Corsi people on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


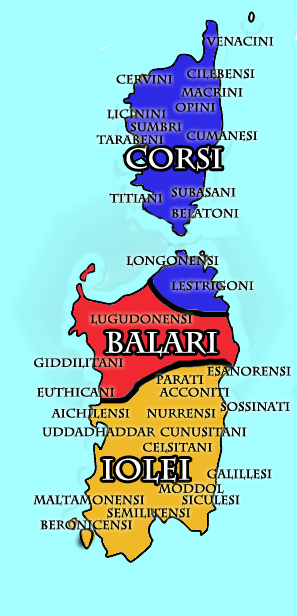 The Corsi were an ancient people of
The Corsi were an ancient people of Pausanias Description of Greece
/ref>


 The Corsi were an ancient people of
The Corsi were an ancient people of Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; ; ) is the Mediterranean islands#By area, second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, and one of the Regions of Italy, twenty regions of Italy. It is located west of the Italian Peninsula, north of Tunisia an ...
and Corsica
Corsica ( , , ; ; ) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the Regions of France, 18 regions of France. It is the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of the Metro ...
, to which they gave the name, as well as one of the three major groups among which the ancient Sardinians
Sardinians or Sards are an Italians, Italian ethno-linguistic group and a nation indigenous to Sardinia, an island in the western Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean which is administratively an Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with special st ...
considered themselves divided (along with the Balares and the Ilienses). Noted by Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
(III, 3), they dwelt at the extreme north-east of Sardinia, in the region today known as Gallura, near the Tibulati and immediately north of the Coracenses.
According to historian Ettore Pais and archeologist Giovanni Ugas, the Corsi probably belonged to the Ligurian people. Similar was also the opinion of Seneca, who claimed that the ''Corsi'' from Corsica, where he had then been staying in exile, were of mixed origin, resulting from the continuous mingling of various ethnic groups of foreign origin, like the Ligures, the Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
and the Iberians
The Iberians (, from , ''Iberes'') were an ancient people settled in the eastern and southern coasts of the Iberian Peninsula, at least from the 6th century BC. They are described in Greek and Roman sources (among others, by Hecataeus of Mil ...
. In the myth, reported by Sallust
Gaius Sallustius Crispus, usually anglicised as Sallust (, ; –35 BC), was a historian and politician of the Roman Republic from a plebeian family. Probably born at Amiternum in the country of the Sabines, Sallust became a partisan of Julius ...
, the peopling of Corsica is traced back to Corsa, a Ligurian woman who when grazing her cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are calle ...
, went to the island, which then took her name. Pausanias in the ''Description of Greece'' wrote:/ref>
See also
* List of ancient Corsican and Sardinian tribes * Paleo-Corsican language * Nuragic civilization * Torrean civilizationReferences
Bibliography
* * Ancient peoples of Sardinia {{europe-ethno-group-stub