Jupiter I) is the innermost of the four Galilean moons of Jupiter; with a diameter of 3642 kilometers, it is the fourth-largest moon in the Solar System, and is only marginally larger than
 Europa (Jupiter II), the second of the four Galilean moons, is the second closest to Jupiter and the smallest at 3121.6 kilometers in diameter, which is slightly smaller than
Europa (Jupiter II), the second of the four Galilean moons, is the second closest to Jupiter and the smallest at 3121.6 kilometers in diameter, which is slightly smaller than  The prominent markings that criss-cross the moon seem to be mainly
The prominent markings that criss-cross the moon seem to be mainly
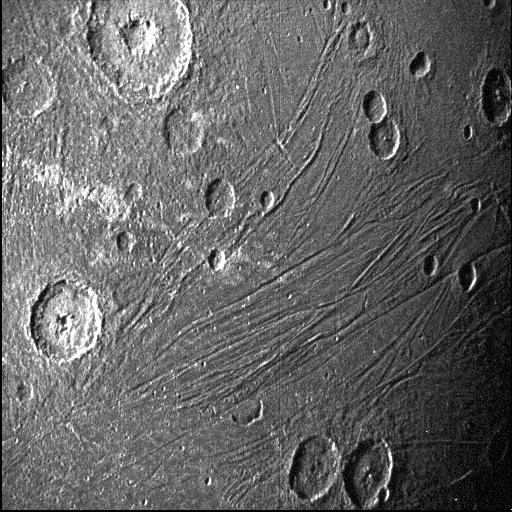 Ganymede (Jupiter III), the third Galilean moon, is named after the mythological Ganymede, cupbearer of the
Ganymede (Jupiter III), the third Galilean moon, is named after the mythological Ganymede, cupbearer of the
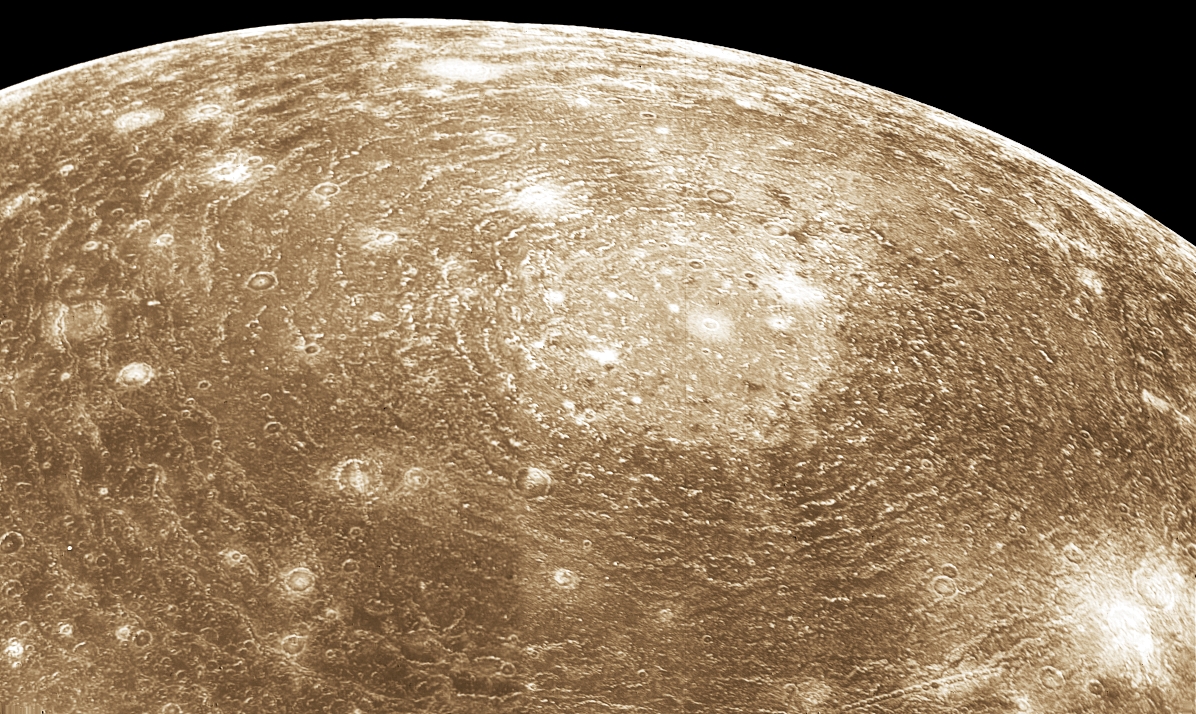 Callisto (Jupiter IV) is the fourth and last Galilean moon, and is the second-largest of the four, and at 4820.6 kilometers in diameter, it is the third largest moon in the Solar System, and barely smaller than Mercury, though only a third of the latter's mass. It is named after the Greek mythological nymph
Callisto (Jupiter IV) is the fourth and last Galilean moon, and is the second-largest of the four, and at 4820.6 kilometers in diameter, it is the third largest moon in the Solar System, and barely smaller than Mercury, though only a third of the latter's mass. It is named after the Greek mythological nymph
 Fluctuations in the orbits of the moons indicate that their mean density decreases with distance from Jupiter. Callisto, the outermost and least dense of the four, has a density intermediate between ice and rock whereas Io, the innermost and densest moon, has a density intermediate between rock and iron. Callisto has an ancient, heavily cratered and unaltered ice surface and the way it rotates indicates that its density is equally distributed, suggesting that it has no rocky or metallic core but consists of a homogeneous mix of rock and ice. This may well have been the original structure of all the moons. The rotation of the three inner moons, in contrast, indicates differentiation of their interiors with denser matter at the core and lighter matter above. They also reveal significant alteration of the surface. Ganymede reveals past tectonic movement of the ice surface which required partial melting of subsurface layers. Europa reveals more dynamic and recent movement of this nature, suggesting a thinner ice crust. Finally, Io, the innermost moon, has a sulfur surface, active volcanism and no sign of ice. All this evidence suggests that the nearer a moon is to Jupiter the hotter its interior. The current model is that the moons experience tidal heating as a result of the gravitational field of Jupiter in inverse proportion to the square of their distance from the giant planet. In all but Callisto this will have melted the interior ice, allowing rock and iron to sink to the interior and water to cover the surface. In Ganymede a thick and solid ice crust then formed. In warmer Europa a thinner more easily broken crust formed. In Io the heating is so extreme that all the rock has melted and water has long ago boiled out into space.
