cortex (anatomy) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In anatomy and zoology, the cortex (plural cortices) is the outermost (or superficial) layer of an
In anatomy and zoology, the cortex (plural cortices) is the outermost (or superficial) layer of an
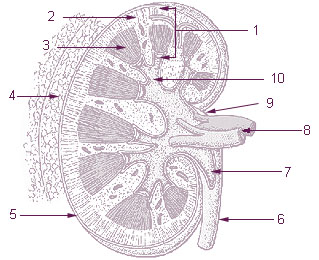 * The renal cortex, between the renal capsule and the renal medulla; assists in ultrafiltration
* The
* The renal cortex, between the renal capsule and the renal medulla; assists in ultrafiltration
* The
 In anatomy and zoology, the cortex (plural cortices) is the outermost (or superficial) layer of an
In anatomy and zoology, the cortex (plural cortices) is the outermost (or superficial) layer of an organ
Organ may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a part of an organism
Musical instruments
* Organ (music), a family of keyboard musical instruments characterized by sustained tone
** Electronic organ, an electronic keyboard instrument
** Hammond ...
. Organs with well-defined cortical layers include kidneys, adrenal glands, ovaries, the thymus, and portions of the brain
The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head ( cephalization), usually near organs for special ...
, including the cerebral cortex, the best-known of all cortices.
Etymology
The word is of Latin origin and means bark, rind, shell or husk.Notable examples
 * The renal cortex, between the renal capsule and the renal medulla; assists in ultrafiltration
* The
* The renal cortex, between the renal capsule and the renal medulla; assists in ultrafiltration
* The adrenal cortex
The adrenal cortex is the outer region and also the largest part of an adrenal gland. It is divided into three separate zones: zona glomerulosa, zona fasciculata and zona reticularis. Each zone is responsible for producing specific hormones. It is ...
, situated along the perimeter of the adrenal gland; mediates the stress response through the production of various hormones
* The thymic cortex, mainly composed of lymphocytes; functions as a site for somatic recombination of T cell receptors, and positive selection
In population genetics, directional selection, is a mode of negative natural selection in which an extreme phenotype is favored over other phenotypes, causing the allele frequency to shift over time in the direction of that phenotype. Under dir ...
* The cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the cerebrum, plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness.
* Cortical bone is the hard outer layer of bone; distinct from the spongy, inner cancellous bone tissue
* Ovarian cortex is the outer layer of the ovary and contains the follicles.
* The lymph node cortex is the outer layer of the lymph node.
Cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is typically described as comprising three parts: the sensory, motor, and association areas. These sensory areas receive and process information from the senses. The senses of vision, audition, and touch are served by the primary visual cortex, the primary auditory cortex, and primary somatosensory cortex. The cerebellar cortex is the thin gray surface layer of thecerebellum
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebel ...
, consisting of an outer molecular
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
layer or stratum moleculare, a single layer of Purkinje cells (the ganglionic layer), and an inner granular layer or stratum granulosum. The cortex is the outer surface of the cerebrum and is composed of gray matter.
The motor areas are located in both hemispheres of the cerebral cortex. Two areas of the cortex are commonly referred to as motor: the primary motor cortex
The primary motor cortex (Brodmann area 4) is a brain region that in humans is located in the dorsal portion of the frontal lobe. It is the primary region of the motor system and works in association with other motor areas including premotor co ...
, which executes voluntary movements; and the supplementary motor areas and premotor cortex, which ''select'' voluntary movements. In addition, motor functions have been attributed to the posterior parietal cortex, which guides voluntary movements; and the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, which decides which voluntary movements to make according to higher-order instructions, rules, and self-generated thoughts.
References
Anatomy {{Anatomy-stub