Fluctuations in the orbits of the moons indicate that their mean density decreases with distance from Jupiter. Callisto, the outermost and least dense of the four, has a density intermediate between ice and rock whereas Io, the innermost and densest moon, has a density intermediate between rock and iron. Callisto has an ancient, heavily cratered and unaltered ice surface and the way it rotates indicates that its density is equally distributed, suggesting that it has no rocky or metallic core but consists of a homogeneous mix of rock and ice. This may well have been the original structure of all the moons. The rotation of the three inner moons, in contrast, indicates differentiation of their interiors with denser matter at the core and lighter matter above. They also reveal significant alteration of the surface. Ganymede reveals past tectonic movement of the ice surface which required partial melting of subsurface layers. Europa reveals more dynamic and recent movement of this nature, suggesting a thinner ice crust. Finally, Io, the innermost moon, has a sulfur surface, active volcanism and no sign of ice. All this evidence suggests that the nearer a moon is to Jupiter the hotter its interior. The current model is that the moons experience tidal heating as a result of the gravitational field of Jupiter in inverse proportion to the square of their distance from the giant planet. In all but Callisto this will have melted the interior ice, allowing rock and iron to sink to the interior and water to cover the surface. In Ganymede a thick and solid ice crust then formed. In warmer Europa a thinner more easily broken crust formed. In Io the heating is so extreme that all the rock has melted and water has long ago boiled out into space.

 Jupiter's regular satellites are believed to have formed from a circumplanetary disk, a ring of accreting gas and solid debris analogous to a
Jupiter's regular satellites are believed to have formed from a circumplanetary disk, a ring of accreting gas and solid debris analogous to a
File:Jupiter-moons.jpg, Jupiter and all of the Galilean moons as seen through a amateur telescope (
Sky & Telescope utility for identifying Galilean moons
Interactive 3D visualisation of Jupiter and the Galilean moons
NASA's Stunning Discoveries on Jupiter's Largest Moons , Our Solar System's Moons
A Beginner's Guide to Jupiter's Moons
* Dominic Ford
The Moons of Jupiter
With a chart of the current position of the Galilean moons. {{DEFAULTSORT:Galilean Moons Copernican Revolution Moons of Jupiter Moons with a prograde orbit Solar System
moons of Jupiter
There are 97 Natural satellite, moons of Jupiter with confirmed orbits . This number does not include a number of meter-sized moonlets thought to be shed from the inner moons, nor hundreds of possible kilometer-sized outer irregular moons that ...
. They are, in descending-size order, Ganymede, Callisto
CALLISTO (''Cooperative Action Leading to Launcher Innovation in Stage Toss-back Operations'') is a reusable VTVL Prototype, demonstrator propelled by a small 40 kN Japanese LOX-LH2 rocket engine. It is being developed jointly by the CNES, French ...
, Io, and Europa
Europa may refer to:
Places
* Europa (Roman province), a province within the Diocese of Thrace
* Europa (Seville Metro), Seville, Spain; a station on the Seville Metro
* Europa City, Paris, France; a planned development
* Europa Cliffs, Alexan ...
. They are the most readily visible Solar System objects after Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant, with an average radius of about 9 times that of Earth. It has an eighth the average density of Earth, but is over 95 tim ...
, the dimmest of the classical planet
A classical planet is an astronomical object that is visible to the naked eye and moves across the sky and its backdrop of fixed stars (the common stars which seem still in contrast to the planets), appearing as wandering stars. Visible to huma ...
s; though their closeness to bright Jupiter makes naked-eye observation very difficult, they are readily seen with common binoculars
Binoculars or field glasses are two refracting telescopes mounted side-by-side and aligned to point in the same direction, allowing the viewer to use both eyes (binocular vision) when viewing distant objects. Most binoculars are sized to be held ...
, even under night sky
The night sky is the nighttime appearance of celestial objects like stars, planets, and the Moon, which are visible in a clear sky between sunset and sunrise, when the Sun is below the horizon.
Natural light sources in a night sky include moonlig ...
conditions of high light pollution
Light pollution is the presence of any unwanted, inappropriate, or excessive artificial Visible spectrum, lighting. In a descriptive sense, the term ''light pollution'' refers to the effects of any poorly implemented lighting sources, during the ...
. The invention of the telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using len ...
allowed astronomers to discover the moons in 1610. Through this, they became the first Solar System objects discovered since humans have started tracking the classical planets, and the first objects to be found to orbit any planet
A planet is a large, Hydrostatic equilibrium, rounded Astronomical object, astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets b ...
beyond Earth.
They are planetary-mass moon
A planetary-mass moon is a planetary-mass object. They are large and ellipsoidal (sometimes spherical) in shape. Moons may be in hydrostatic equilibrium due to tidal or radiogenic heating, in some cases forming a subsurface ocean. Two moons in t ...
s and among the largest objects in the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
. All four, along with Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
, Triton
Triton commonly refers to:
* Triton (mythology), a Greek god
* Triton (moon), a satellite of Neptune
Triton may also refer to:
Biology
* Triton cockatoo, a parrot
* Triton (gastropod), a group of sea snails
* ''Triton'', a synonym of ''Triturus' ...
, and Earth's Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
, are larger than any of the Solar System's dwarf planet
A dwarf planet is a small planetary-mass object that is in direct orbit around the Sun, massive enough to be hydrostatic equilibrium, gravitationally rounded, but insufficient to achieve clearing the neighbourhood, orbital dominance like the ...
s. The largest, Ganymede, is the largest moon in the Solar System and surpasses the planet Mercury in size (though not mass). Callisto is only slightly smaller than Mercury in size; the smaller ones, Io and Europa, are about the size of the Moon. The three inner moons — Io, Europa, and Ganymede — are in a 4:2:1 orbital resonance
In celestial mechanics, orbital resonance occurs when orbiting bodies exert regular, periodic gravitational influence on each other, usually because their orbital periods are related by a ratio of small integers. Most commonly, this relation ...
with each other. While the Galilean moons are spherical, all of Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
's remaining moons have irregular forms because they are too small for their self-gravitation
Self-gravity is gravitational force exerted by a system, particularly a celestial body or system of bodies, onto itself. At a sufficient mass, this allows the system to hold itself together.Chamberlin, T. C. The Planetesimal Hypothesis. Journal o ...
to pull them into spheres.
The Galilean moons are named after Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642), commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei ( , , ) or mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a poly ...
, who observed them in either December 1609 or January 1610, and recognized them as satellites of Jupiter in March 1610; they remained the only known moons of Jupiter until the discovery of the fifth largest moon of Jupiter Amalthea in 1892. Galileo initially named his discovery the Cosmica Sidera ("Cosimo
Cosimo is the Italian form of the Greek name ''Kosmas'' (latinised as ''Cosmas'').
Cosimo may refer to:
Characters
* Cosimo Piovasco di Rondò, hero of Italo Calvino's 1957 novel ''The Baron in the Trees''
Given name Medici family
* Cosimo ...
's stars") or Medicean Stars, but the names that eventually prevailed were chosen by Simon Marius. Marius discovered the moons independently at nearly the same time as Galileo, 8 January 1610, and gave them their present individual names, after mythological characters that Zeus
Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the List of Greek deities, Greek pantheon. He is a sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus.
Zeus is the child ...
seduced or abducted, which were suggested by Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, Natural philosophy, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best know ...
in his ''Mundus Jovialis'', published in 1614. Their discovery showed the importance of the telescope as a tool for astronomers by proving that there were objects in space that cannot be seen by the naked eye. The discovery of celestial bodies orbiting something other than Earth dealt a serious blow to the then-accepted (among educated Europeans) Ptolemaic world system, a geocentric theory in which everything orbits around Earth.
History
Discovery
As a result of improvements thatGalileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642), commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei ( , , ) or mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a poly ...
made to the telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using len ...
, with a magnifying capability of 20×, he was able to see celestial bodies more distinctly than was previously possible. This allowed Galileo to observe in either December 1609 or January 1610 what came to be known as the Galilean moons.
On 7 January 1610, Galileo wrote a letter containing the first mention of Jupiter's moons. At the time, he saw only three of them, and he believed them to be fixed stars near Jupiter. He continued to observe these celestial orbs from 8 January to 2 March 1610. In these observations, he discovered a fourth body, and also observed that the four were not fixed stars, but rather were orbiting Jupiter.
Galileo's discovery proved the importance of the telescope as a tool for astronomers by showing that there were objects in space to be discovered that until then had remained unseen by the naked eye. More importantly, the discovery of celestial bodies orbiting something other than Earth dealt a blow to the then-accepted Ptolemaic world system, which held that Earth was at the center of the universe and all other celestial bodies revolved around it. Galileo's 13 March 1610, ''Sidereus Nuncius
''Sidereus Nuncius'' (usually ''Sidereal Messenger'', also ''Starry Messenger'' or ''Sidereal Message'') is a short astronomical treatise (or ''pamphlet'') published in Neo-Latin by Galileo Galilei on March 13, 1610. It was the first published ...
'' (''Starry Messenger''), which announced celestial observations through his telescope, does not explicitly mention Copernican heliocentrism
Copernican heliocentrism is the astronomical scientific modeling, model developed by Nicolaus Copernicus and published in 1543. This model positioned the Sun at the center of the Universe, motionless, with Earth and the other planets orbiting arou ...
, a theory that placed the Sun
The Sun is the star at the centre of the Solar System. It is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light a ...
at the center of the universe. Nevertheless, Galileo accepted the Copernican theory.
A Chinese historian of astronomy, Xi Zezong
Xi Zezong (June 6, 1927, Yuanqu, Shanxi – December 27, 2008, Beijing) was a Chinese astronomer, historian, and translator. He was a member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and an awardee of the Astronomy Prize.
He identified a possible r ...
, has claimed that a "small reddish star" observed near Jupiter in 364 BCE by Chinese astronomer Gan De
Gan De (; fl. 4th century BC), also known as the Lord Gan (Gan Gong), was an ancient Chinese astronomer and astrologer born in the State of Qi. Along with Shi Shen, he is believed to be the first in history known by name to compile a star catal ...
may have been Ganymede. If true, this might predate Galileo's discovery by around two millennia.
The observations of Simon Marius are another noted example of observation, and he later reported observing the moons in 1609. However, because he did not publish these findings until after Galileo, there is a degree of uncertainty around his records.
Names
 In 1605, Galileo had been employed as a mathematics tutor for
In 1605, Galileo had been employed as a mathematics tutor for Cosimo de' Medici
Cosimo di Giovanni de' Medici (27 September 1389 – 1 August 1464) was an Italian banker and politician who established the House of Medici, Medici family as effective rulers of Florence during much of the Italian Renaissance. His power derive ...
. In 1609, Cosimo became Grand Duke Cosimo II of Tuscany
Tuscany ( ; ) is a Regions of Italy, region in central Italy with an area of about and a population of 3,660,834 inhabitants as of 2025. The capital city is Florence.
Tuscany is known for its landscapes, history, artistic legacy, and its in ...
. Galileo, seeking patronage from his now-wealthy former student and his powerful family, used the discovery of Jupiter's moons to gain it. On 13 February 1610, Galileo wrote to the Grand Duke's secretary:
Galileo initially called his discovery the Cosmica Sidera ("Cosimo's stars"), in honour of Cosimo alone. Cosimo's secretary suggested to change the name to Medicea Sidera ("the Medician stars"), honouring all four Medici brothers (Cosimo, Francesco, Carlo Carlo is a given name. It is an Italian form of Charles. It can refer to:
*Carlo (name)
*Monte Carlo
*Carlingford, New South Wales, a suburb in north-west Sydney, New South Wales, Australia
*A satirical song written by Dafydd Iwan about Prince Char ...
, and Lorenzo). The discovery was announced in the ''Sidereus Nuncius
''Sidereus Nuncius'' (usually ''Sidereal Messenger'', also ''Starry Messenger'' or ''Sidereal Message'') is a short astronomical treatise (or ''pamphlet'') published in Neo-Latin by Galileo Galilei on March 13, 1610. It was the first published ...
'' ("Starry Messenger"), published in Venice
Venice ( ; ; , formerly ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 islands that are separated by expanses of open water and by canals; portions of the city are li ...
in March 1610, less than two months after the first observations.
On 12 March 1610, Galileo wrote his dedicatory letter to the Duke of Tuscany, and the next day sent a copy to the Grand Duke, hoping to obtain the Grand Duke's support as quickly as possible. On 19 March, he sent the telescope he had used to first view Jupiter's moons to the Grand Duke, along with an official copy of ''Sidereus Nuncius
''Sidereus Nuncius'' (usually ''Sidereal Messenger'', also ''Starry Messenger'' or ''Sidereal Message'') is a short astronomical treatise (or ''pamphlet'') published in Neo-Latin by Galileo Galilei on March 13, 1610. It was the first published ...
'' (''The Starry Messenger'') that, following the secretary's advice, named the four moons the Medician Stars. In his dedicatory introduction, Galileo wrote:
Other names put forward include:
* I. ''Principharus'' (for the "prince" of Tuscany), II. ''Victripharus'' (after Vittoria della Rovere
Vittoria della Rovere (7 February 1622 – 5 March 1694) was Grand Duchess of Tuscany as the wife of Grand Duke Ferdinando II. She had four children with her husband, two of whom would survive infancy: the future Cosimo III, Tuscany's longes ...
), III. ''Cosmipharus'' (after Cosimo de' Medici
Cosimo di Giovanni de' Medici (27 September 1389 – 1 August 1464) was an Italian banker and politician who established the House of Medici, Medici family as effective rulers of Florence during much of the Italian Renaissance. His power derive ...
) and IV. ''Fernipharus'' (after Duke Ferdinando de' Medici) – by Giovanni Battista Hodierna
Giovanni Battista Hodierna, also spelled as Odierna (April 13, 1597 – April 6, 1660) was an Italian astronomer at the court of Giulio Tomasi, Duke of Palma (Palma di Montechiaro). He compiled a catalogue of comets and other celestial object ...
, a disciple of Galileo and author of the first ephemerides
In astronomy and celestial navigation, an ephemeris (; ; , ) is a book with tables that gives the trajectory of naturally occurring astronomical objects and artificial satellites in the sky, i.e., the position (and possibly velocity) over time. ...
(''Medicaeorum Ephemerides'', 1656);
* ''Circulatores Jovis'', or ''Jovis Comites'' – by Johannes Hevelius
Johannes Hevelius
Some sources refer to Hevelius as Polish:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Some sources refer to Hevelius as German:
*
*
*
*
*of the Royal Society
* (in German also known as ''Hevel''; ; – 28 January 1687) was a councillor and mayor of Danz ...
;
* ''Gardes'', or ''Satellites'' (from the Latin ''satelles, satellitis'', meaning "escorts") – by Jacques Ozanam
Jacques Ozanam (16 June 1640 in Sainte-Olive, Ain – 3 April 1718 in Paris) was a French mathematician.
Biography
Jacques Ozanam was born in Sainte-Olive, Ain, France.
In 1670, he published trigonometric and logarithmic tables more accura ...
.
The names that eventually prevailed were chosen by Simon Marius, who discovered the moons independently at the same time as Galileo: he named them at the suggestion of Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, Natural philosophy, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best know ...
after lovers of the god Zeus (the Greek equivalent of Jupiter), in his ''Mundus Jovialis'', published in 1614:
Galileo steadfastly refused to use Marius' names and invented as a result the numbering scheme that is still used nowadays, in parallel with proper moon names. The numbers run from Jupiter outward, thus I, II, III and IV for Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto respectively. Galileo used this system in his notebooks but never actually published it. The numbered names (Jupiter ''x'') were used until the mid-20th century when other inner moons were discovered, and Marius' names became widely used.
Argus Panoptes
Argus or Argos Panoptes (, "All-seeing Argos") is a many-eyed giant in Greek mythology. Known for his perpetual vigilance, he served the goddess Hera as a watchman. His most famous task was guarding Io, a priestess of Hera, whom Zeus had transf ...
(right) on Hera's orders
File:Wall painting - Europa and the bull - Pompeii (IX 5 18-21) - Napoli MAN 111475 - 02.jpg, Europa on the back of Zeus turned into a bull
File:Zeus abducts Ganymede, large terracotta, before 470 BC, AM Olympia, Olym26.jpg, Ganymede (left) abducted by Zeus (right)
File:Wall painting - Artemis and Kallisto - Pompeii (VII 12 26) - Napoli MAN 111441.jpg, Callisto (leftmost) with Eros and other nymphs, with Artemis seated
Determination of longitude
Galileo's discovery had practical applications. Safe navigation required accurately determining a ship's position at sea. Whilelatitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
could be measured well enough by local astronomical observations, determining longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east- west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lett ...
required knowledge of the time of each observation synchronized to the time at a reference longitude. The longitude problem
The history of longitude describes the centuries-long effort by astronomers, cartographers and navigators to discover a means of determining the longitude (the east-west position) of any given place on Earth. The measurement of longitude is impo ...
was so important that large prizes were offered for its solution at various times by Spain, The Netherlands, and The United Kingdom.
Galileo proposed determining longitude based on the timing of the orbits of the Galilean moons. The times of the eclipses of the moons could be precisely calculated in advance and compared with local observations on land or on ship to determine the local time and hence longitude. Galileo applied in 1616 for the Spanish prize of 6,000 gold ducat
The ducat ( ) coin was used as a trade coin in Europe from the later Middle Ages to the 19th century. Its most familiar version, the gold ducat or sequin containing around of 98.6% fine gold, originated in Venice in 1284 and gained wide inter ...
s with a lifetime pension of 2,000 a year, and almost two decades later for the Dutch prize, but by then he was under house arrest for possible heresy.
The main problem with the Jovian moon technique was that it was difficult to observe the Galilean moons through a telescope on a moving ship, a problem that Galileo tried to solve with the invention of the celatone
The celatone was a device invented by Galileo Galilei to observe Jupiter's moons with the purpose of finding longitude on Earth. It took the form of a piece of headgear with a telescope taking the place of an eyehole.
Modern versions
In 201 ...
. Others suggested improvements, but without success.
Land mapping surveys had the same problem determining longitude, though with less severe observational conditions. The method proved practical and was used by Giovanni Domenico Cassini
Giovanni Domenico Cassini (8 June 1625 – 14 September 1712) was an Italian-French mathematician, astronomer, astrologer and engineer. Cassini was born in Perinaldo, near Imperia, at that time in the County of Nice, part of the Savoyard sta ...
and Jean Picard
Jean Picard (21 July 1620 – 12 July 1682) was a French astronomer and priest born in La Flèche, where he studied at the Jesuit Collège Royal Henry-Le-Grand.
He is principally notable for his accurate measure of the size of the Earth, ...
to re-map France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
.
Members
Some models predict that there may have been several generations of Galilean satellites in Jupiter's early history. Each generation of moons to have formed would have spiraled into Jupiter and been destroyed, due to tidal interactions with Jupiter's proto-satellite disk, with new moons forming from the remaining debris. By the time the present generation formed, the gas in the proto-satellite disk had thinned out to the point that it no longer greatly interfered with the moons' orbits. Other models suggest that Galilean satellites formed in a proto-satellite disk, in which formation timescales were comparable to or shorter than orbital migration timescales. Io isanhydrous
A substance is anhydrous if it contains no water. Many processes in chemistry can be impeded by the presence of water; therefore, it is important that water-free reagents and techniques are used. In practice, however, it is very difficult to achie ...
and likely has an interior of rock and metal. Europa is thought to contain 8% ice and water by mass with the remainder rock. These moons are, in increasing order of distance from Jupiter:
Io
 Io (Jupiter I) is the innermost of the four Galilean moons of Jupiter; with a diameter of 3642 kilometers, it is the fourth-largest moon in the Solar System, and is only marginally larger than
Io (Jupiter I) is the innermost of the four Galilean moons of Jupiter; with a diameter of 3642 kilometers, it is the fourth-largest moon in the Solar System, and is only marginally larger than Earth's moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It orbits around Earth at an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth's diameter). The Moon rotates, with a rotation period (lunar day) that is synchronized to its orbital period (lunar mo ...
. It was named after Io, a priestess of Hera
In ancient Greek religion, Hera (; ; in Ionic Greek, Ionic and Homeric Greek) is the goddess of marriage, women, and family, and the protector of women during childbirth. In Greek mythology, she is queen of the twelve Olympians and Mount Oly ...
who became one of the lovers of Zeus
Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the List of Greek deities, Greek pantheon. He is a sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus.
Zeus is the child ...
. It was referred to as "Jupiter I", or "The first satellite of Jupiter" until the mid-20th century.
With over 400 active volcanos, Io is the most geologically active object in the Solar System. Its surface is dotted with more than 100 mountains, some of which are taller than Earth's Mount Everest
Mount Everest (), known locally as Sagarmatha in Nepal and Qomolangma in Tibet, is Earth's highest mountain above sea level. It lies in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas and marks part of the China–Nepal border at it ...
. Unlike most satellites in the outer Solar System (which have a thick coating of ice), Io is primarily composed of silicate rock surrounding a molten iron or iron sulfide core.
Although not proven, data from the Galileo orbiter indicates that Io might have its own magnetic field. Io has an extremely thin atmosphere made up mostly of sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless gas with a pungent smell that is responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is r ...
(SO2). If a surface data or collection vessel were to land on Io in the future, it would have to be extremely tough (similar to the tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engine; ...
-like bodies of the Soviet Venera
The Venera (, 'Venus') program was a series of space probes developed by the Soviet Union between 1961 and 1984 to gather information about the planet Venus.
Thirteen probes successfully entered the Venusian atmosphere, including the two ...
landers) to survive the radiation and magnetic fields that originate from Jupiter.
Europa
 Europa (Jupiter II), the second of the four Galilean moons, is the second closest to Jupiter and the smallest at 3121.6 kilometers in diameter, which is slightly smaller than
Europa (Jupiter II), the second of the four Galilean moons, is the second closest to Jupiter and the smallest at 3121.6 kilometers in diameter, which is slightly smaller than Earth's Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It orbits around Earth at an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth's diameter). The Moon rotates, with a rotation period (lunar day) that is synchronized to its orbital period (lunar mo ...
. The name comes from a mythical Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
n noblewoman, Europa
Europa may refer to:
Places
* Europa (Roman province), a province within the Diocese of Thrace
* Europa (Seville Metro), Seville, Spain; a station on the Seville Metro
* Europa City, Paris, France; a planned development
* Europa Cliffs, Alexan ...
, who was courted by Zeus
Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the List of Greek deities, Greek pantheon. He is a sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus.
Zeus is the child ...
and became the queen of Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
, though the name did not become widely used until the mid-20th century.
It has a smooth and bright surface, with a layer of water surrounding the mantle of the planet, thought to be 100 kilometers thick. The smooth surface includes a layer of ice, while the bottom of the ice is theorized to be liquid water. The apparent youth and smoothness of the surface have led to the hypothesis that a water ocean exists beneath it, which could conceivably serve as an abode for extraterrestrial life
Extraterrestrial life, or alien life (colloquially, aliens), is life that originates from another world rather than on Earth. No extraterrestrial life has yet been scientifically conclusively detected. Such life might range from simple forms ...
. Heat energy from tidal flexing ensures that the ocean remains liquid and drives geological activity. Life may exist in Europa's under-ice ocean. So far, there is no evidence that life exists on Europa, but the likely presence of liquid water has spurred calls to send a probe there.
 The prominent markings that criss-cross the moon seem to be mainly
The prominent markings that criss-cross the moon seem to be mainly albedo feature
In planetary geology, an albedo feature is a large area on the surface of a planet (or other Solar System body) which shows a contrast in brightness or darkness (albedo) with adjacent areas.
Historically, albedo features were the first (and usu ...
s, which emphasize low topography. There are few craters on Europa because its surface is tectonically active and young. Some theories suggest that Jupiter's gravity is causing these markings, as one side of Europa is constantly facing Jupiter. Volcanic water eruptions splitting the surface of Europa and even geysers have also been considered as causes. The reddish-brown color of the markings is theorized to be caused by sulfur, but because no data collection devices have been sent to Europa, scientists cannot yet confirm this. Europa is primarily made of silicate
A silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used ...
rock and likely has an iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
core. It has a tenuous atmosphere composed primarily of oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
.
Ganymede
 Ganymede (Jupiter III), the third Galilean moon, is named after the mythological Ganymede, cupbearer of the
Ganymede (Jupiter III), the third Galilean moon, is named after the mythological Ganymede, cupbearer of the Greek gods
In ancient Greece, deities were regarded as immortal, anthropomorphic, and powerful. They were conceived of as individual persons, rather than abstract concepts or notions, and were described as being similar to humans in appearance, albeit larg ...
and Zeus
Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the List of Greek deities, Greek pantheon. He is a sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus.
Zeus is the child ...
's beloved. Ganymede is the largest natural satellite in the Solar System at 5262.4 kilometers in diameter, which makes it larger than the planet Mercury – although only at about half of its mass since Ganymede is an icy world. It is the only satellite in the Solar System known to possess a magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior Dynamo ...
, likely created through convection
Convection is single or Multiphase flow, multiphase fluid flow that occurs Spontaneous process, spontaneously through the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoy ...
within the liquid iron core.
Ganymede is composed primarily of silicate rock and water ice, and a salt-water ocean is believed to exist nearly 200 km below Ganymede's surface, sandwiched between layers of ice. The metallic core of Ganymede suggests a greater heat at some time in its past than had previously been proposed. The surface is a mix of two types of terrain—highly cratered dark regions and younger, but still ancient, regions with a large array of grooves and ridges. Ganymede has a high number of craters, but many are gone or barely visible due to its icy crust forming over them. The satellite has a thin oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
that includes O, O2, and possibly O3 (ozone
Ozone () (or trioxygen) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , break ...
), and some atomic hydrogen
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral hydrogen atom contains a single positively charged proton in the nucleus, and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb for ...
.
Callisto
 Callisto (Jupiter IV) is the fourth and last Galilean moon, and is the second-largest of the four, and at 4820.6 kilometers in diameter, it is the third largest moon in the Solar System, and barely smaller than Mercury, though only a third of the latter's mass. It is named after the Greek mythological nymph
Callisto (Jupiter IV) is the fourth and last Galilean moon, and is the second-largest of the four, and at 4820.6 kilometers in diameter, it is the third largest moon in the Solar System, and barely smaller than Mercury, though only a third of the latter's mass. It is named after the Greek mythological nymph Callisto
CALLISTO (''Cooperative Action Leading to Launcher Innovation in Stage Toss-back Operations'') is a reusable VTVL Prototype, demonstrator propelled by a small 40 kN Japanese LOX-LH2 rocket engine. It is being developed jointly by the CNES, French ...
, a lover of Zeus who was a daughter of the Arkadian King Lykaon and a hunting companion of the goddess Artemis. The moon does not form part of the orbital resonance
In celestial mechanics, orbital resonance occurs when orbiting bodies exert regular, periodic gravitational influence on each other, usually because their orbital periods are related by a ratio of small integers. Most commonly, this relation ...
that affects three inner Galilean satellites and thus does not experience appreciable tidal heating
Tidal heating (also known as tidal working or tidal flexing) occurs through the tidal friction processes: orbital and rotational energy is dissipated as heat in either (or both) the surface ocean or interior of a planet or satellite. When an objec ...
. Callisto is composed of approximately equal amounts of rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wale ...
and ices
ICES (formerly known as the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences) is an independent, non-profit corporation that applies the study of health informatics for health services research and population-wide health outcomes research in Ontario ...
, which makes it the least dense of the Galilean moons. It is one of the most heavily cratered satellites in the Solar System, and one major feature is a basin around 3000 km wide called Valhalla
In Norse mythology, Valhalla ( , ; , )Orchard (1997:171–172) is described as a majestic hall located in Asgard and presided over by the god Odin. There were five possible realms the soul could travel to after death. The first was Fólkvang ...
.
Callisto is surrounded by an extremely thin atmosphere composed of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
and probably molecular oxygen
There are several known allotropes of oxygen. The most familiar is molecular oxygen (), present at significant levels in Earth's atmosphere and also known as dioxygen or triplet oxygen. Another is the highly reactive ozone (). Others are:
* Atomic ...
. Investigation revealed that Callisto may possibly have a subsurface ocean of liquid water at depths less than 300 kilometres. The likely presence of an ocean within Callisto indicates that it can or could harbour life
Life, also known as biota, refers to matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes. It is defined descriptively by the capacity for homeostasis, Structure#Biological, organisation, met ...
. However, this is less likely than on nearby Europa
Europa may refer to:
Places
* Europa (Roman province), a province within the Diocese of Thrace
* Europa (Seville Metro), Seville, Spain; a station on the Seville Metro
* Europa City, Paris, France; a planned development
* Europa Cliffs, Alexan ...
. Callisto has long been considered the most suitable place for a human base for future exploration of the Jupiter system since it is furthest from the intense radiation of Jupiter's magnetic field.
Comparative structure

Size

Latest flyby
Origin and evolution
 Jupiter's regular satellites are believed to have formed from a circumplanetary disk, a ring of accreting gas and solid debris analogous to a
Jupiter's regular satellites are believed to have formed from a circumplanetary disk, a ring of accreting gas and solid debris analogous to a protoplanetary disk
A protoplanetary disk is a rotating circumstellar disc of dense gas and dust surrounding a young newly formed star, a T Tauri star, or Herbig Ae/Be star. The protoplanetary disk may not be considered an accretion disk; while the two are sim ...
. They may be the remnants of a score of Galilean-mass satellites that formed early in Jupiter's history.
Simulations suggest that, while the disk had a relatively high mass at any given moment, over time a substantial fraction (several tenths of a percent) of the mass of Jupiter captured from the Solar nebula was processed through it. However, the disk mass of only 2% that of Jupiter is required to explain the existing satellites. Thus there may have been several generations of Galilean-mass satellites in Jupiter's early history. Each generation of moons would have spiraled into Jupiter, due to drag from the disk, with new moons then forming from the new debris captured from the Solar nebula. By the time the present (possibly fifth) generation formed, the disk had thinned out to the point that it no longer greatly interfered with the moons' orbits. The current Galilean moons were still affected, falling into and being partially protected by an orbital resonance
In celestial mechanics, orbital resonance occurs when orbiting bodies exert regular, periodic gravitational influence on each other, usually because their orbital periods are related by a ratio of small integers. Most commonly, this relation ...
which still exists for Io, Europa, and Ganymede. Ganymede's larger mass means that it would have migrated inward at a faster rate than Europa or Io. Tidal dissipation in the Jovian system is still ongoing and Callisto
CALLISTO (''Cooperative Action Leading to Launcher Innovation in Stage Toss-back Operations'') is a reusable VTVL Prototype, demonstrator propelled by a small 40 kN Japanese LOX-LH2 rocket engine. It is being developed jointly by the CNES, French ...
will likely be captured into the resonance in about 1.5 billion years, creating a 1:2:4:8 chain.
Visibility
All four Galilean moons are bright enough to be viewed from Earth without atelescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using len ...
, if only they could appear farther away from Jupiter. (They are, however, easily distinguished with even low-powered binoculars
Binoculars or field glasses are two refracting telescopes mounted side-by-side and aligned to point in the same direction, allowing the viewer to use both eyes (binocular vision) when viewing distant objects. Most binoculars are sized to be held ...
.) They have apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the Irradiance, brightness of a star, astronomical object or other celestial objects like artificial satellites. Its value depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and any extinction (astronomy), ...
s between 4.6 and 5.6 when Jupiter is in opposition
Opposition may refer to:
Arts and media
* ''Opposition'' (Altars EP), 2011 EP by Christian metalcore band Altars
* The Opposition (band), a London post-punk band
* ''The Opposition with Jordan Klepper'', a late-night television series on Comedy ...
with the Sun, and are about one unit of magnitude dimmer when Jupiter is in conjunction. The main difficulty in observing the moons from Earth is their proximity to Jupiter, since they are obscured by its brightness. The maximum angular separations of the moons are between 2 and 10 arcminutes
A minute of arc, arcminute (abbreviated as arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a degree. Since one degree is of a turn, or complete rotation, one arcminute is of a tu ...
from Jupiter, which is close to the limit of human visual acuity
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of visual perception, vision, but technically rates an animal's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity depends on optical and neural factors. Optical factors of the eye ...
. Ganymede and Callisto, at their maximum separation, are the likeliest targets for potential naked-eye observation.
Meade LX200
The Meade LX200 is a family of commercial telescopes produced by Meade Instruments launched in 1992 with 8" (20.32 cm) and a 10" (25.4 cm) Schmidt–Cassegrain models on computerized altazimuth mounts. Two larger models, a 12" (30.4 ...
).
File:Jupiter.mit.Io.Ganymed.Europa.Calisto.Vollmond.10.4.2017.jpg, Jupiter with the Galilean moons and the full Moon as seen around conjunction on 10 April 2017
File:Galilean satellite triple conjunction 2015-01-24.jpg, Two Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the Orbiting Solar Observatory, first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most ...
views of a rare triple transit of Jupiter by Europa, Callisto and Io (24 January 2015), alt=Small satellites visible against the vastness of the largest planet in the solar system
Orbit animations
GIF animations depicting the Galilean moon orbits and the resonance of Io, Europa, and GanymedeSee also
*Jupiter's moons in fiction
Jupiter, the largest planet in the Solar System, has appeared in works of fiction across several centuries. The way the planet has been depicted has evolved as more has become known about its composition; it was initially portrayed as being entir ...
* Colonization of the Jovian System
Notes
References
External links
Sky & Telescope utility for identifying Galilean moons
Interactive 3D visualisation of Jupiter and the Galilean moons
NASA's Stunning Discoveries on Jupiter's Largest Moons , Our Solar System's Moons
A Beginner's Guide to Jupiter's Moons
* Dominic Ford
The Moons of Jupiter
With a chart of the current position of the Galilean moons. {{DEFAULTSORT:Galilean Moons Copernican Revolution Moons of Jupiter Moons with a prograde orbit Solar System